Method for manufacturing thin-film structure
A manufacturing method and structure technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, microstructure technology, microstructure devices, etc., can solve the problem of stress difference between corrosion film and substrate, and achieve the effect of improving soft melting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
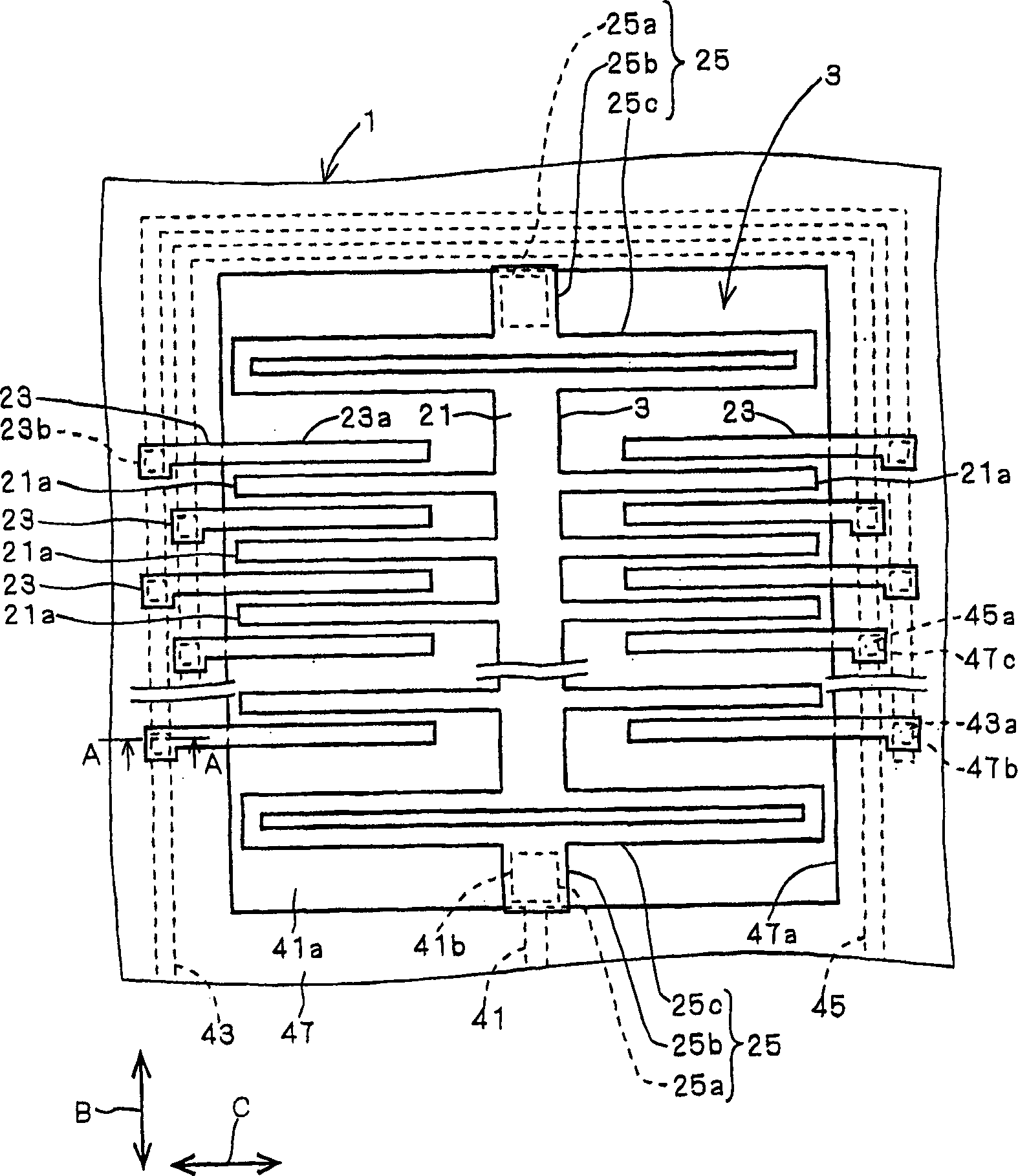
[0022] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the semiconductor acceleration sensor manufactured by applying the thin film structure manufacturing method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention has a substrate 1 as a sensor substrate, and a sensor unit 3 formed on the substrate 1 and having a function of detecting acceleration.
