Identification of SNPs associated with hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia and defective carbohydrate metabolism
A technology for hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, applied in the field of diagnostic compositions, capable of solving problems such as impossible diagnosis or treatment of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
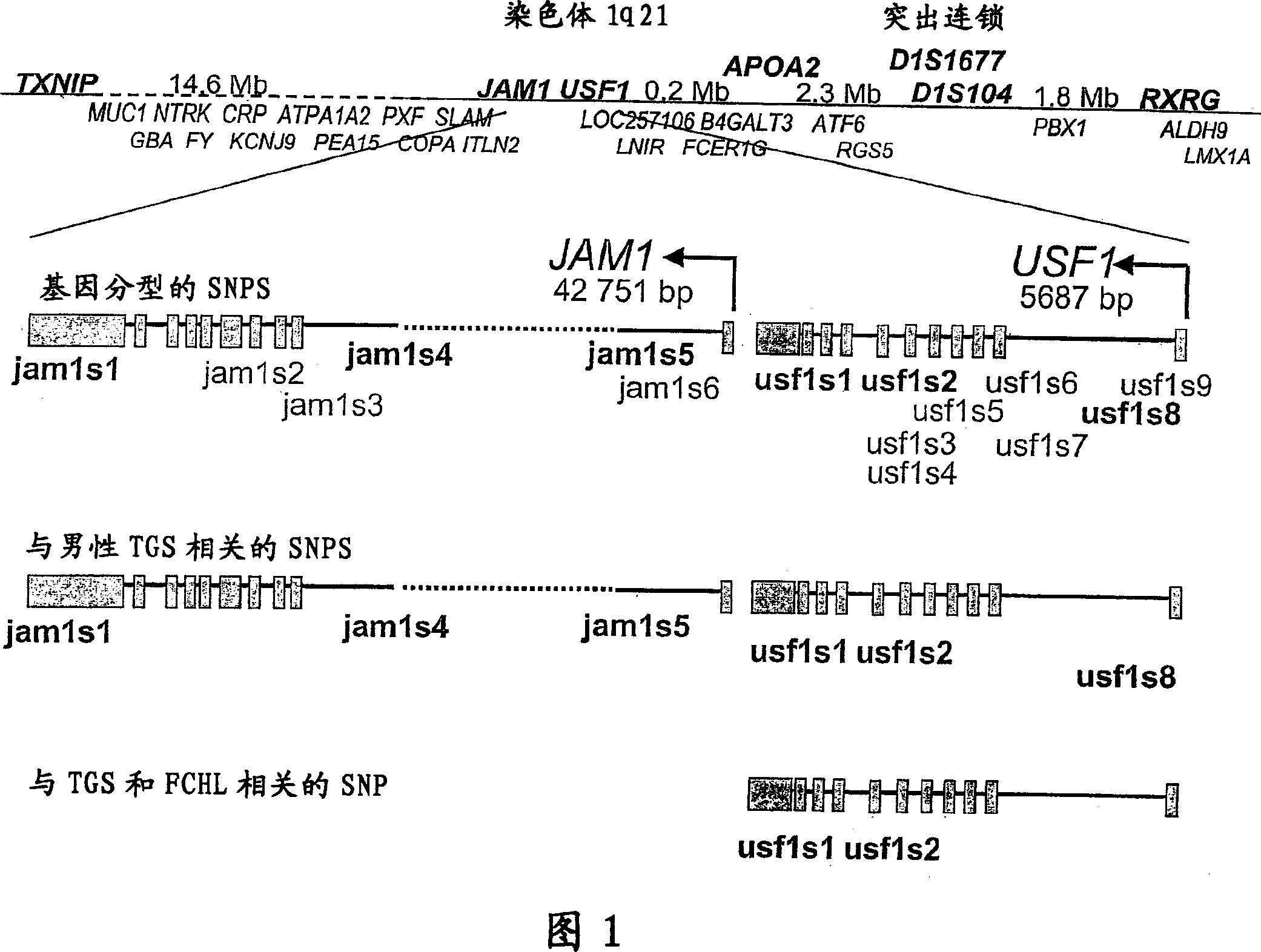
[0178] Example 1: The test program of Examples 2-5. All FCHL families analyzed have probands with severe CHD and lipid phenotype, and an average of 5-6 family members with FCHL. These FCHL families showing extreme and well-defined disease phenotypes were analyzed to identify potential genes on 1q21 that cause FCHL. We selected the regional candidate gene method and sequenced 4 candidate genes of functionally related regions on 1q21. The TXNIP, USF1, retinoic acid X receptor gamma (RGRG) and apolipoprotein A2 (APOA2) genes were sequenced to identify all possible variants. Among these genes, TXNIP initially represented the most promising position candidate gene, because it has been shown to be the basis for the genotype of mixed hyperlipidemia in mice. 17 . Based on their functional candidacy and the close locations (4 , And the 10 most promising SNPs from an expanded sample of 721 family members from 60 FCHL families (see below). The results of the 60 SNPs are shown in Supplementar...
