Patents
Literature
41 results about "Deficient cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for treating cell proliferative disorders and viral infections
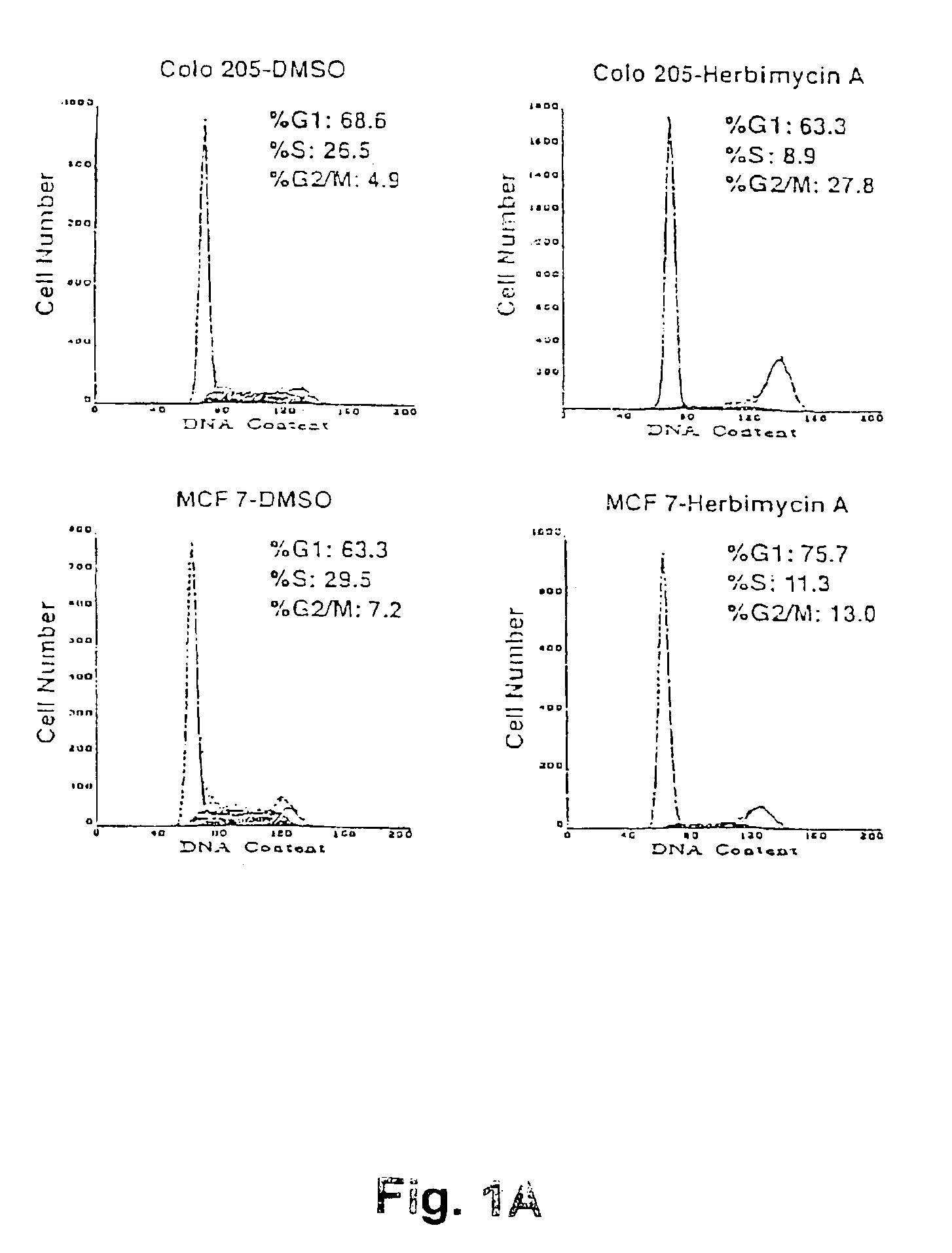
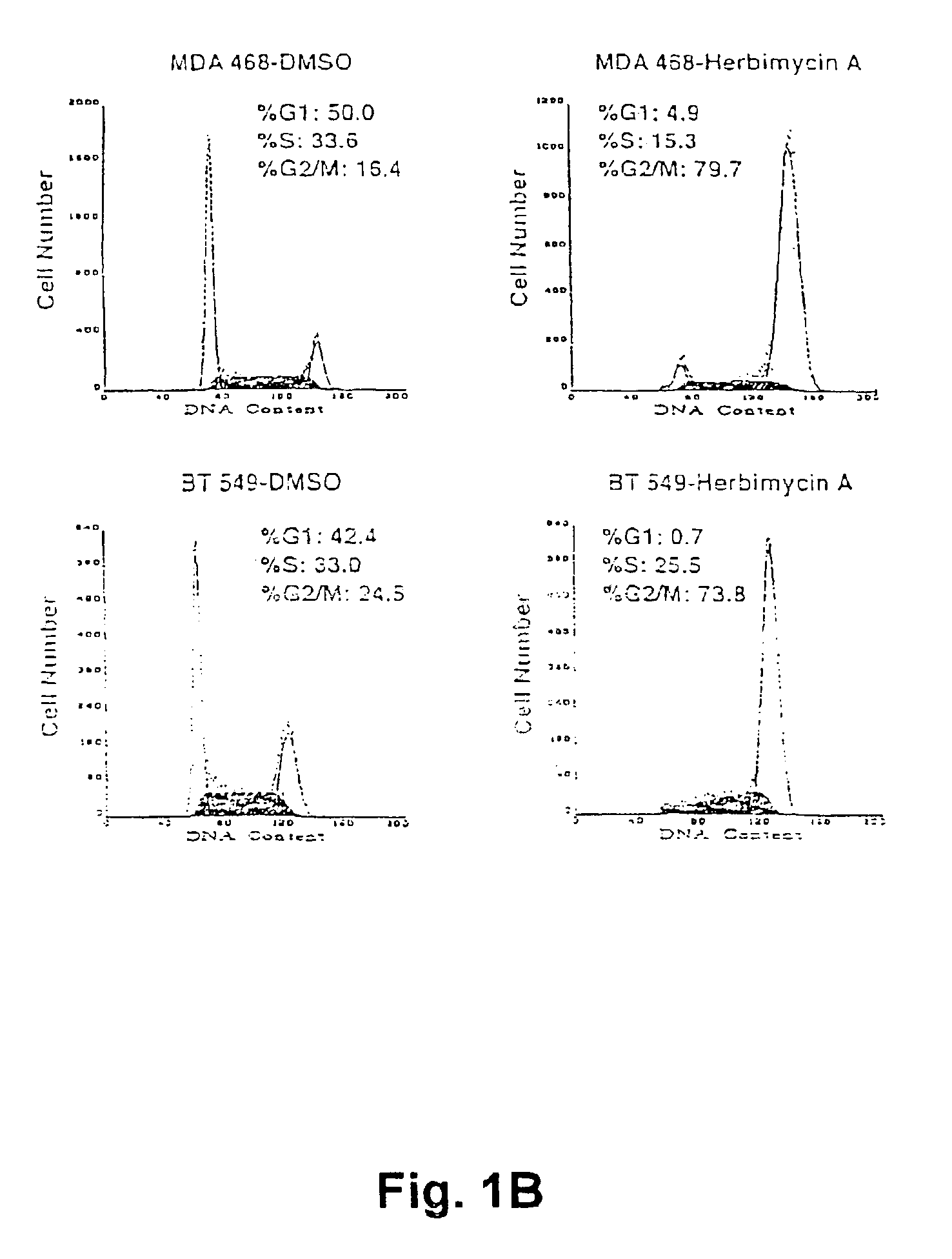
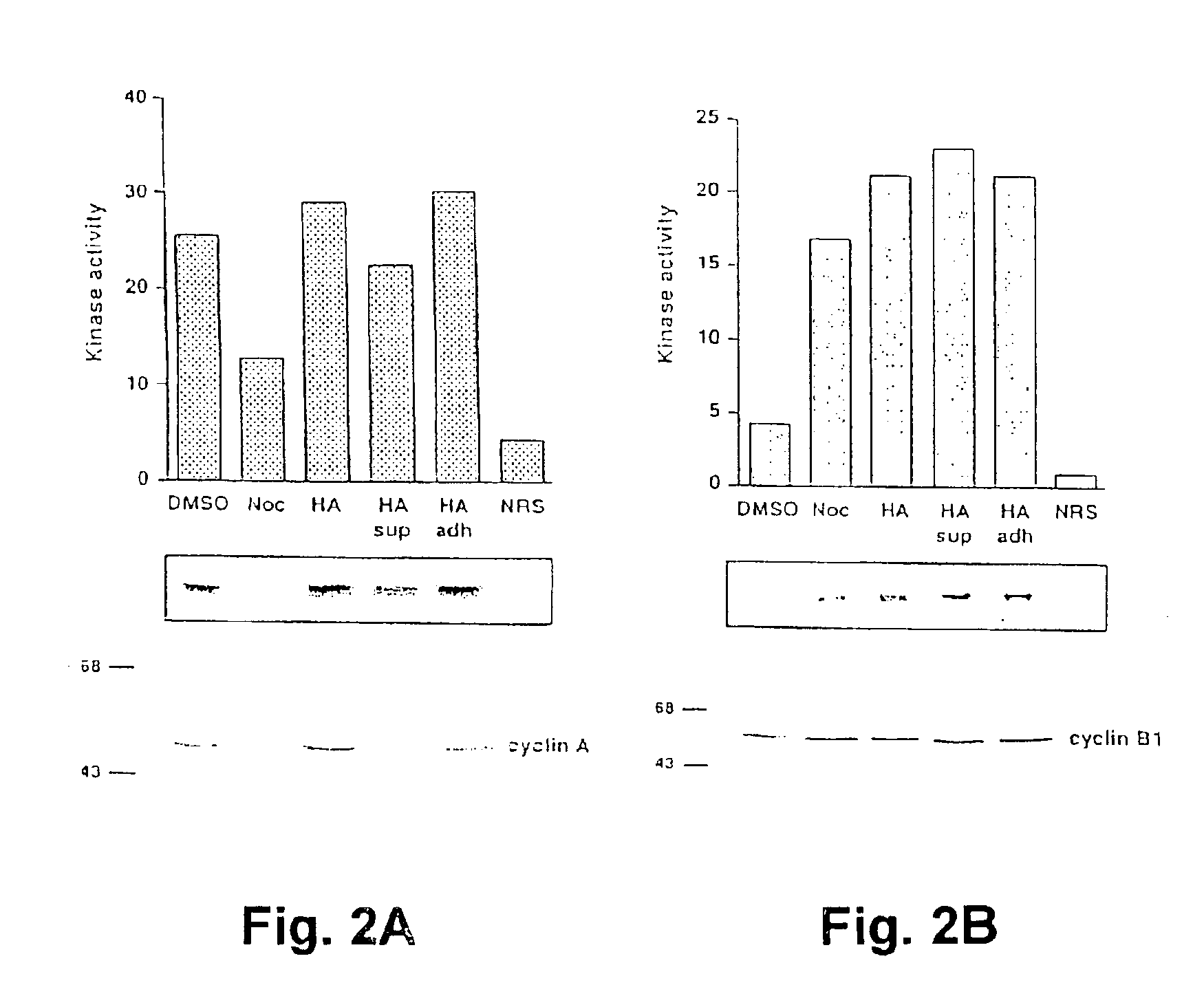
The present invention concerns methods for treating cell proliferative diseases, tumors associated with viral infections, and certain viral infections. The disclosed methods use compounds which inhibit heat shock protein 90 proteins. Such methods block Rb negative or deficient cells in the G2 / M phase of the cell cycle and rapidly causes their destruction.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
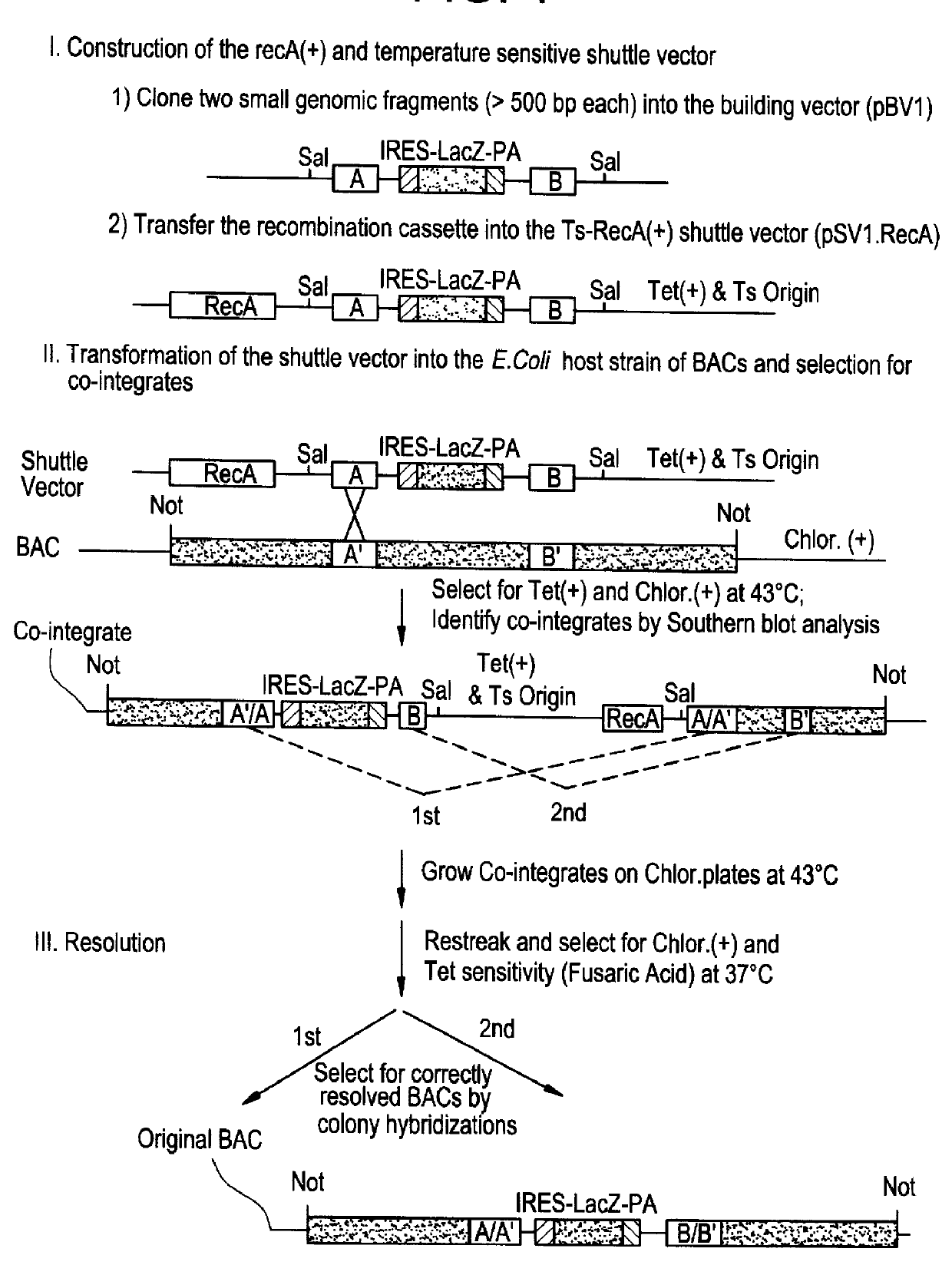
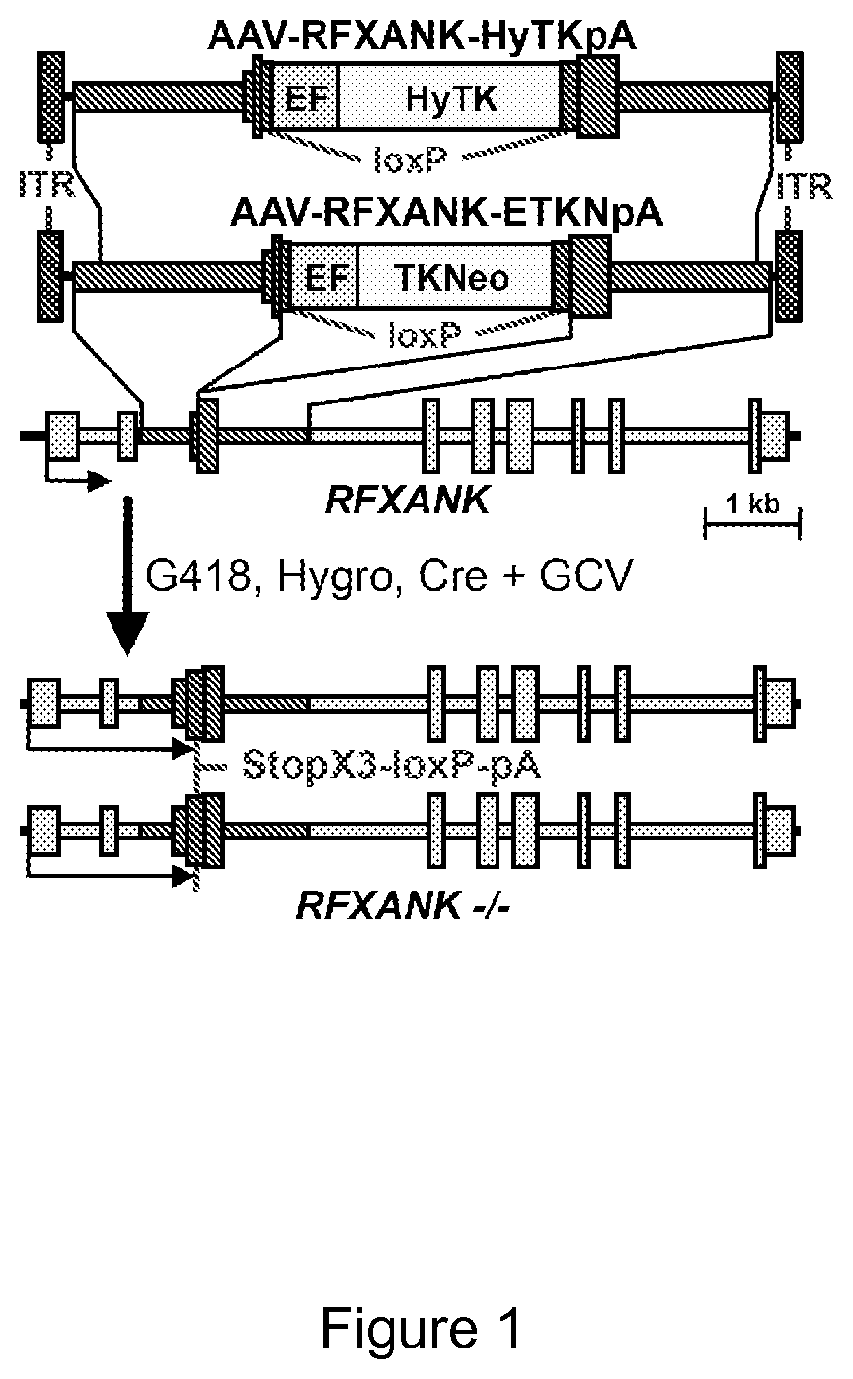
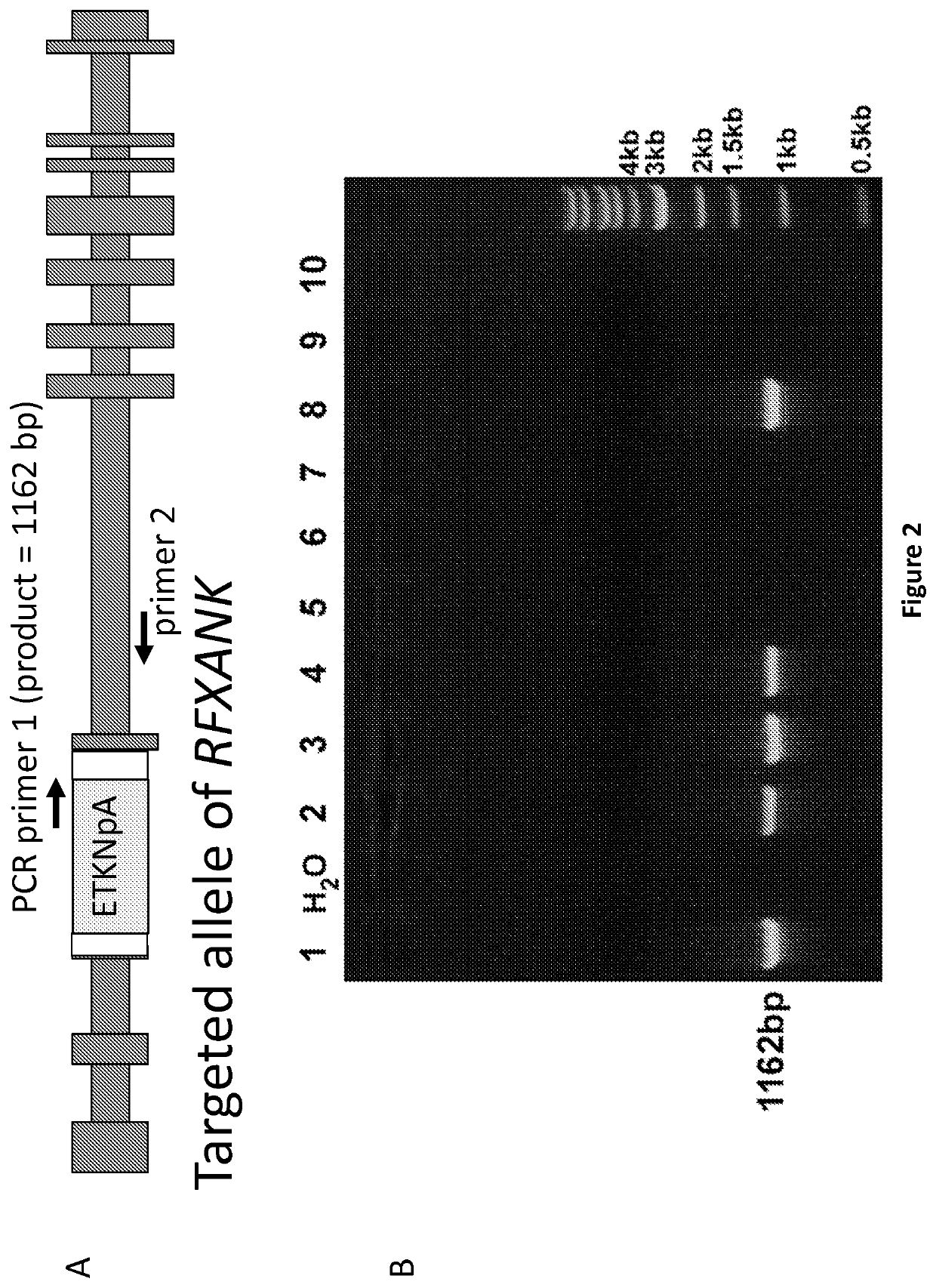
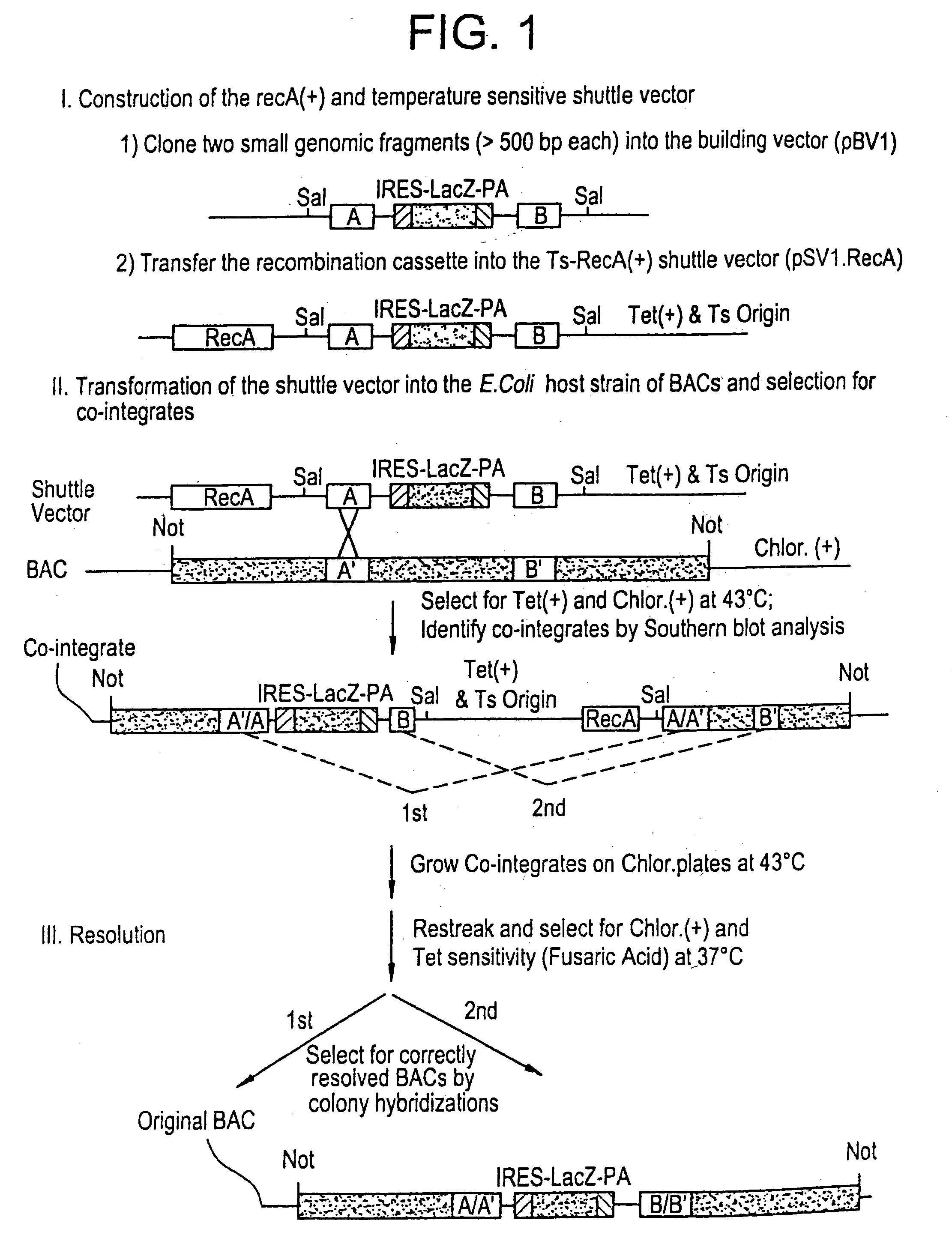
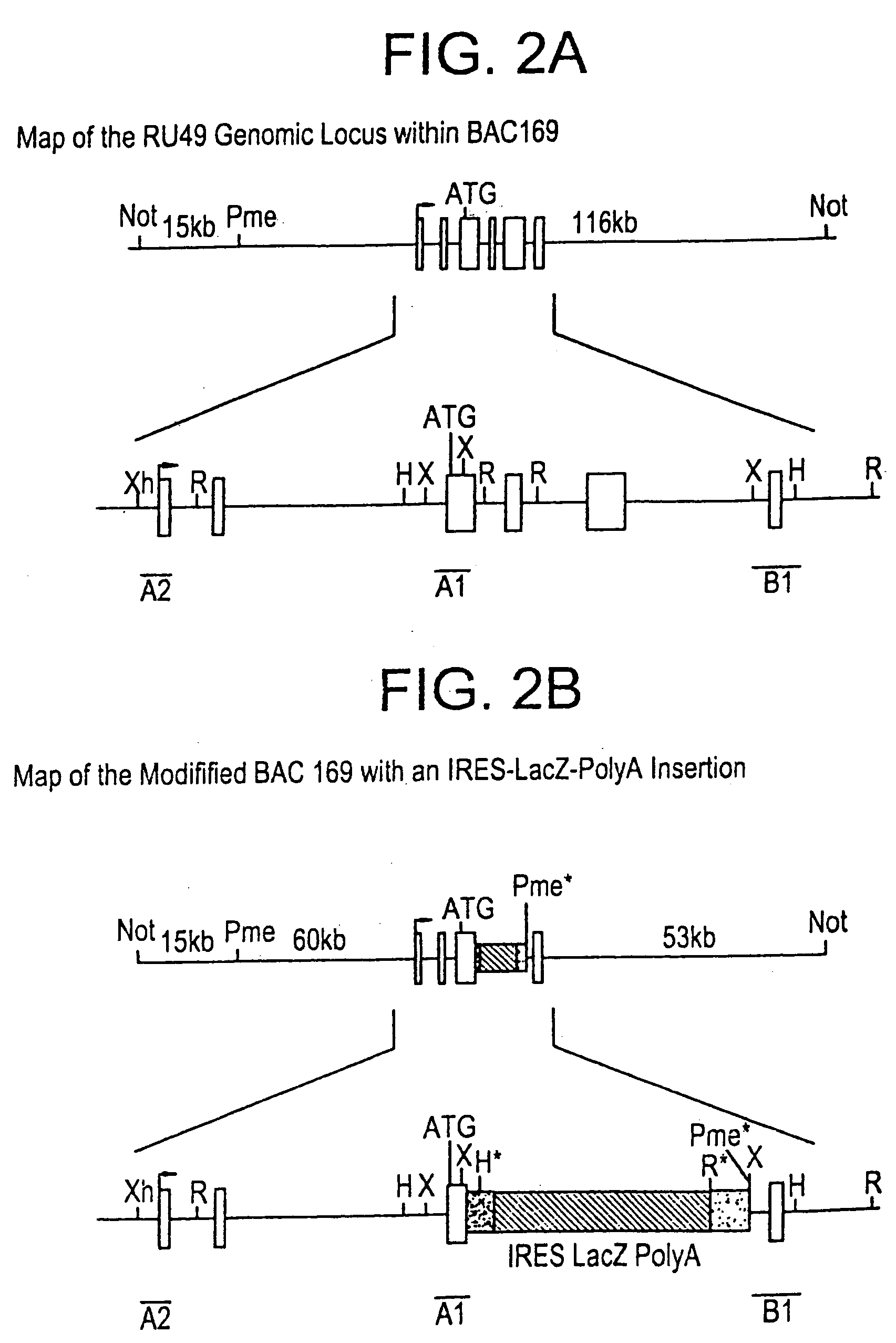
Methods of performing homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertion, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene can be contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
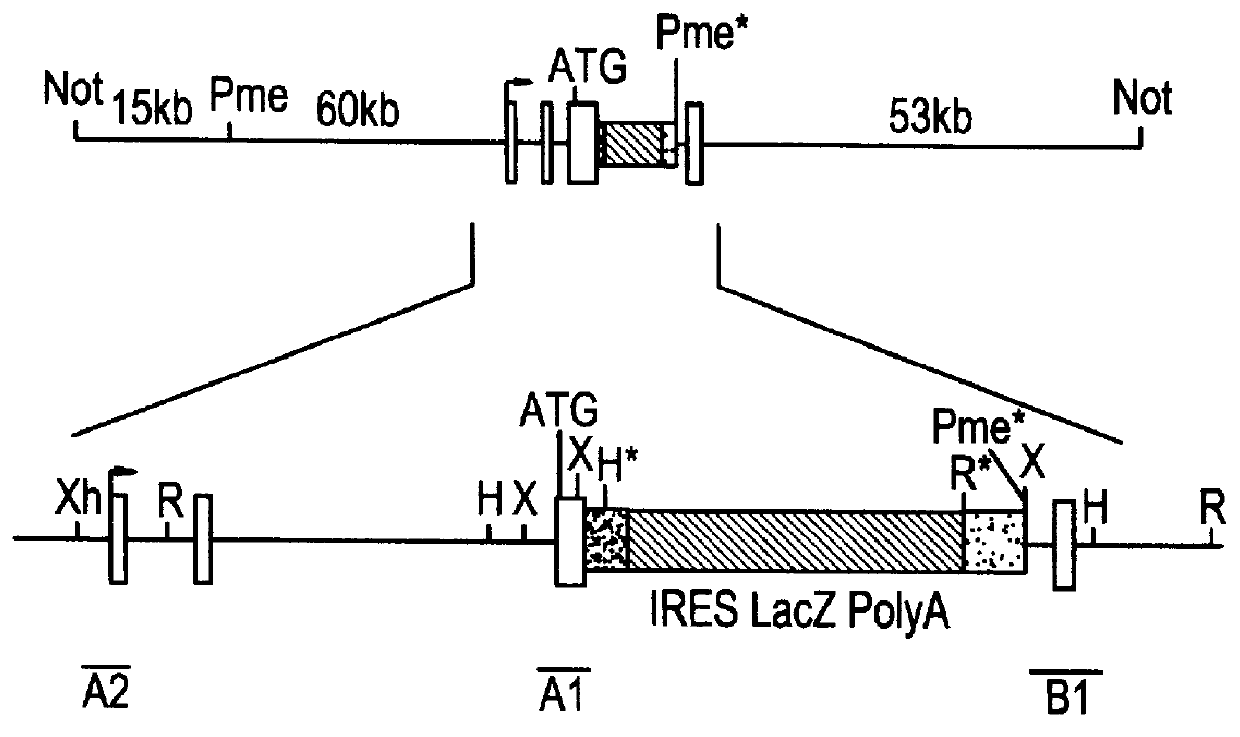
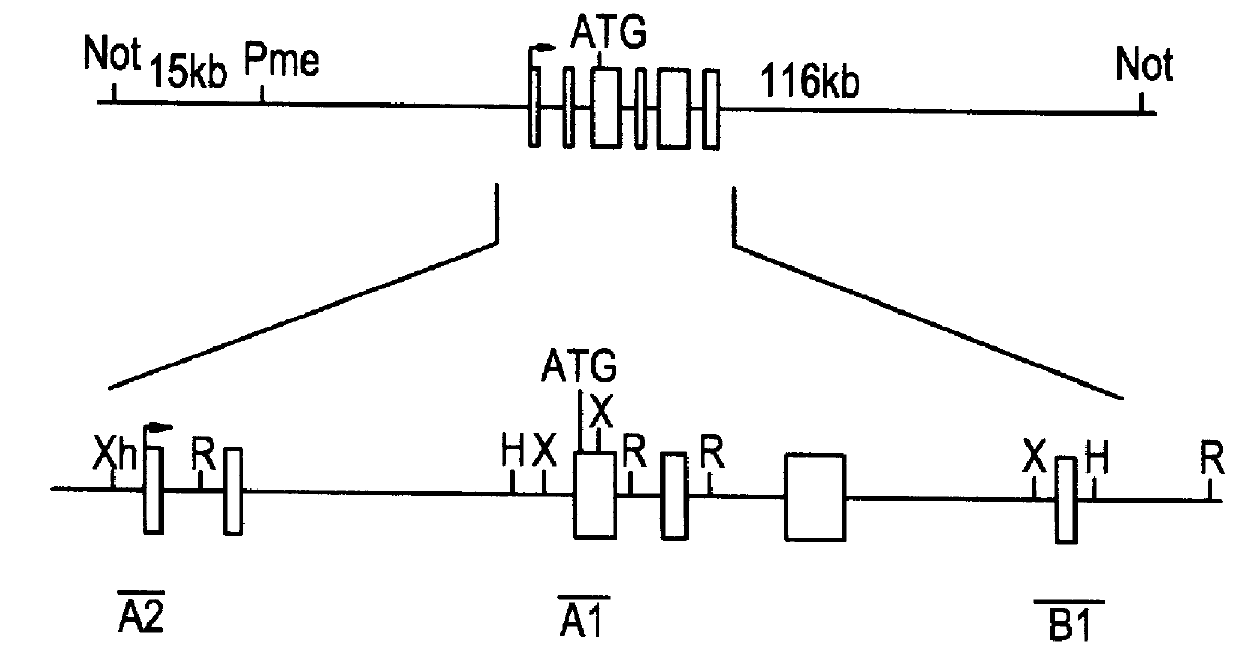
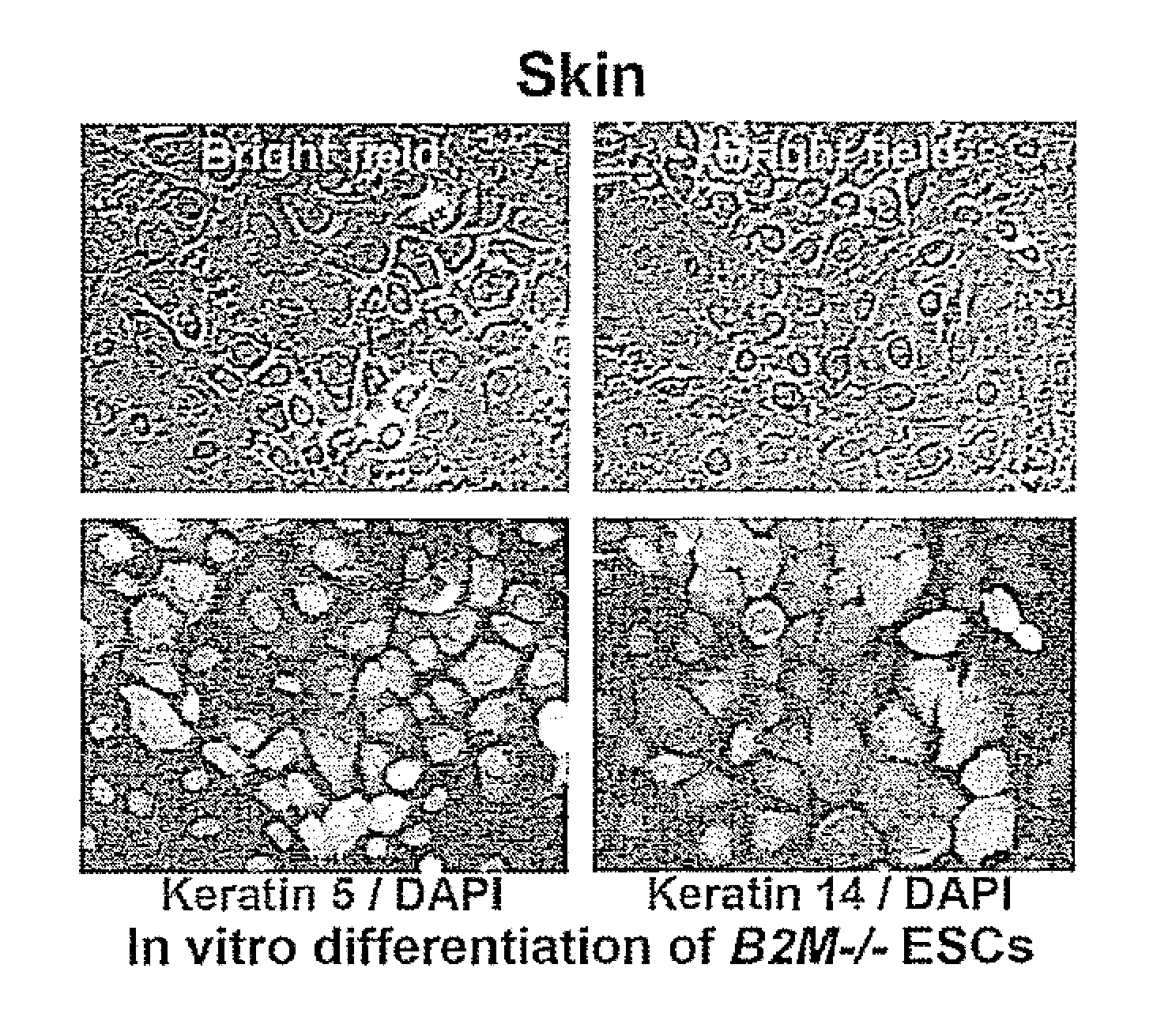
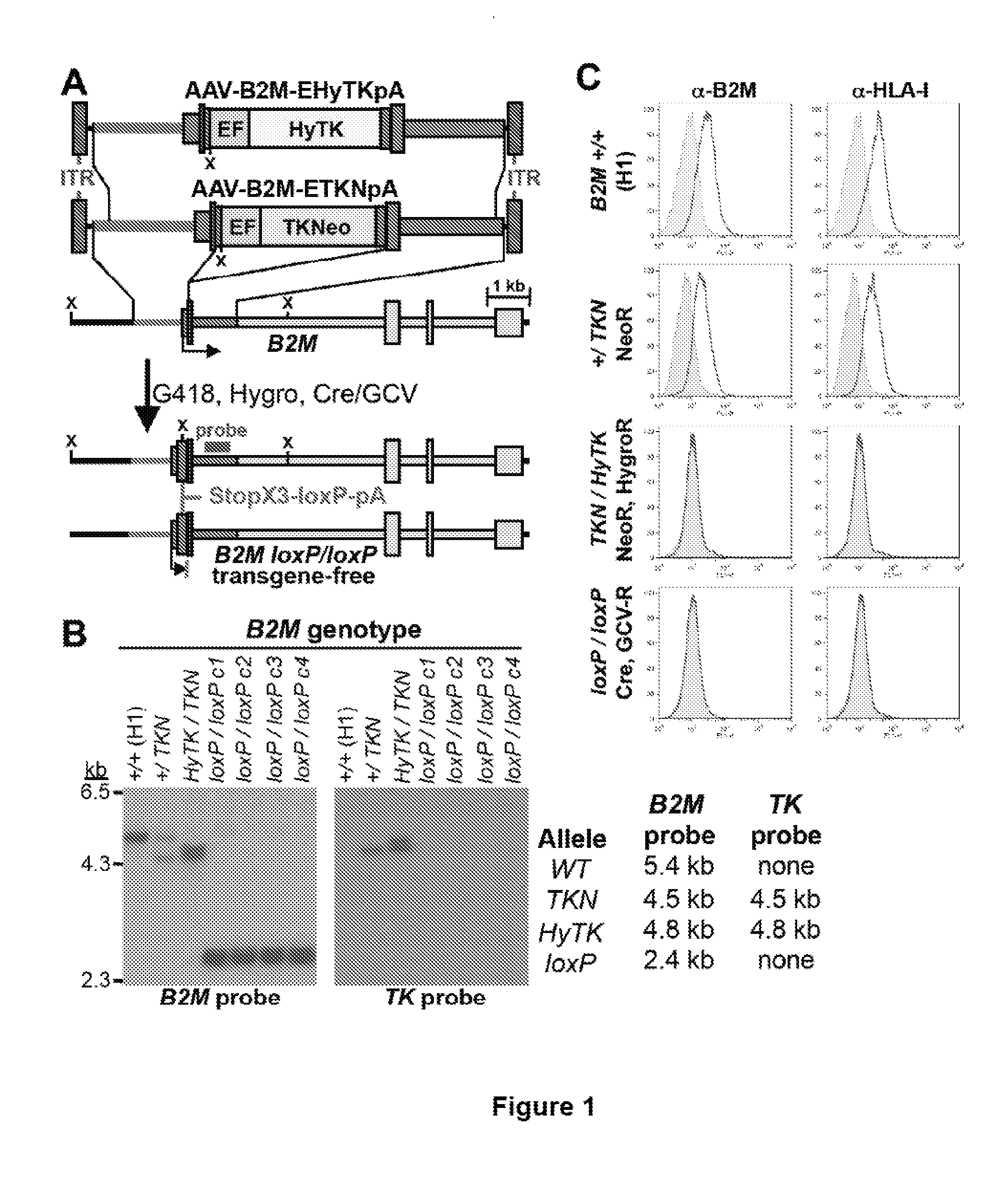
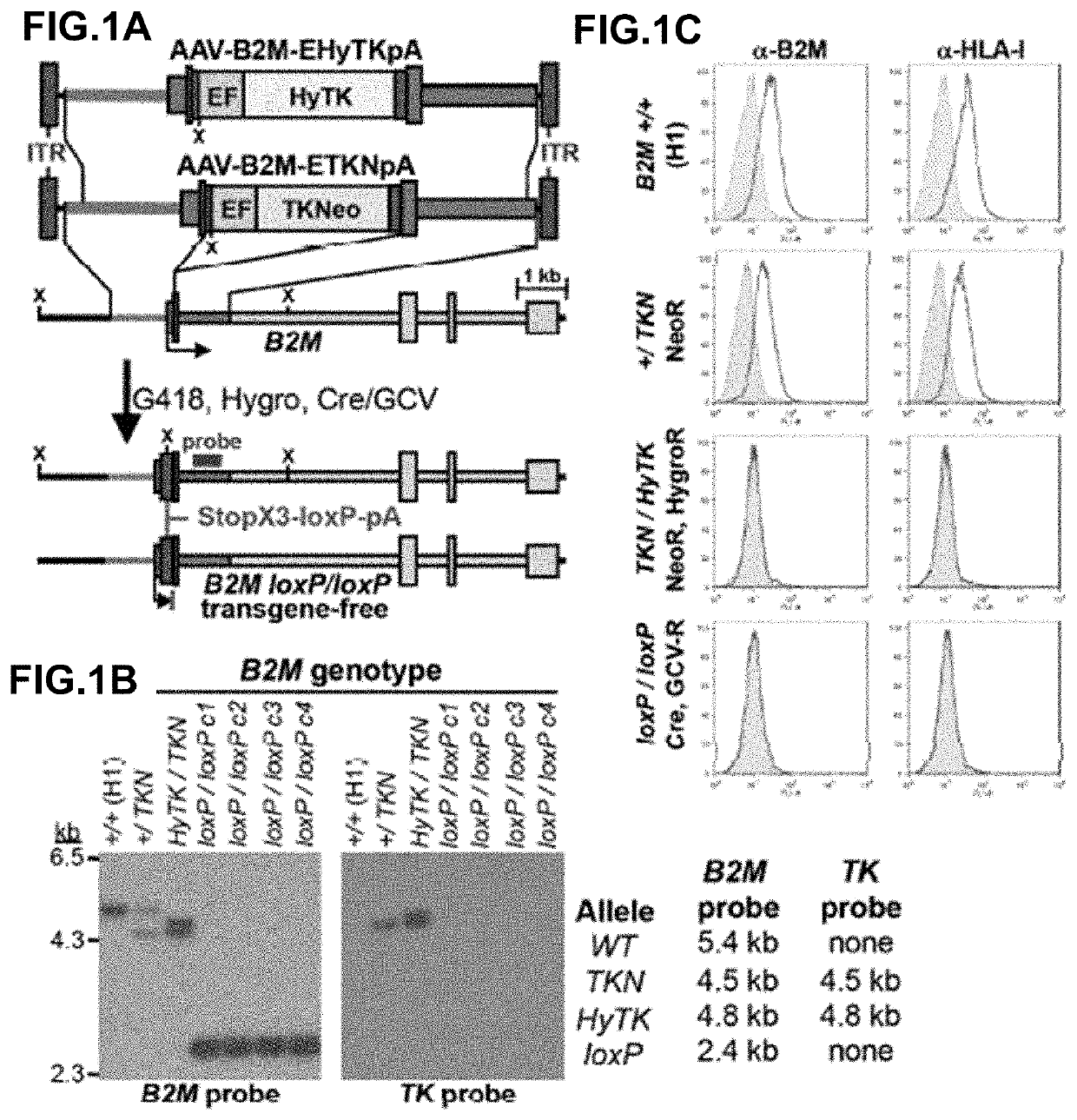
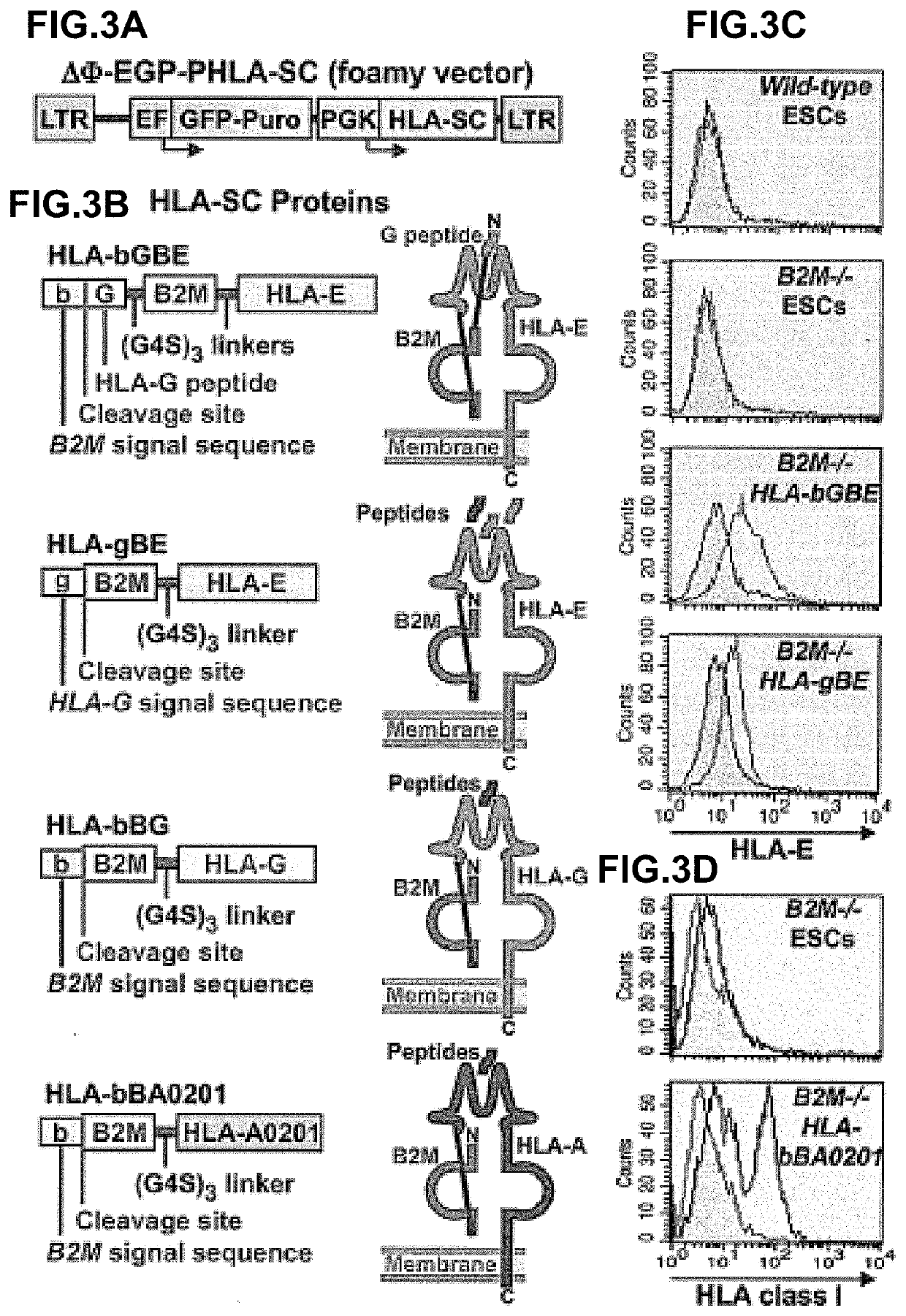
Beta-2 microglobulin-deficient cells
The invention provides isolated primate cells preferably human cells that comprise a genetically engineered disruption in a beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) gene, which results in deficiency in MHC class I expression and function. Also provided are the method of using the cells for transplantation and treating a disease condition.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
HLA Class II Deficient Cells, HLA Class I Deficient Cells Capable of Expressing HLA Class II Proteins, and Uses Thereof
