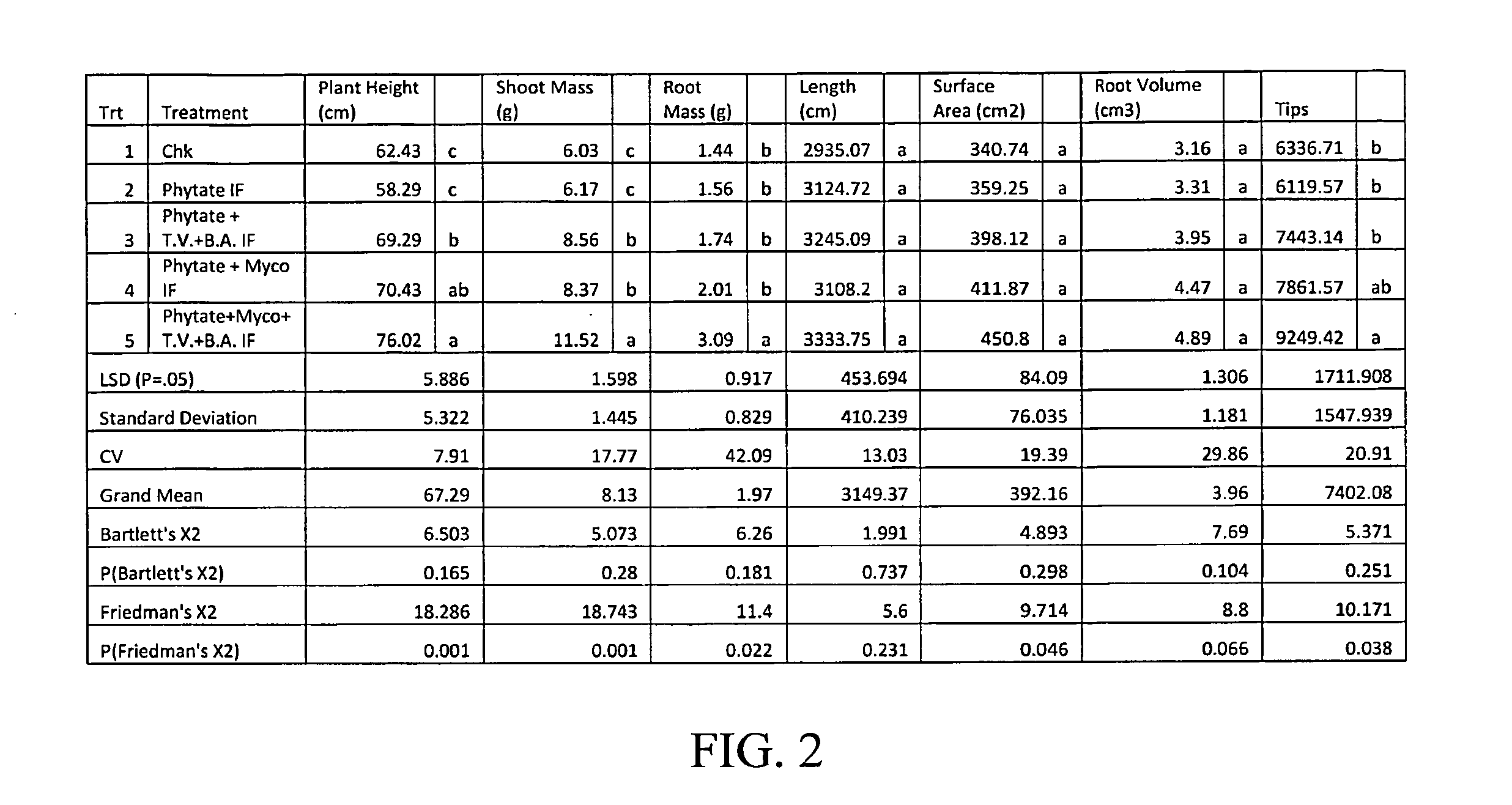
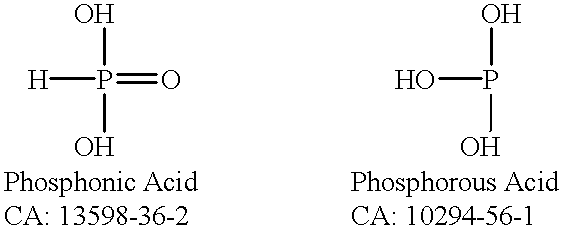
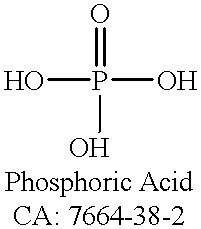
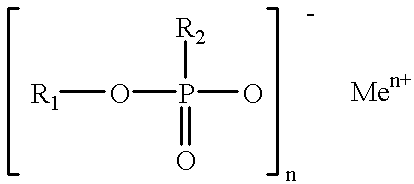
Patents
Literature
637results about "Organic phosphatic fertilisers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for treating sludge and manufacturing bioorganically-augmented high nitrogen-containing inorganic fertilizer
ActiveUS20080230484A1Reduce logisticsReduces liabilityByproduct vaporizationExcrement fertilisersPhosphateRetention time
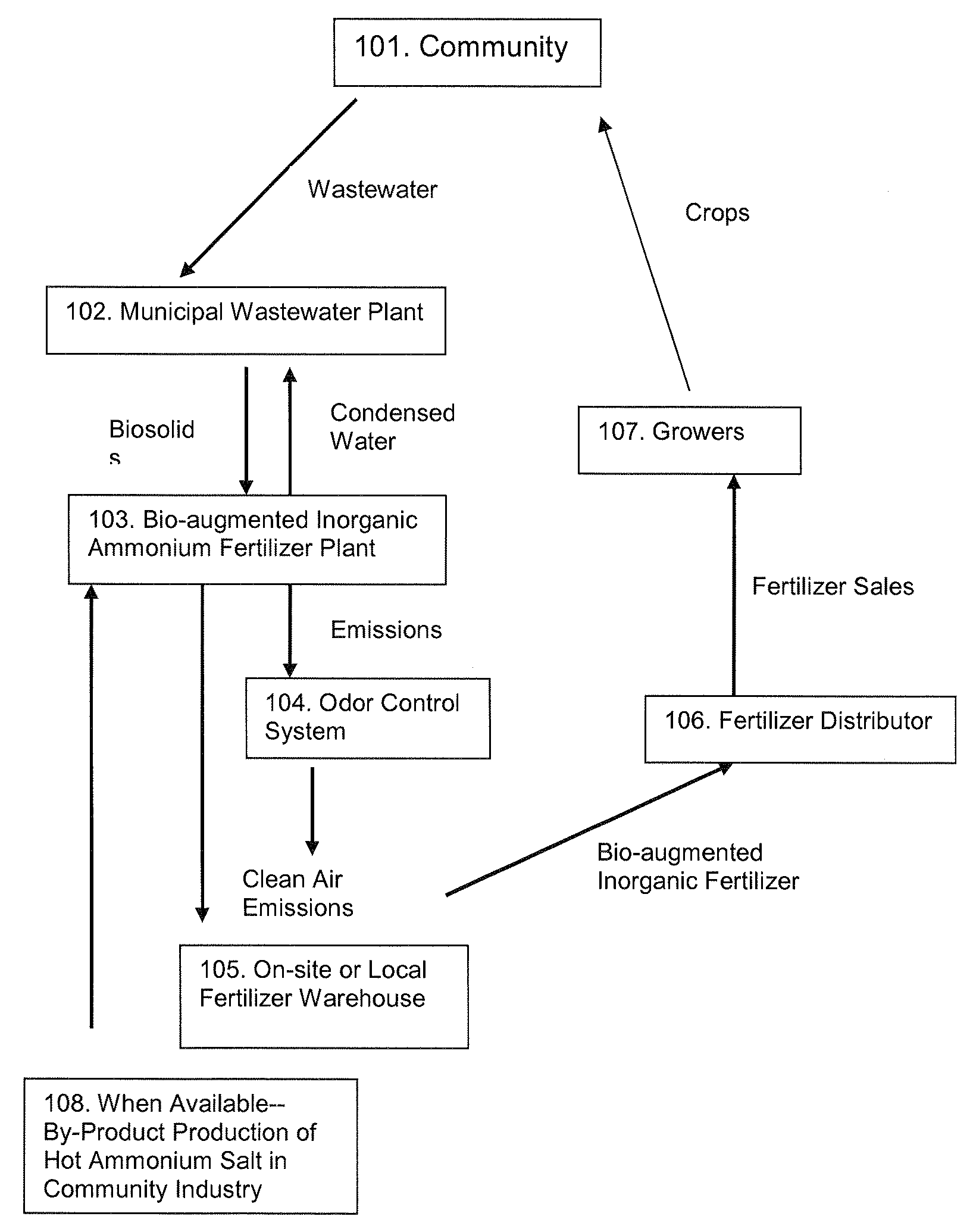
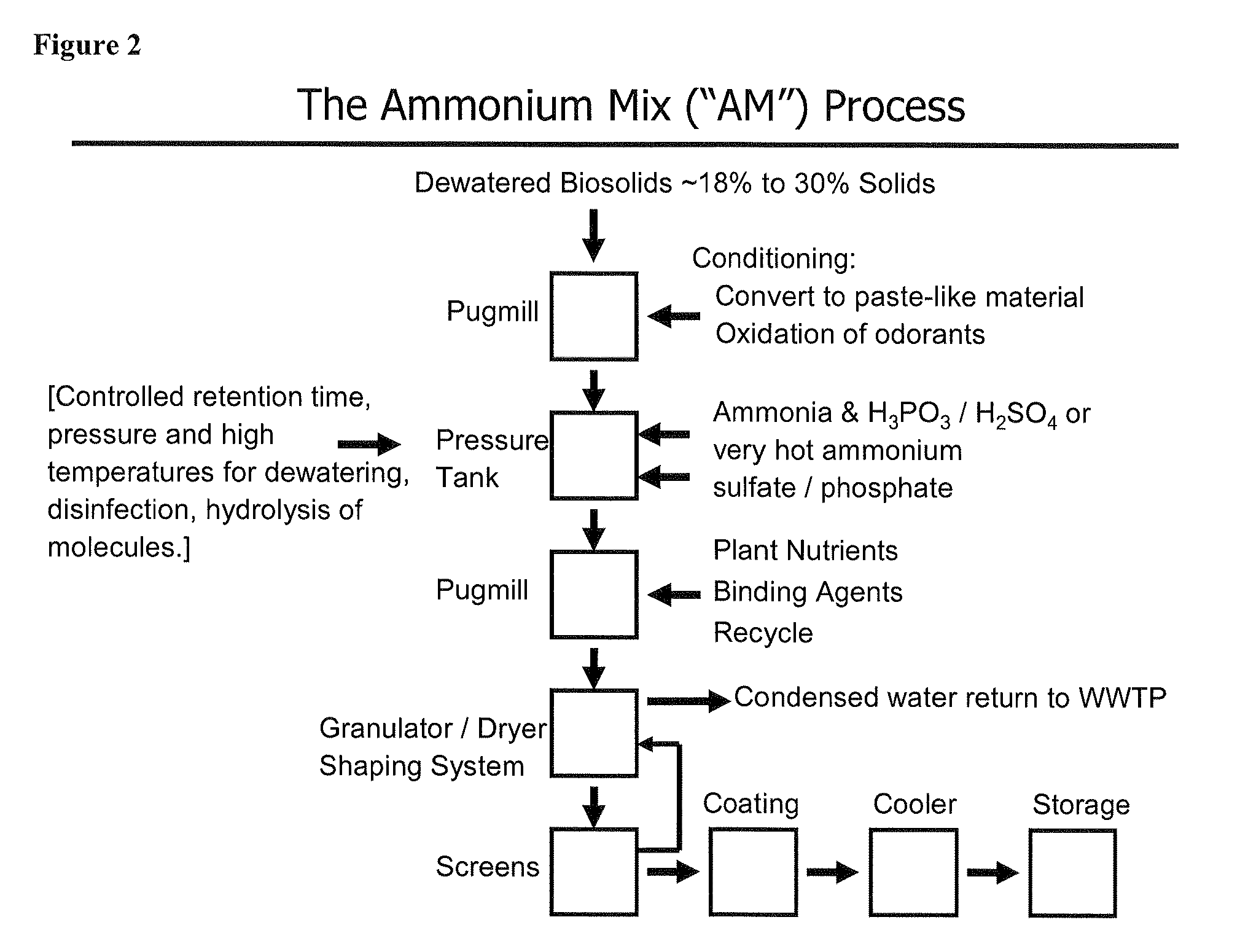
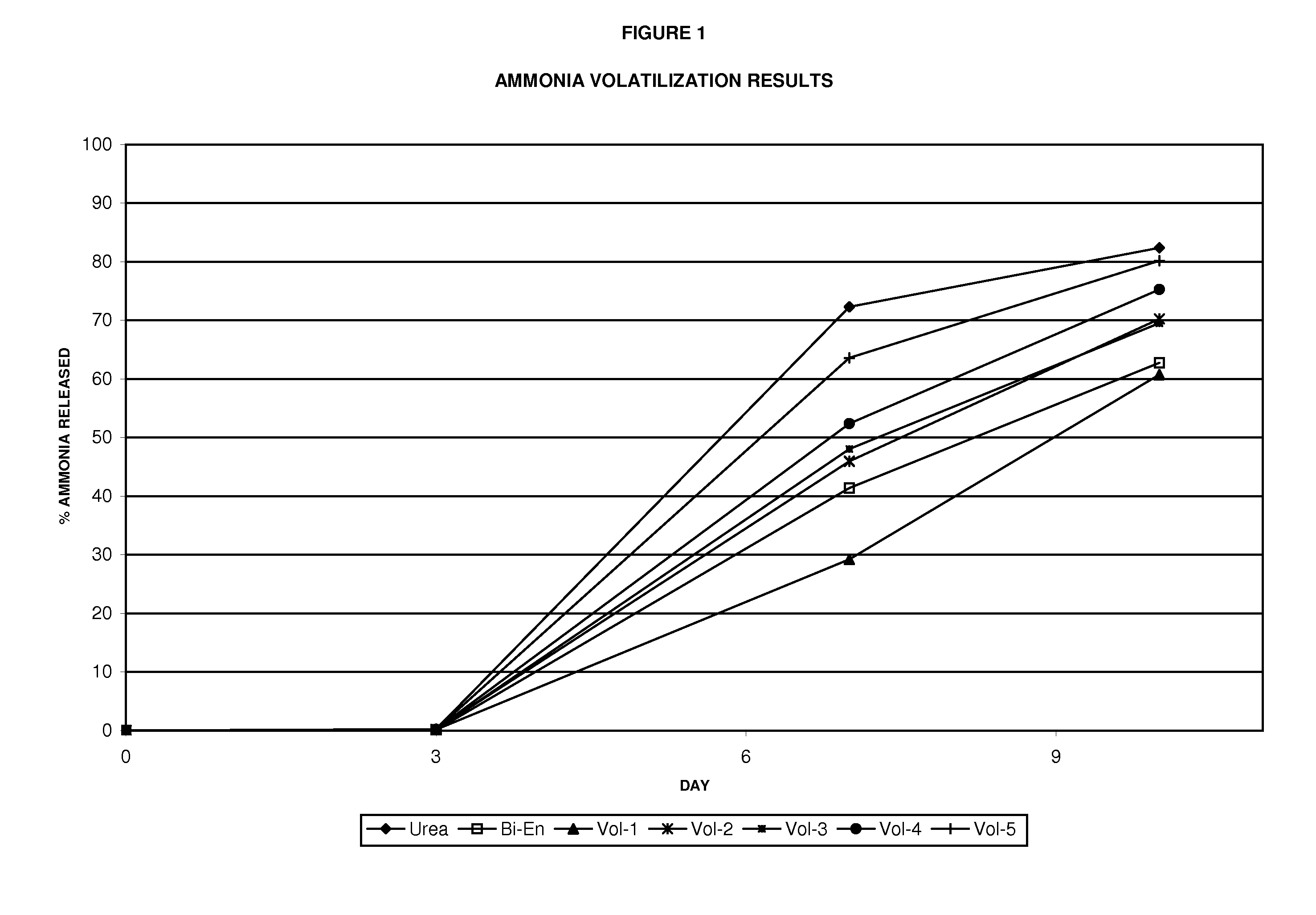
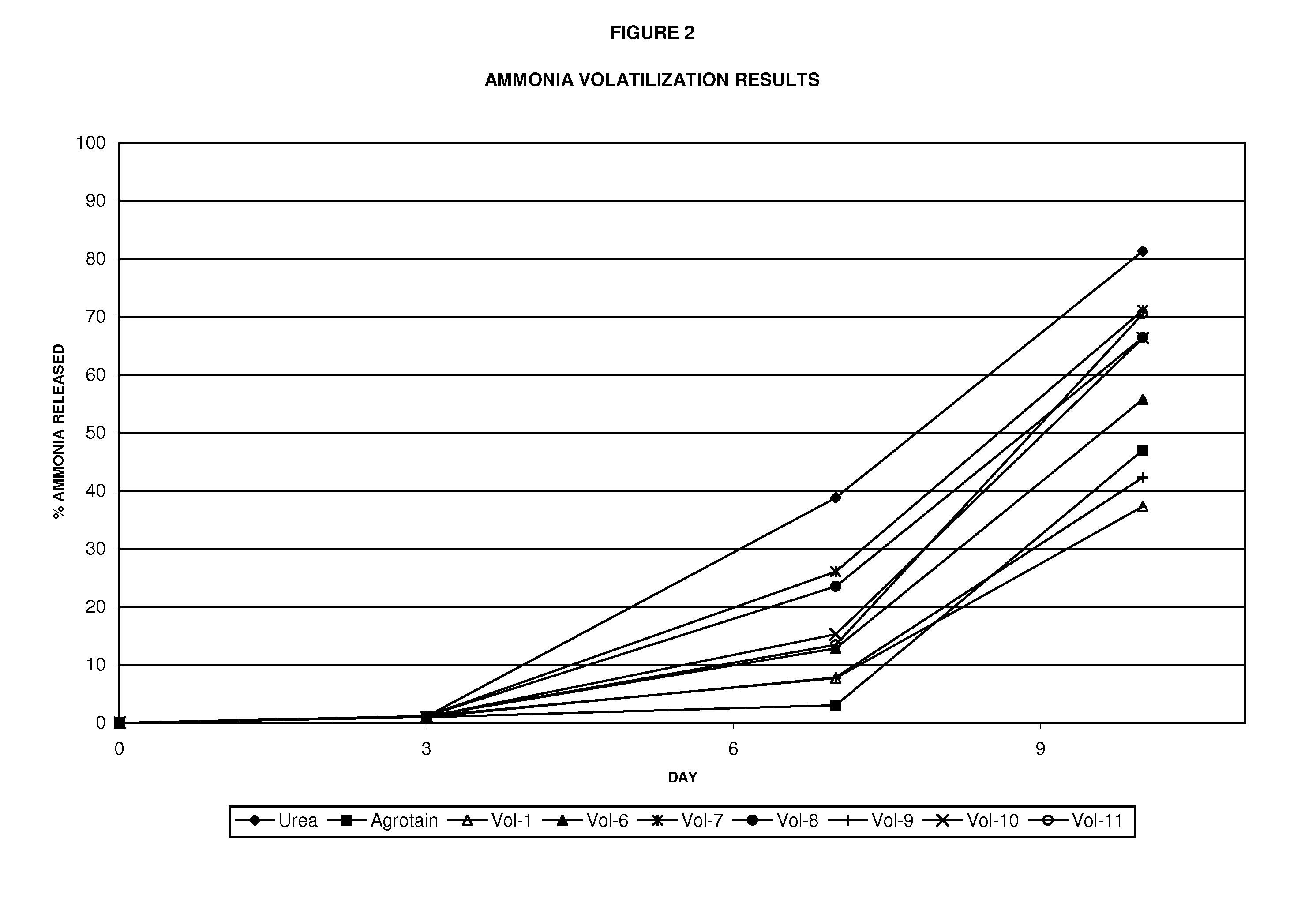
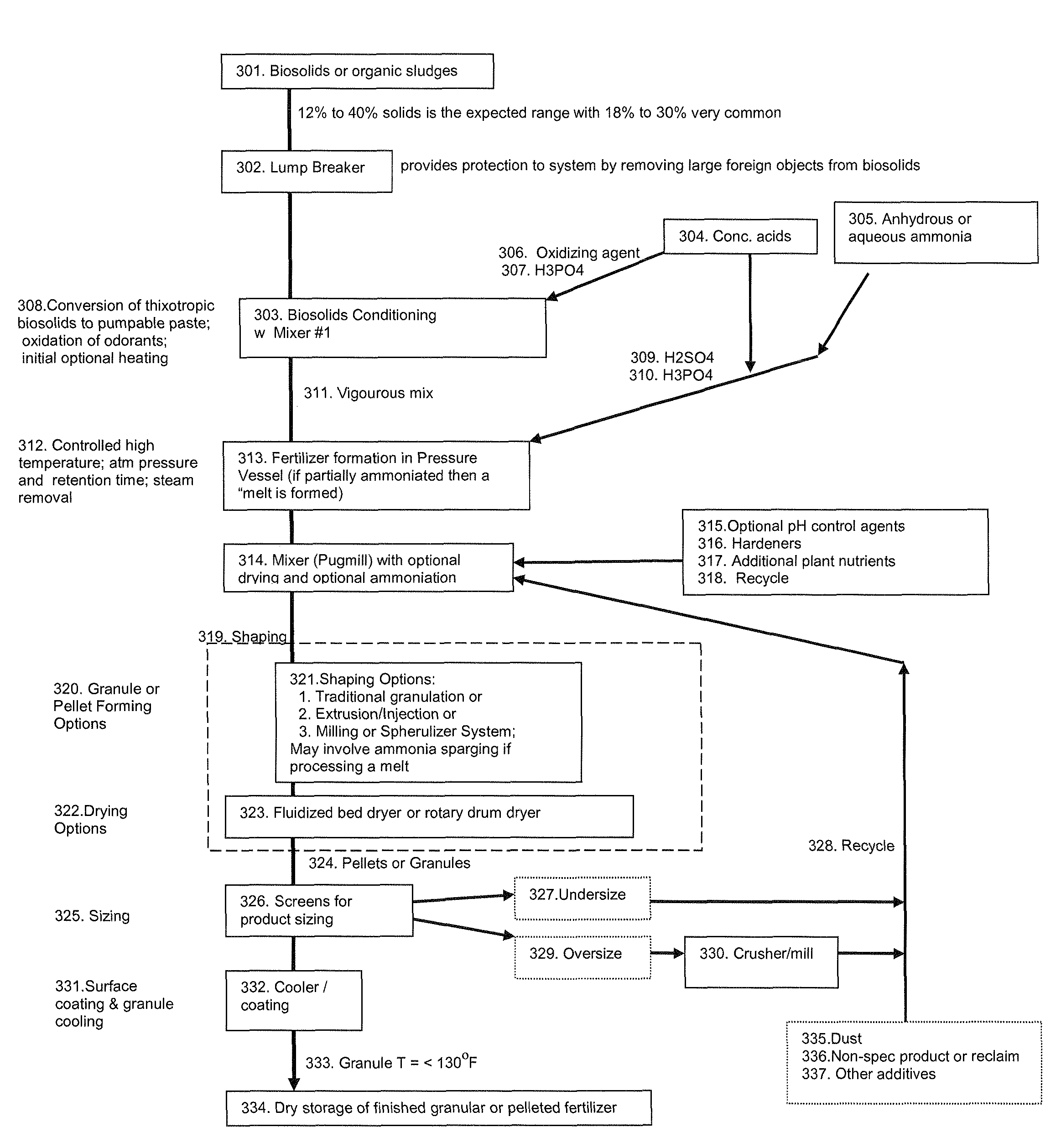
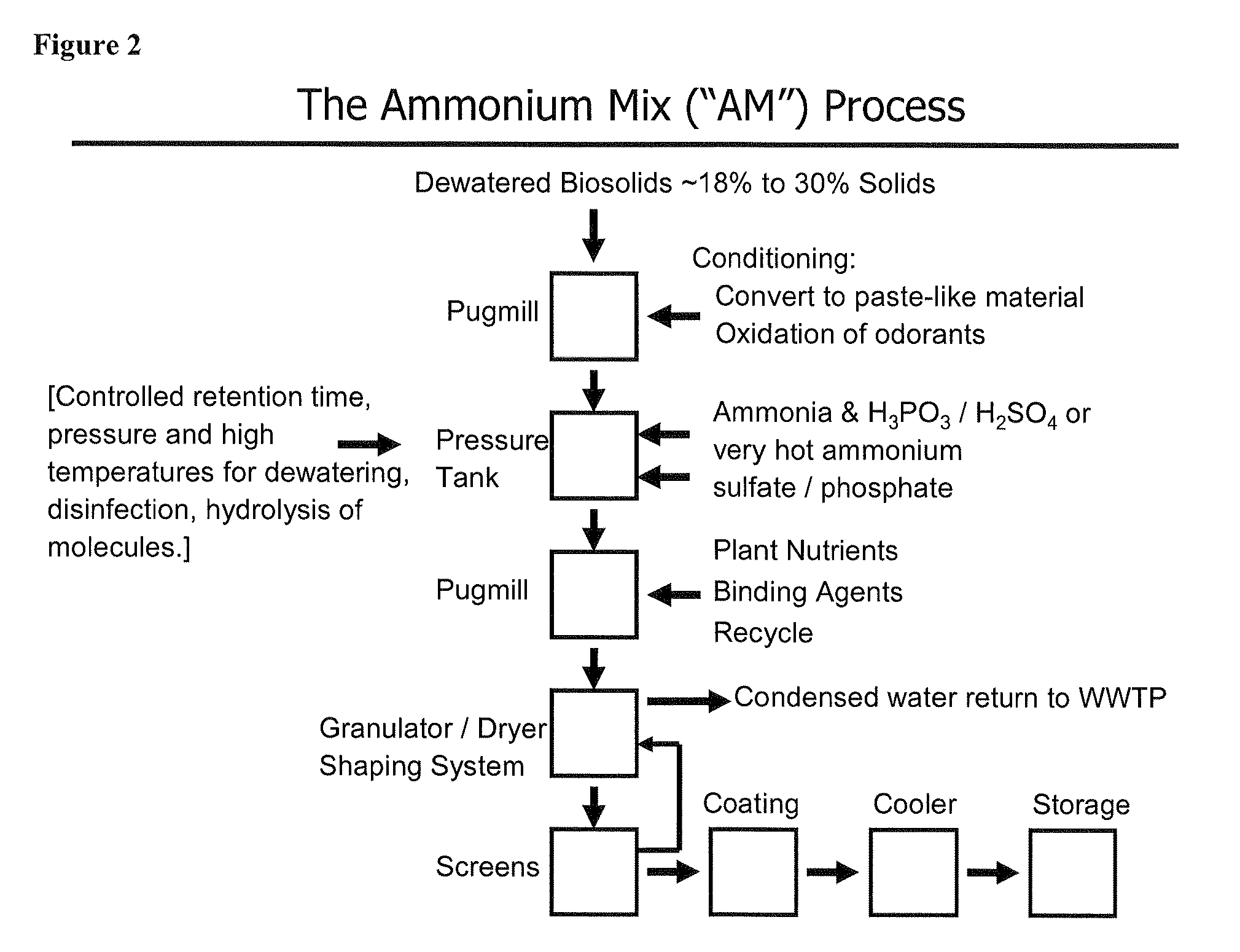
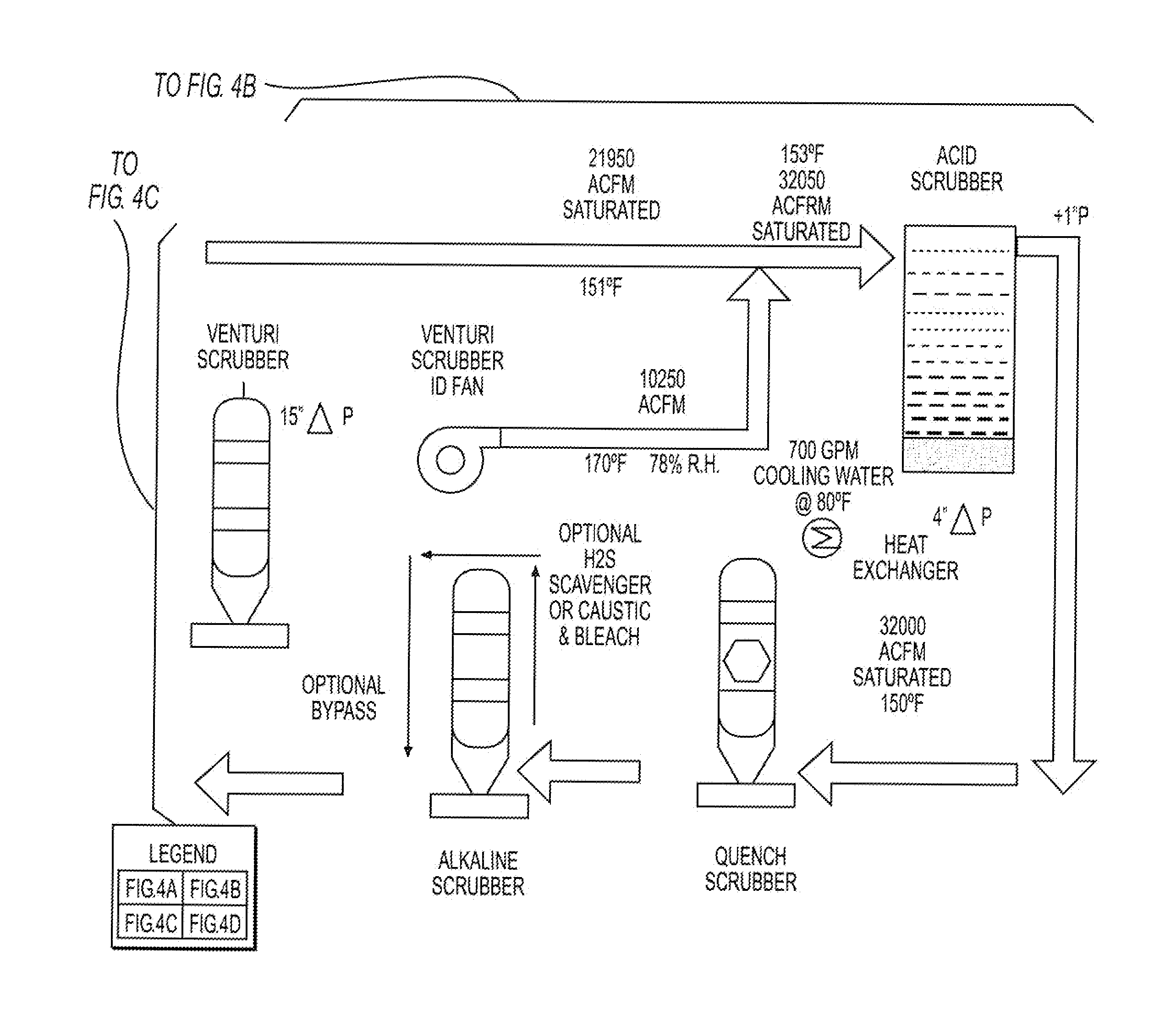
