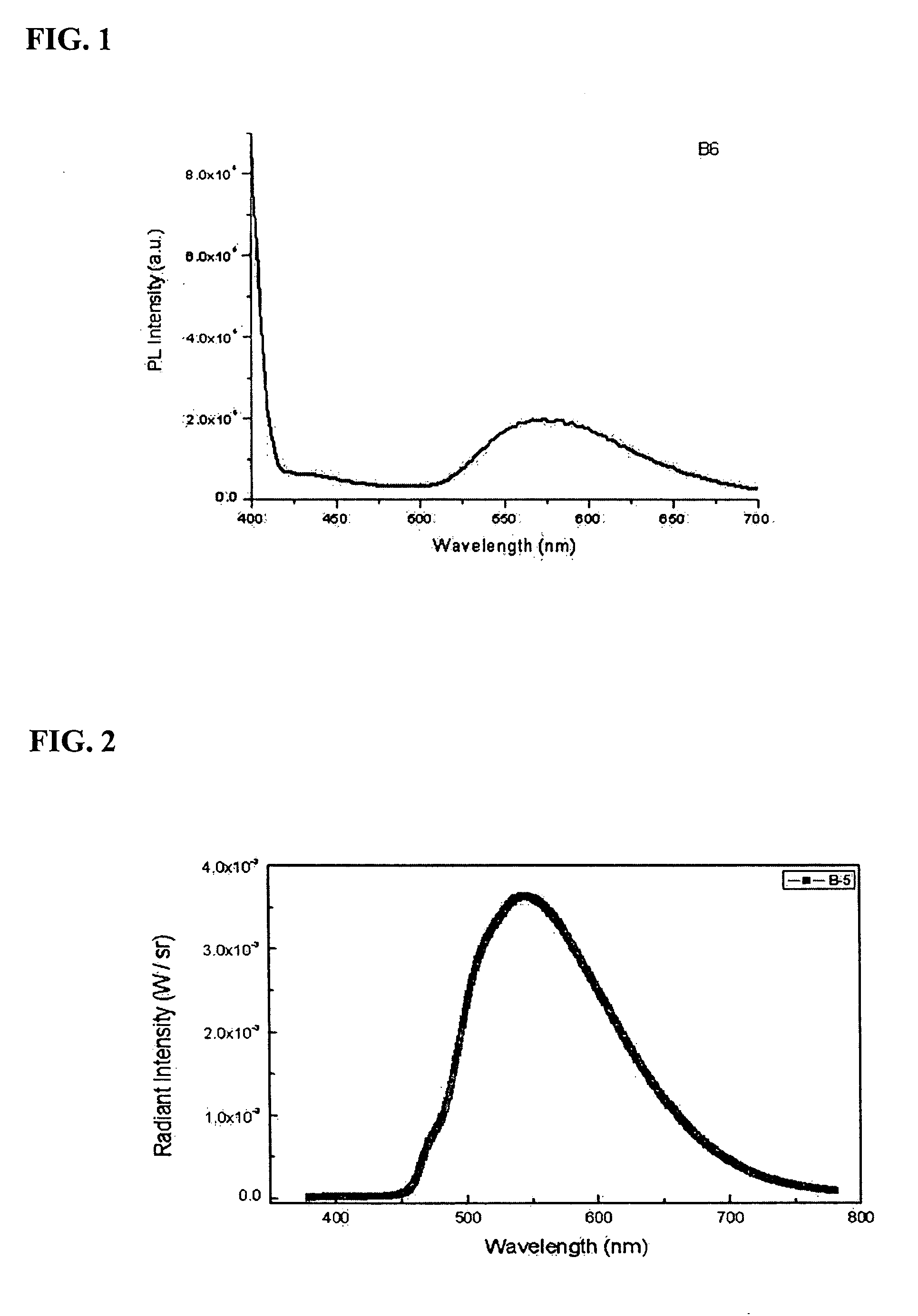
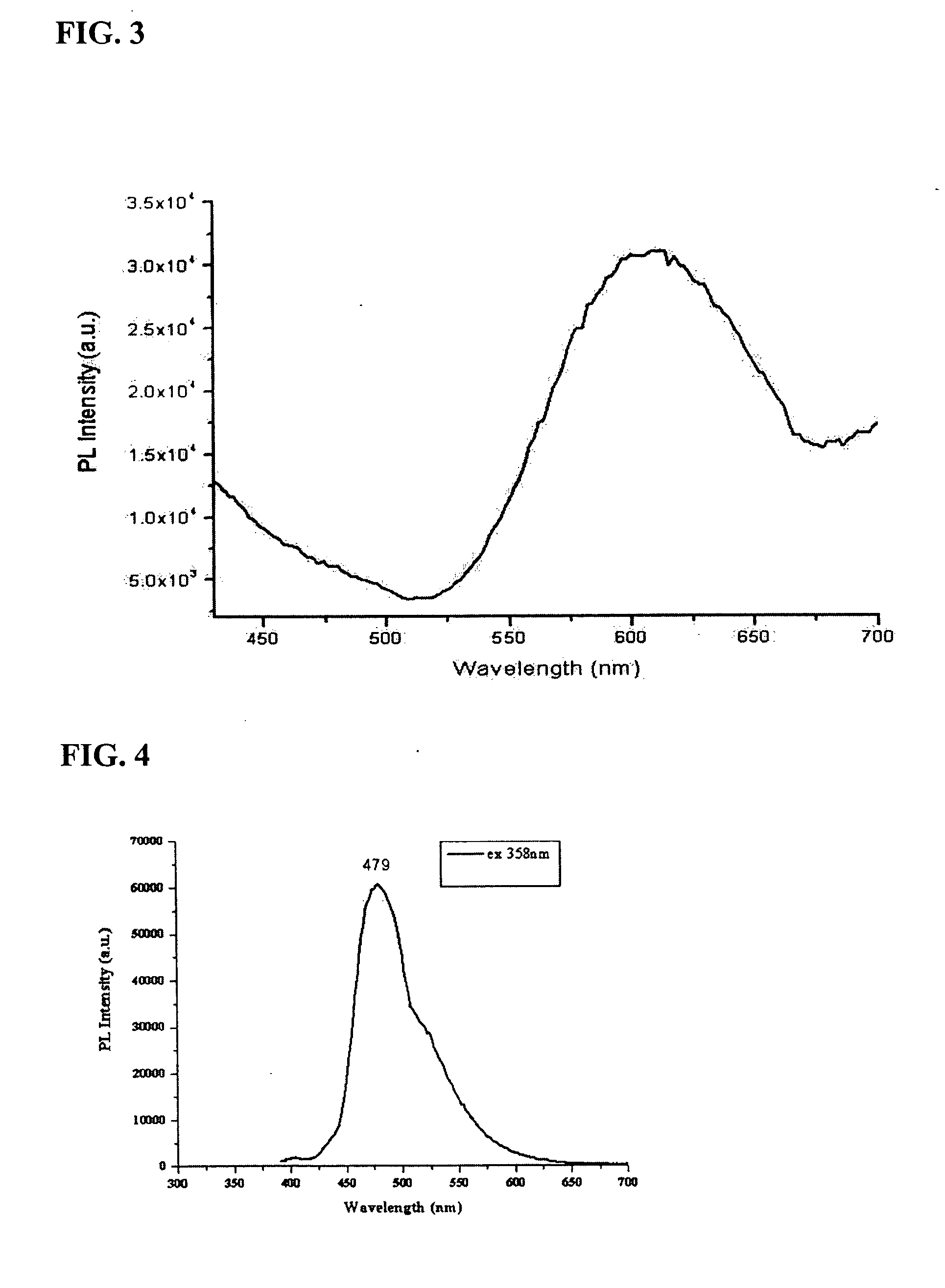
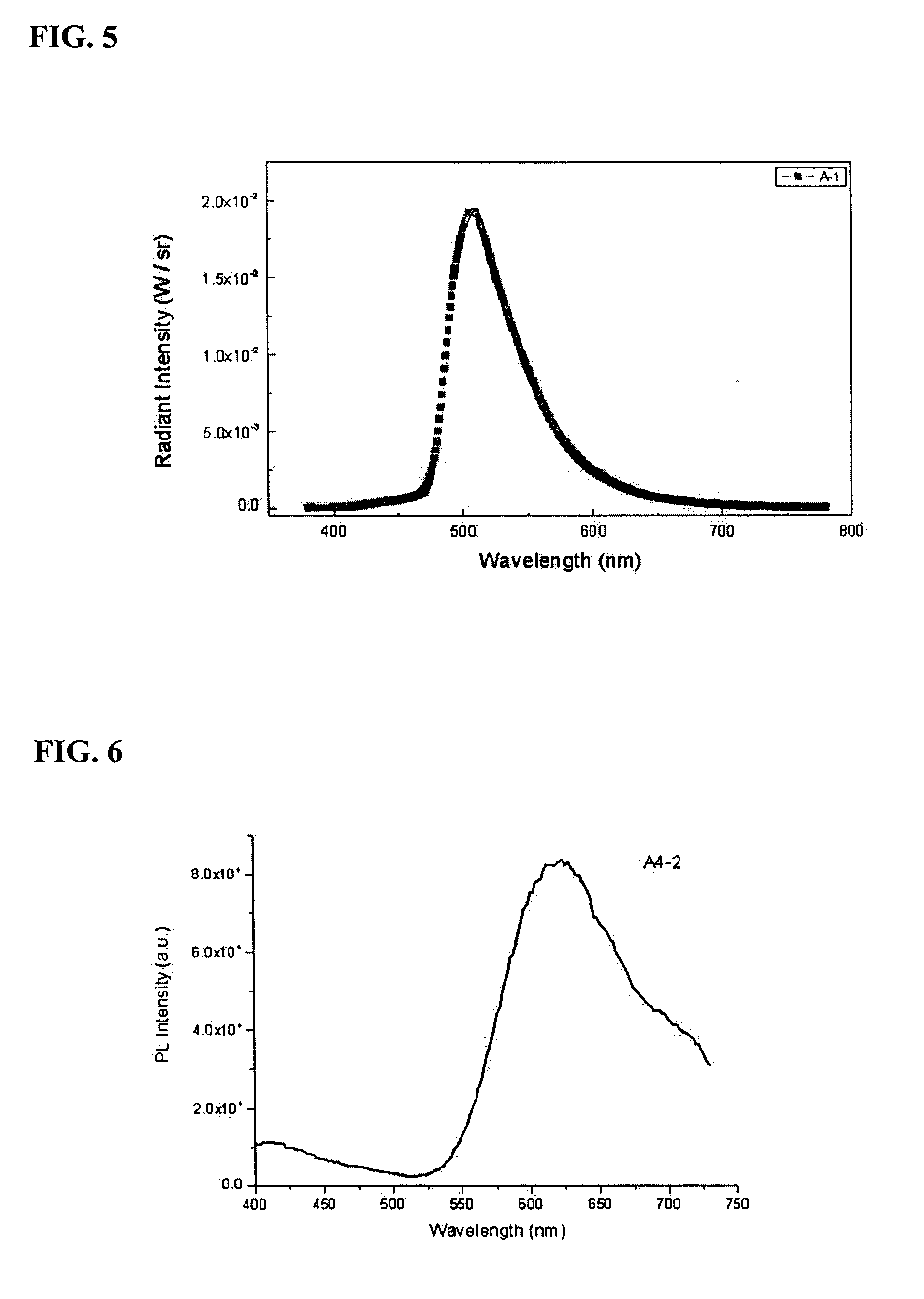
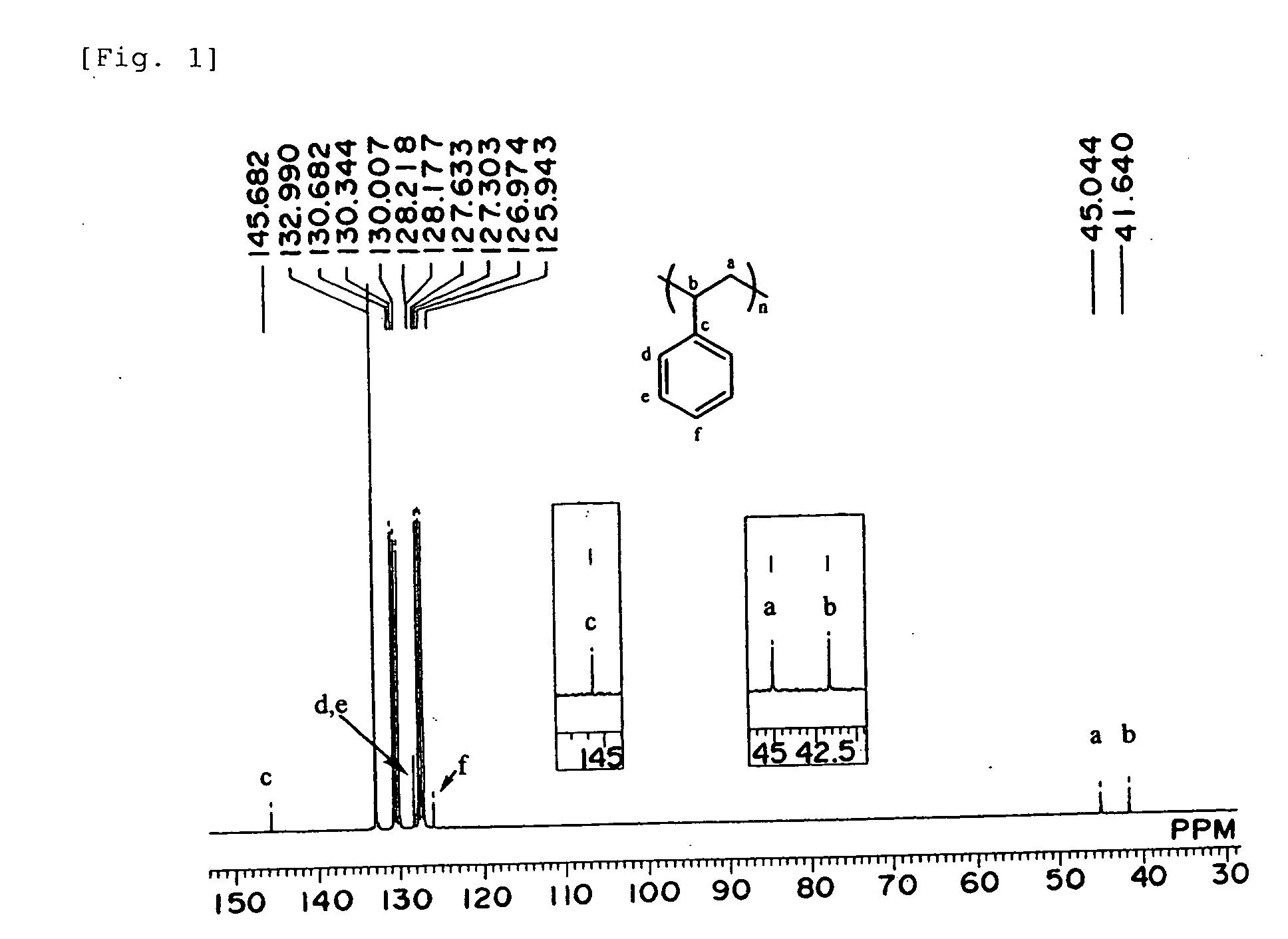
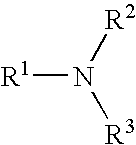Patents
Literature
467 results about "Ate complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
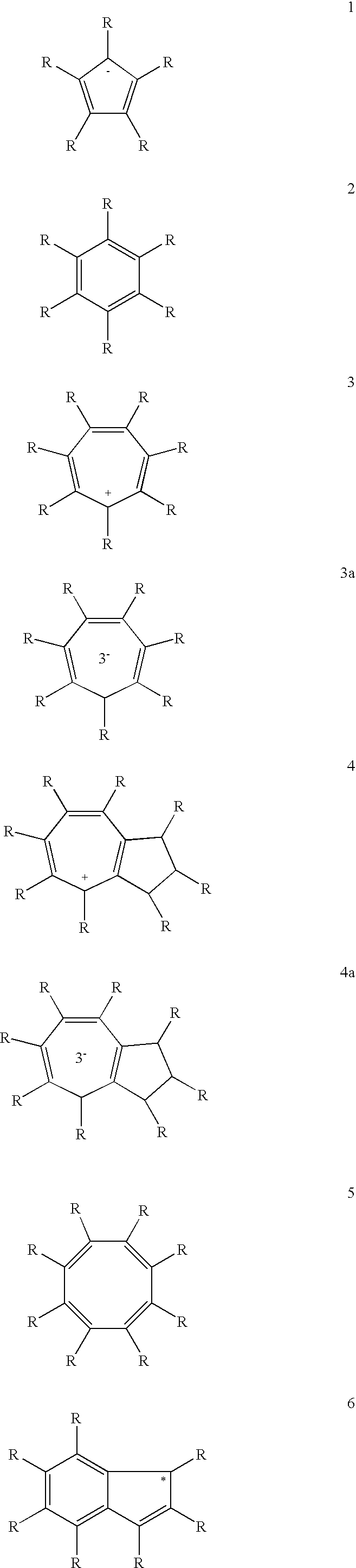
An ate complex in chemistry is a salt formed by the reaction of a Lewis acid with a Lewis base whereby the central atom (from the Lewis acid) increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge. (Note that in this definition the meaning of valence is equivalent to coordination number). Often in chemical nomenclature the phrase ate is suffixed to the element in question. For example, the ate complex of a boron compound is called a borate. Thus trimethylborane and methyllithium react to form the ate compound Me₄B⁻Li⁺, lithium tetramethylborate(1-). This concept was introduced by Georg Wittig in 1958. Ate complexes are common for metals, including the transition metals (groups 3-11), as well as the metallic or semi-metallic elements of group 2, 12, 13. They are also well-established for third-period or heavier elements of groups 14-18 in their higher oxidation states.
