Patents
Literature
50 results about "Monocotyle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of making an anti-infective composition for treating oral infections
This invention concerns a method of making an anti-infective composition for oral administration using an agent selected from the group consisting of lactoferrin protein and lysozyme protein. The method comprises three steps. The nucleic acid, which encodes a lactoferrin or lysozyme protein, is expressed in a monocot seed. The protein is isolated from the seed. This protein isolation compromises greater than 3% of the total soluble protein in the monocot seed. The protein is then formulated for oral administration.
Owner:VENTRIA BIOSCIENCE
Application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice
The invention relates to application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. Nucleotide sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Encoded protein sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Conditions that are met for the nucleotide sequences and the encoded protein sequences include: first, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1, or the sequences highly homologous to the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1; second, other encodable sequencecs with the same protein as the DNA sequences shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.2; third, the sequences the same functional as the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1, or sub-segments contained in the highly homologous DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is applied to breeding of the drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. An expression vector of the MYB44 gene can be introduced into plant cells by biotechnology. Transforming hosts, available to use the expression vector containing the MYB44 gene, can be monocotyledons such as rice, corn and wheat. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is also applicable to dicotyledons such as tobacco and soybean. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is used to breed drought-resistant salt-tolerant plant varieties.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Artificial breeding method of locust
The invention provides an artificial breeding method of a locust. The method is characterized in that geographical place is selected, wherein the place has sufficient sunlight, good drainage, and is in peace, in east-west direction, and far away from a cotton field, an orchard and other places to which pesticides are generally applied, so as to prevent locust from poisoning and death as well as facilitate water drainage in the rainy season. The breeding method is easy to master, simple to manage, free of limitation from area, suitable for all people to breed, and low in requirements on operators; the feed in the method includes maize, wheat, corn seedling and some monocotyledons, so that the feed is low in price, and the breeding cost is low; the locust reproduction rate is high, the reproduction cycle is short, and the economic benefit is high; the building adopted in the method is a greenhouse which is simple to construct and low in cost; proper place benefits the breeding; in addition, a rainproof layer covers the outer side of the greenhouse, so that the locust can be effectively prevented from being influenced by natural rainwater, and the production and survival rate can be ensured.
Owner:DIQISHUN TIANJIN FARMING TECH DEVCO
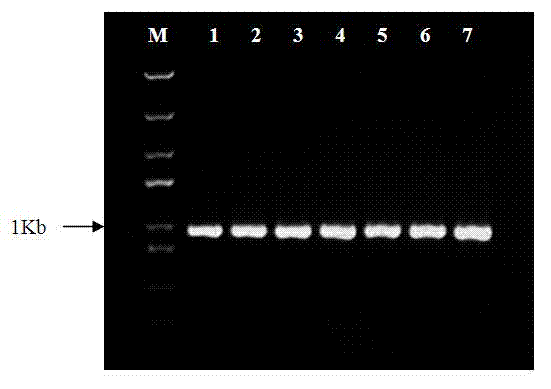
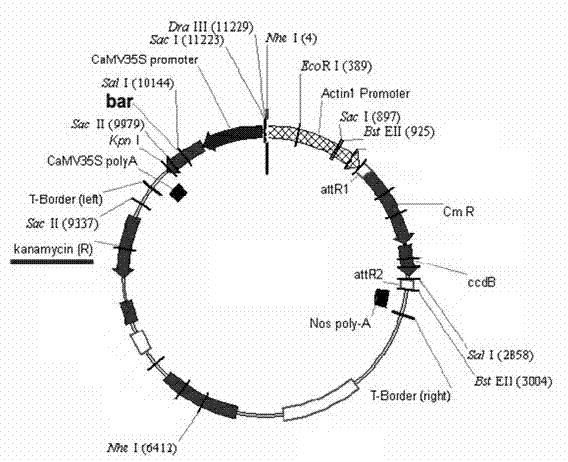
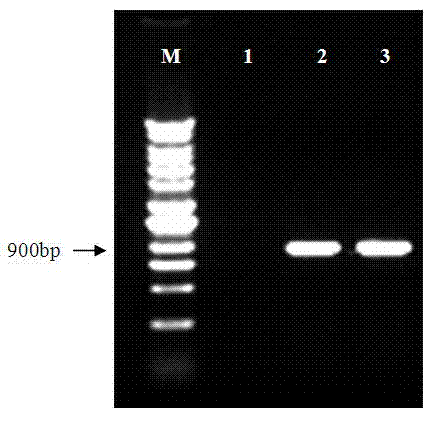
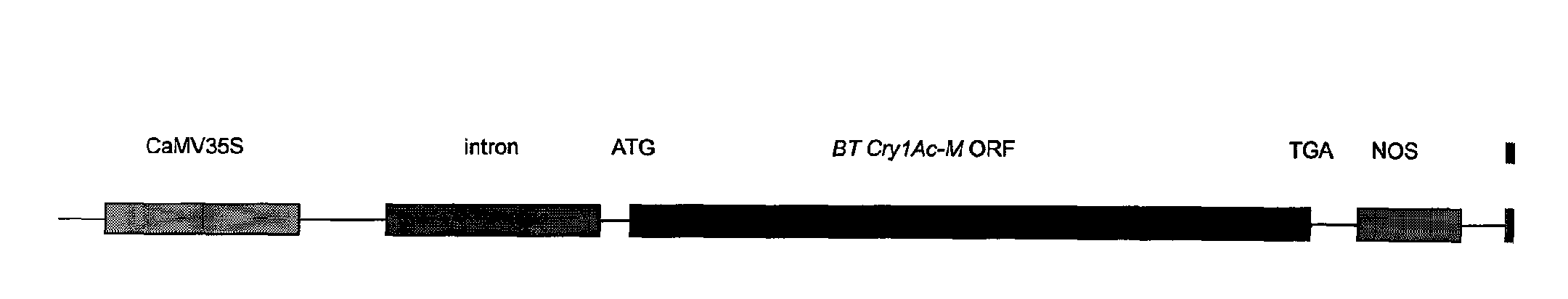
Artificial synthesized Bt insecticidal gene for transgenic anti-insect plants
The invention discloses an artificial synthesized Bt insecticidal gene for transgenic anti-insect plants, further, the invention relates to the optimization and transformation systematically to a coding frame and a codon of a CrylAc anti-insect gene, according to an activity analysis to Bt protein in different regions and in accordance with the coding characteristics of the monocotyledons, obtaining anti-insect gene CrylAc-M which can be expressed in a monocotyledons efficiently, with the optimized codon and coding frame. The CrylAc-M gene after being transformed is connected on an expression carrier with CaMV35S-Adhl as promoter, and then the Bt gene CrylAc-Adhl is transferred into a maize inbred line with highly efficient conversion rate by a gene gun co-transformation method. A transgenic progeny is positive through Bt protein testing and a field anti-insect test of the field is tested to be highly resistant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Marker Assisted Selection for Transformation Traits in Maize
InactiveUS20080078003A1Increased yieldIncrease yield and nutritional qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationTransformation efficiencyMarker-assisted selection
Methods for producing corn with increased transformability are provided. Markers for increased transformability are provided as well as their use to obtain corn plants with increased transformability. Locations on chromosomes that effect transformation efficiency of monocots are identified.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
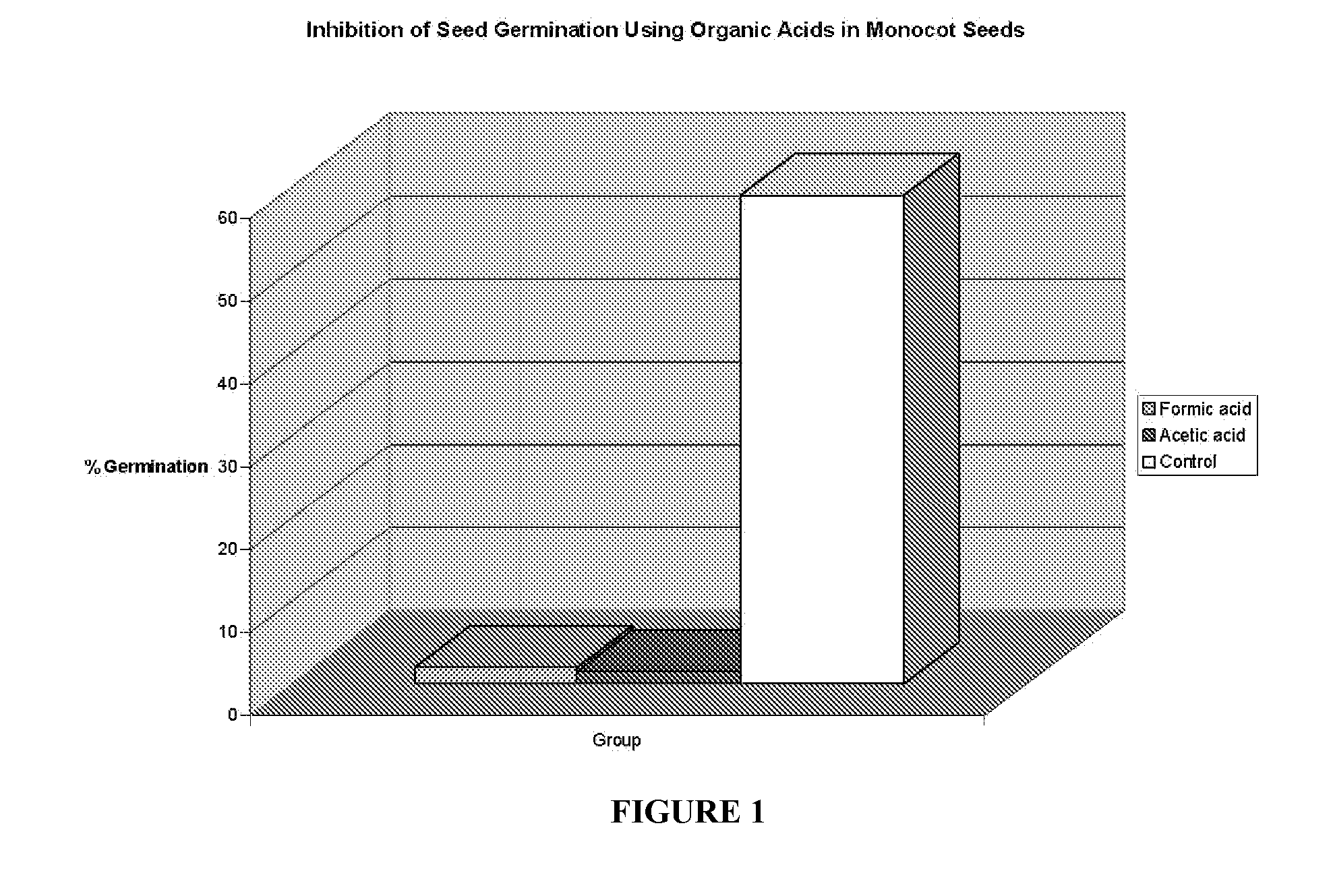
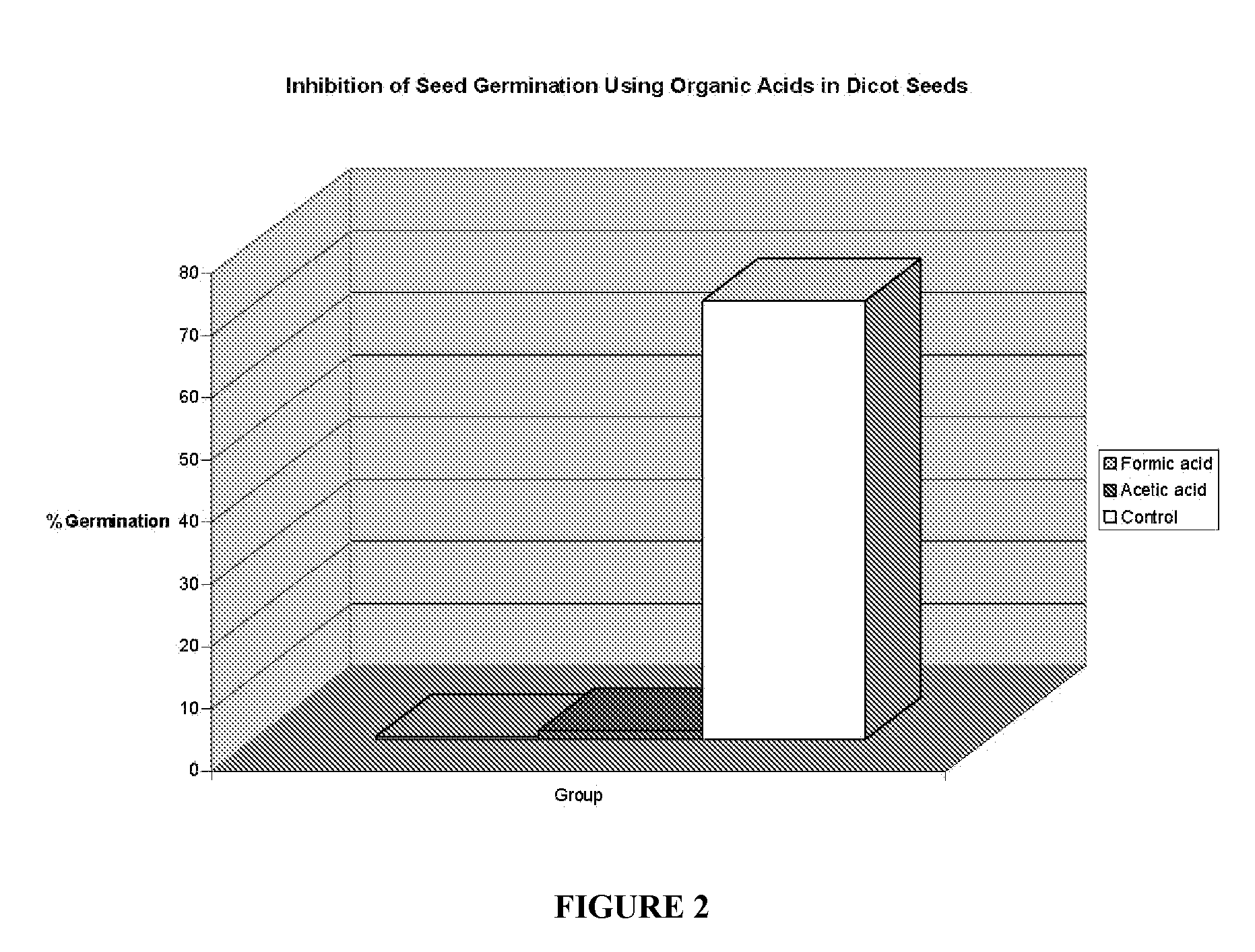
Formic acid as an herbicide
The present invention discloses that, formic acid or salt thereof, is an effective pre-emergent and post-emergent herbicide. Formic acid biodegrades to carbon dioxide and water thus posing not threat the environment. With proper formulation and the use of respiratory protection, formic acid also poses no threat to the applicator. Formic acid is demonstrated in this invention to control both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
Owner:MARRONE BIO INNOVATIONS
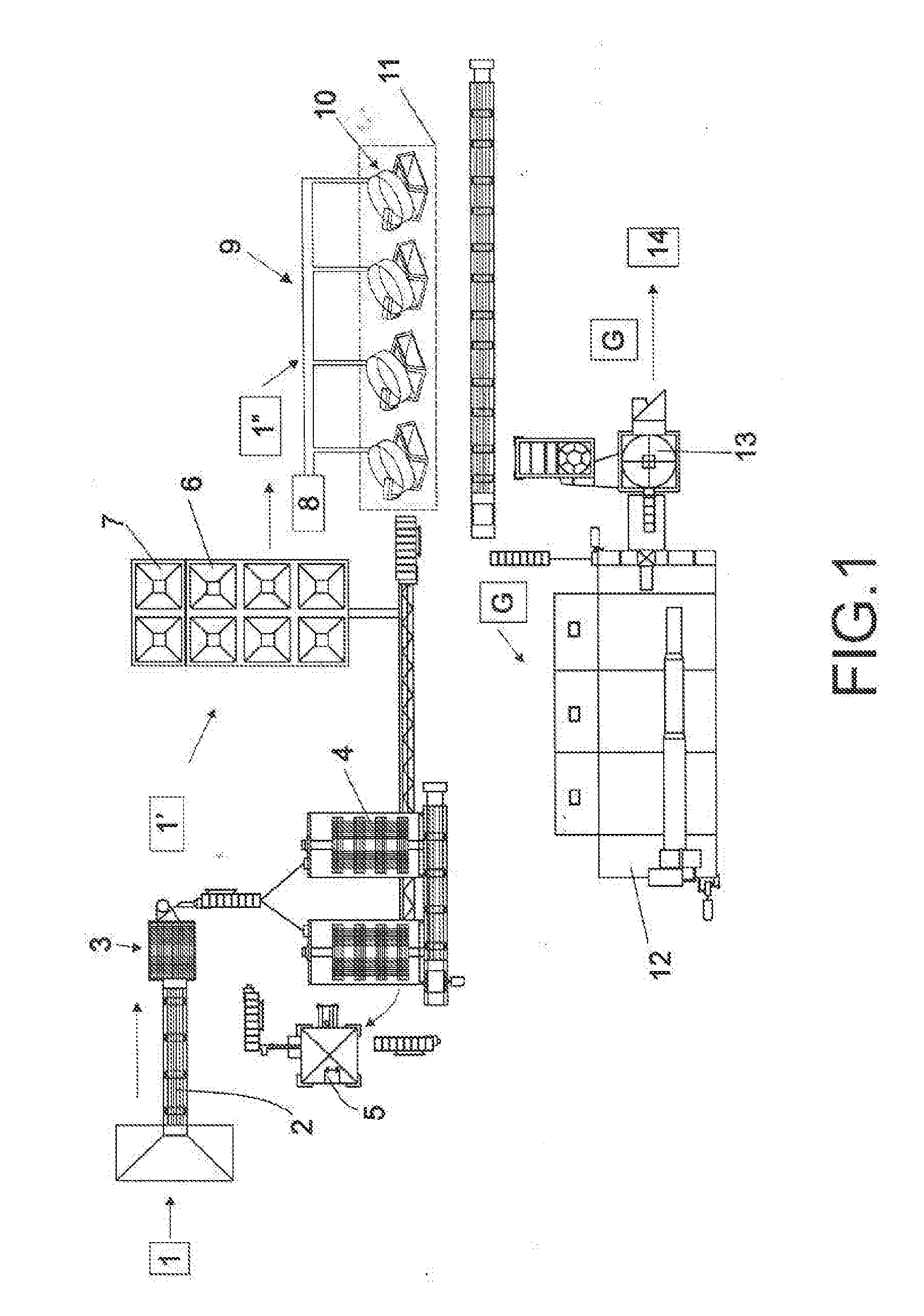
Process for making biopreform from monocotyledonous caudex plant, biopreform obtained thereby, and use thereof
InactiveUS20040126561A1Simpler pyrolyticImprove accuracyAdhesive processesSynthetic resin layered productsAnatomical featureBiology
