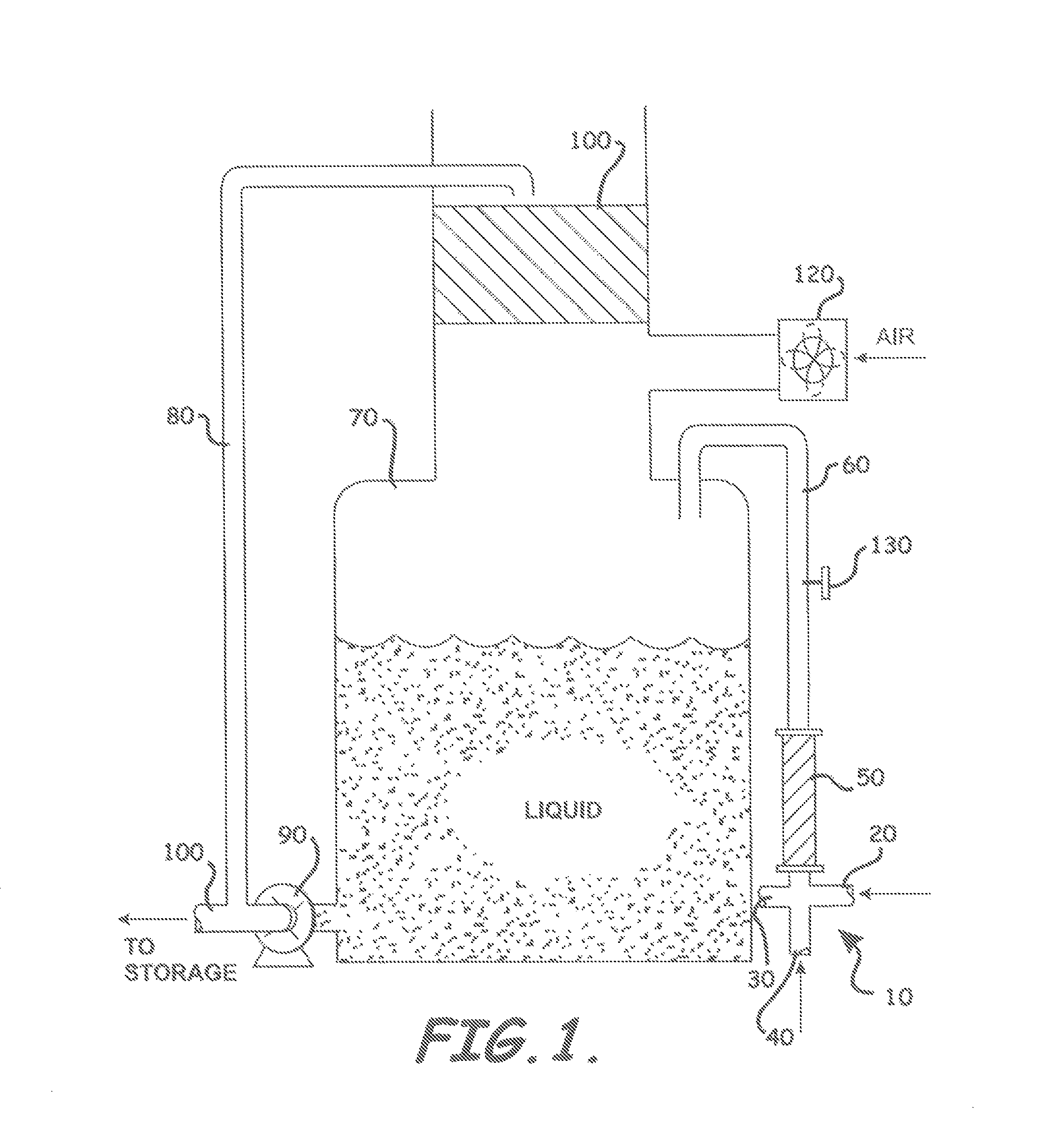
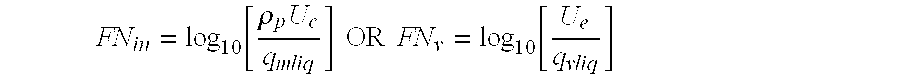Patents
Literature
170results about "Phosphatic fertiliser granulation/pelletisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
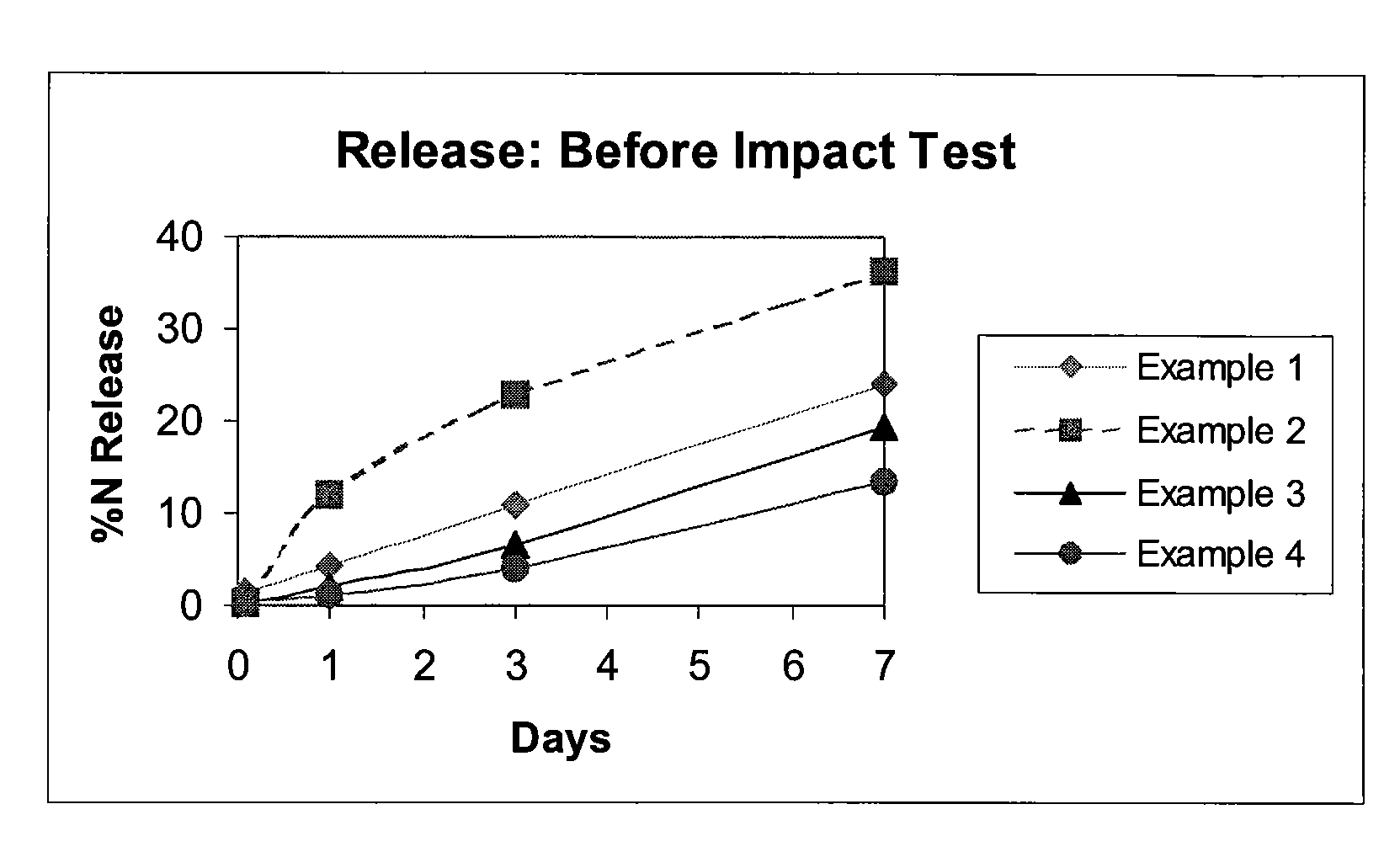
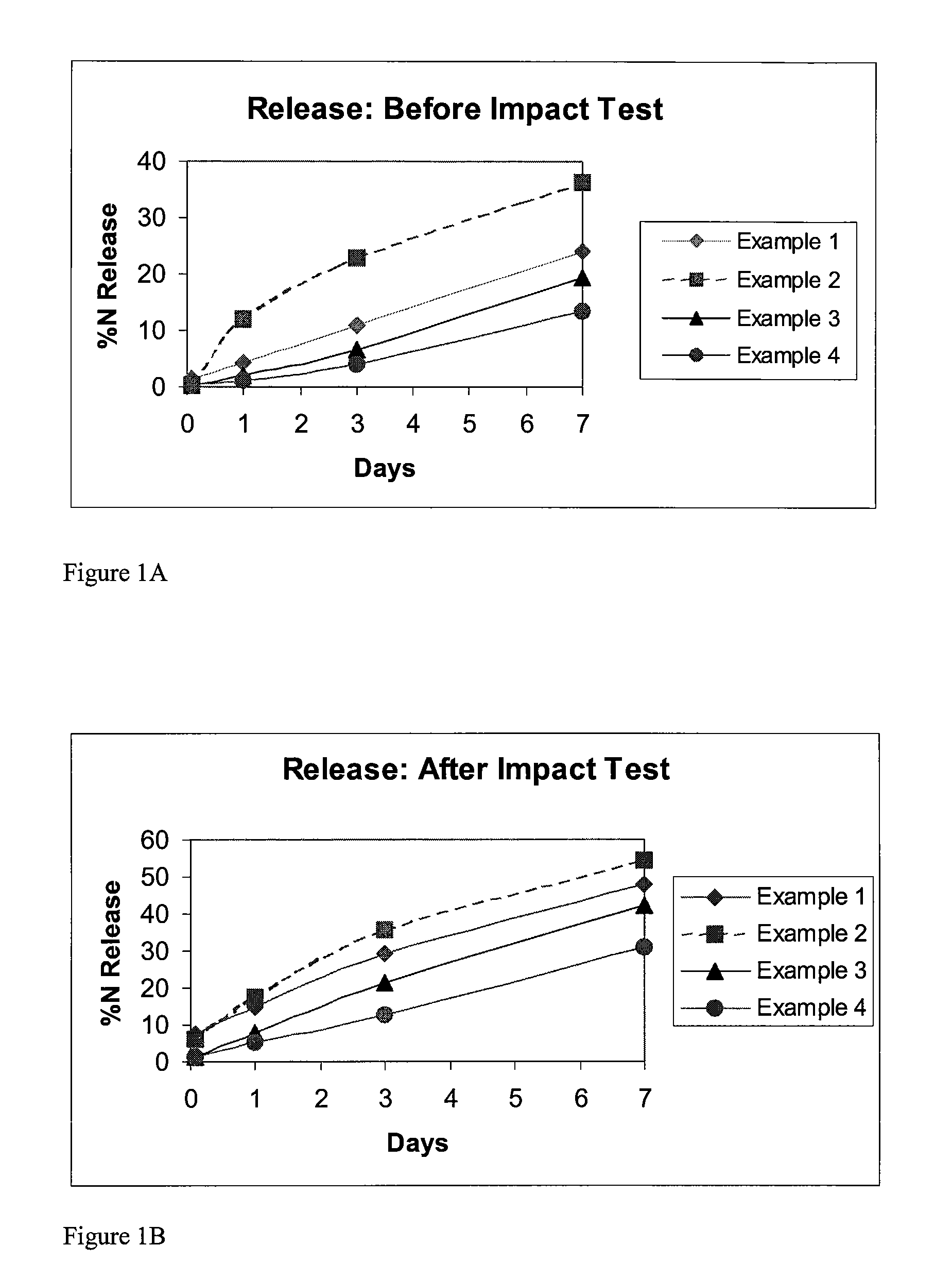
Controlled release fertilizer composition
ActiveUS7771505B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce the amount requiredBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersControlled releaseWater insoluble
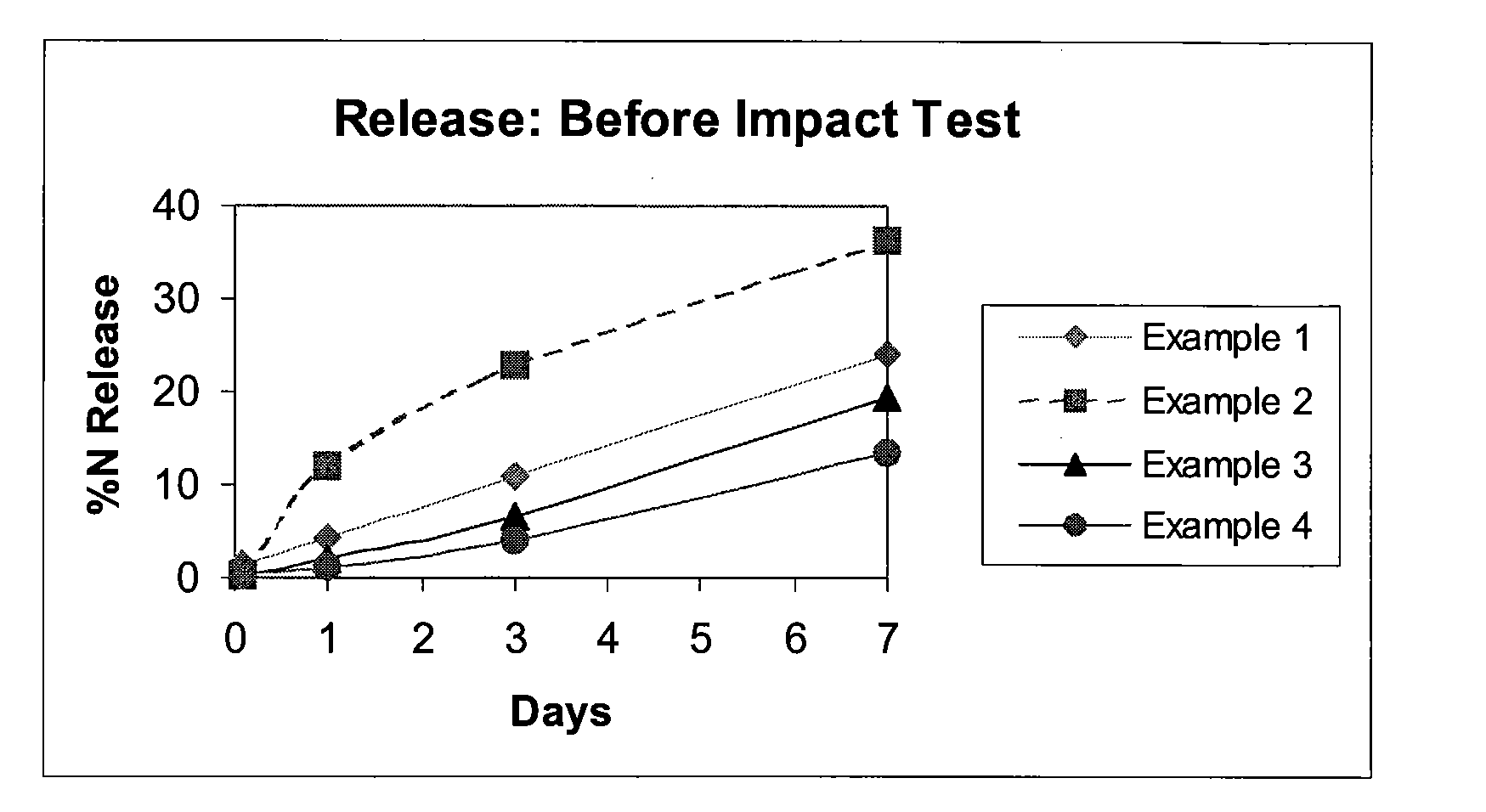
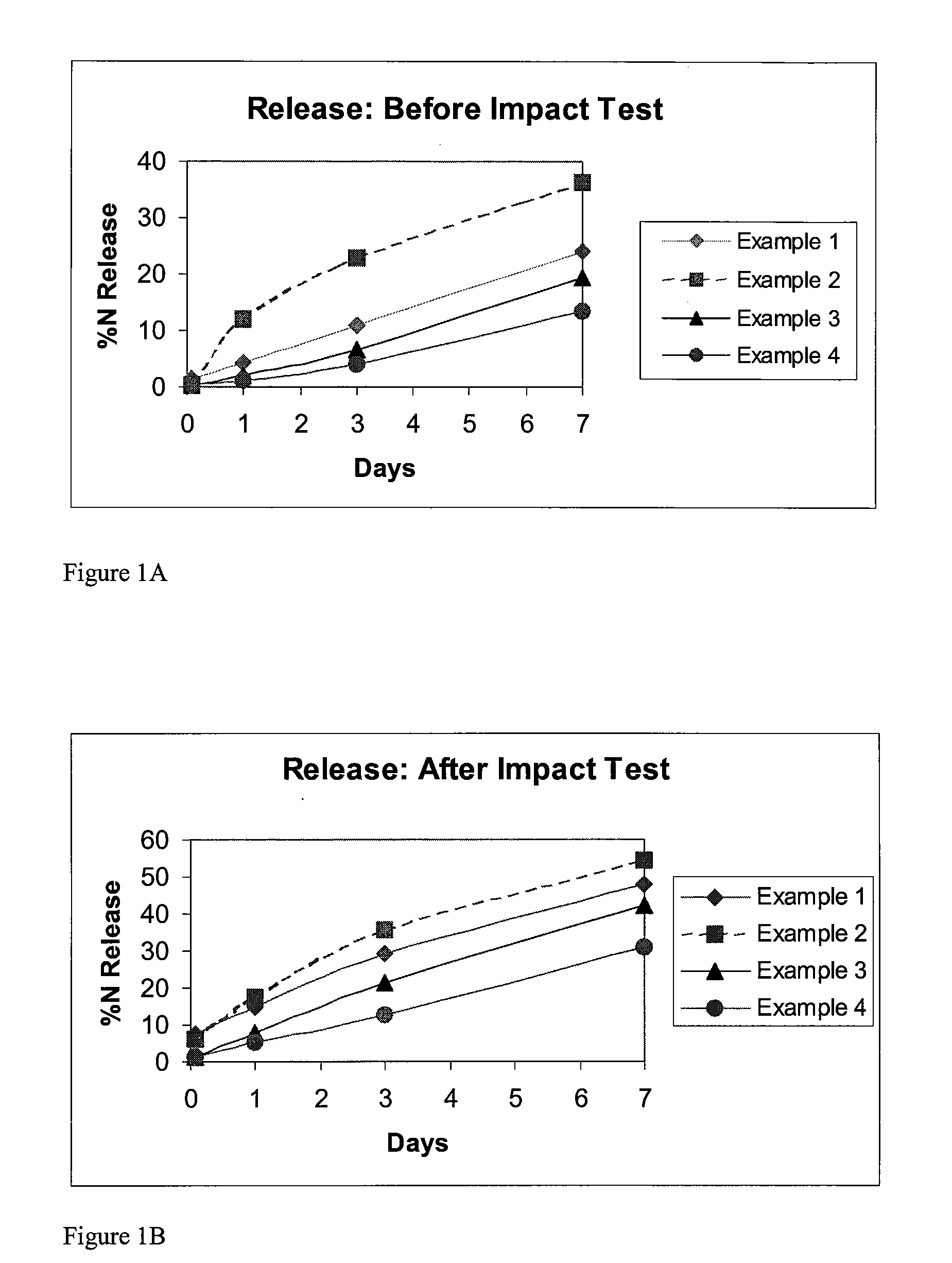
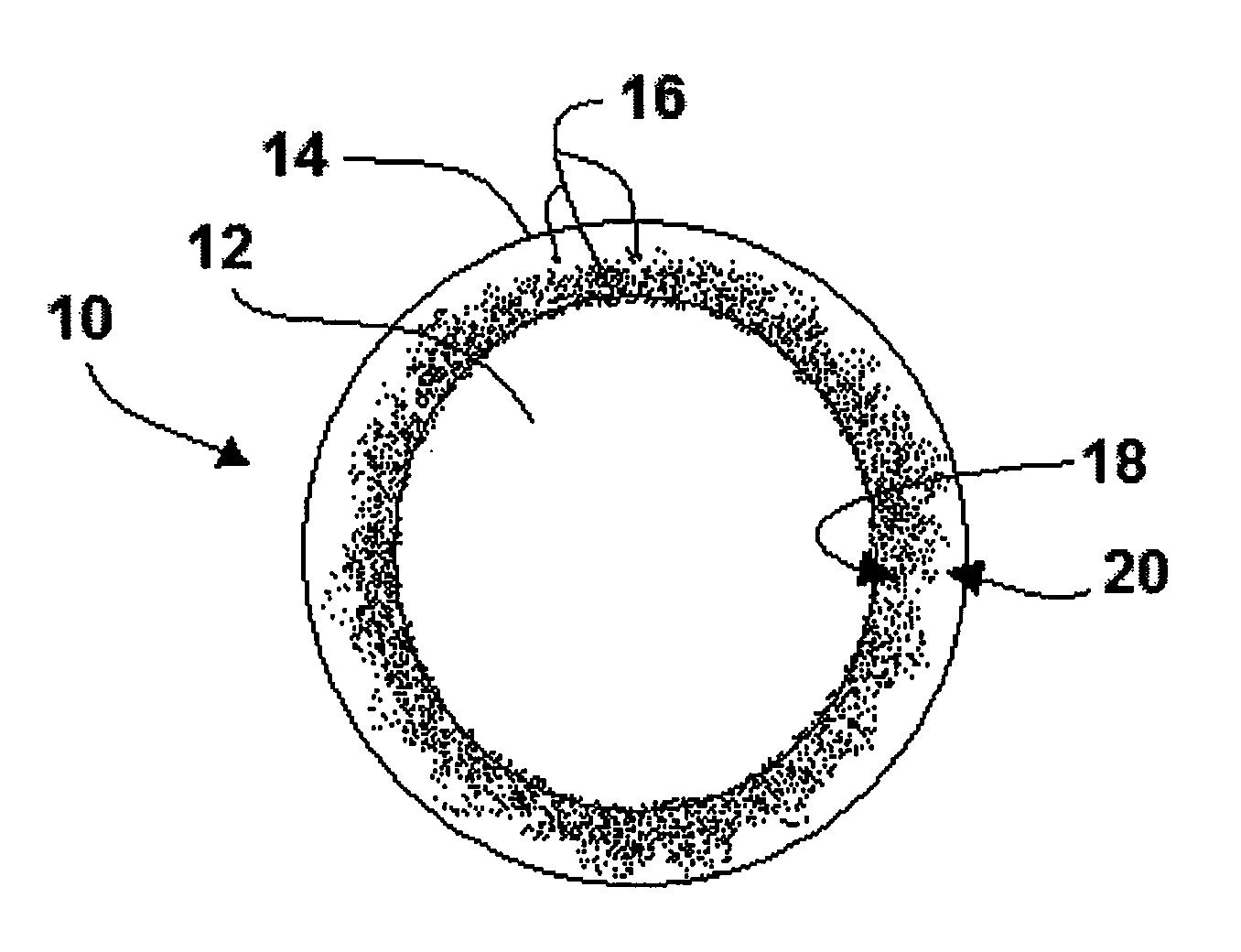
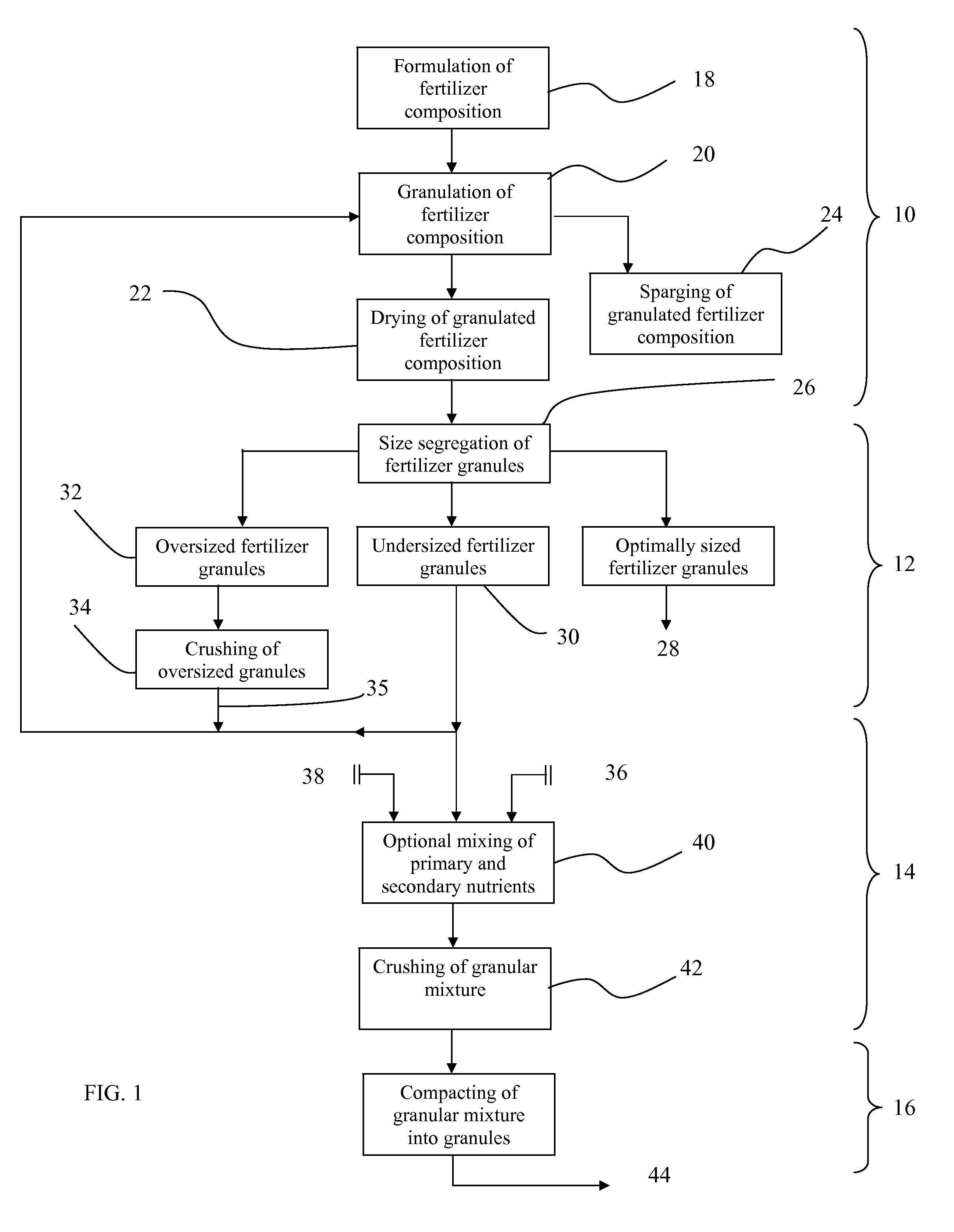
A controlled release fertilizer composition and methods to produce the controlled release fertilizer composition are described. The controlled release fertilizer composition comprises a water soluble fertilizer core that