Monocdyledon plant cells and plants which synthesise modified starch
A technology of monocotyledonous plants and plant cells, which is used in the production of this starch, food and baked goods, and can solve the problems of expensive and time-consuming chemical modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
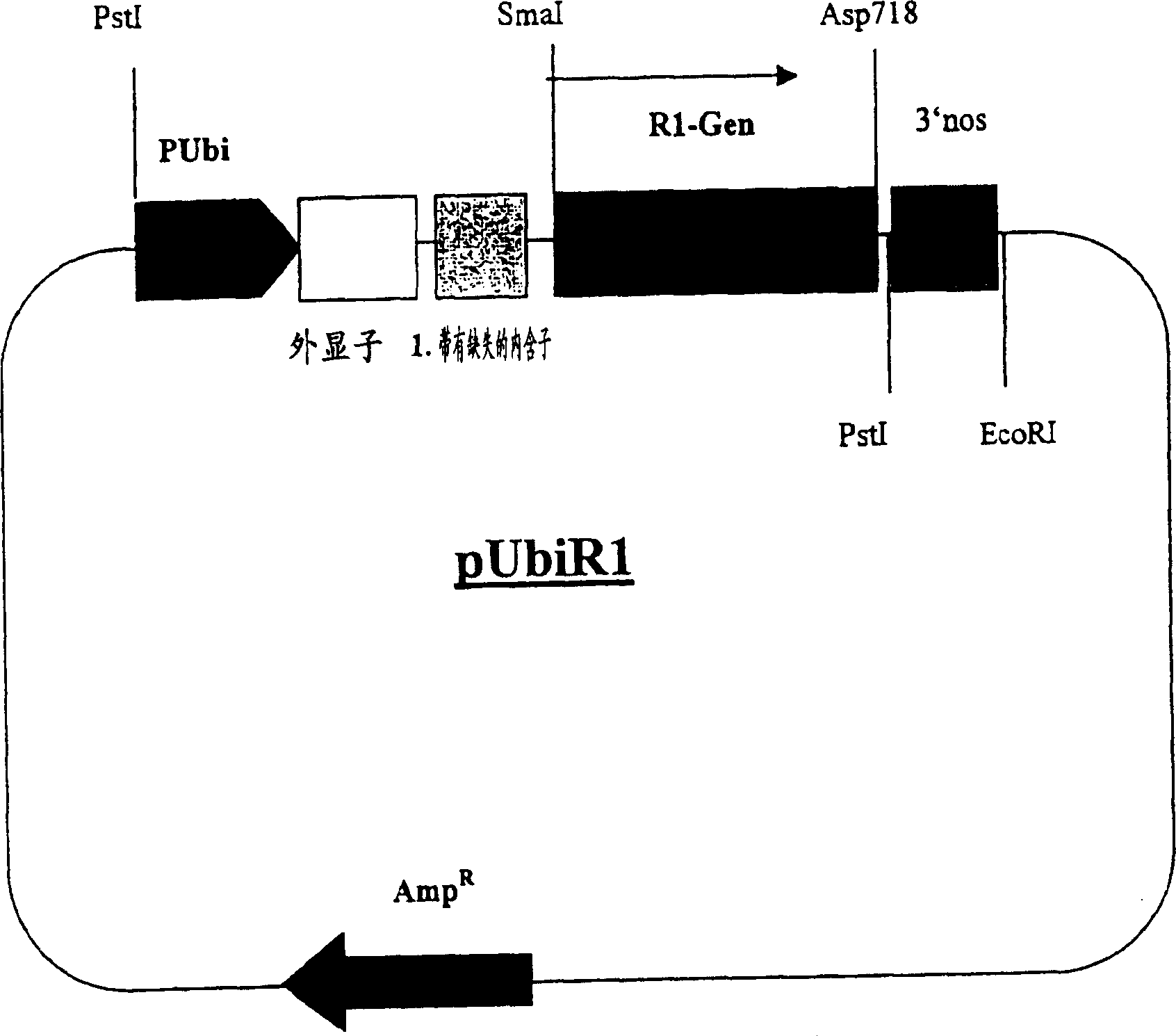
[0245] Preparation of vector pUbiR1 for transformation of wheat plants
[0246] To prepare the vector pUbiR1, first prepare the vector pUbi.cas as follows:
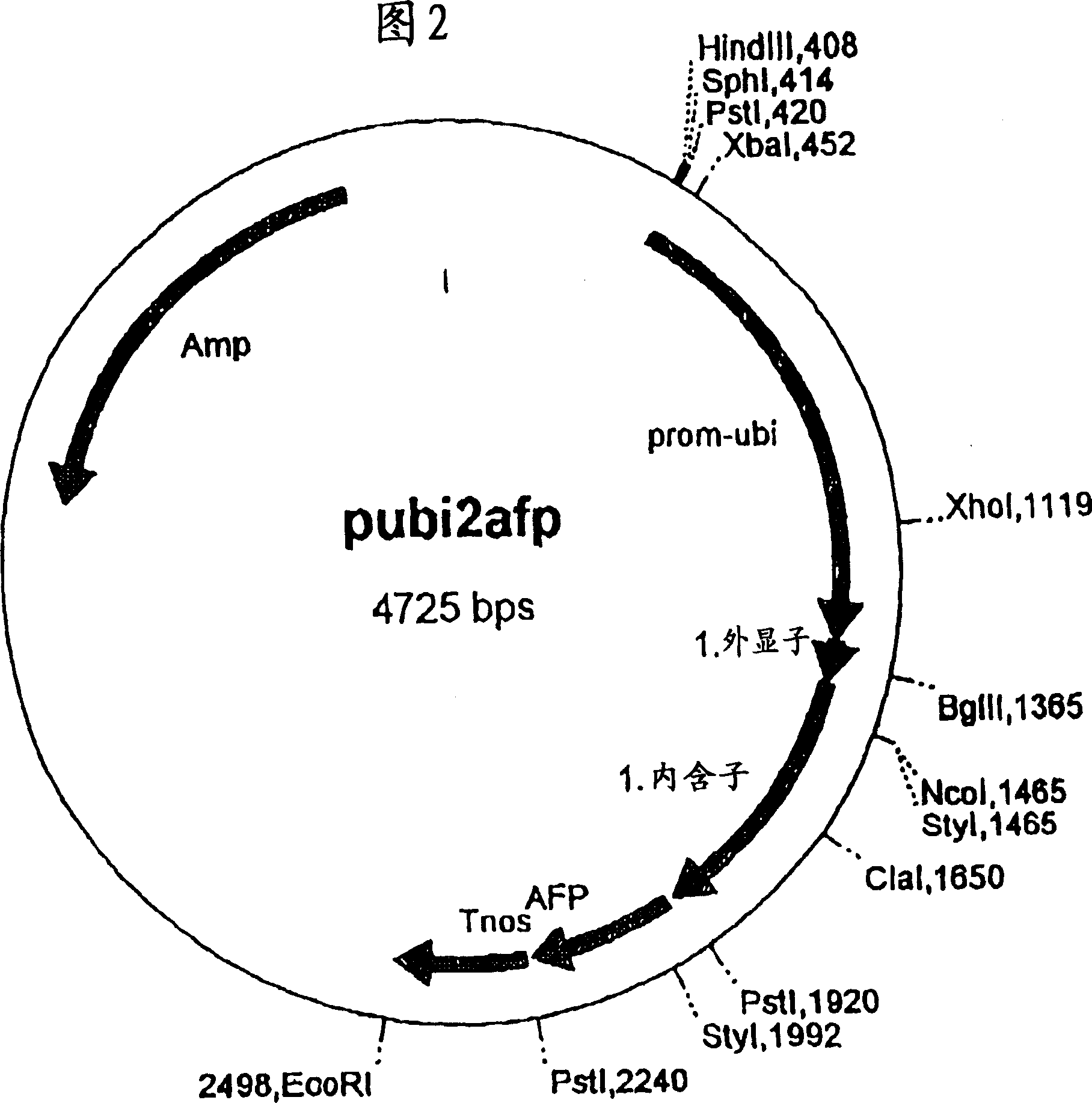
[0247] Vector pUbi2afp (see Figure 2) was partially digested with restriction enzymes PstI / EcoRI. The resulting 4.19 Kb fragment contained the pUC19 vector (Yannish-Perron et al., 1985, Gene 33:103-119), the 1.5 Kb ubiquitin promoter and the first exon of the ubi gene and the shortened ubiquitin 1 Intron (ClaI deletion) (Christensen et al., Plant Mol. Biol. 18, (1992), 675-689), used after gel elution.
[0248] The nos terminator was isolated from the vector pAct.cas (product number CambiaTG0063, Cambia, GPO Box 3200, Canberra ACT 2601, Australia) as a PstI / EcoRI fragment, and the two fragments were ligated to generate the vector pUbi.cas.
[0249] Subsequently, the cDNA (SEQ ID No.1) of the potato R1 gene was isolated as a partial digest (SmaI / Asp718 fragment) from the vector pRL2 (WO97 / 11188, Example 4, deposited in t...
Embodiment 2
[0251] Production of wheat plants expressing the potato R1 gene, and analysis of the phosphate content of starch from these plants
[0252] Transformation of wheat was carried out using biolistic transformation (Becker et al., Plant J. 5(2), (1994), 229-307). Vector pUbiR1 and vector p35SacS for biolistic co-transformation (see Figure 4 ) or pAct1-Fneo / CaIgus (Müller et al., Plant Science 114, (1996), 71-82, see Figure 5 ) were used in the same molar ratio in the DNA pellet precipitation batches.
[0253] The vector p35SAcS was prepared as follows: the pat gene of Streptomyces viridans (Wohlleben et al., Gene 70, (1988), 25-37) was amplified by polymerase chain reaction. The primers used were designed to create BamHI restriction sites on both sides of the amplicon. The BamHI fragment was then cloned into the BamHI restriction site placed between the 35S promoter and 35S terminator of vector pDH51 (Pietzrak et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 14, (1986), 5857-5868). The cassette c...
