Traffic network flow control using dynamically modified metrics for redundancy connections
A business volume, interconnected network technology, applied in the field of data transmission between routers, which can solve problems such as complex implementation and correct configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] It should be noted that herein, any reference to "one embodiment" or "an embodiment" refers to a specific feature, structure or characteristic related to the embodiment included in at least one embodiment of the present invention. The appearances of the phrase "in one embodiment" in various places in the specification are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment.
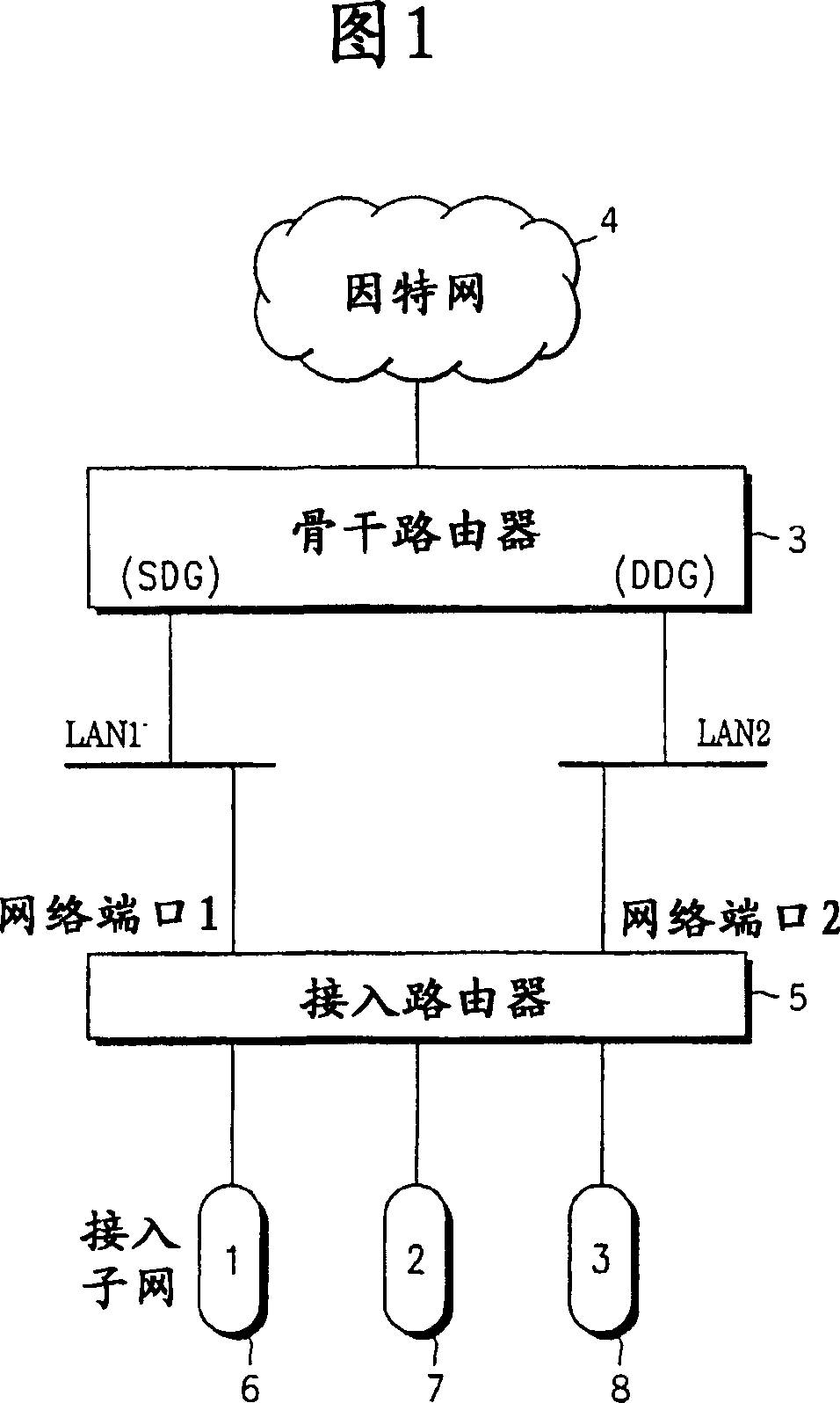
[0025] Figure 1 depicts a block diagram of a system to which various aspects of the invention are applicable. A backbone router 3 connected to the Internet 4 uses a redundant connection to an access router 5 via local area networks (LANs) LAN1 and LAN2. The access router 5 performs access for individual Internet users who have access to the Internet via, for example, cable, digital subscriber line (DSL) or a dial-up connection via a dial-up modem.
[0026] Access router 5 implements a logical IP subnet at its user access end (also referred to herein as "access subnet 6-8"). Inside the access sub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com