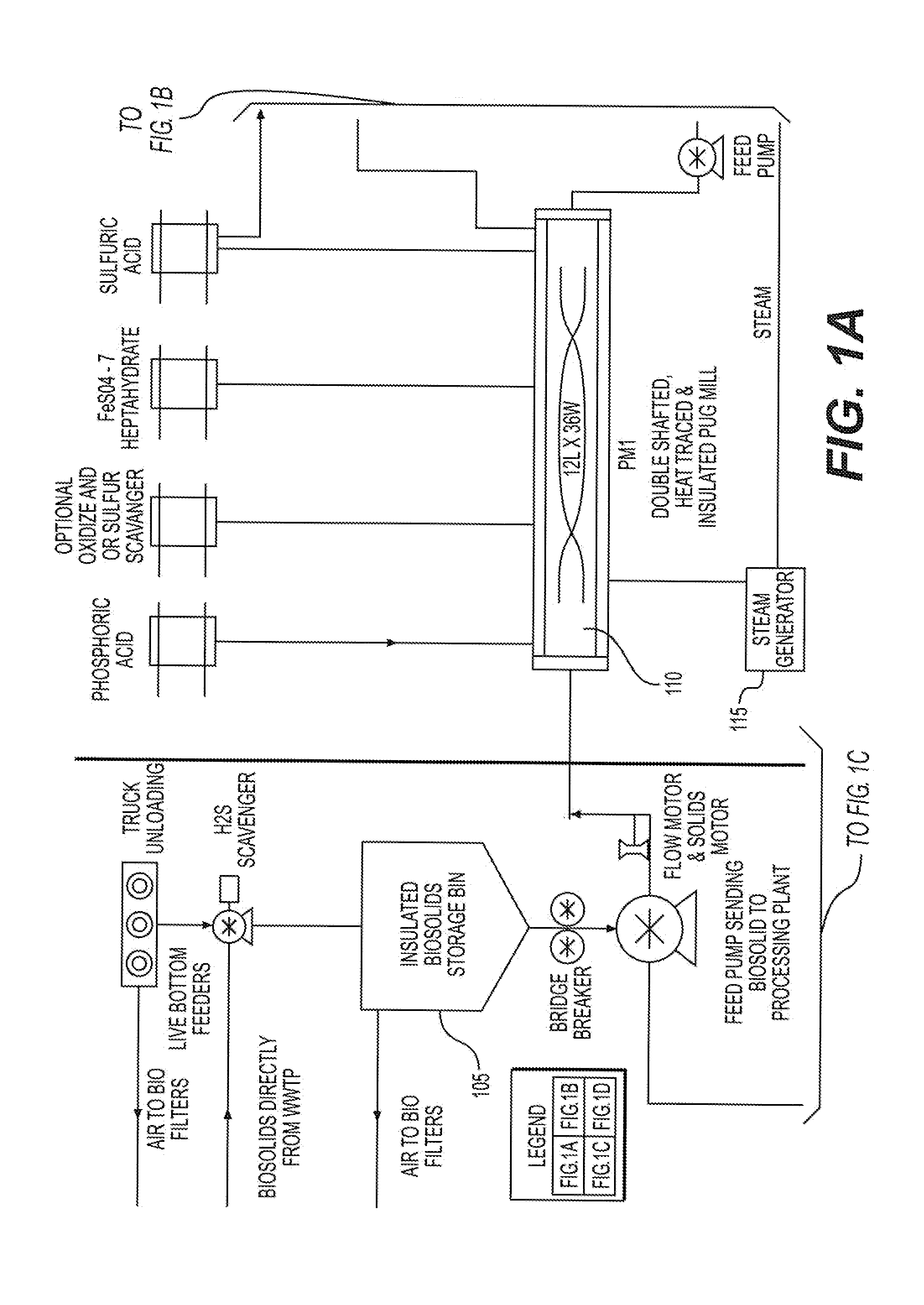
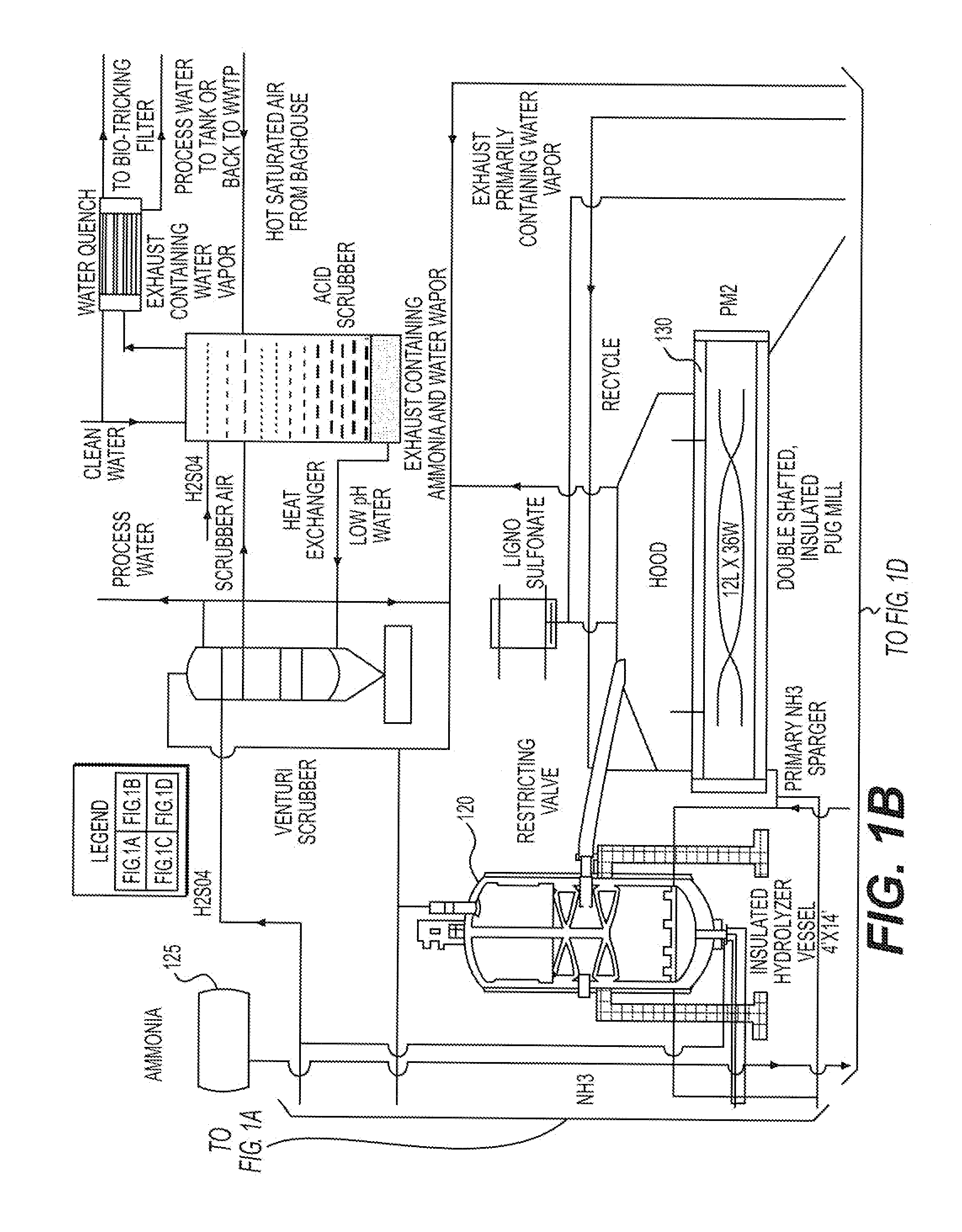
The invention describes a new method for treating sludge, which can result in the production of high nitrogen organically-augmented inorganic fertilizer that incorporates municipal sludges or biosolids or organic sludges that can compete with traditional fertilizers such as ammonium phosphate, ammonium sulfate and urea on the commodity fertilizer marketplace. The method takes advantage of the thixotropic property of dewatered biosolids or organic sludge to create a pumpable paste-like material from the biosolids or organic sludge that is then treated with an oxidizer to reduce odorant effects and an acid. This mix is then interacted with concentrated sulfuric and or phosphoric acids and an ammonia source or alternatively a hot or molten melt or salt of ammonium sulfate / phosphate to form a fertilizer mix. The present invention controls the heat, atmospheric pressure and retention time of the fertilizer mix in the reaction vessel. When a fertilizer melt is formed ammoniation is subsequently completed by the specific use of vaporized ammonia. The invention can also be an add-on to commercial production of ammonium salts. The fertilizer produced by the present invention contains more than 8 wt. % nitrogen and preferably 15 wt. % nitrogen. The invention is oriented to be tailored to the biosolids production for individual municipal waste treatment plants in order to keep the fertilizer manufacturing plants of the present invention small with a minimization of logistics and liability.
