Anti-scatter-grid
An anti-scatter grid, X-ray technology, applied in radiation/particle processing, using diaphragm/collimator, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, small pixel size, difficult to make metal foil, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
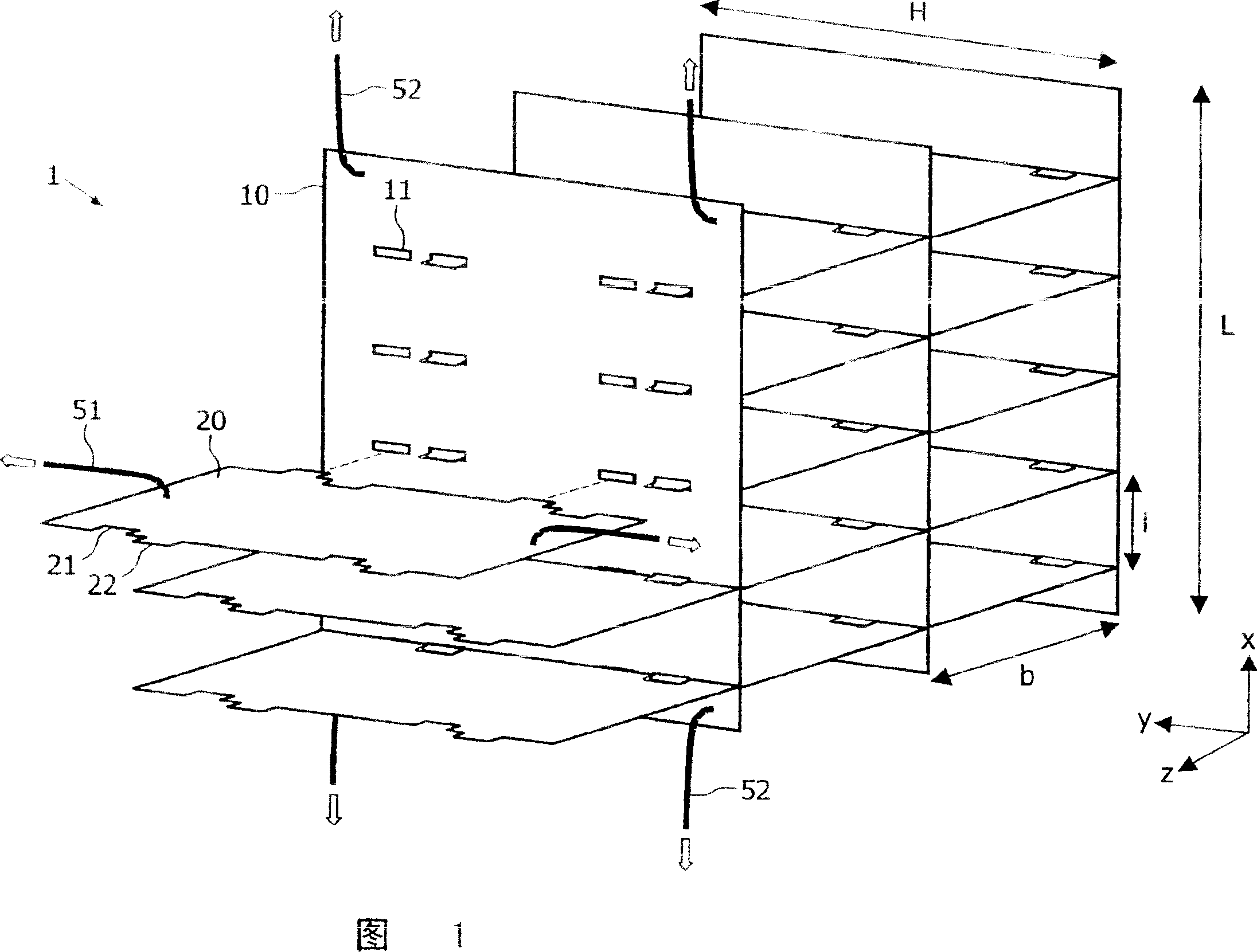
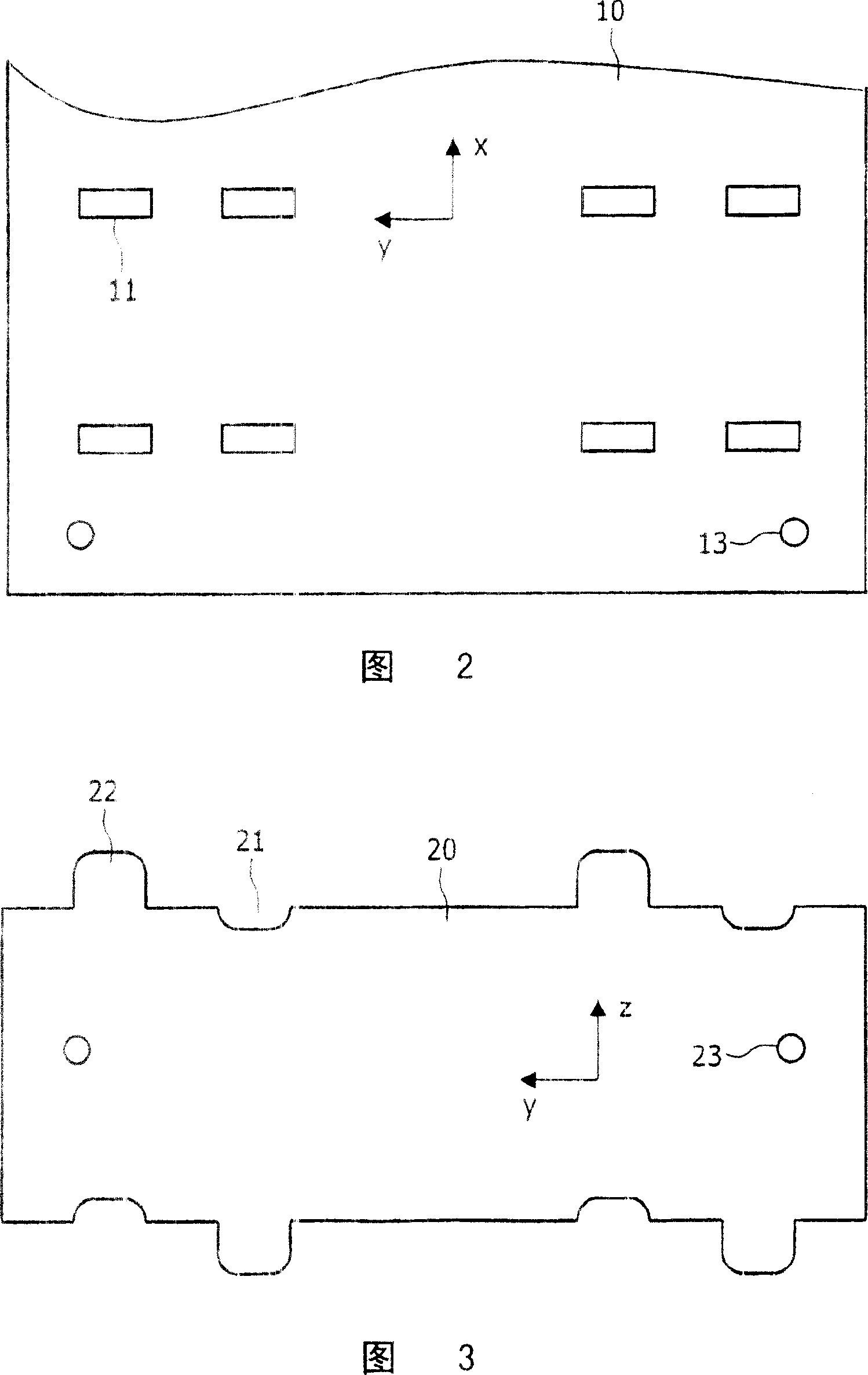
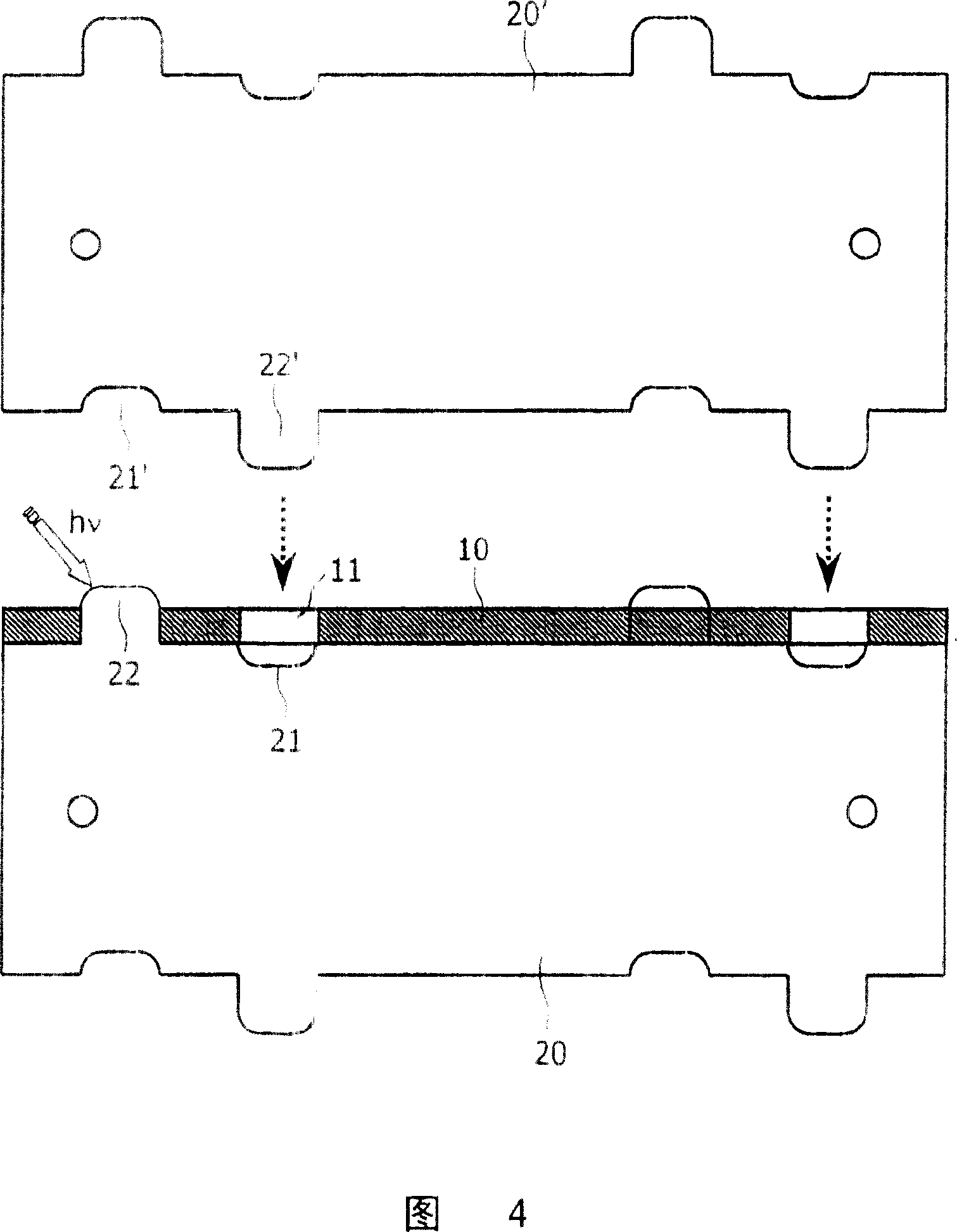
[0036] Figure 1 shows a part of an anti-scatter-grid 1 in a partially assembled state. The grid is said to be "two-dimensional" because it comprises walls 10, 20 running in two perpendicular directions x, z. These walls form a rectangular grid or matrix of channels through which radiation (eg X-rays) can pass in the y-direction to components placed behind the grid (eg detectors, not shown). Rays that are not aligned with the channels of the anti-scatter grid 1 will be absorbed when they hit the grid walls. The material of the walls 10, 20 is usually a metal with a high absorption coefficient for the radiation to be filtered, for example a heavy metal like tungsten or molybdenum in the case of X-rays. Furthermore, it should be noted that this figure represents only a small portion of an anti-scatter grid, which typically includes hundreds or thousands of channels. The height H of the anti-scatter grid corresponds to the length that the rays must pass through the grid, usually...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com