[0023] Sensor part 3 such as figure 1 As shown, there are a mass body 21 functioning as a movable electrode, a plurality of fixed electrodes 23 , and a plurality of beams 25 . Mass body 21 , fixed electrode 23 , and beam 25 correspond to the thin film body of the present invention, and are formed of doped polysilicon obtained by doping a conductive material such as polysilicon with impurities such as phosphorus.
[0024] The mass body 21 is arranged at a predetermined interval from the substrate 1 and has a plurality of movable electrode portions 21 a extending in a direction C perpendicular to the direction B of the detected accelerati...
Embodiment approach 2
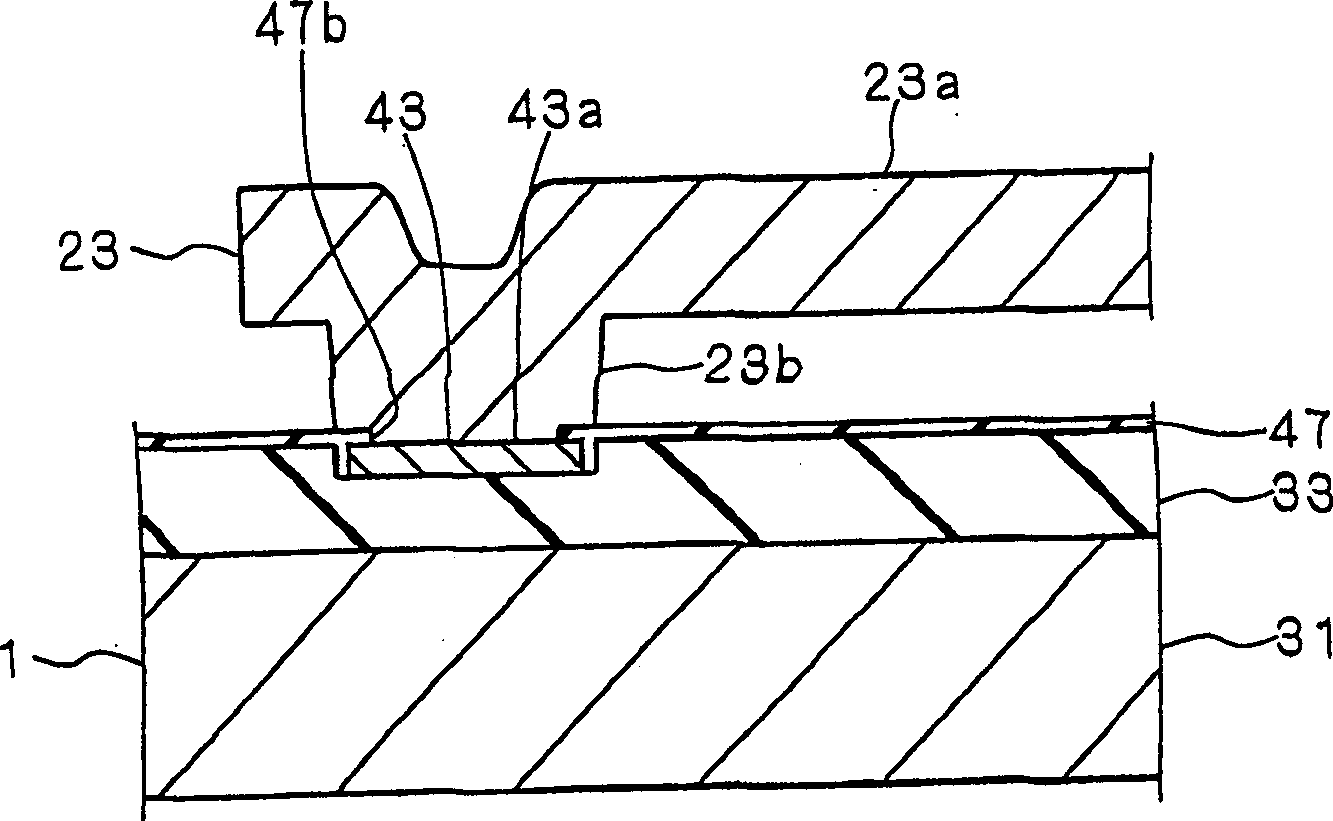
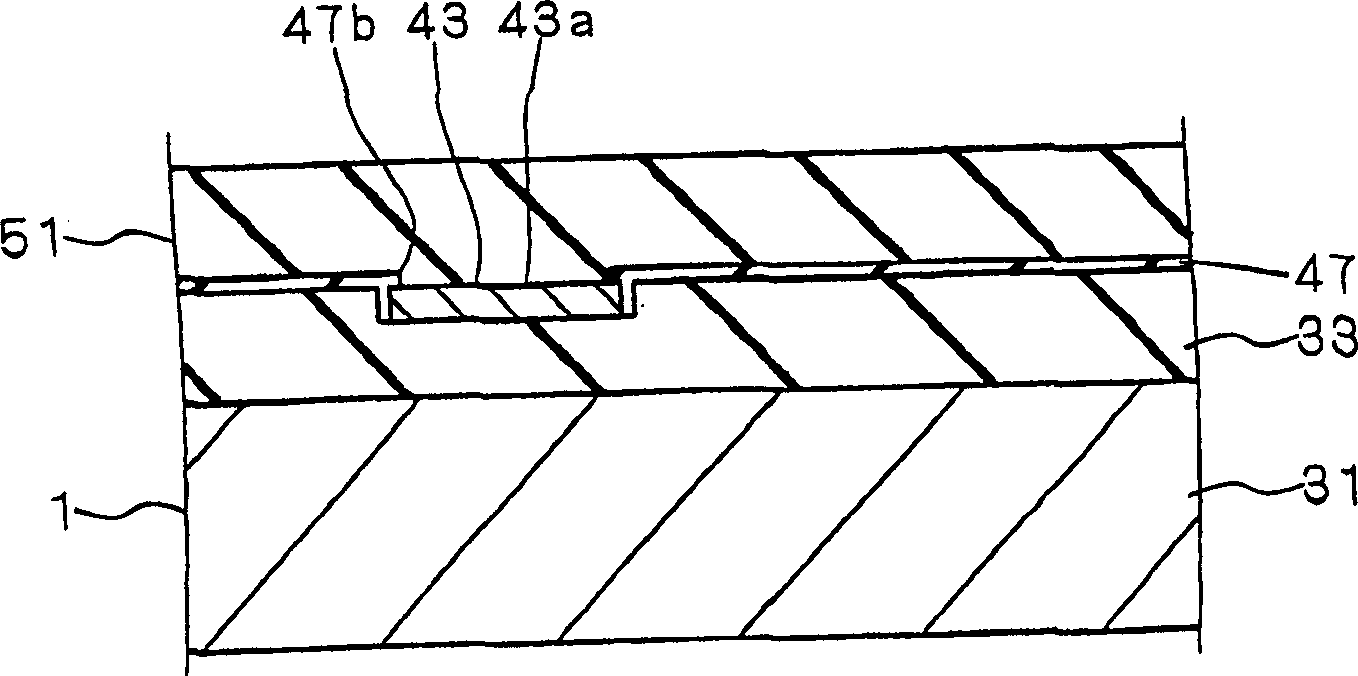
[0038] The manufacturing method of the thin film structure according to this embodiment is also applicable to figure 1 and figure 2 The semiconductor acceleration sensor shown. In addition, the substantial difference between the manufacturing method according to the present embodiment and the manufacturing method according to the above-mentioned first embodiment lies in the difference in the method of manufacturing the etching film 51 . Therefore, here, only the substantial differences between the manufacturing method according to this embodiment and the manufacturing method according to Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0039]In the manufacturing method according to the present embodiment, the etching film 51 is formed of a BPSG (borophosphosilicateglass) film of a silicon oxide film whose phosphorus concentration is set within a predetermined range. In this embodiment, the concentration of phosphorus in the BPSG film is also set to a value greater than 3 mol % and less th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com