Inhibition by 3-deoxyflavonoids of t-lymphocyte activation and therapies related thereto
A compound, alkyl technology, applied in the field of inhibiting T lymphocyte activity and related therapy through 3-deoxyflavonoids, can solve the problem of not being a therapeutic candidate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
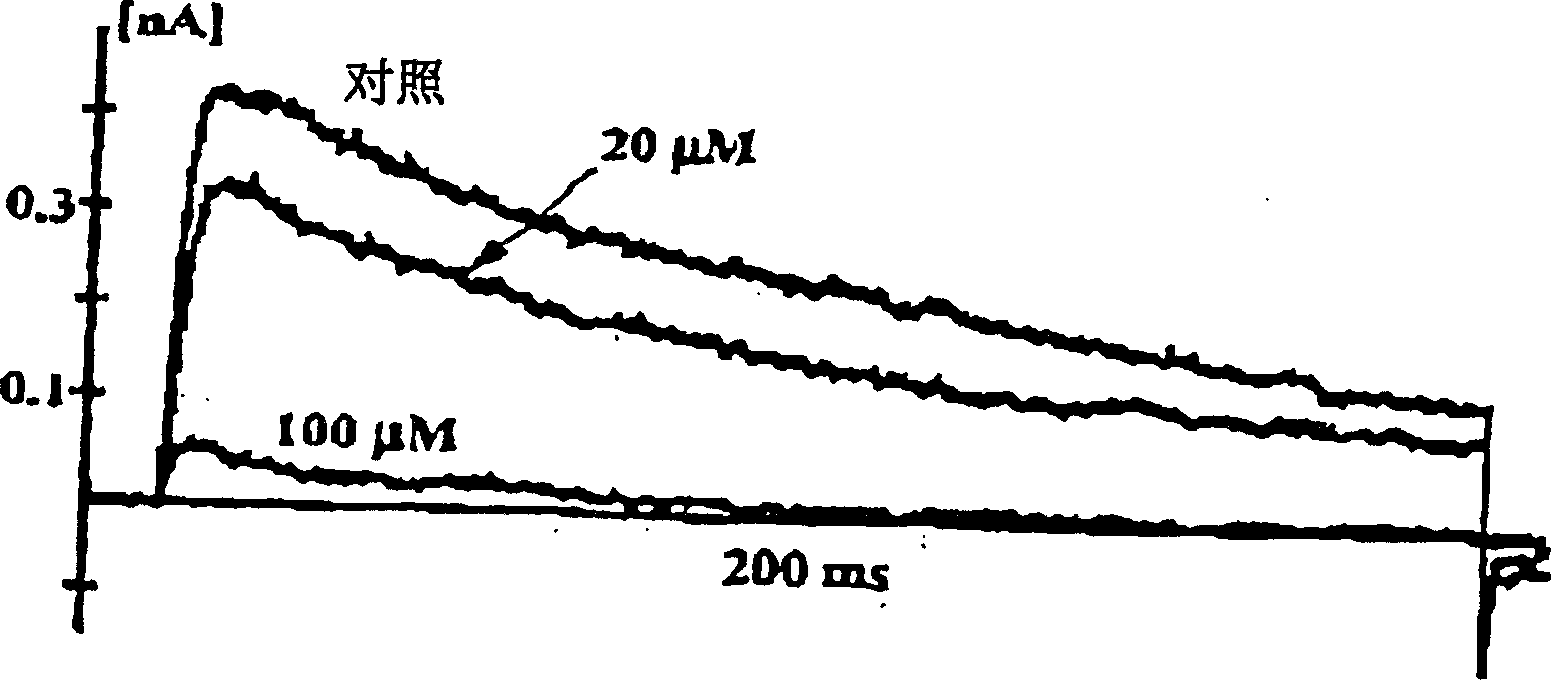
[0098] Kv1.3 channels were inhibited using the patch clamp method described by Fanger (2000) J. Biol Chem. 276:12249. It can be found from Figure 1 below that at a concentration of 20 μM, luteolin blocked about 25% of the Kv1.3 channel current, and at a concentration of 100 μM, luteolin blocked 100% of the Kv1.3 channel current. The curves are also shown in FIG. 1 . The results clearly demonstrate that luteolin and related 3-deoxyflavonoids are effective in blocking Kv1.3 channels and thus in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 The effect of 3-deoxyflavonoids on the cytotoxicity of T lymphocytes
