Quasi dynamic route optimization method of vehicle-mounted guiding system for evading delaying risk
An in-vehicle navigation and risk aversion technology, applied in directions such as road network navigators, can solve the problems of deviation, blocked travel time, low-cost transmission of real-time information acquisition, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency, improving search efficiency, and reducing search time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
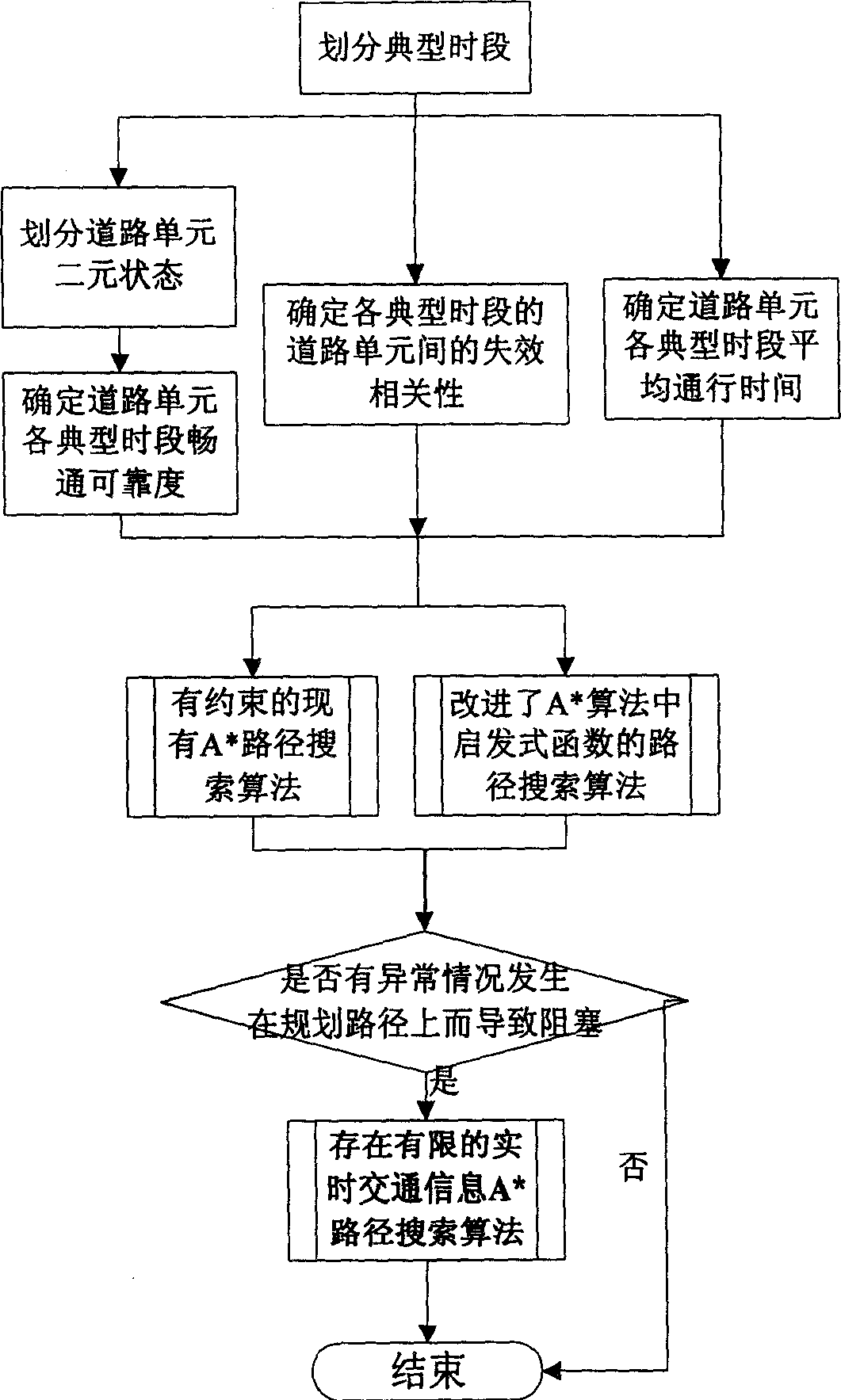
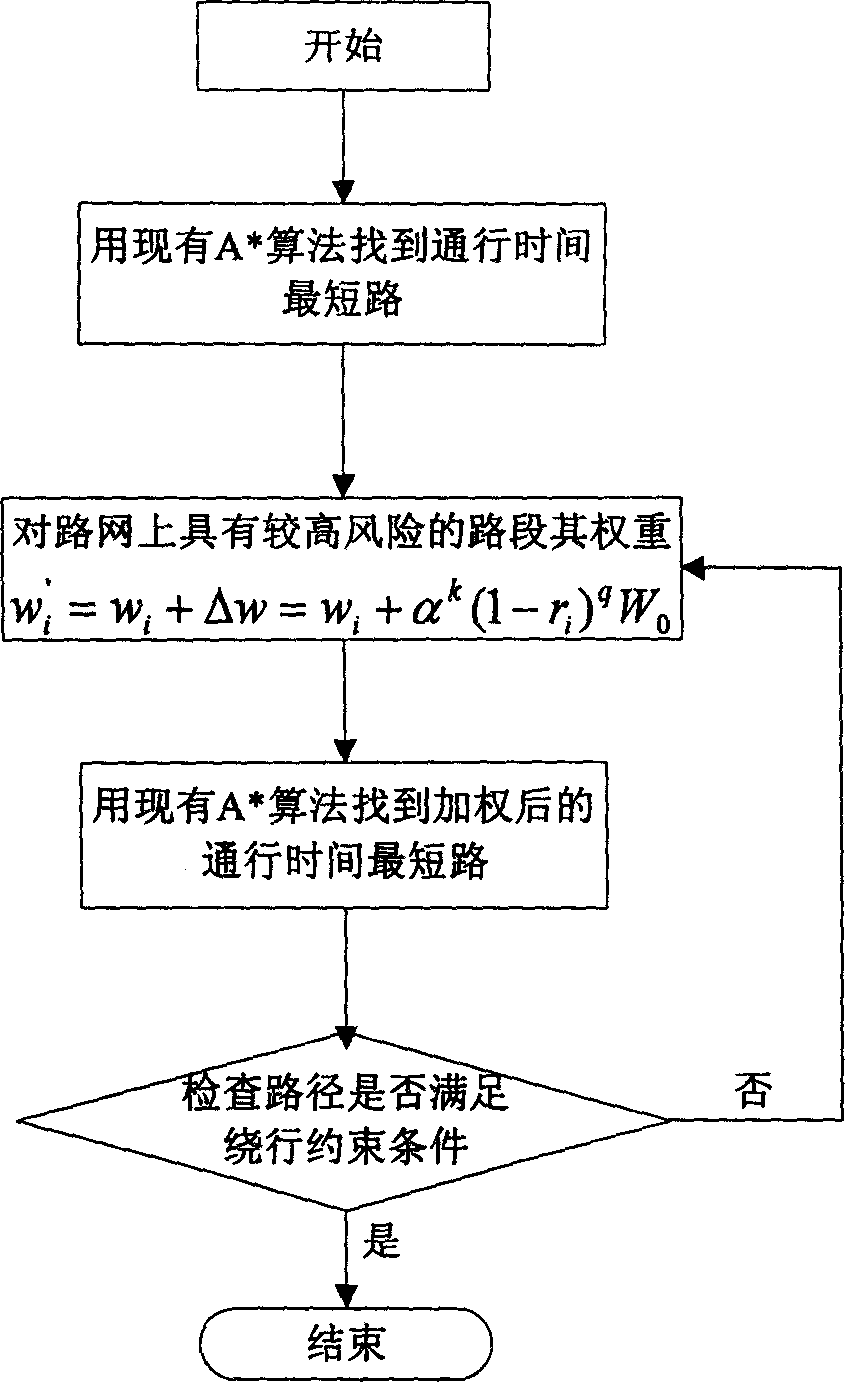