The invention provides isolated primate cells preferably human cells that comprise a genetically engineered disruption in a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II-related gene, which results in deficiency in MHC class II expression and function. This invention also provides isolated cells further comprising a genetically engineered disruption in a beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) gene, which results in HLA class I / class II deficiency. Also provided are the method of using the cells for transplantation and treating a disease condition.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Protease-deficient cells
A gram-negative bacterial cell is described that is deficient in a chromosomal gene present in a wild-type such cell which gene shares at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of the yfcK gene and encodes an aminopeptidase. Alternatively, a gram-negative bacterial cell is deficient in a chromosomal gene present in a wild-type such cell which gene encodes an aminopeptidase that shares at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of aminopeptidase b2324. Either of these types of cells, when comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous polypeptide, produces an N-terminal unclipped polypeptide when it is cultured and the polypeptide recovered, with virtually no N-terminal clipped polypeptide produced as an impurity. Conversely, a method is provided for cleaving an N-terminal amino acid from a polypeptide comprising contacting the polypeptide with an aminopeptidase sharing at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of aminopeptidase b2324.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for suppressing multiple drug resistance in cancer cells
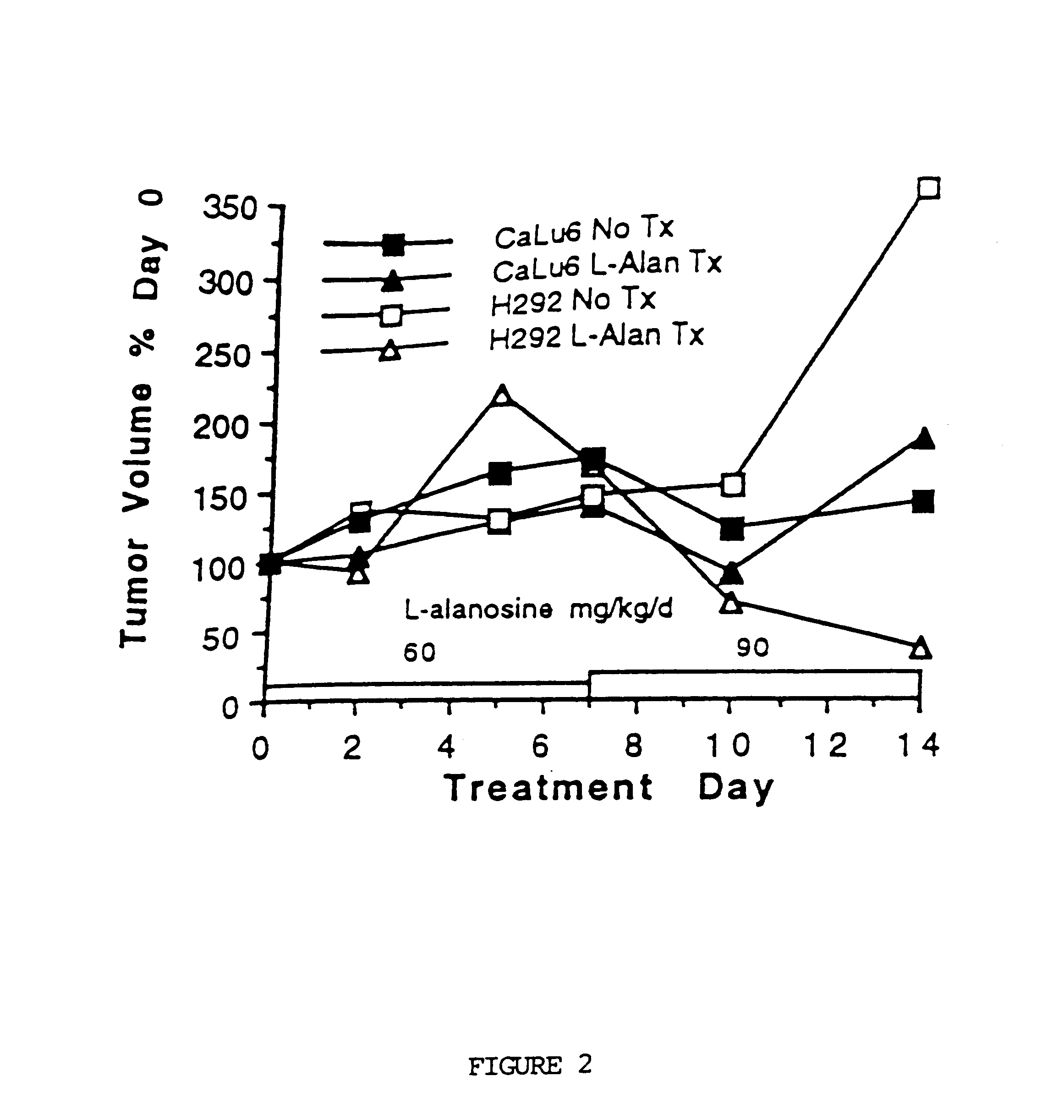
Methods for treating and preventing the onset and maintainance of multiple drug resistance (MDR) in animals undergoing chemotherapy for cancer are provided. According to the methods, target cells are depleted of adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) such that the cells are unable to support P-glycoprotein activity. According to one method, a population of target cells is obtained from a host and assayed for loss of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAse) activity. MTAse catabolizes methylthioadenosine to adenine for endogenous salvage incorporation into the intracellular AMP pool. MTAse deficient cells are treated with a purine synthesis inhibitor, such