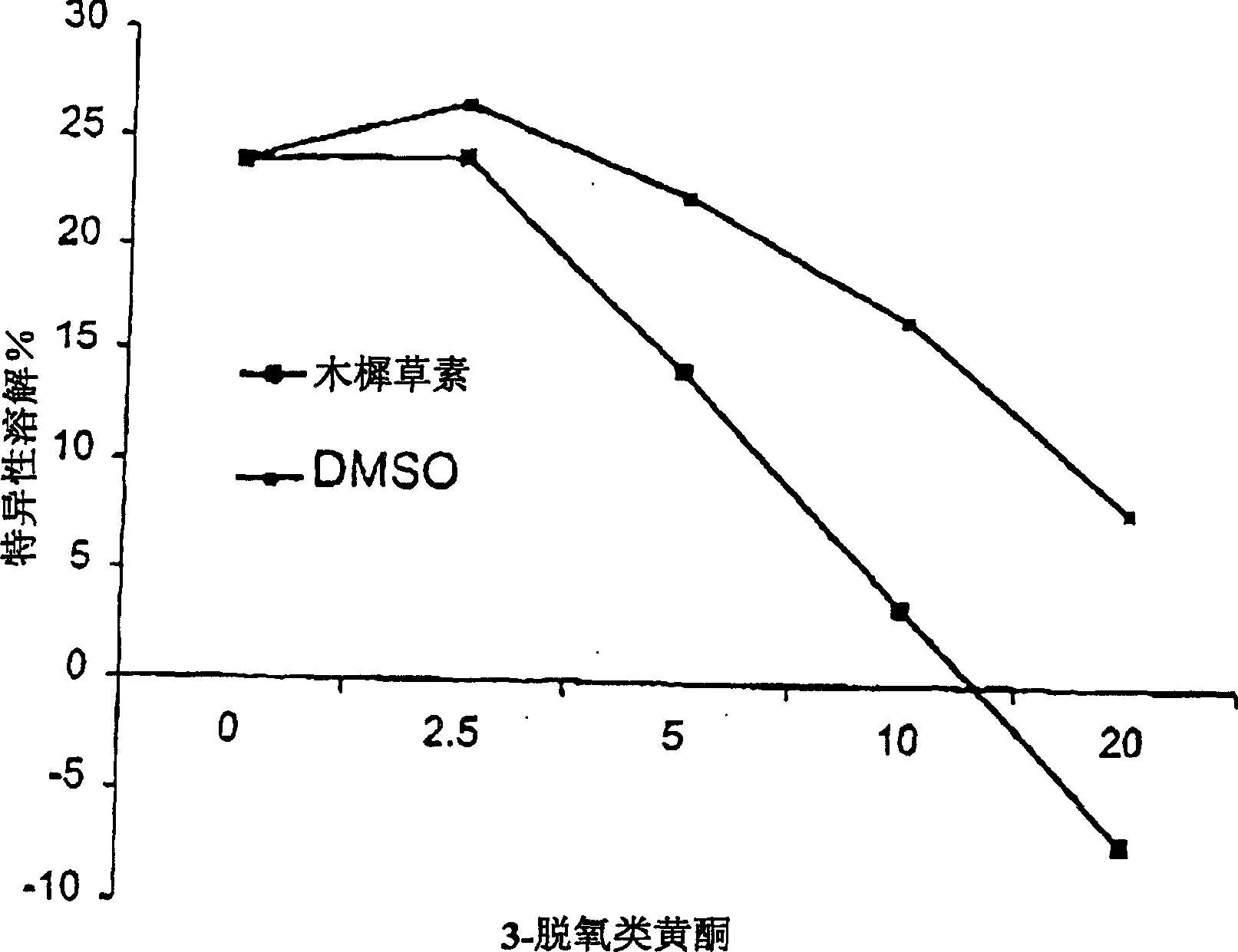
[0100] A cytotoxic T lymphocyte line (CTL-named CTL264) specific for a peptide antigen (aa 264-272, known as peptide 264) derived from the tumor suppressor protein p53 was used as a target to test luteolin whether it has any effect on CTL cytotoxicity of 264 peptide-pulsed T2 target cells. T2 target cells were pulsed with 264 peptide for 2 hours, labeled with Calceln-AM, and washed three times after 30 minutes. The mixture of T2 cells and CTL264 was incubated for 4 hours. 100 [mu]l of the supernatant was transferred to a 96-well flat bottom microtiter plate and the fluorescence (538 nm) was read to measure calcein released due to cell lysis. We unexpectedly found that luteolin significantly inhibited CTL cytotoxicity against 264-pulsed T2 target cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2).