A method of making biopreform from the stem of monocotyledonous caudex plant, that is suitable for liquid infiltration and gaseous transportation of materials, is disclosed. Wood from caudex stem of trees such as coconut (Cocos nucifera), palmyra palm (Borassus flabellifer), date palm (Phoenics dactylifera), is used as a precursor material which is transformed under simple pyrolitic conditions under self-generated ambient atmosphere to biopreform having microstructural features typical of a monocotyledonous caudex tree. The biopreform is capable of liquid infiltration and gaseous transportation processing of materials in an appreciably shorter processing periods, because of its preservation of the structural and anatomical features of the parent plants with high precision.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Anti-insect protein Cry1A.401 and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102584961AHigh expressionBroaden the Spectrum of Insect ResistanceBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyAcid amino sequences
The invention provides an anti-insect protein Cry1A.401, which is characterized by comprising: (1) an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, or (2) an amino acid sequence which is obtained by performing substitution, deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acids on the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2 and has equal function. As proved by an in-vitro experiment, a modified and synthesized Bt gene toxoggenic protein has a remarkable insecticidal effect on corn borers. The anti-insect protein Cry1A.401 can be stably and efficiently expressed in monocotyledons, and is further applied to production of anti-insect transgenic plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
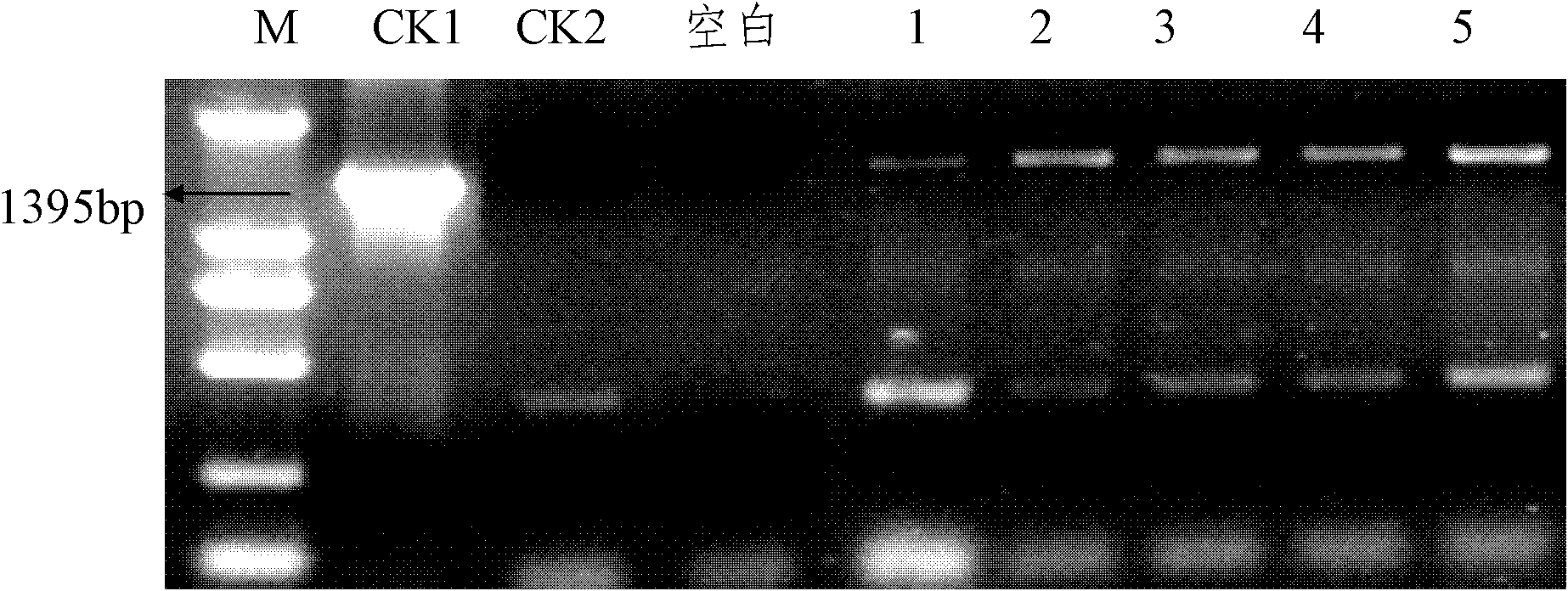
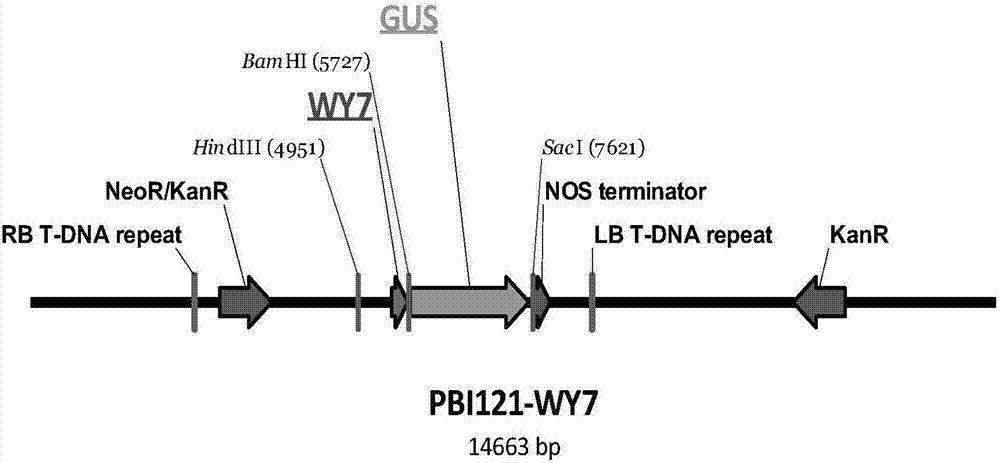
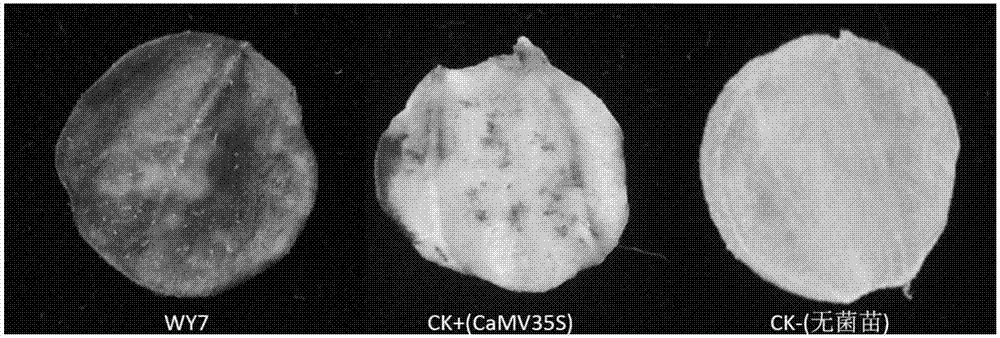
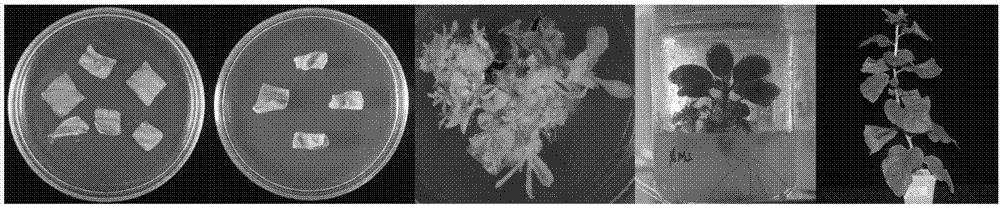
Endogenous promoter WY7 of powdery mildew of rubber tree and application of endogenous promoter WY7
The invention discloses an endogenous promoter WY7 of powdery mildew of a rubber tree and application of the endogenous promoter WY7. The promoter WY7 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ IDNO:1, or the promoter has a variant having the function of the promoter. The invention further relates to a nucleic acid construction body comprising the promoter, a carrier, a reconstitution cell, atransgenic plant, an explant and a callus. The promoter is used for regulating the expression of exogenous target genes in the dicotyledon and the monocotyledon, and provides a brand new tool and choice for the expression of genes of the transgenic plant.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
N,N-diethyl-2-(2-methoxy-5-nitrophenoxyl)-ethylamine as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108675933AThe promotion effect is obviousGood regulationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDicotyledonEther
The invention provides a new compound, namely N,N-diethyl-2-(2-methoxy-5-nitrophenoxyl)-ethylamine. The N,N-diethyl-2-(2-methoxy-5-nitrophenoxyl)-ethylamine has an amino ether skeleton and can regulate the growth of plants. The compound is used for performing biological activity experiment on monocotyledon wheat, dicotyledon mung beans and peanuts. The experiment result indicates that for the mungbeans, the peanuts and the wheat, the compound has a remarkable acceleration effect when the concentration is low and has a certain inhibition effect when the concentration is high.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
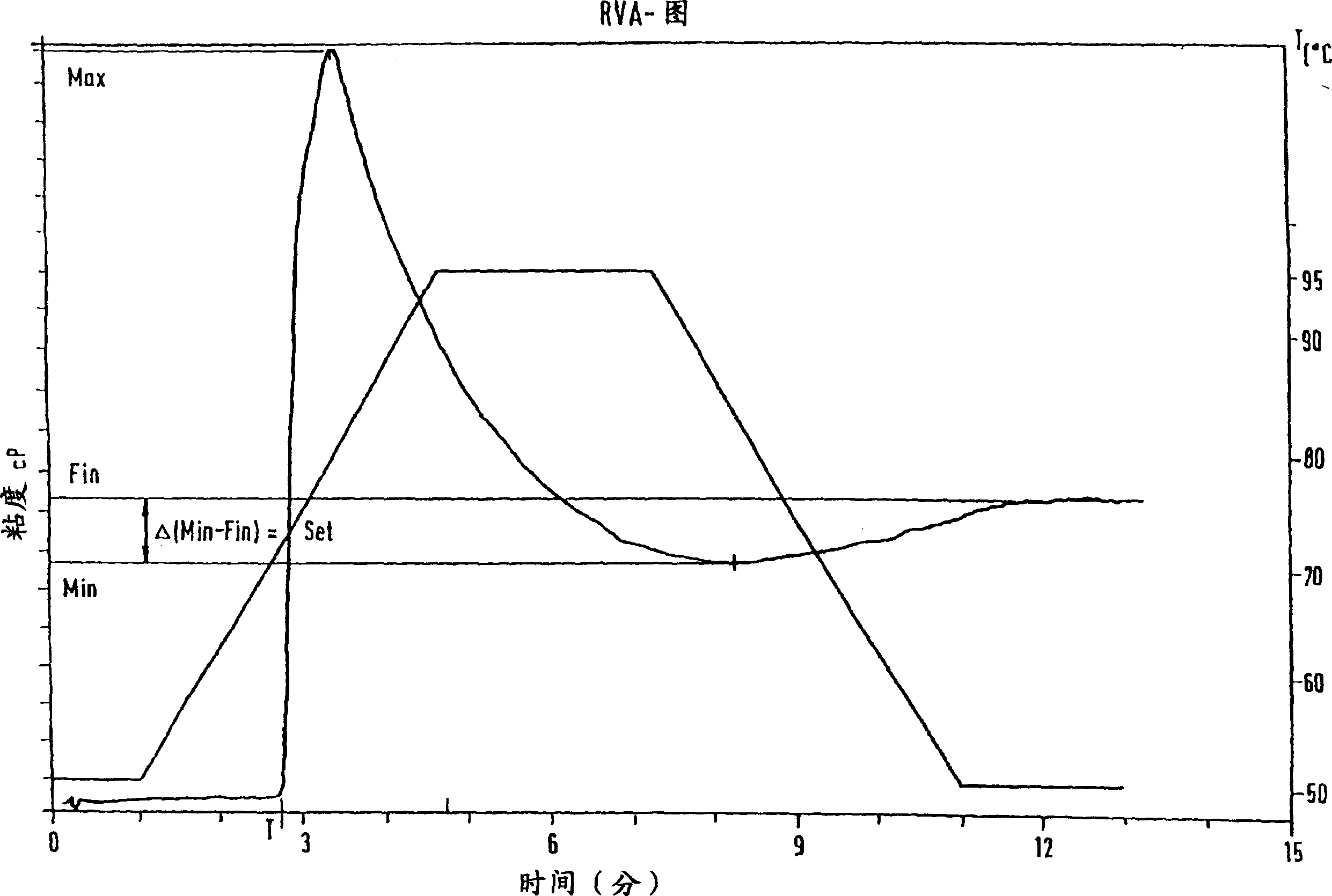
Monocdyledon plant cells and plants which synthesise modified starch
InactiveCN1541273ADecrease in enthalpy of fusionDough treatmentFood genetic modificationPhosphorylationPlant cell
The present invention relates to monocotyledon plant ells and plants which are genetically modified, wherein the genetic modification consists of the introduction of an extraneous nucleic acid molecule which codes for a protein with the biological activity of an R1 protein. The present invention further relates to means and methods for the production thereof. Plant cells and plants of this type synthesise a modified starch, which is characterised in that is has an increased phosphate content and / or a modified phosphorylation pattern and / or an increased final viscosity in an RVA profile and / or a reduced peak temperature in DSC analysis and / or an increased gel strength in the texture analysis compared with starch from corresponding non-genetically modified monocotyledon plants. Therefore, the present invention also relates to the starch which is synthesised from the plant cells and plants according to the invention, and to methods of producing said starch. The present invention further relates to wheat flours which contain said modified starches, and to food products and bakery products which contain said wheat flours and / or starch.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Granulated organic and organomineral fertilizer supplemented with biological additive and process for the production of granulated organic and organomineral fertilizer supplemented with biological additive
PendingUS20160176766A1Simple processLow costPhosphatic fertiliser granulation/pelletisationOrganic fertilisersMonocotyleDicotyledon
A granulated organic and organomineral fertilizer supplemented with biological additive and process for the production of granulated organic and organomineral fertilizer supplemented with biological additive is physically presented in the form of granules (G), having its formulation defined by the combination of organic and mineral matter (N,P,K), to which it is added, in addition, a bioburden in the form of bacteria, fungus and yeast that are selected to crops of interest, whether grasses, legumes, monocotyledons and dicotyledons, the granules (G) receive the bioburden at the time of its granulation; the selection of bioburden to be included in granules (G) is established according to the soil and crop analysis to be cultivated.