is coated with a polymeric layer, intermediate layer, and a sulfur layer. If desired, the sulfur layer can be coated with an outer water-insoluble layer.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
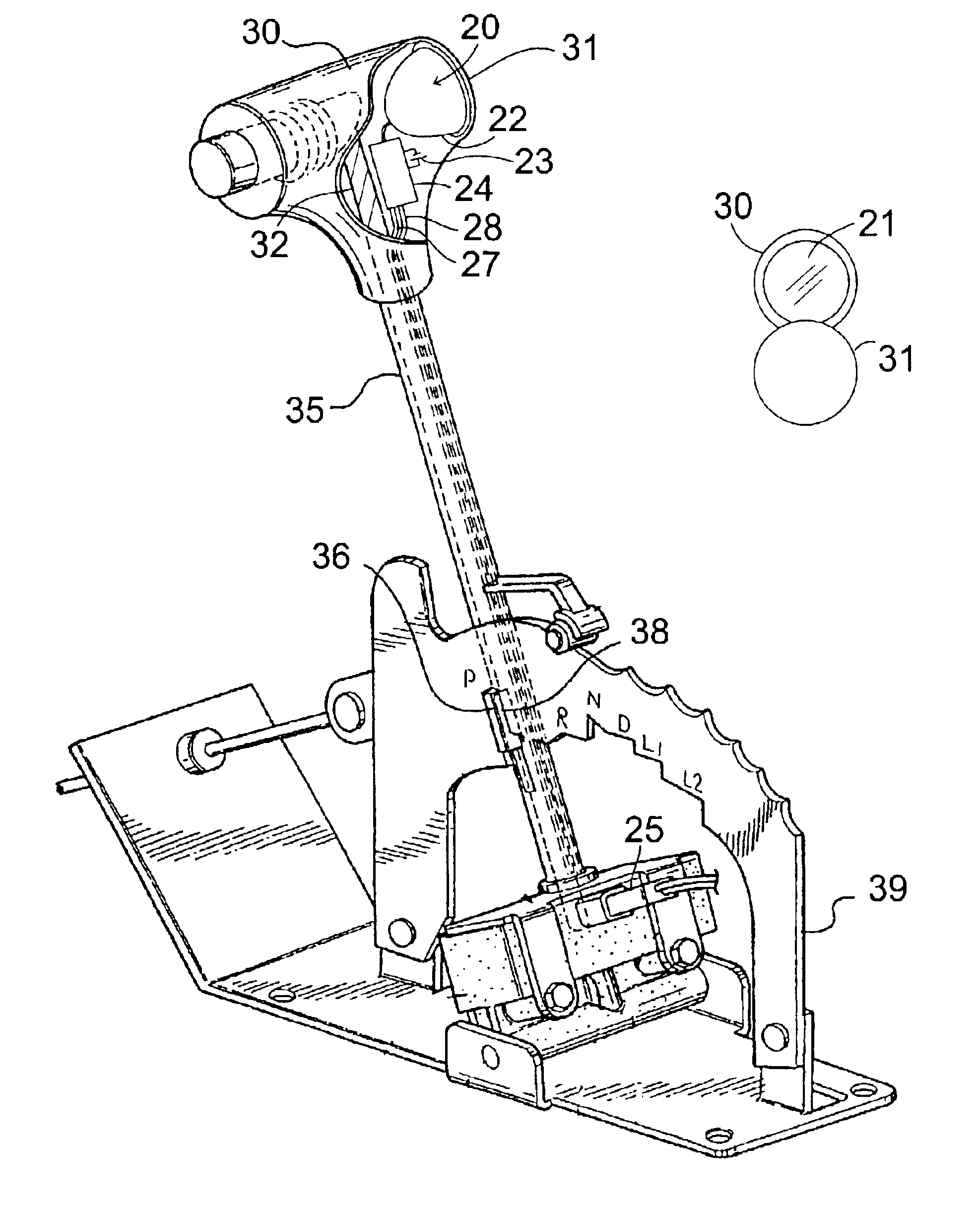
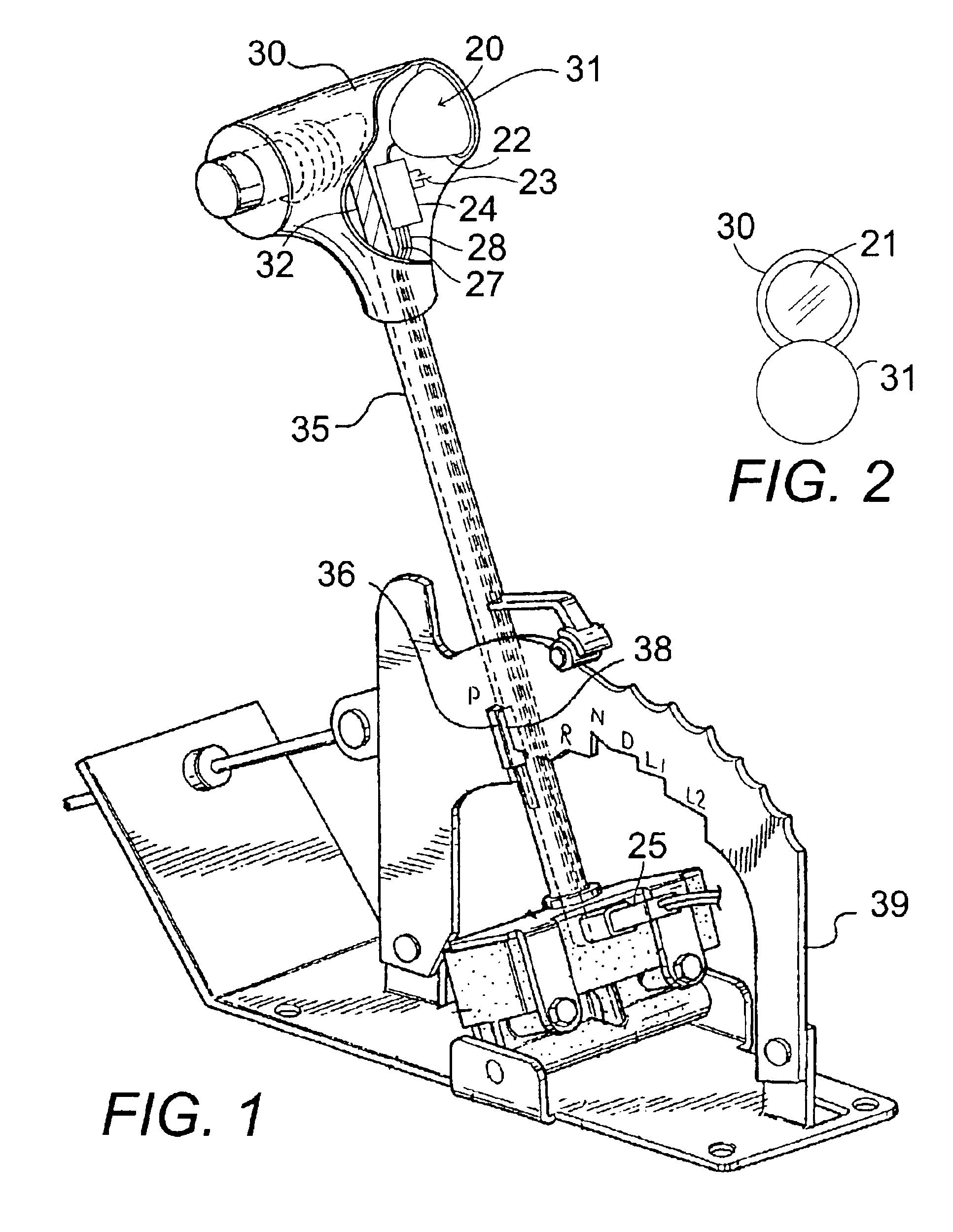
Biometric shifter lock control
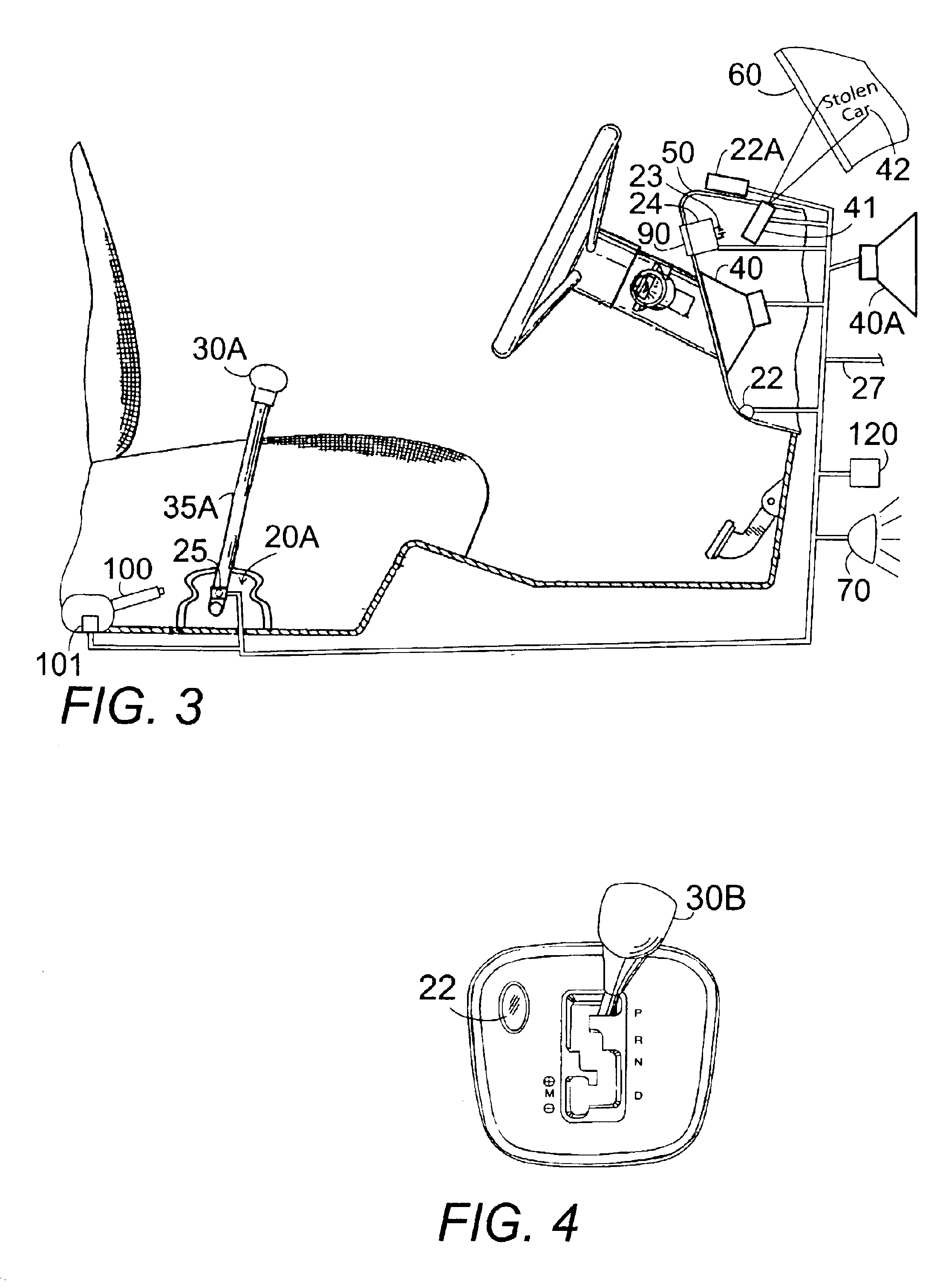
InactiveUS6927671B2Electric signal transmission systemsImage analysisBiometric dataSpeech identification
A biometric anti-theft gear shifter lock control for vehicles, equipment, and machinery, and other transmission actuation devices on land, water, and air, using a gear shifter. A biometric sensor scans in biometric information from a user to a central processing unit (CPU). The CPU finding a match for an authorized user deactivates a shift lock which may be built into an automatic shift vehicle or a solenoid or other switch added to a standard shift vehicle. It sounds an alarm for an unauthorized user. The control may be positioned on a gear shift knob with a flip-type protective cover. The biometrics device could be a fingerprint scanner, a retina scanner, a voice recognition system or other device programmed to operate only upon recognition of a unique biometrically measurable characteristic of one or more authorized users whose biometric data is programmed into the system.
Owner:DEBONO JOSEPH M
Fertilizer combination products including fertilizer granules and cellulosic granules carrying pesticides and other active ingredients
Blends of fertilizer granules and highly absorbent cellulosic granules carrying one or more pesticidal or other active ingredients that resist the formation of actives dust or segregation of the granules and that ensure even and efficient application of both the fertilizer and the active ingredients.
