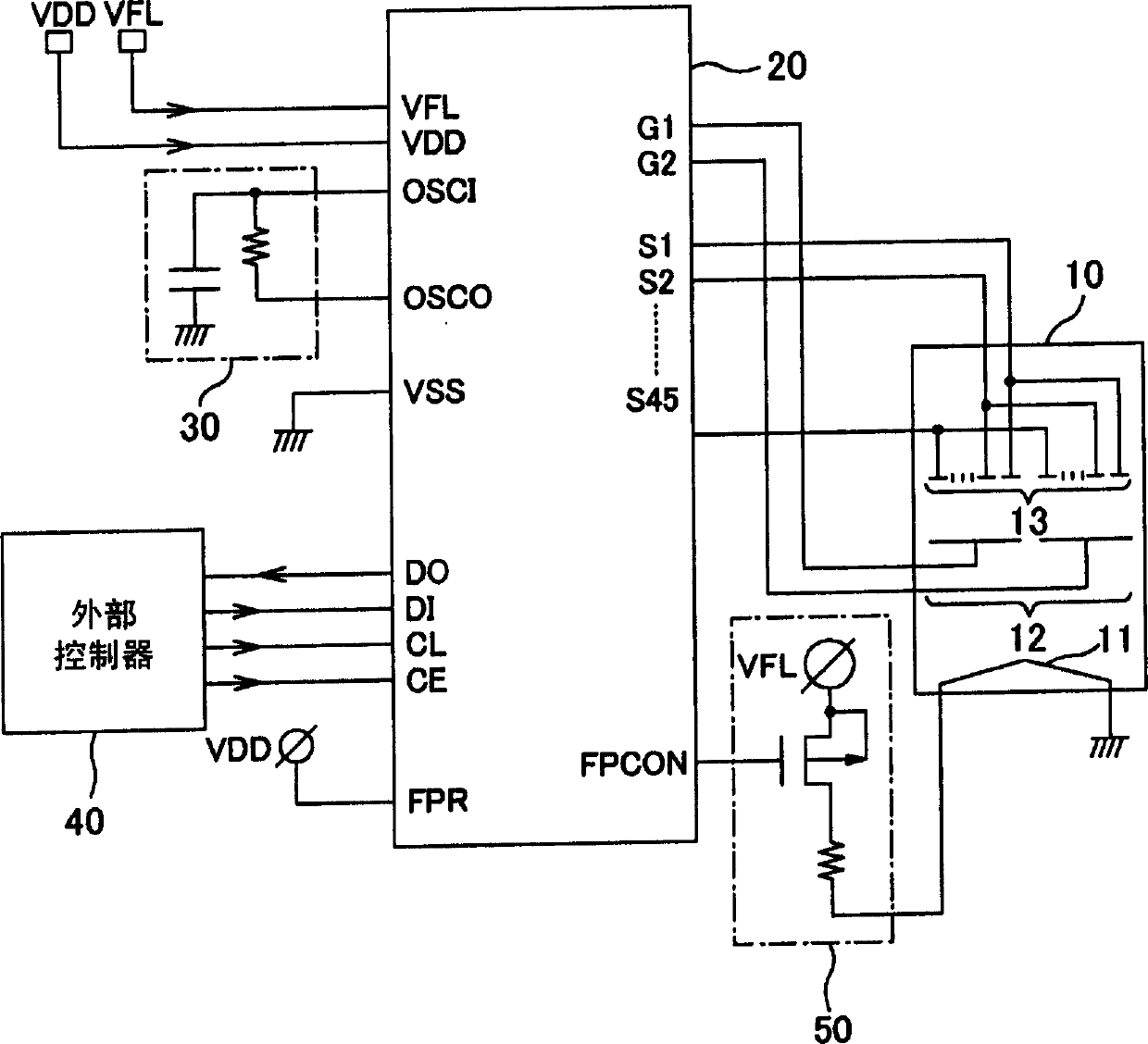
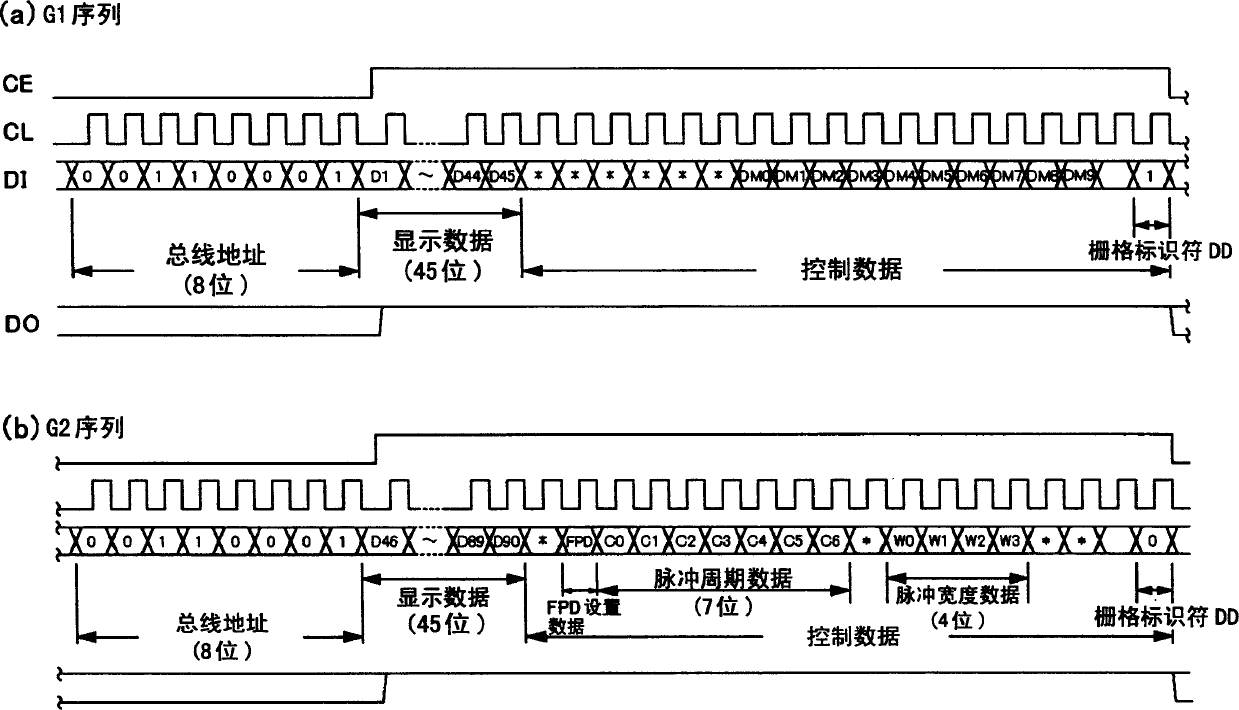
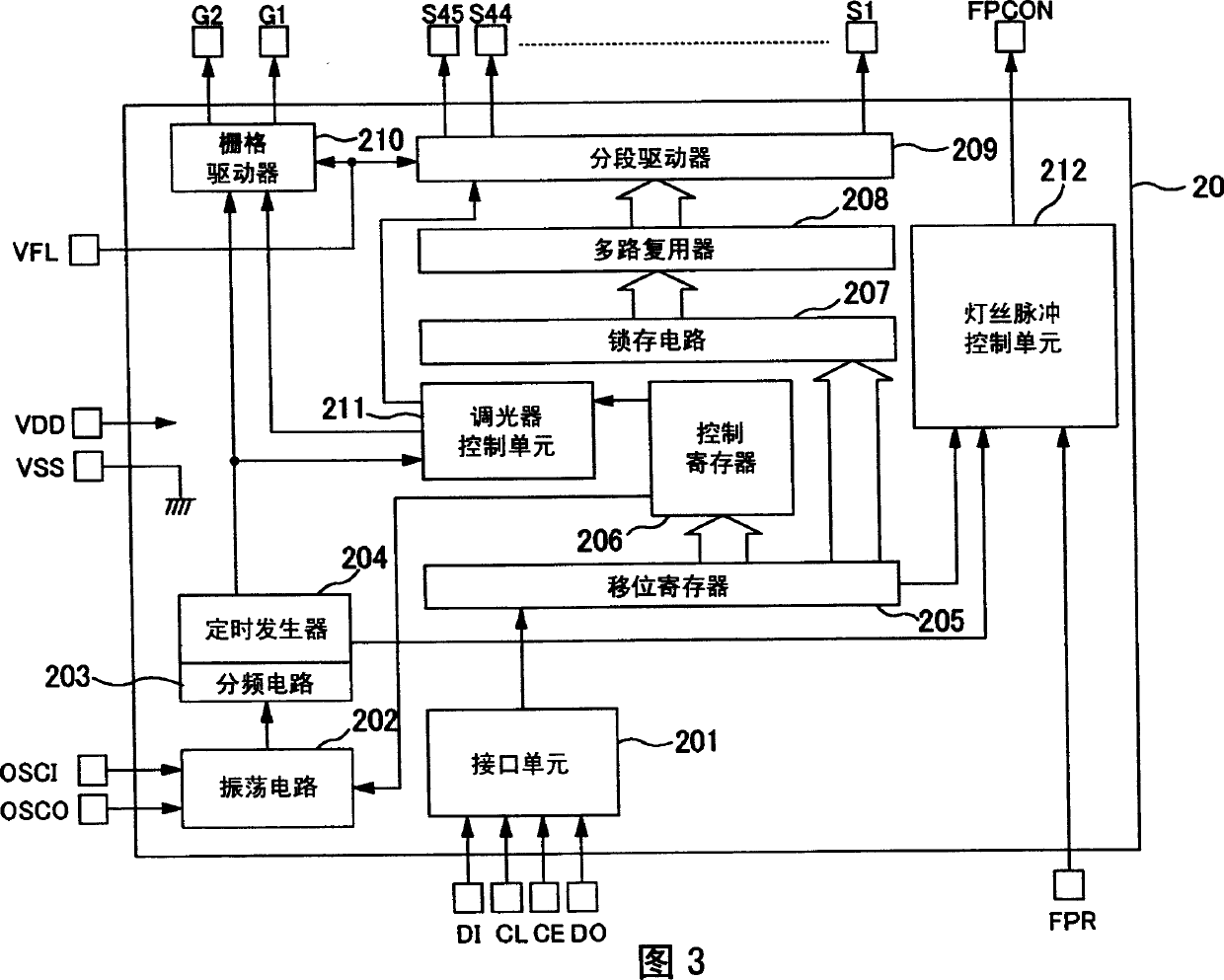
Driving circuit of vacuum fluorescent display
A technology for driving circuits and displays, applied to static indicators, instruments, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of improving convenience and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0070] ==Filament Pulse Control Unit==
[0071] As a first embodiment according to the present invention, in the case of invalidating the pulse driving signal, the filament pulse control unit 212 has a voltage to drive the grid electrode 12 and the segment electrode 13 only when they are at (hereinafter referred to as "Startup Time Period") to deactivate the function.
