Amide compound and preparation method and application thereof
An amide compound and reaction technology, applied in the field of pesticides, can solve the problems of poor control effect on broad-leaved weeds, and achieve the effect of simple operation, high yield and good herbicidal activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
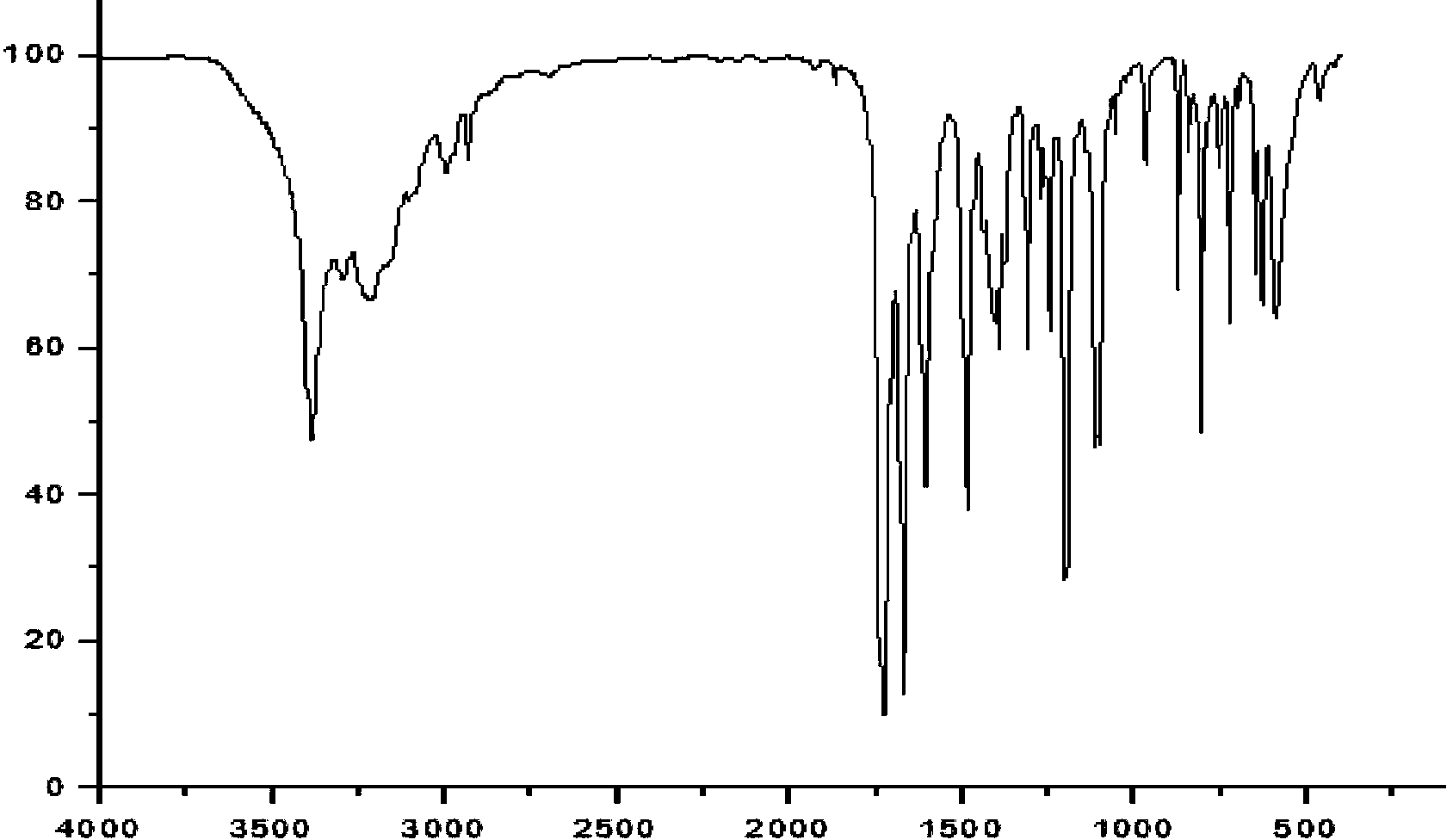
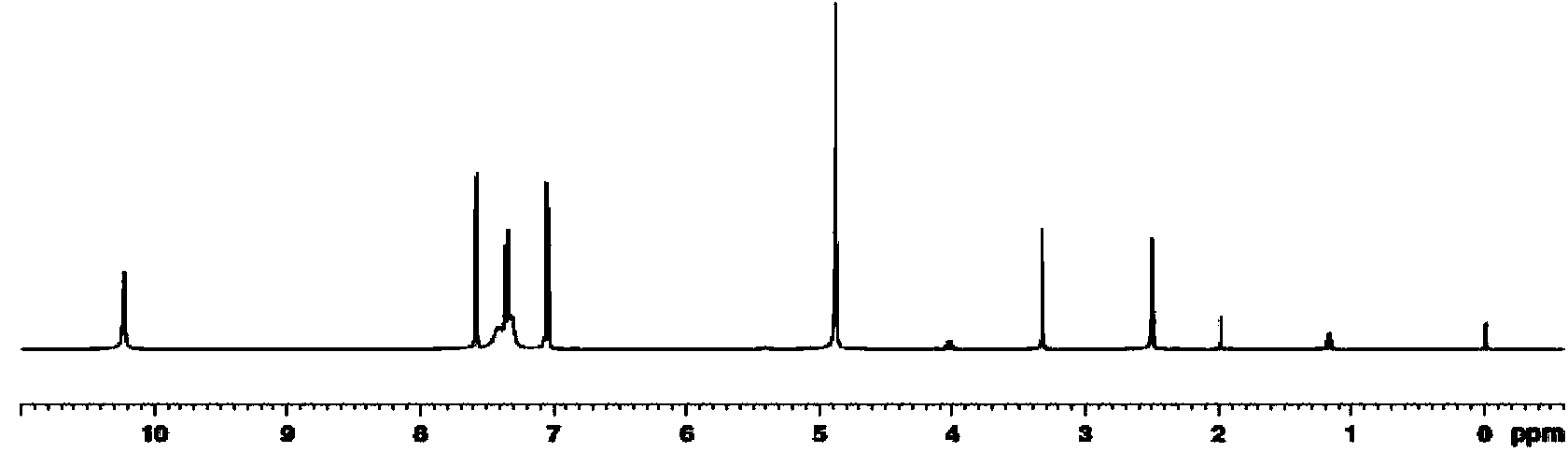
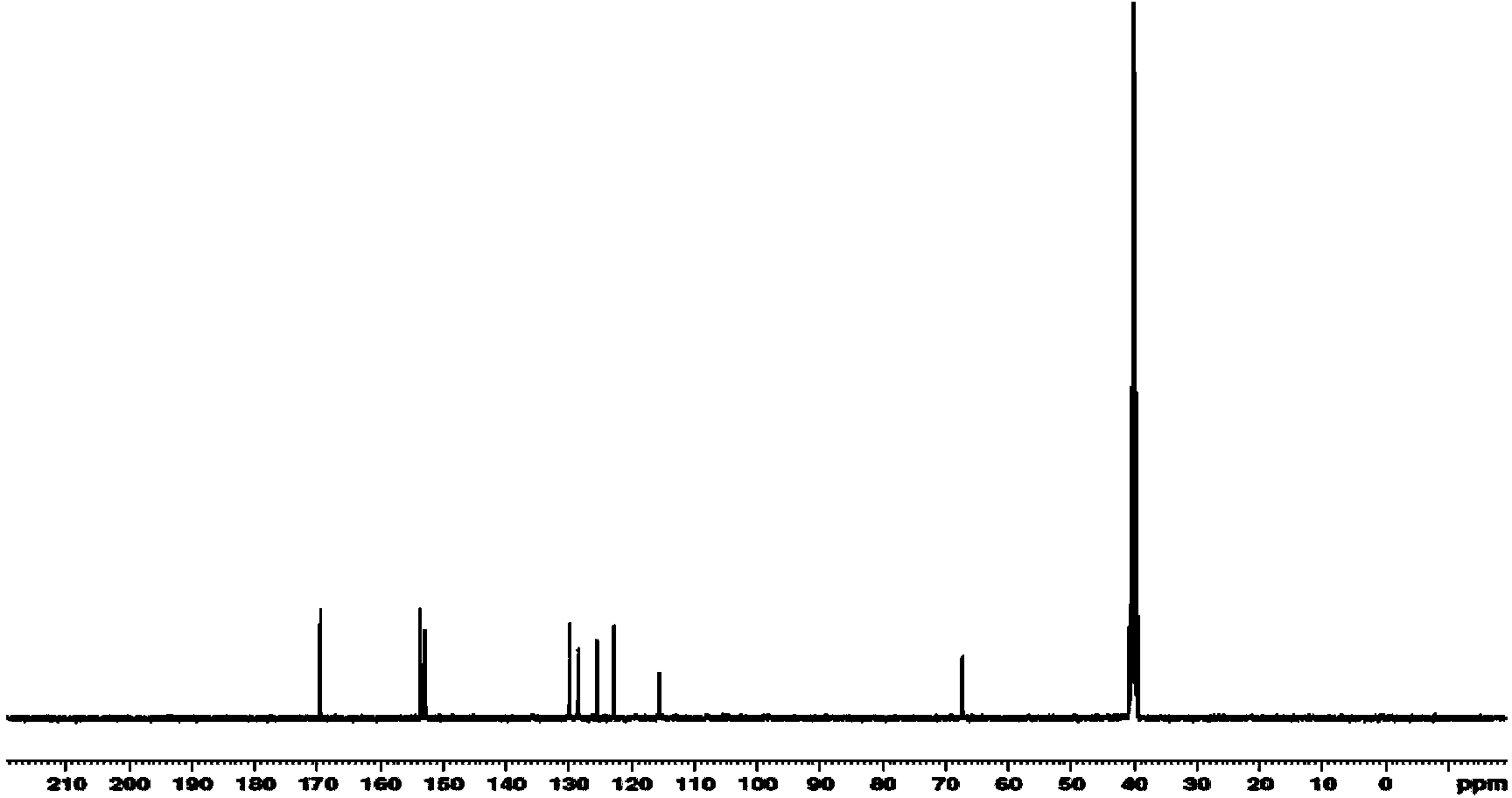
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] (1) Synthesis of compound I
[0022] Add 2 g of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 8.8 mL of thionyl chloride into a 50 mL single-necked round-bottom flask, and carry out a reflux reaction at about 67°C under a magnetic stirrer for 3 hours to obtain a pungent PALE YELLOW LIQUID WITH ODOR. The reaction solution was distilled under reduced pressure in a water bath at 40°C under a vacuum of -0.07 Mpa to remove excess thionyl chloride to obtain 1.84 g of light yellow oily liquid, which was 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetyl chloride (compound I: ).