Owner:GENERATE LENDING LLC +1
Controlled release fertilizer composition
ActiveUS7771505B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce the amount requiredBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersControlled releaseWater insoluble
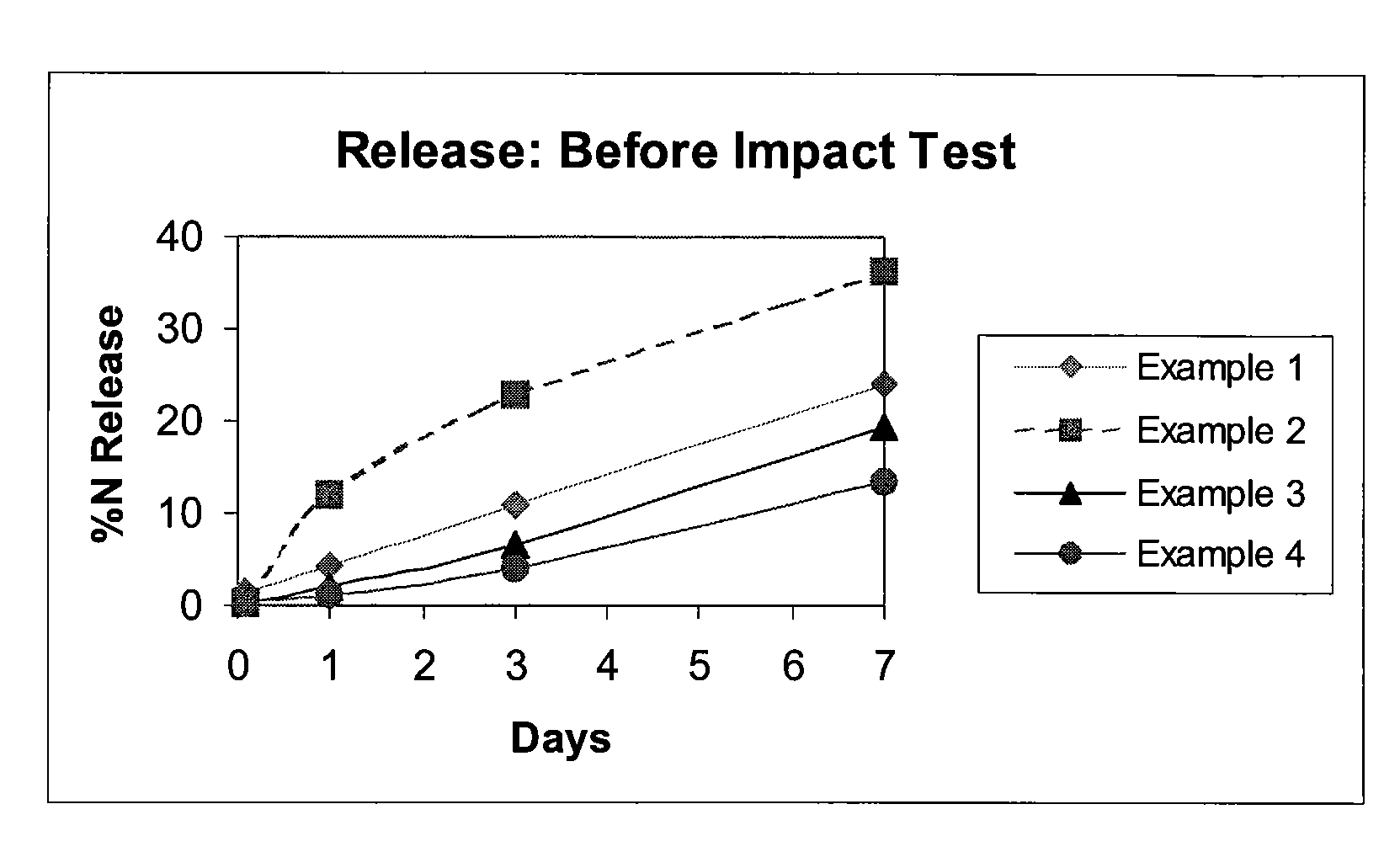
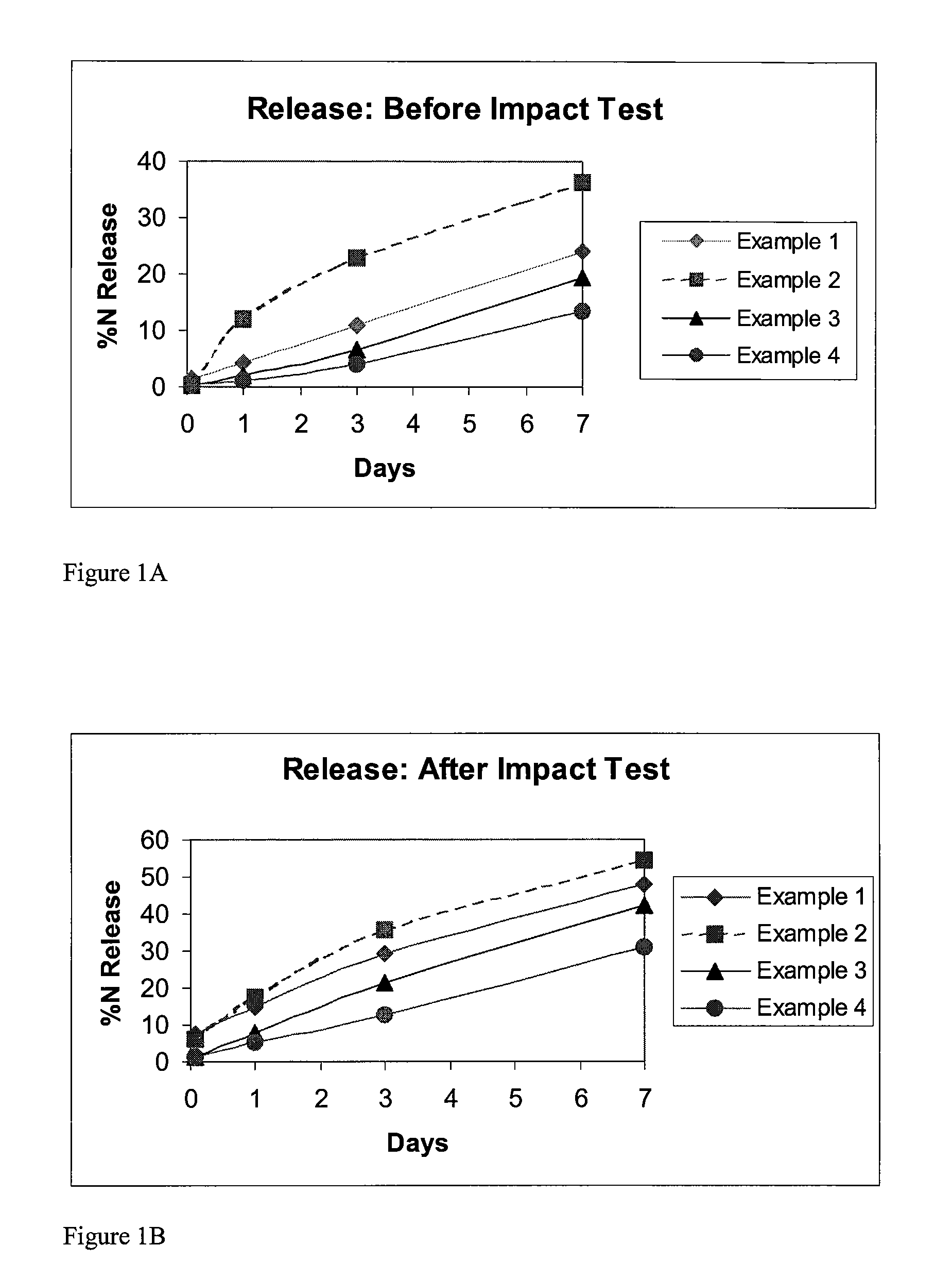
A controlled release fertilizer composition and methods to produce the controlled release fertilizer composition are described. The controlled release fertilizer composition comprises a water soluble fertilizer core that is coated with a polymeric layer, intermediate layer, and a sulfur layer. If desired, the sulfur layer can be coated with an outer water-insoluble layer.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Water-dispersible pellets
A water-dispersible particle for delivery of nitrogen to a plant is disclosed. The water-dispersible particle also delivers an active ingredient such as a plant hormone to a desirable plant or a pesticide or herbicide to an undesirable organism. Methods for making and using the water-dispersible particle are described.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Highly available particulate controlled release nitrogen fertilizer
InactiveUS6048378ASpeed up the conversion processImprove efficiencyBiocideGranulation in rotating dishes/pansParticulatesWater insoluble
A method preparing controlled release nitrogen in particulate fertilizers which exhibit single growing season availabilities to plants of about 80 percent or higher. The method utilizes relatively low urea and ammonia to formaldehyde mol ratios of about 1.7 urea to 0.1 ammonia to 1 formaldehyde to assure high conversions to controlled release nitrogen with low free ureas, and carefully controlled elevated temperatures, acid dehydration condensation catalyst concentrations and short dehydration reaction times of about 2-4 minutes to provide effective conversion of hydroxymethyl nitrogen compounds by dehydration condensation reaction to controlled release methylene nitrogen compounds. Quick neutralization of the dehydration catalyst in a turbulent mixing reactor minimizes the formation of undesirable methylene nitrogen polymers which are hot water insoluble and unavailable to plants in a single growing season.