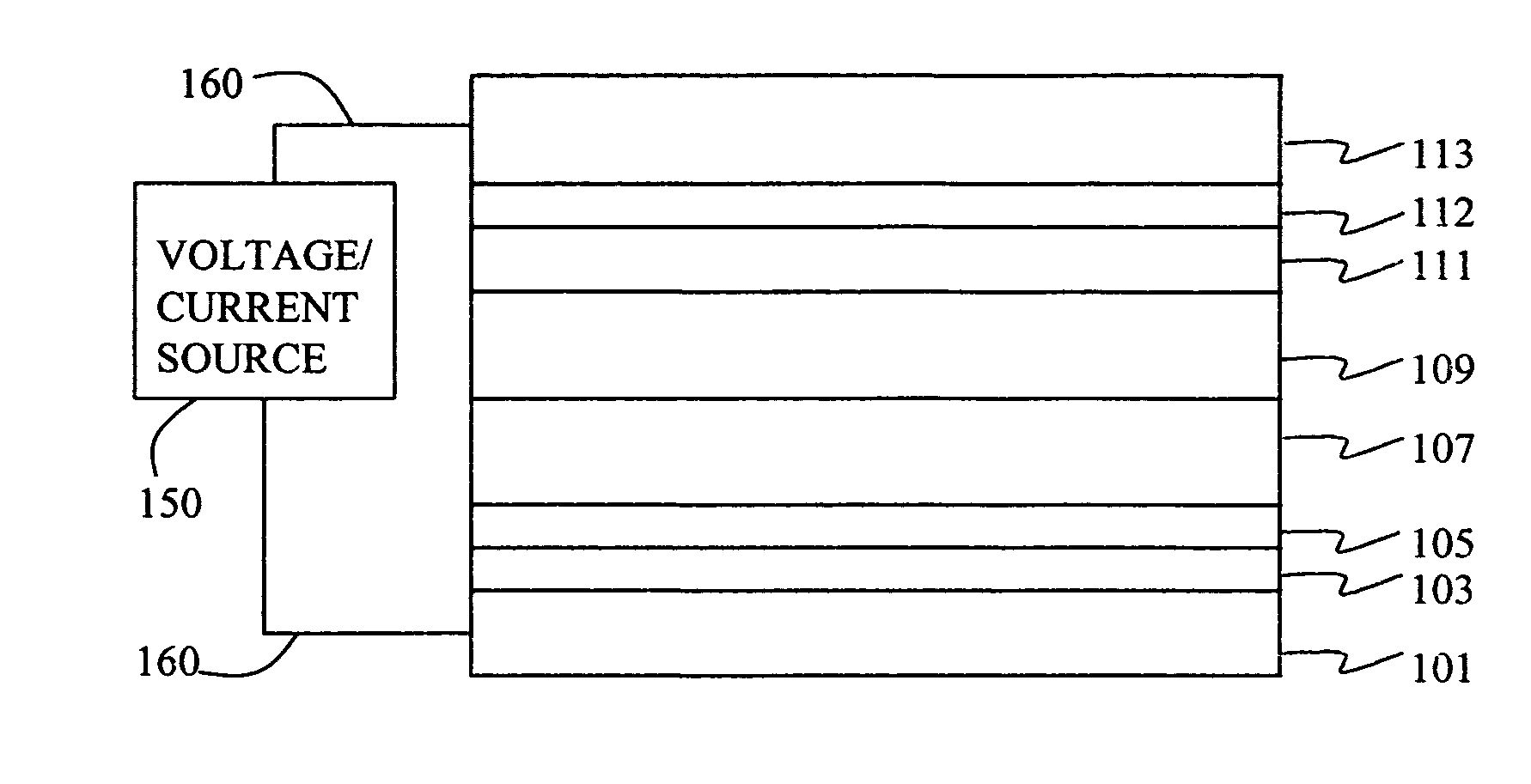
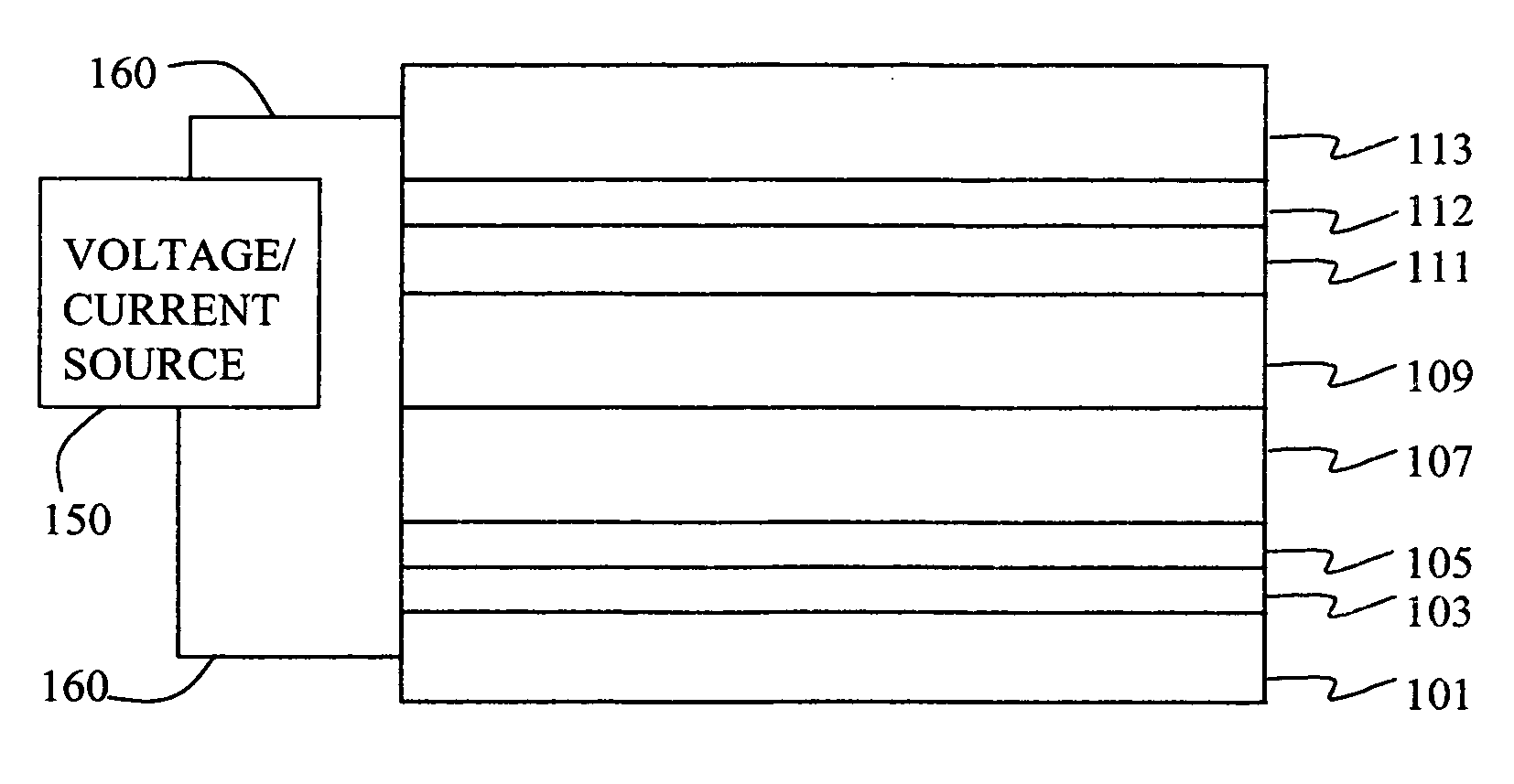
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092753A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsAnthraceneHydrogen
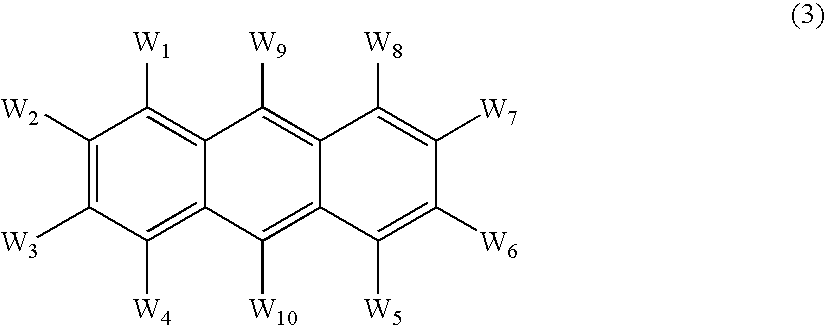
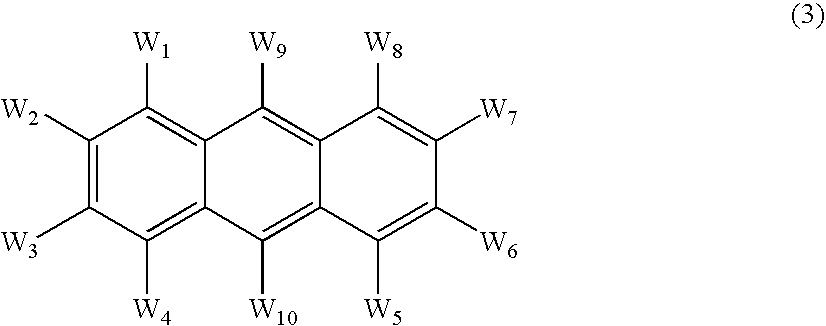
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, wherein (i) the light-emitting layer comprises up to 10 volume % of a light emitting compound and at least one anthracene host compound of Formula (3): wherein W1-W10 independently represents hydrogen or an independently selected substituent, and (ii) a further layer located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, contains (a) 10-volume % or more of an anthracene compound of Formula (3) and (b) at least one salt or complex of an element selected from Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB of the Periodic Table. Such devices exhibit reduced drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092755A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsHydrogenLow voltage
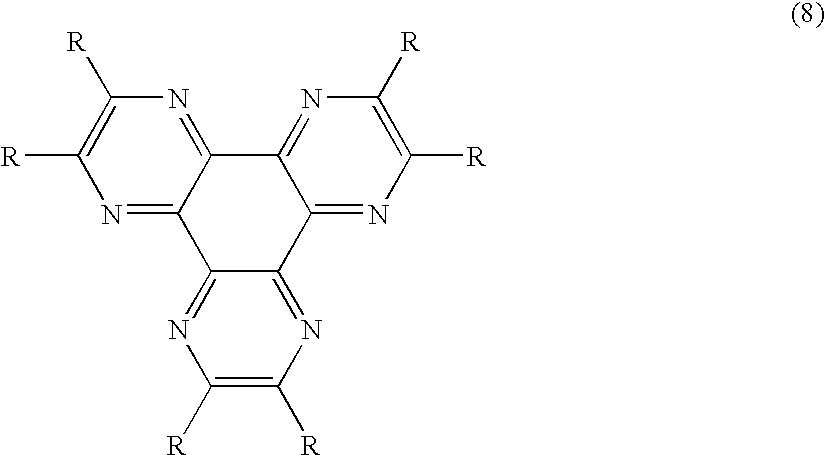
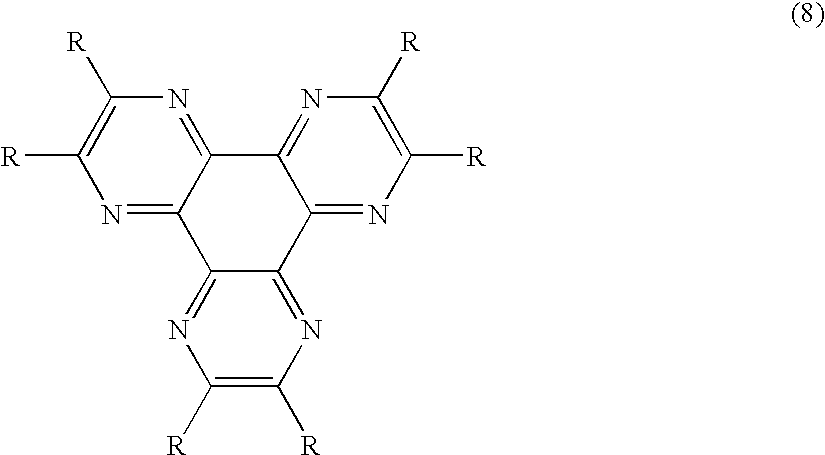
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, and comprises; (i) a further layer located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, containing (a) 10 vol % or more of a carbocyclic fused ring aromatic compound, and (b) at least one salt or complex of a Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB element of the Periodic Table, and (ii) an additional layer, located between the anode and the light emitting layer, containing a compound of Formula (8) wherein: each R independently represents hydrogen or an independently selected substituent, at least one R representing an electron-withdrawing substituent having a Hammett's sigma para value of at least 0.3. Such devices exhibit reduce drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic electroluminescent display element, finder screen display device, finder and optical device
InactiveUS6468676B1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesNitrosoAlkaline earth metal
An organic electroluminescent display element has at least a positive electrode, an organic luminescent film, an electron injection layer and a negative electrode. Each of the positive and negative electrodes is formed of a transparent conductive film, the electron injection layer is formed of a thin transparent film made of a halogenide of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal, or an organic metal complex containing an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal as a metal, and the organic metal complex is at least one complex selected from the group consisting of acetylacetonate complexes, alpha-nitroso-beta-naphthol complexes, salicylaldoxime complexes, cupferron complexes, benzoinoxime complexes, bipyridine complexes, phenanthroline complexes, crown complexes, proline complexes and benzoylacetone complexes.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
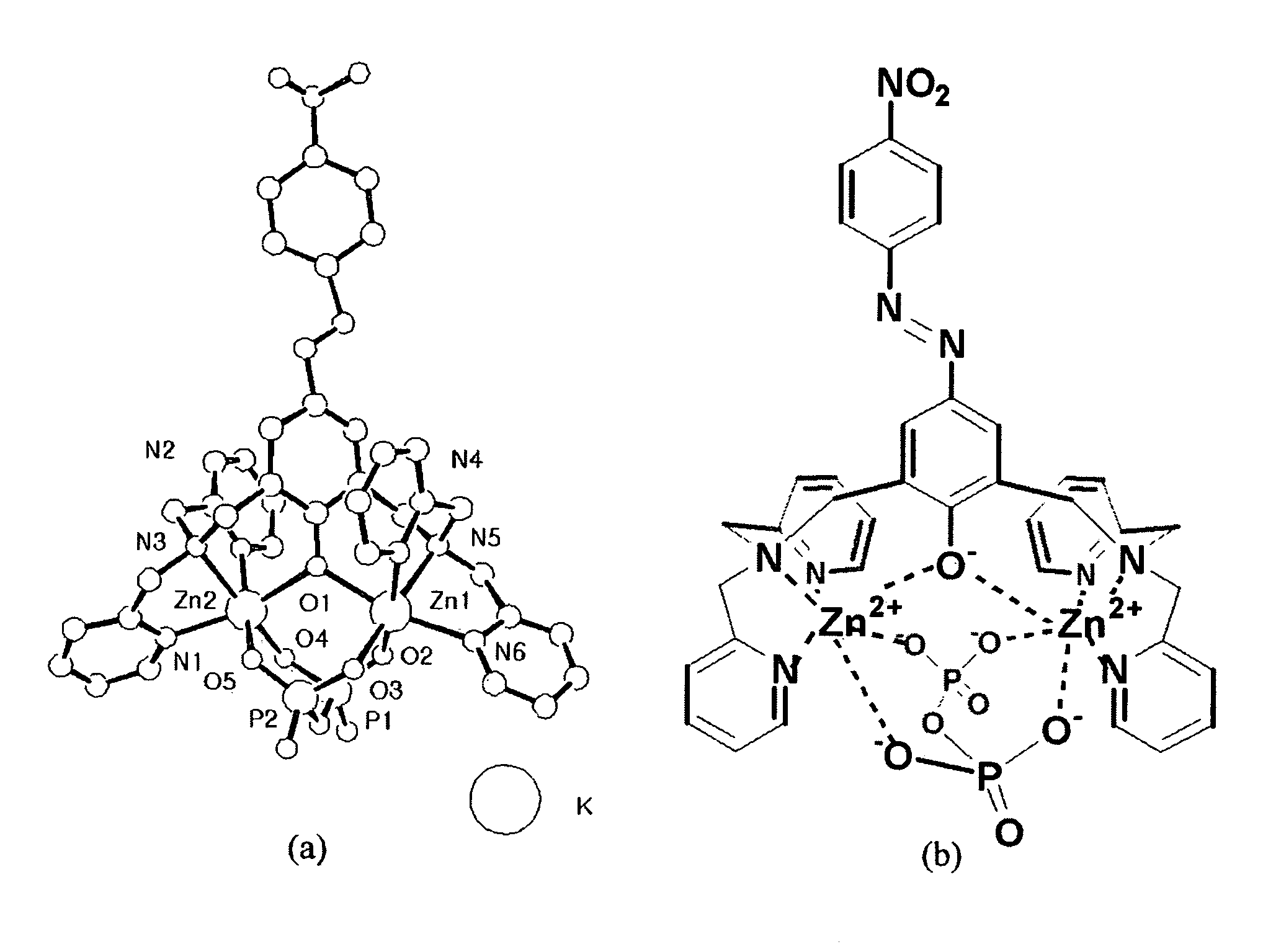
Novel dinuclear metal complex and pyrophosphate assay using the same
InactiveUS20050119497A1Increase electron densityEnhanced electron donationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsElectronic densityPyrophosphate
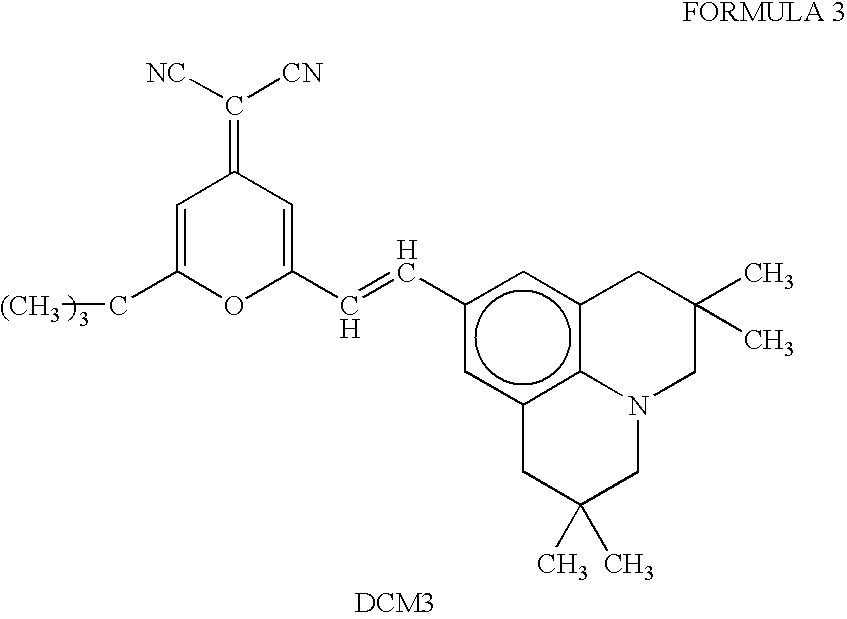
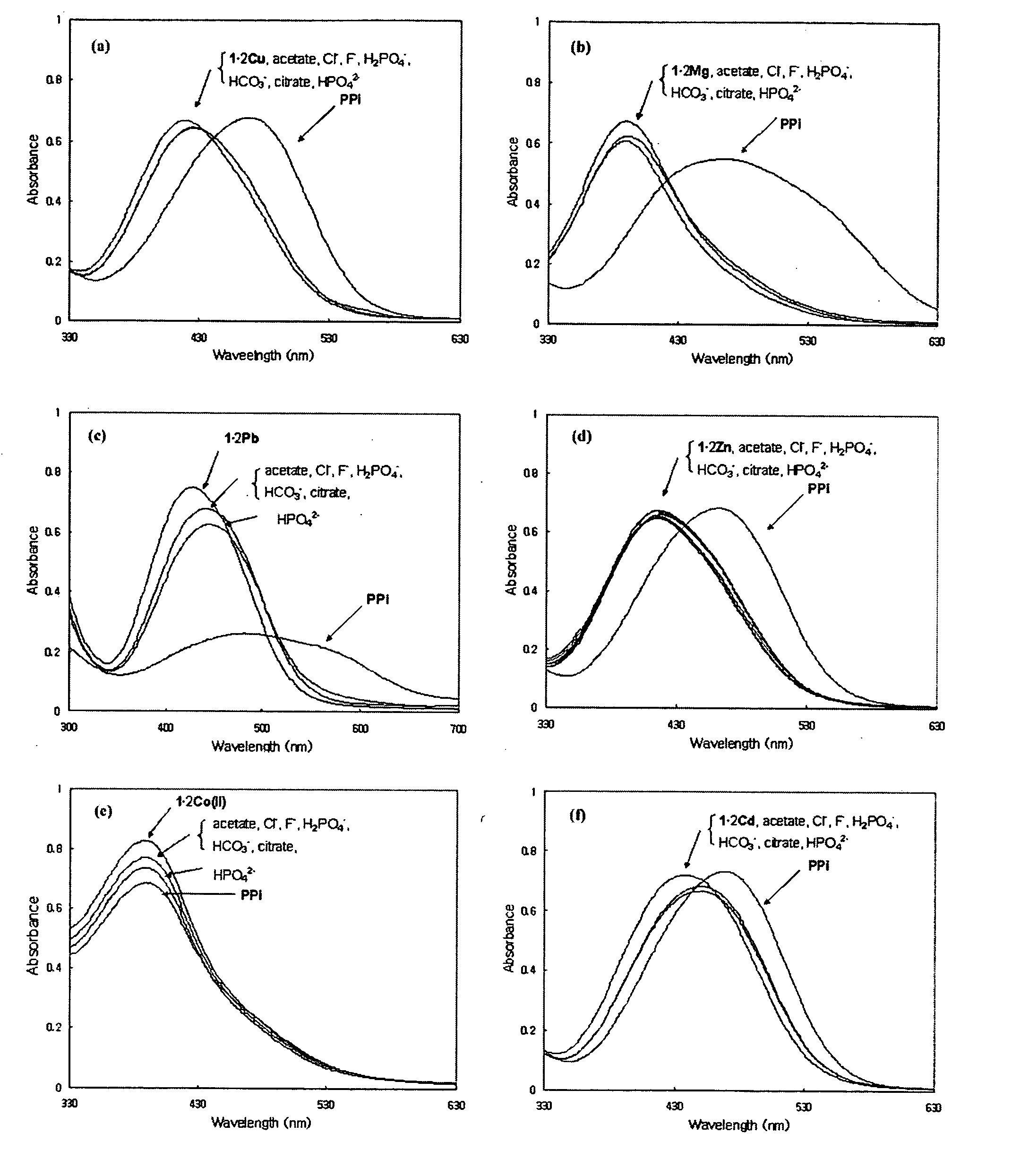
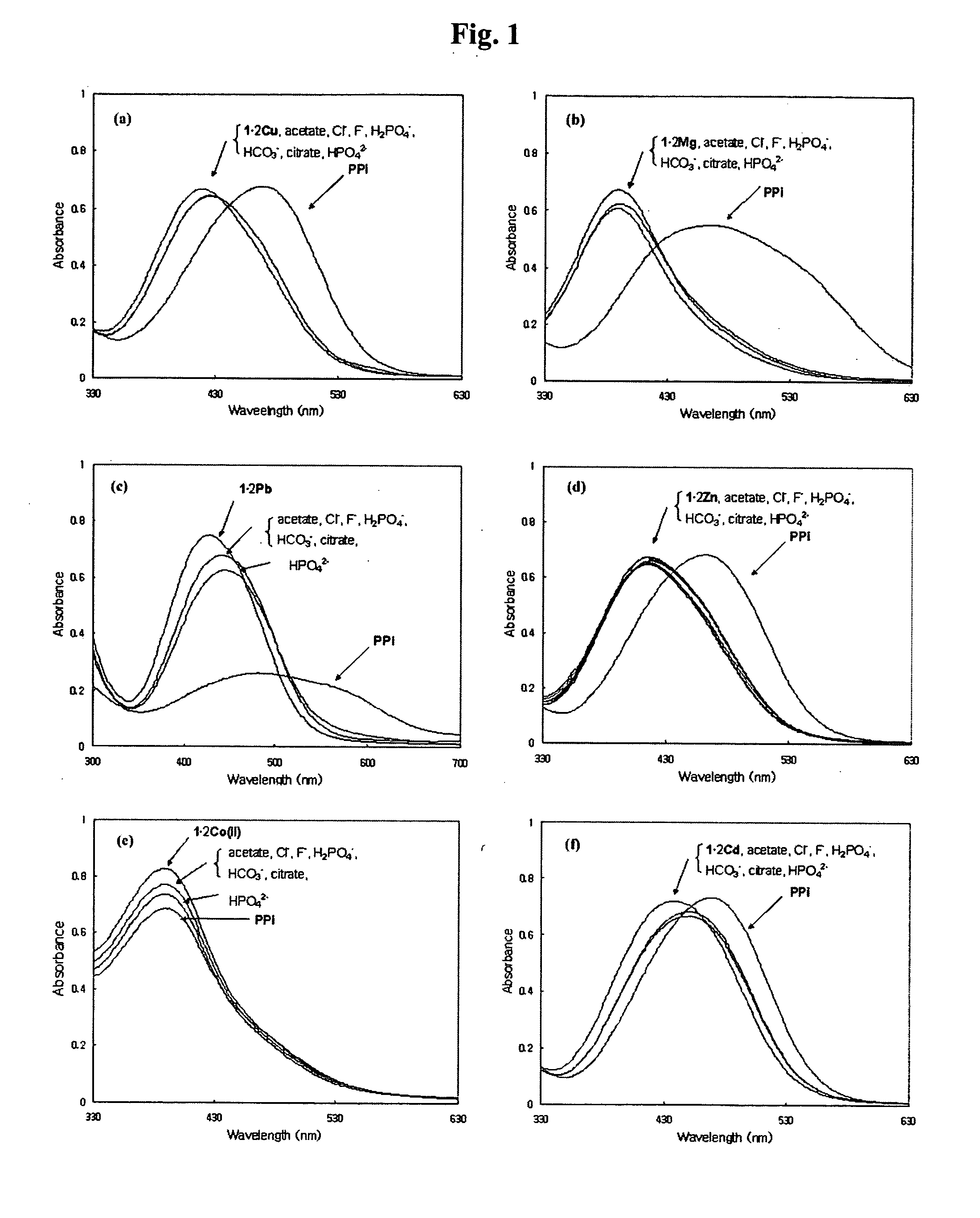
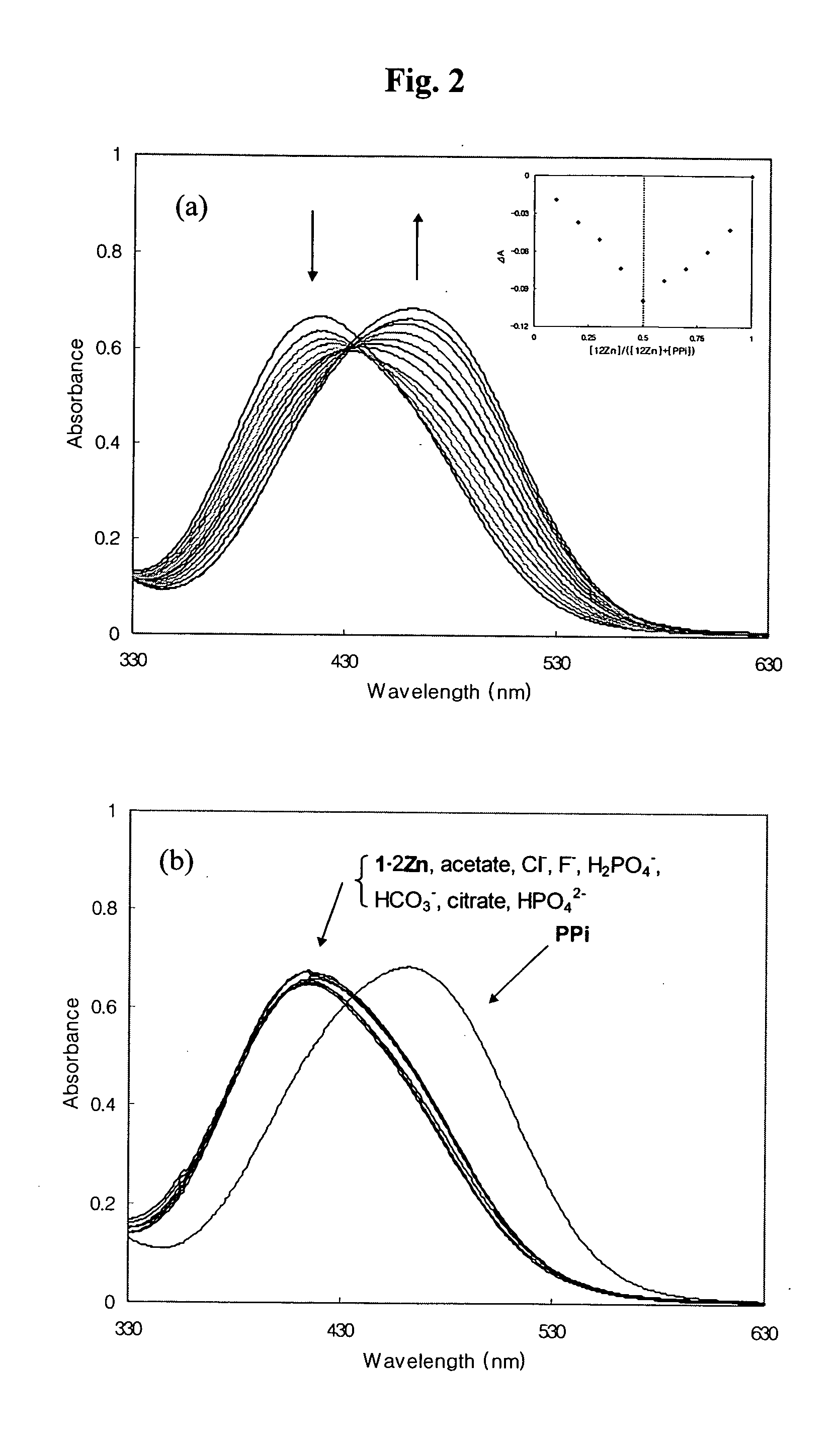
A novel coordination complex formed by dinuclear metal complexation is provided. The complex is a dinuclear metal complex of a compound, wherein the compound comprises a conjugation ring system substituted with: a) an electron donating group selected from —OH, —SH and —NH2; b) an indicating group selected from a chromogenic group, a fluorescent group and an electrochemical group; and c) two binding auxiliary groups, in combination with the electron donating group each of which being coordinated with the metal to provide an anion bonding site, wherein as the complex binds to a anion, the coordination of the electron donating group with the metal is weakened and electron donation of the electron donating group to the conjugation ring system is reinforced such that the reinforced electron donation by the electron donating group is transferred through the conjugation ring system to the indicating group to produce an indicating signal concomitant with the change of its electronic density. The coordination complex shows high sensitivity and high selectivity for pyrophosphate over other anions in an aqueous solvent over a wide pH range. Therefore, the complex is useful for pyrophosphate assay as a pyrophosphate sensor.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV FOUND
