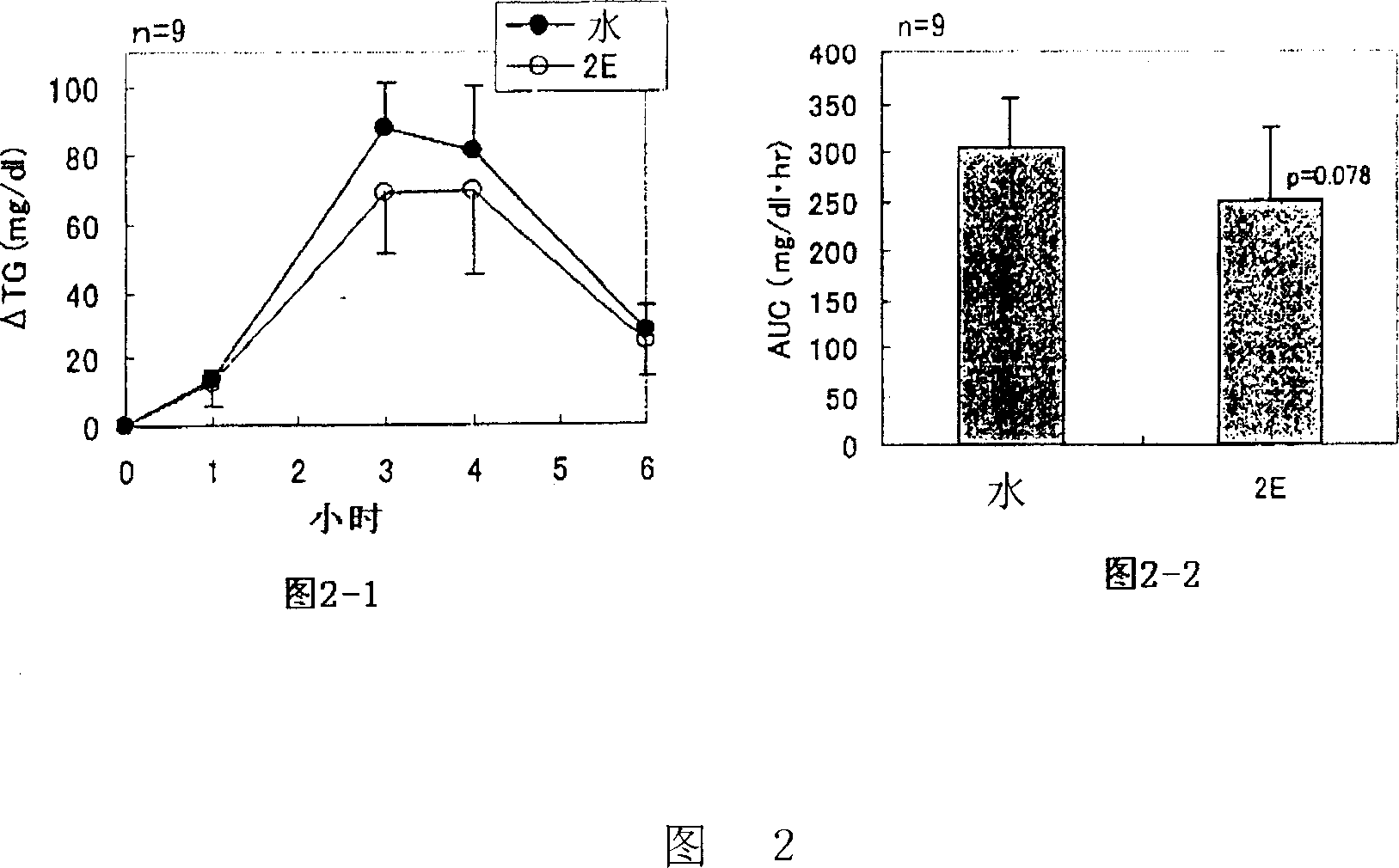
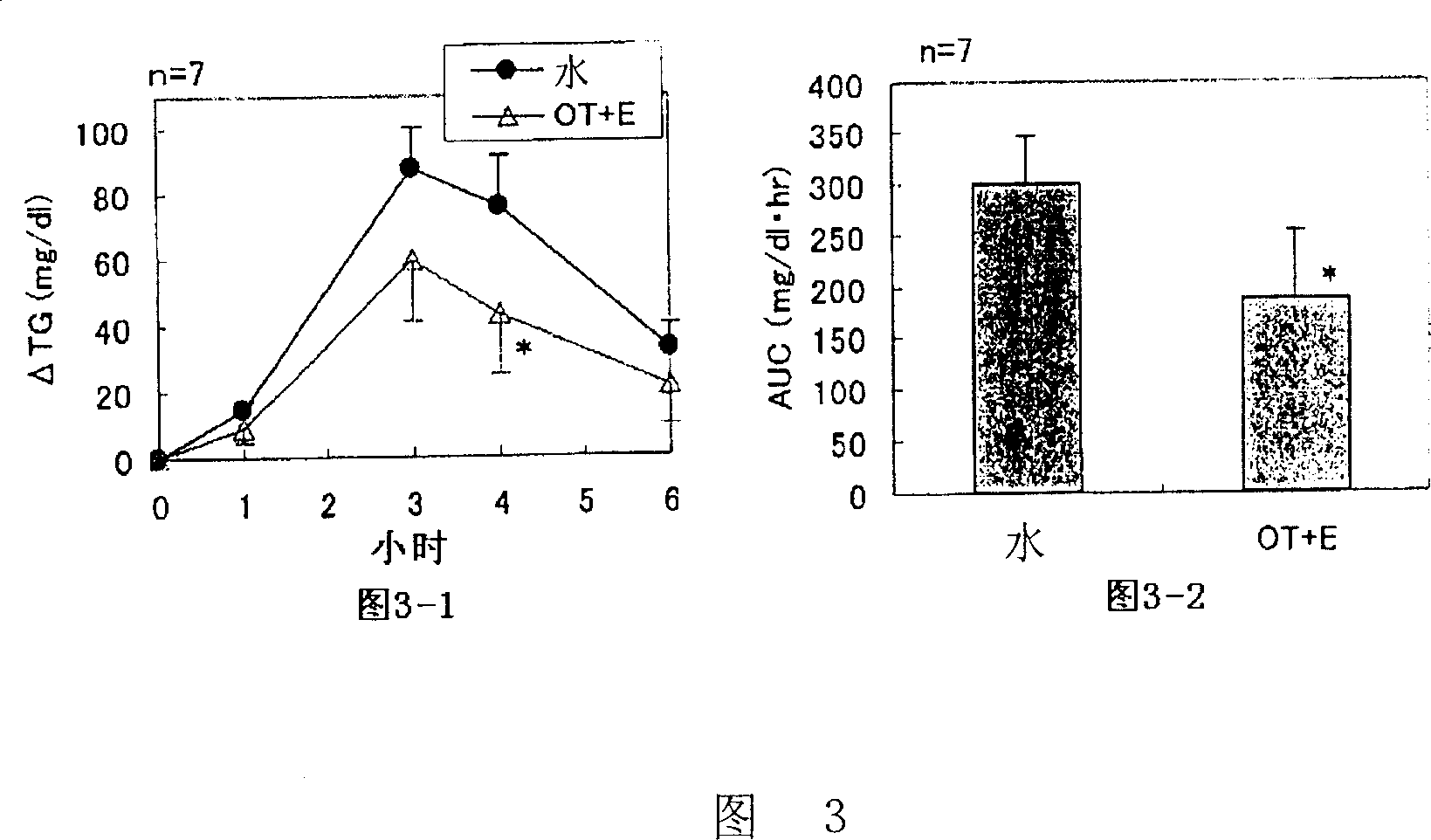
Lipase activity inhibitor containing high-molecular weight polyphenol fraction, tea extract and process for producing the same
A technology of activity inhibitor and tea extract, which is applied in the field of lipase activity inhibitor, tea extract and its manufacture containing high molecular polyphenol components, can solve unknown problems and achieve high safety, The effect of inhibiting lipase activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] tea extraction
[0069] (1) The extraction efficiency of solid components in oolong tea was compared when 1.67 g of sodium bicarbonate was dissolved in 1 L of warm water at 90°C (pH value was 8.22) and when no sodium bicarbonate was added (pH value was 6.79). 100 g of oolong tea leaves were added to each of 1 L of warm water, and the mixture was extracted by stirring slowly for 20 minutes while maintaining the temperature at 90°C.
[0070] When measuring the Brix concentration and pH value of the extract, the Brix was 3.76 and the pH value was 5.06 without sodium bicarbonate, and the Brix was 4.27 and the pH value was 6.15 when sodium bicarbonate was added. As a result of using sodium bicarbonate, it can be clearly seen from the appearance that a concentrated extract is obtained, and this increase in the extraction of solid components can also be confirmed from the Brix value.
[0071] (2) Dissolve 1.67 g of sodium bicarbonate in 1 L of warm water at 90° C., and add 10...