Owner:SUPERBAC BIOTECH SOLUTIONS SA
Inducible promoter containing W box as well as construction method and application to genetic engineering
InactiveCN101886077AApparent response activityAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA preparationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention provides an inducible promoter containing a W box as well as a construction method and the application to genetic engineering. The inducible promoter at least contains a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. The construction method comprises the following step of: fusing a stress-response-stressed W box identified in dicotyledon arabidopsis thaliana with a CaMV35S promoter core sequence to construct an inducible promoter. The inducible promoter containing the W box in the invention can strongly response the invasion of rice blast fungus and the feeding of rice cnaphalocrocis medinalis in transgenic rice, has obvious response activity on the treatment of small-molecule compounds with disease resistance after separation identification and has poor response activity on abiotic stress treatment, such as drought, low temperature, high temperature, and the like. The inducible promoter has very important application values in the disease-resistant and pest-resistant genetic engineering of monocotyledon and dicotyledon, and transgenic plant strains also have very important application values in the high throughput screening of small-molecule compounds for inducing plants to resist diseases.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
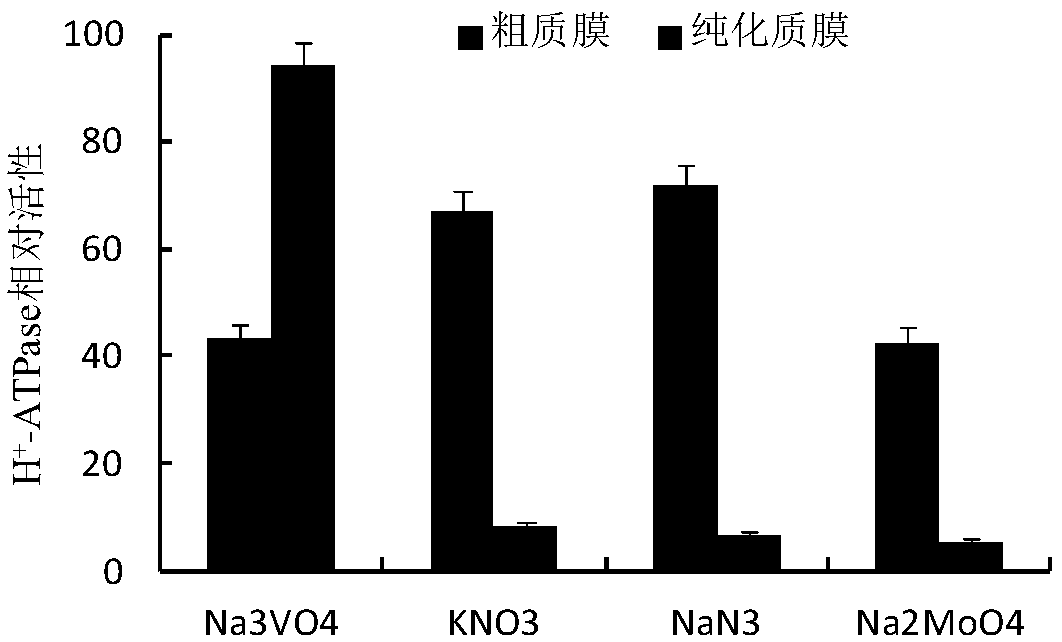
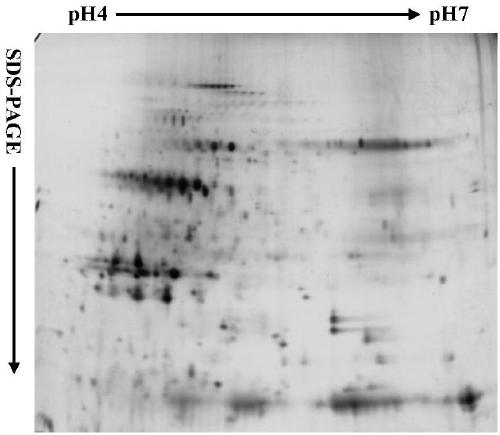
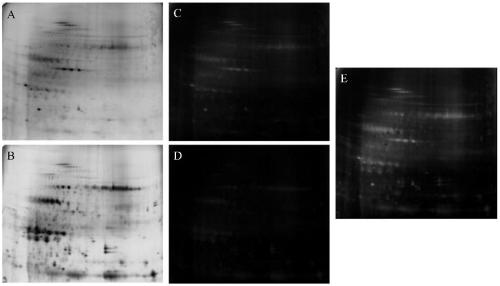
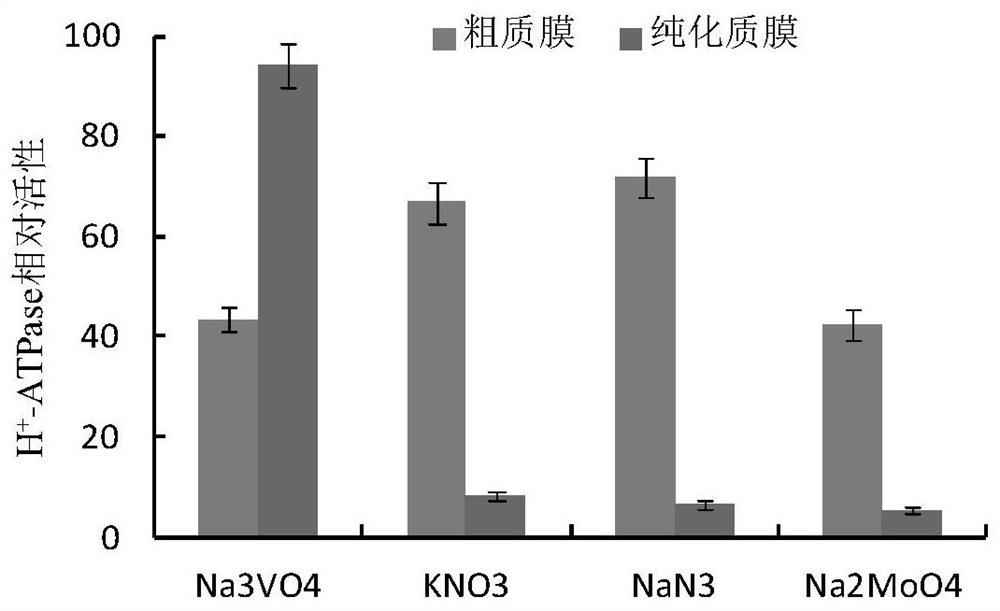
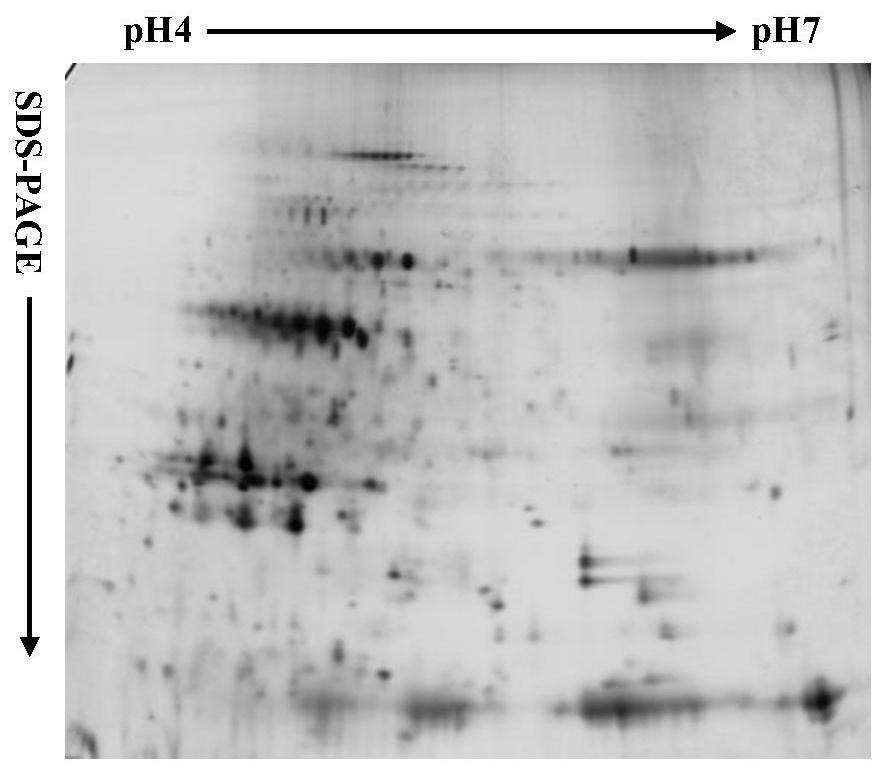
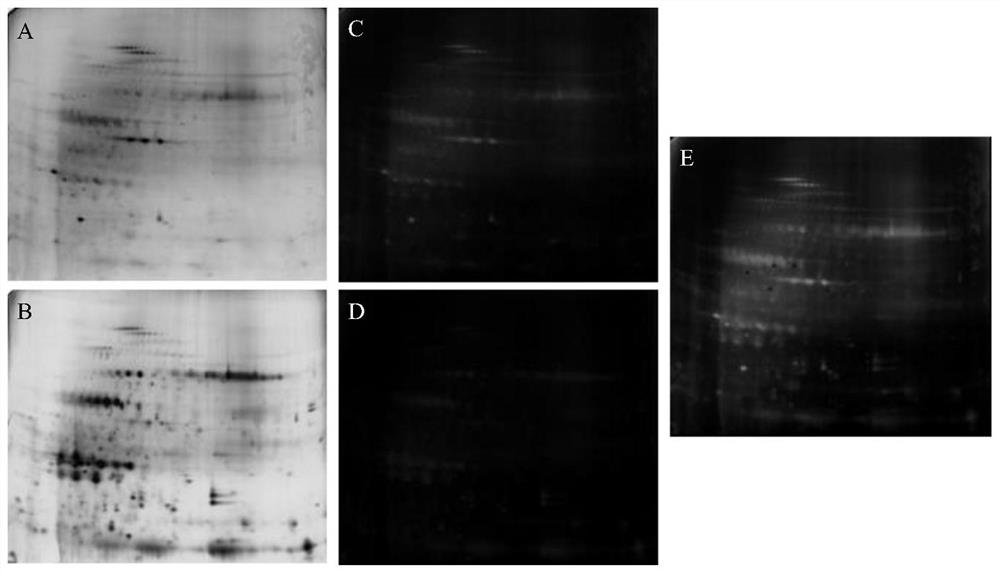
Extracting method for phosphorylated protein suitable for two-dimensional electrophoresis of plasma membranes of rice leaves
ActiveCN109136166AHigh purityStrong specificityPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein spotPlasma membrane protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of proteomic technology, and particularly discloses an extracting method for phosphorylated protein suitable for two-dimensional electrophoresis of plasmamembranes of rice leaves for the first time. The extracting method comprises the steps of extraction for coarse plasma membranes of the rice leaves, purification of the plasma membranes of the rice leaves, enrichment of the phosphorylated protein of the plasma membranes of the rice leaves and the like. The extracting method is simple in operation, high