Use of a Metal Complex as an N-Dopant for an Organic Semiconducting Matrix Material, Organic of Semiconducting Material and Electronic Component, and also a Dopant and Ligand and Process for Producing same
ActiveUS20090212280A1Low oxidation potentialEasy to chargeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarbanionValence electron
A method of using a metal complex as an n-dopant for doping an organic semiconducting matrix material in order to alter the latter's electrical characteristics is provided. In order to provide n-doped organic semiconductors with matrix materials having a low reduction potential, while achieving high conductivities, the n-dopant is a neutral electron-rich metal complex with a neutral or charged transition metal atom as a central atom and having at least 16 valence electrons. The complex can be polynuclear and can possess at least one metal-metal bond. At least one ligand can form a π complex with the central atom, which can be a bridge ligand, or it can contain at least one carbanion-carbon atom or a divalent atom. Methods for providing the novel n-dopants are provided.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Electrochemical device comprising aliphatic nitrile compound
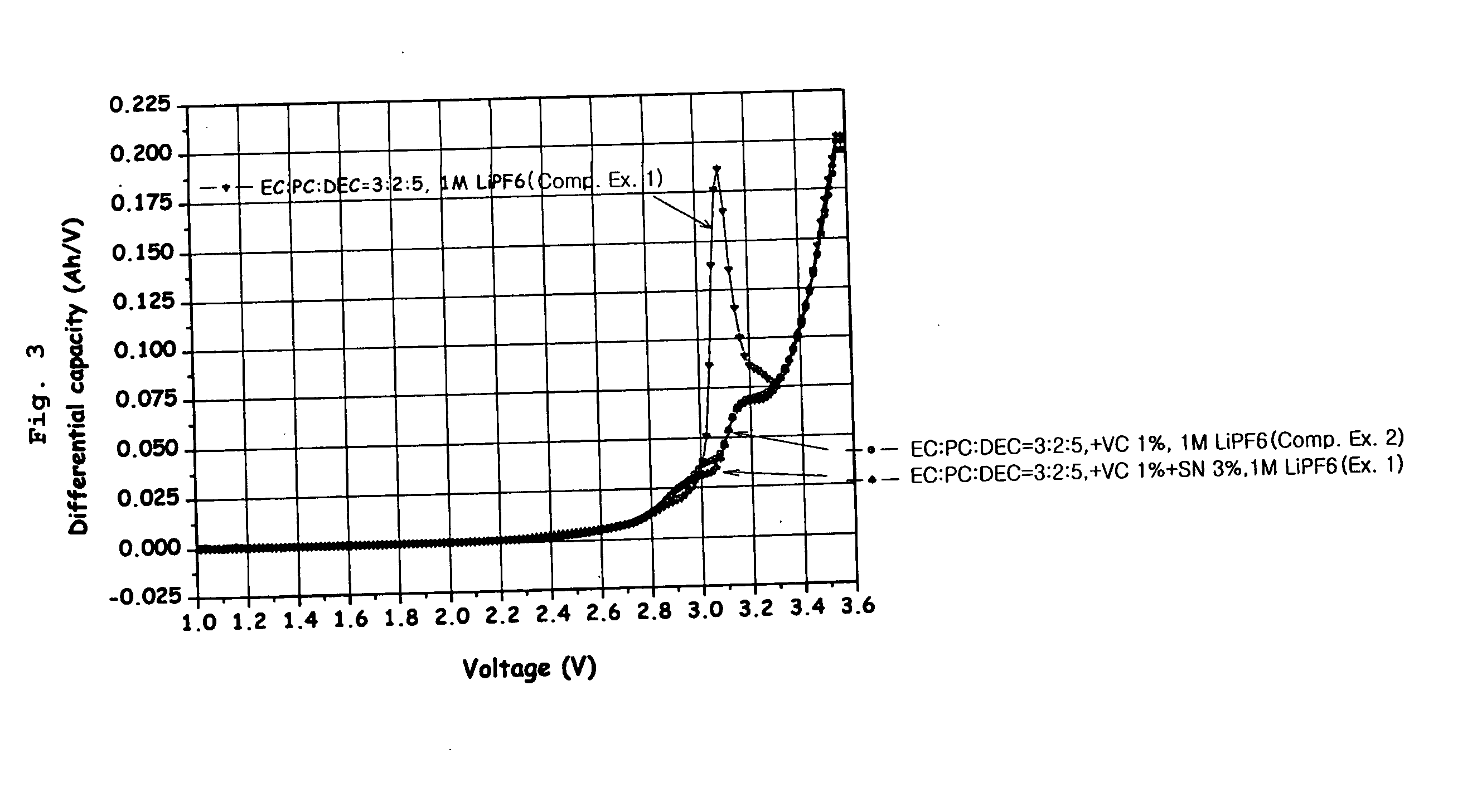
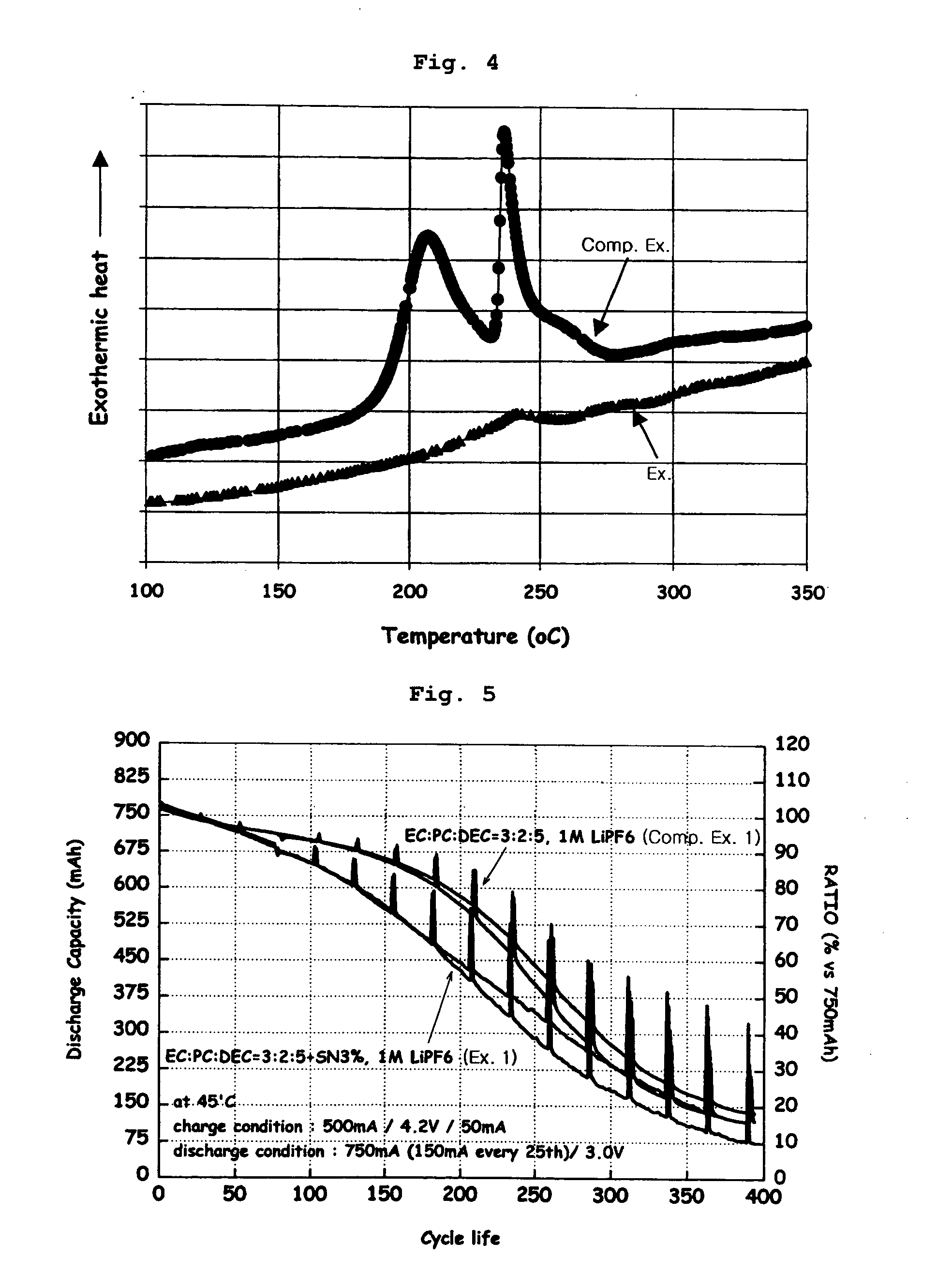
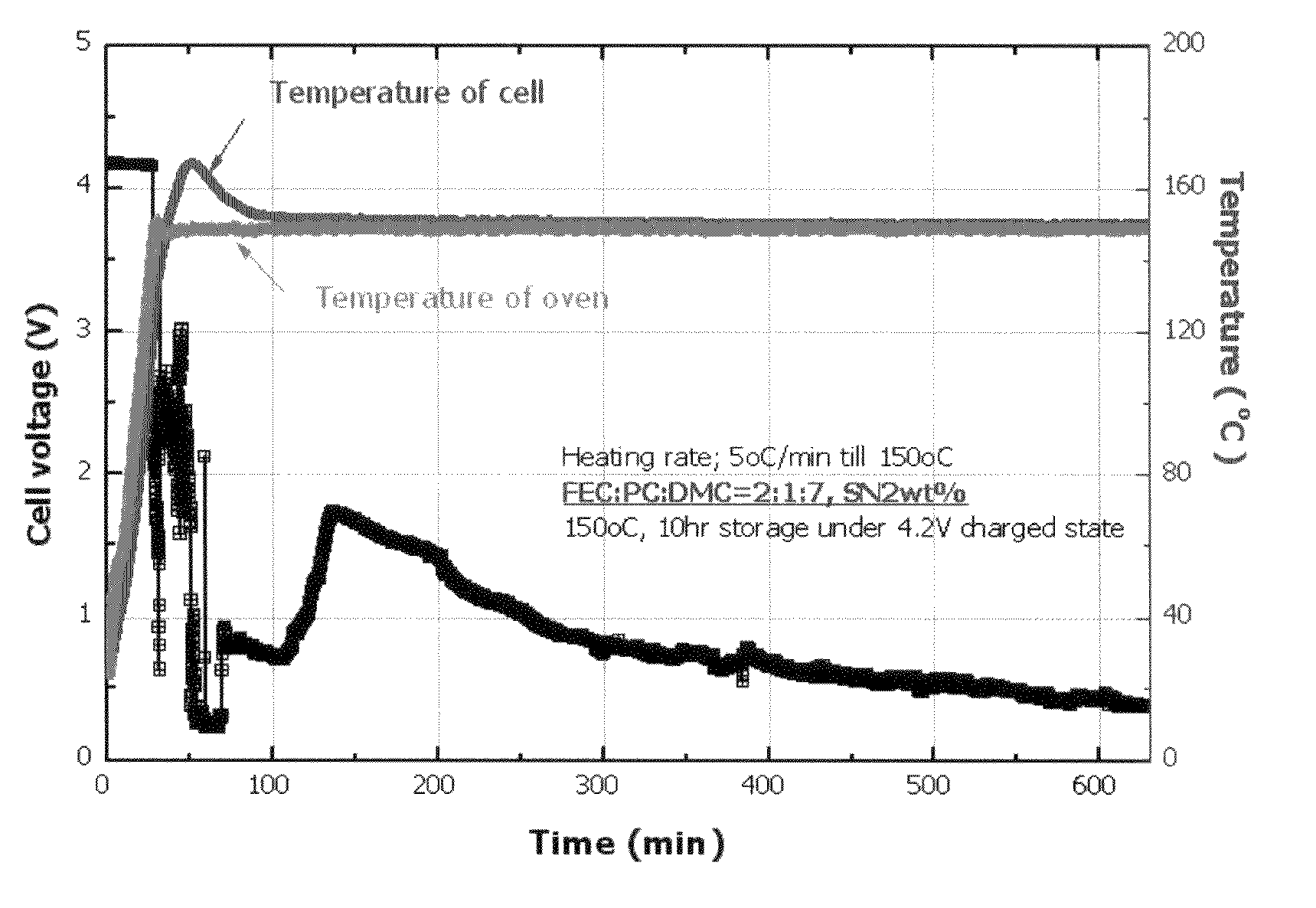
ActiveUS20050208371A1Low cycle lifeInhibit gas generationNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsFinal product manufacturePhysical chemistryEther
The present invention provides a cathode having a protection layer formed by a complex between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic nitrile compound, as well as an electrochemical device comprising the cathode. Also, the present invention provides an electrochemical device comprising: (1) a cathode having a protection layer formed by a complex between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic nitrile compound; (2) an anode having a passivation layer formed by a compound selected from the group consisting of vinylene carbonate, its derivative and an ether compound; and (3) an electrolyte solution containing a lithium salt and a solvent.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Metal complexes, methods, and uses thereof
Metal complexes that exhibit multiple radiative decay mechanisms, together with methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Metal alloy fine particles and method for producing thereof
A novel method for preparing fine particles comprising a transition metal and a noble metal which are monodispersed and have almost no particle diameter distribution, and are transferable to a CuAu-I type L10 ordered phase, with safety and at a low cost, wherein a salt or a complex of at least one transition metal selected from Fe and Co and a salt or a complex of at least one transition metal selected from Pt and Pd (exclusive of the combination of Co—Pd) is dissolved in an organic solvent miscible with water or an alcohol in the presence of an organic protecting agent, and the resultant solution is heated under reflux in the presence of an alcohol in an inert atmosphere, to thereby prepare a binary alloy comprising a transition metal and a noble metal, or a salt or a complex of at least one element selected from the group consisting of Cu, Bi, Sb, Sn, Pb and Ag is further dissolved in the above solvent and the resultant solution is heated under reflux in the presence of an alcohol in an inert atmosphere, to thereby prepare a ternary alloy comprising a transition metal, a noble metal and an additional element.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Dinuclear metal complex and pyrophosphate assay using the same
