Measuring apparatus
A kind of measuring equipment and equipment technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, and material analysis using microwave means, which can solve problems such as instability, increased manufacturing costs of polishing pads, and inability to reach semiconductor wafers, etc., to achieve Effect of manufacturing cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
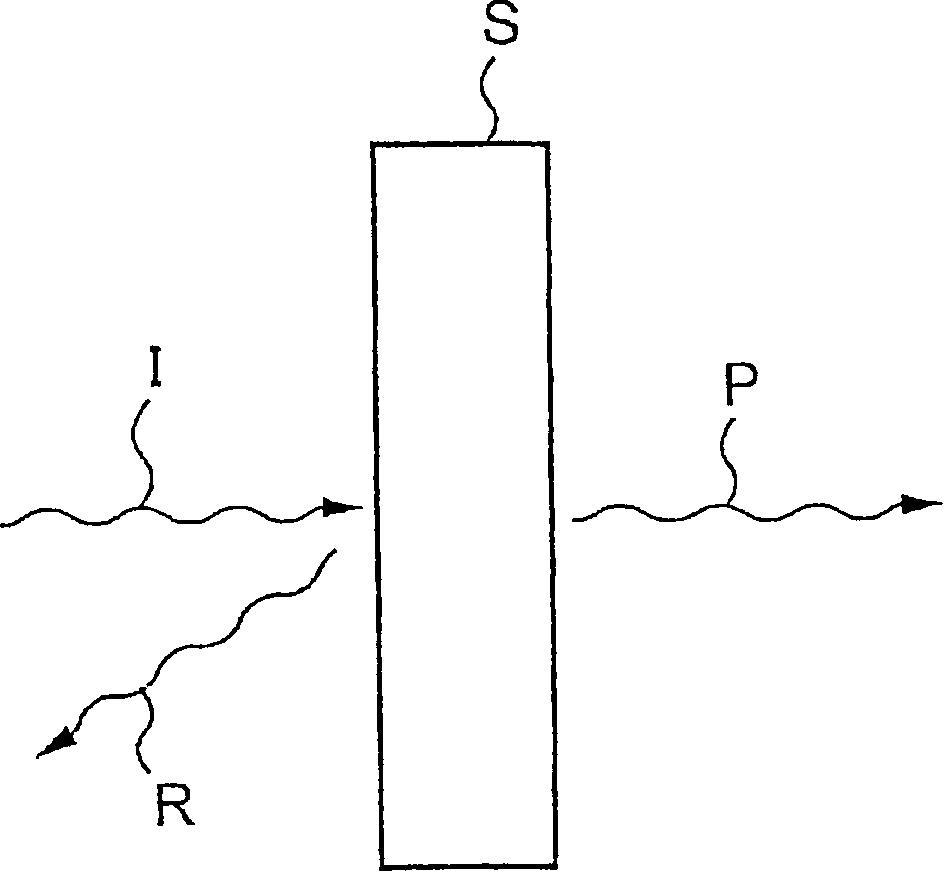
[0041] A measuring device according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Figure 1A is a schematic diagram showing the principle of the measuring device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 1A As shown, when microwaves (incident waves) are transmitted to the object S