[0072] FIG. 4 shows a schematic block diagram as a filament control unit 212 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0073] As shown in the figure, the filament pulse control unit 212 includes a pulse driving signal generation unit 70 , an FPD (filament pulse disable) control unit 60 and a pulse driving signal polarity setting unit 110 .
[0074] The pulse driving signal generation unit 70 generates a pulse driving signal having a predetermined duty ratio according to the internal clock signal B supplied from the timing generator 204 .
[0075] FDD control unit 60 comprises: FPDIS signal...
no. 2 example
[0103] As a second example according to the present invention, in the case of validating the pulse driving signal, the filament pulse control unit 212 has the function of setting the pulse width of the pulse driving signal according to the pulse width data and the pulse period data received from the external controller 40 or function of either one of the pulse periods.
[0104] In order to describe the above functions, first, embodiments of pulse width data and pulse period data will be described with reference to FIGS. 9 and 10 .
[0105] ==Pulse Width Data== FIG. 9 is a reference table related to the setting of pulse width data.
[0106] As shown, the pulse width data transferred from the external controller 40 is, for example, 4-bit serial data Wn (W0˜W3), where W0 is LSB (Least Significant Bit). The external controller 40 transmits 4-bit serial data Wn (W0 to W3) to the VFD drive circuit 20 as pulse width data, and the serial data Wn is included in the 16-bit control data...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com