Owner:KADANT GRANTEK
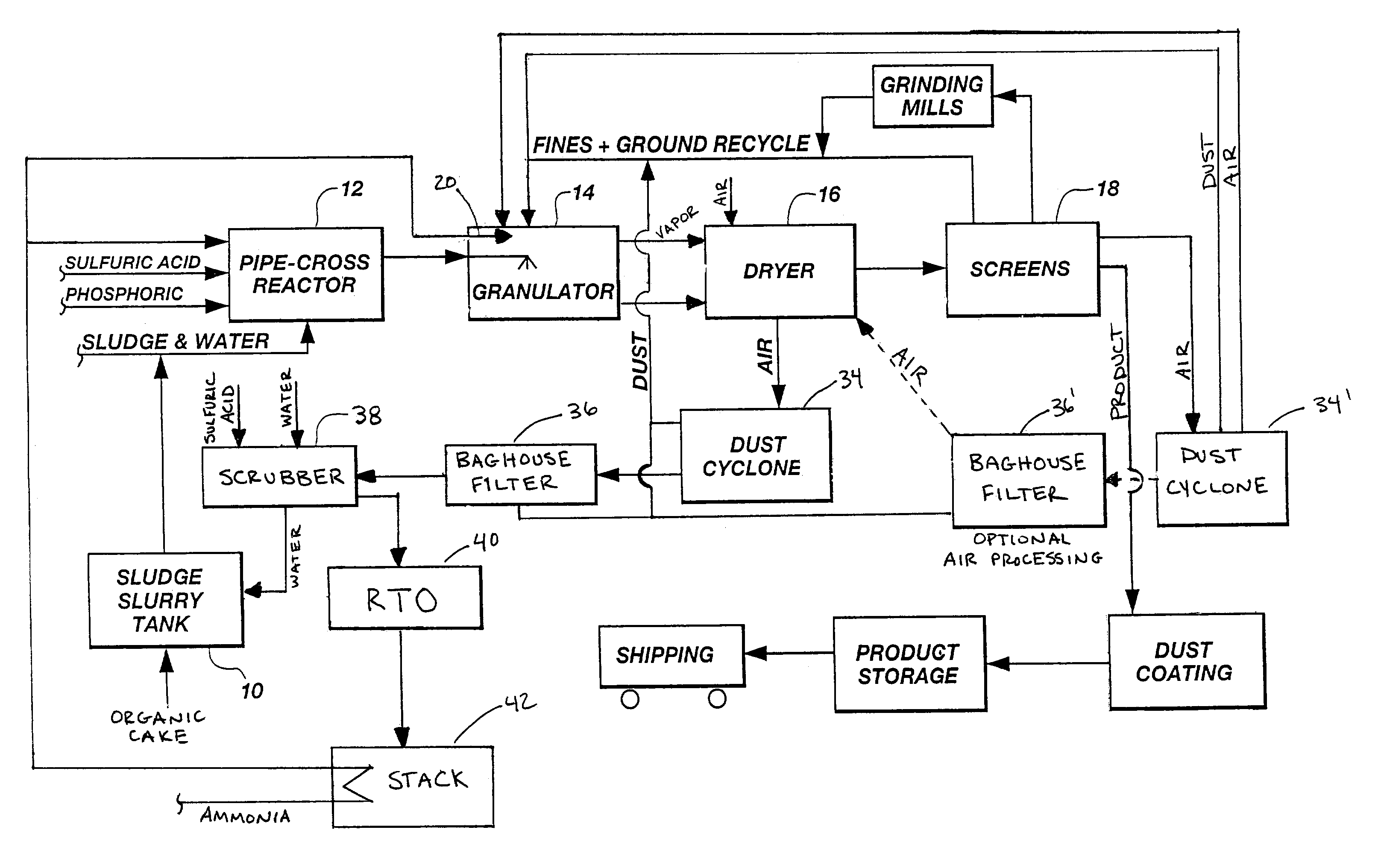
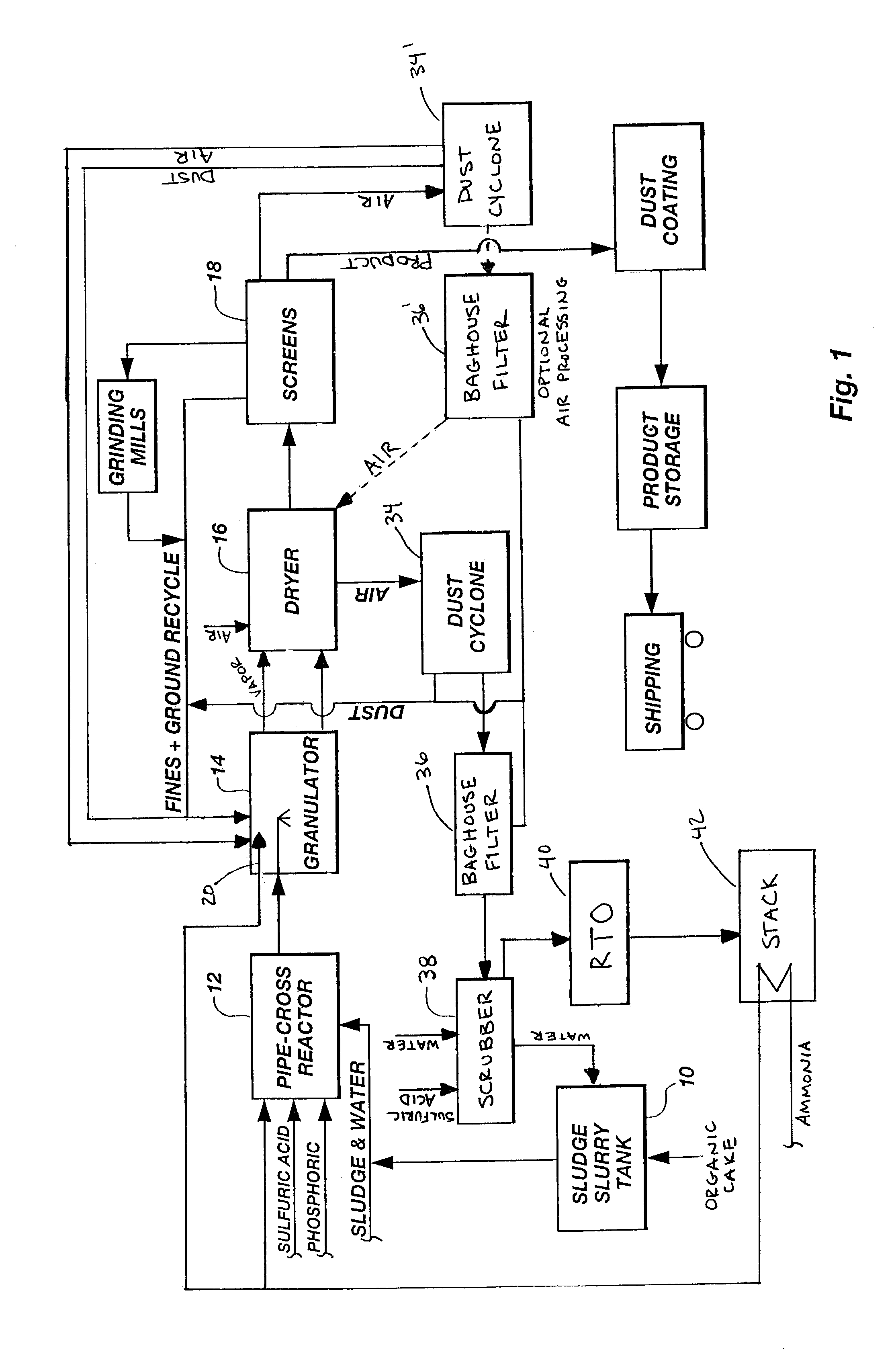
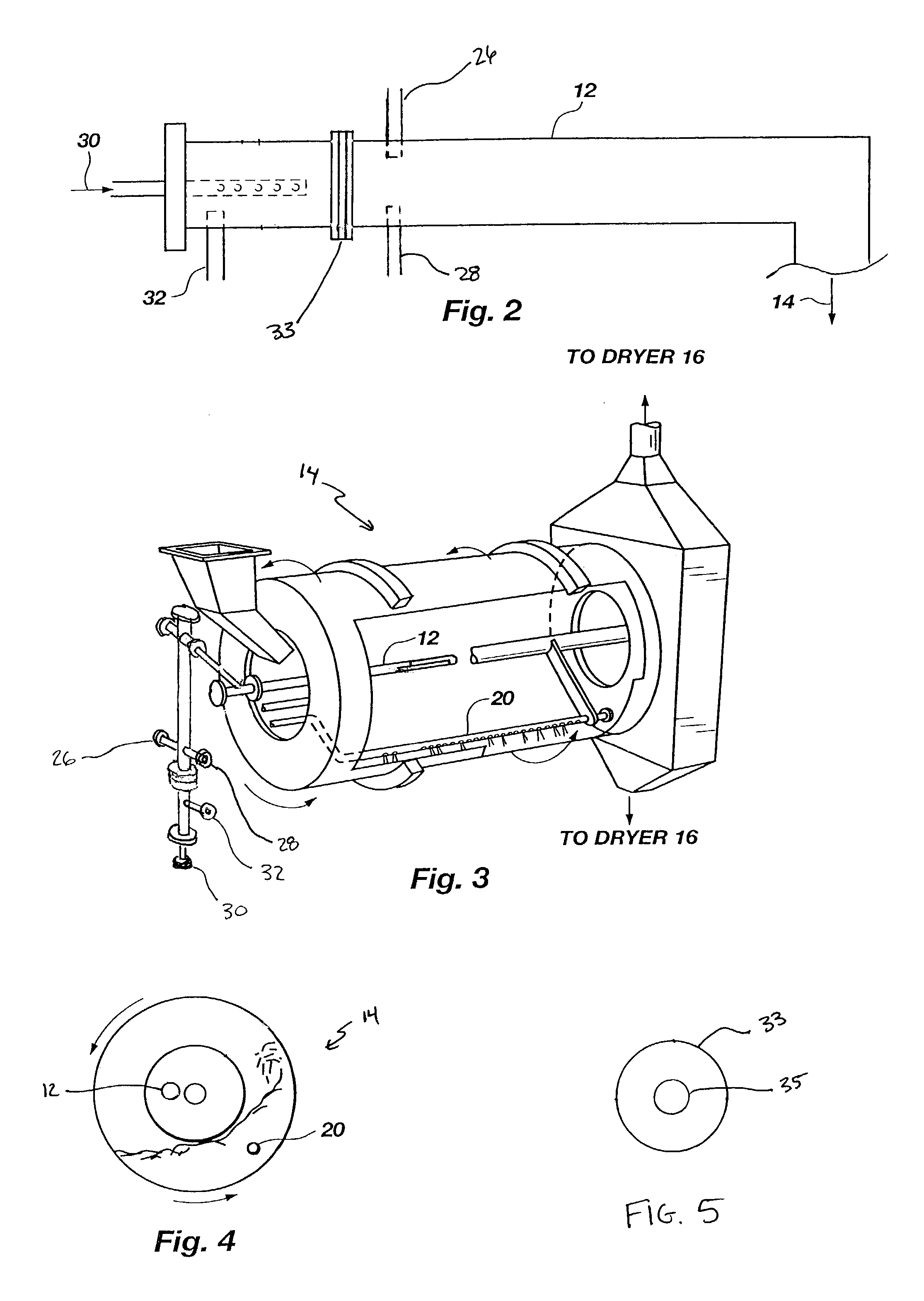
Organic recycling with a pipe-cross or tubular reactor
ActiveUS7128880B2Reduce moisture contentSimple compositionPhosphatesAnimal corpse fertilisersWater vaporSludge
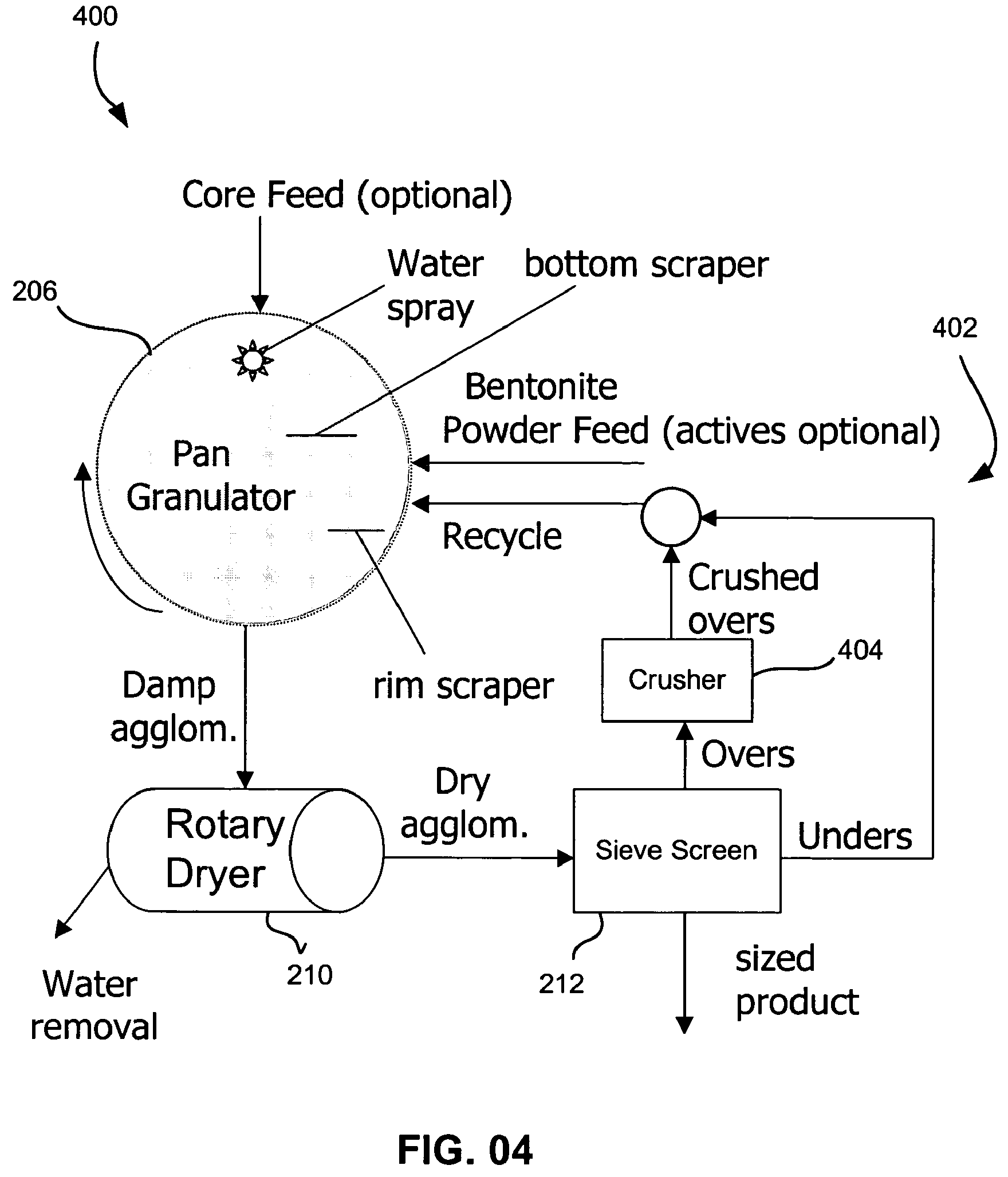
The invention is directed to a process for enhancing the plant nutrient value of relatively low analysis organic waste material (e.g. sewage sludge) involves treating the waste material with an acid and base in a pipe-cross reactor or tubular to form a melt; spraying the melt onto a recycling bed of fines in a granulator and flashing off the water contained in the melt as steam; rolling the melt onto recycled fine particles in a granulator to form granulated particles; and drying these granulated particles to form an enhanced plant nutrient value composition (e.g. a fertilizer or soil conditioner having a greater NPK value than the original relatively low analysis organic waste material). The process further includes drawing off the fumes from the granulator, passing them through a dryer with the granulated particles, and subsequently oxidizing the fumes to eliminate volatile organic compounds and / or gaseous hydrocarbon pollutants be converting such into carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER LLC
Soil conditioning agglomerates containing calcium
InactiveUS6936087B2High mechanical strengthGood curative effectBiocideCalcareous fertilisersParticulatesWater soluble
Mechanically strong, water-disintegrable agglomerates made from a particulate calcium source, a water-soluble binder and optionally containing a primary plant nutrient source and / or micronutrient source and a process for forming such agglomerates are disclosed. The agglomerates may be used as a soil liming agent and for introducing nutrient values into cultivated soil. Also disclosed is a method for introducing nutrient values into cultivated soil so as to inhibit leaching of the nutrient values from the soil and improve utilization of the nutrient values by plants grown in the soil.