Embodiment 3
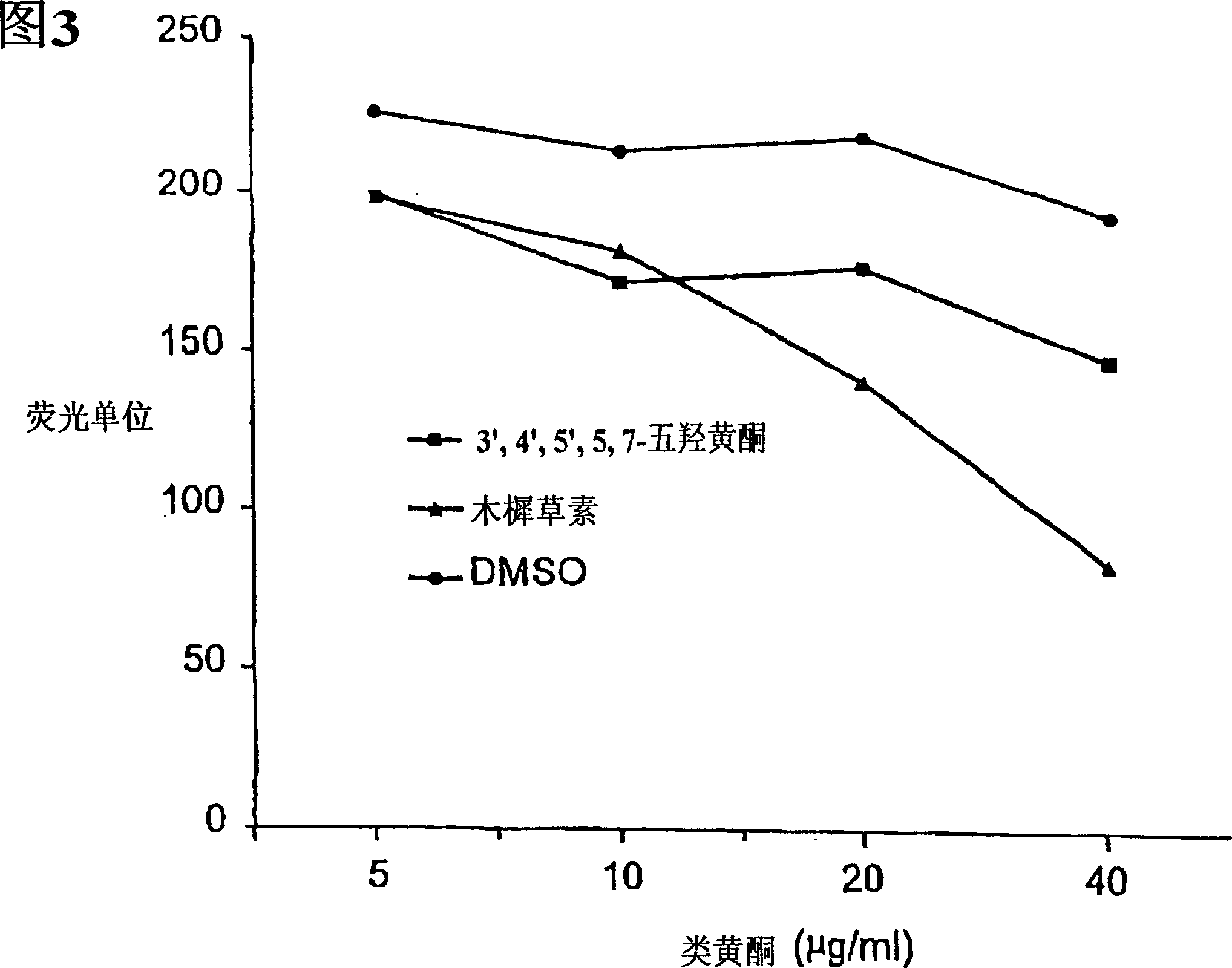
[0102]In cytotoxic T lymphocytes, spontaneous calcein release was determined by incubation of target cells in RPMI-10. Maximum calcein release was determined by incubation of target cells in Triton X-100. Data are recorded as the average of three determinations. Figure 3 shows inhibition of calcein release by 3-deoxyflavonoids luteolin and 3',4',5',5,7-quercetin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com