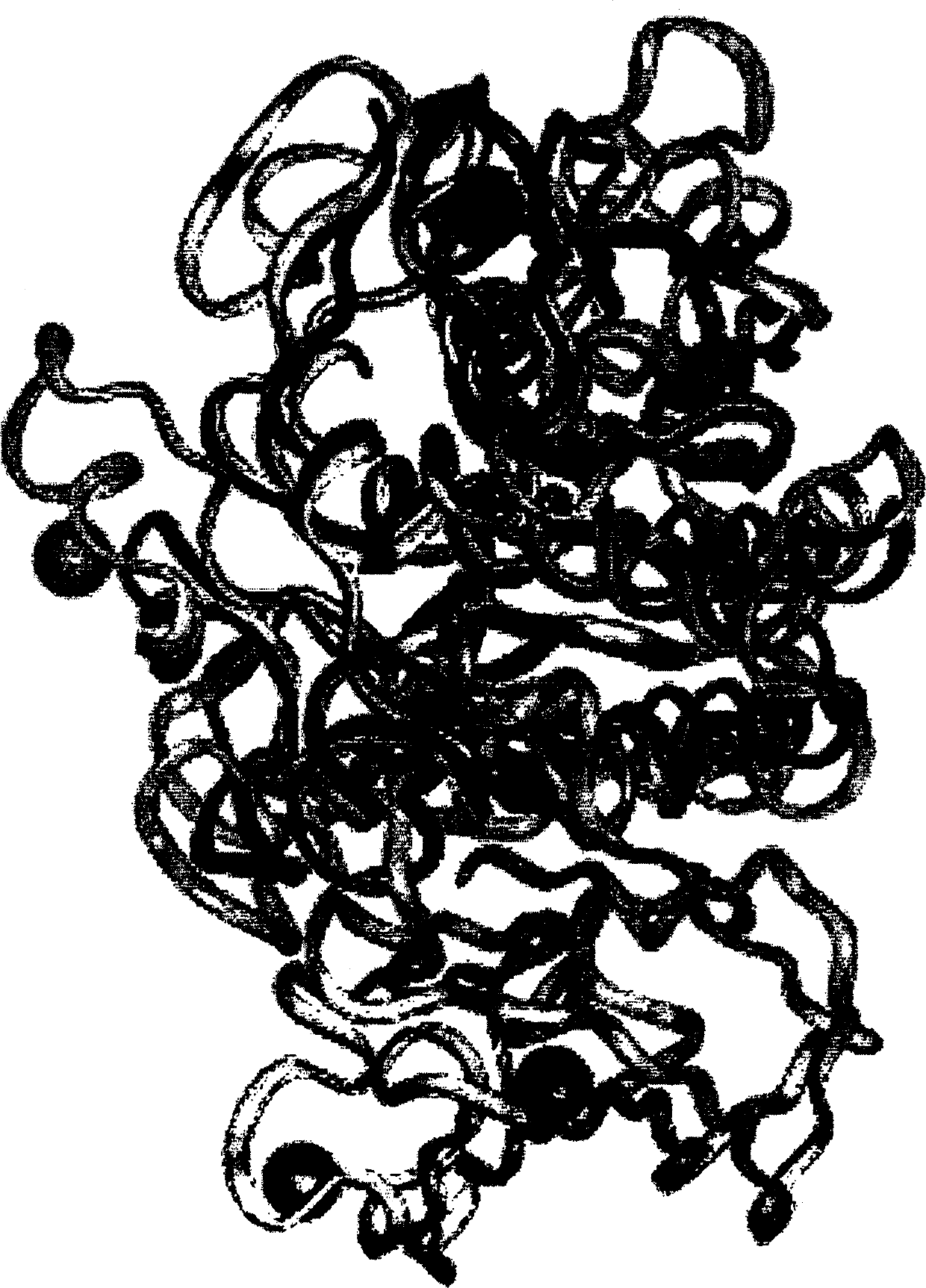
Subtilases
A technology of subtilase and JP170, which is applied in the field of modifying subtilase using protein modeling based on the three-dimensional structure of JP170, can solve the problem that the three-dimensional structure of subtilase is not disclosed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0517] Removal of ion-binding sites in BPN'-like subtilases
[0518] The regions in JP170 and TY145 mentioned below have been chosen to transfer from JP170 and TY145 into Savinse. The Savinase region (BPN' numbering) was deleted and the JP170 and TY145 regions were inserted instead by using the molecular method for making subtilase variants described herein. Since the region of Savinase is in contact with the ion binding site, the purpose of this modification is to remove the ion binding site from Savinase.
[0519] Savinase region A194-L196
[0520] JP170 Areas P209-P217 and
[0521] Savinase region L75-L82
[0522] TY145 area H83-Y92,
[0523] Or the modifier can be
[0524] Savinase region A194-L196
[0525] JP170 Areas P209-P217 and
[0526] Savinase region L75-L82
[0527] JP170 Area N79-K83,
[0528] Construction and expression of enzyme variants
[0529] Site-directed mutagenesis:
[0530] Site-directed variants of the JP170 subtilases of the invention contai...
Embodiment 2
[0539] Purification and assessment of enzyme concentration
[0540] Subtilisin variants were purified after fermentation using Hydrophobic Charge Induction Chromatography (HCIC) followed by vacuum filtration. To trap enzymes, HCIC uses a cellulose matrix bound with 4-mercapto-ethyl-pyridine (4-MEP).
[0541] Cellulose matrix beads, 80-100 μm in size, were mixed with medium containing yeast extract and transformed B. _ Incubate in microplates at pH 9.5.
[0542] Since 4-MEP is hydrophobic at pH > 7 and the subtilisin variants are hydrophobic at pH 9.5, there is a hydrophobic interaction between the secreted enzyme and 4-MEP on the beads. After incubation, media and cell debris are removed by vacuum filtration while beads and enzymes sit on the filter.
[0543] To elute the enzyme from the beads, the pH was lowered by washing the filter with elution buffer (pH 5). The enzyme is thus separated from the beads and can be recovered from the buffer.
[0544] Concentrations of pu...
Embodiment 3
[0548] Automated Mechanical Stress Assay (AMSA)
[0549] AMSA determination method description:
[0550] To assess the wash performance of selected JP170 subtilase variants in detergent compositions, wash experiments were carried out. The subtilases of the present application were tested using the Automated Mechanical Stress Assay (AMSA). The wash performance of a large number of small volume enzyme detergent solutions can be examined using the AMSA assay. The AMSA plate has a number of wells for the test solution and a lid that squeezes the fabric swatches tightly to wash in the wells. During washing, the plate, test solution, fabric and cover are shaken vigorously to bring the test solution into contact with the fabric and to apply mechanical stress in a regular periodic oscillation. For further description see WO 02 / 42740, especially the paragraph "Specific method embodiments" on pages 23-24.
[0551] commercially available detergent
Base
Europea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com