Owner:MAGIC GREEN CORP
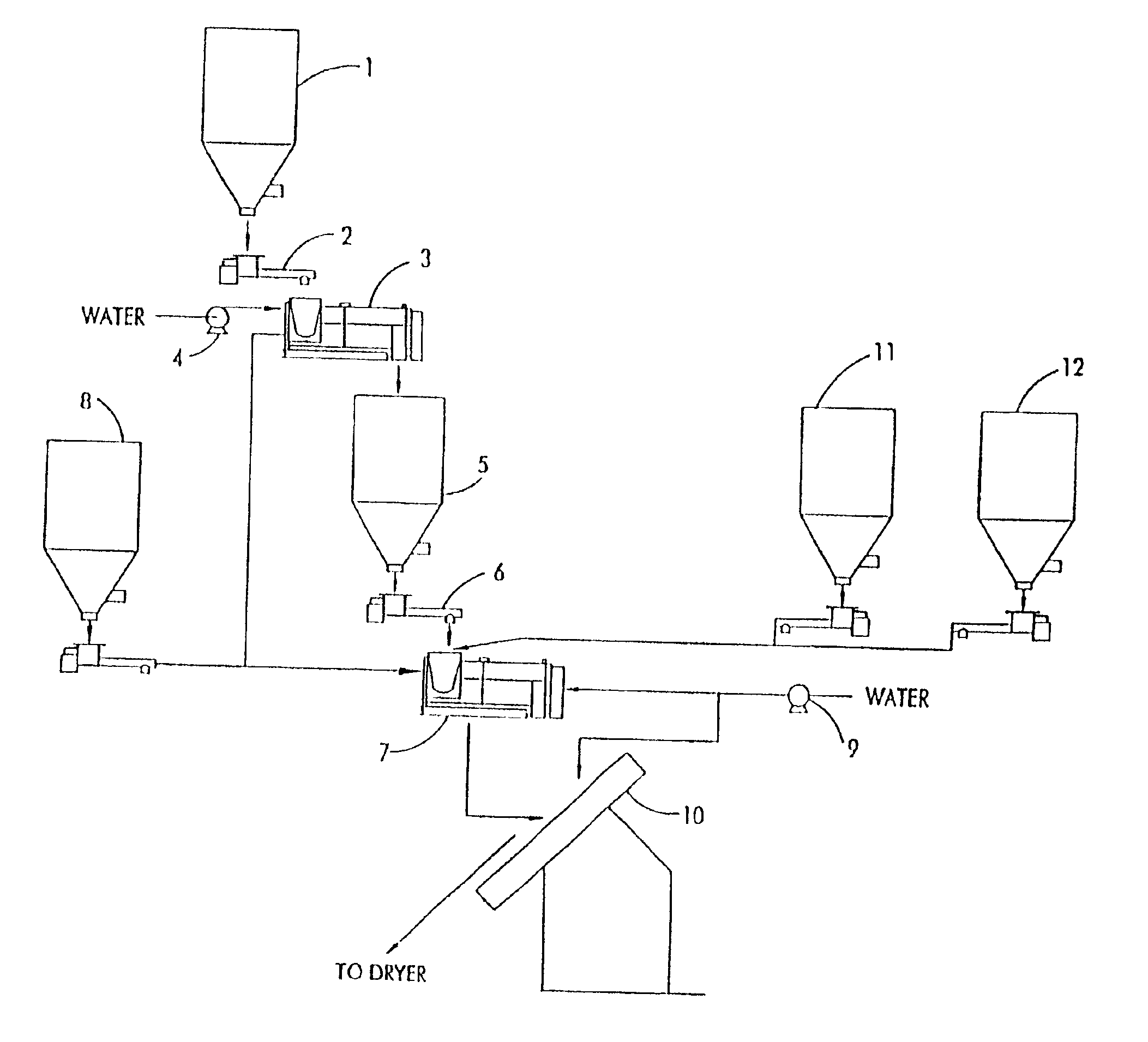
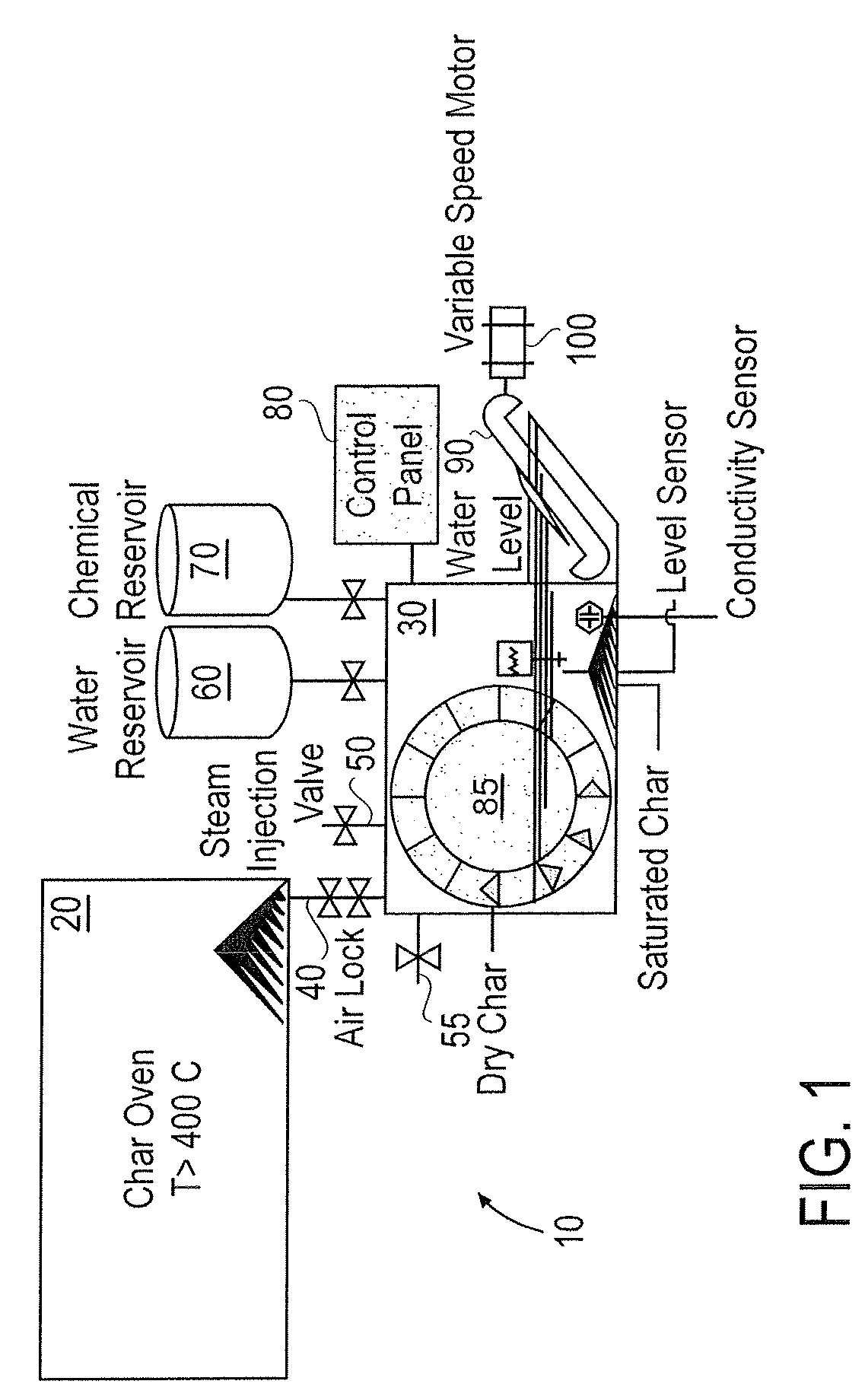
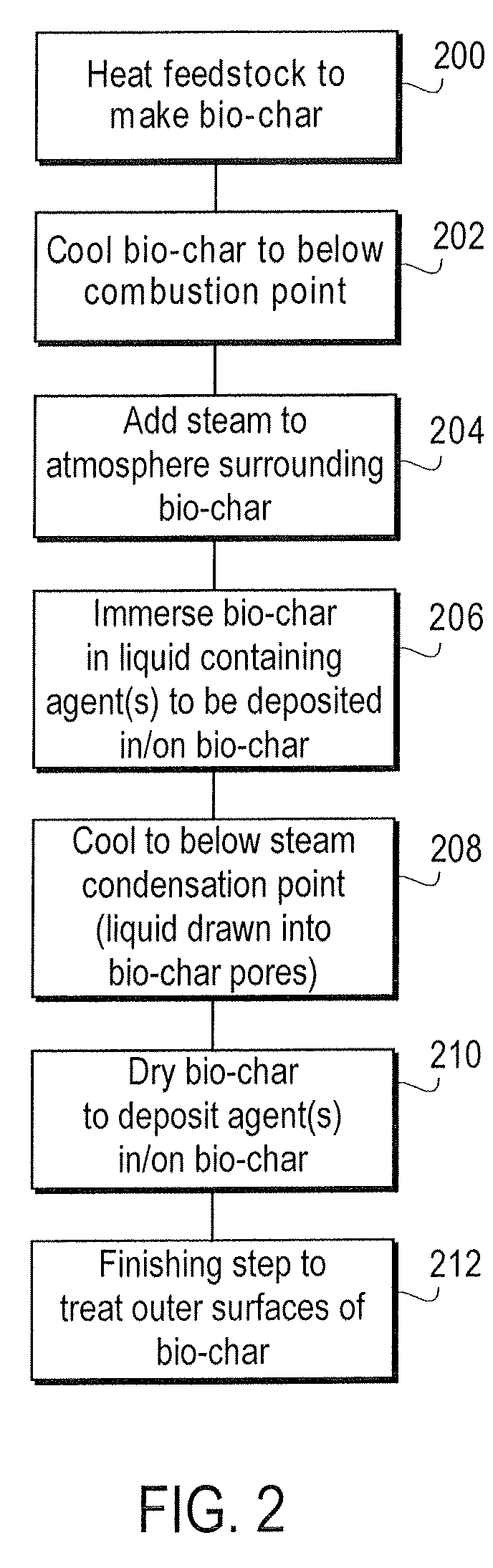
Method and apparatus for depositing agents upon and within bio-char
Methods and apparatuses for depositing agents relatively deep within pores of bio-char. Bio-char is first produced in an airtight oven by heating biomass feedstock. The bio-char is then cooled and steam is diffused into the pores of the bio-char. The steam-laden bio-char is immersed in a liquid bath containing soluble agents that are to be deposited in the pores of the bio-char. The liquid bath cools the char to below the condensation temperature of the steam, whereupon the condensing steam generates a partial vacuum within the pores, drawing the liquid into the pores. The bio-char is then removed from the liquid bath and dried so that the liquid within the pores evaporates, leaving behind the soluble agent. Accordingly, the invention yields bio-char that has soluble agent embedded relatively deep within its pores.