as L-alanosine, which starves the cells of adenine and suppresses P-glycoprotein activity. MTAse competent cells are also treated for MDR with purine synthesis inhibitors. In conjunction with treatment according to the invention, MTAse competent and deficient cells are also treated for malignancy with other anti-cancer drugs. A method for protecting non-malignant cells from adenine starvation during treatment of malignant cells according to the invention is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis
InactiveUS20100022495A1Promote apoptosisReduce and prevent ER stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseHAMARTOMATOUS DISEASES
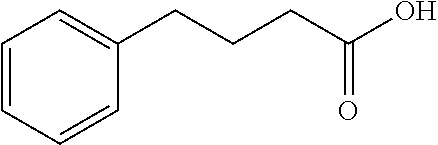
Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been found to be associated with the genetic disease tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis is cause by defects in the two genes, TSC1 and TSC2. Agents that modulate ER stress may be used to treat tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomatous diseases. In particular, 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA) has been shown to reduce ER stress is TSC-deficient cells. Other compounds useful in reducing ER stress are chemical chaperones such as trimethylamine N-oxide arid glycerol may also be useful in treating tuberous sclerosis. The present invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from tuberous sclerosis using ER stress reducers such as PBA, TUDCA, UDCA, and TMAO. Methods of screening for ER stress reducers by identifying agents that reduce levels of ER stress markers in TSC-deficient cells are also provided. These agents may find use in methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating tuberous sclerosis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Modulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis
InactiveUS20140011761A1Promote apoptosisReduce and prevent ER stressBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsHAMARTOMATOUS DISEASESReticulum cell
Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been found to be associated with the genetic disease tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis is cause by defects in the two genes, TSC1 and TSC2. Agents that modulate ER stress may be used to treat tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomatous diseases. In particular, 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA) has been shown to reduce ER stress is TSC-deficient cells. Other compounds useful in reducing ER stress are chemical chaperones such as trimethylamine N-oxide arid glycerol may also be useful in treating tuberous sclerosis. The present invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from tuberous sclerosis using ER stress reducers such as PBA, TUDCA, UDCA, and TMAO. Methods of screening for ER stress reducers by identifying agents that reduce levels of ER stress markers in TSC-deficient cells are also provided. These agents may find use in methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating tuberous sclerosis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Hat acetylation promoters and uses of compositions thereof in promoting immunogenicity
InactiveUS20100166781A1Improving immunogenicityPromoting surfaceAntibacterial agentsBiocideMHC class IFactor ii
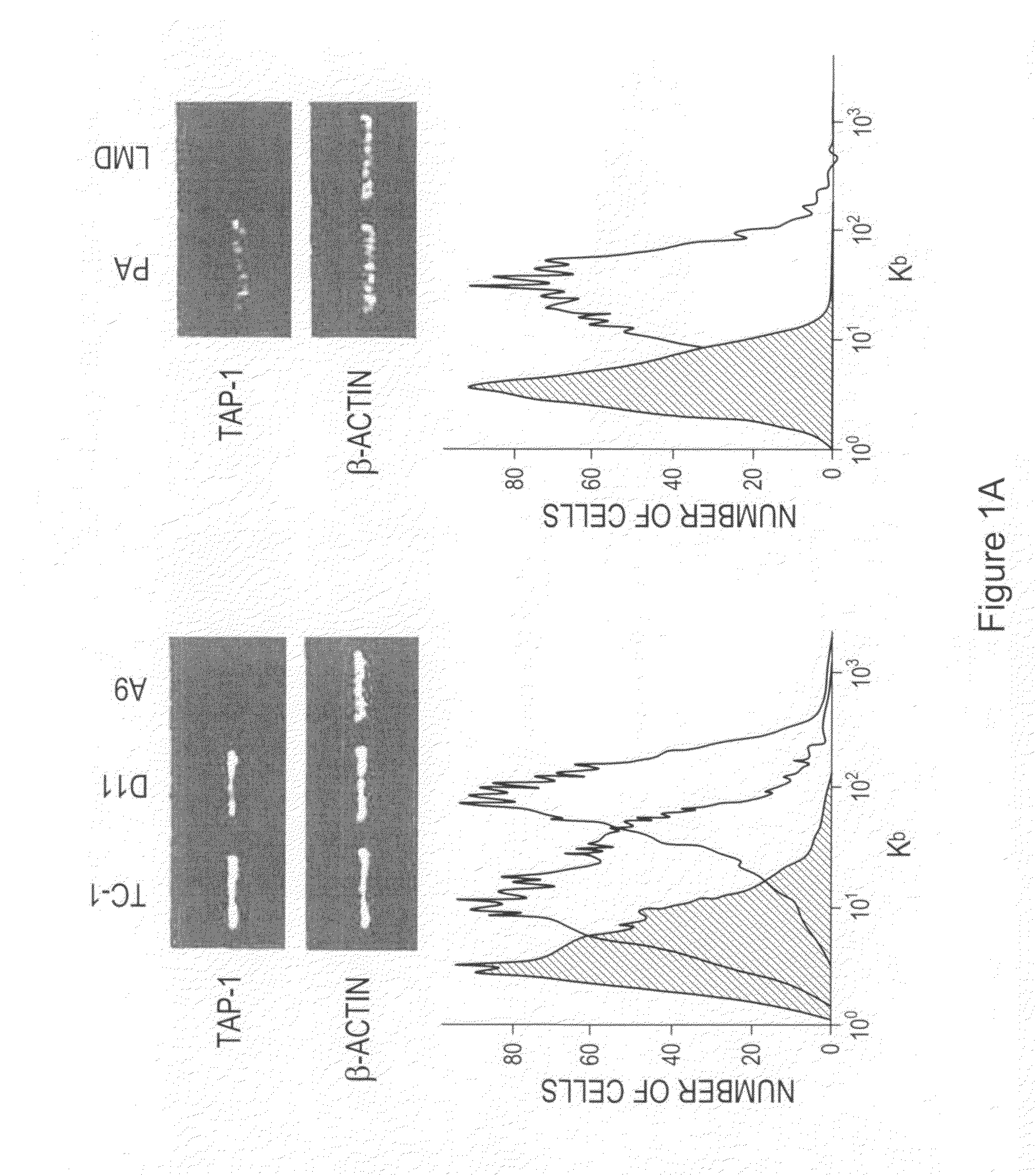
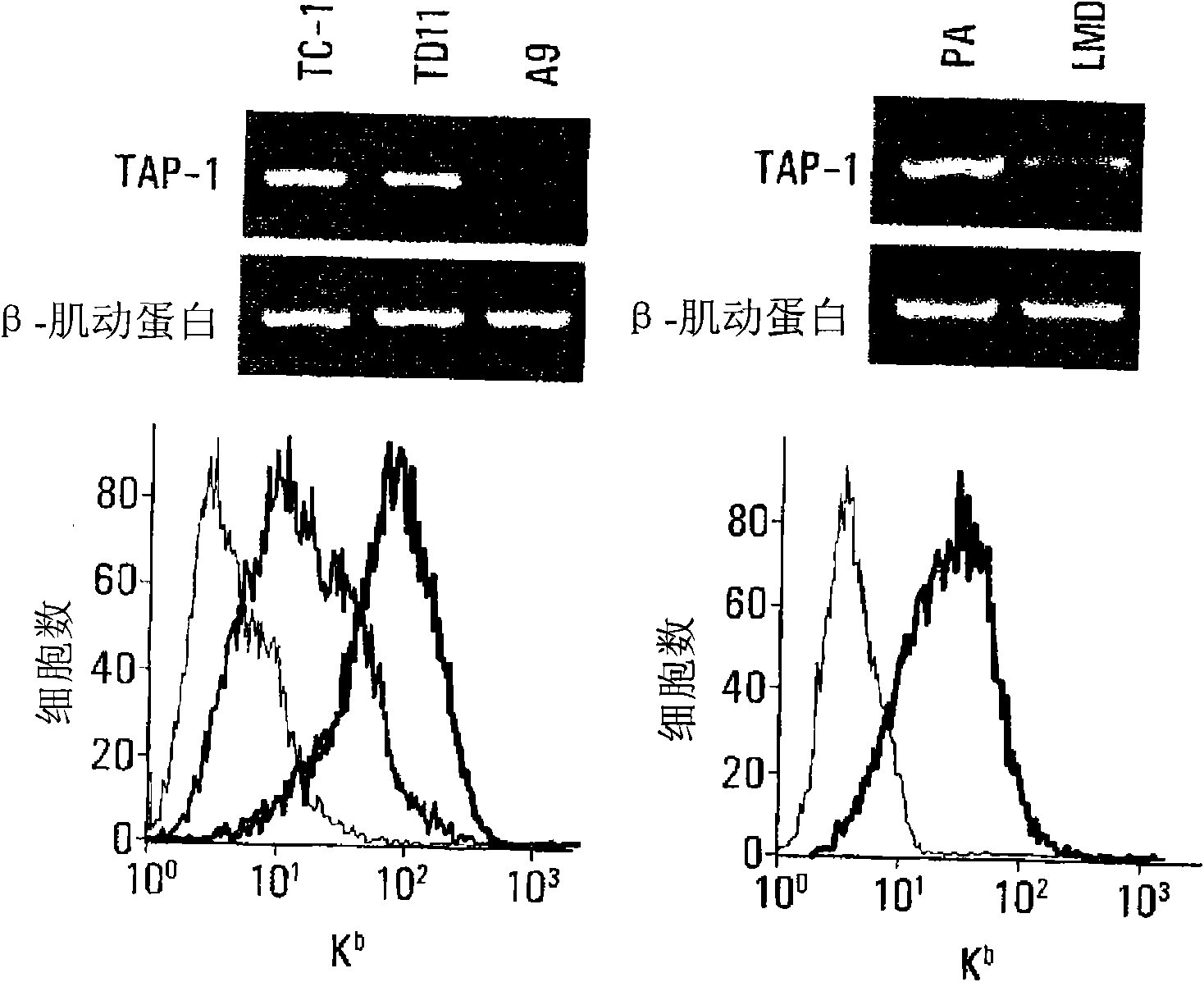
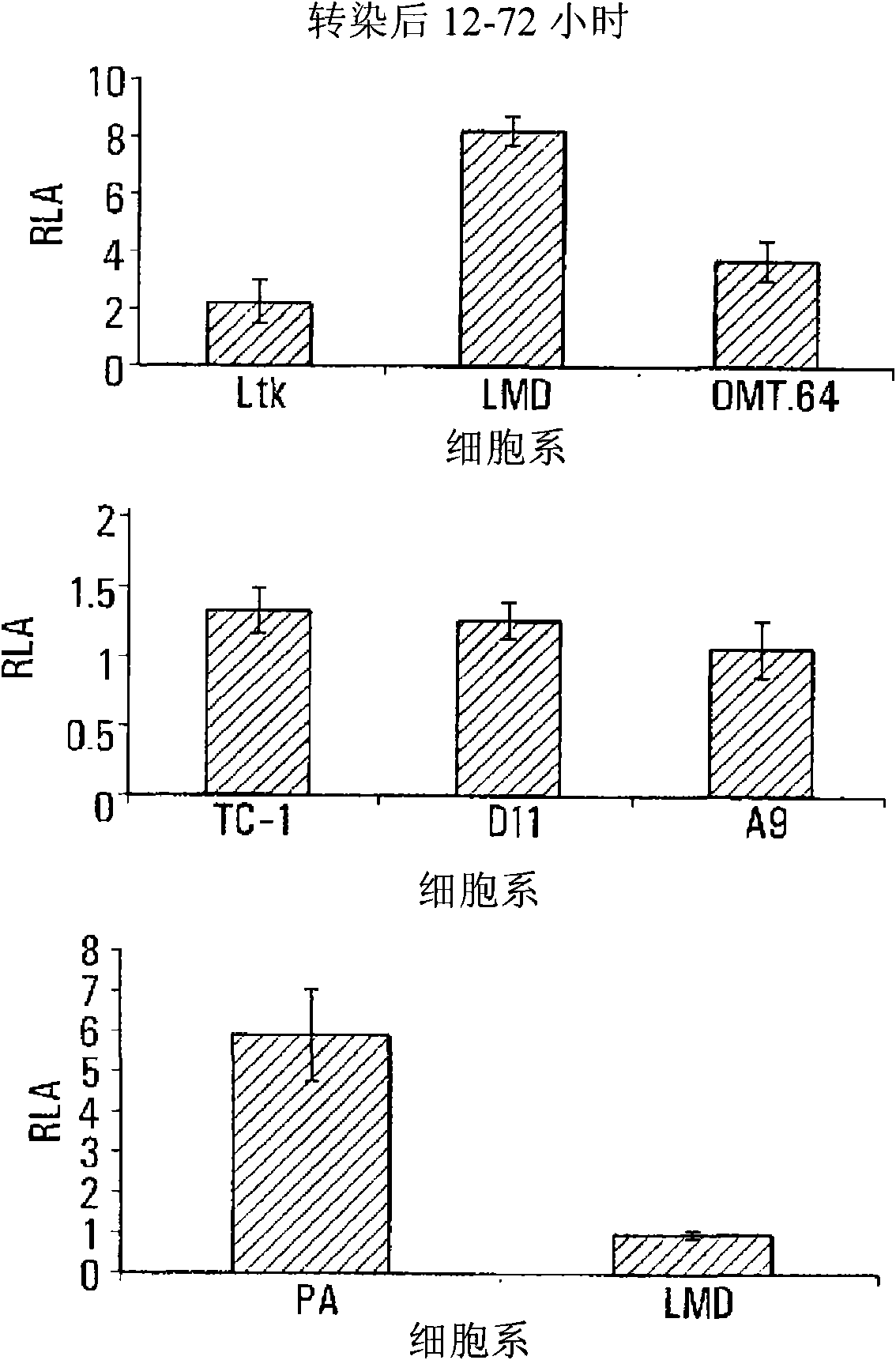
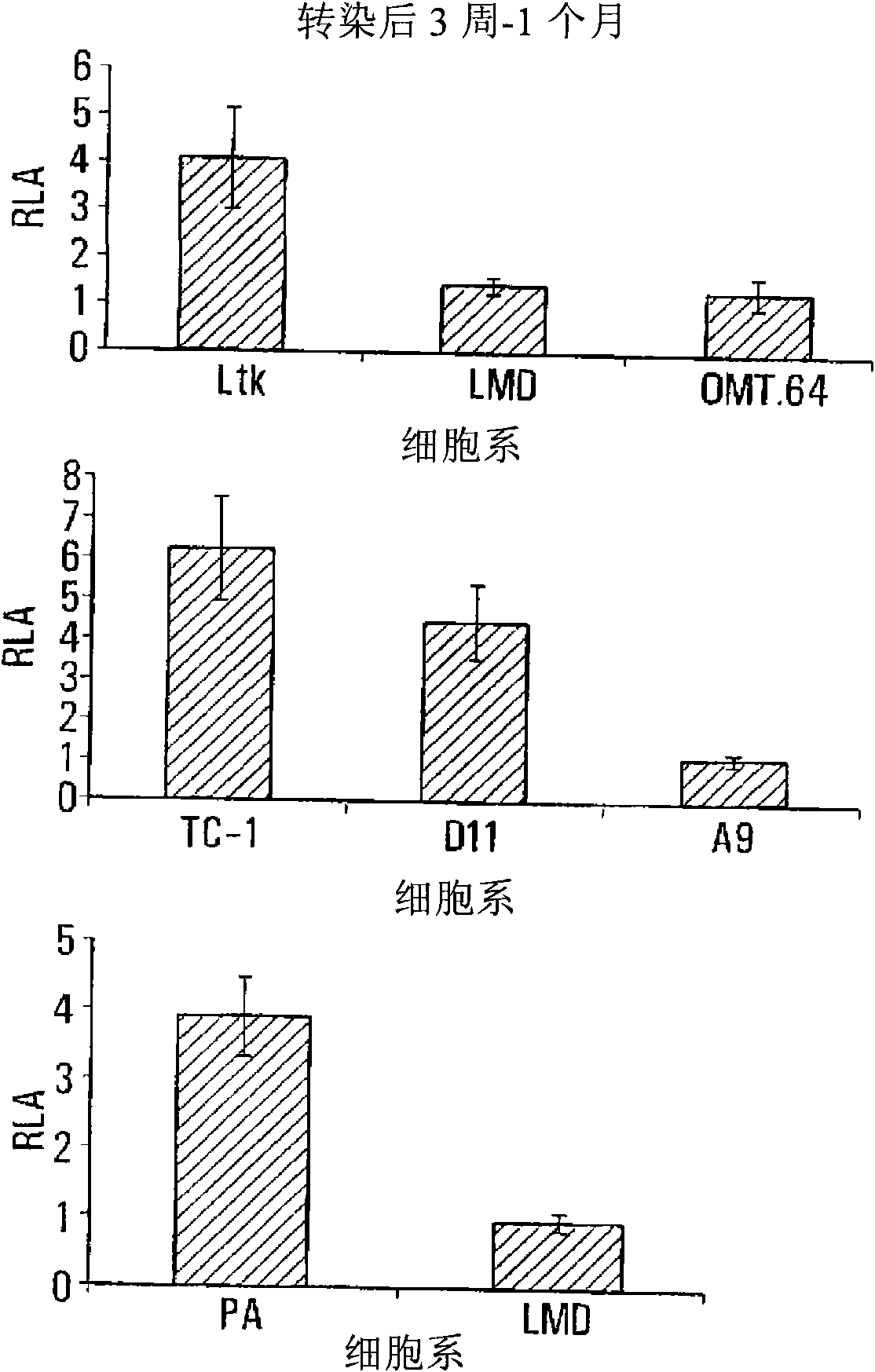
The invention provides processes and compositions for enhancing the immunogenicity of TAP-1 expression-deficient cells by increasing the presentation of MHC Class I surface molecules for detection by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte cells through increased TAP-1 expression, which comprises administering to the TAP-1 expression-deficient cells a TAP-1 expression increasing amount of a bio-acceptable substance that promotes transcription of TAP-1 gene in the cells to cause enhanced MHC Class I surface expression of the cells. The bio-acceptable substance may be a histone H3 deacetylase inhibitor, such as trichostatin A, a transcriptional co-activator having intrinsic histone acetyl transferase activity or a histone acetyl transferase comprising at least one member of the CBP / p300 protein family. The process and compositions increase the immunogenicity of the target cells to enhance their destruction by cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Owner:JEFFERIES WILFRED