in extracting efficiency and low in cost, thepurity of the plasma membranes of the rice leaves can reach 93% or above, and the yield of the enriched phosphorylated protein of the plasma membranes from protein of the plasma membranes is 3.33-3.89%. The extracting method is suitable for the plant materials with difficultly extracted phosphorylated protein of the plasma membranes and fewer interferents; the obtained phosphorylated protein of the plasma membranes contains fewer impurities and interferents and can meet the requirements of two-dimensional electrophoresis, the obtained two-dimensional electrophoretogram is clear in background,uniform in protein spot distribution and fewer in longitudinal trailing and horizontal transverse grain phenomenon and has good repeatability, and the extracting method is suitable for preparation and analysis of phosphorylated proteomes of the plasma membranes of monocotyledons.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Amide compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103910647AImprove herbicidal activityEasy to operateBiocideOrganic compound preparationAcetyl chlorideStructural formula
The invention discloses an amide compound. The amide compound has the following chemical structural formula. The structural formula is as shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting 2,4-dichlorbenzoxy acetyl chloride and urea to obtain the amide compound. The amide compound has excellent herbicidal activity, particularly the herbicidal activity on dicotyledon weeds is obviously superior to that of monocotyledon weeds. The preparation method of the amide compound is simple in operation and high in yield.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Promoter OsP002, preparation method and applications thereof
Owner:华大基因杨凌创新研究院有限公司
Inducible promoter containing JERE (Jasmonic Acid and Elicitor Responsive Element) box as well as construction method and application to genetic engineering
InactiveCN101886080AAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA preparationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
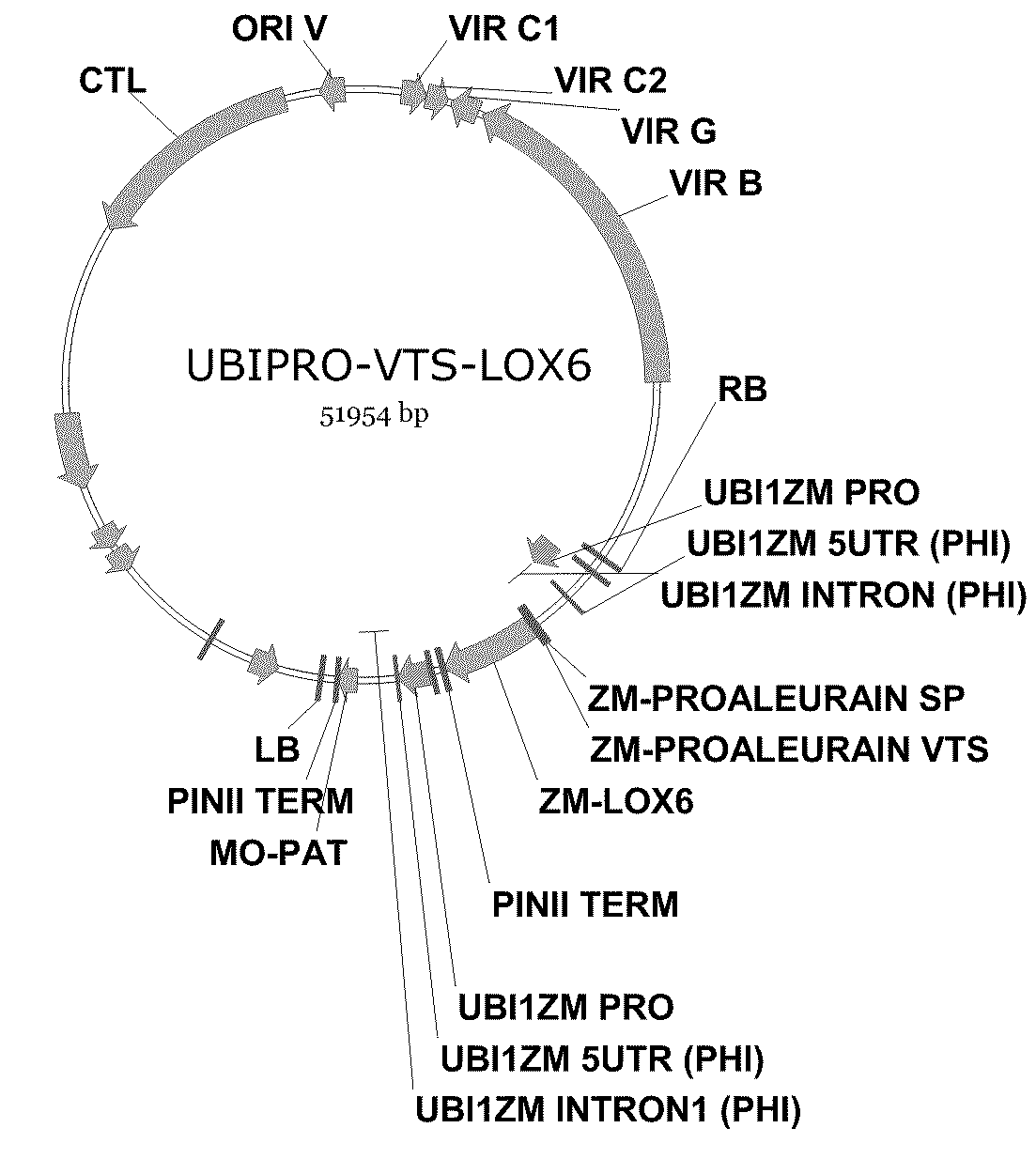
Methods For Improving Plant Growth
InactiveUS20090293147A1Improve planting effectHigh expressionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesAnimal ForagingWild type
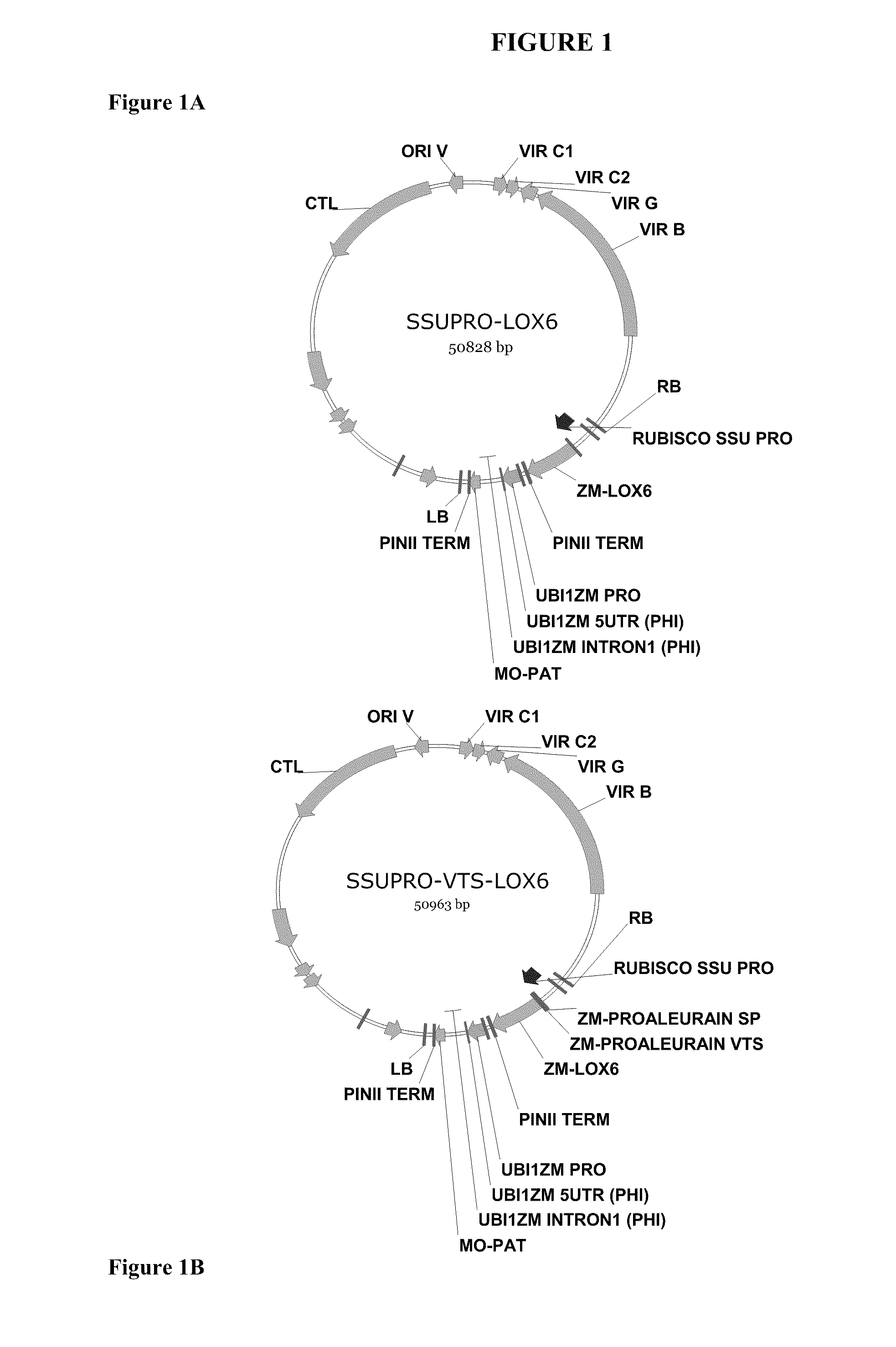
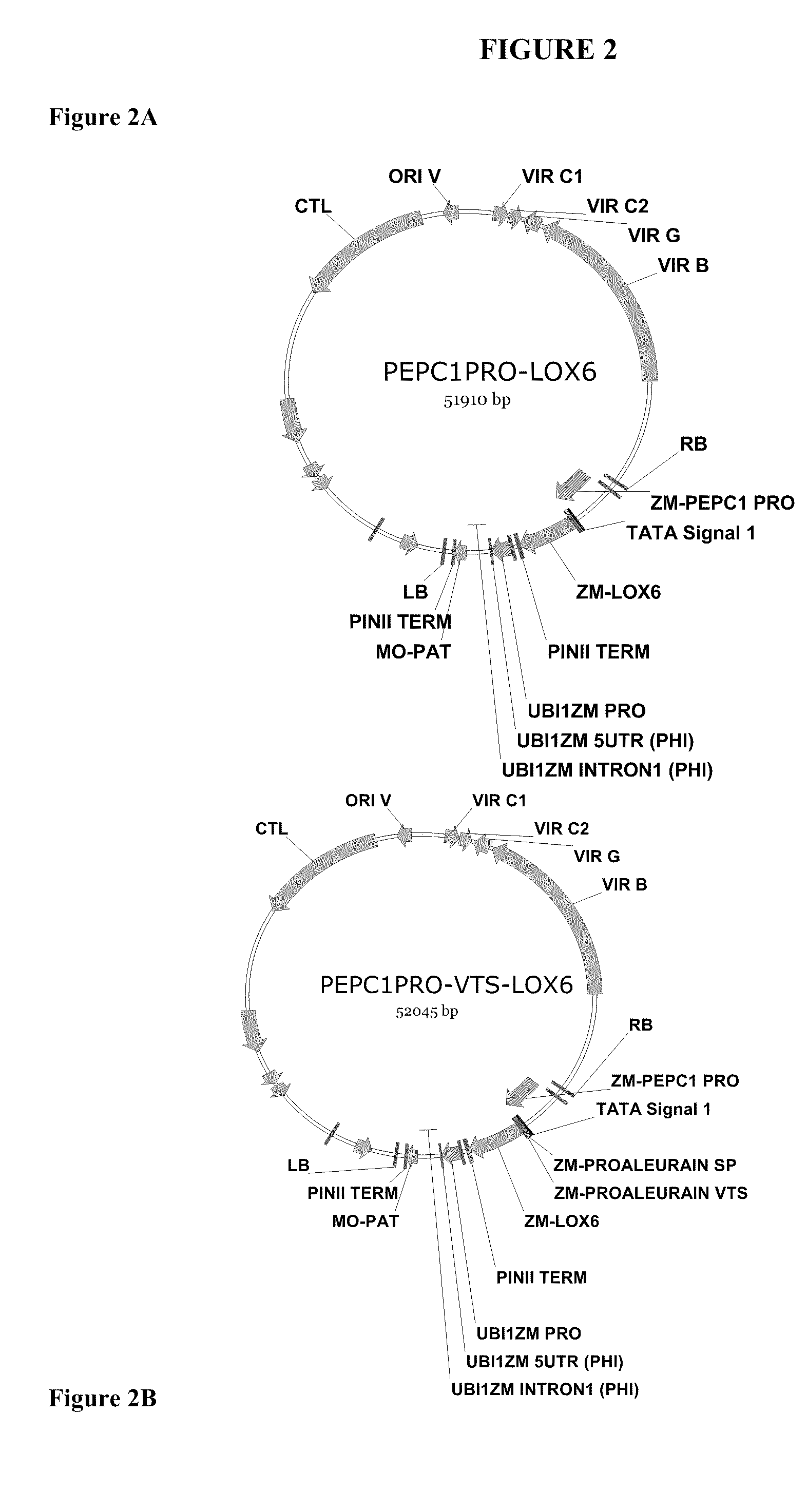
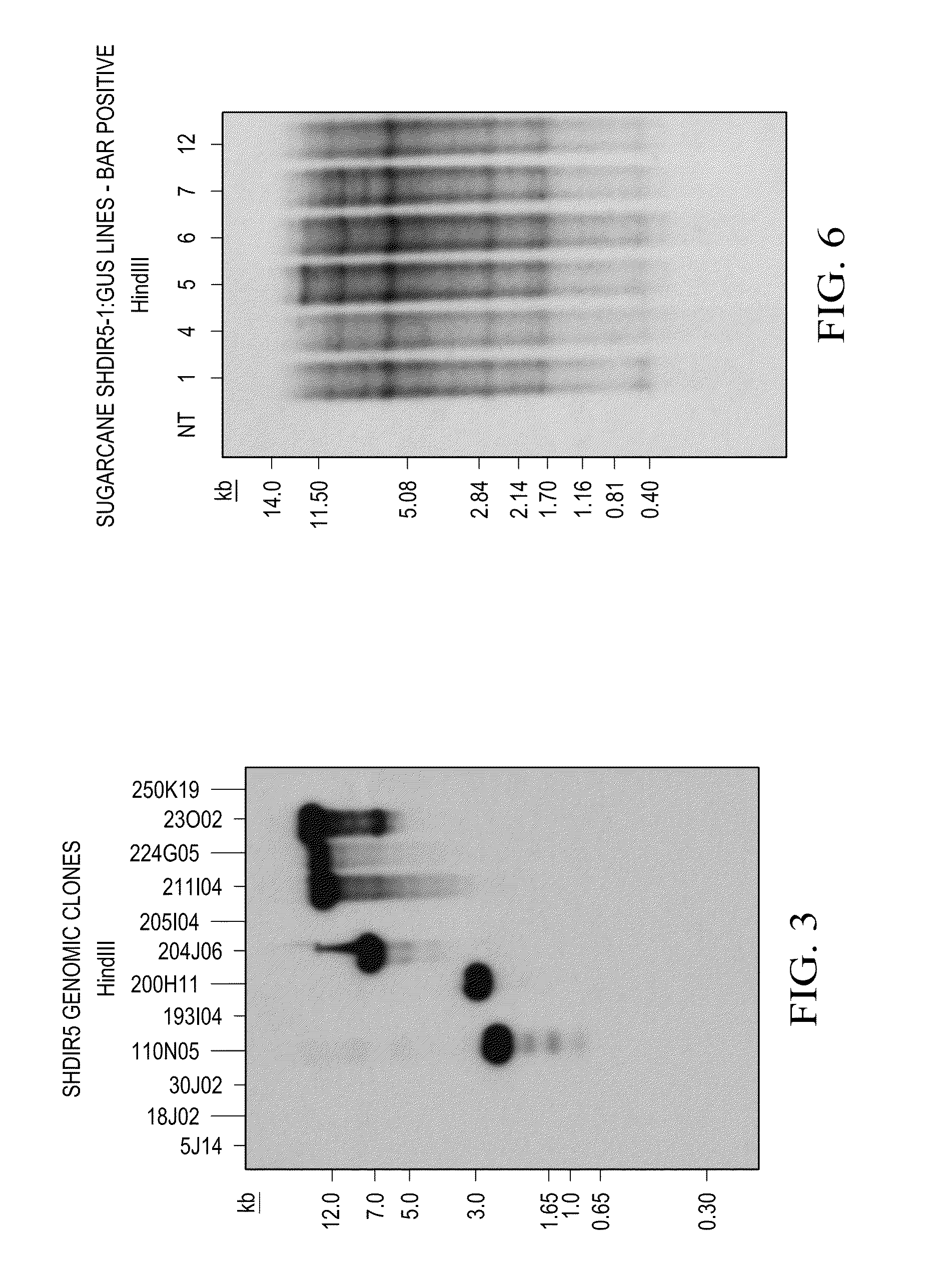
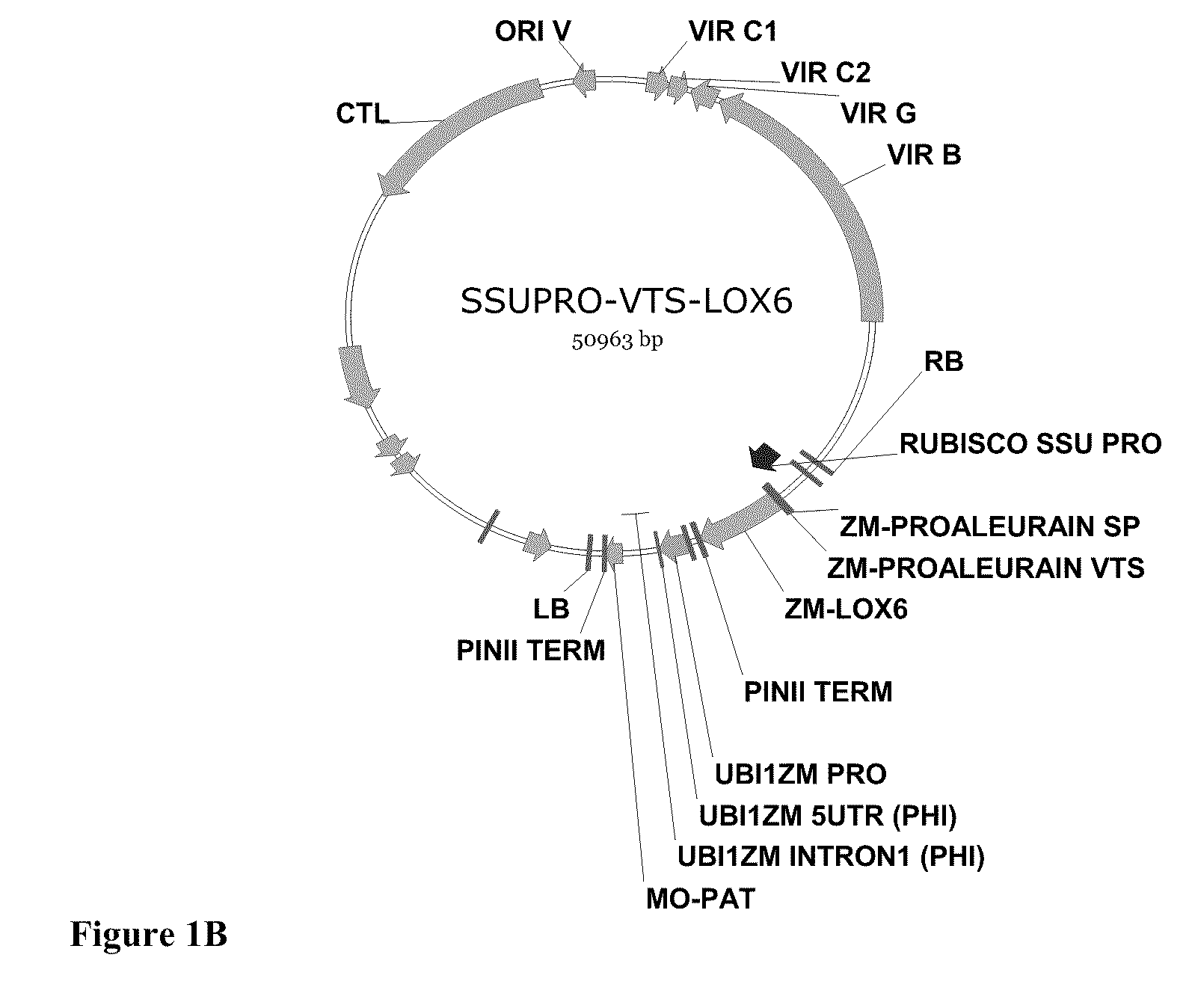
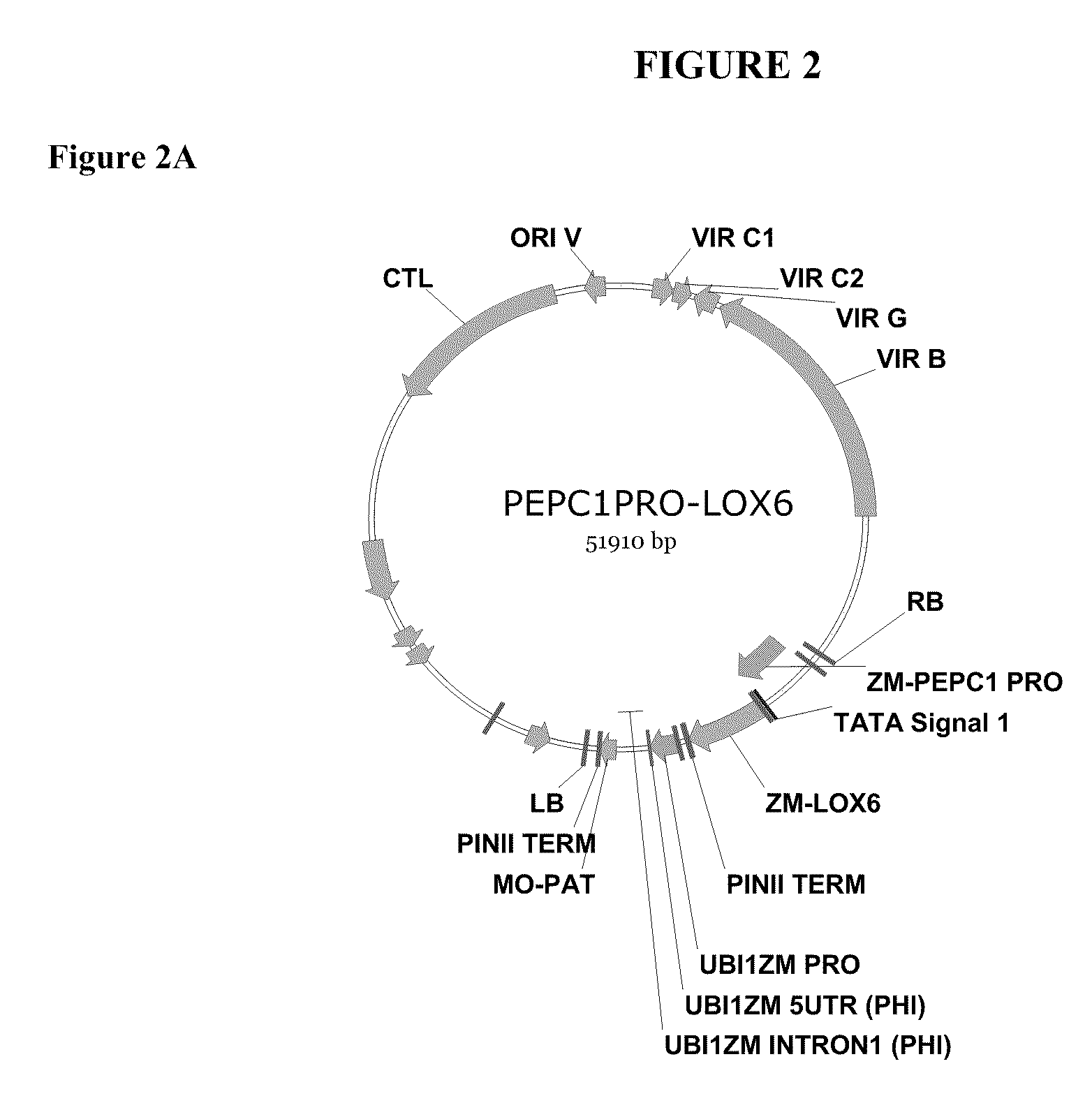