Owner:CARBON TECH HLDG LLC
Fertilizer composition containing micronutrients and methods of making same
ActiveUS20110214465A1Prevent and reduce chemical/physicalBiocideCalcareous fertilisersDiscrete particleNutrient
A fertilizer composition including a base fertilizer granule with a barrier coating and one or more micronutrients. The base fertilizer material is coated with a barrier coating, and then a coating of one or more micronutrients. Alternatively, the base fertilizer material is coated with a barrier coating having discrete particles of micronutrients dispersed throughout. The barrier coating acts to physically and chemically isolate the micronutrient particles from the underlying fertilizer composition such that more of the micronutrient is available to the soil solution, and ultimately to the root zone of the plant.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Process for the production of detergent granules
InactiveUS7018972B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsPigmenting treatmentSolid componentOrganic chemistry
A process for the preparation of detergent granules, the process comprising:(i) a first step of admixing in a mechanical granulator, a solid component and a first liquid binder, to produce a powder; and(ii) a second step of admixing in a low shear granulator, the powder produced in step (i), and a second liquid binder, to produce the detergent granules;the second liquid binder having a different composition from the first liquid binder and the weight ratio of the first liquid binder to the second liquid binder being from 15:1 to 1:1, preferably from 10:1 to 1:1, more preferably from 5:1 to 1:1, most preferably from 3:1 to 2:1.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Controlled Release Fertilizer Composition
ActiveUS20100011825A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce the amount requiredBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersControl releaseSulfur
A controlled release fertilizer composition and methods to produce the controlled release fertilizer composition are described. The controlled release fertilizer composition comprises a water soluble fertilizer core that is coated with a polymeric layer, intermediate layer, and a sulfur layer. If desired, the sulfur layer can be coated with an outer water-insoluble layer.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Encapsulated particle
ActiveUS20100326152A1Improve moisture resistanceImprove the immunityBiocideGlass/slag layered productsPolyolFire retardant
An encapsulated particle comprises a core particle and a polyurethane layer disposed about the core particle. The core particle can be various particles, such as fertilizer, biocides, flame retardants, seeds, etc. The polyurethane layer comprises the reaction product of an isocyanate component and an isocyanate-reactive component. The isocyanate-reactive component comprises a graft polyol having a continuous phase and polymeric particles. A method of forming the encapsulated particle comprises the steps of providing the core particle, applying the isocyanate and isocyanate-reactive components to the core particle, and reacting the isocyanate and isocyanate-reactive components to form the polyurethane layer. The encapsulated particle has excellent physical properties, such as increased water repellency, resiliency and shelf life.
Owner:BASF AG
Coated fertilizer particles
InactiveUS20120090367A1Simple compositionAmmonium nitratesOrganic phosphatic fertilisersNitrogenPolymer chemistry
Owner:TIGER SUL CANADA CO +1
Phosphate and potash(PK)-containing compound fertilizer
InactiveUS20070062232A1Increase temperatureEasy to operateSuperphosphatesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityAlkaline earth metal
The primary object of the invention is to provide a method of producing novel phosphate and potash (PK) containing compound fertilizers in the form of powders showing good handle-ability by which method the phosphate components contained in an incinerated ash residue of chicken droppings is improved in solubility and thus rendered effective or available and, at the same time, the free CaO-derived alkali is neutralized, as well as such novel phosphate and potash(PK) containing compound fertilizers. The above object can be accomplished by adding an alkaline earth metal compound to the powdery incinerated ash residue of chicken droppings, adding a mineral acid to the resulting mixture, allowing the reaction to proceed and raising the reaction system temperature by utilizing the heat of reaction of the powdery alkaline earth metal compound with the mineral acid to thereby promote the reaction between the free CaO contained in the incinerated ash residue of chicken droppings and so forth with the mineral acid and convert the phosphate components to citric acid-soluble P2O5 and, at the same time, maintaining the product neutral or weakly acidic.
