Method of barrier layer surface treatment to enable direct copper plating on barrier metal
A metal surface and metal technology, applied in the field of barrier layer surface treatment, can solve the problem of difficult seed crystal stage coverage and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
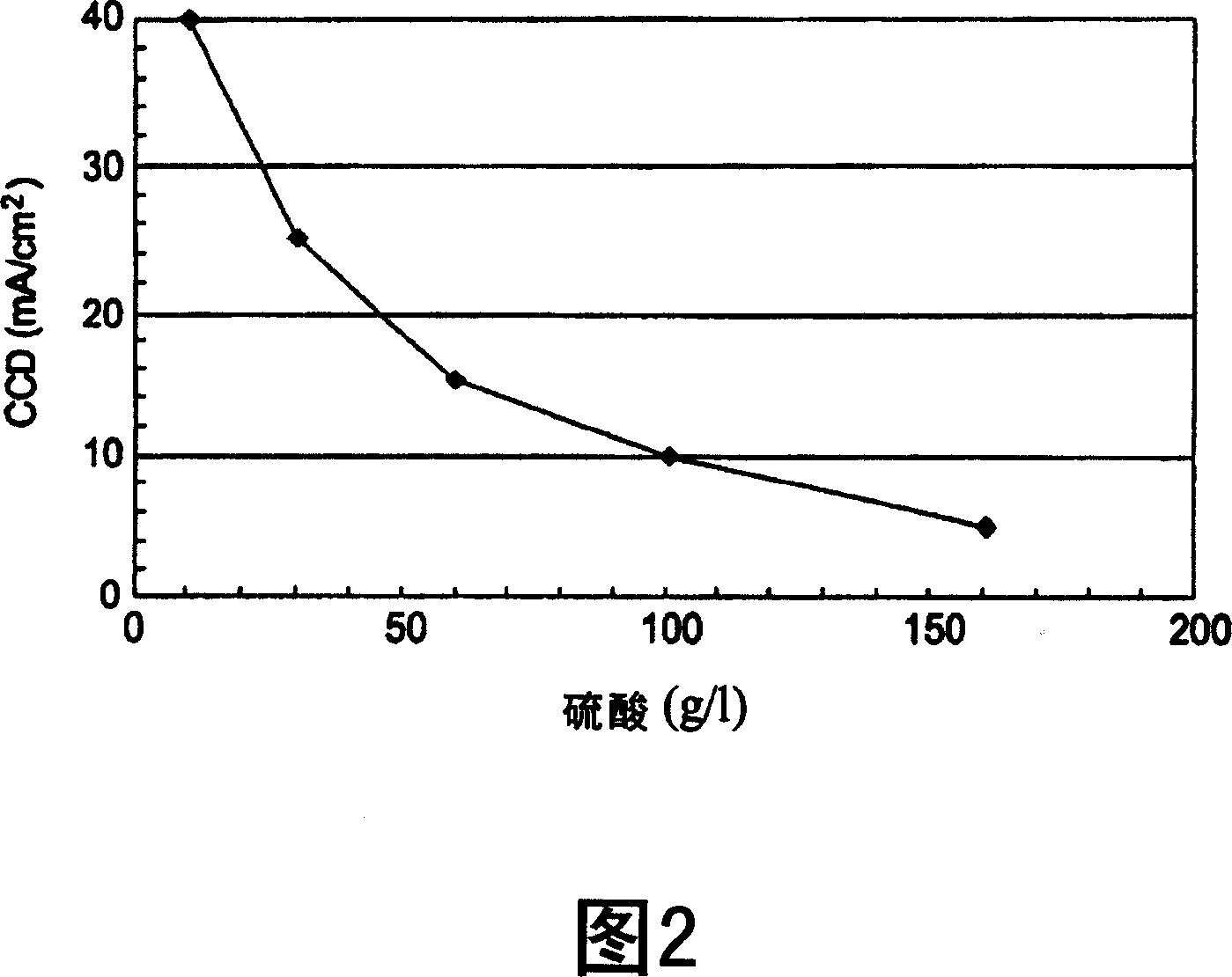
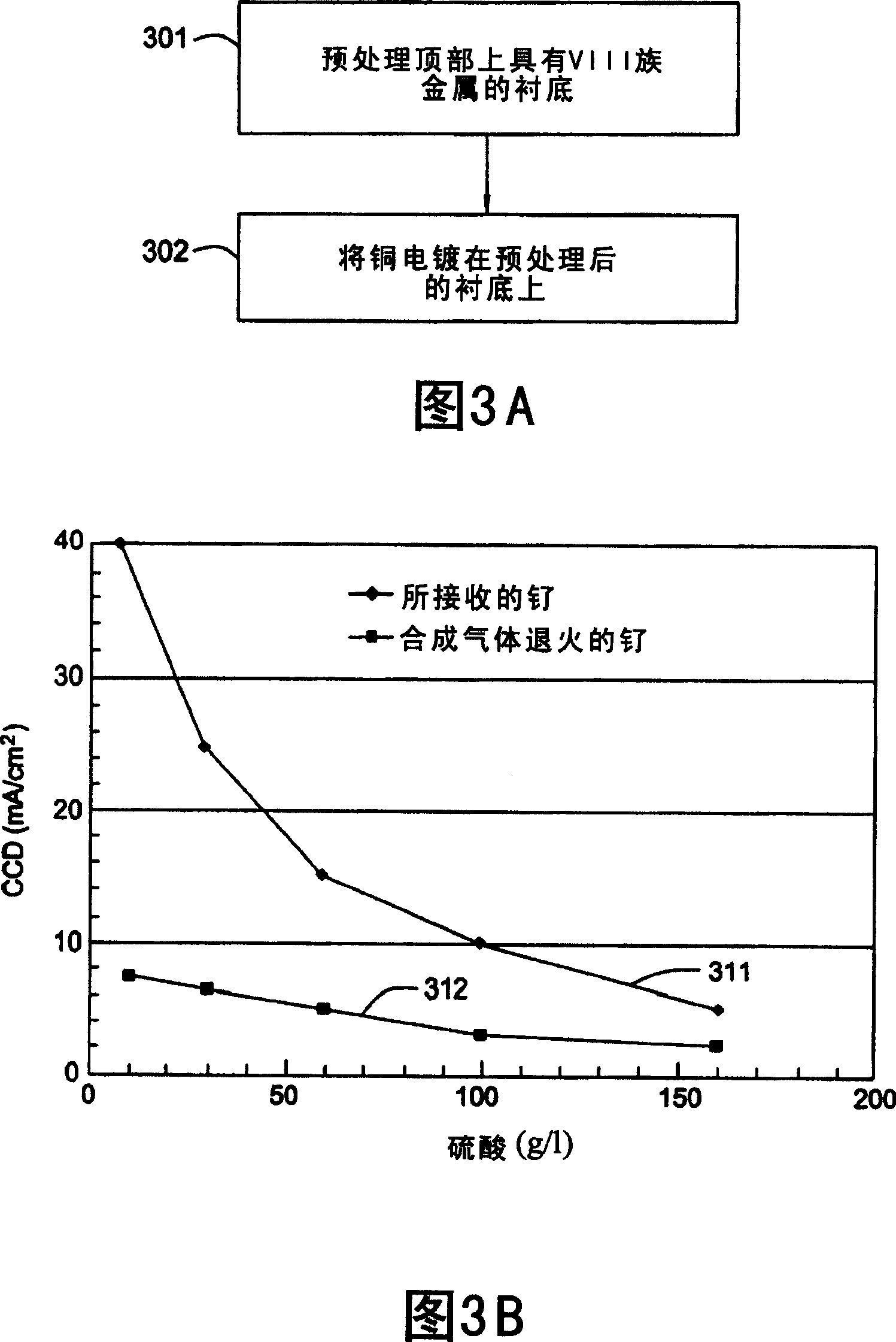
[0020] Ruthenium (Ru) thin films deposited by CVD, ALD or PVD may be potential candidates for seedless diffusion barriers between intermetal dielectrics (IMDs) and copper interconnects for sub-45nm technologies. Ruthenium is a Group VIII metal with low resistivity (resistivity ~7 μW-cm) and high thermal stability (high melting point ~2300°C). Ruthenium is relatively stable even in the presence of oxygen and water at ambient temperature. Ruthenium has twice the thermal and electrical conductivity of tantalum (Ta). Ruthenium does not form alloys with copper below 900°C and exhibits good adhesion to copper. Accordingly, the semiconductor industry has become interested in using ruthenium as a copper barrier layer. The low resistivity of ruthenium is an advantage when attempting to fill ruthenium-coated features with copper without a seed layer.