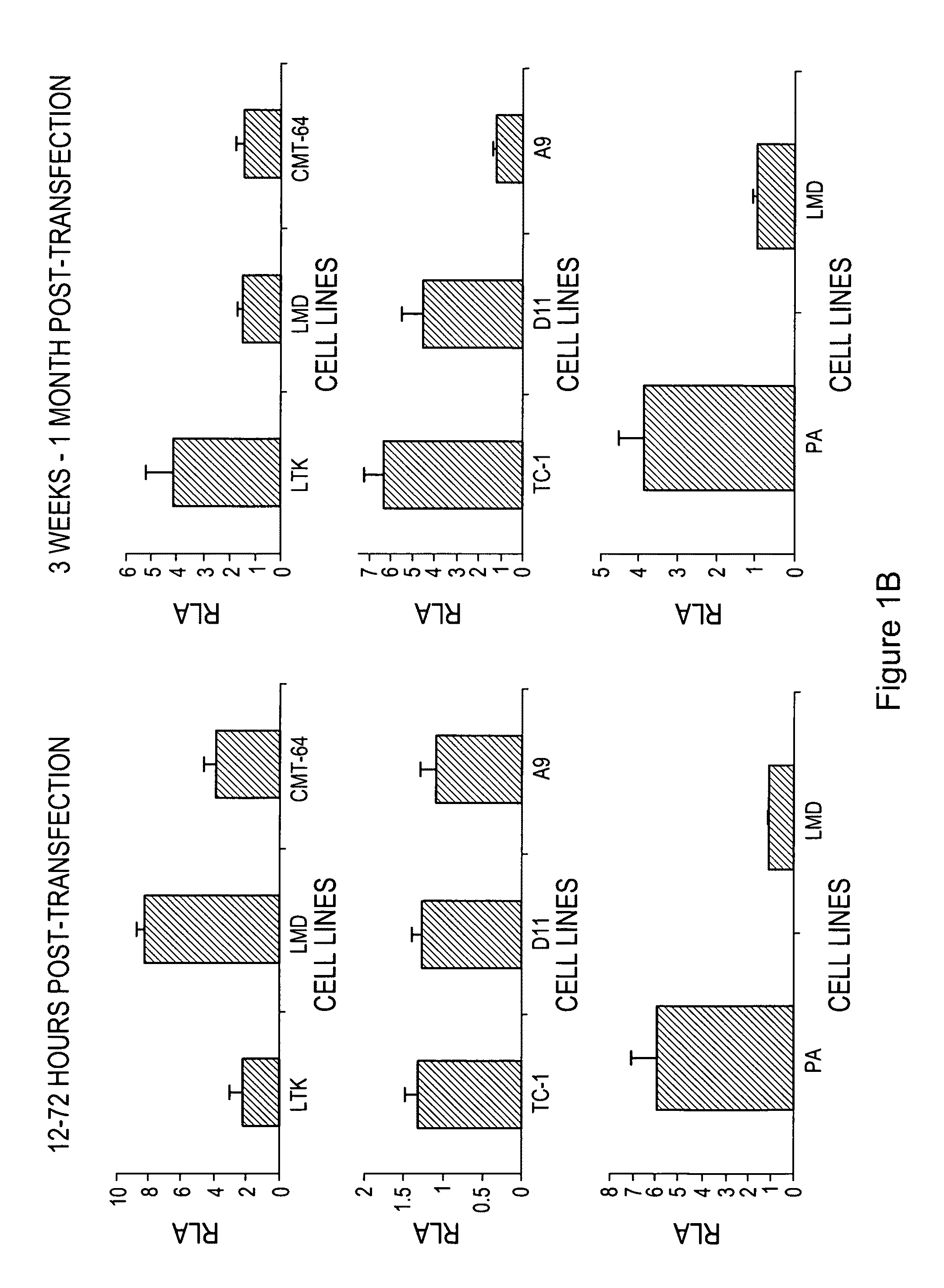
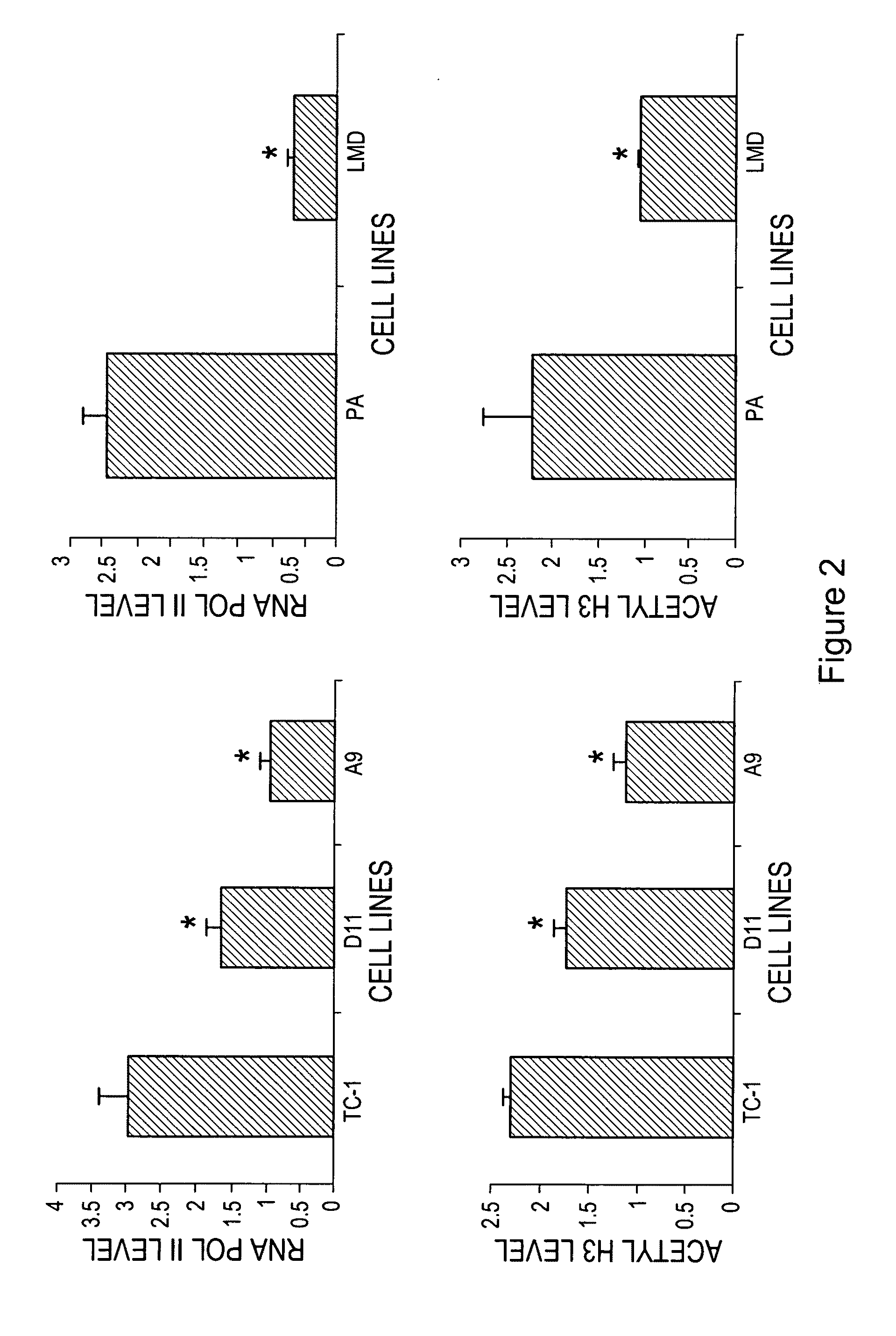
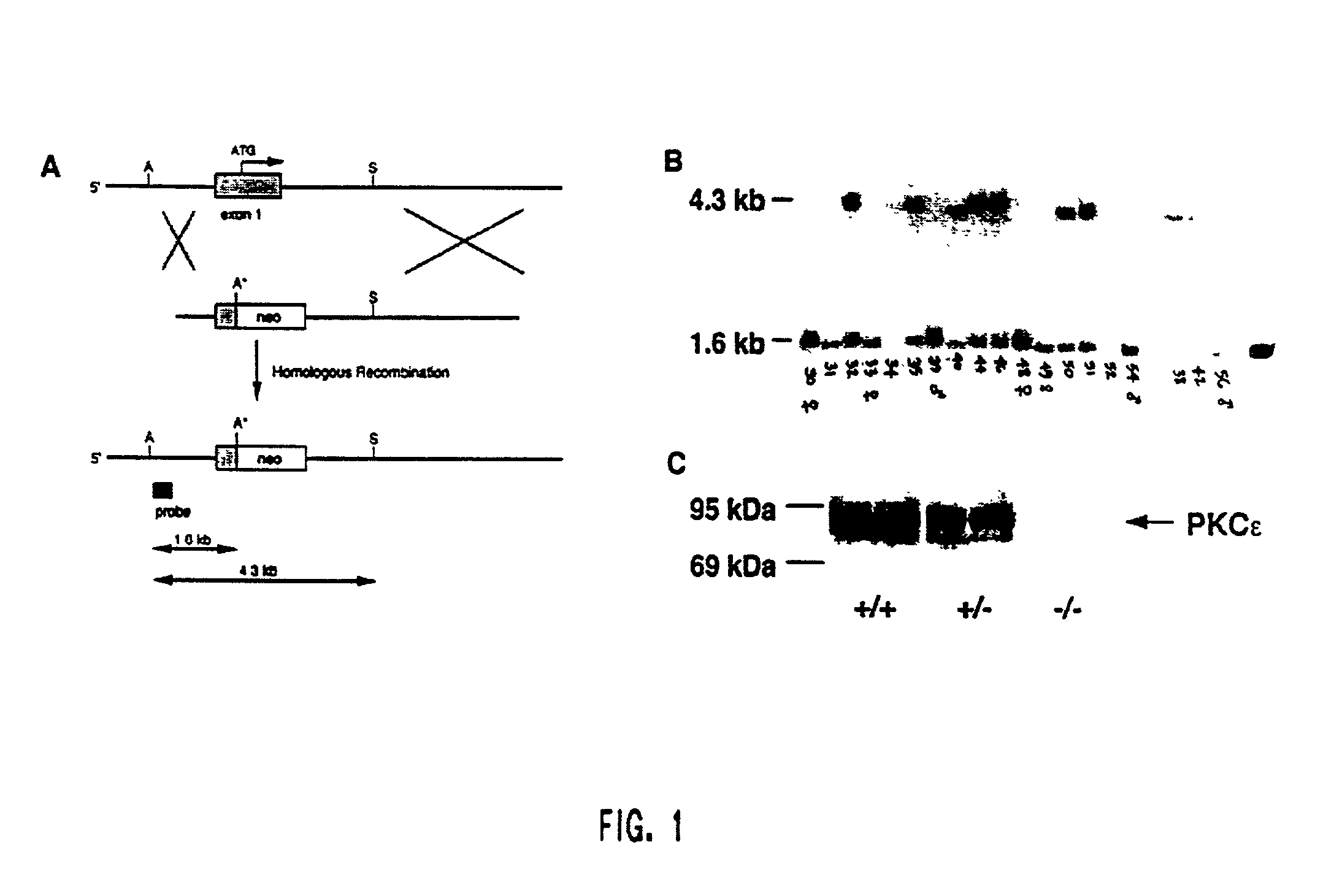
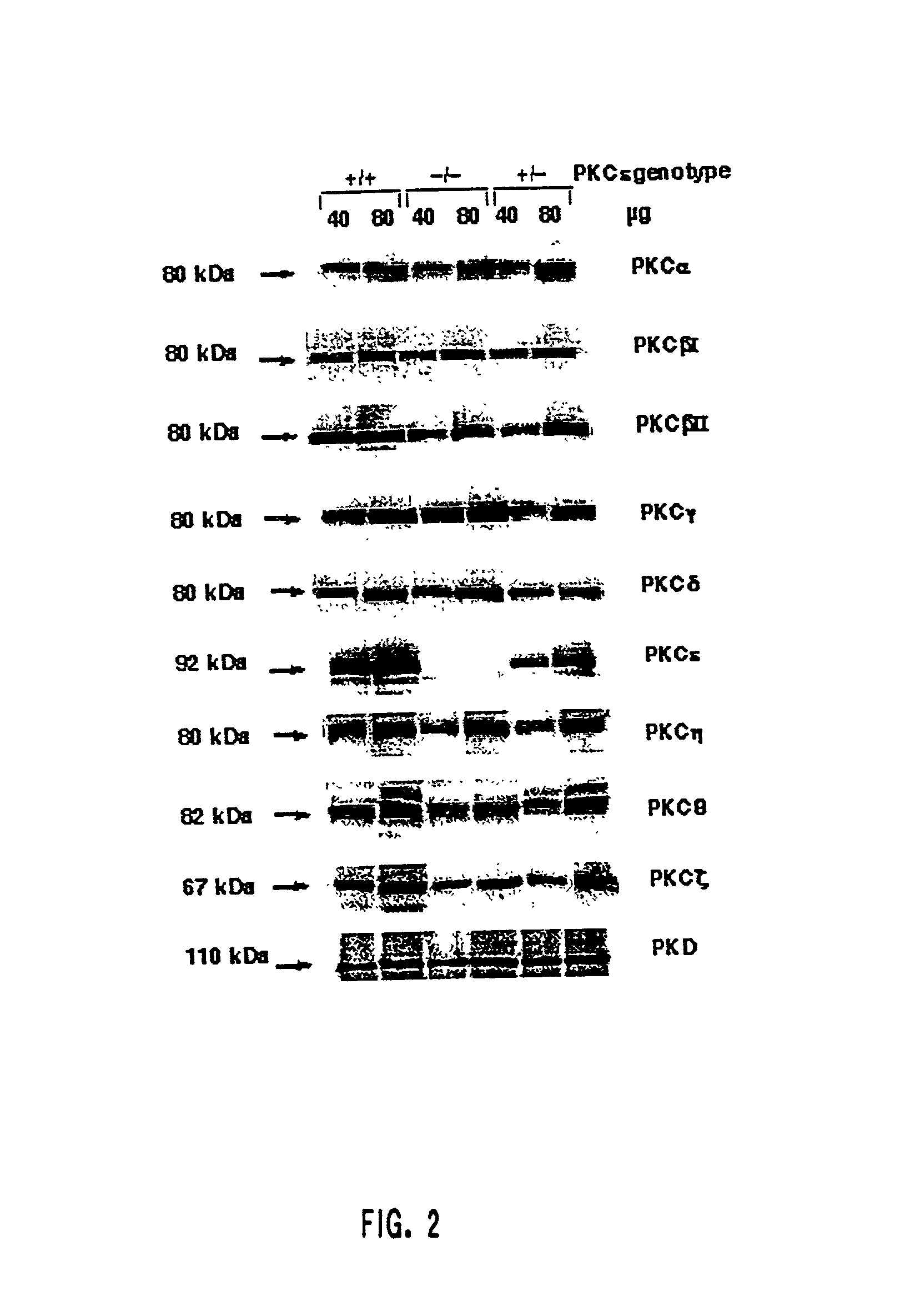
Protein kinase c epsilon as modulator of anxiety, alcohol consumption and self-administration of drugs of abuse
InactiveUS20020124272A1Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawal syndromeAlcoholisms
The present invention is directed to the production of PKC isozyme epsi (PKCepsi)-deficient cells and non-human animals. The present invention is further directed to the identification of PKCepsi as a target for drugs that reduce anxiety. According to the present invention, PKCepsi-inhibiting compounds act in synergy with drugs acting at the GABAA receptor. The present invention is also directed to the use of modulators of PKCepsi to modulate alcohol consumption, self-administration of other drugs of abuse, and the effects of alcohol consumption as well as the use of inhibitors of PKCepsi, either alone or in conjunction with allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors, to treat conditions, such as addiction, withdrawal syndrome, skeletal muscle spasms, convulsive seizures, and epilepsy, that are amenable to treatment by allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors. Additional aspects of the present invention are diagnostic methods for identifying individuals at risk for becoming alcoholics or abusers of other drugs and kits for performing such diagnostic methods. The present invention relates to: cells and non-human animals deficient for the PKC isozyme epsi (PKCepsi); the use of PKCepsi as a target for drugs; the use of inhibitors of PKCepsi in methods of reducing anxiety and treating conditions associated with insufficient activity of the GABAA receptor; the use of modulators of PKCepsi in methods of modulating alcohol consumption, modulating self-administration of other drugs of abuse, and altering the effects of alcohol; pharmaceutical compositions comprising inhibitors of PKCepsi and allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors; and the identification of individuals with enhanced susceptibility to alcoholism or other forms of addiction.