[0023] (2) Synthesis of Compound II
[0024] Dissolve 1.84 g of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetyl chloride in 10 mL of tetrahydrofuran solvent, add 0.5 g of urea, heat on a constant temperature heating magnetic stirrer, and reflux at 70 °C for 5 h to obtain a yellow-white emulsion. Distill under reduced pressure in a water bath at 40°C under a vacuum of -0.07 Mpa to remove tetrahydrofuran and obtain white crystals. Dissolve the crystals wi...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Dissolve 1.84 g of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetyl chloride in 3.5 mL of pyridine solvent, add 0.75 g of urea, heat to 90°C in a water bath under a magnetic stirrer, and reflux for 5 hours to obtain a reddish-brown sticky substance. Distill under reduced pressure in a water bath at 70°C and a vacuum of -0.07 Mpa to remove pyridine to obtain a dark red solid, which was extracted 5 times with ethyl acetate. Ethyl acetate was removed by distillation under pressure to obtain white crystals. Dissolve the crystals with 20 mL of pyridine under the system conditions of 60°C, remove incompatible impurities by hot suction filtration, carry out vacuum distillation again at 75°C in a water bath, and vacuum -0.07 Mpa to remove pyridine, and recondense in dichloromethane to obtain the target product ( Compound II) 1.07 g, the yield is 60%.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Dissolve 1.84 g of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetyl chloride in 5 mL of tetrahydrofuran solvent, add 1.5 g of urea, heat to 70 °C, stir and reflux for 5 h, and obtain a yellow-white emulsion. Distill under reduced pressure in a water bath at 40°C under a vacuum of -0.07 Mpa to remove tetrahydrofuran and obtain white crystals. Dissolve the crystals with 20 mL of pyridine under the system conditions of 60°C, remove incompatible impurities by hot suction filtration, conduct vacuum distillation again at 75°C in a water bath, and vacuum degree -0.07 Mpa to remove pyridine, recrystallize in dichloromethane, and dry to obtain The target product (compound II) was 1.25 g, and the yield was 70%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com