The present invention provides methods and compositions for making and using transgenic plants that exhibit increased nitrogen storage capacity compared to wild-type plants. Methods of the invention comprise inducing overexpression of monocot-derived vegetative storage proteins (VSPs) in plants, particularly in monocots. In some embodiments, at least one nucleotide construct comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding the ZmLox6 protein or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof is introduced into a plant. Depending upon the objective, the nucleotide construct may optionally comprise an operably linked coding sequence for a vacuolar sorting signal or plastid transit peptide in order to direct storage of the ZmLox6 protein or biologically active fragment or variant thereof into the vacuolar compartment or plastid compartment, respectively, of the cells in which the VSP is expressed. The invention further provides methods for producing plants with increased nitrogen content and / or increased nutritional value, which is desirable in commercial crops, including those used for forage, silage, and grain production.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
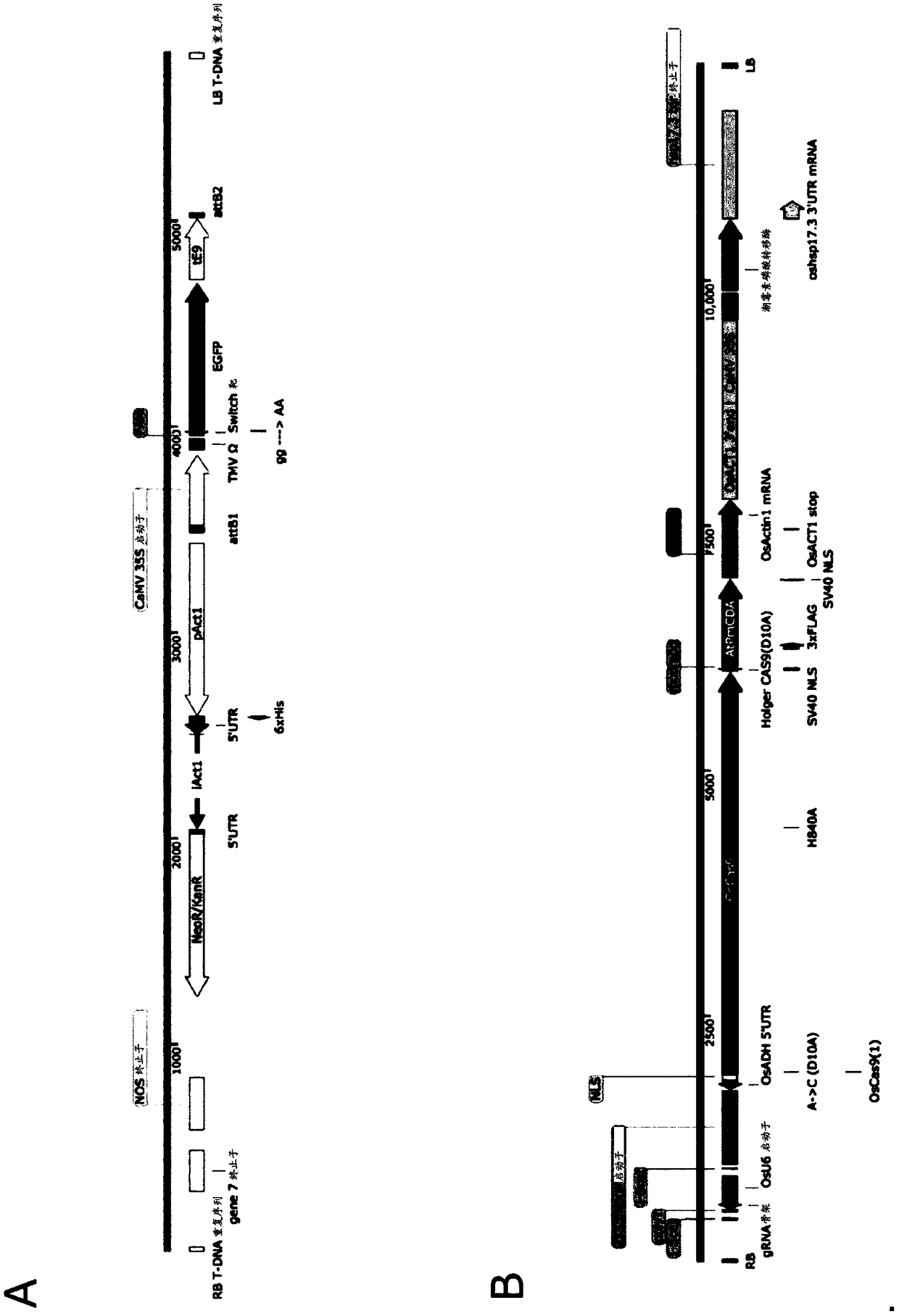
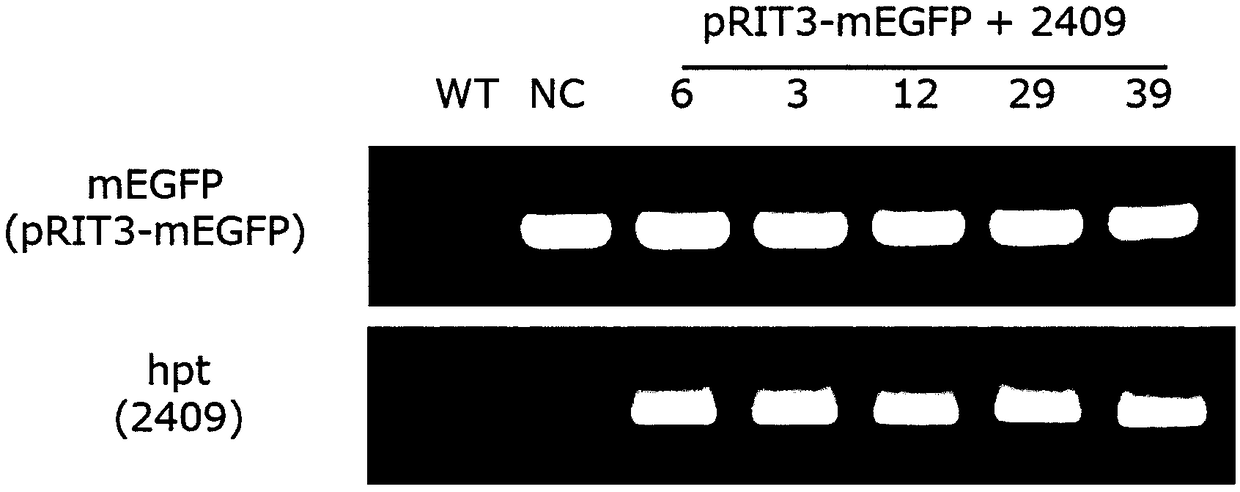
Method for converting monocot plant genome sequence in which nucleic acid base in targeted DNA sequence is specifically converted, and molecular complex used therein
ActiveCN108495932AImprove securityHigh mutation introduction efficiencyHydrolasesTransferasesMonocotyleNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for modifying a targeted site in double-stranded DNA possessed by monocot plant cells, which includes a step for, by bringing a complex, in which a nucleic acidsequence-recognizing module that specifically bonds with a target nucleotide sequence in a selected double-stranded DNA is bonded with a nucleic acid base converting enzyme, into contact with the double-stranded DNA, converting one or more nucleotides at the targeted site to one or more different nucleotides, deleting one or more nucleotides at the targeted site, or inserting one or more nucleotides to the targeted site, without cleaving at least one of the strands of the double-stranded DNA at the targeted site, wherein the contact between the double-stranded DNA and the complex is achievedby introducing a nucleic acid coding for the complex to the monocot plant cells. In addition, also provided is the complex to be used in this method, in which the nucleic acid sequence-recognizing module that specifically bonds with a target nucleotide sequence in a double-stranded DNA possessed by monocot plant cells is bonded with a nucleic acid base converting enzyme.