InactiveUS7279588B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsElectronic densityPyrophosphate
A novel coordination complex formed by dinuclear metal complexation is provided. The complex is a dinuclear metal complex of a compound, wherein the compound comprises a conjugation ring system substituted with: a) an electron donating group selected from —OH, —SH and —NH2; b) an indicating group selected from a chromogenic group, a fluorescent group and an electrochemical group; and c) two binding auxiliary groups, in combination with the electron donating group each of which being coordinated with the metal to provide an anion bonding site, wherein as the complex binds to a anion, the coordination of the electron donating group with the metal is weakened and electron donation of the electron donating group to the conjugation ring system is reinforced such that the reinforced electron donation by the electron donating group is transferred through the conjugation ring system to the indicating group to produce an indicating signal concomitant with the change of its electronic density. The coordination complex shows high sensitivity and high selectivity for pyrophosphate over other anions in an aqueous solvent over a wide pH range. Therefore, the complex is useful for pyrophosphate assay as a pyrophosphate sensor.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV FOUND
Treatment fluids containing a boron trifluoride complex and methods for use thereof
Treatment fluids for use in subterranean formations, particularly sandstone and other siliceous formations, may contain a source of fluoride ions to aid in mineral dissolution. In some cases, it may be desirable to generate the fluoride ions from a fluoride ion precursor, particularly a hydrofluoric acid precursor, such as a boron trifluoride complex. Methods described herein can comprise providing a treatment fluid that comprises an aqueous base fluid, a boron trifluoride complex, and a chelating agent composition, and introducing the treatment fluid into a subterranean formation,
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
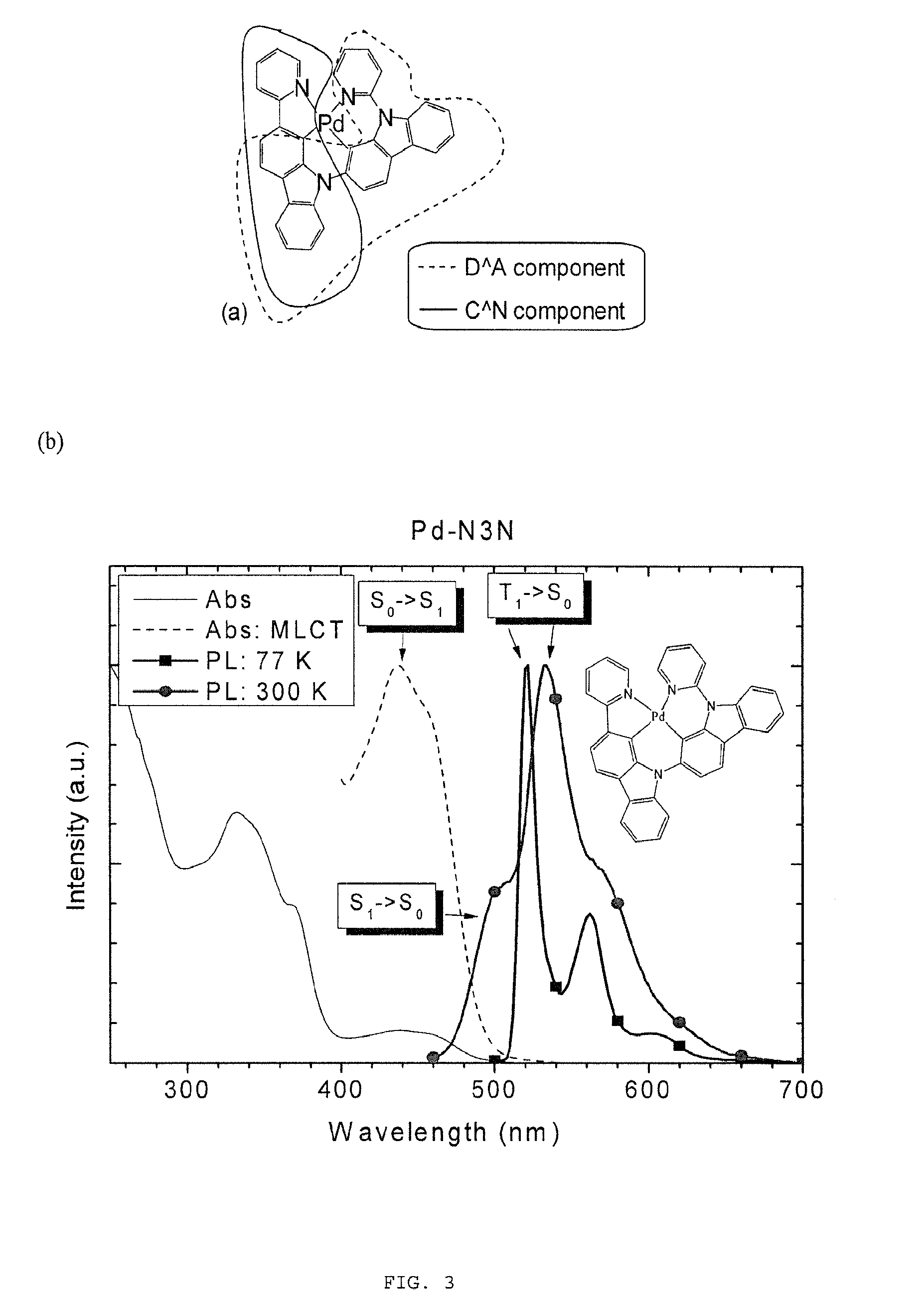
Iridium (III) complex with heteroatom linking group and organic electroluminescent device using the same
ActiveUS20050287391A1Efficient emissionsEffective lightingIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensIridiumHeteroatom
A high-efficient phosphorescent iridium (III) complex with a heteroatom linking group and an organic electroluminescent (EL) device using the same. The iridium complex of the present invention complex can efficiently emit light ranging from a blue region to a red region in a triplet MLCT state. The iridium (III) complex can be used in formation of an organic layer of an organic EL device. Since the iridium complex of the present invention can be used as a high-efficiency phosphorescent material, the iridium complex of the present invention can produce white light emission when used together with a green-emitting material or a red-emitting material as well as emission at the wavelength range of 400-650 nm.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Polymerization Catalyst Compositions Containing Metallocene Complexes and Polymers Produced by Using the Same
InactiveUS20070232758A1Quality improvementWide applicationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymerization catalystsMetal
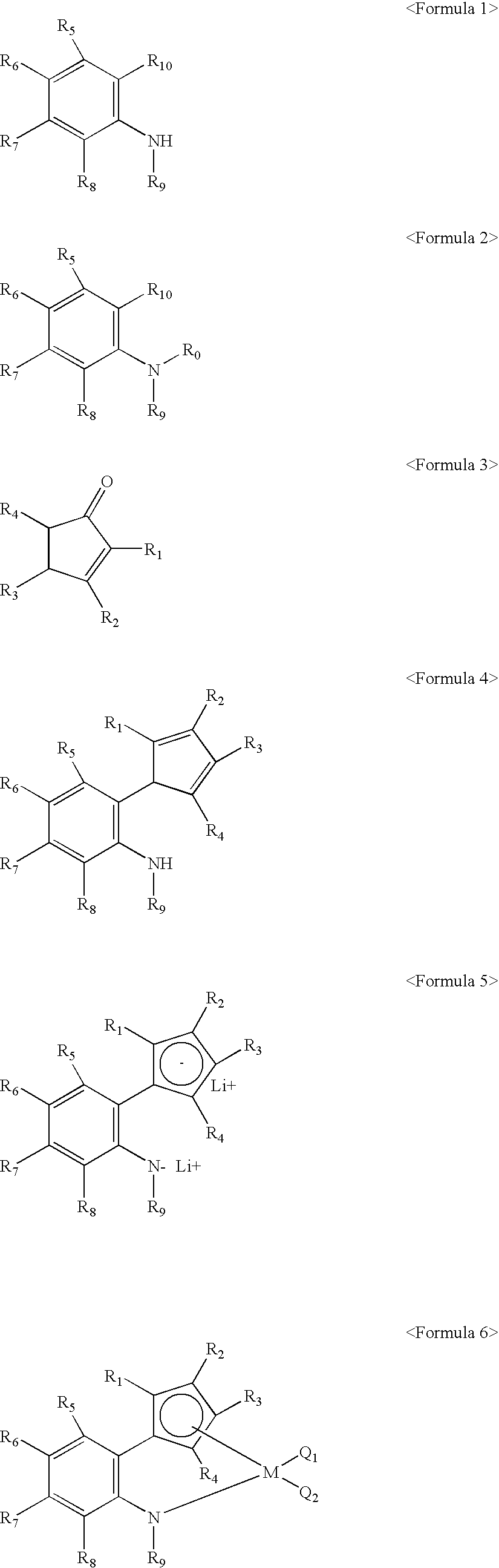
The present invention provides a novel catalyst composition comprising a metallocene complex, and a novel producing method for various polymer compounds. Preferably, the invention provides a novel polymer compound, and a producing method thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a polymerization catalyst composition, comprising: (1) a metallocene complex represented by the general formula (I), including: a central metal M which is a group III metal atom or a lanthanoid metal atom; a ligand Cp* bound to the central metal and including a substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl derivative; monoanionic ligands Q1 and Q2; and w neutral Lewis base L; and (2) an ionic compound composed of a non-ligand anion and a cation: where w represents an integer of 0 to 3.