Owner:AGRINUTRIENTS TECH GRP INC
Compositions of Substantially Spherical Particles and Methods of Making Thereof
InactiveUS20140047884A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic phosphatic fertilisersActive agentChemistry
An improved composition comprising substantial spherical UFP particles and an active agent, such as NBPT, and optionally other components is used as an additive for liquid and solid fertilizers, typically containing urea. Methods of making the compositions and their use are also disclosed.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Fertilizer combination products including fertilizer granules and cellulosic granules carrying pesticides and other active ingredients
Blends of fertilizer granules and highly absorbent cellulosic granules carrying one or more pesticidal or other active ingredients that resist the formation of actives dust or segregation of the granules and that ensure even and efficient application of both the fertilizer and the active ingredients.
Owner:KADANT GRANTEK
Method for producing a fertilizer with micronutrients
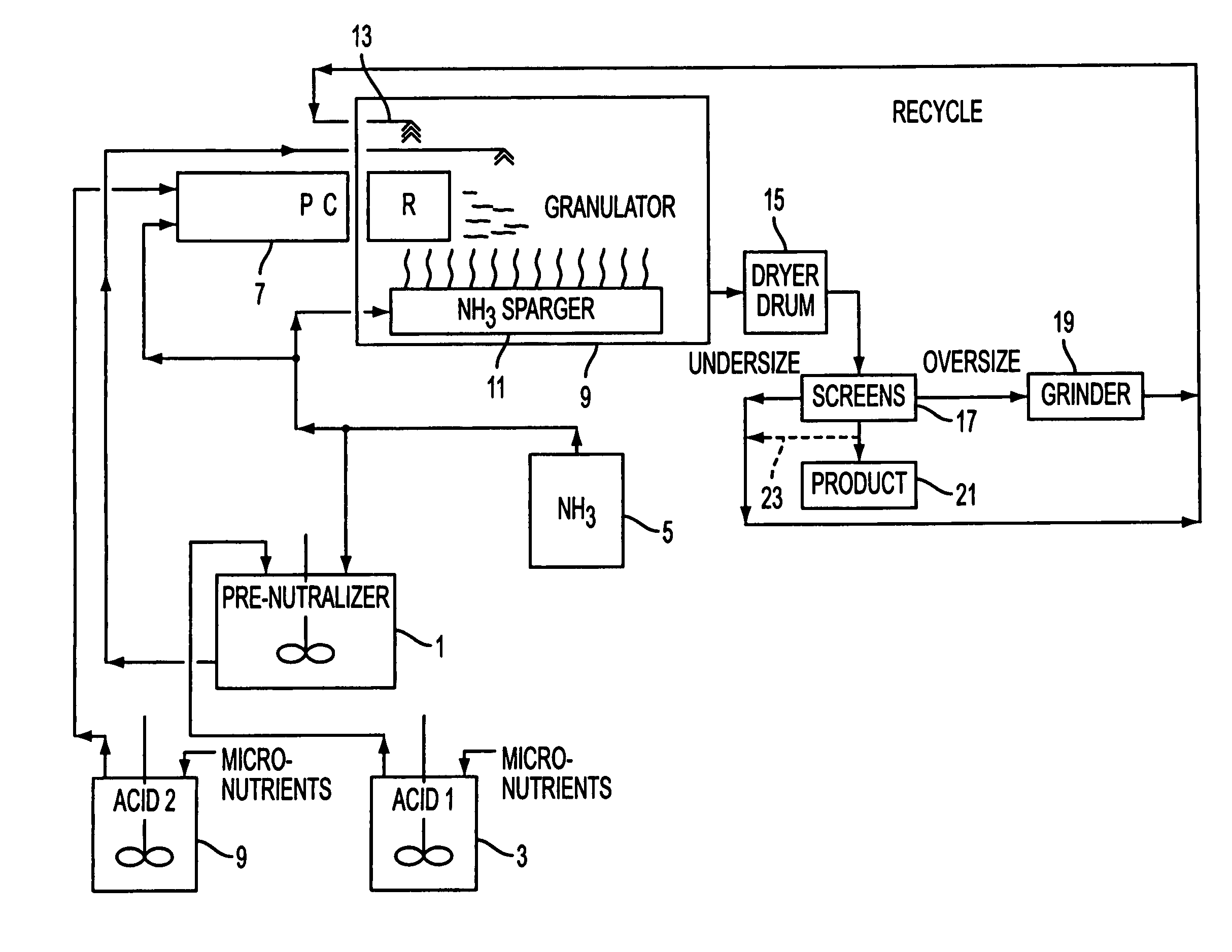
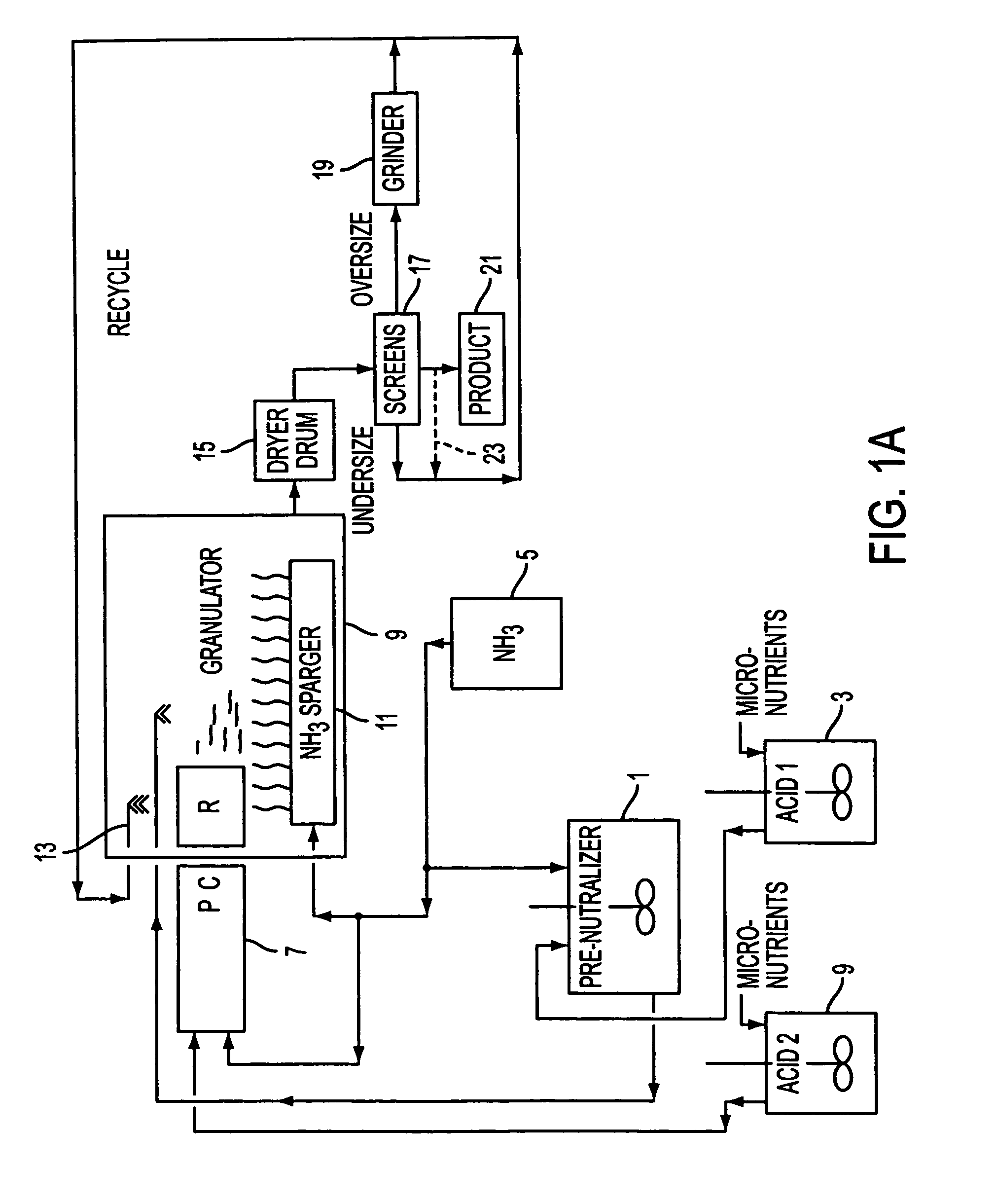
ActiveUS7497891B2Avoid suffocationAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphoric acidAmmonia
According to a method of producing a phosphate fertilizer, a first portion of the phosphate is produced in a pipe cross reactor, and a second portion of the phosphate is produced in a pre-neutralizer. Both the first and second portions of the phosphate are supplied to a granulator. Ammonia is added to the granulator to react with the first and second portions of the phosphate. To produce the first portion of the phosphate, a micronutrient is added to phosphoric acid to produce an enriched acid, and the enriched acid and ammonia are added to the pipe cross reactor where they are allowed to react to produce ammonium phosphate.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Soil conditioning agglomerates containing calcium
InactiveUS6936087B2High mechanical strengthGood curative effectBiocideCalcareous fertilisersParticulatesWater soluble
Mechanically strong, water-disintegrable agglomerates made from a particulate calcium source, a water-soluble binder and optionally containing a primary plant nutrient source and / or micronutrient source and a process for forming such agglomerates are disclosed. The agglomerates may be used as a soil liming agent and for introducing nutrient values into cultivated soil. Also disclosed is a method for introducing nutrient values into cultivated soil so as to inhibit leaching of the nutrient values from the soil and improve utilization of the nutrient values by plants grown in the soil.
Owner:MAGIC GREEN CORP
Detoxification of soil
InactiveUS6336772B1Economy of resultSpeed of resultBiocideContaminated soil reclamationPesticide contaminationOrganism
Compositions for and method of degrading organic chemicals in soil. The composition is a nutrient medium serving as a substrate for micro-organisms in the soil, preferably containing a major proportion of a source of carbon skeleton and energy, a macronutrient component preferably including nitrogen and other macronutrients, and a micronutrient component, preferably also a complexing agent and a vitamin / co-factor component. This nutrient material is added to soil, e.g. soil contaminated by a pesticide, to cause proliferation of micro-organisms which are effective, or which develop effectiveness to degrade the organic chemicals. Preferably the micro-organisms are those naturally present in the soil but useful micro- organisms may be added with the nutrient medium.
Owner:YAMASHITA THOMAS T
Homogeneous granules of slow-release fertilizer and method of making the same
A process for making homogeneous granules of slow-release fertilizer to deliver high doses of slow-release nitrogen in pellets that disperse or fall apart when contacted by moisture. The method includes mixing particles of slow-release nitrogen with particles of a potassium source and particles of a phosphorus source, to make a homogeneous blend of the particles. Then, the blended particles are moistened with water or an aqueous solution of urea to moisten the homogeneous blend. After moistening, the blended particles are contacted with an aqueous suspension of urea-formaldehyde resin to bind the particles into homogeneous granules. The aqueous suspension of urea formaldehyde resin preferably has a urea:formaldehyde ratio of about 1:1.
Owner:LEBANON SEABOARD CORP
Urea fertilizer containing central volatilization inhibitor particles to reduce release of ammonia and processes for making same
A urea fertilizer having reduced ammonia volatilization upon application to soil including a central particle having an outer surface and comprising ammonia volatilization inhibiting compounds containing one or more of boron and iodine, and a coating of urea on the outer surface of the central particle, and further a process of making the fertilizer including the steps of: granulating ammonia volatilization inhibiting compounds containing one or more of boron and iodine, with a binder to produce volatilization inhibitor particles; screening the inhibitor particles to a preselected particle size; spraying melted urea onto the surface of the inhibitor particles to produce a coating on the inhibitor particles; granulating the coated inhibitor particles with sprayed melted urea to produce granules of urea coated central volatilization particles; and cooling the granules.
Owner:NEW FERTILIZER TECH LLC
Process for treating sludge and manufacturing bioorganically-augmented high nitrogen-containing inorganic fertilizer
ActiveUS7947104B2Reduce responsibilityEliminate needByproduct vaporizationExcrement fertilisersRetention timePhosphate
The invention describes a new method for treating sludge, which can result in the production of high nitrogen organically-augmented inorganic fertilizer that incorporates municipal sludges or biosolids or organic sludges that can compete with traditional fertilizers such as ammonium phosphate, ammonium sulfate and urea on the commodity fertilizer marketplace. The method takes advantage of the thixotropic property of dewatered biosolids or organic sludge to create a pumpable paste-like material from the biosolids or organic sludge that is then treated with an oxidizer to reduce odorant effects and an acid. This mix is then interacted with concentrated sulfuric and or phosphoric acids and an ammonia source or alternatively a hot or molten melt or salt of ammonium sulfate / phosphate to form a fertilizer mix. The present invention controls the heat, atmospheric pressure and retention time of the fertilizer mix in the reaction vessel. When a fertilizer melt is formed ammoniation is subsequently completed by the specific use of vaporized ammonia. The invention can also be an add-on to commercial production of ammonium salts. The fertilizer produced by the present invention contains more than 8 wt. % nitrogen and preferably 15 wt. % nitrogen. The invention is oriented to be tailored to the biosolids production for individual municipal waste treatment plants in order to keep the fertilizer manufacturing plants of the present invention small with a minimization of logistics and liability.