Embodiment 2
[0080] separate
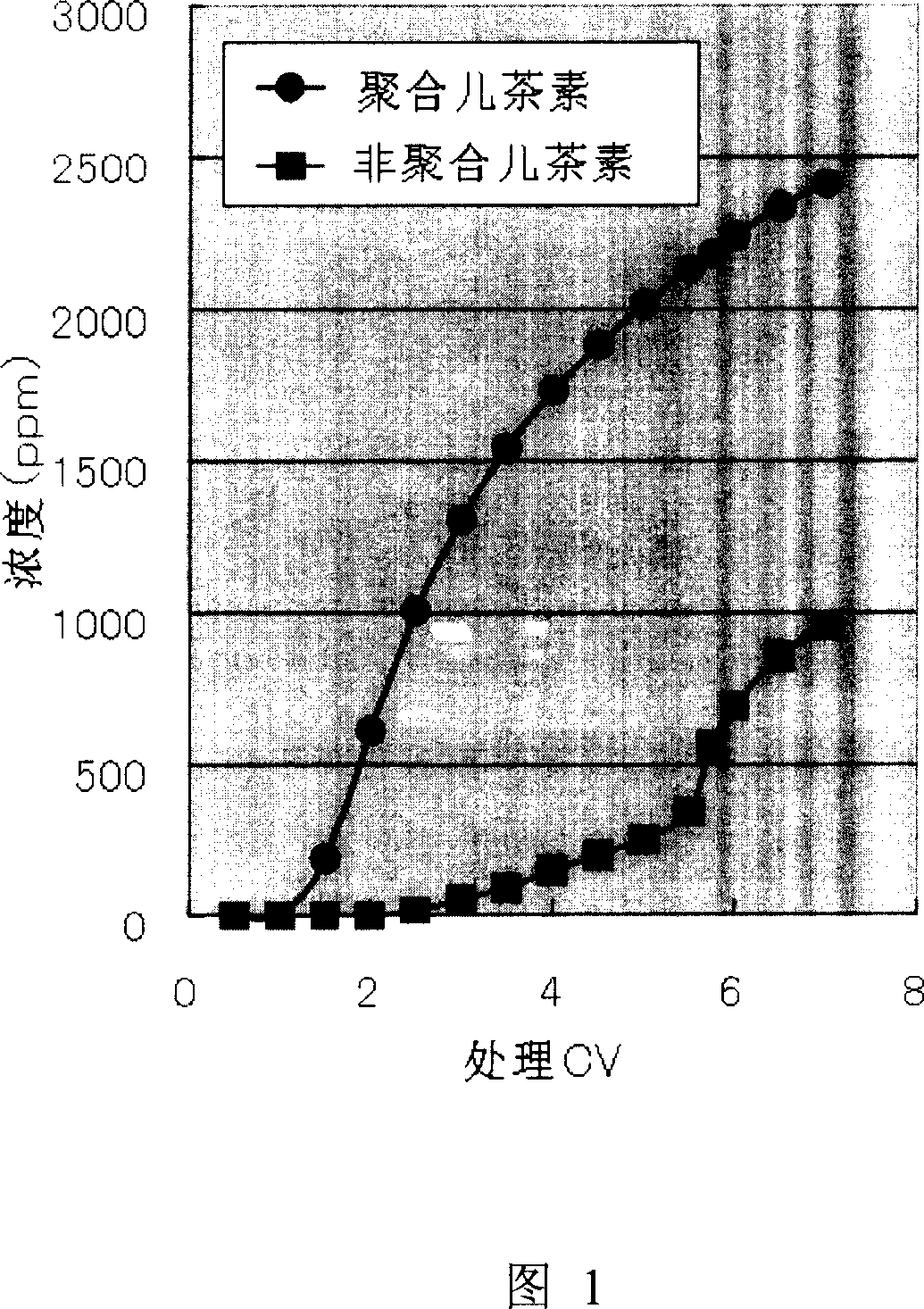
[0081] After degassing, 50 ml of commercially available granular activated carbon (for example, GW-H32 / 60 manufactured by Kuraray Co., Ltd.) was packed into a chromatography column. Here, the oolong tea extract obtained in Example 1 was used to flow at a flow rate of SV=3, and the components were separated. At this time, the temperatures of the extract and the column were set at 20, 40, 50, and 60° C., and the analytical values of the separated liquids separated into about 5 CV are shown in Table 2.
[0082] polymerized catechin
[0083] In this way, the higher the temperature is, the more selectively the non-polymerized catechin can be separated and removed during separation. Figure 1 shows an example of changes in components during separation at 60°C.
Embodiment 3
[0085] Trial manufacturing
[0086] With 0.15% sodium bicarbonate solution (95 DEG C), 600kg of oolong tea leaves are extracted by chromatographic column method to obtain about 6000Kg of extract. The liquid temperature was kept at 60 to 65° C., and non-polymerized catechin and caffeine were selectively removed by passing through 400 kg of granular activated carbon (GW-H32 / 60 manufactured by Kuraray Co., Ltd.). The passage liquid was concentrated under reduced pressure to prepare about 900 kg of a tea extract having a Brix of 10 or more.
[0087] The polymerized catechin (OTPP) in the obtained tea extract was 14648 ppm, and the adsorbed catechin (EGCG+GCG+ECG+CG) was 366 ppm accordingly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com