Owner:KOBE UNIV
Application of SCWBC11 protein in culture of male sterility line of rice
The invention discloses an application of a SCWBC11 protein in culture of a male sterility line of rice, and provides an application of a substance which is expressed by an OSWBC11 protein coding gene in a silent or inactivated target plant to culture of a male sterile plant. In the application, the amino acid sequence of the OSWBC11 protein is the sequence 2 in the sequence table. The target plant is dicotyledon or monocotyledon and monocotyledon is specifically rice. Experiments verify that by adopting an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference method, OSWBC11 protein expression interference is carried out on wild rice Nipponbare, so that the protein function is lost and rice cannot produce pollen, thereby forming the male sterility line. Therefore, the protein has an important application value to the forming mechanism of pollen of rice and the application of the protein to crossbreeding of rice can be explored.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for inactivating target transcription factor using artificial small interfering peptide and use thereof
ActiveUS20160138036A1High precision and efficiencyInhibitory activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTranscription factor activityProtein level
The present invention relates to a method for targeted inactivation of transcription factor using an artificial small interfering peptide and a use thereof. According to the present invention, an artificial small interfering peptide (a-siPEP) as a truncated from of the transcription factor for regulating transcription by dimerization was produced. It was also confirmed that, as a-siPEP forms a heterodimer with a transcription factor, DNA binding and transport into a nucleus of the transcription factor are inhibited, so that inactivation of the transcription factor is achieved at protein level. The method for inhibiting transcription factor activity using a-siPEP can replace a gene knock-out method and it allows protein-level inhibition of a transcription factor. Also, it is a transcription regulation method with high precision and high efficiency that can be applied for both monocot and dicot plants.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Compositions, organisms, systems, and methods for expressing a gene product in plants
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to compositions, organisms, systems, and methods for expressing a gene product in a plant (e.g., a monocot) using a promoter operable in one or more plant tissues and / or cells. In some embodiments, an artificial nucleic acid may comprise an expression control sequence having the sequence selected from the sequence of nucleotides 1-4710 of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the sequence of nucleotides 1137-4710 of SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the expression control sequence has stem-regulated promoter activity in at least one monocot (e.g., at least two monocots).
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Methods and Compositions For Increasing the Nitrogen Storage Capacity of a Plant
InactiveUS20090094712A1Improve planting effectMinimize impactSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationCropBiological organism
The present invention provides methods and compositions for making and using transgenic plants that exhibit increased nitrogen storage capacity compared to wild-type plants. Methods of the invention comprise inducing overexpression of monocot-derived vegetative storage proteins (VSPs) in plants, particularly in monocots. In some embodiments, at least one nucleotide construct comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding the ZmLox6 protein or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof is introduced into a plant. Depending upon the objective, the nucleotide construct may optionally comprise an operably linked coding sequence for a vacuolar sorting signal or plastid transit peptide in order to direct storage of the ZmLox6 protein or biologically active fragment or variant thereof into the vacuolar compartment or plastid compartment, respectively, of the cells in which the VSP is expressed. The invention further provides methods for producing plants with increased nitrogen content and / or increased nutritional value, which is desirable in commercial crops, including those used for forage, silage, and grain production.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Process for making biopreform from monocotyledonous caudex plant stem, biopreform obtained thereby and use thereof
A method of making biopreform from the stem of monocotyledonous caudex plant, that is suitable for liquid infiltration and gaseous transportation of materials, is disclosed. Wood from caudex stem of trees such as coconut (Cocos nucifera), palmyra palm (Borassus flabellifer), date palm (Phoenics dactylifera), is used as a precursor material which is transformed under simple pyrolitic conditions under self-generated ambient atmosphere to biopreform having microstructural features typical of a monocotyledonous caudex tree. The biopreform is capable of liquid infiltration and gaseous transportation processing of materials in an appreciably shorter processing periods, because of its preservation of the structural and anatomical features of the parent plants with high precision.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
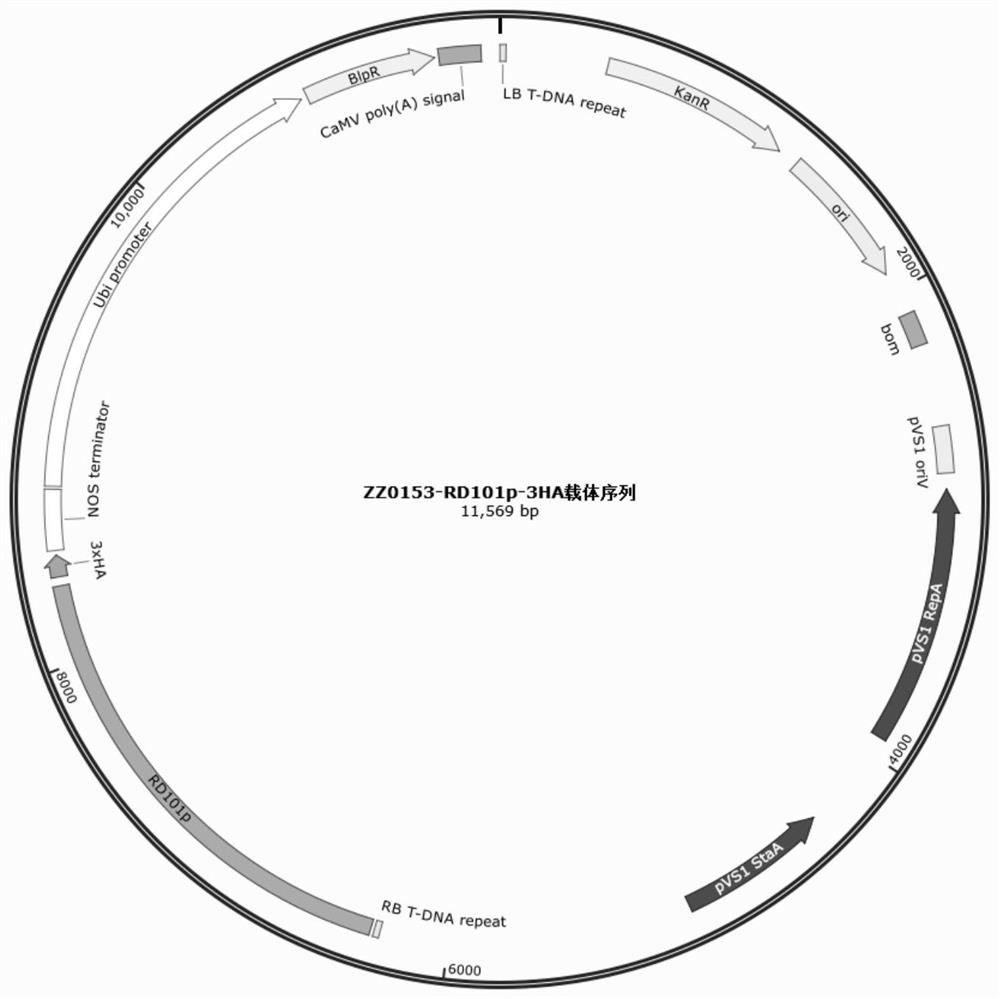