Owner:GALLO CLINIC & RES CENT +1
Compositions and methods for treating and preventing cardiomyopathy and heart disease
ActiveUS7846426B2Reduce concentrationReduces susceptibility to calcium overloadMuscular disorderTissue cultureMuscular dystrophyHeart disease
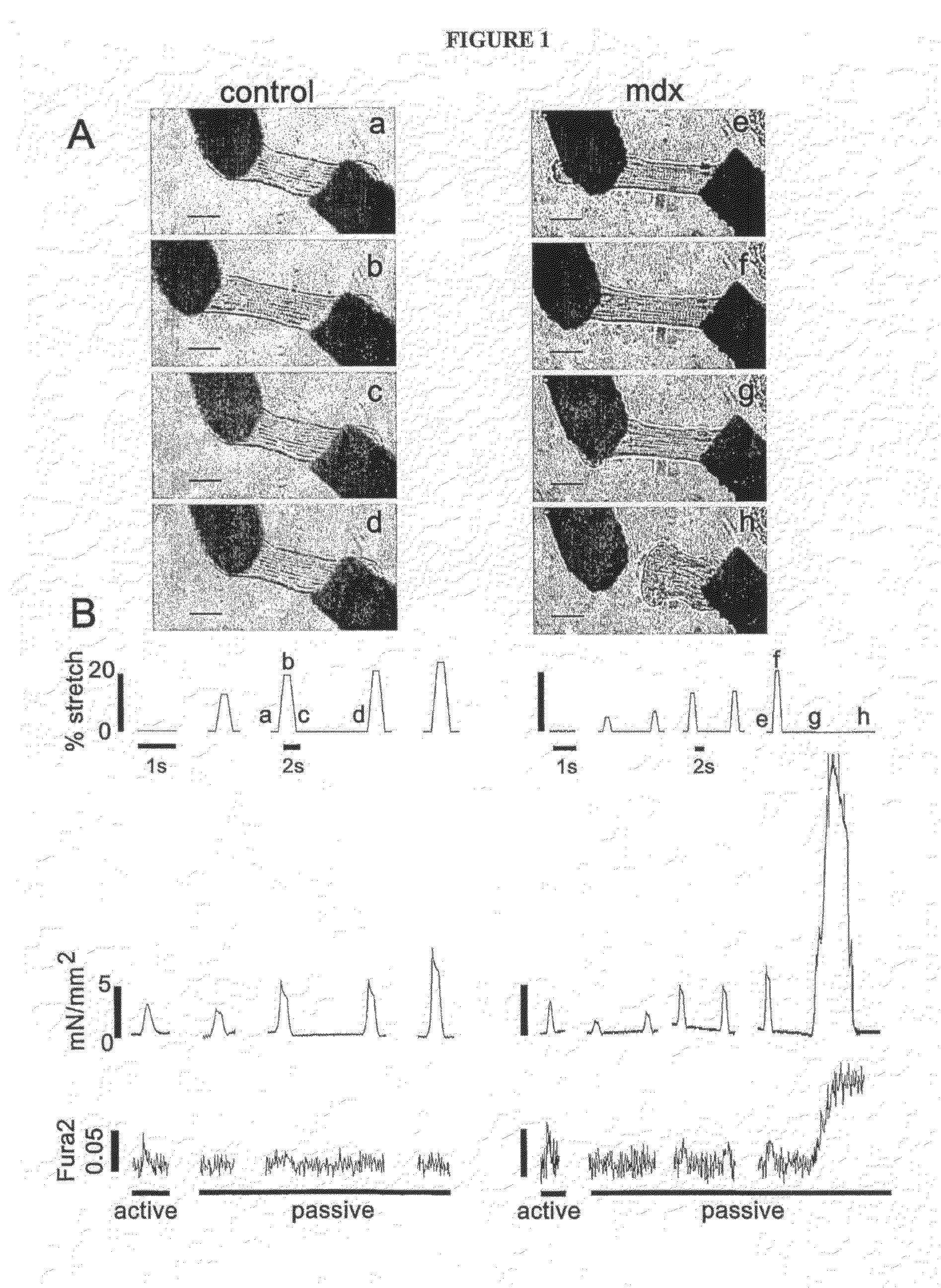
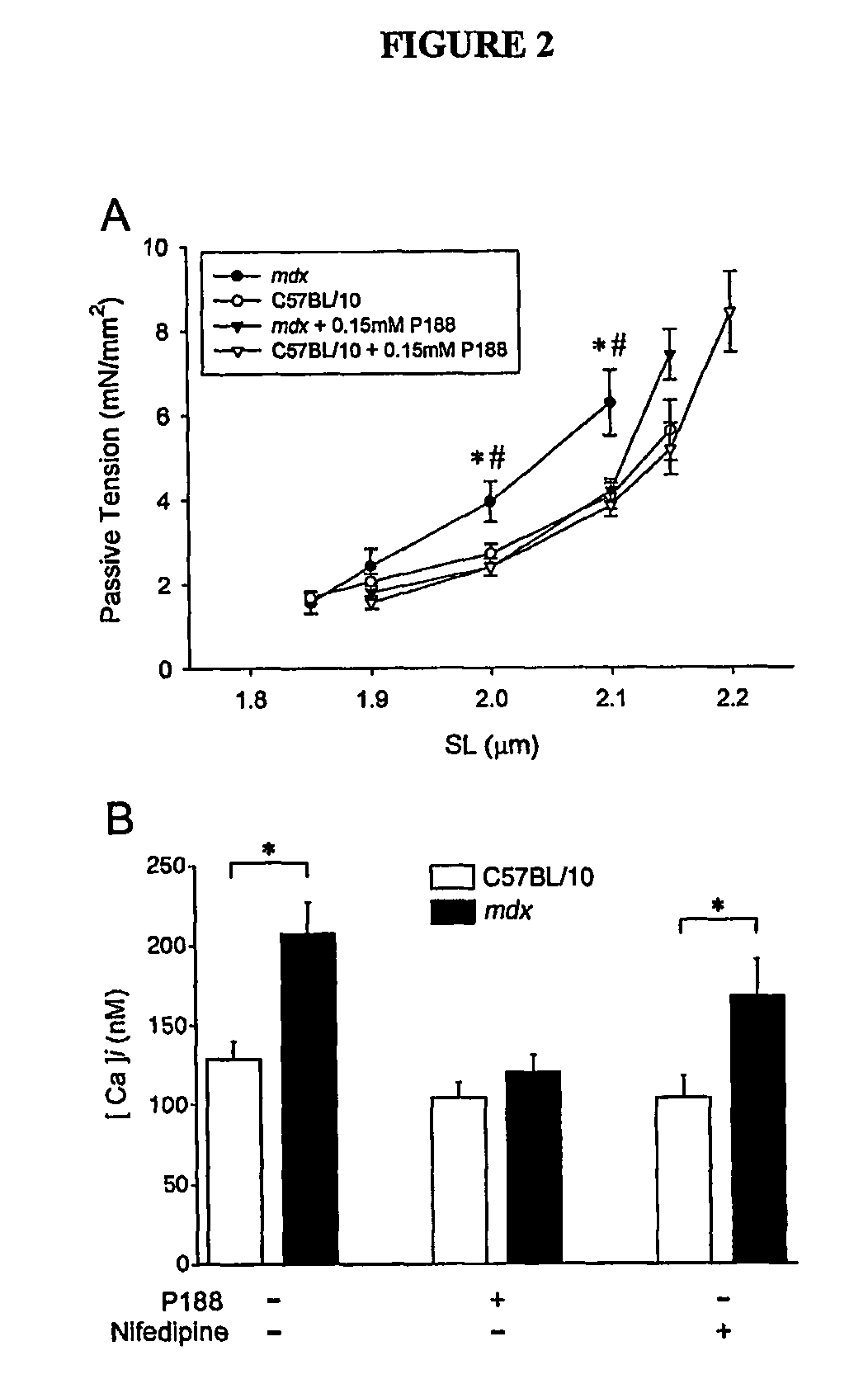
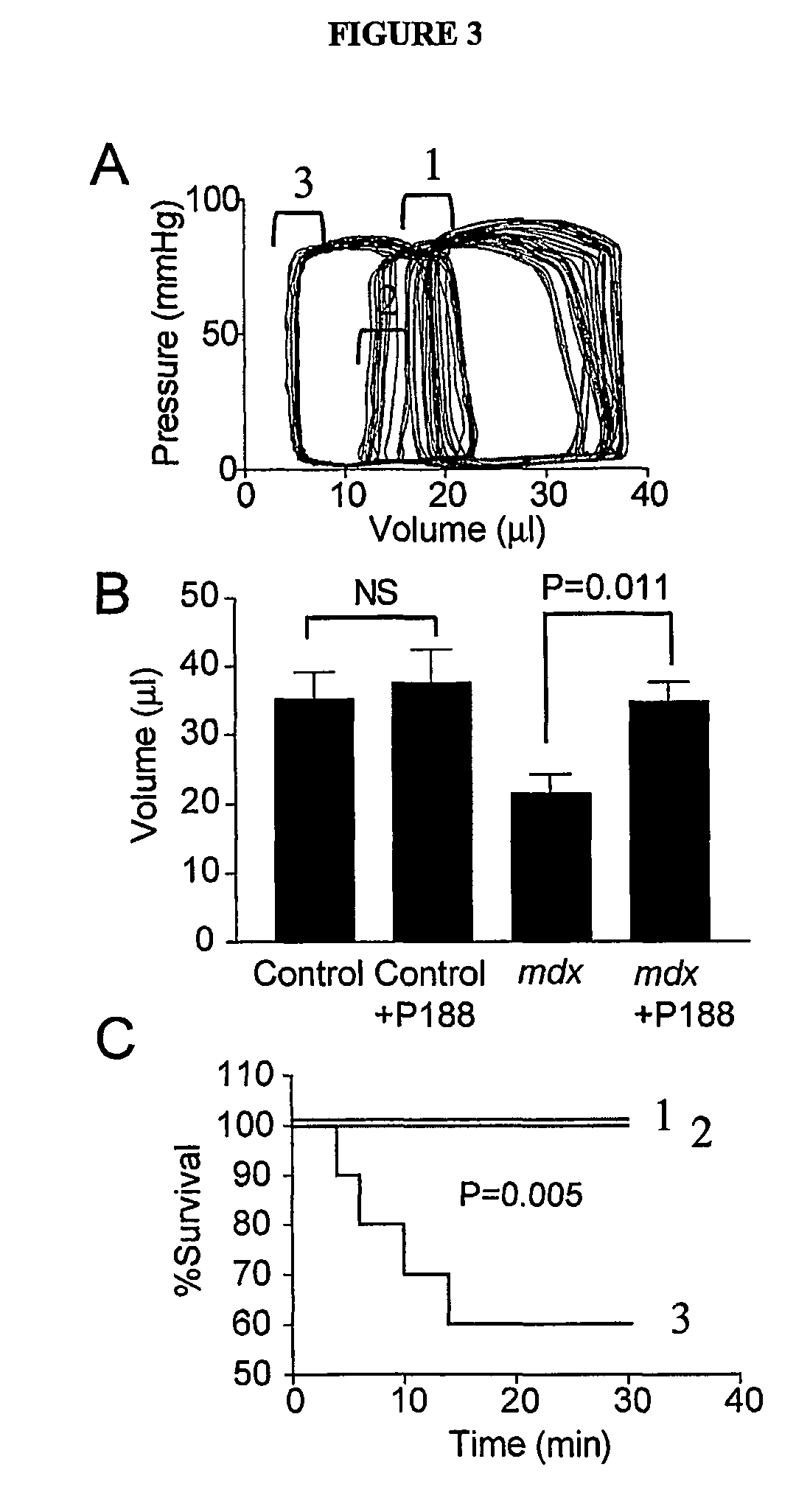
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating and preventing heart disease. In particular, the present invention provides compositions comprising poloxamers (e.g., poloxamer 188—P188) and methods of using the same for treating and preventing heart disease (e.g., in subjects with muscular dystrophy) and for treating cells and tissue damage caused by ischemia and cell death (e.g., for treating dystrophin-deficient cells (e.g., myocytes)).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Biomarkers of miR-34 activity
InactiveCN105473742AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellMdm2 Protein
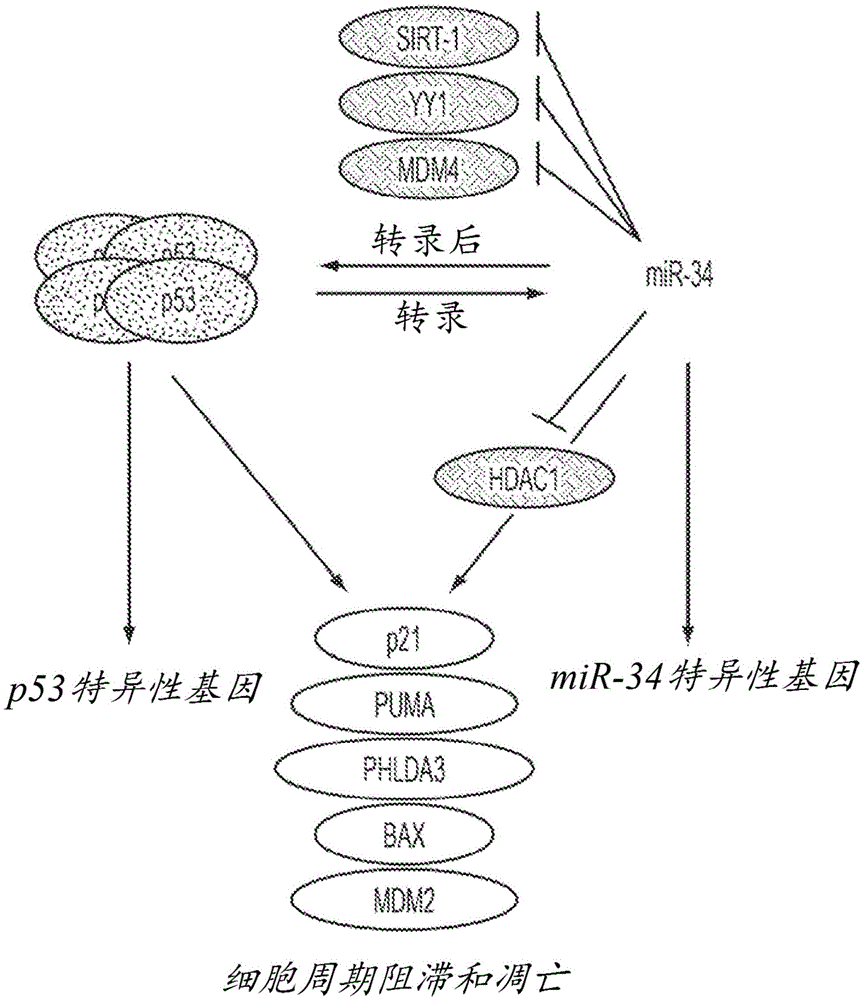
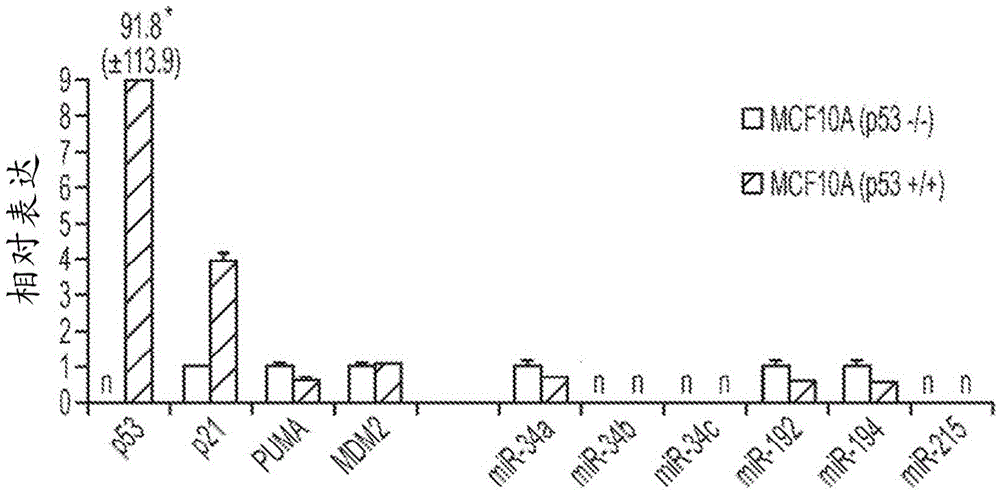
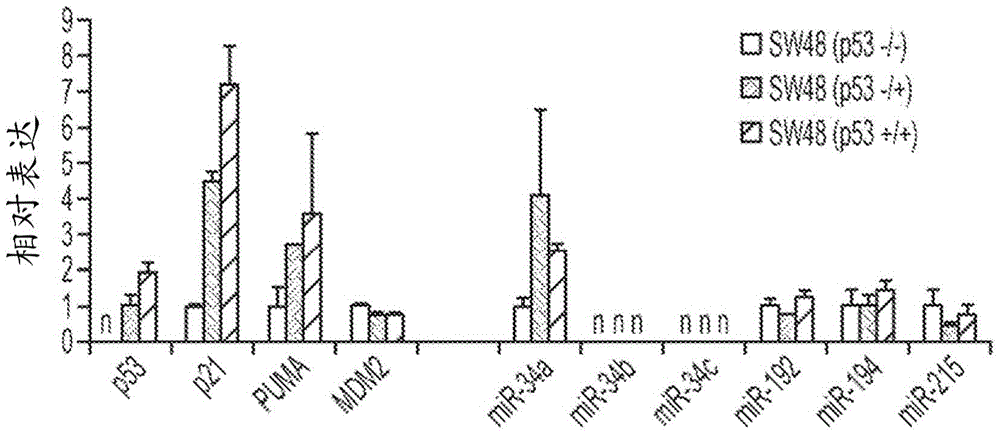
This invention is based in part on the discovery that miR-34 is independent of p53. It has been discovered that miR-34 functions in a TP53 -independent tumor suppression pathway. Specifically, miR-34-induced inhibition of cancer cell growth was found to be the same in p53-normal and p53-deficient cells. Thus, miR-34 has a more central role during tumor suppression that is uncoupled from p53. In the absence of p53, miR-34, unlike certain other miRNAs, is sufficient to induce an up-regulation of genes known to be regulated by p53, including but not limited to p21<CIP1 / WAF1>(CDKN1A), PUMA, BAX, NOXA, PHLDA3, and MDM2 and a down-regulation of HDAC1. Therefore, these biomarkers can be used as biomarkers of miR-34 activity. The invention is further based on the discovery that some of these biomarkers are indispensable for a therapeutic response to miR-34 activity, and are thus prerequisite biomarkers of miR-34 activity.
Owner:MIRNA THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods for treating lysosomal storage disease