Owner:RIKEN
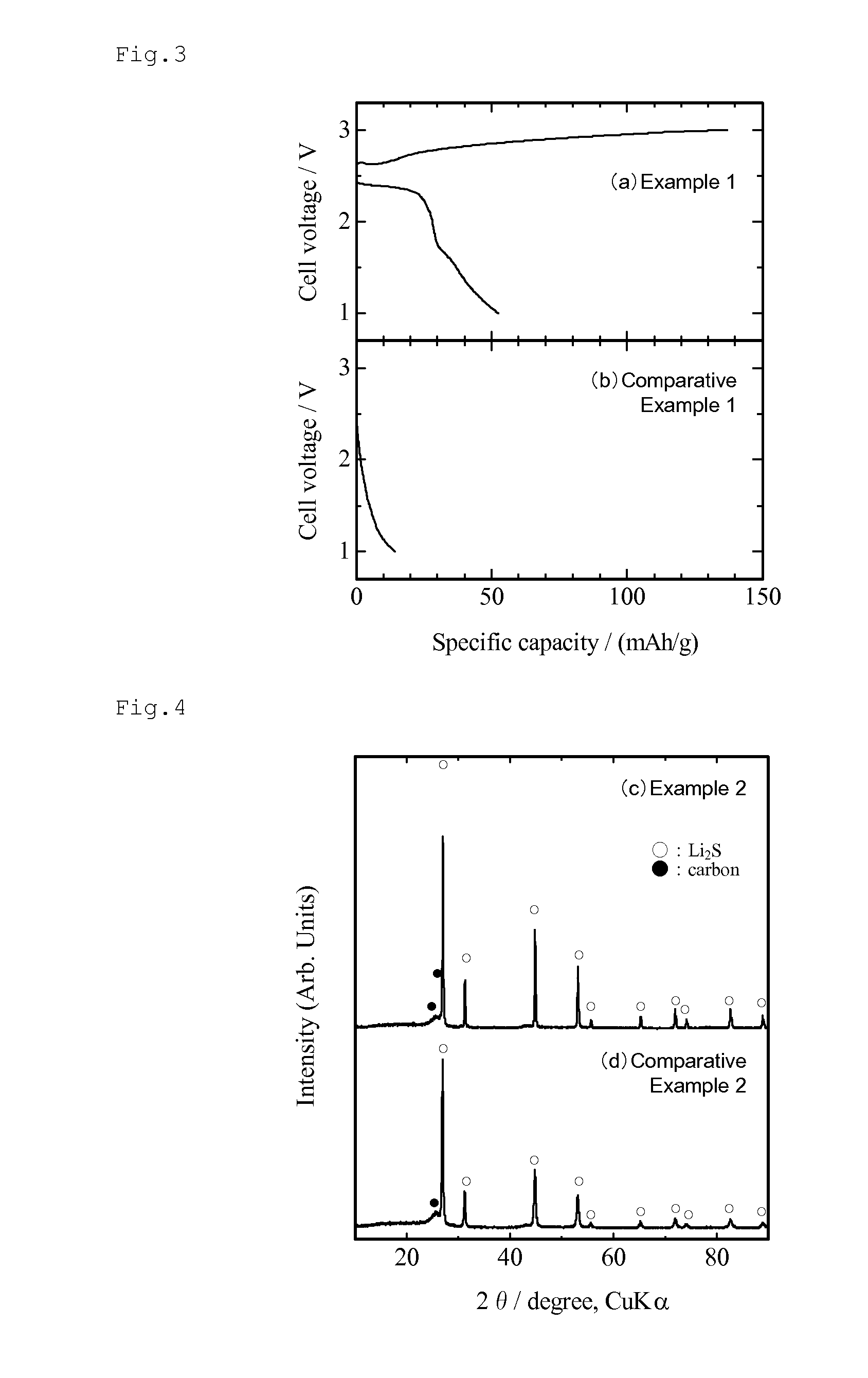
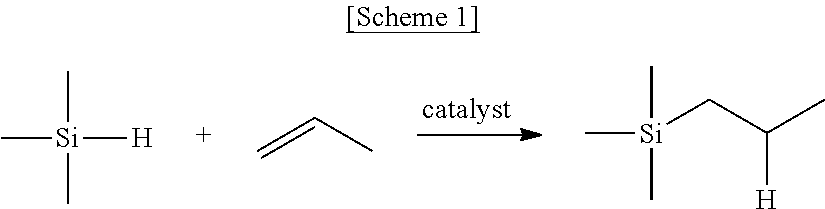
Lithium sulfide-carbon complex, process for producing the complex, and lithium ion secondary battery utilizing the complex
ActiveUS20110171537A1Improve electronic conductivityImprove conductivityElectrochemical processing of electrodesCarbon compoundsCarbon compositesPulsed DC
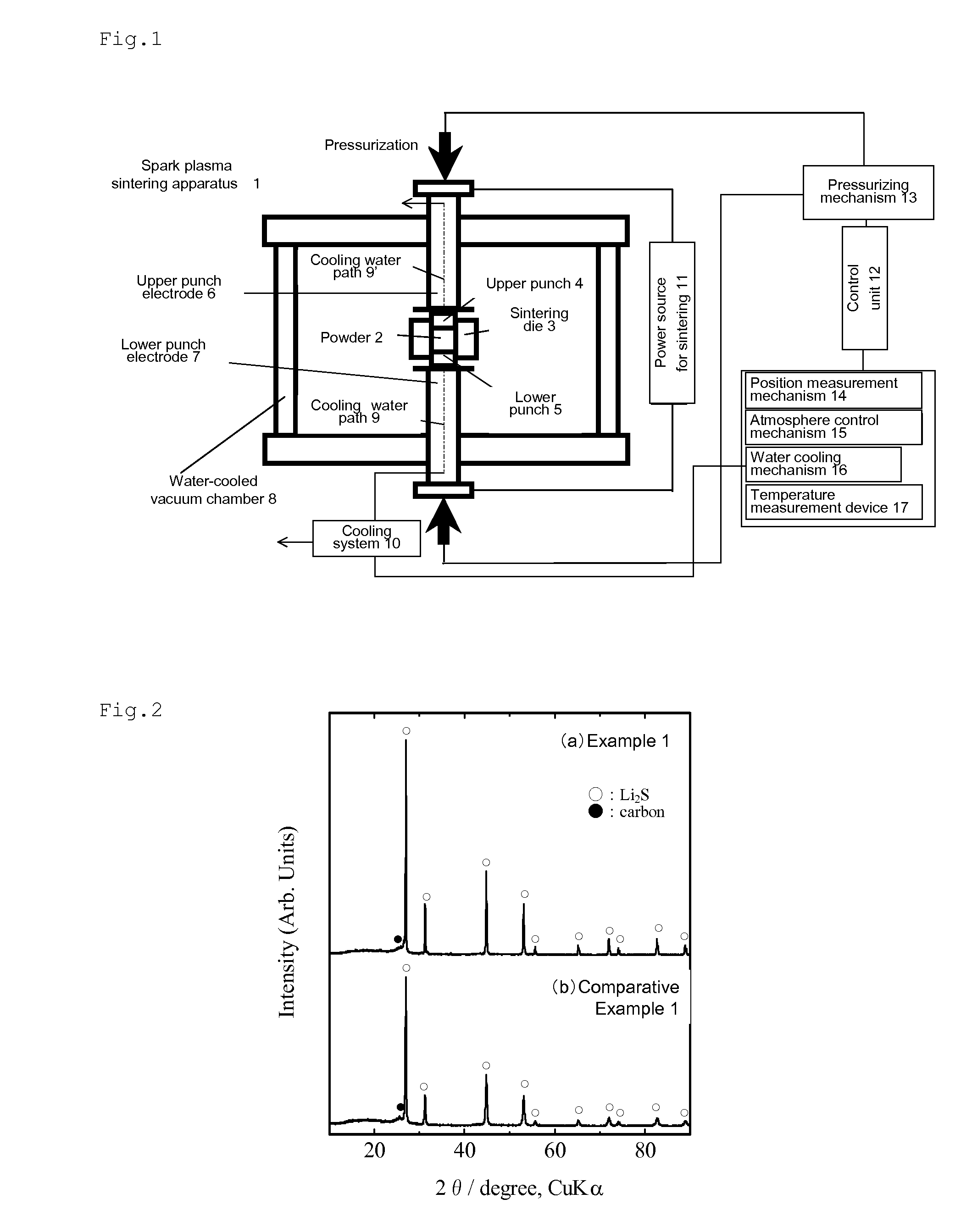
The present invention provides a process for producing a lithium sulfide-carbon composite, the process comprising placing a mixture of lithium sulfide and a carbon material having a specific surface area of 60 m2 / g or more in an electrically-conductive mold in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, and applying a pulsed direct current to the mold while pressurizing the mixture in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, thereby subjecting the lithium sulfide and the carbon material to heating reaction; and a lithium sulfide-carbon composite obtained by this process, the composite having a carbon content of 15 to 70 weight %, and a tap density of 0.4 g / cm3 or more when the carbon content is 30 weight % or more, or a tap density of 0.5 g / cm3 or more when the carbon content is less than 30 weight %. The present invention can improve the electronic conductivity of lithium sulfide, which is expected to be put into practical use as a high-capacity positive electrode active material, so as to further enhance the performance of lithium sulfide as a positive electrode active material for lithium ion secondary batteries.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
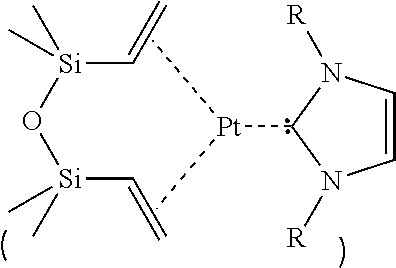
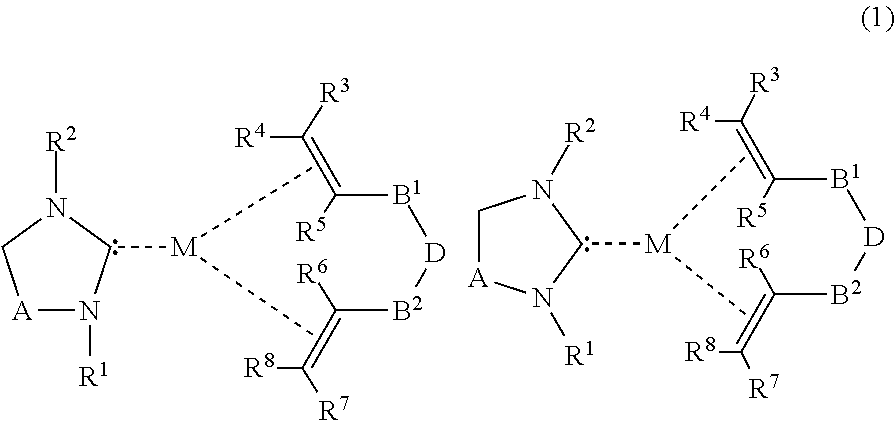
Saturated n-heterocyclic carbene-ligand metal complex derivatives, preparing method thereof, and preparing method of silane compound by hydrosilylation reaction using the same as catalyst
InactiveUS20110160454A1Improve stabilityEfficient executionSilicon organic compoundsGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsSilane compoundsRegioselectivity
Provided are a saturated N-heterocyclic carbene-ligand metal complex derivative, a method for preparing the same, and a method for preparing a silane compound by hydrosilylation using the same as a catalyst. To describe in more detail, the metal complex derivative has a saturated N-heterocyclic carbene derivative and an olefin ligand at the same time. A silane compound is prepared by hydrosilylation in the presence of the metal complex derivative as a catalyst. The provided metal complex derivative of the present invention has superior stability during hydrosilylation reaction and is capable of effectively performing the hydrosilylation reaction at low temperature even with small quantity. Further, a product with superior regioselectivity may be obtained. In addition, after the hydrosilylation reaction is completed, the metal complex derivative may be recovered and recycled.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Electrode for energy storage devices and electrochemical supercapacitor based on said electrode
ActiveUS20070065719A1Extended service lifeImprove reliabilityHybrid capacitor electrodesLiquid electrolytic capacitorsPolymer scienceRedox polymers
An electrode comprises an electrically conductive substrate, a layer of energy accumulating redox polymer deposited onto the substrate, the redox polymer comprising a polymer metal complex with a substituted tetra-dentate Schiff's base selected from the group: poly-[Me(R, R′—Y)], wherein Me is a transition metal; Y is a bridge group binding the atoms of Nitrogen in the Schiff's base; R is an electron-donating substituent comprising a functional group (X)O—, —COO(X), where (X) is an alkali metal; R′ is Hydrogen or Halogen; and wherein the polymer metal complex has the following structure: The electrochemical capacitor comprises a case housing the above-described positive electrode and a negative electrode disposed inside the case, and an electrolyte filling the space between the electrodes.