Owner:GENERATE LENDING LLC +1
Bioorganically-augmented high value fertilizer
ActiveUS20110154873A1Method is newBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersClosed loopNitrogen
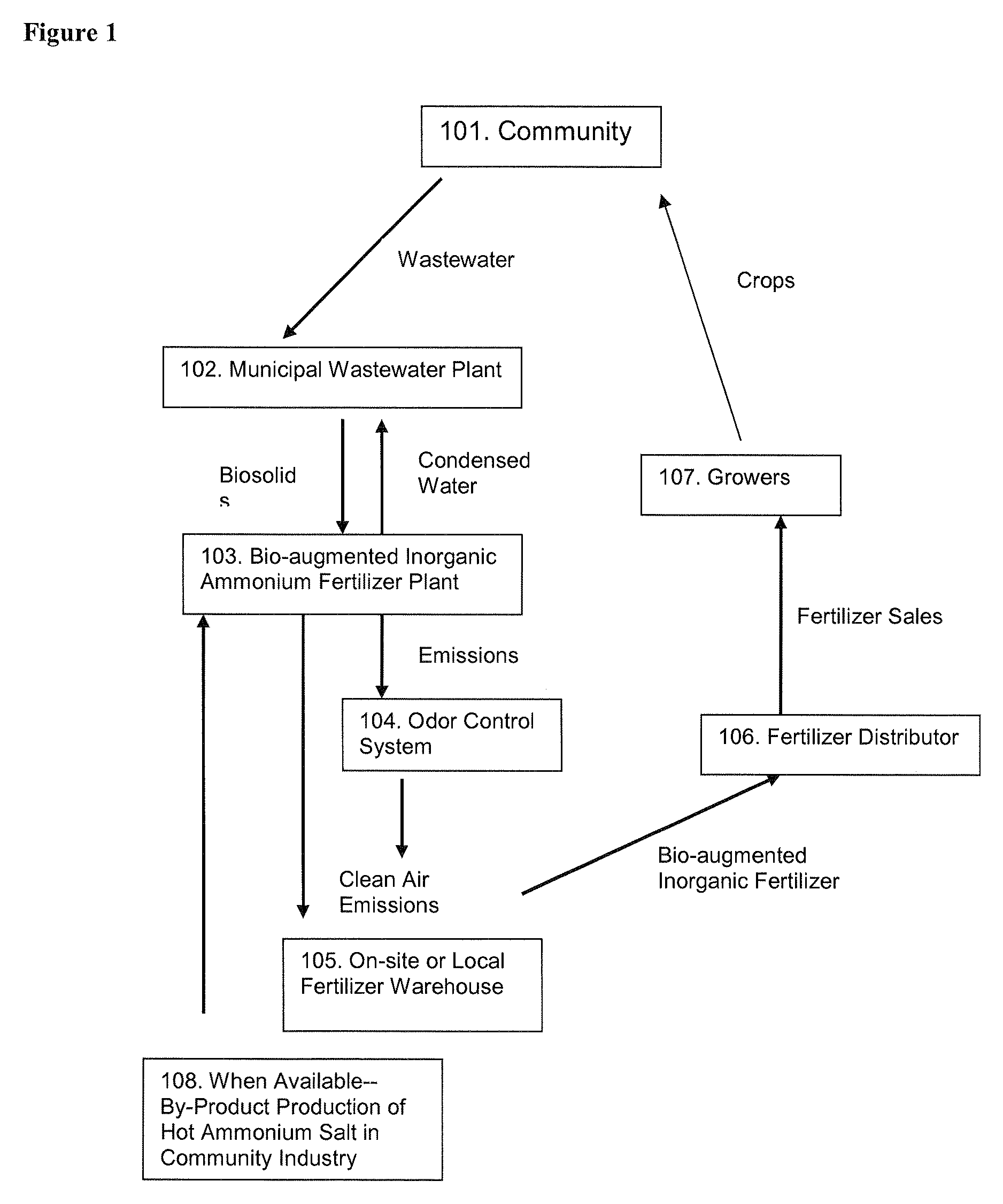
The invention is directed to processes for treating biosolids that result in high-value, nitrogen-containing, slow-release, organically-augmented inorganic fertilizer that are competitive with less valuable or more costly conventional commercially manufactured fertilizers. The process involves conditioning traditional waste-water biosolids and processing the conditioned biosolids continuously in a high throughput manufacturing facility. The exothermic design and closed loop control of the primary reaction vessel decreases significantly the amount of power necessary to run a manufacturing facility. The process utilizes green technologies to facilitate decreased waste and enhanced air quality standards over traditional processing plants. The fertilizer produced from recovered biosolid waste is safe and meets or exceeds the United States Environment Protection Agency (USEPA) Class A and Exceptional Quality standards and is not subject to restrictions or regulations.
Owner:GENERATE LENDING LLC +1
Amino alcohol solutions of N-(n-butyl)thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) and urea fertilizers using such solutions as urease inhibitors
ActiveUS20110259068A1Good water solubilityReduce flammabilityBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersAlcoholUrease Inhibitors
A method of producing reduced volatility of urea fertilizers comprising: dissolving N-(n-butyl)-thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) in an amino alcohol having the formula 1—(H)x—N—((CH2)m—OH)n where m is 1-3, x is 0 or 1, and n is 2 when x is 1 and 3 when x is 0: or the formula 2—(H)y—N—((CH2)—CHOH—CH3)z such that the length of the carbon chain where the secondary hydroxyl group is located is 3, y is 0 or 1, and z is 2 when y is 1 and 3 when y is 0 to form an NBPT solution; and combining a urea fertilizer in granular or liquid form with the NBPT solution.
Owner:WHITEHURST ASSOCS
Fertilizer composition containing micronutrients and methods of making same
ActiveUS20110214465A1Prevent and reduce chemical/physicalBiocideCalcareous fertilisersDiscrete particleNutrient
A fertilizer composition including a base fertilizer granule with a barrier coating and one or more micronutrients. The base fertilizer material is coated with a barrier coating, and then a coating of one or more micronutrients. Alternatively, the base fertilizer material is coated with a barrier coating having discrete particles of micronutrients dispersed throughout. The barrier coating acts to physically and chemically isolate the micronutrient particles from the underlying fertilizer composition such that more of the micronutrient is available to the soil solution, and ultimately to the root zone of the plant.
Owner:THE MOSAIC COMPANY
Amino alcohol solutions of N-(n-butyl)thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) and urea fertilizers using such solutions as urease inhibitors
InactiveUS8163058B2Good water solubilityReduce flammabilityBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersAlcoholUrease Inhibitors
A method of producing reduced volatility of urea fertilizers comprising: dissolving N-(n-butyl)-thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) in an amino alcohol having the formula 1—(H)x—N—((CH2)m—OH)n where m is 1-3, x is 0 or 1, and n is 2 when x is 1 and 3 when x is 0: or the formula 2—(H)y—N—((CH2)—CHOH—CH3)z such that the length of the carbon chain where the secondary hydroxyl group is located is 3, y is 0 or 1, and z is 2 when y is 1 and 3 when y is 0 to form an NBPT solution; and combining a urea fertilizer in granular or liquid form with the NBPT solution.
Owner:WHITEHURST ASSOCS
Soilless vegetable culture nutrient solution and preparation method
InactiveCN106699386AImprove stabilityHigh content of effective nutrientsCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAdditive ingredientNutrient solution
The invention relates to the field of nutrient solutions, in particular to a soilless vegetable culture nutrient solution and a preparation method. The soilless vegetable culture nutrient solution is prepared from sodium nitrate, urea phosphate, potassium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, magnesium chloride, Fe-EDTA, boric acid, manganese chloride, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, sodium molybdate, mixed nitrogen-fixing bacterium solution and a nostoc extracting solution. The nutrient solution is simple and convenient to prepare, comprehensive in nutrient ingredient, high in biological activity and good in homogeneity, can decompose self-toxic materials produced by vegetables, remarkably improve the resistance, yield and the quality of the vegetables.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Controlled Release Fertilizer Composition
ActiveUS20100011825A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce the amount requiredBiocideOrganic phosphatic fertilisersControl releaseSulfur
A controlled release fertilizer composition and methods to produce the controlled release fertilizer composition are described. The controlled release fertilizer composition comprises a water soluble fertilizer core that is coated with a polymeric layer, intermediate layer, and a sulfur layer. If desired, the sulfur layer can be coated with an outer water-insoluble layer.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Techniques for managing priority queues and escalation considerations in USB wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20090254685A1Organic phosphatic fertilisersData switching networksCommunications systemNetwork packet
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Conditioned urea-based granular fertilizers and methods of making thereof
InactiveUS20130174623A1High trafficOrganic phosphatic fertilisersAgriculture gas emission reductionCakingChemistry
The present invention provides methods for preparing flowable urea-based granular fertilizers, wherein the urea-based granular fertilizer has become wet; comprising contacting the urea-based granular fertilizer with a conditioner; and optionally other components to form a more flowable urea-base granular fertilizer. Methods for preventing urea-based granular fertilizer caking and urea-based granular fertilizer compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Use of synergistic microorganisms and nutrients to produce signals that facilitate the germination and plant root colonization of mycorrhizal fungi in phosphorus rich environments
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Compositions for plants containing phosphonate and phosphate salts, and derivatives thereof
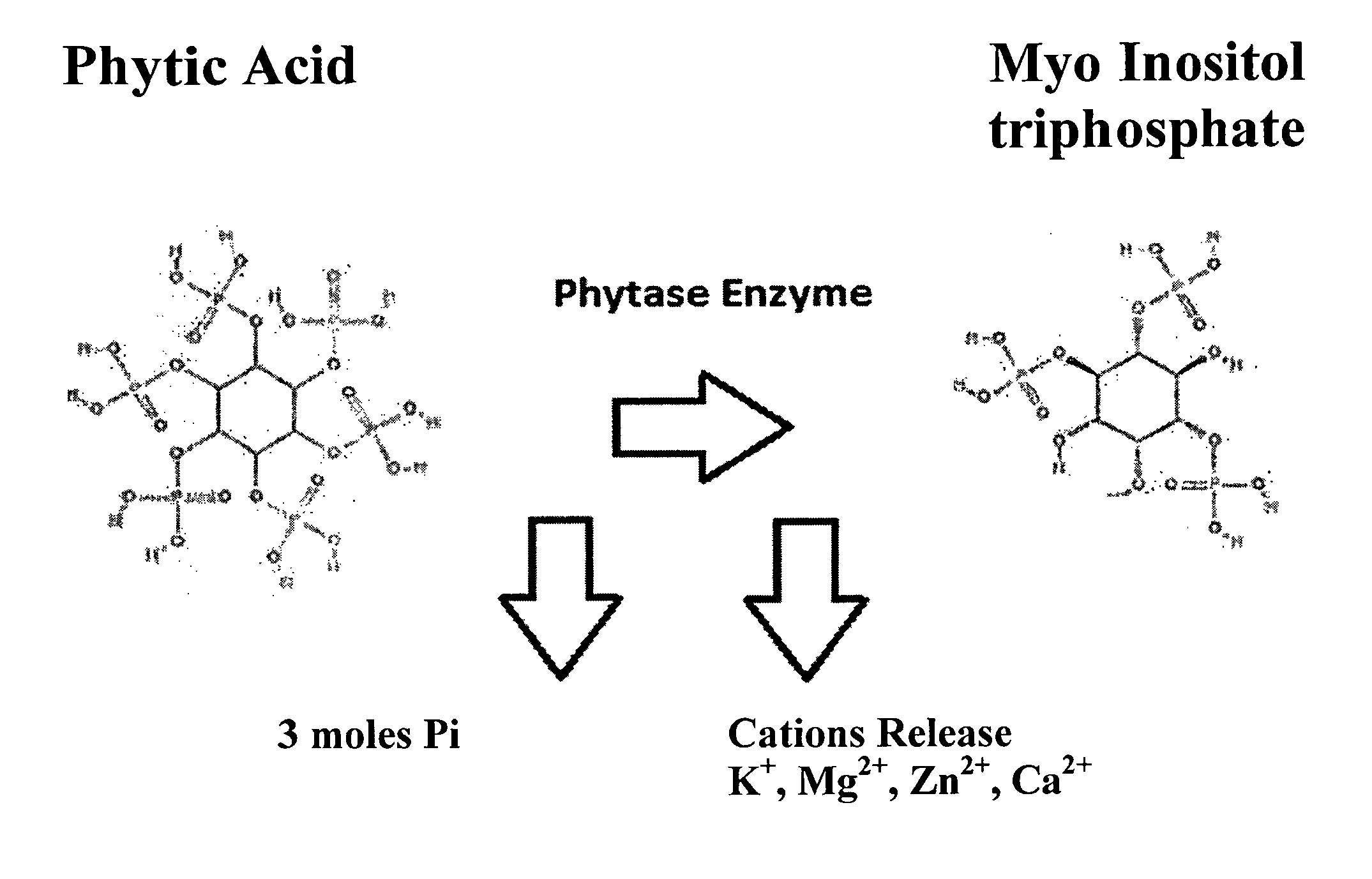
InactiveUS6338860B1Maximum protectionAvoid infectionBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsPhosphatePhytophthora
A fungicidal composition for plants containing phosphonate (PO3) and phosphate (PO4) salts, and derivatives thereof is disclosed. The composition provides a single product which may be employed to control a Phytophthora infestans infection in plants.