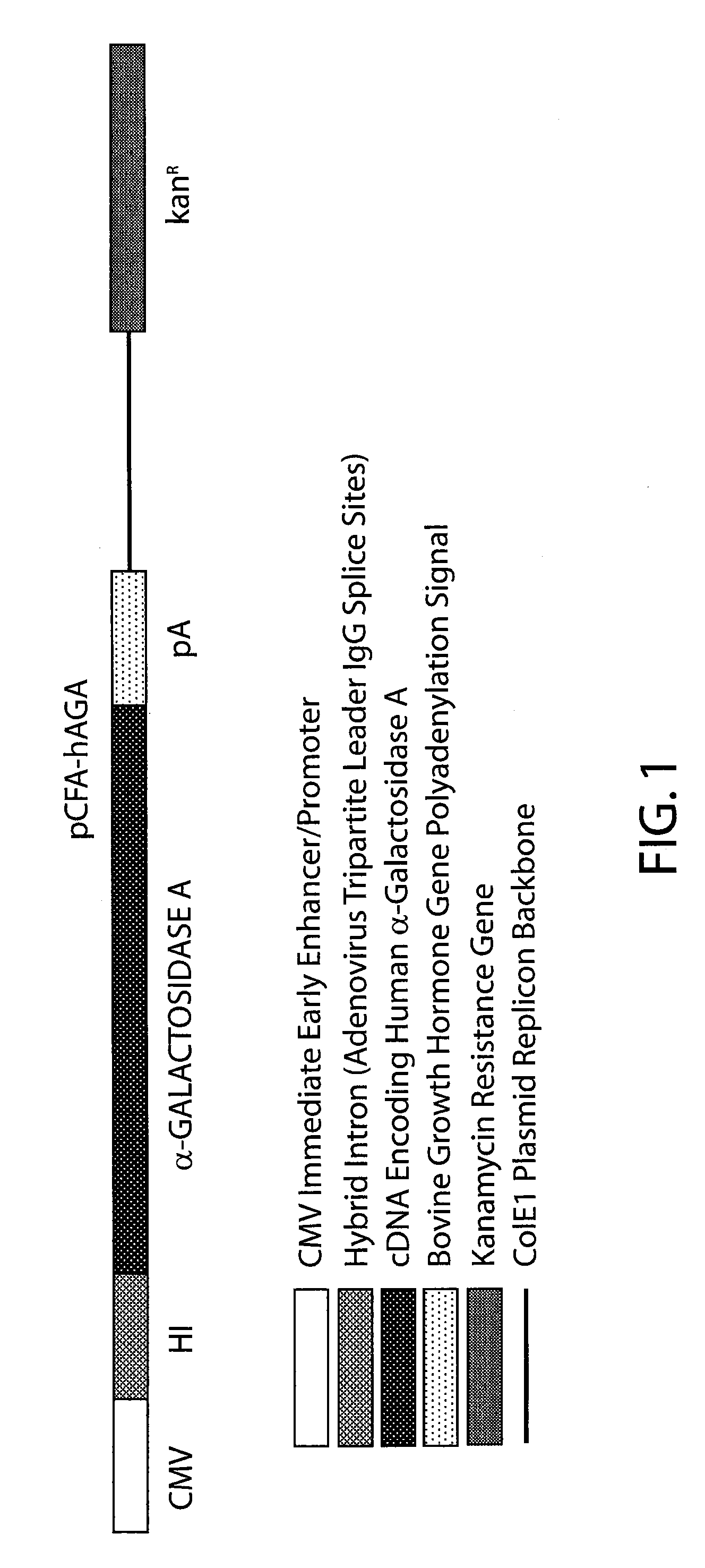
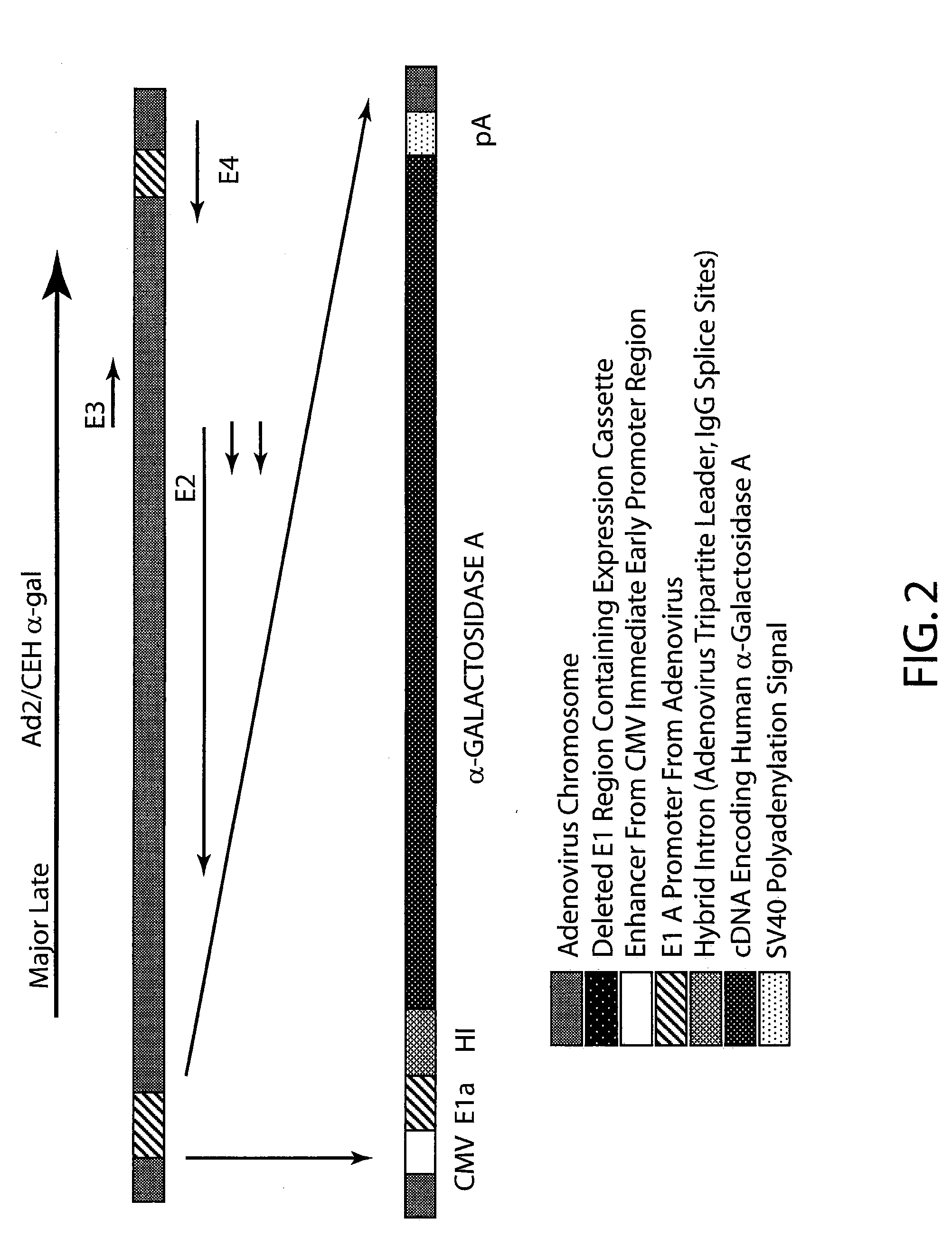
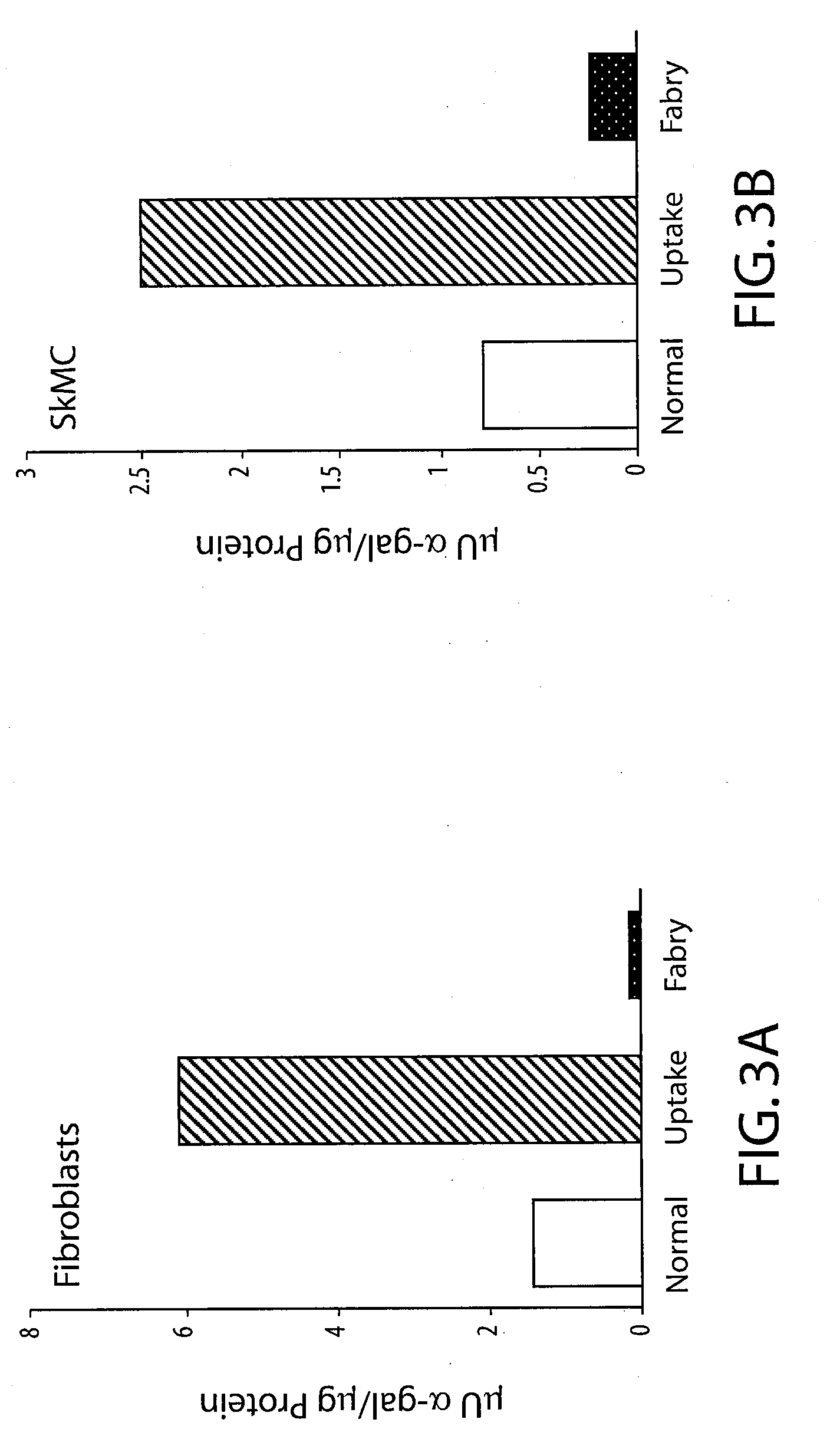
The present invention provides recombinant viral and non-viral vectors comprising a transgene encoding a biologically active human lysosomal enzyme that are able to infect and / or transfect and sustain expression of the biologically active human lysosomal enzyme transgene in mammalian cells deficient therein. In addition, methods are provided for providing a biologically active human lysosomal enzyme to cells deficient therein, which comprises introducing into the cells a vector comprising and expressing a transgene encoding the biologically active human lysosomal enzyme, wherein the vector is taken up by the cells, the transgene is expressed and biologically active enzyme is produced. The cells may be infected and / or transfected by the vector, dependent upon whether the vector is a viral vector and / or plasmid or the like. The invention also provides a method of supplying a biologically active human lysosomal enzyme to other distant cells deficient therein wherein the transfected and / or infected cells harboring the vector secrete the biologically active enzyme which is then taken up by the other deficient cells. In a preferred embodiment the present invention provides for sustained production of biologically human active α-galactosidase A in cells of Fabry individuals that are deficient in said enzyme.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Lifting firming mask and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109363976AImprove hydrophilic abilityGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientSkin elasticity
The invention discloses lifting firming mask and a preparation method thereof. The lifting firming mask comprises a thickener, a humectant, a preservative, water, Chondrus crispus, Euglena gracilis polysaccharide / hydrolyzed collagen and polyurethane-35. In the mask herein, the Chondrus crispus accounts for 1-3% by weight, the Euglena gracilis polysaccharide / hydrolyzed collagen accounts for 4-15% by weight, and polyurethane-35 accounts for 2-8% by weight. The components, such as Chondrus crispus, Euglena