Owner:POWERMERS
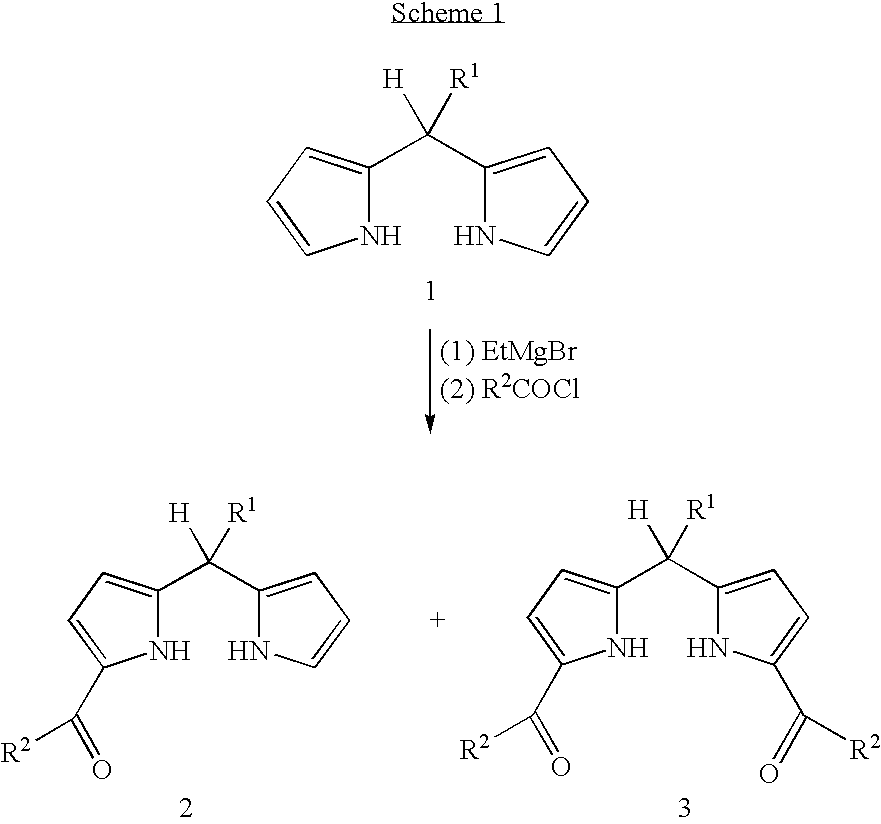
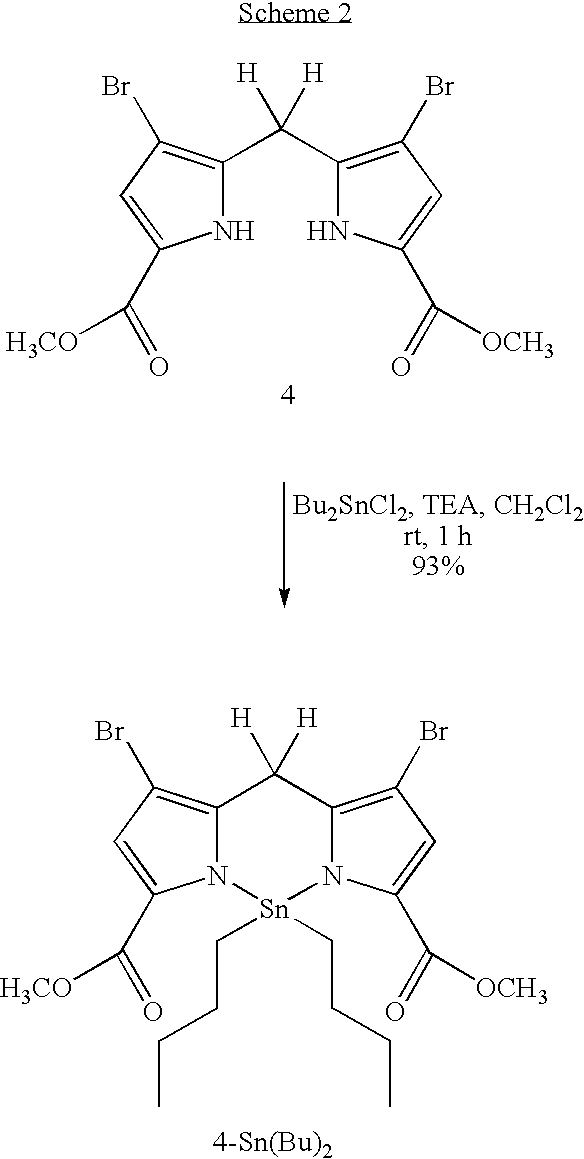
Facile synthesis of 1,9-diacyldipyrromethanes
InactiveUS6924375B2Improve isolationEasy to prepareTin organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsArylPyrrole
The present invention provides a method of making a metal complex. The method comprises the steps of: (a) acylating a dipyrromethane or a 1-monoacyldipyrromethane to form a mixed reaction product comprising a 1,9-diacyidipyrromethane; (b) combining the reaction product with a compound of the formula R2MX2 in the presence of a base, where R is alkyl or aryl, M is Sn, Si, Ge, or Pb (preferably Sn), and X is halo, OAc, acac, or OTf, to form a product comprising a metal complex of the formula DMR2 in the mixed reaction product, wherein D is a 1,9-diacyldipyrromethane; and then (c) separating the metal complex from the mixed reaction product. The method may be utilized for the convenient synthesis and separation of 1,9-diacyldipyrromethanes. Metal complex intermediates useful in such methods are also described.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Photosensitizing transition metal complex and its use for photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20050081911A1Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilityRuthenium organic compoundsElectrolytic capacitorsRheniumO-Phosphoric Acid
A photosensitizing transition metal complex of the formula (Ia) MLY1, (Ib) MLX3 (Ic) MLY2X, (Id) MLY3X or (Ie) MLY4X in which M is a transition metal selected from ruthenium, osmium, iron, rhenium and technetium, preferably ruthenium or osmium. X is a co-ligand independently selected from NCS—, Cl—, Br—, I—, CN—, H2O; pyridine unsubstituted or substituted by at least one group selected from vinyl, primary, secondary or tertiary amine, OH and C1-30 alkyl, preferably NSC and CN—; L is a tridentate polypyridine ligand, carrying at least one carboxylic, phosphoric acid or a chelating group and one substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 50 carbon atoms, substituted or unsubstituted alkylamide group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms or substituted or unsubstituted aralkyl group having 7 to 50 carbon atoms. A dye-sensitized electrode includes a substrate having an electrically conductive surface, an oxide semiconductor film formed on the conductive surface, and the above sensitizer of formula (Ia), (Ib), (Ic), (Id) or (Ie) as specified above, supported on the film. A solar cell includes the above electrode, a counter electrode, and an electrolyte deposited there between.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for preparing transition metal complexes, transition metal complexes prepare using the method, catalyts composition containing the complexes
ActiveUS20100062927A1High yieldTransition metal complexOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsTitanium organic compoundsPolyolefinVolumetric Mass Density
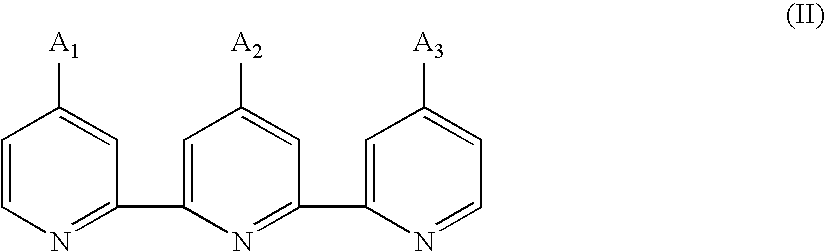
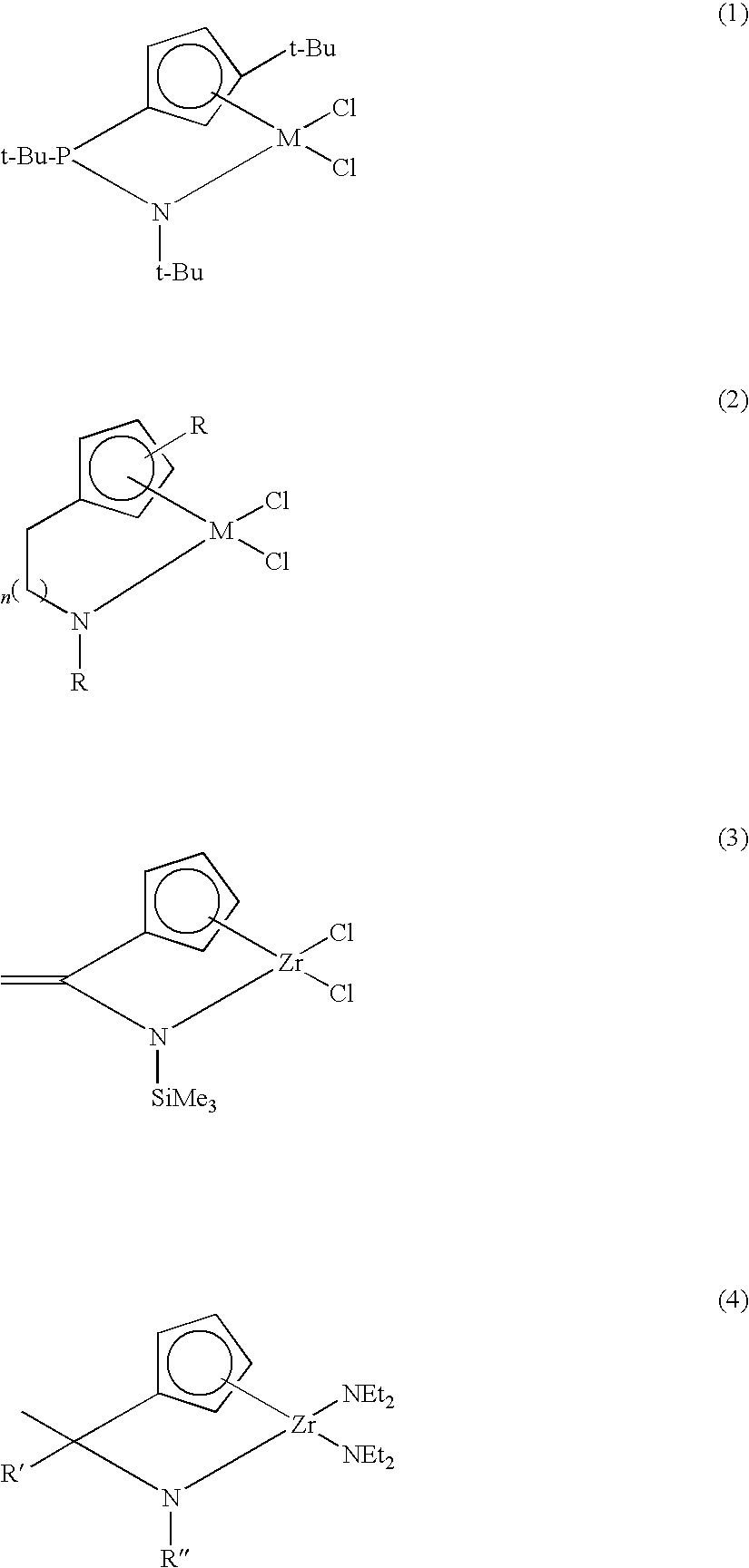
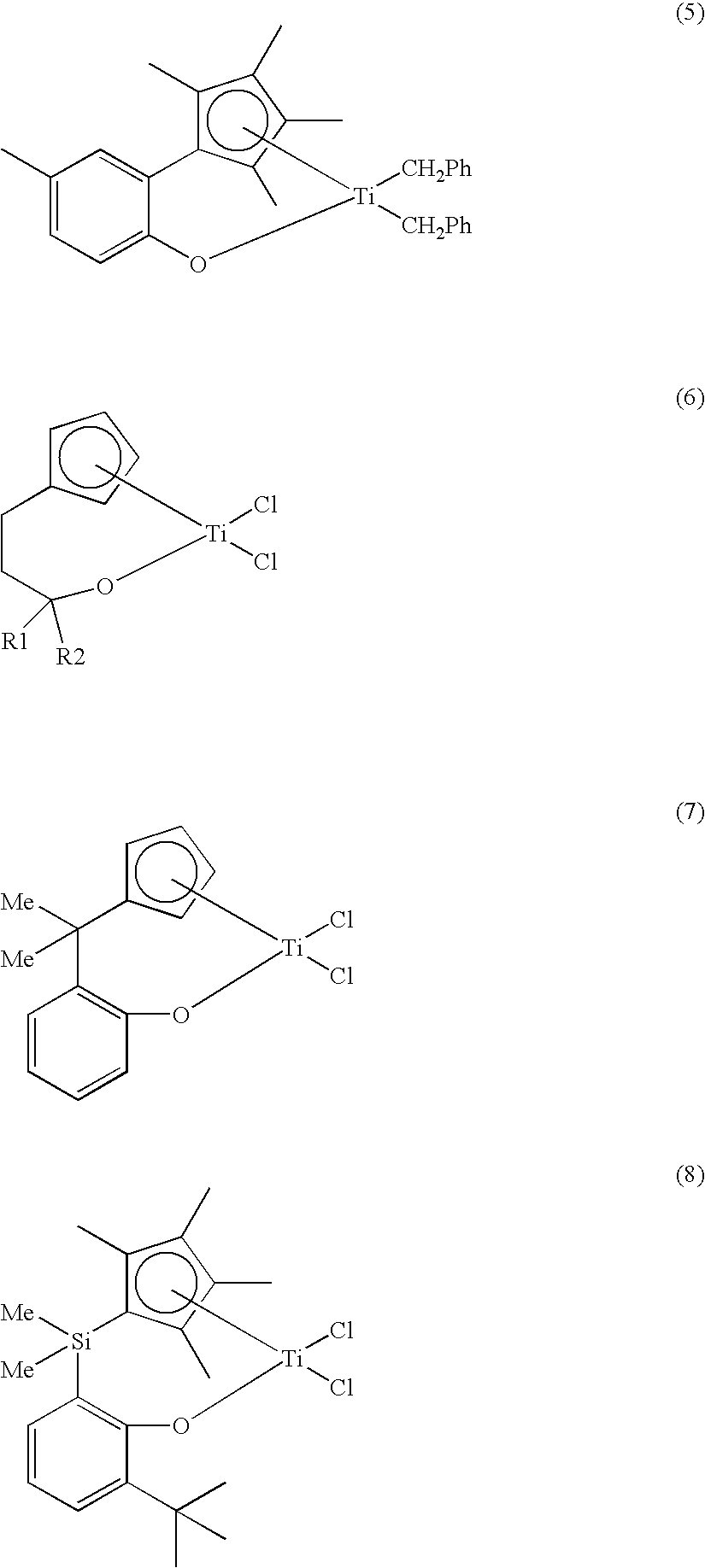
The present invention provides a novel transition metal complex where a monocy-clopentadienyl ligand to which an amido group is introduced is coordinated, a method for synthesizing the complex, and olefin polymerization using the same. The method for preparing a transition metal complex according to the present invention comprises a step of blocking a by-reaction of a nitrogen atom using a compound containing a protecting group, and thus it is possible to prepare a transition metal complex in a simpler manner in a high yield. Further, the transition metal complex according to the present invention has a pentagon ring structure having an amido group connected by a phenylene bridge in which a stable bond is formed in the vicinity of a metal site, and thus, sterically monomers can easily approach the transition metal complex. When a catalyst composition comprising the transition metal complex is applied in copoly-merization of ethylene and monomers having large steric hindrance, a very low density polyolefin copolymer having a density of less than 0.910 g / cc, in addition to a polyolefin having a high molecular weight and a linear low density, can be prepared. Furthermore, the reactivity is also very high.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Method for preparing Salen-metal complex
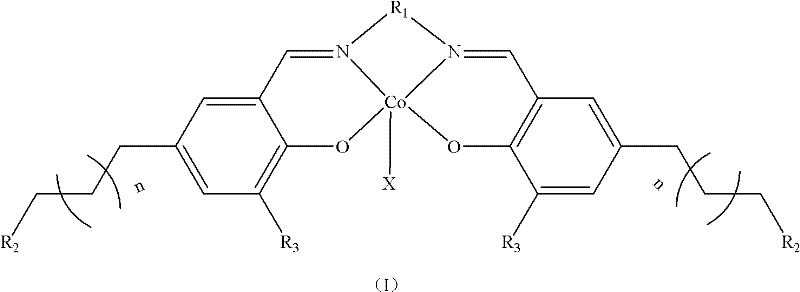
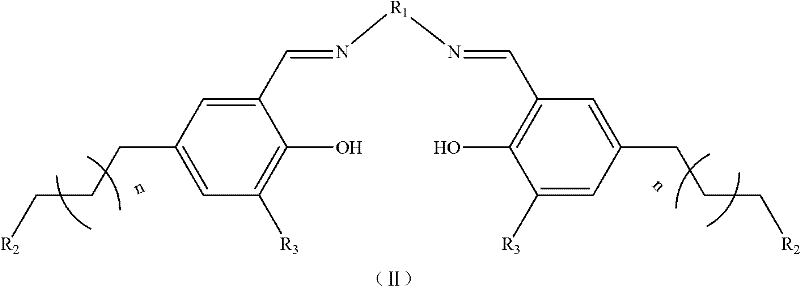
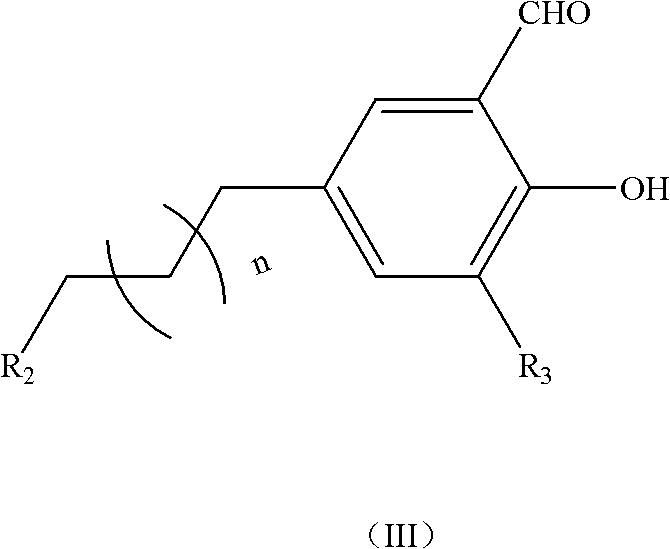
InactiveCN102212085ALow costHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCobalt organic compoundsSodium methoxideFiltration
The invention provides a method for preparing a Salen-metal complex. The method comprises the following steps of: under the argon atmosphere, adding ligands(II), sodium methoxide, absolute methanol soluble ligands(II) and sodium methoxide into a reactor in sequence; stirring the mixture for 2 minutes, and adding 1mol / L cobalt acetate anhydrous / methanol solution dropwise, wherein the molar ratio of the ligands(II) to sodium methoxide to cobalt acetate is 1:1:1; and making the mixture reacted at the room temperature for 24 hours, adding anionic salt which has the same molar weight as the cobalt acetate, stirring the mixture for three days in the air, stopping the reaction, concentrating the mixture, performing dissolution and filtration by adding methylene chloride, drying the filtrate by anhydrous sodium sulfate overnight, filtering the mixture, concentrating under reduced pressure, and drying the mixture under the vacuum condition to obtain the Salen-metal complex. The Salen-metal complex prepared by the method has the advantages of simple method, low cost and high catalytic efficiency.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Three-element determination method of nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material
ActiveCN104316643AImprove measurement accuracyHigh precisionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationMurexideAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a three-element determination method of a nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material. The method comprises the following steps: determining the total quantity of cobalt, nickel and manganese ions by EDTA titration and recording titration consumption volume; sampling to an alkaline medium of ammonia chloride and ammonium to form nickel amine, oxidizing cobalt by utilizing hydrogen peroxide, complexing with ammonium to form a trivalent cobalt ammonia complex to generate manganese dioxide precipitate, filtering out the precipitate to obtain the filter liquid, titrating the filter liquid by utilizing EDTA in the presence of murexide serving as an indicator to determine the content of nickel, and recording the titration consumption volume; enabling the ammonia gas to escape from the solution after the nickel is determined through titration under the alkaline and heating condition and generating cobalt hydroxide precipitate at the same time, dissolving the cobalt hydroxide precipitate by utilizing acid, measuring the content of cobalt through EDTA titration, and recording the titration consumption volume; and calculating the respective content of the three elements according to the EDTA consumption volume in each step, the concentration of EDTA and the sample mass. The method is accurate in detection, high in detection efficiency, safe, environment-friendly and applicable to the detection of content of three elements in an anode material.