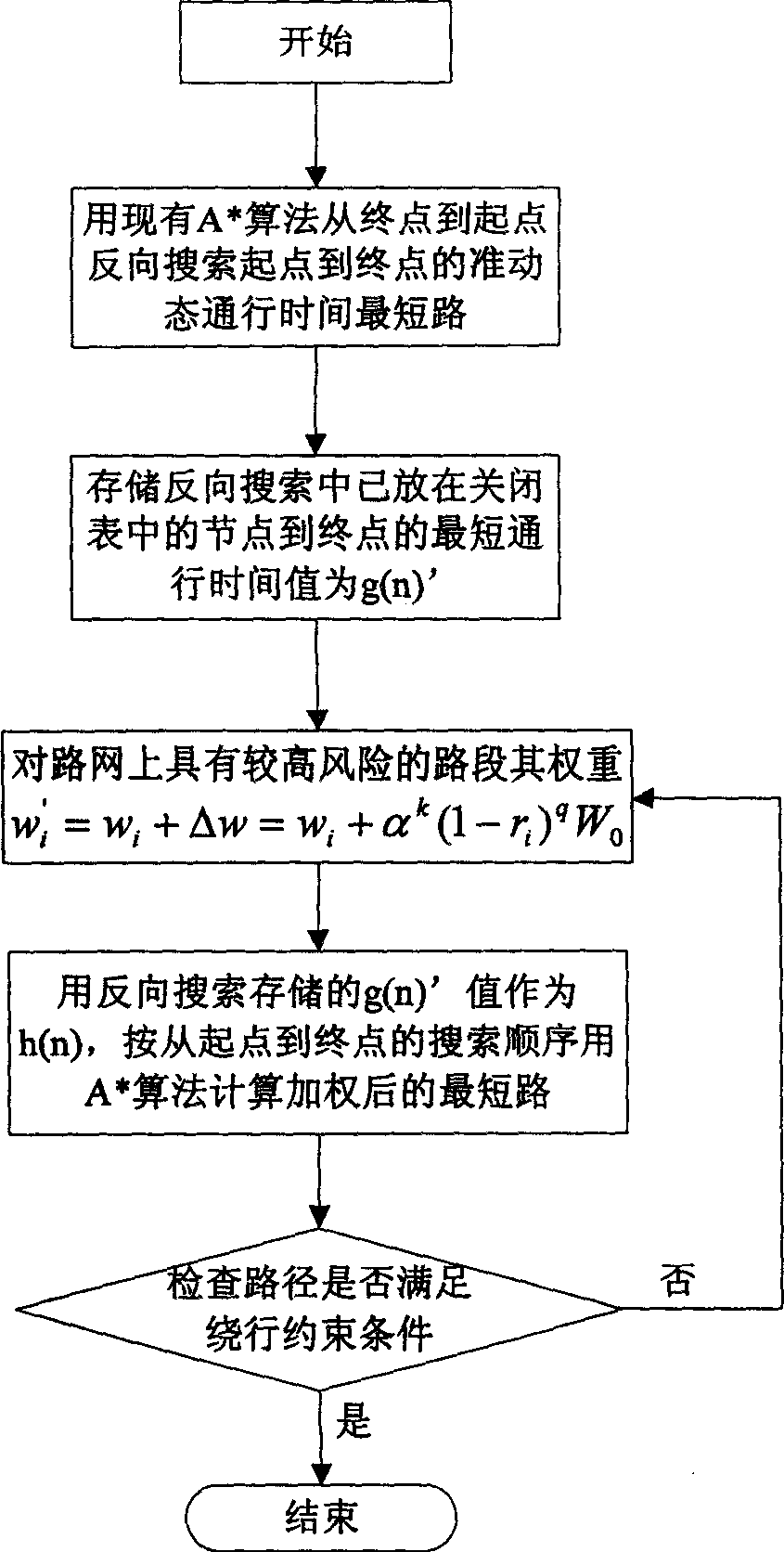
[0109] We built a virtual road network with a computer, and randomly assigned the average passing time and unimpeded reliability of road units to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the algorithm. The algorithm is tested under different random networks and conditions. First, a small network with 36 nodes and 60 road units is searched for a reliable route with detour constraints at the starting point of travel under three conditions. The experimental results can show the rationality of the invention, and the experimental results using a large road network with 2800 nodes show the search efficiency of the invention.
[0110] small network attached Figure 5 As shown, the nodes are represented by circles, the node numbers are marked in the circles, and the road units are represented by thin gray lines. The average speed (km / h) and reliability under normal conditions are marked next to the relevant road cell. The normal average speed is between 30-60, and the reliability...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com