Embodiment 3
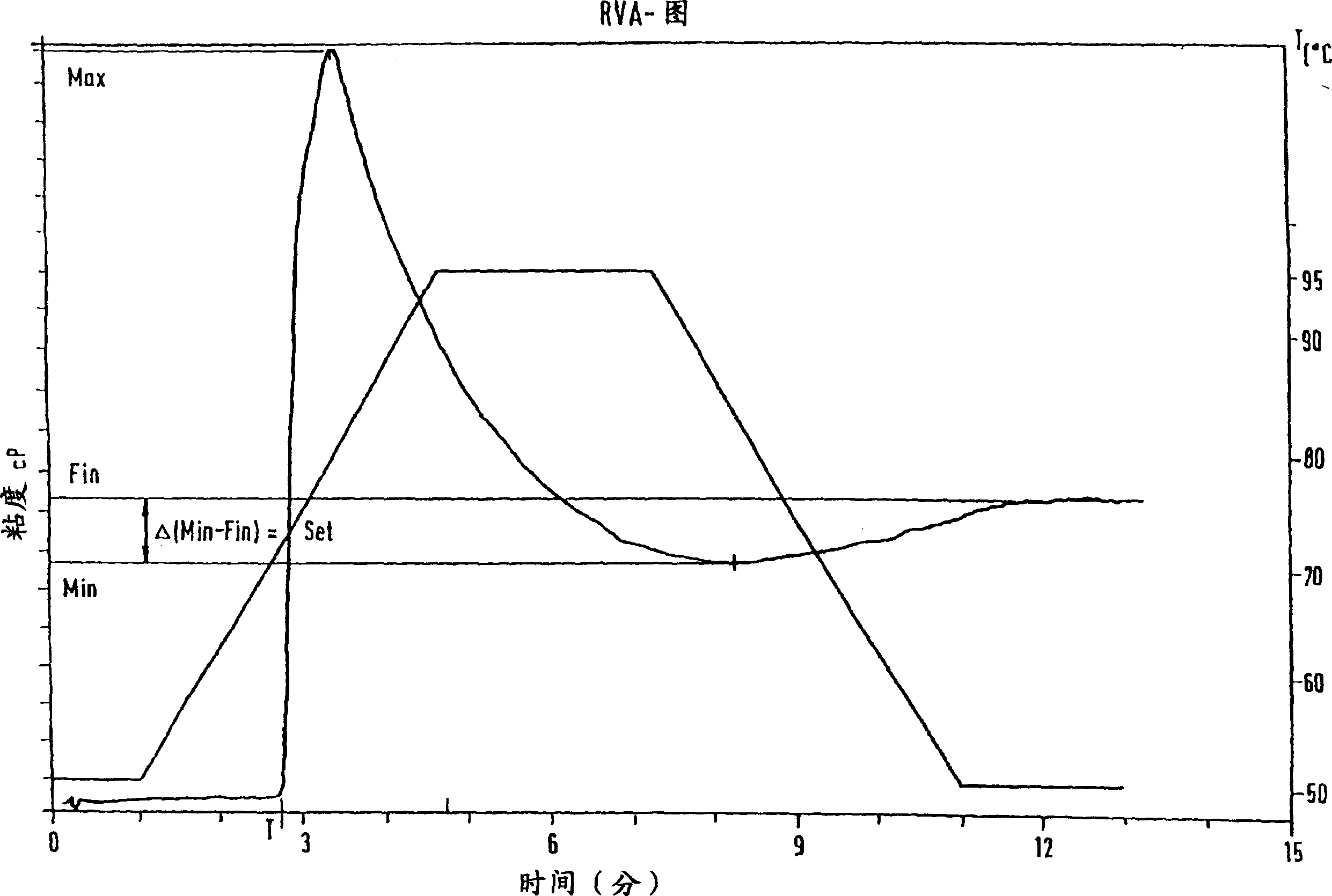
[0273] RVA Analysis of Plant Starch from Transgenic Wheat Plants Expressing the Potato R1 Gene, and Study of Gel Strength
[0274] Starches from the wheat plants described in Examples 1 and 2 were subjected to RVA analysis.
[0275] The results of the RVA analysis (experimental: see Methods) showed that the sticky behavior of starch from transgenic wheat plants expressing the potato R1 gene was significantly altered compared to starch from corresponding wild-type wheat plants (Florida variety) that were not genetically modified (see Table 2).
[0276] Table 2:
[0277] Series number RVA RVA RVA RVA RVA
[0278] Max Min Fin Set T
[0279](%) (%) (%) (%) (%)
[0280] Wild type (Florida) 100 100 100 100 100
[0281] 19(T0) 98.7 113.8 116.8 120.7 102
[0282] 20-25(T1) 155.3 190 193.8 198.8 99
[0283] 37(T0) 143.8 156.2 148.8 139 101
[0284] 40-11-8(T2) 156.2 185.5 187.7 190.6 97
[0285] legend:
[0286] RVA=Rapid Visco Analyzer
[0287] Max = see ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com