Method for converting monocot plant genome sequence in which nucleic acid base in targeted DNA sequence is specifically converted, and molecular complex used therein
A monocotyledonous plant and nucleic acid base technology, applied in the field of genome sequence modification, can solve the problem of low frequency of insertion/deletion mutations, and achieve the effect of excellent safety and high mutation introduction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0137] 1. Vector construction
[0138] (1) Construction of Target-AID evaluation carrier
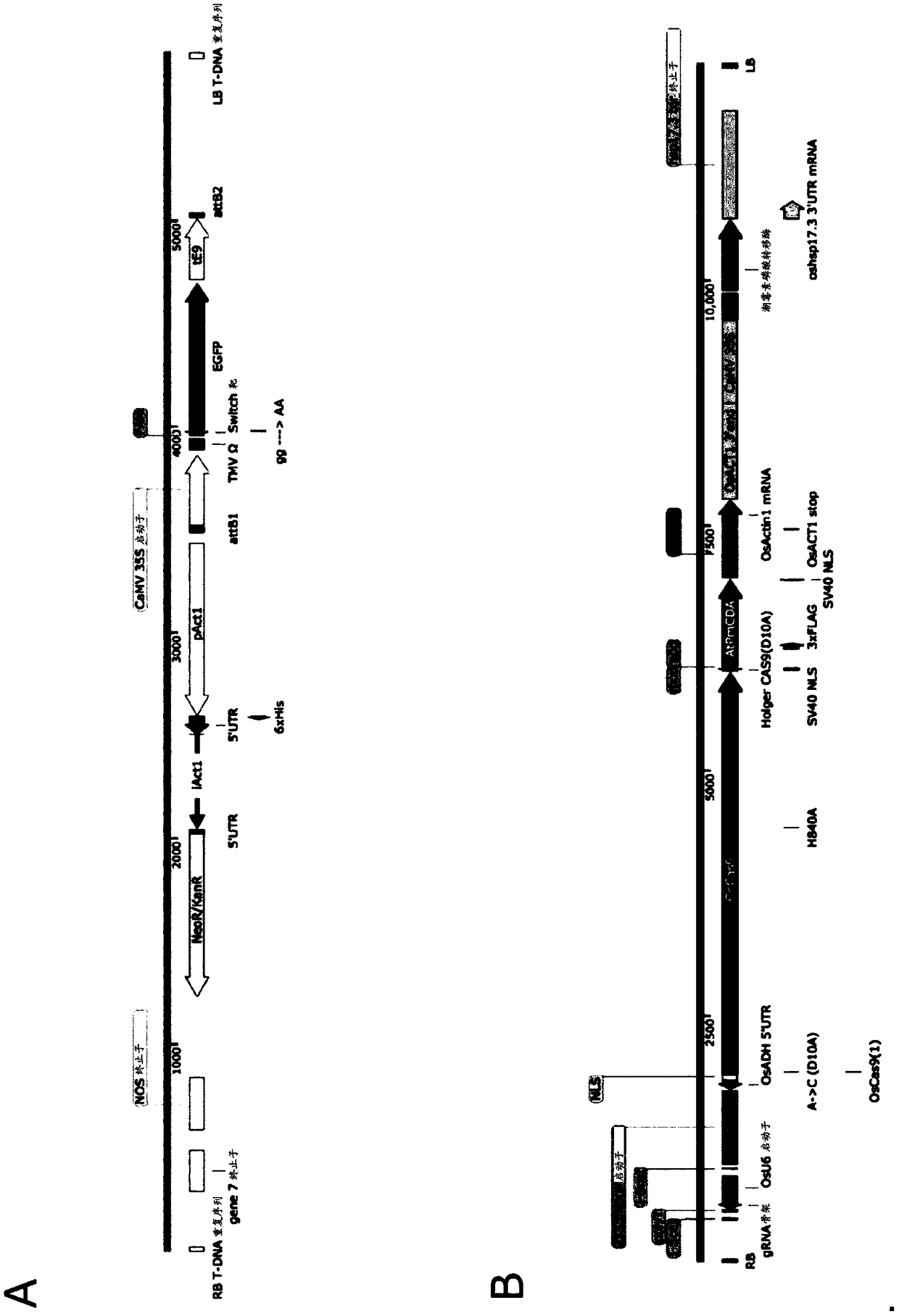
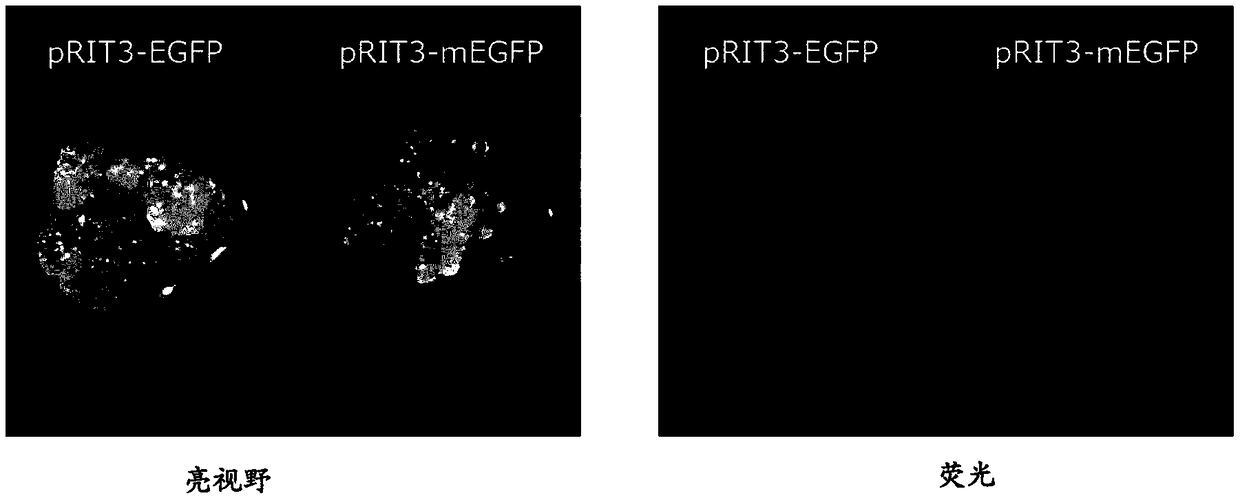
[0139] Produced by conventional methods with figure 1 The structure shown in A is pRIT3-EGFP (with EGFP ORF; SEQ ID NO: 9) and pRIT3-mEGFP (the stop codon is present directly after the EGFP start codon; SEQ ID NO: 10).