Embodiment 2
[0181] Example 2: USF1 gene as a candidate gene
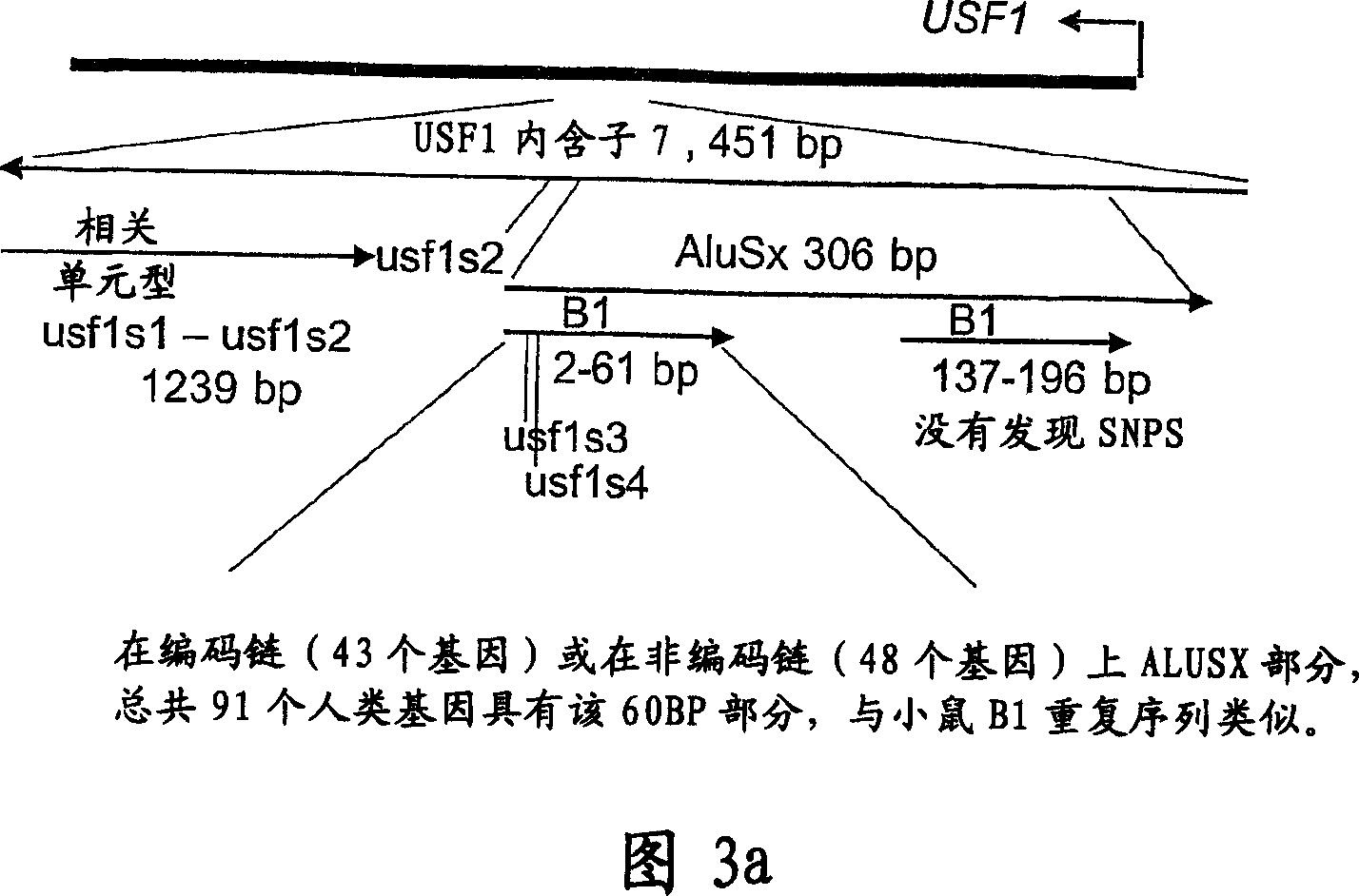
[0182] We identified a total of 23 SNPs of the 5867bp sequence of the USF1 gene (Supplementary Table 2): 3 of them are silent variants in exons, and the rest are located in non-coding regions and putative promoters. Eight of the 23 SNPs are new. Initially, we genotyped the SNPs in the USF1 gene: usf1s1 (exon 11), usf1s2 (intron 7) and usf1s7 (exon 2) (Table 2-3 shows the genotyped The corresponding rs number of SNPs).
[0183] Table 1: Multipoint HHRR and gamete competition analysis of usf1s1 (=RS3737787) and usf1s2 (=RS2073658) SNPs
[0184] TCHL all
TG all
FCHL men
TG man
Multiple HHRR
Gamete competition
ns(ns)
0.00002
(0.005)
0.05(ns)
0.00006 (0.008)
0.009(ns)
0.0004
0.04)
0.00003(0.003)
0.0000009
(0.004)
Progressive p-value
Gamete competition
0.00004
0.00006
0.0004
0.00001
(Gene drooping)
Test p value
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0197] Example 3: Haplotype analysis of JAM-USF1 gene region
[0198] Using the HBAT program, we obtained evidence of shared haplotypes in the usf1s1 and usf1s2 regions (Table 3). These observations are supported by multiple HHRR analysis (Table 3). For haplotype 1-1 (1 indicates a common allele), using -o selection results in a p-value of 0.0007.
[0199] Table 3 Haplotype analysis in men affected by TG using the HBAT program (the results of multi-locus GENO-PDT and multiple HHRR are given below for comparison)
[0200] Test
[0201] This choice not only measures the preferential inheritance of sensitive haplotypes to the sick, but also estimates its less preferential inheritance to the unaffected, making it useful here, because the unaffected individuals in these expanded families also contain important information. Table 3 also shows the results of HBAT-e selection and the correlation test for specific linkages. Since this test counts the implicit conditions in the li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com