Improvements in cancer treatment and cancer treatment efficacy prediction by blocking and detecting protease inhibitors
A protease inhibitor, inhibitor technology, applied in the field of cancer treatment, can solve problems such as apoptosis and loss of differentiation of breast epithelial cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0149] Establishment and determination of cell lines from genetically deleted animals
[0150] According to the present invention, in order to study the importance of specific gene products for the sensitivity of cancer to anti-tumor therapy, cell lines were established from wild-type and gene-deficient animals. These cell lines can then be used in screening systems to study the link between various anti-tumor treatments and cell death, as well as to identify blockers of the anti-apoptotic function of protease inhibitors.
[0151] This example describes the establishment and characterization of an immortal fibrosarcoma cell line from a mouse deficient in the PAI-1 gene.
[0152] mouse
[0153] Mice were placed on a 12-h day / night cycle and fed with normal chow. The generation of PAI-1- / - mice has been previously described (Carmeliet P et al., Dec 1993, J Clin Invest 92(6):2746-55). Mapping PAI-1 gene-mapped mice with META TM / Bom-nu(=META TM / Bomnu / nu) (Brünner N et al....
Embodiment 2
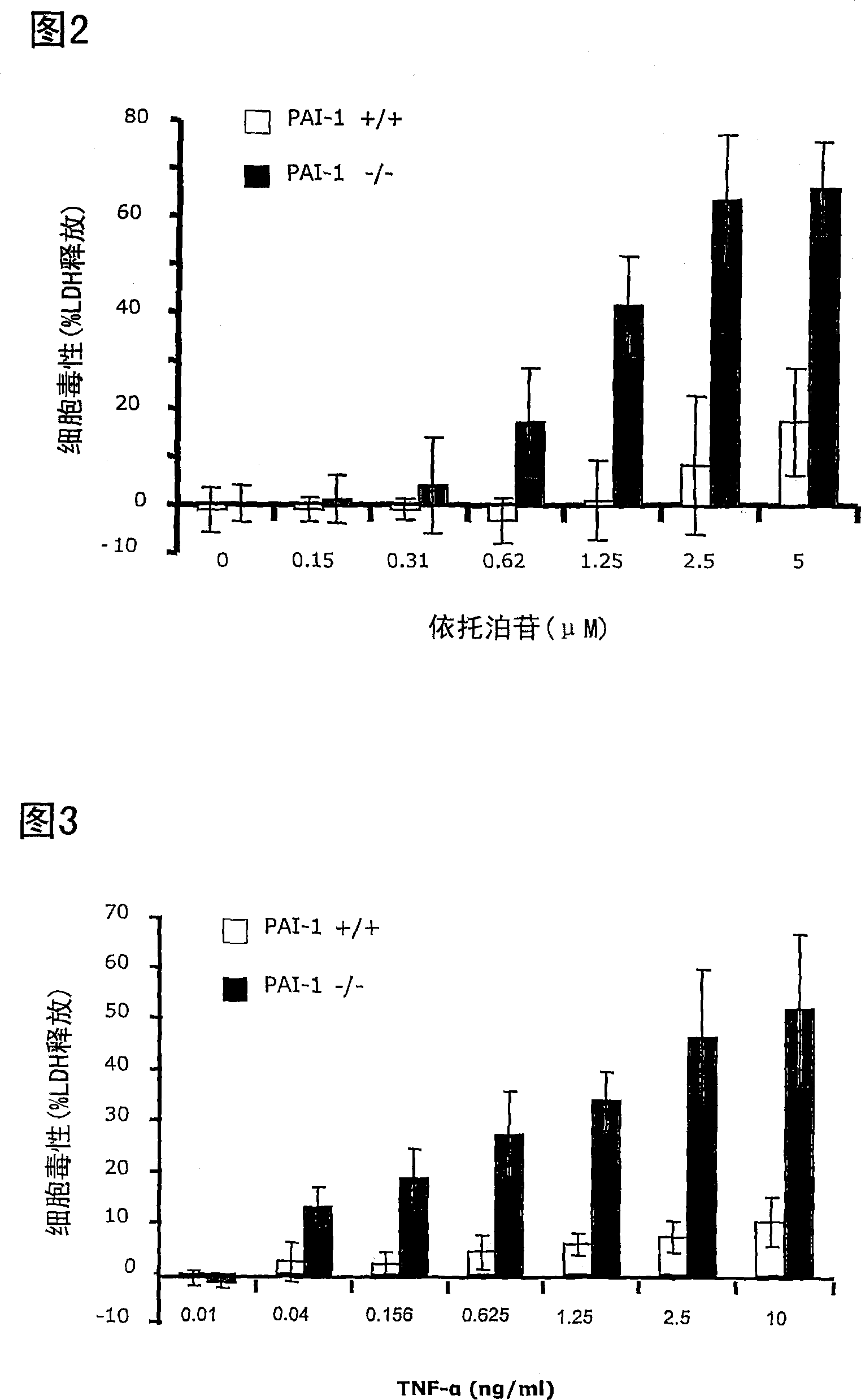
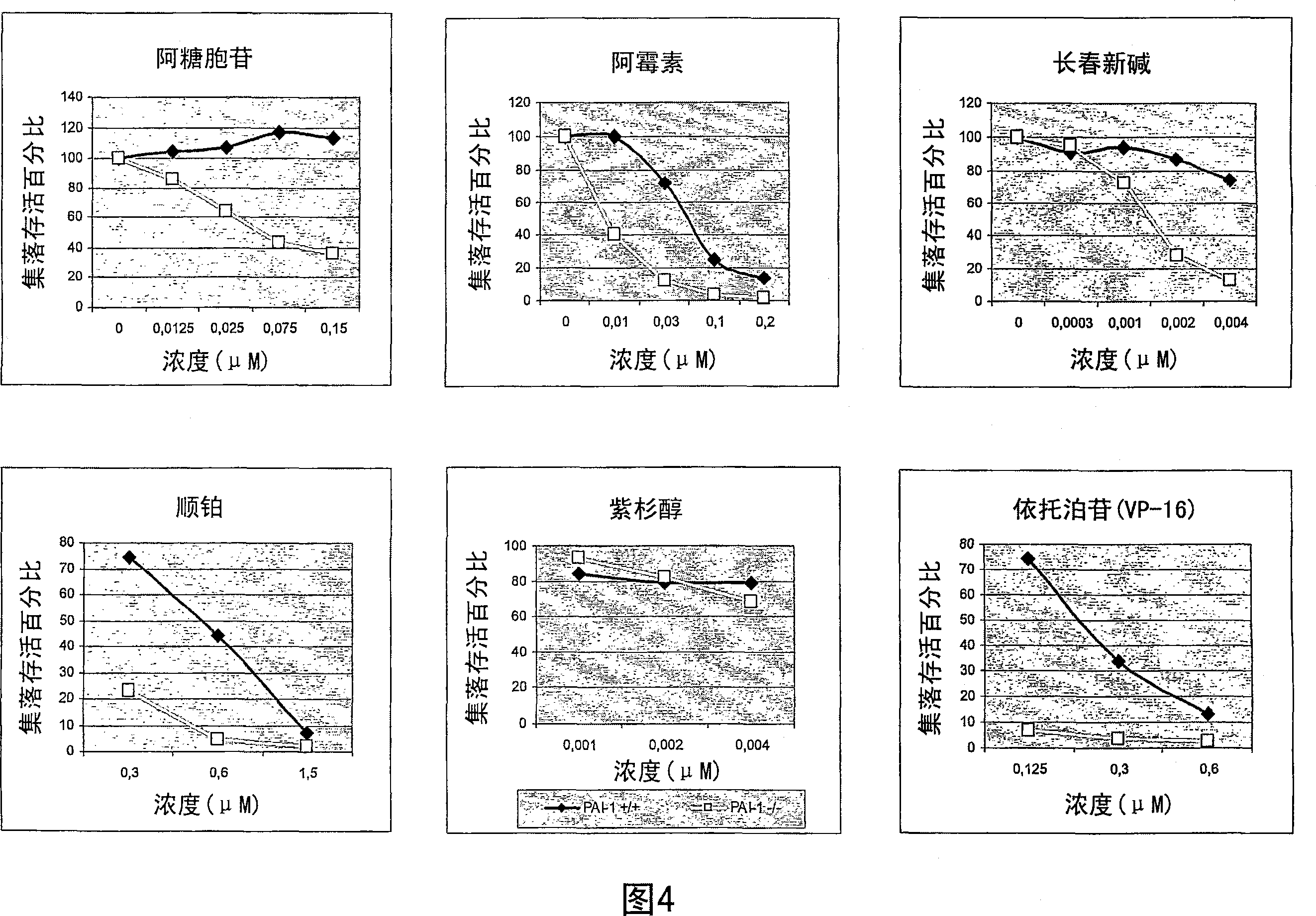
[0192] Testing the Chemosensitivity of Fibrosarcoma Cell Lines Using a Colony Formation Assay
[0193] A number of protease inhibitors have been described to protect cells from apoptosis. Because many types of antineoplastic treatments kill cells by inducing apoptosis, it can be expected that cell lines lacking expression of protease inhibitors will be more sensitive to antineoplastic treatments that induce apoptosis.
[0194] This example describes the detection of chemosensitivity of wild-type and PAI-1 gene-deficient cell lines to various cytotoxic drugs.
[0195] cell line
[0196] The cell lines described in Example 1 were used. The cells were at passage 35 (wild type cells) and passage 50 (cells lacking PAI-1 gene).
[0197] Colony Formation Assay
[0198] Drug (35 μl) and cells (0.35 ml) were mixed, and a mixture of 3.15 ml agar and medium was added thereto (agar: boil 990 mg Bacto agar and 30 ml PBS for 60 minutes; medium: heat M199 and FCS 10% to 37°C; mixtur...