[0140] (2) Construction of Target-AID carrier
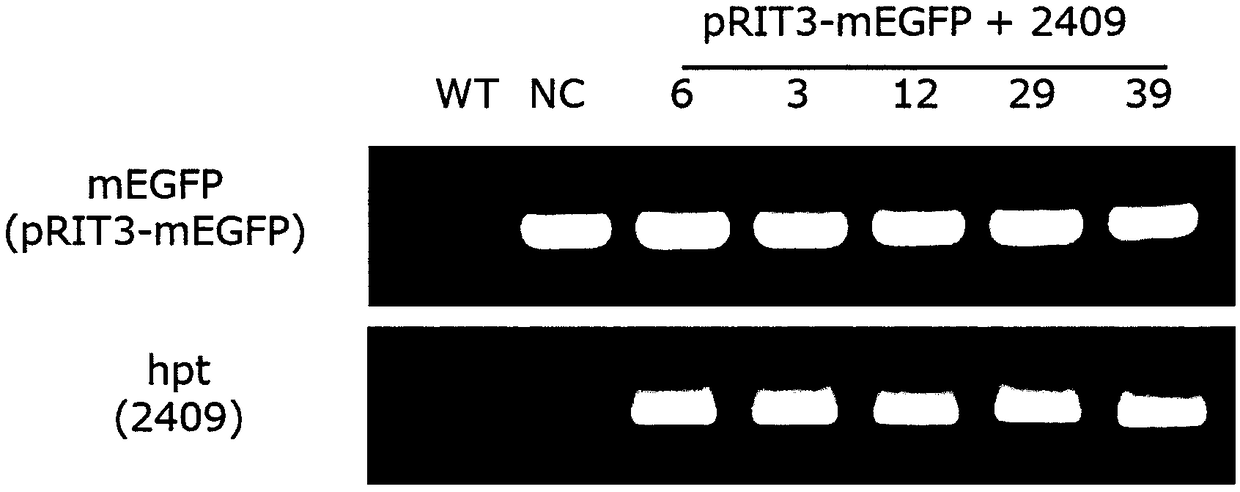
[0141] Generated by the following with figure 1Target-AID vectors 2408 (encoding dCas9; SEQ ID NO:11) and 2409 (encoding D10A mutant; SEQ ID NO:12) of the structure shown in B: pZH_OsU6gRNA_MMCas9 (PlantMol Biol (2015) 88:561-572 ) OS Opt.Cas9 was substituted with DNA encoding (with double mutations of H840A and D10A, or only D10A mutation) mutant Cas9, and a nuclear localization signal (NLS) encoding derived from SV40 was added at both ends downstream of it sequence and fused it to DNA encoding PmCDA1 optimized for codon usage in Arabidopsis.
[0142] 2. Introduction of Target-AID and vector for evaluation into Ag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com