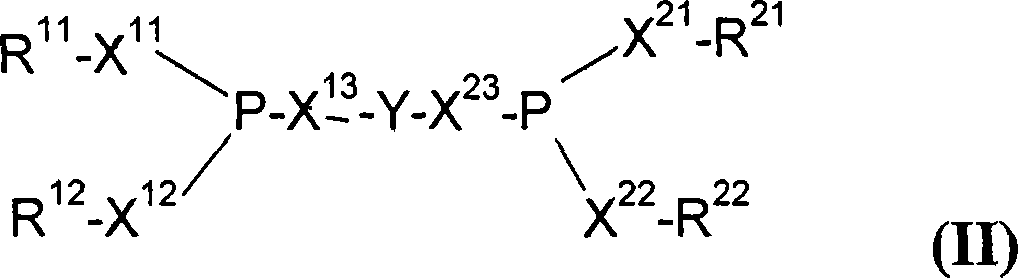Separation of nickel(0) complexes and phosphorus-containing ligands from nitrile mixtures
A technology of phosphorus ligands and complexes, applied in the purification/separation/stabilization of organic compounds, purification/separation of carboxylic acid nitriles, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc., can solve poor selection Sexuality related, short life of catalyst system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0155] In a glass flask, a 5-gram mixture of ADN, 3PN and tricresyl phosphite (TTP) as a ligand was prepared in a protective gas atmosphere (argon) (refer to the attached table for the composition), and then 5 grams of cyclohexane was added . Stir at the indicated temperature to combine the ingredients. After switching off the stirring unit, the phase separation was observed visually during the continuous heating. The system was rated as not separating into separate phases when two separate phases could not be visually discerned after 5 minutes. The results are listed in Table 1.
[0156] ADN
Embodiment II
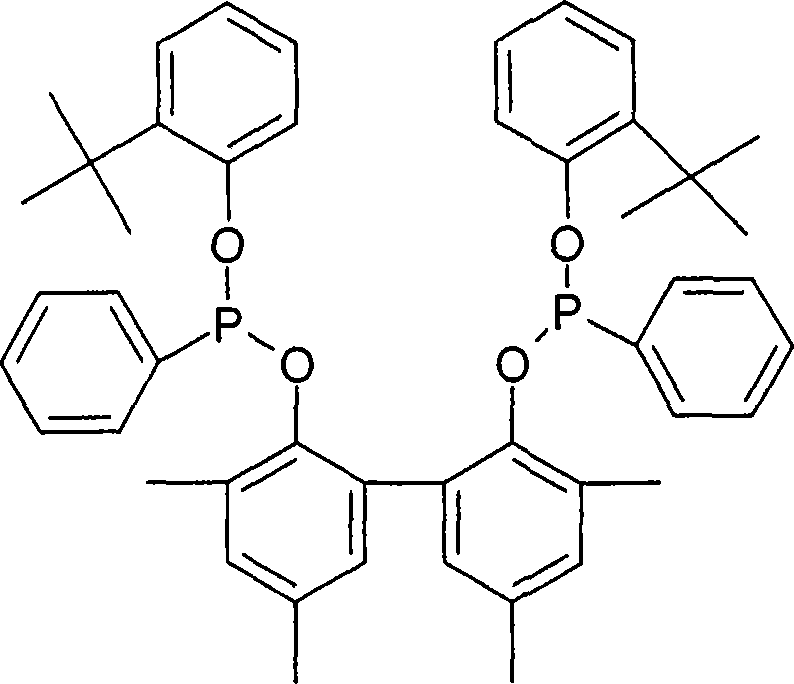
[0158] The steps are equivalent to those in Example 1, except that the chelating ligand of formula A is used instead of tricresyl phosphite. The results are listed in Table 2.
[0159] Formula A:
[0160]
[0161] ADN
Embodiment III
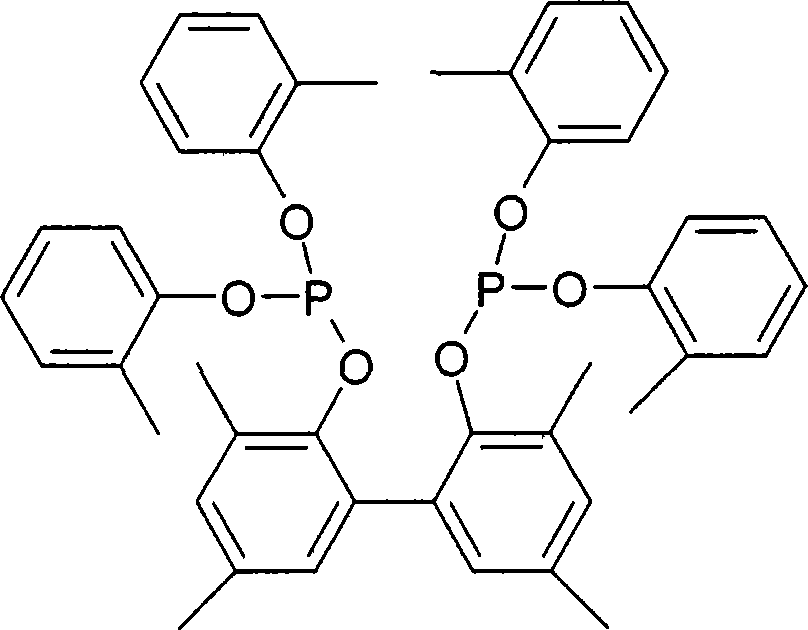
[0163] The steps are equivalent to those in Example I, except that the chelating ligand of formula B is used instead of tricresyl phosphite. The results are listed in Table 3.
[0164] ADN
Ligand
Formula B
3PN
phase separation
20°C
phase separation
40℃
phase separation
60℃
20%
10%
70%
no
no
no
30%
10%
60%
yes
yes
no
30%
20%
50%
yes
yes
no
60%
20%
20%
yes
yes
yes
[0165] Formula B:
[0166]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com