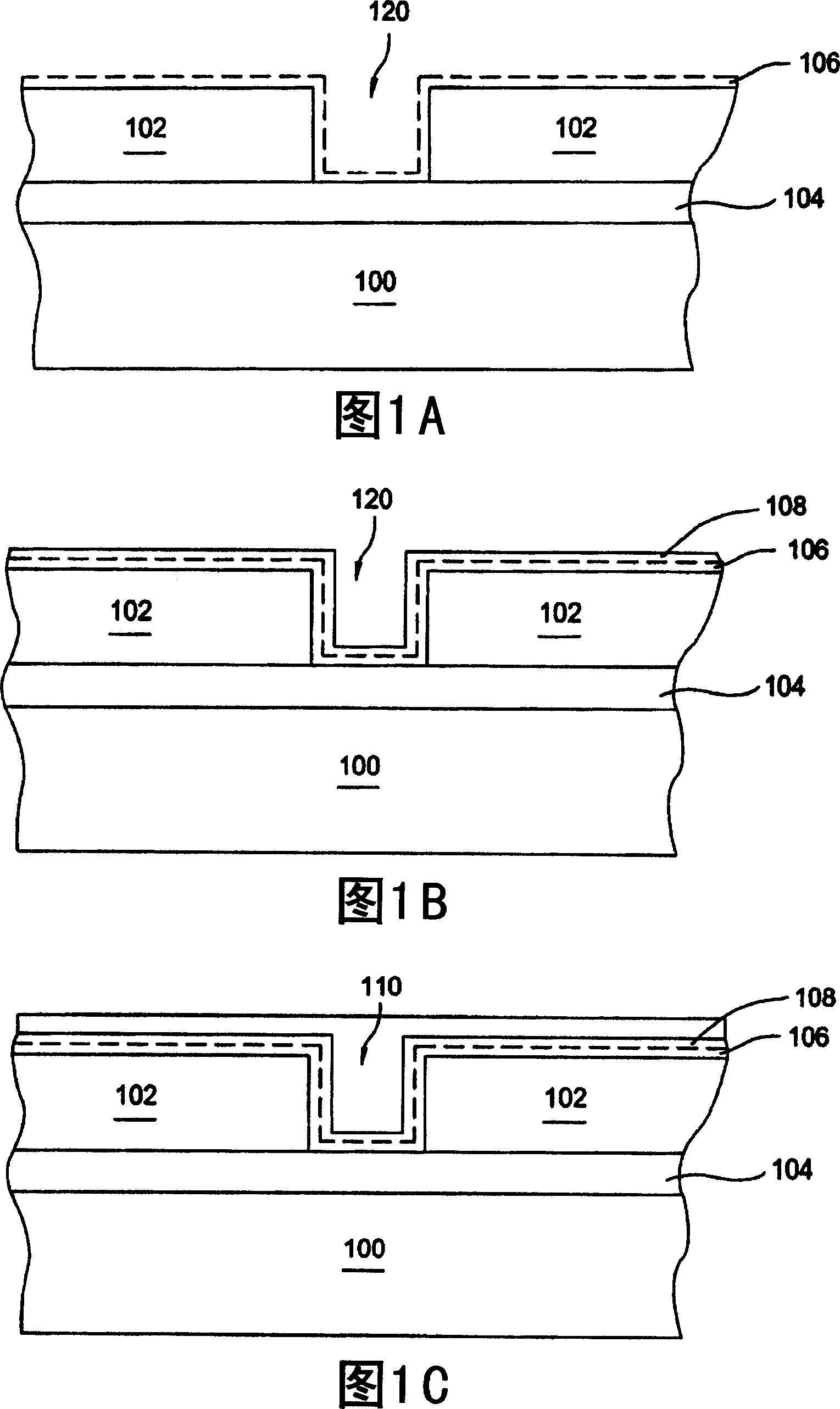
[0021] 1A-1C illustrate cross-sectional views of a substrate at various stages in a copper interconnect fabrication sequence incorpor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com