Owner:MURAKASHI LIME IND
Homogeneous granules of slow-release fertilizer and method of making the same
A process for making homogeneous granules of slow-release fertilizer to deliver high doses of slow-release nitrogen in pellets that disperse or fall apart when contacted by moisture. The method includes mixing particles of slow-release nitrogen with particles of a potassium source and particles of a phosphorus source, to make a homogeneous blend of the particles. Then, the blended particles are moistened with water or an aqueous solution of urea to moisten the homogeneous blend. After moistening, the blended particles are contacted with an aqueous suspension of urea-formaldehyde resin to bind the particles into homogeneous granules. The aqueous suspension of urea formaldehyde resin preferably has a urea:formaldehyde ratio of about 1:1.
Owner:LEBANON SEABOARD CORP
Method for producing fertilizer grade DAP having an increased nitrogen concentration from recycle
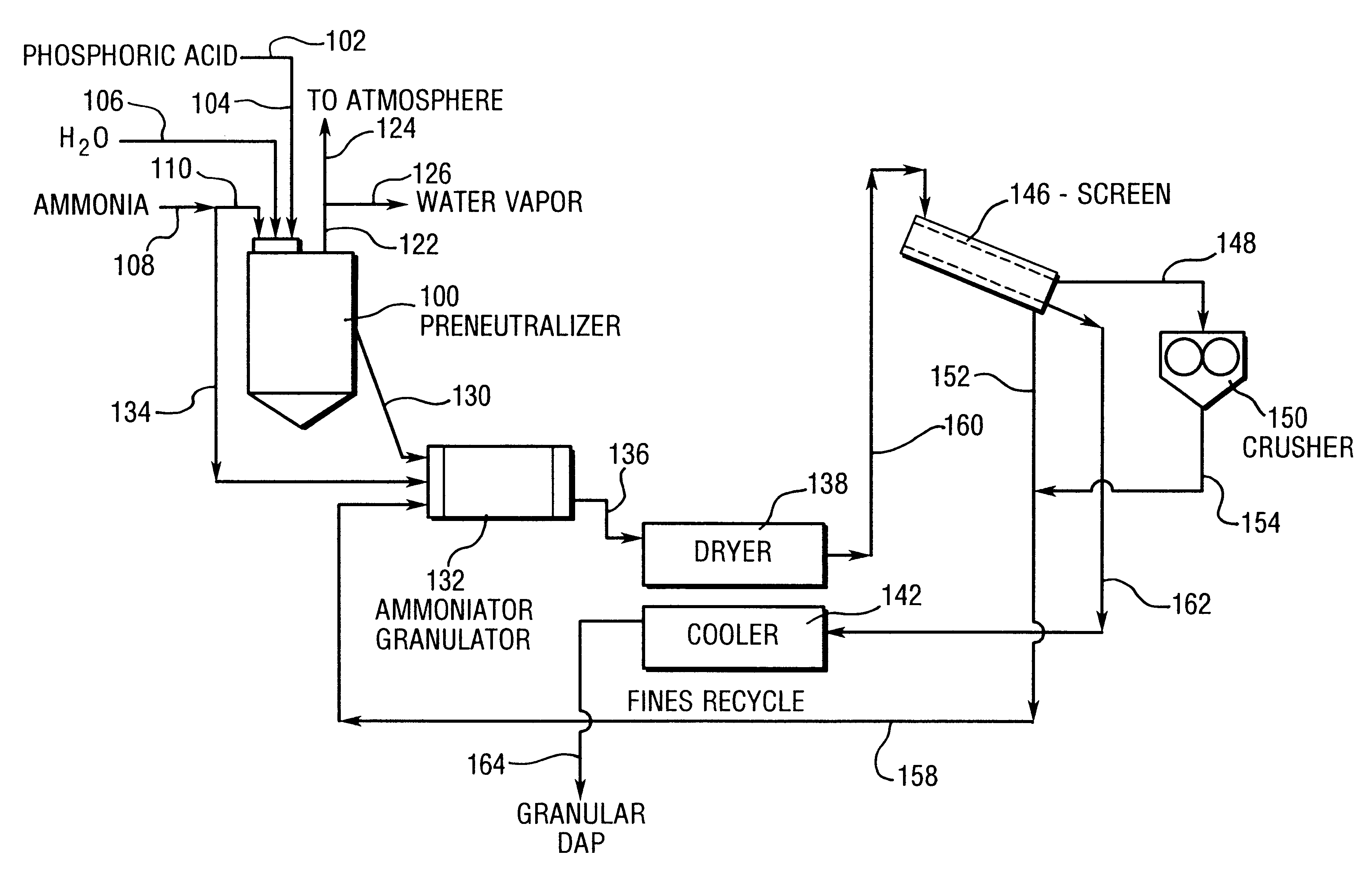
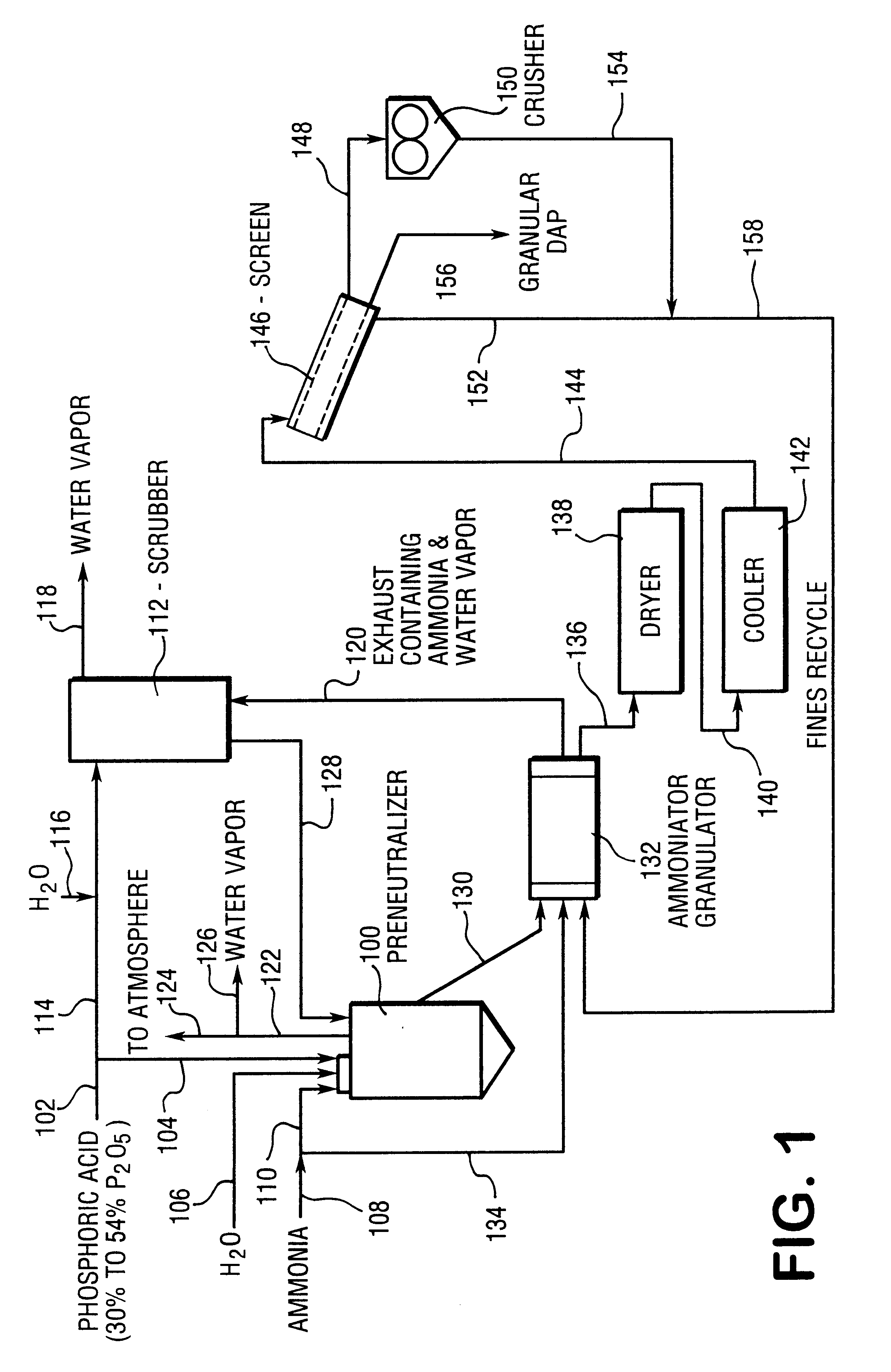
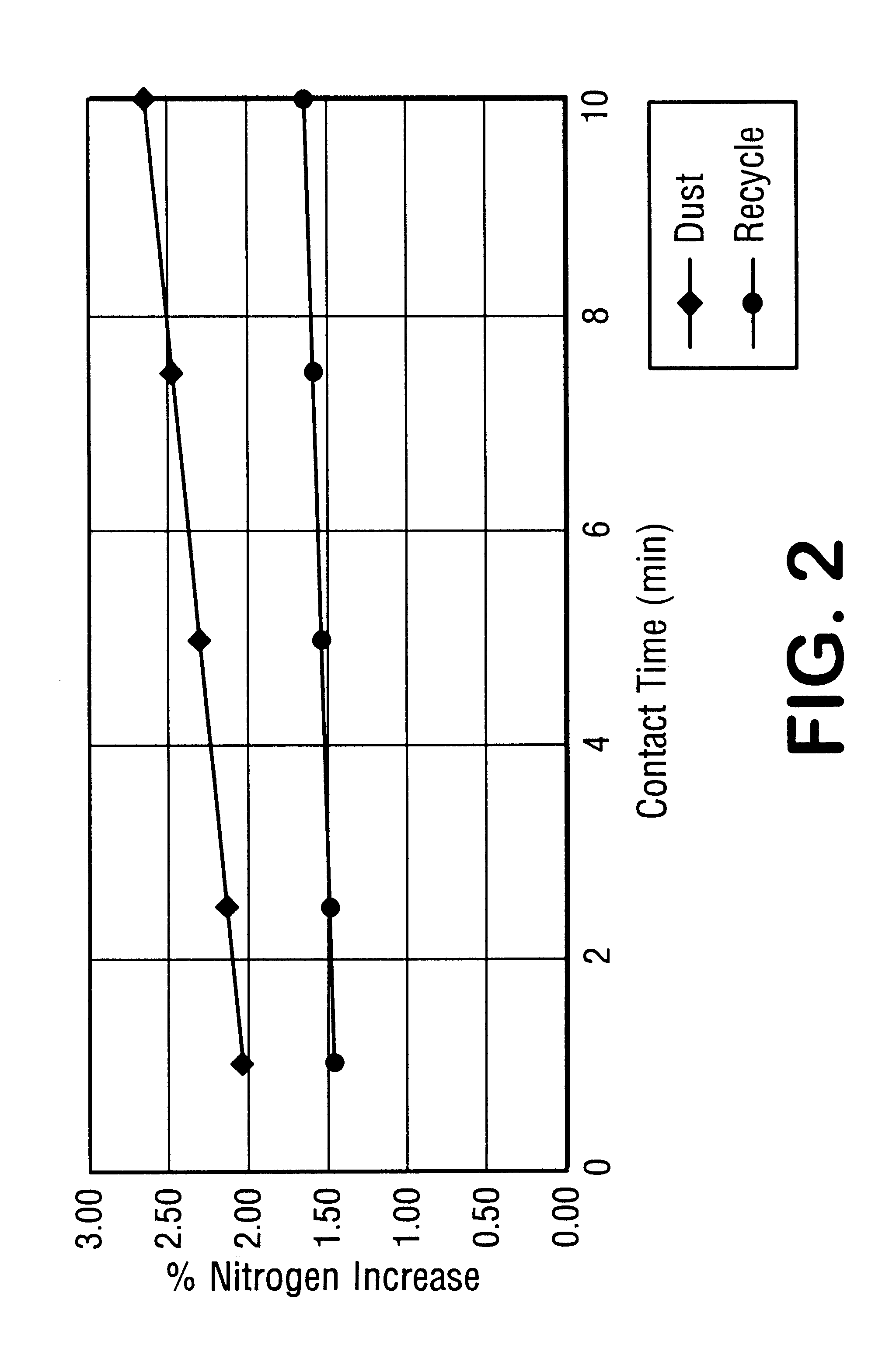
InactiveUS6241796B1Small particle sizeEnhancing ammoniacal nitrogen concentrationPhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesAmmoniacal nitrogenContact time
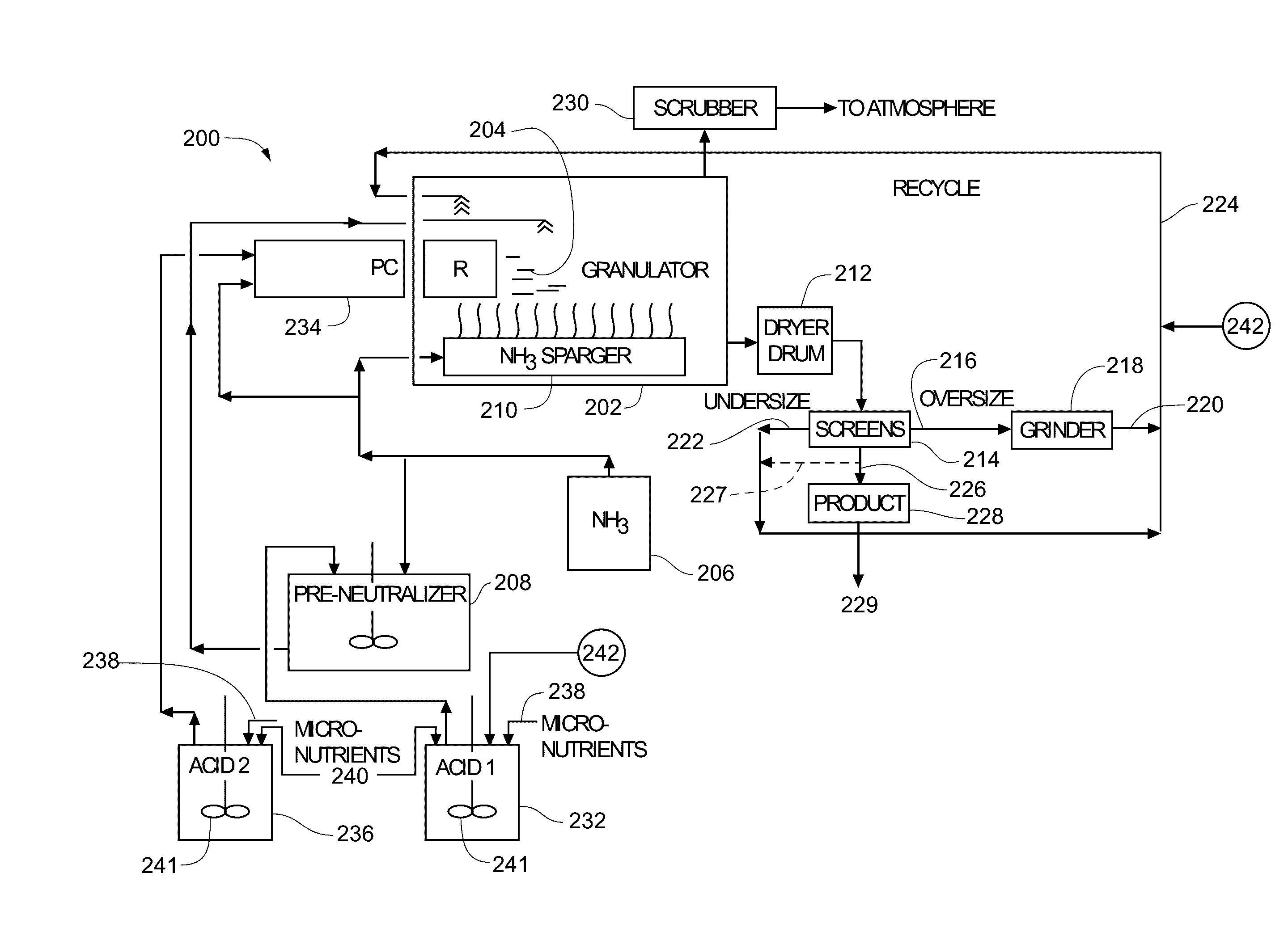
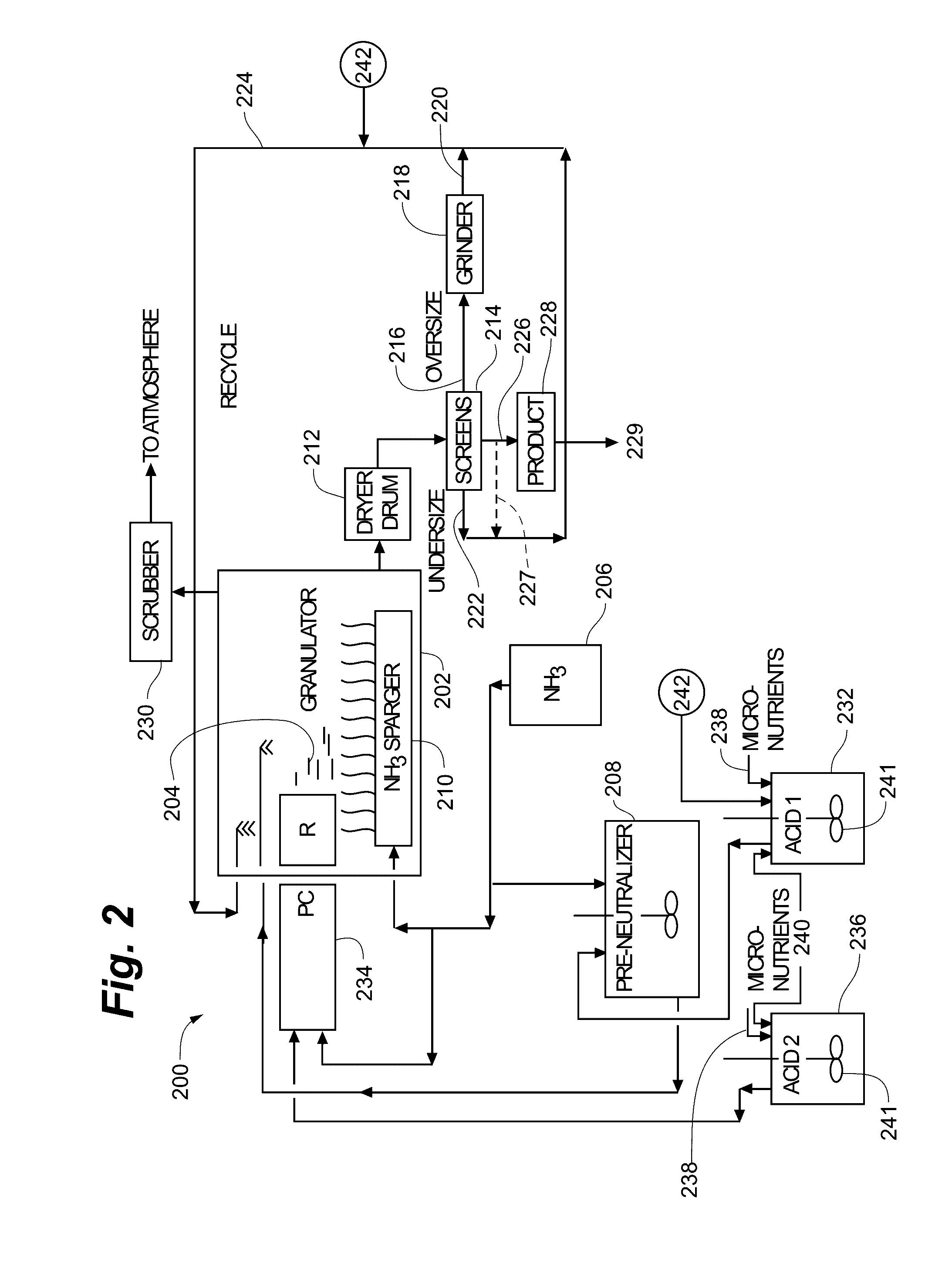
A process for the preparation of granular fertilizer grade DAP (a product composed of ammonium phosphates, principally diammonium phosphate, resulting from the ammoniation of phosphoric acid, as defined in Official Publication No. 52 of the Association of American Plant Food Officials, dated 1999) comprising partially preneutralizing orthophosphoric acid with ammonia, completing the ammoniation of the orthophosphoric acid with ammonia in a rotary ammoniator-granulator to provide granular DAP, sizing the granular DAP to provide the granular DAP product, reducing the particle size of the oversized granular DAP, and recycling the undersized granular DAP and the sized-reduced oversized granular DAP to the ammoniator-granulator. The ammoniacal nitrogen concentration of the granular DAP recycle, hence the granular DAP product, is enhanced by subjecting the finely-divided recycled granular DAP to anhydrous gaseous ammonia which is at a super atmospheric pressure and which is at a temperature sufficient to maintain said anhydrous ammonia in the gaseous state. The increase in the ammoniacal nitrogen concentration is a function of the absolute ammonia pressure, the initial moisture content of the granular DAP recycle, and the contact time of the ammonium with the granular DAP recycle.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Polyphosphate fertilizer combinations
A composite particle and a population of particles comprising a water-insoluble polyphosphate composition, methods of producing, and methods of using the same are provided. The polyphosphate composition may comprise at least one alkaline earth metal selected from calcium and magnesium and optionally at least one nutrient ion selected from the group consisting of potassium, ammonium, zinc, iron, manganese, copper, boron, chlorine, iodine, molybdenum, selenium or sulfur.
Owner:AGTEC INNOVATIONS
Adsorbent and/or catalyst and binder system and method of making and using therefor
InactiveUS20010009884A1Reduce and eliminate amountReduce the amount requiredPressurized chemical processCarbon compoundsCross-linkSorbent
The invention relates to a method for producing an adsorbent and / or catalyst and binder system comprising I) mixing components comprising (a) a binder comprising a colloidal metal oxide or colloidal metalloid oxide, (b) an oxide adsorbent and / or catalyst particle, and (c) an acid, (ii) removing a sufficient amount of water from the mixture to cross-link components a and b to form an adsorbent and / or catalyst and binder system. The invention also relates to particles made by the process, binders, and methods for remediating contaminants in a stream.
Owner:STREAMLINE CAPITAL
Reinforced-resin coated plant food granules
InactiveUS6045810AGuaranteed economic efficiencyImprove the immunityBiocidePowder deliveryControl releaseWater insoluble
A reinforced-resin coated, attrition resistant controlled release plant food containing water soluble central spheroids of plant nutrients amounting to between 75 and 98 percent and water insoluble resin coatings amounting to between 2 and 25 percent covering the central spheroids with the insoluble resin coatings reinforced with finely divided water insoluble plant nutrients formed in-situ by the chemical coreaction of a plurality of water soluble plant nutrients. The reinforcing nutrients amount to between 5 and 25 percent of the resin coating. A method is provided for preparing the new reinforced-resin coated plant foods with the reinforcing solids distributed throughout the insoluble resins or between thin layers of resins.