Owner:JINGMEN GEM NEW MATERIAL +1
Composition and method for improving density and hardness of fluid bed catalysts
InactiveUS20060199730A1Heterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPreparation by hydrocarbon ammoxidationOxidation stateVolumetric Mass Density
A catalyst composition for the oxidation and ammoxidation of hydrocarbons comprising a plurality of silica sol particles with different average particle sizes, and a complex of metal catalytic oxides having the formula: AaBbCcBidMOeOx, wherein (i) A is one or more of Li, Na, K, Cs, Rb, In, and TI B is one or more of Ni, Mn, Co, Mg, Ca, and Zn C is one or more of Fe, Cr, Ce, Cu, V, W, Sb, Sn, Ge, P, B, Ga, Te, Nb, and Ta, a is 0.0-1.0 b is 0.0-12.0 c is 1.0-12.0 d is 0.0-2.0 e is 12.0-14.0; or AaBbSb12Ox, wherein (ii) A is one or more of Fe, Cr, Ce, V, U, Sn, Ti, Ga, and Nb B is one or more of Mo, W, Co, Cu, Te, Bi, Ni, Ca, and Ta a is 0.1-16 b is 0.0-12.0. In both (i) and (ii), the value of x depends on the oxidation state of the metals used. Furthermore, a process for producing said ammoxidation catalyst is disclosed.
Owner:YKK CORP +1
Metal complex, light-emitting device, and display apparatus
InactiveUS20070228940A1Improve efficiencyIncrease brightnessIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic light emitting deviceNitrogen
A metal complex is provided which is used for an organic EL device and an organic light-emitting device which outputs light with high luminance and high efficiency. The metal complex has a structure in which a nitrogen atom in a 6- to 8-membered non-aromatic cyclic group is bonded to a metal atom. The organic light-emitting device includes a pair of electrodes which are an anode and a cathode, and an organic compound layer interposed between the electrodes. The organic compound layer contains the metal complex represented by the following structural formula.
Owner:CANON KK
Non-Aqueous Organo Liquid Delivery Systems containing dispersed Poly (organic acids) that improve availability of macro & micro-nutrients to plants
ActiveUS20160332929A1Prevent spoilageAvoid premature germination problemBiocideBio-organic fraction processingOrganic baseCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to improving the efficiency of man-made and / or natural organic-based animal manure fertilizers by administration of formulations containing poly(organic acids), [P(OA)]s, and / or their salts dispersed in a Non-aqueous Organic Solvent Delivery System (NOSDS). Utilizing a NOSDS allows for coating all components in a fertilizer formulation including but not limited to Urea, Manure, mono-ammonium phosphate (MAP), di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), solid micronutrients such as lime, zinc chloride, etc.) with a layer of [P(OA)]s and / or their salts that liberates, in a plant available form, the micronutrient metals and macronutrients, that are bound as insoluble salts and complexes in the soil. The carboxylic groups of a [P(OA)] that can exist within the [P(OA)] as carboxylic acids, carboxylic anhydrides and / or carboxylic imides, dispersed within the NOSDS, can be neutralized with one or more metals in the form of elemental metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal alkylates and metal carbonates and / or nitrogen containing compounds such as ammonia, ammonium hydroxide or organoamines to form a stable dispersion that can contain completely complexed micronutrients and provide the vehicle for the delivery of these nutrients to soils and / or as a coating to the surfaces fertilizer granules and seeds.
Owner:SOILGENIC TECH LLC
Non-Aqueous Electrolyte and Electrochemical Device With an Improved Safety
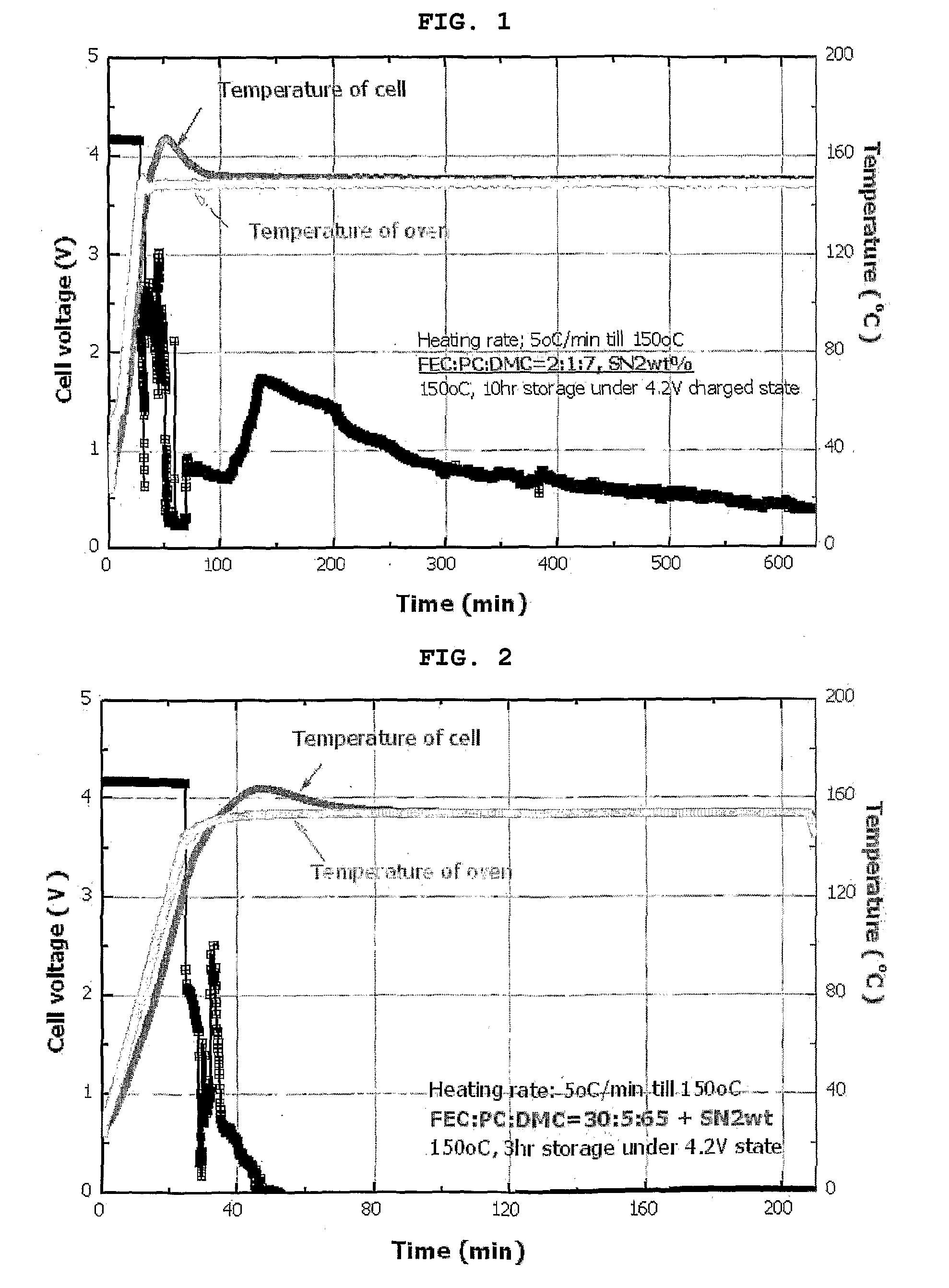
ActiveUS20090047582A1Avoid problemsFinal product manufactureOrganic electrolyte cellsDecompositionSolvent
Disclosed are a non-aqueous electrolyte comprising a lithium salt and a solvent, the electrolyte containing, based on the weight of the electrolyte, 10-40 wt % of a compound of Formula 1 or its decomposition product, and 1-40 wt % of an aliphatic nitrile compound, as well as an electrochemical device comprising the non-aqueous electrolyte. Also disclosed is an electrochemical device comprising: a cathode having a complex formed between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic nitrile compound; and an anode having formed thereon a coating layer containing a decomposition product of the compound of Formula 1. Moreover, disclosed is an electrochemical device comprising: a cathode having a complex formed between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic nitrile compound; and a non-aqueous electrolyte containing the compound of Formula 1 or its decomposition product. In addition, disclosed is an electrochemical device comprising: an anode having formed thereon a coating layer containing a decomposition product of the compound of Formula 1; and a non-aqueous electrolyte containing the compound of Formula 1 or its decomposition product.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