Owner:PS 37 IP2
Fertilizer Suspension and Method of Preparation
A concentrated, homogenous, stable, water-soluble fertilizer suspension comprising: water-soluble mineral nutrients of at least nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, and magnesium; and an organic stabilizing additive; and wherein the pourable, aqueous suspension has water-soluble mineral nutrients amounting to at least about 80 percent by weight (wt. %) of the suspension.
Owner:HGCI INC
Fertilizers containing animal nutrient core packet
InactiveUS20120017659A1Alleviate and eliminate deficiencyHigh nutrient contentOrganic phosphatic fertilisersAmmonium nitrate fertilisersCore ParticleIndividual animal
A fertilizer supplying animal nutrients including a core particle having an outer surface and comprising compounds containing animal nutrients, and a coating of urea on the outer surface of the core particle, and further a process of making the fertilizer including the steps of: screening animal nutrient core particles comprising a powdered substance containing an animal nutrient, to a preselected particle size; spraying melted urea onto the surface of the nutrient core particles to produce a coating on the nutrient core particles; granulating the nutrient core particles with sprayed melted urea to produce nutrient core granules; and cooling the nutrient core granules.
Owner:NEW FERTILIZER TECH LLC
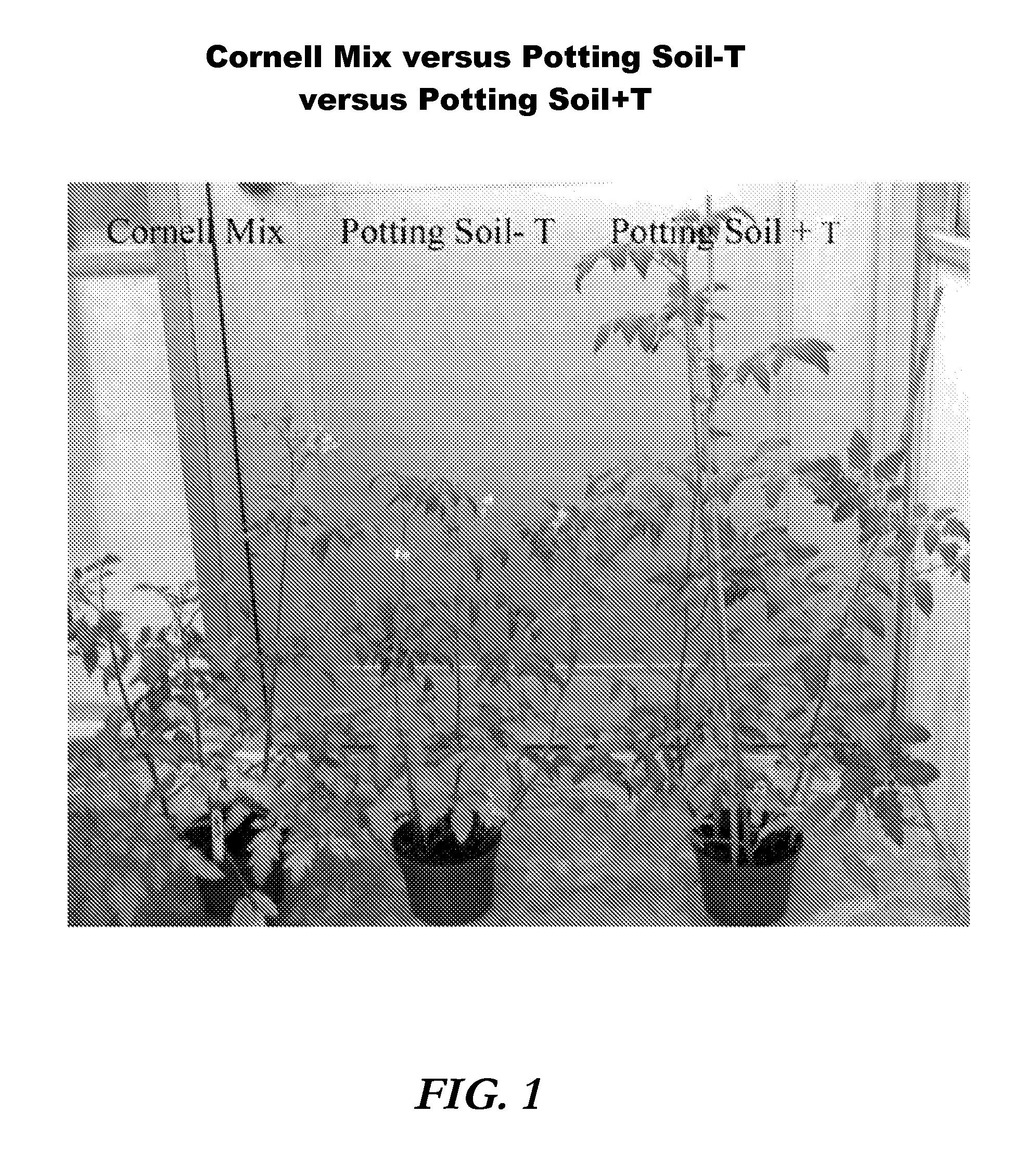
Plant propagation medium and methods of making and using it
ActiveUS20130055635A1Easy to useIncrease in mediumSeed and root treatmentExcrement fertilisersPlant propagationMoisture
The present invention provides a plant propagation medium, the improvement comprising a manure having a moisture content of 10 to 35 wt % with a salt level sufficient to achieve a conductivity of less than 0.35 dS / m. Also disclosed is a method of manufacturing a manure product and the manure product itself.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
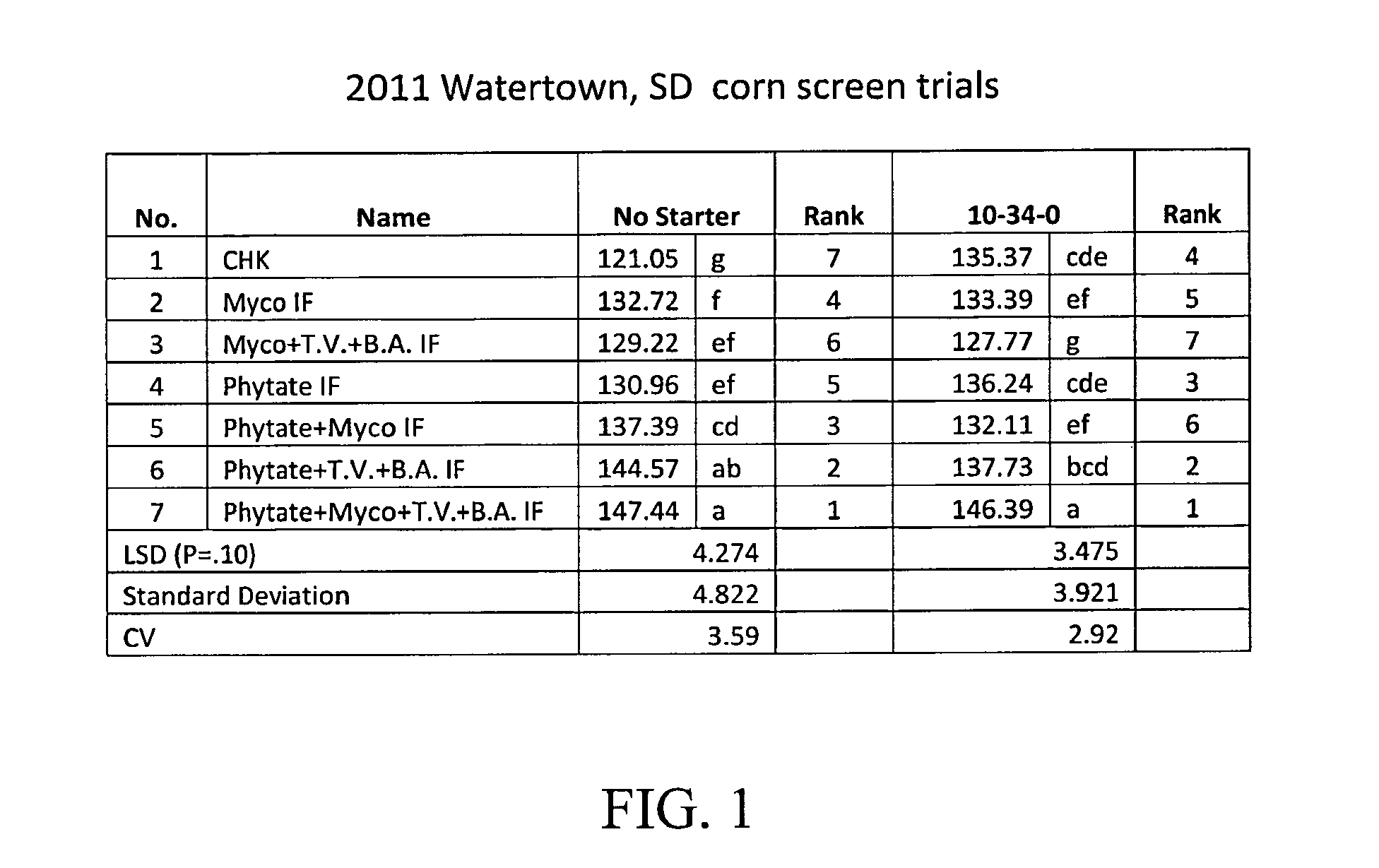
Multifunctional Organic Agricultural Fertilizer Composition and Process for Preparation Thereof
ActiveUS20170166488A1Reduce volatilityInhibit complexation/tieOrganic phosphatic fertilisersAgriculture gas emission reductionAdjuvantStimulant
The invention disclosed herein is a multifunctional agricultural organic bio-complexed composition comprising essential and non-essential nutritional elements; useful as a fertilizer, nutrient, bio-stimulant, complexing agent, pH controller, pH indicator, pH corrector, hard water salts in-activator, surface tension reducer, Spreader, penetrator, adjuvant, alkaline hard water ill effects mitigator, water conditioner and drip system irrigation cleaner. The invention also disclosed herein a process for preparation thereof.