Owner:B & B INT LLC
Acid combination one step reaction process for agricultural use products and associated methods
ActiveUS8216972B1High analysisSolution clarificationBiocideMagnesium fertilisersFungicidePhosphorous acid
A process for the manufacture of an aqueous composition that is a combination of a fungicide and fertilizer comprising the following steps:(1) dissolving phosphorous acid in phosphoric acid to form a solution of an acid mixture;(2) reacting the acid mixture of step (1) with an aqueous hydroxide solution creating an exothermic reaction under pressure; and,(3) cooling the reaction product to between about 35° C. to about 65° C.The reaction product prepared according to the above process can also be used as a bactericide.
Owner:PLANT FOOD SYST
Fertilizer composition and method for preparing the same
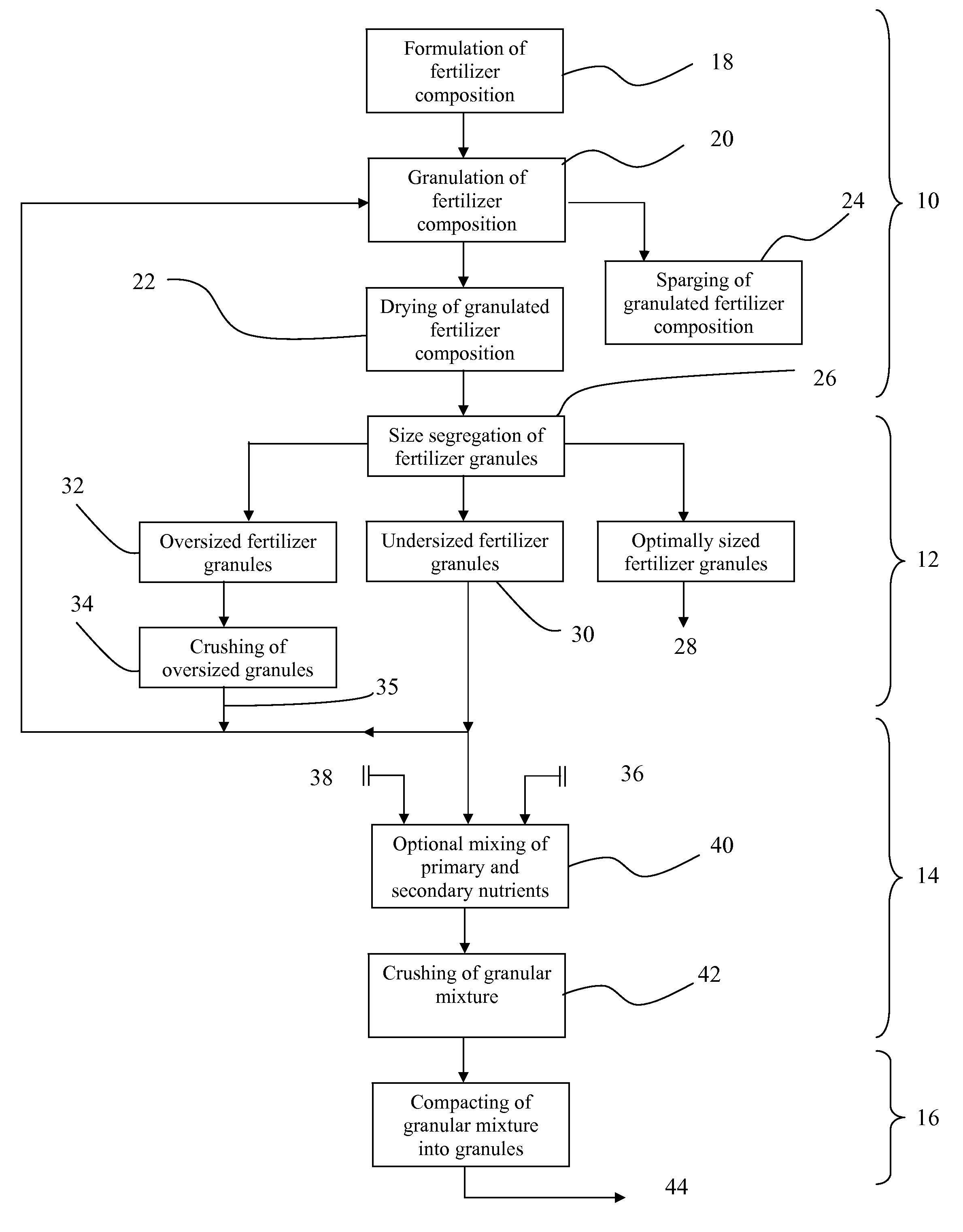
ActiveUS20140260467A1Increase surface areaMaximize surface areaBiocideCalcareous fertilisersSmall particleNutrient
A method of producing a granulated and compacted fertilizer having incorporated micronutrients in which the granulated primary nutrient and micronutrients are mixed at smaller particle sizes before being compacted into a larger, easier to handle particle sizes.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Nutrient yielding bio-renewable controlled release fertilizer coatings
InactiveUS8764873B2Prevent and reduce tendencyDecrease in hydrophilic natureBiocideBio-organic fraction processingControl releaseAnimal waste
Animal waste is processed to form a biomaterial that is employed as a coating layer for typical fertilizer particles. The biomaterial coating layer can be used neat or with additives and serves to do one or more or any combination of the following: (a) impart a slow or controlled release property to the fertilizer, (b) prevent or reduce the tendency of the fertilizer particles to cake together, or (c) prevent or reduce the tendency of the fertilizer particles to create dust. The biomaterial coating layer can also release nutrients when used as part of a fertilizer composition.
Owner:IMPERIAL COMMODITIES
Acid combination one step reaction process for agricultural use products and associated methods
ActiveUS8193119B2Minimizes or eliminates wasteful “free water”Avoid reactionBiocidePhosphatesPhosphorous acidContinuous reactor
A process for the manufacture of an aqueous composition that is a combination of a fungicide and fertilizer comprising the following steps:(1) dissolving phosphorous acid in phosphoric acid to form a solution of an acid mixture;(2) reacting the acid mixture of step (1) with an aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at a temperature of about 65° C. to about 260° C. in a continuous reactor while maintaining the ratio of potassium to phosphorous in various mole ratios thereby forming a reaction mixture comprising potassium phosphates, potassium polyphosphates, potassium phosphites, and potassium polyphosphites and potassium phosphate phosphite copolymers; and,(3) cooling the reaction mixture rapidly at least 1° C. to 60° C., to below about 35° C. to about 65° C.Using a similar process a composition having fungicidal properties is prepared by reaction phosphoric acid with potassium hydroxide.The reaction mixtures prepared according to each of the above processes are also part of this invention.
Owner:PLANT FOOD SYST
Method of agglomeration
ActiveUS7964529B2Low densityShorten the trackPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesLitterOdor control
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Acid treatment for fertilizers to increase zinc solubility and availability
ActiveUS20170044078A1Improve availabilityGood water solubilityMaterial granulation and coatingAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityZinc uptake
Methods and system for increasing the water solubility and availability of zinc in granular fertilizers using acid treatments. The treatment of granular fertilizers with an acidic solution increases an amount of water-soluble zinc, which in turn, increases the efficiency of zinc uptake and reduces the costs and equipment otherwise needed to mitigate zinc deficiencies.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Liquid phosphite fertilizer
ActiveUS20150007626A1Promote growthAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphite saltPotassium
A water soluble liquid fertilizer concentrate is provided that includes a bio-available phosphorus source, said phosphorus source consisting essentially of a phosphite salt. At least one of a bio-available nitrogen source and a bio-available potassium source are also provided. At least one micronutrient of calcium, magnesium, cobalt, iron, manganese, copper, boron, zinc, or molybdenum is present in the concentrate as an aqueous solute or soluble chelates. In some embodiments, the at least one phosphite salt is present at between 30 to 57 total weight percent dissolved in water and optionally contains a phosphate salt. A process of fertilizing a crop includes diluting the fertilizer concentrate with water to obtain a liquid fertilizer solution. The liquid fertilizer solution is then applied to the crop and after by allowing sufficient time, the fertilizer solution promotes growth of the crop.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Fertilizer composition incorporating fibrous material for enhanced particle integrity
InactiveUS8979970B2Reduce formationSuperphosphatesAnimal corpse fertilisersFiberDiammonium phosphate
Fertilizer granules and methods of producing fertilizer granules. The fertilizer granules are formed from a fertilizer composition, such as a phosphate fertilizer, includes a fibrous material for the purpose of increasing the granule strength preventing or reducing attrition or dusting formation during storage, transport, and / or handling of the fertilizer. Dust formation can be reduced fifty percent or more. The base fertilizer composition can include a phosphate fertilizer, such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) or diammonium phosphate (DAP), and optionally one or more micronutrients or secondary nutrients, such as elemental sulfur. The fibrous material is pulp or paper sludge, for example.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Agglomeration of alumina and binder therefor
InactiveUS7449030B2Aluminium compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationPseudoboehmiteMaterials science
A method for the agglomeration of alumina particles, the method comprising the steps of comminuting a plurality of alumina particles having a soda content of less than approximately 0.4% by weight to a D50 of less than 12 μm, adding a quantity of pseudo-boehmite as an aqueous suspension having a pH of from about 2 to 6 to the plurality of alumina particles to form a mixture such that the quantity of pseudo-boehmite is between about 0.8 wt % and 5 wt % based on weight of the mixture, and spray drying the mixture to produce agglomerated granules.
Owner:ALCOA WORLD ALUMINA
Agglomeration of alumina and binder therefor
InactiveUS20050118096A1Catalyst activation/preparationPhosphatic fertiliser granulation/pelletisationPseudoboehmiteMaterials science
A method for the agglomeration of alumina particles, the method comprising the steps of comminuting a plurality of alumina particles having a soda content of less than approximately 0.4% by weight to a D50 of less than 12 μm, adding a quantity of pseudo-boehmite as an aqueous suspension having a pH of from about 2 to 6 to the plurality of alumina particles to form a mixture such that the quantity of pseudo-boehmite is between about 0.8 wt % and 5 wt % based on weight of the mixture, and spray drying the mixture to produce agglomerated granules.
Owner:ALCOA WORLD ALUMINA
Process for the Manufacture of Bio-release Fertilizers of Zinc-iron-manganese, Iron-manganese-copper and Zinc-iron-manganese-copper
InactiveUS20100206032A1Improve nutrient availabilityImprove usabilityFertilisers by pryogenic processesPhosphatic fertiliser granulation/pelletisationPyrolusiteCompounds of zinc
A process for the preparation of water insoluble bio-release micronutrient fertilizers, containing iron and manganese with either zinc and / or copper, comprising (a) heating orthophosphoric acid at a temperature of 130° C.-150° C. with a mixture of (i) source of iron oxide, (ii) manganese dioxide or pyrolusite, and (iii) either or both compounds of zinc or copper selected from zinc ash or zinc oxide and cupric oxide, or cupric sulphate or cupric chloride and (iii) a basic compound such as oxide or carbonate of magnesium or calcium, to produce a multi-metallic polyphosphate; (b) neutralisation of the polyphosphate with a basic compound followed by drying and pulverisation to obtain a solid powdery material.
Owner:NAT RES DEV CORP
Dual purpose agricultural compositions
ActiveUS8461079B1Quick vigorous growthEffectively competeBiocideMagnesium fertilisersSalicylic acidPotassium hydroxide
A composition which provides bactericidal, fungicidal and insecticidal activity when treating plants with effective amounts. The composition comprises the blending of: (1) an aqueous salicylate solution from salicylic acid reacted in an aqueous media with ammonium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide; (2) a reaction mixture that provides fungicidal activity and fertilizes plants when applied in an effective amount and which comprises potassium phosphates, potassium polyphosphate, potassium phosphites, and potassium polyphosphite and potassium phosphate phosphite copolymers; and, optionally, (3) aqueous potassium acetate.
Owner:PLANT FOOD SYST
Method and apparatus used for preparing ammonium phosphate fertilizer from phosphoric acid sediment
InactiveCN103435376ASimplify the process of filter press washingPhosphatesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserO-Phosphoric AcidGaseous ammonia
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus used for preparing ammonium phosphate fertilizer from phosphoric acid sediment. The method comprises following steps: the phosphoric acid sediment with a P2O5 content of 30 to 35% is mixed with diluted phosphoric acid with a concentration of 18 to 20% so as to obtain intermediate mixture I with a phosphoric acid content of 20 to 25%; the intermediate mixture I and gaseous ammonia with a concentration of 99% are subjected to neutralization reaction at a N mole / P mole ratio of 1.3-1.35, and a certain amount of sulfuric acid is added so as to neutralize unreacted gaseous ammonia; the N mole / P mole ratio is increased to 1.4-1.45 so as to obtain intermediate mixture II; and the intermediate mixture II is subjected to condensation, granulation and screening treatment. Gaseous ammonia is used for neutralizing the intermediate mixture I with a phosphoric acid content of 21 to 25%, ammonium bicarbonate or liquid ammonia are not used, and reaction contact area and reaction speed of gaseous ammonia and the intermediate mixture I are enlarged and increased respectively, so that filter-pressing washing process of the phosphoric acid sediment is simplified, comprehensive utilization of the phosphoric acid sediment is realized, and the quality of the ammonium phosphate products is improved.
Owner:山东明瑞化工集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com