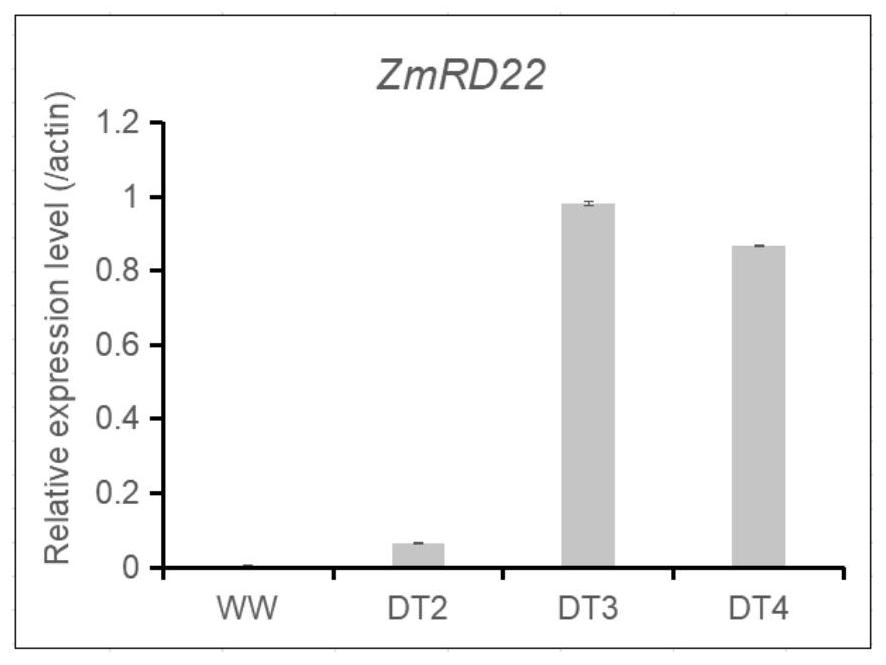
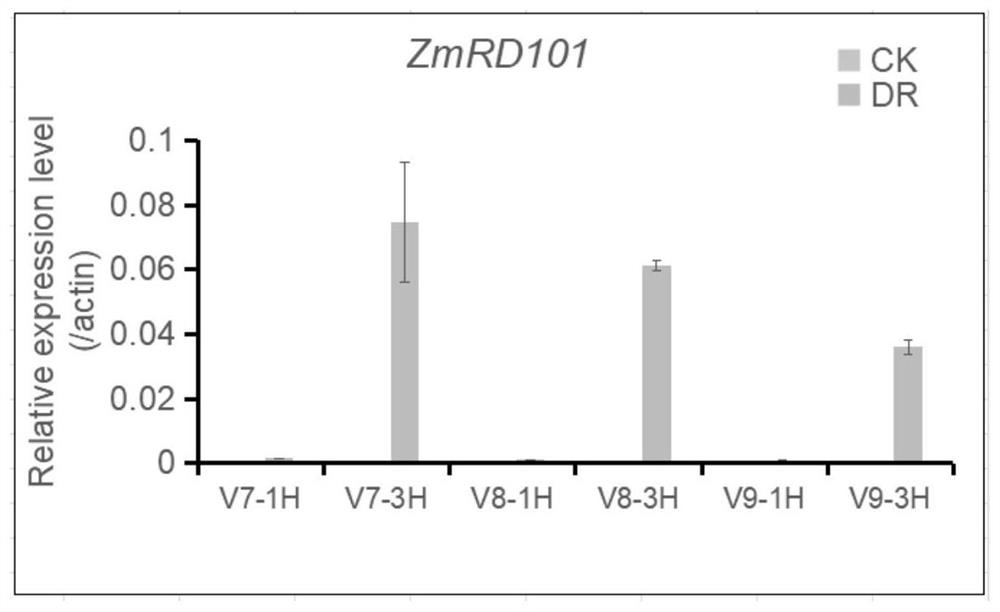
Maize drought induced expression gene ZmRD101 promoter and application thereof
The invention discloses a corn drought induced expression gene ZmRD101 promoter and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the corn drought induced expression gene ZmRD101 promoter is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The promoter of the gene ZmRD101 has the characteristics of induced high expression under drought and low expression in normal growth, and can be used in the field of transgenic breeding. A plant expression vector containing the promoter is constructed and transformed into a genome of a plant such as monocotyledon corn, and a target gene is driven to be specifically and highly expressed under drought and to be low expressed under a normal state. The strain can be used for balancing the contradiction between yield and stress resistance, is used for cultivating a new breeding material, and provides a basis for further stress-resistant breeding of corn.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
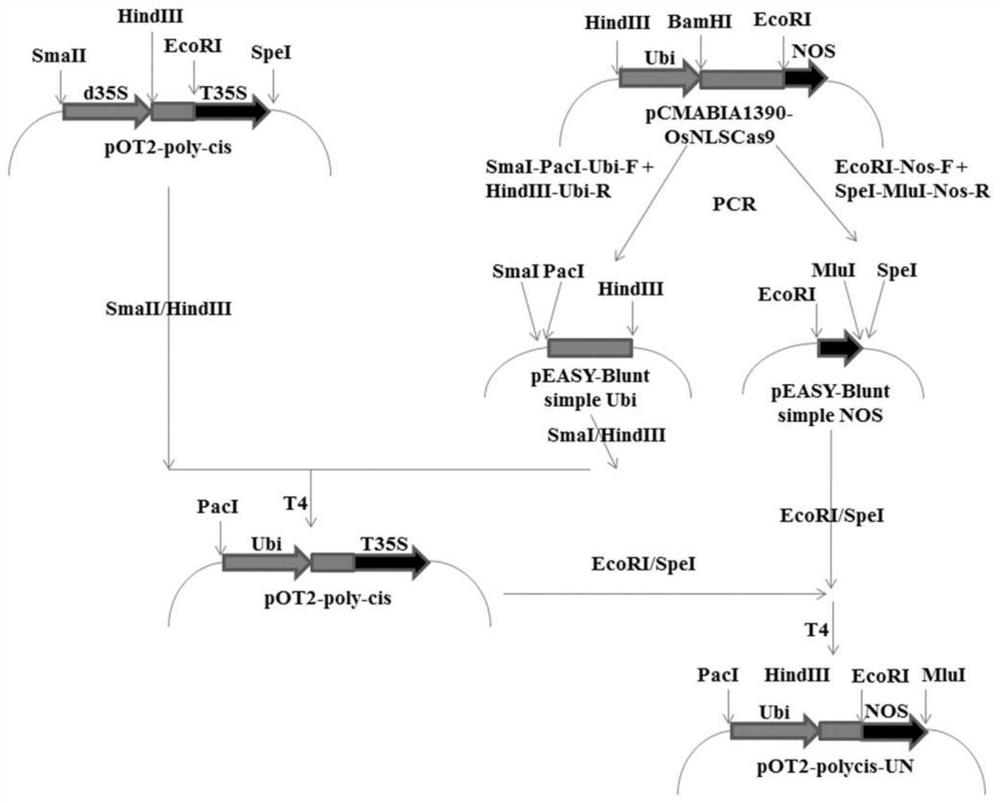
A kind of construction method of monocot miRNA efficient overexpression vector
ActiveCN109161558BAvoid introducingGood for functional studiesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyMonocotyle
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a method for constructing a high-efficiency monocot miRNA overexpression vector, comprising the following steps: S1, preparing a linking sequence corresponding to the target miRNA; S2, cloning the linking sequence described in S1 To the cloning vector, to obtain the promoter-junction-terminator structure; S3, the stem-loop structure for overexpressing the target miRNA is introduced into the promoter-junction-terminator structure of S2, so that it has at least Two stem-loop structures; S4, the promoter-junction sequence-terminator structure obtained by S3 is cloned into a binary vector by double enzyme digestion. The invention has high connection efficiency, simple and easy operation, avoids the introduction of unnecessary transgenic components, is beneficial to the research on the function of miRNA in monocotyledonous plants, and is more conducive to the phenotype observation and result interpretation of subsequent transgenic plants.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
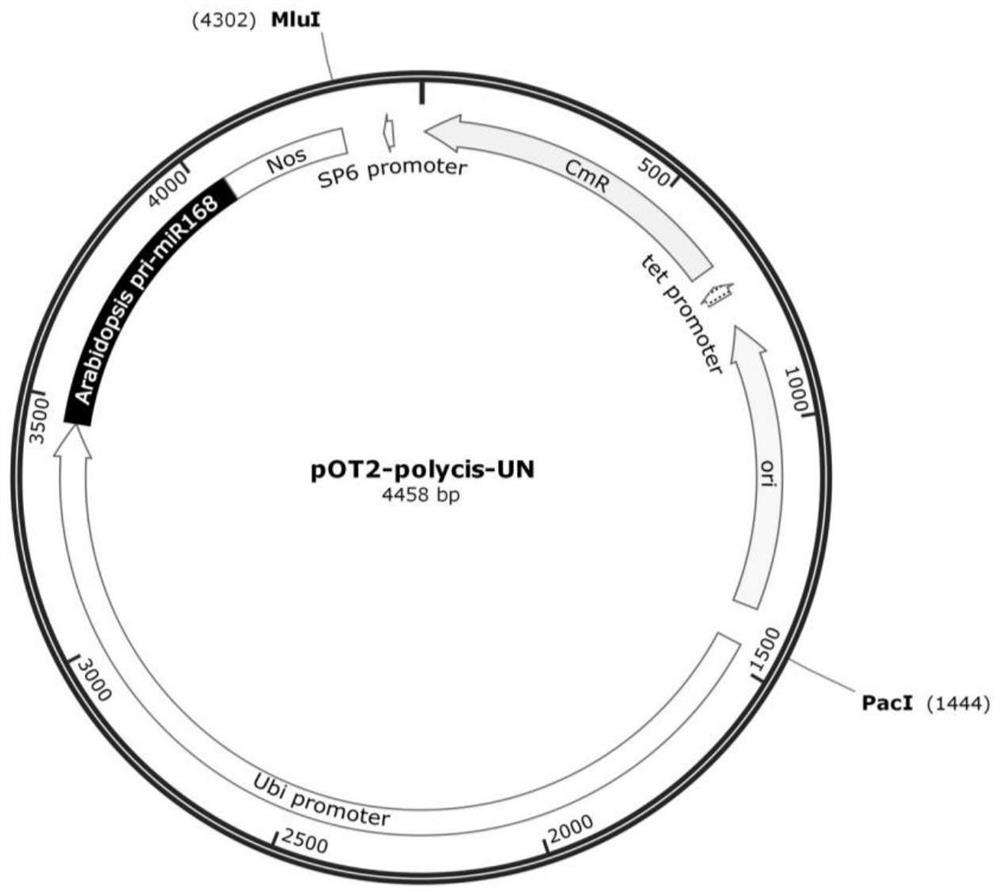
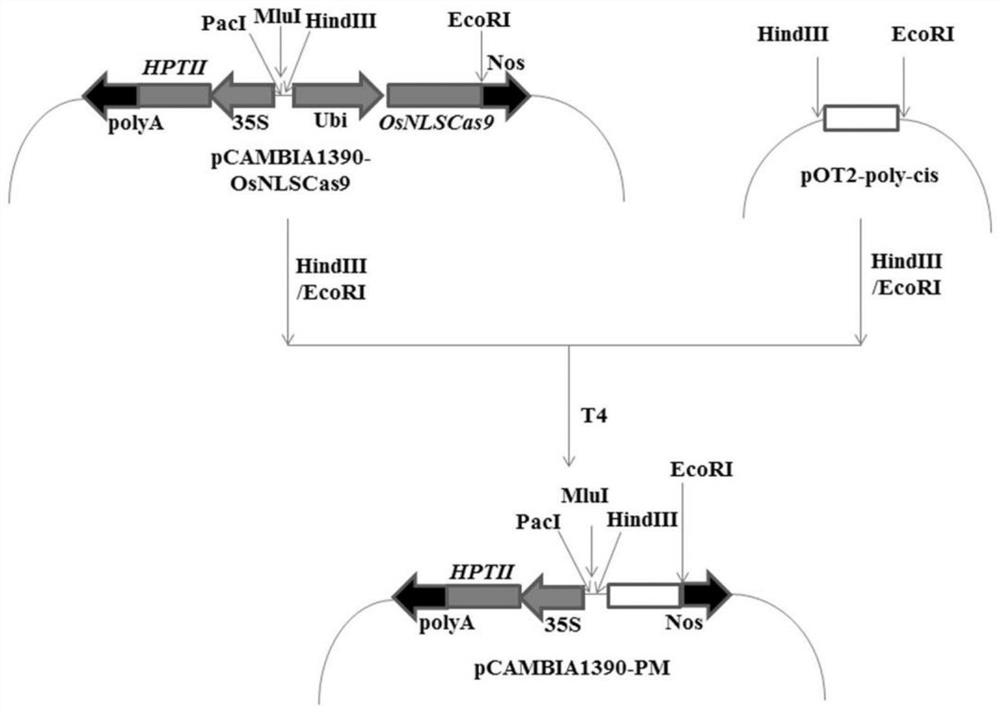
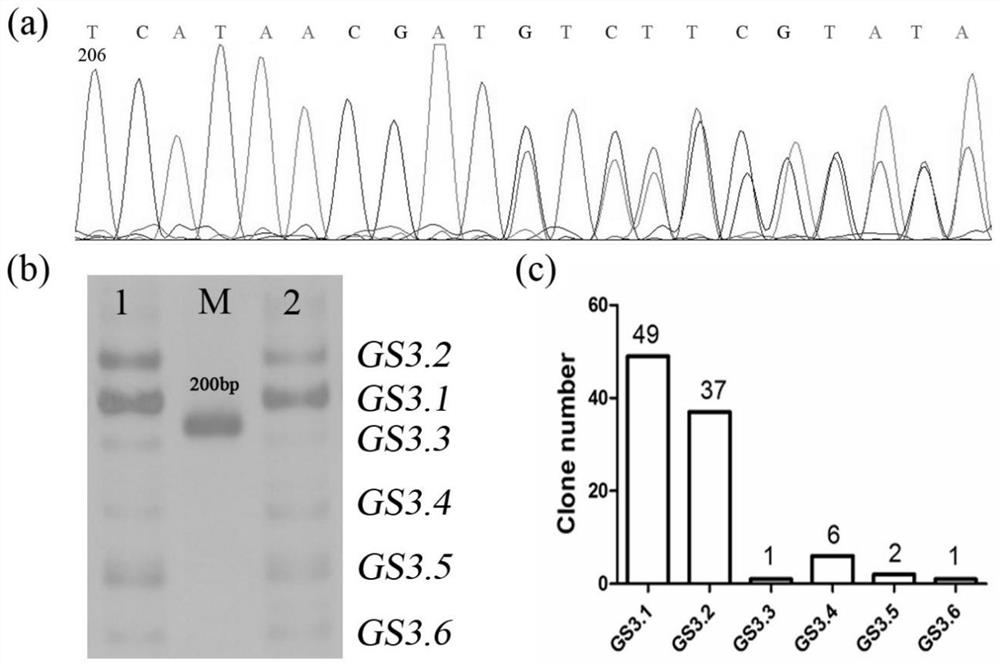
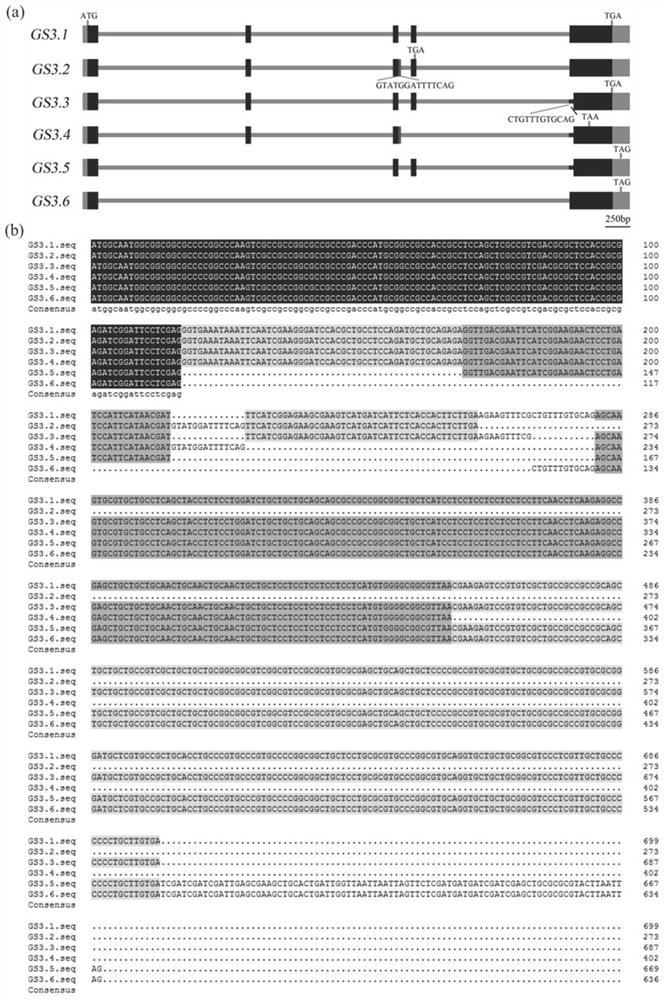
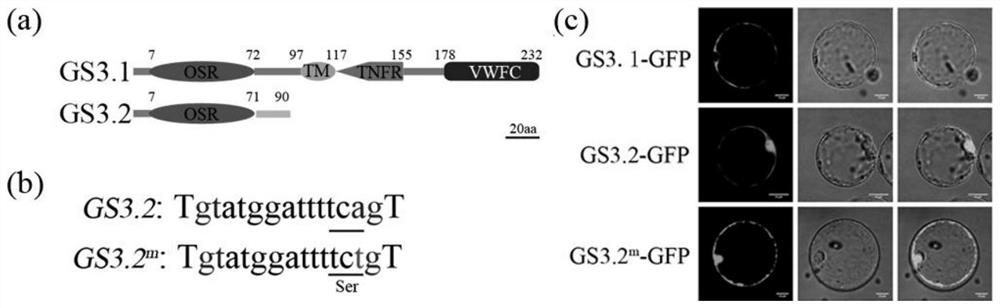
Application of rice spliceosomes GS3.2 in regulation and control of rice grain traits
InactiveCN113604476AInhibition of negative regulationLower levelPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyMonocotyle
The invention discloses application of rice spliceosomes GS3.2 in regulation and control of rice grain traits. The invention identifies that a GS3 gene has a plurality of spliceosomes GS3.1-GS3.6, wherein the main spliceosomes are GS3.1 and GS3.2, which respectively account for about 50% and 40% of a total transcript, while GS3.2 reduces the level of GS3.1 form at the RNA level on the one hand, and competitively inhibits signal transduction of GS3.1 at the protein level on the other hand, thereby inhibiting the negative regulation and control effect of GS3.1 and achieving the effect of maintaining the normal size of rice grains. On that basis, the invention inhibits the negative grain size regulation and control function of GS3.1 by expressing GS3.2 in a GS3.1 high-expression strain, thereby achieving the purpose of maintaining the normal size of rice grains. The invention not only solves the problem that the functional differentiation mechanism of the dicotyledon AGG3 and the monocotyledon GS3 is still unclear, but also can be applied to the fields of actual production, breeding and the like of rice as a new rice grain trait regulation and control means.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Isolated nucleic acid molecules from the genome of citrus leprosis virus and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090265816A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesOligonucleotide PrimerImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules found in the genome of the Citrus Leprosis Virus (CiLV), which is associated to Citrus Leprosis (CiL) disease. The cloned CiLV nucleic acid molecules can be used as probes or can be used to design oligonucleotide primers useful in assays, such as a polymerase chain reaction, for detecting the presence of CiLV in biological samples, particularly leaves, roots and other tissues or organs of plants, such as plants from the genera Citrus and Poncirus. The invention comprises introducing the mentioned nucleic acid molecules in cloning vectors and cloning the recombinant nucleic acid molecules in cells, such as prokaryotes (e.g., bacteria like E. coli), and eukaryotes (e.g., yeast, COS, CHO, and other cells). The cloned CiLV nucleic acid molecules are expressed in cells to provide immunogenic proteins which can be used to raise antibodies against the CiLV, which can then be used to detect the presence of the CiLV virus in biological samples. It also comprises the nucleic acid molecules represented in SEQ ID Nos. 5 and 8, in whole or part, as well as transgenic plants, such as monocots and dicots, containing the CiLV nucleic acid molecules, in any kind of combination, so that expression increases resistance to CiL disease.