to be measured, the microwaves are reflected by the object S. Microwaves reflected from the object S (hereinafter referred to as reflected waves R) have amplitudes and phases that vary with the structure and physical properties of the object S such as thickness and the like. Therefore, the structure of the object S can be analyzed by detecting at least one of the amplitude and the phase of the reflected wave R. The structure of an object includes object thickness, internal defects such as voids formed in the object, permittivity, electrical conductivity, and magnetic permeability.
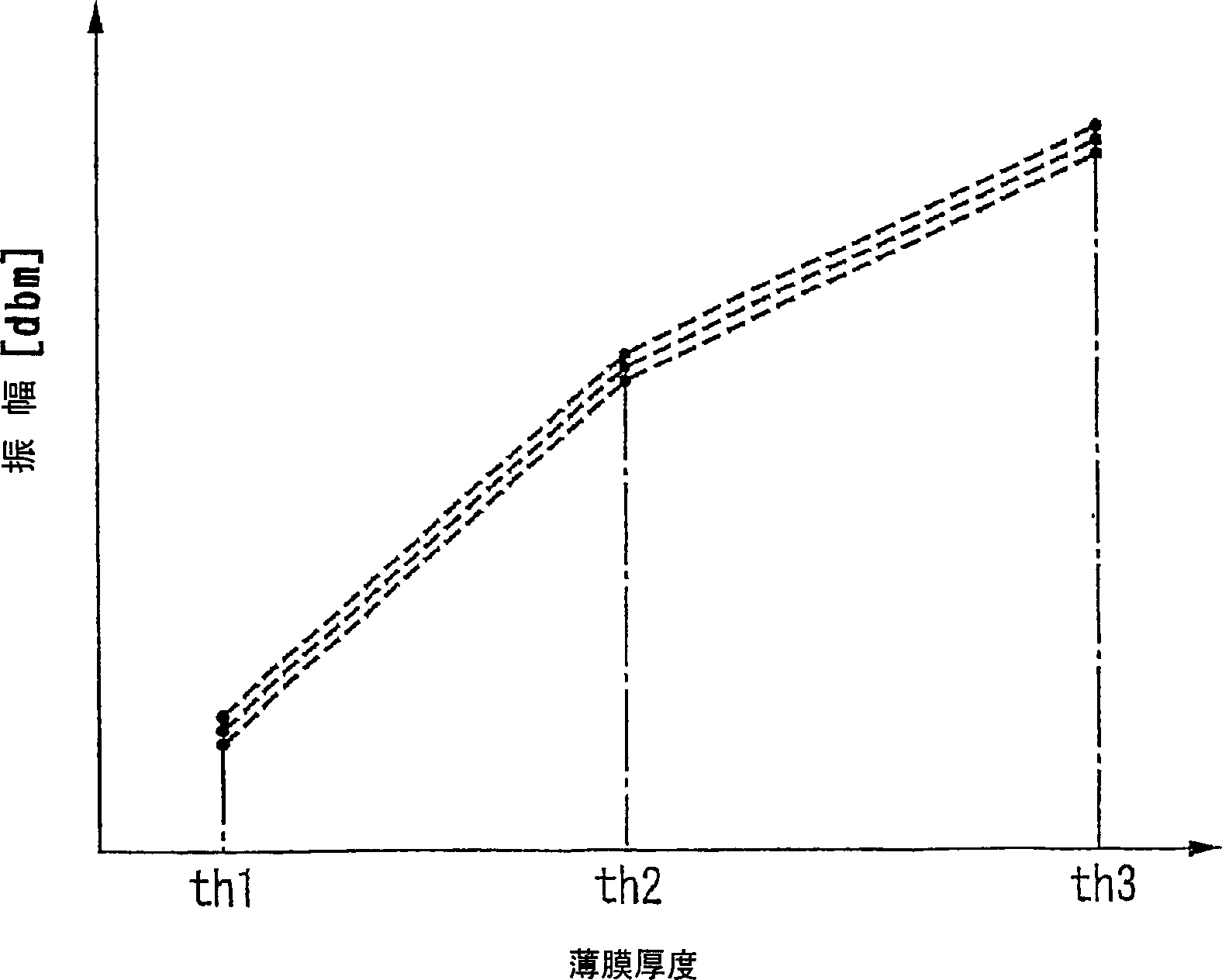
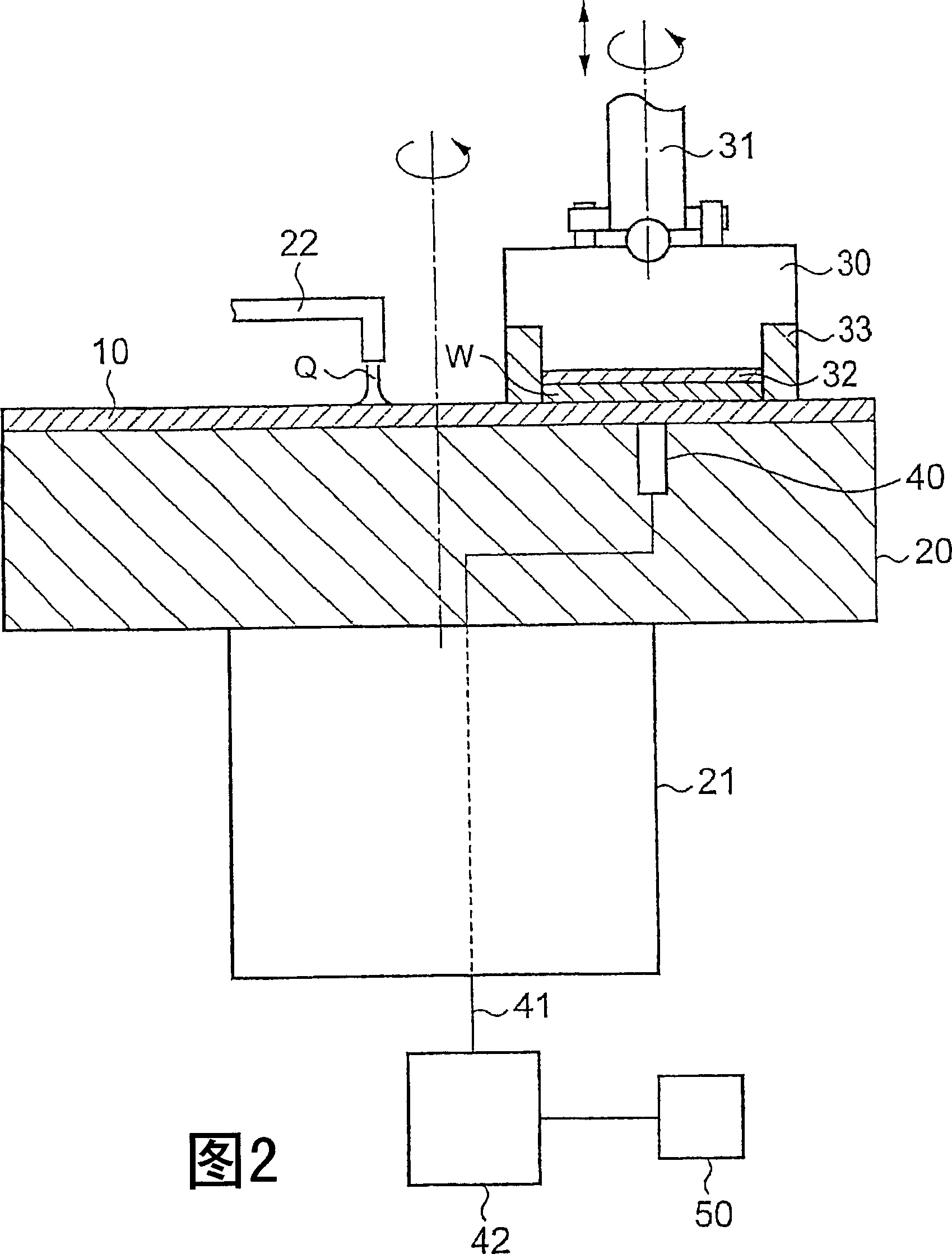
[0042] For example,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com