Owner:CHAUDHRY SUUNIL SUDHAKAR
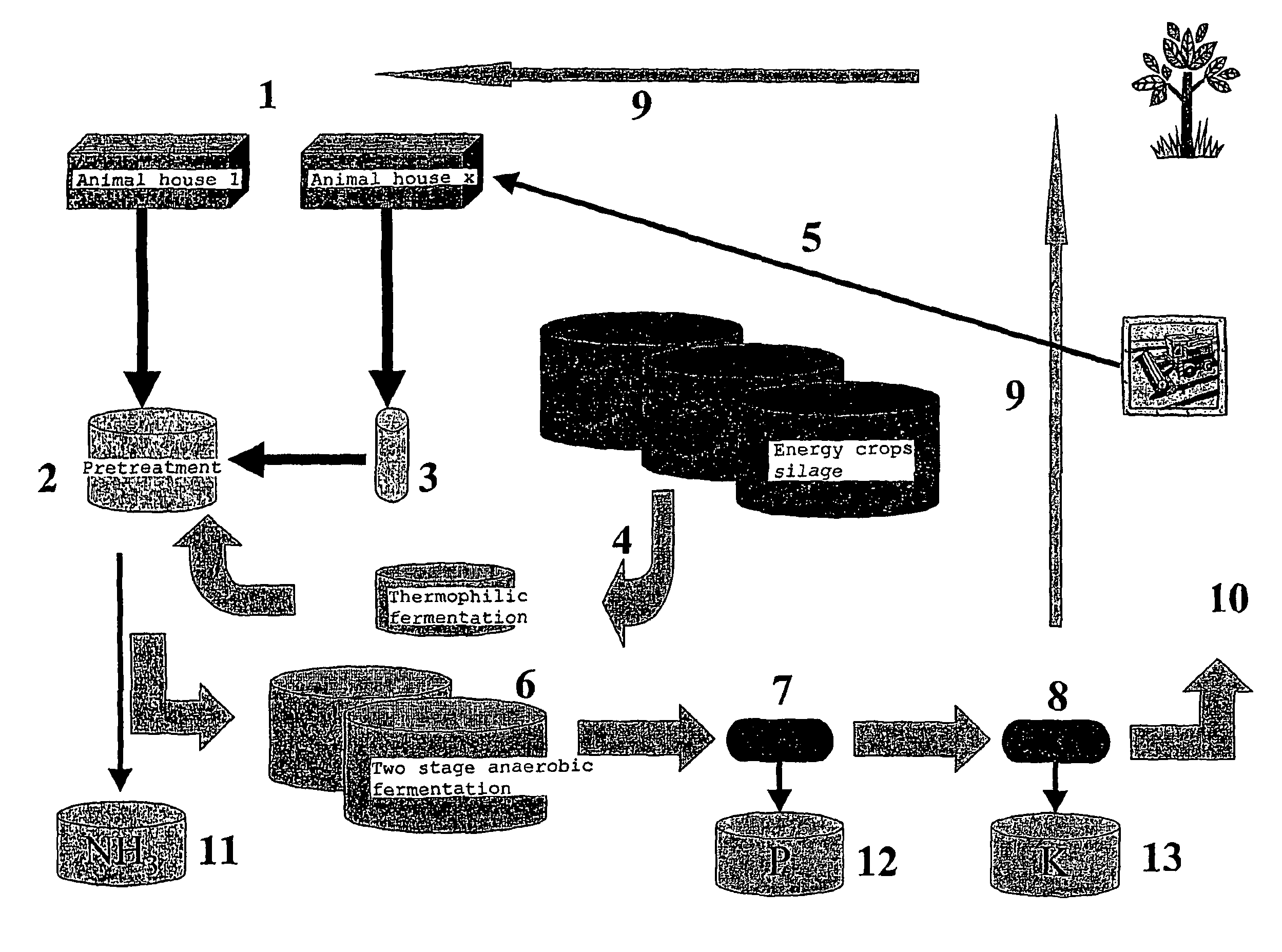
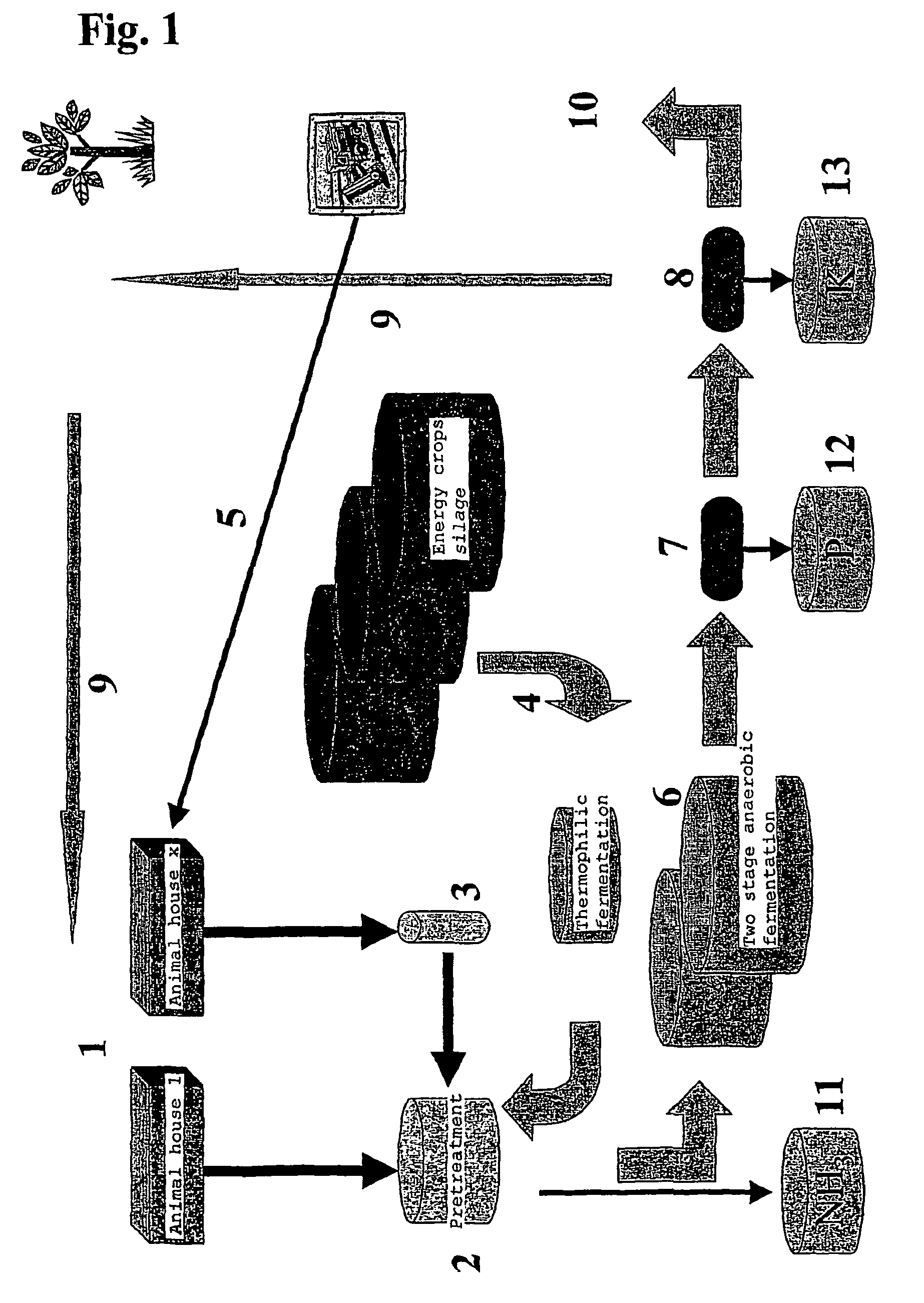
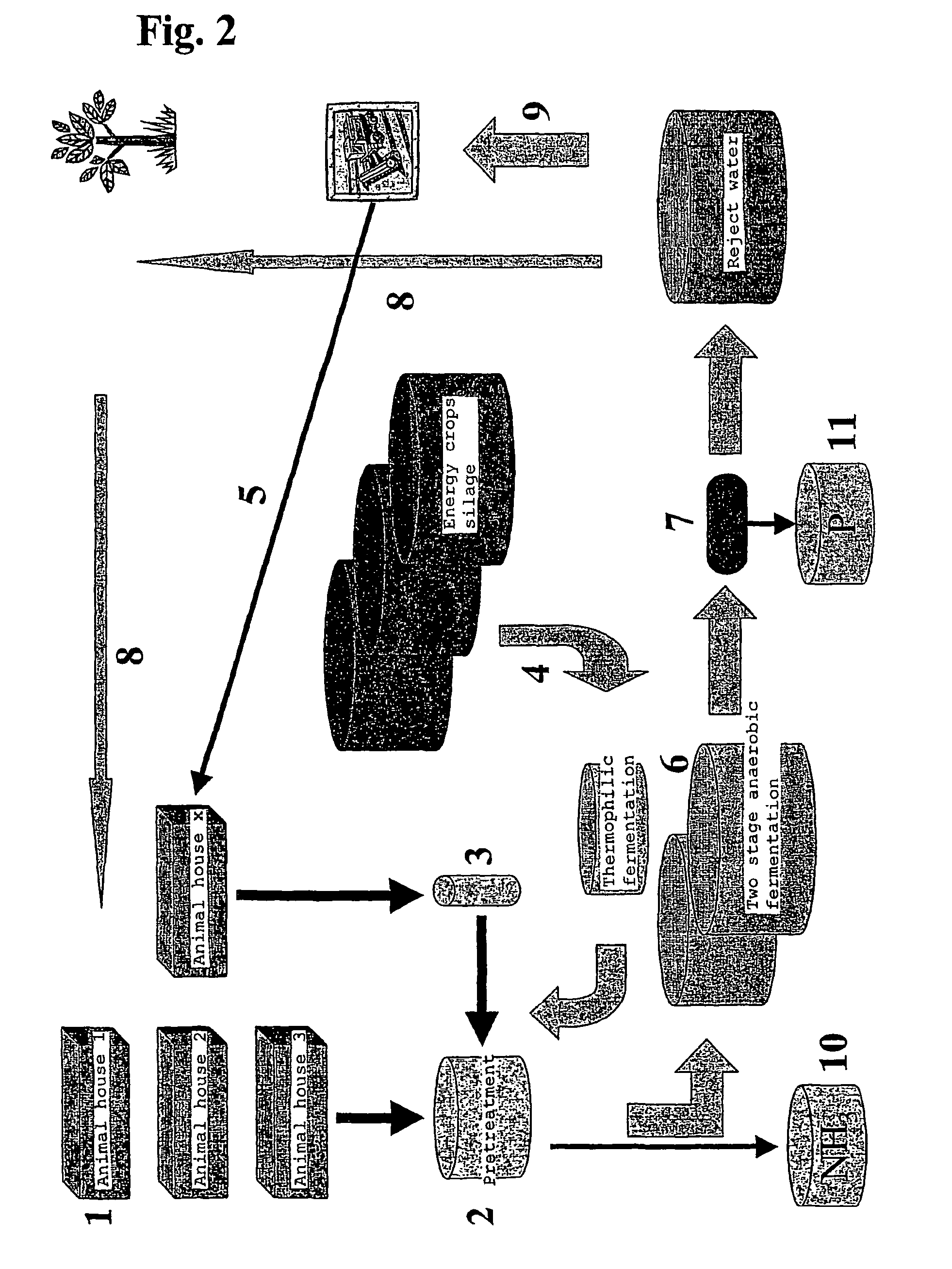
Concept for slurry separation and biogas production
InactiveUS7883884B2High yieldNot subsidisedBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersEngineeringBiogas production
The present invention concerns an anaerobic digestion of animal manures, energy crops and similar organic substrates. The process is capable of refining nutrients comprised in the digested biomass to fertilizers of commercial quality. The invention also provides a method for oprocessing animal carcasses or fractions thereof including meat and bone meal etc., with the objective of providing an alternative means for processing the organic waste material of animal origin while at the same time facilitating the production of fertilizers. The risk of spreading BSE prions or any other prions to animals or humans is thus substantially reduced if not eliminated. The biogas and slurry separation system according to the present invention is preferably integrated with the operations of animal husbandries into a total concept in which the internal and external performances of animal husbandries are optimised. The internal performances concern quality aspects related to the management of the animal houses and include industrial hygiene, animal welfare, gaseous and dust emissions and food safety. The external performances concern mainly energy production and emissions to the environment of nutrients and greenhouse gases and the sale of high quality food product.
Owner:GFE PATENT AS
Coated fertilizer particles
InactiveUS20120090367A1Simple compositionAmmonium nitratesOrganic phosphatic fertilisersNitrogenPolymer chemistry
Owner:TIGER SUL CANADA CO +1
Dispersible struvite particles
A water-dispersible particle is provided that includes struvite in an amount ranging from 5% to 99.9% by weight of the total dry weight of the particle. A binder component is present in an amount from 1% to 95% by weight. The struvite and the binder component on that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. A process for making a water-dispersible particle includes mechanical aggregation of a struvite into a pellet. A binder component is present in the particle in an amount ranging from 1% to 95% by weight. The struvite and the binder component are present in a form such that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. The particle is then dried and ready to be applied.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Compositions of substantially spherical particles and methods of making thereof
InactiveUS9034072B2Group 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic phosphatic fertilisersActive agentChemistry
An improved composition comprising substantial spherical UFP particles and an active agent, such as NBPT, and optionally other components is used as an additive for liquid and solid fertilizers, typically containing urea. Methods of making the compositions and their use are also disclosed.
Owner:KOCH AGRONOMIC SERVICES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com