Owner:FISCHER AGROINDA
A Method for Extracting Rice Leaf Plasma Membrane Phosphorylated Proteins Suitable for Two-dimensional Electrophoresis
ActiveCN109136166BEvenly distributedEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesMonocotylePhosphorylation
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
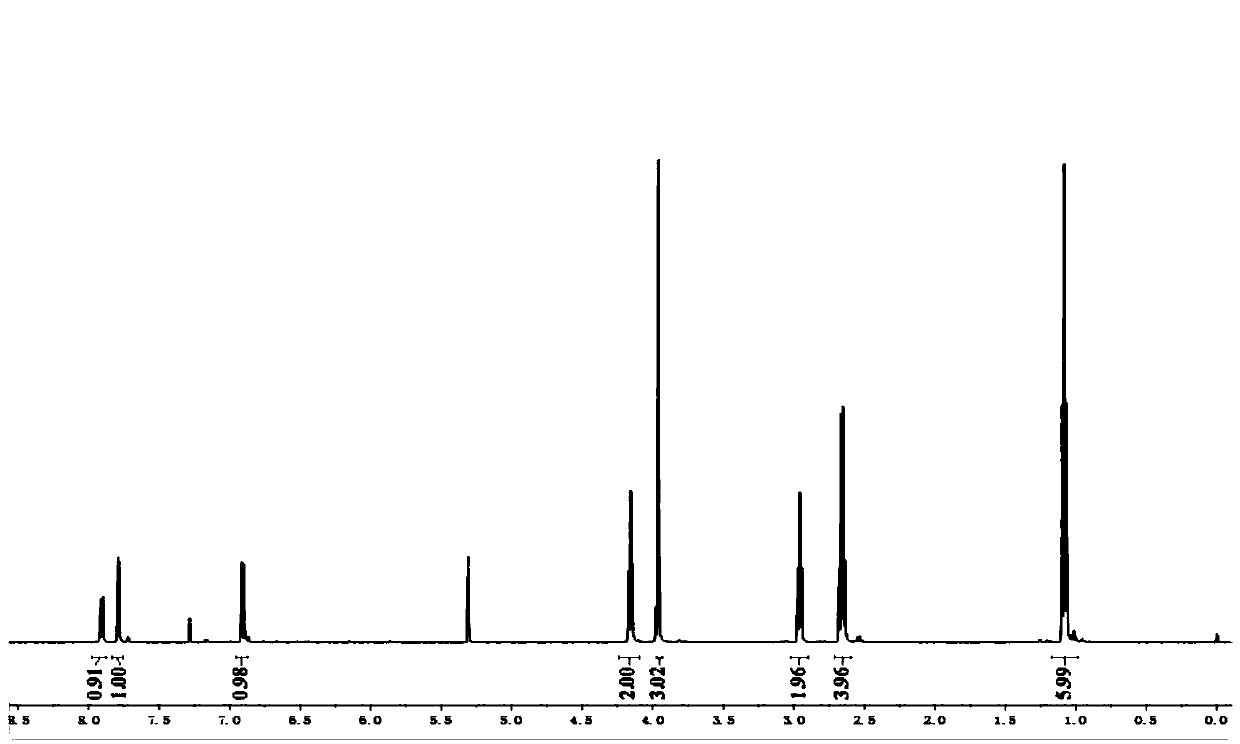
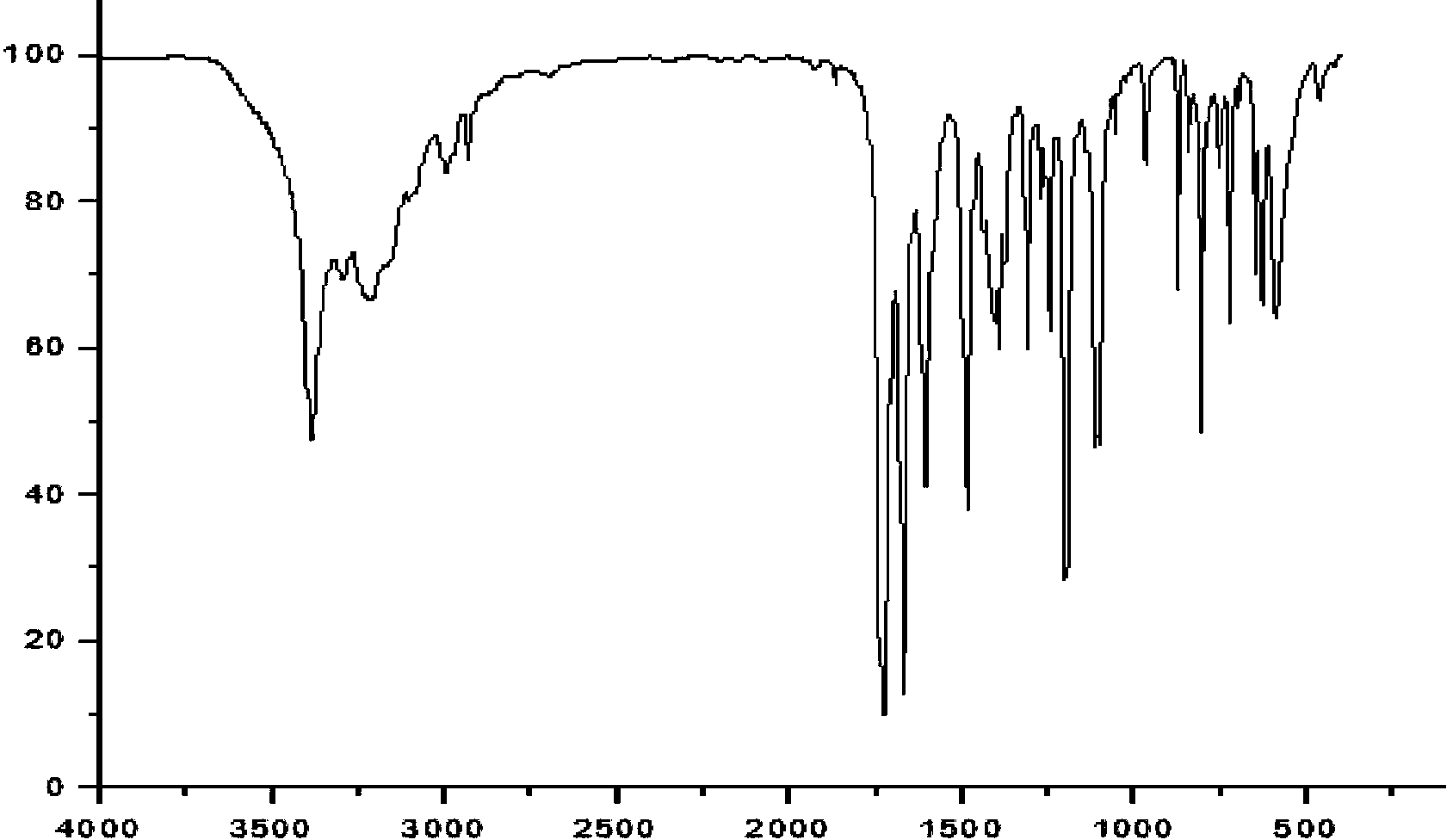
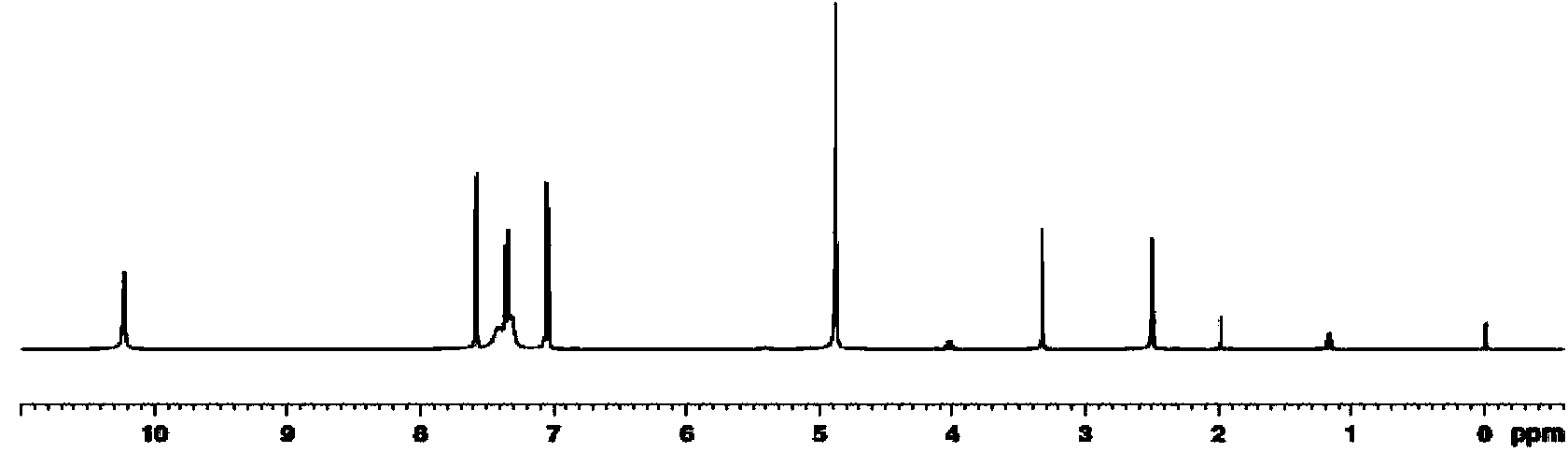
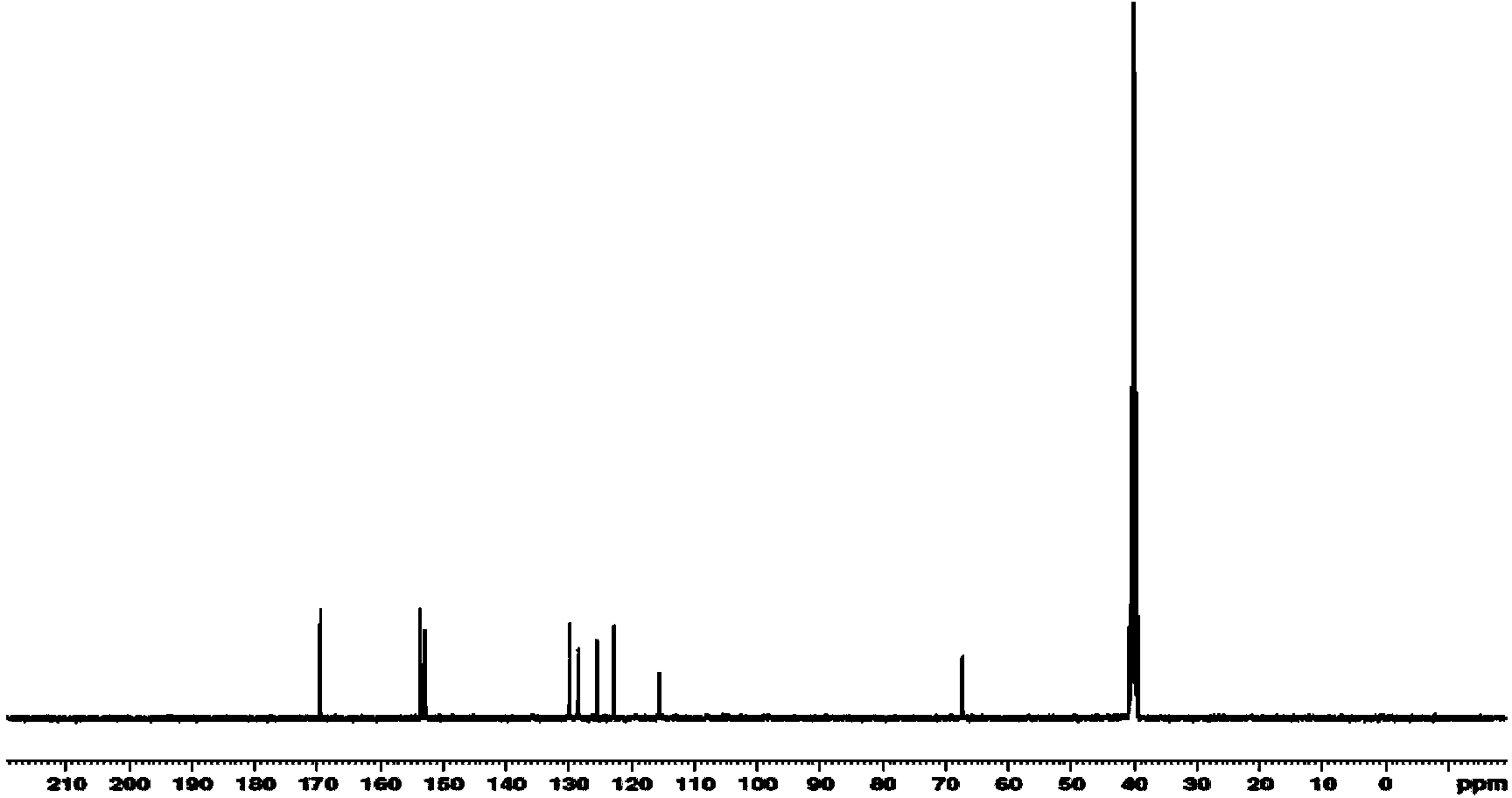
1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110669010AHigh activityImprove stress resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMonocotyleGrowth plant
The invention belongs to the technical field of agrochemistry, and relates to a novel plant growth regulator 1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt compound, a preparation method and use thereof. The structure of the compound is shown by the following formula: the biological activity experiments of the compound are carried out on monocotyledonous plant wheat and dicotyledonous plant soybean respectively. The results show that the compound has obvious plant growth promotion effect when the concentration is low and certain inhibition effect when the concentration is high.It is a broad-spectrum plant growth regulator. Moreover, the production process is simple and easy to realize industrial production, providing a new choice for plant growth regulators.
Owner:HIGH & NEW TECH RES CENT OF HENAN ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


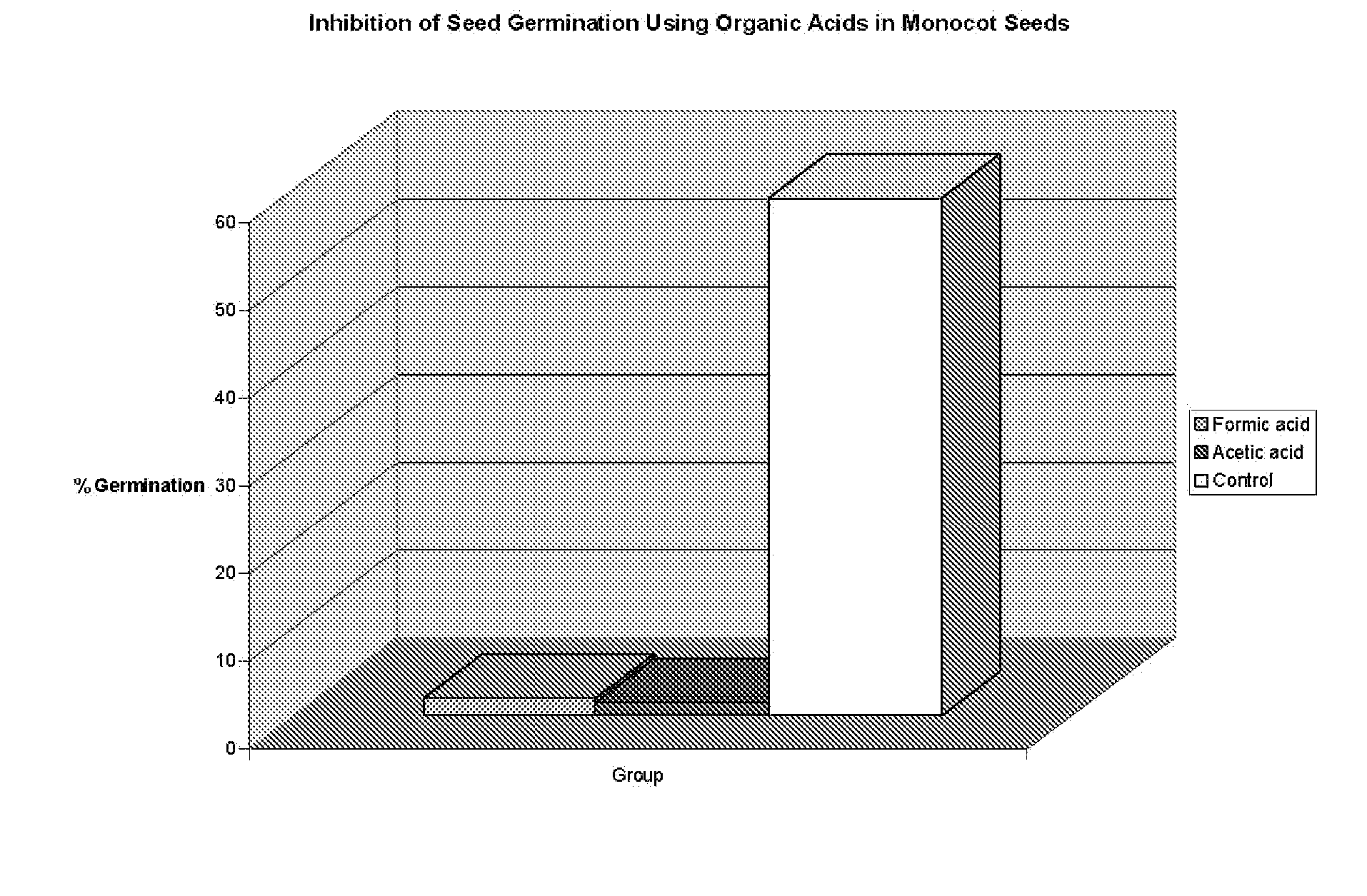




![1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof 1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e7fb047-d874-4a31-9ef0-8a48720d818f/DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.png)
![1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof 1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e7fb047-d874-4a31-9ef0-8a48720d818f/BDA0002269234610000022.png)
![1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof 1-[2-(2-methoxy-5-nitro-phenoxy)]-ethyl 3-methylimidazole salt and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e7fb047-d874-4a31-9ef0-8a48720d818f/BDA0002269234610000051.png)