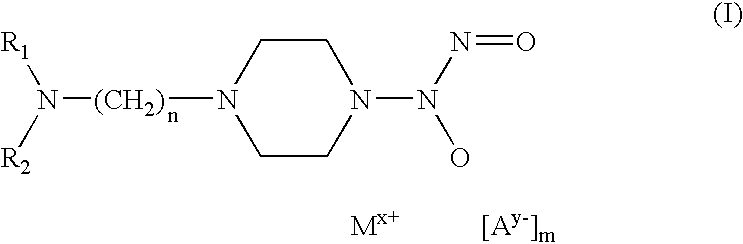
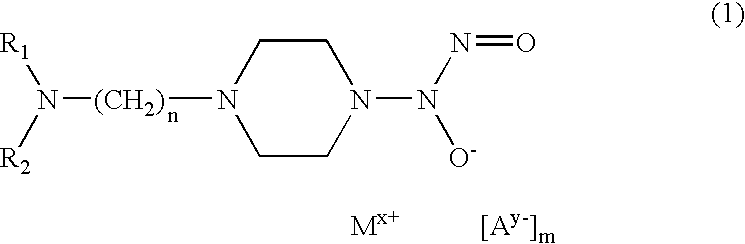
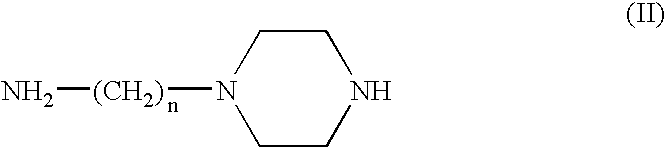
Nitric oxide donors based on metallic centers
A metal complex of a piperazineNONOate derivative of the formula: wherein a) R1 and R2 independently represent hydrogen, linear or branched (C1-C4) alkyl, optionally substituted by 1 or 2 groups selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, (C1-C4) alkoxy, (C1-C4) alkylthio, amino, (C1-C4) alkylamino, di-(C1-C4) alkylamino, carboxy, carbo(C1-C4) alkoxy, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio; orb) R1 and R2 taken together, represent one of the following groups ═CR3-aryl, where R3 represents hydrogen, (C1-C4) linear or branched chain alkyl, optionally substituted by 1 or 2 groups selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, carboxy, aryl; n represents a whole number ranging from 2 to 4; M+ represents a cation of a transition metal or zinc; x represents a whole number which varies from 1 to 3, and indicates the charge units of the cation of the transition metal or of the zinc in relation to its stable oxidation state; A − represents an inorganic or organic anion which forms stable salts with the NONOate metal complex; y represents a whole number which varies from 1 to 3, and indicates the charge of the anion; m represents a whole number including zero, or a fractional, indicating the number of anions required to balance the cationic charge of the NONOate metal complex and is related to the values of x, y, k and w by the relationship: m=(x+k)-(1+w)ywhere w is the number of possible further anionic charge units and k is the number of possible further cationic charge units present in the NONOate ligand substrate. The complex of the invention exhibits an endothelio-protective effect in the coronary system and stimulates re-endothelialization and angiogenesis proceses.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Metal nanoparticles stabilized with a carboxylic acid-organoamine complex
InactiveCN101450387AImprove stabilityExtended storage timeMaterial nanotechnologyMetal-working apparatusCarboxylic saltOrganic group
Metal nanoparticles with a stabilizer complex of a carboxylic acid-amine on a surface thereof are formed by reducing a metal carboxylate in the presence of an organoamine and a reducing agent compound. The metal carboxylate may include a carboxyl group having at least four carbon atoms, and the amine may include an organo group having from 1 to about 20 carbon atoms.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Negative resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, and complex
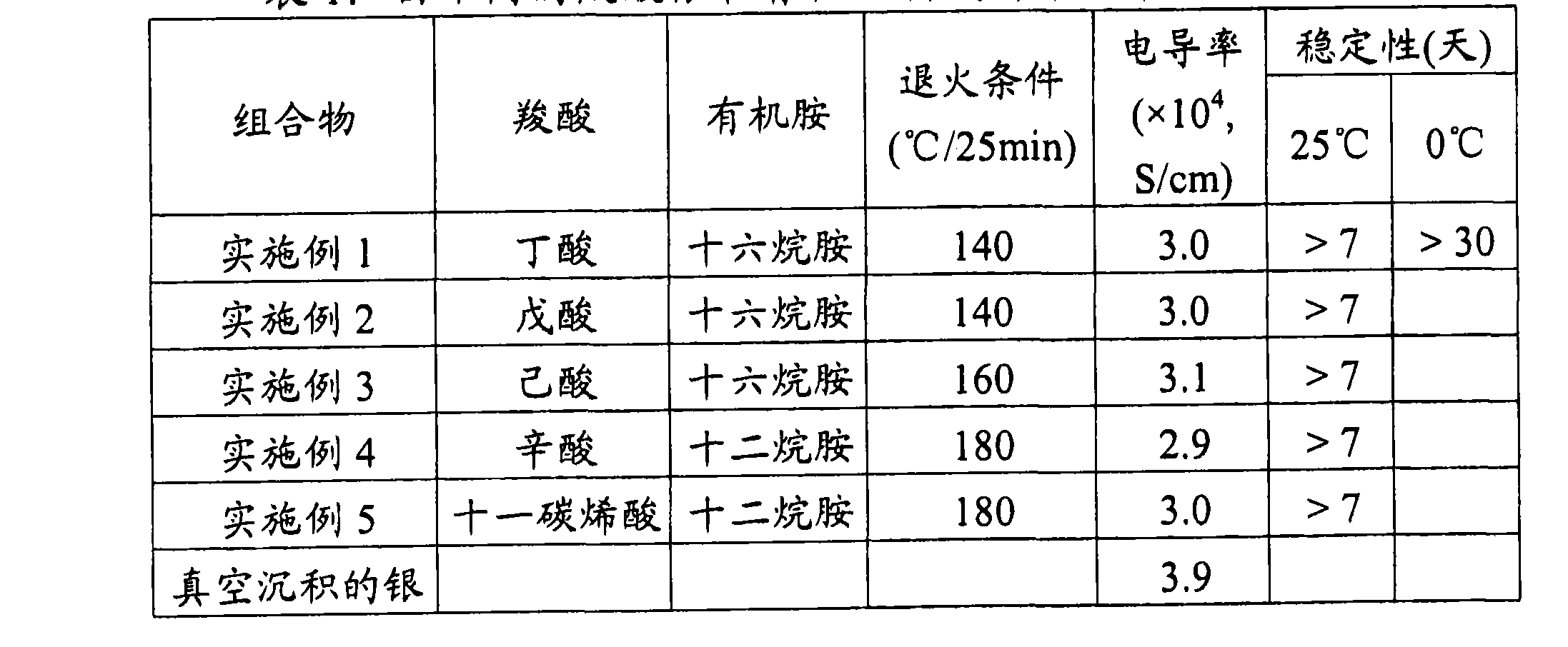
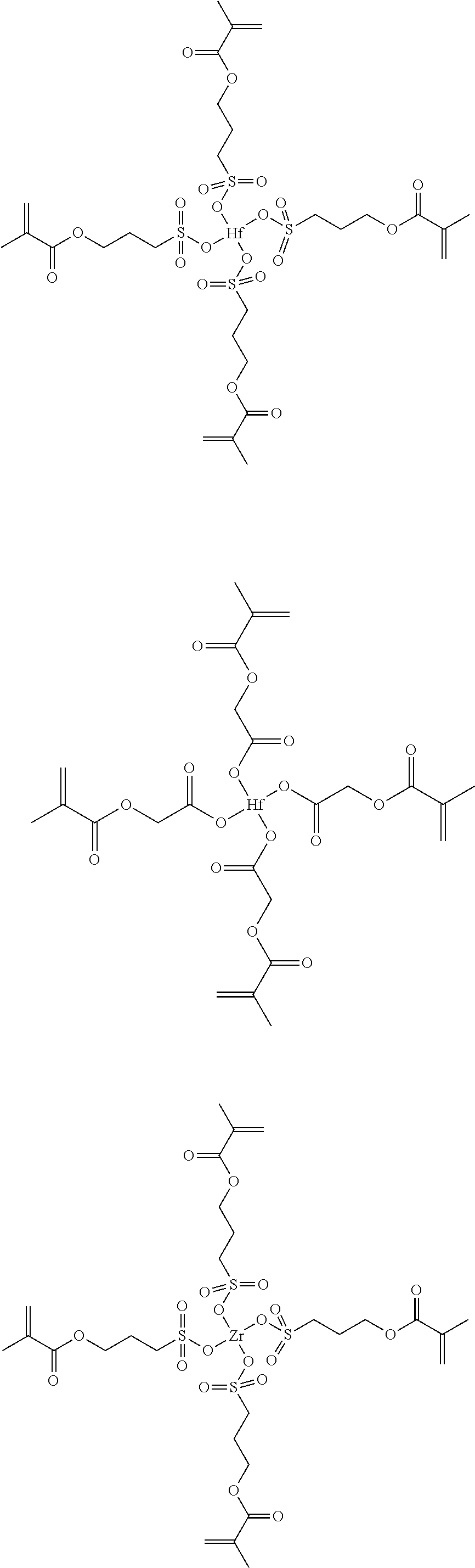
ActiveUS20150192851A1Good time stabilityHigh light absorptionPhotosensitive materialsElectric discharge tubesResistHafnium
A negative resist composition including a complex represented by the general formula (1); and a polymerization initiator. in which M represents hafnium (Hf) or zirconium (Zr), X represents a ligand including a conjugate base of an acid which has an acid dissociation constant (pKa) of 3.8 or less and has a polymerizable group, Y represents a ligand having no polymerizable group, and n represents an integer of 1 to 4.[MXnY4-n] (1)
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Complex catalyst for synthesizing carbonate ester by using homogeneous oxidation carbonylation of alcohol (S), its prepn. tech. and use
InactiveCN1792453ASimple preparation processHigh activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsQuaternary ammonium cationProtein carbonyl
A complex catalyst for preparing carbonate from alcohol by homogeneous oxidizing-carbonylating reaction has a chemical formula MXnLm, where M is metal, X is chosen from halogen, SO4 (or HSO4) radical, CO3 (or HCO3) radical, etc, L is chosen from RN4 ion, RP4 ion, pyridine, etc, and m=1-12. It is prepared through complex reaction between quaternary ammonium (or phosphorus) salt and metal salt. Its application method is also disclosed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
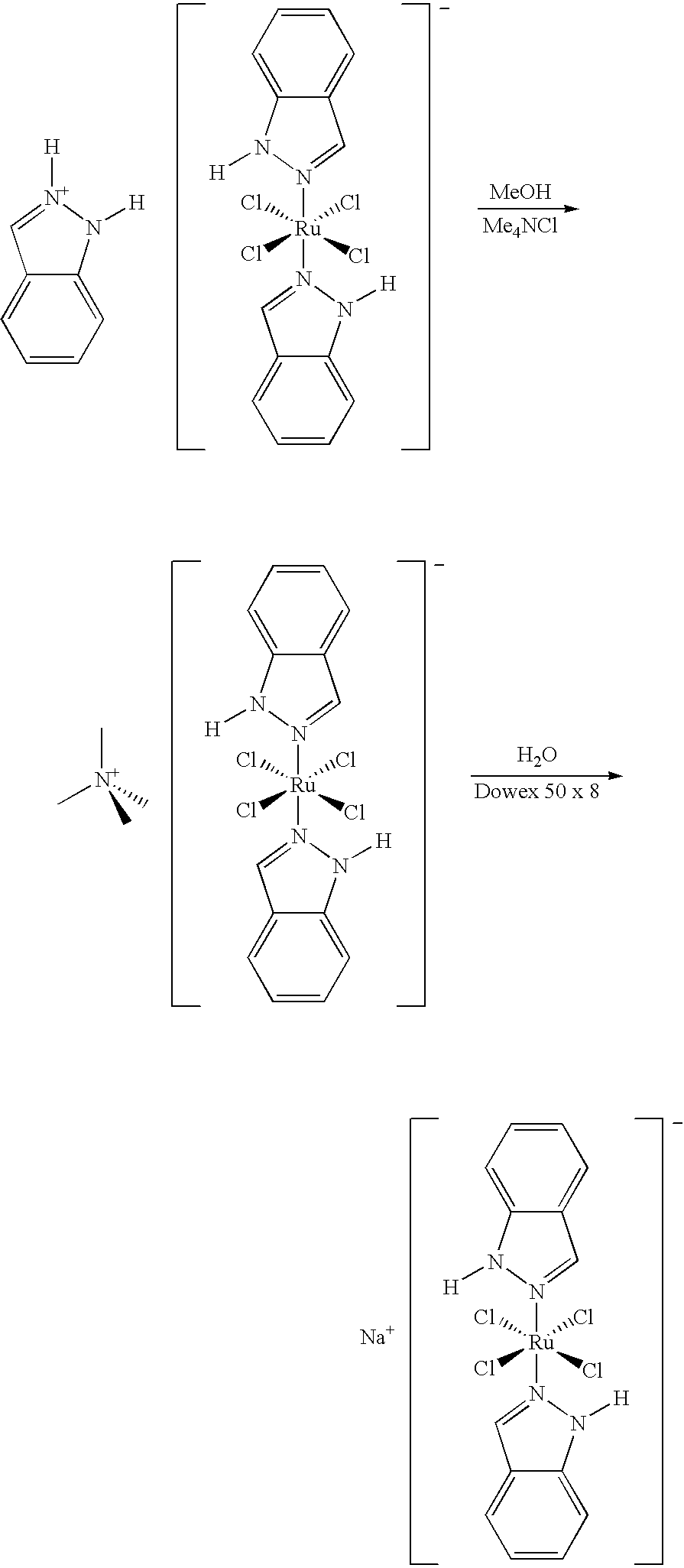
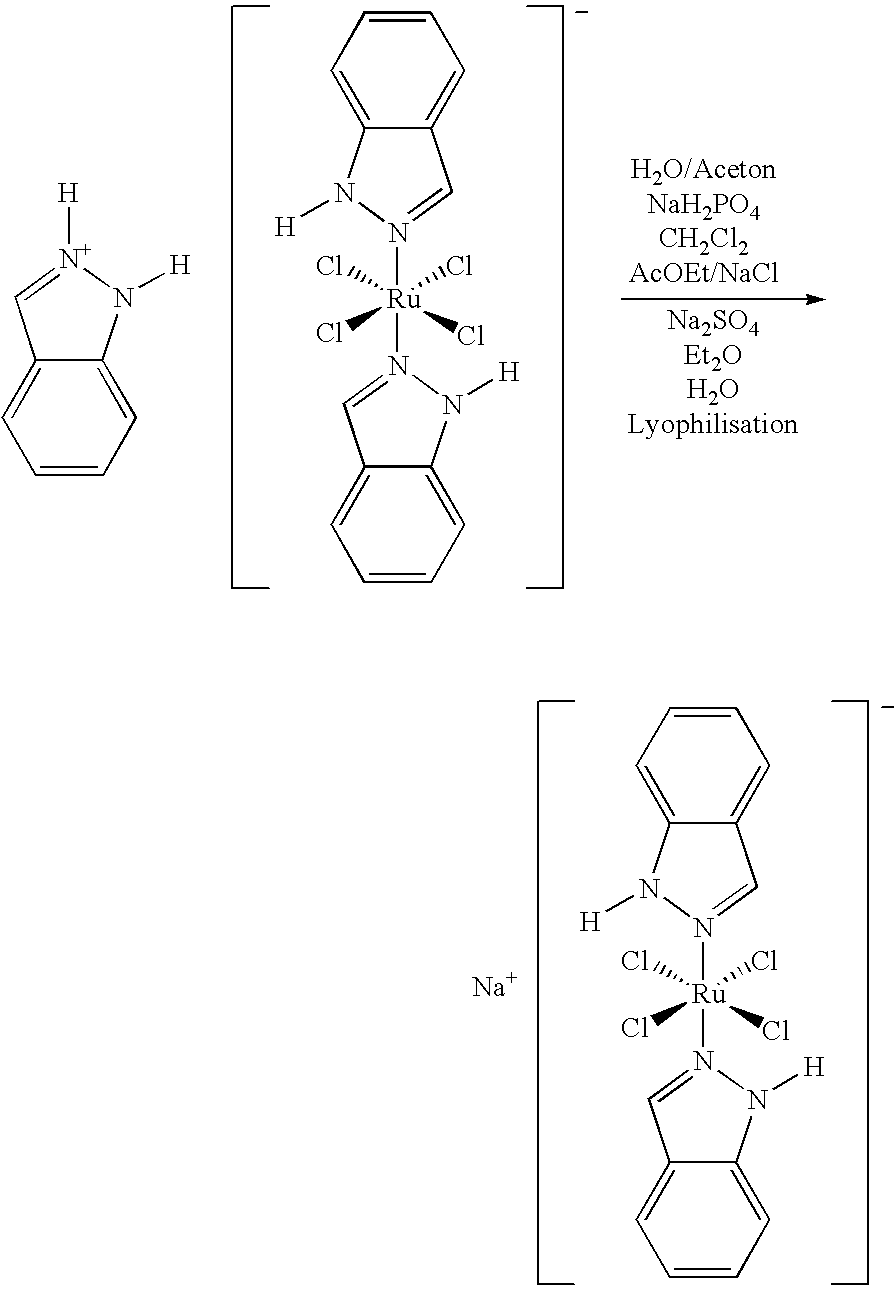
Method of manufacturing a ruthenium complex
A method of making an alkali metal salt of trans-[tetrachlorobis(1H-indazole)ruthenate (III)] is disclosed.
Owner:NIIKI PHARMA ACQUISITION CORP 2
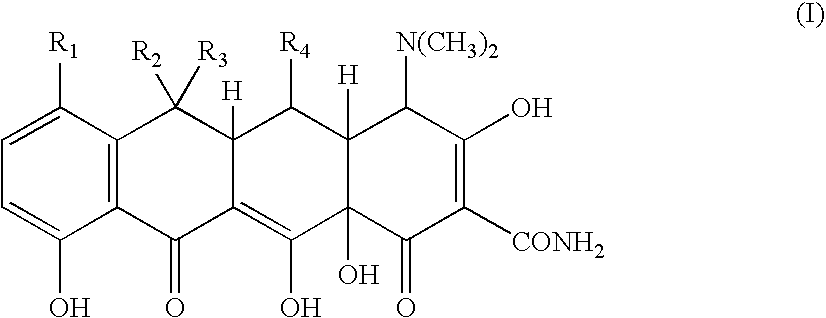
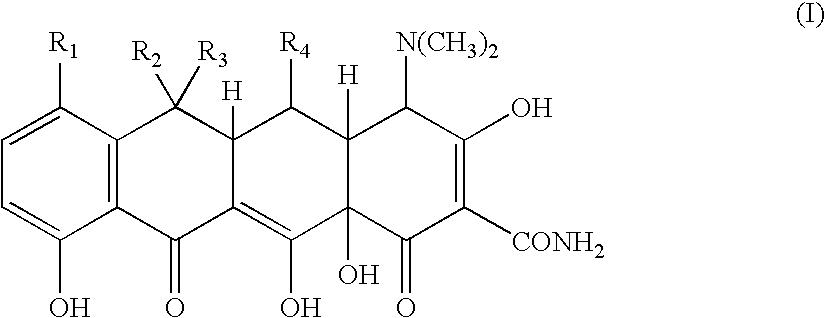
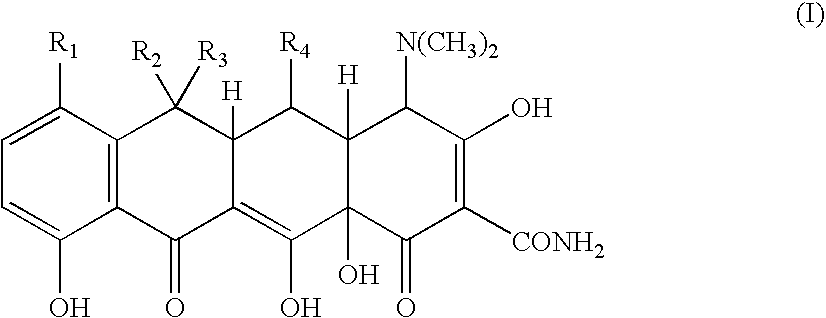
Tetracycline metal complex in a solid dosage form
The present invention is a solid dosage form of a metal complex of a tetracycline of Formula (I) for pharmaceutical administration, wherein R1=Cl, N(CH3)2, or H; R2=CH3, H, or CH2═; R3=CH3, H, OH, or absent; and R4=OH or H, with the proviso that if R2 is CH3 and R3 is H, then R4 is not OH.
Owner:WARNER CHILCOTT CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com