Embodiment 3
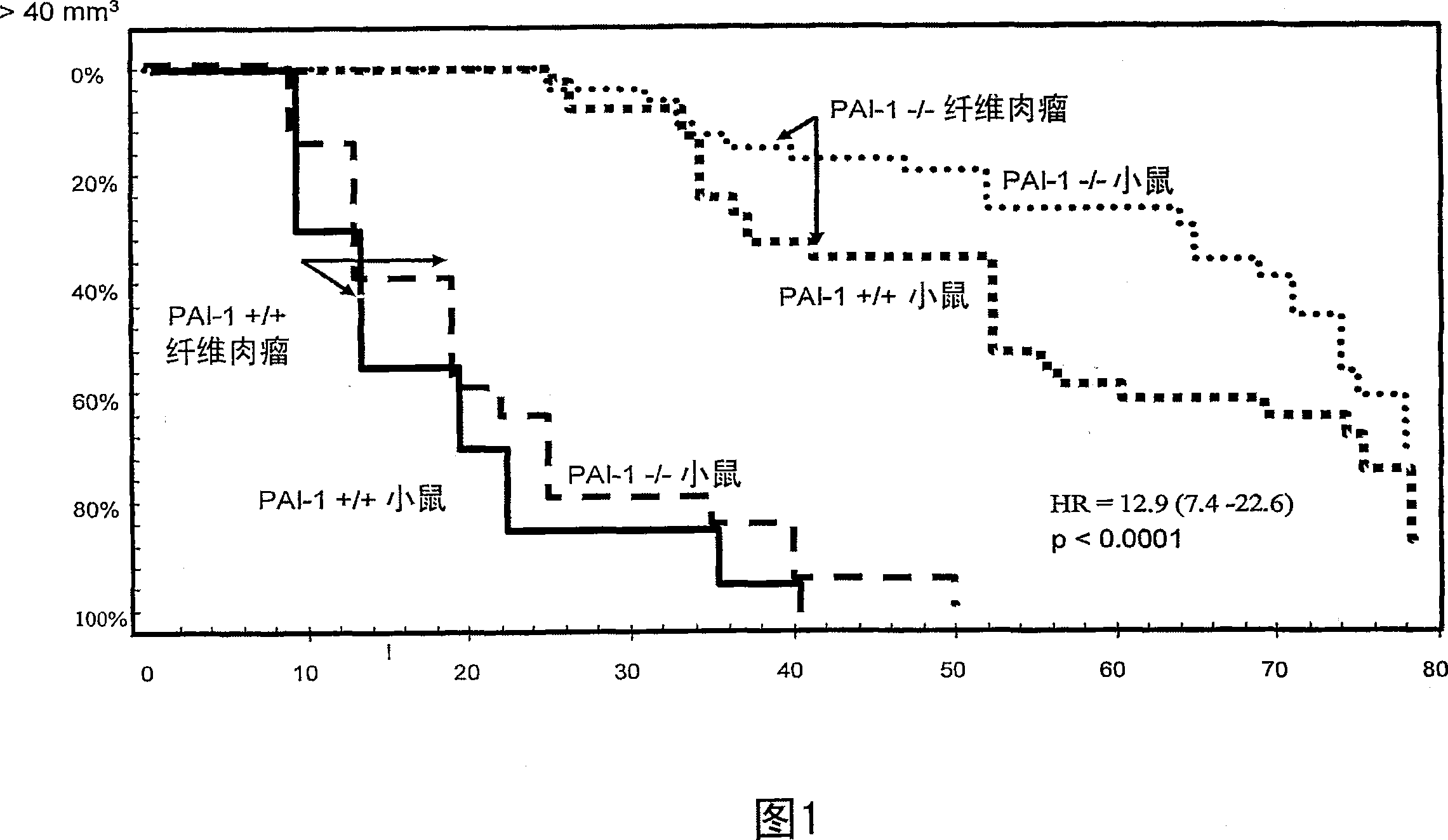
[0225] Effect of PAI-1 Gene Deletion on Etoposide Toxicity in Vivo (VP-16)
[0226] When a cytotoxic drug is administered systemically to a cancer patient, both cancer cells and normal cells elsewhere in the body are also affected by the drug's toxic effects. If cells are sensitized to the toxic effects of a drug, such sensitization will potentially affect cancer cells as well as normal cells.
[0227] In this example, we show that although sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs is enhanced in cancer cells lacking PAI-1 expression, this is not the case when toxicity is studied in normal cells.
[0229] We investigated sensitivity in intact mice by comparing sensitivity in body weight loss between PAI-1+ / + and - / - mice.
[0230] Further, blood was sampled at the nadir (day 3 (WBC)) and day 5 expected from hematological evaluation. The experimental drug used in this study was etoposide.
[0231] Mouse: META TM / Bom nu / nu; PAI-1+ / + and PAI-1- / -. Siz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com