gracilis polysaccharide / hydrolyzed collagen and polyurethane-35, are added herein, and caneffectively permeate the dermal tissue to more quickly improve the collagen structure of dermis, thereby enhancing skin elasticity, improving dryness and loose skin, repairing damaged or nutrient-deficient cells, and evidently defying skin aging; the effect is better than that of one or two of the ingredients. An anti-allergy repair ingredient is added; therefore, the lifting firming mask is suitable for sensitive skin, and can repair the sensitive skin and recovery health of the skin.
Owner:I&B GUANGZHOU BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for inhibiting adenylosuccinate synthetase activity in malignant methylthioadenosine phosphorylase deficient cells
InactiveUS6214571B1High activityMinimize ToxicityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalPhosphoric acid
An in vivo method for depleting mammalian cells of adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) useful in the treatment of certain cancers is provided. According to the method, a population of cells is obtained from a host and assayed for loss of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAse) activity. MTAse catabolizes methylthioadenosine to adenine for endogenous salvage incorporation into the intracellular AMP pool. The preferred method for assaying loss of MTAse activity is a hybridization technique for detection of a homozygous loss of the gene which encodes MTAse. Hosts having MTAse deficient tumors are treated with a therapeutically effective amount of an agent which inhibits the activity of adenylsuccinate synthetase, which converts inosine 5-monophosphate to AMP, thus depleting the tumor cells of substrates for de novo AMP production. L-alanosine is the preferred ASS inhibitory agent for use in the method of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-glypican 3 antibody having modified sugar chain
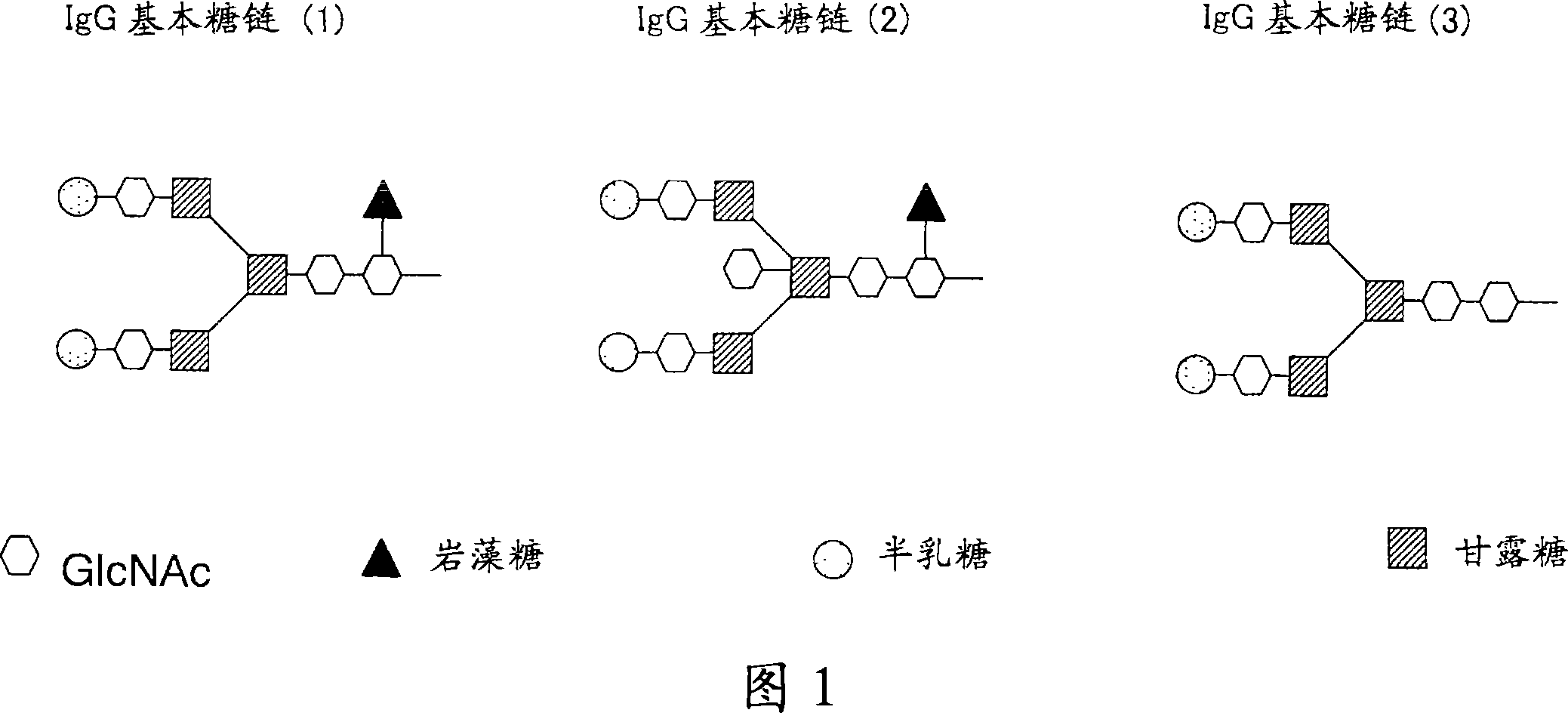
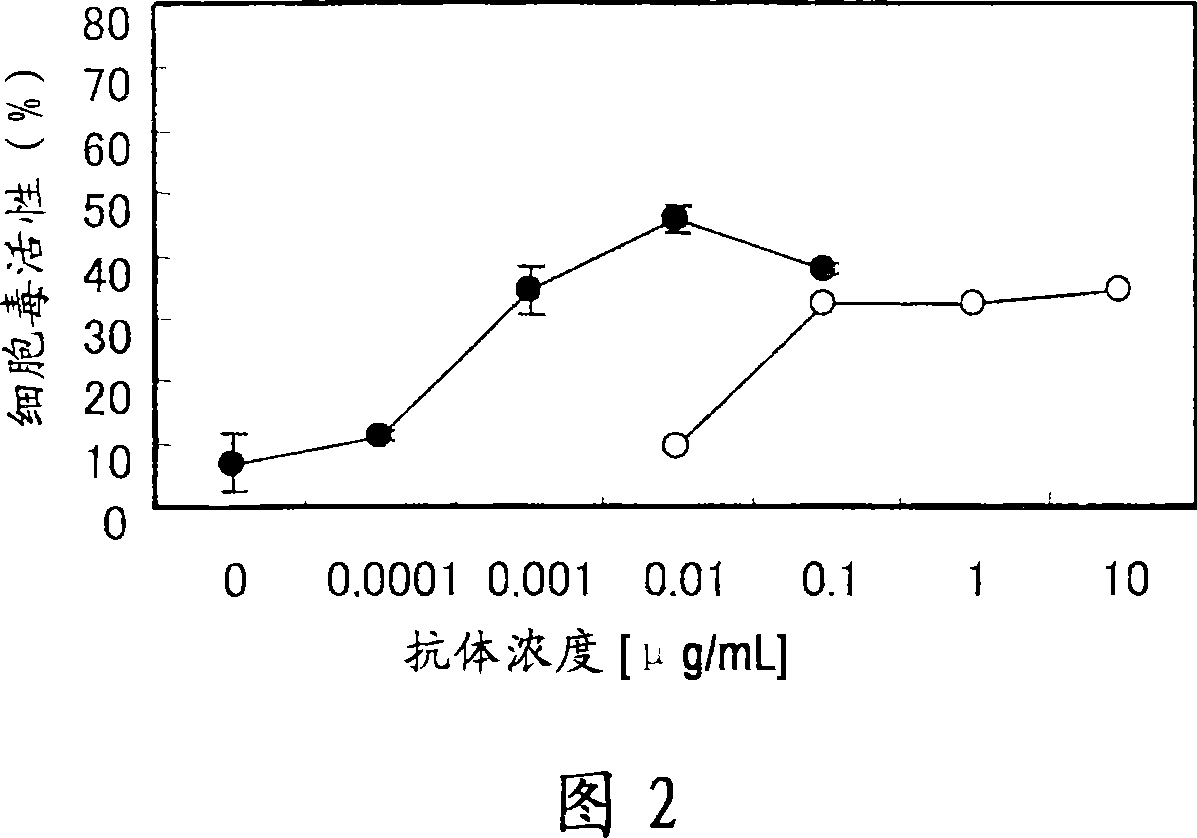
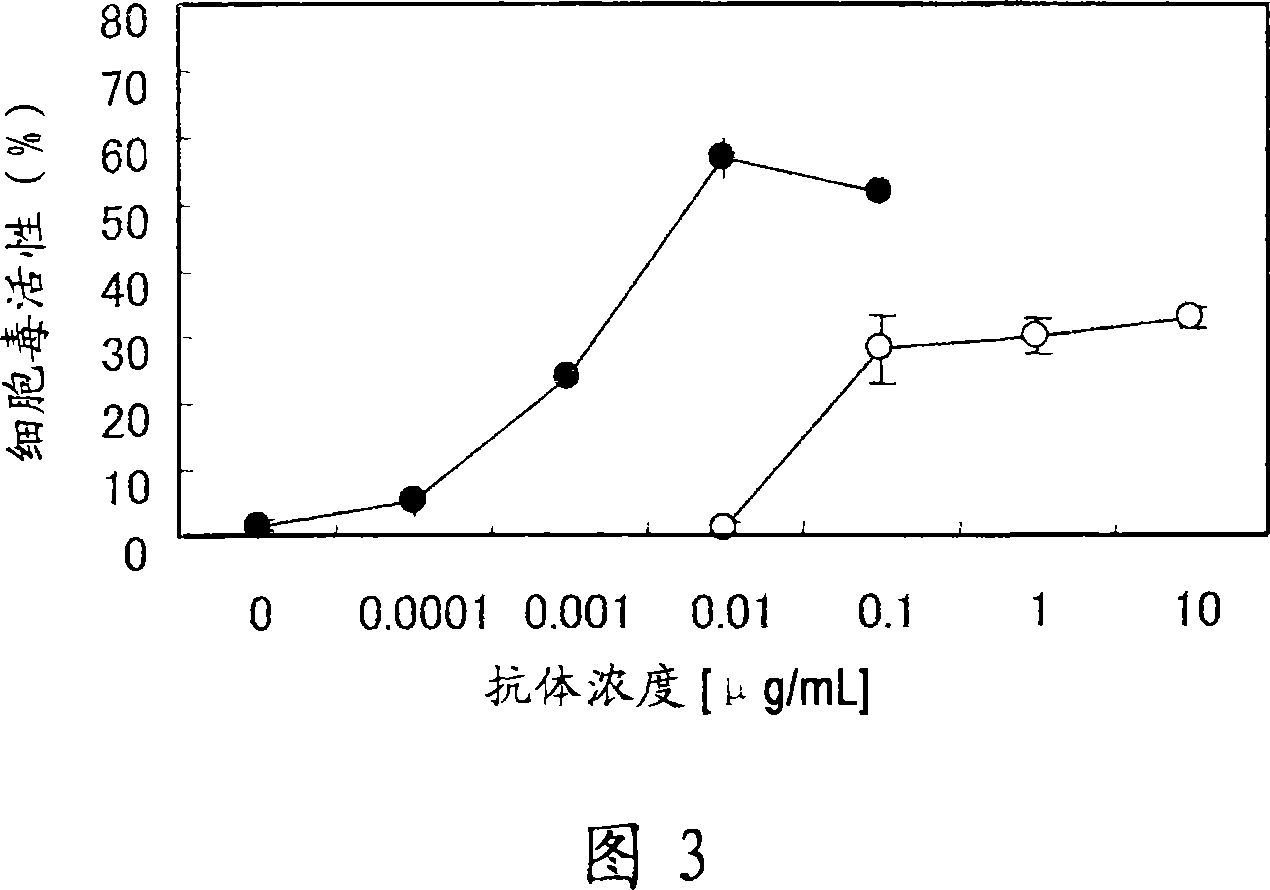
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Beta-2 microglobulin-deficient cells
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
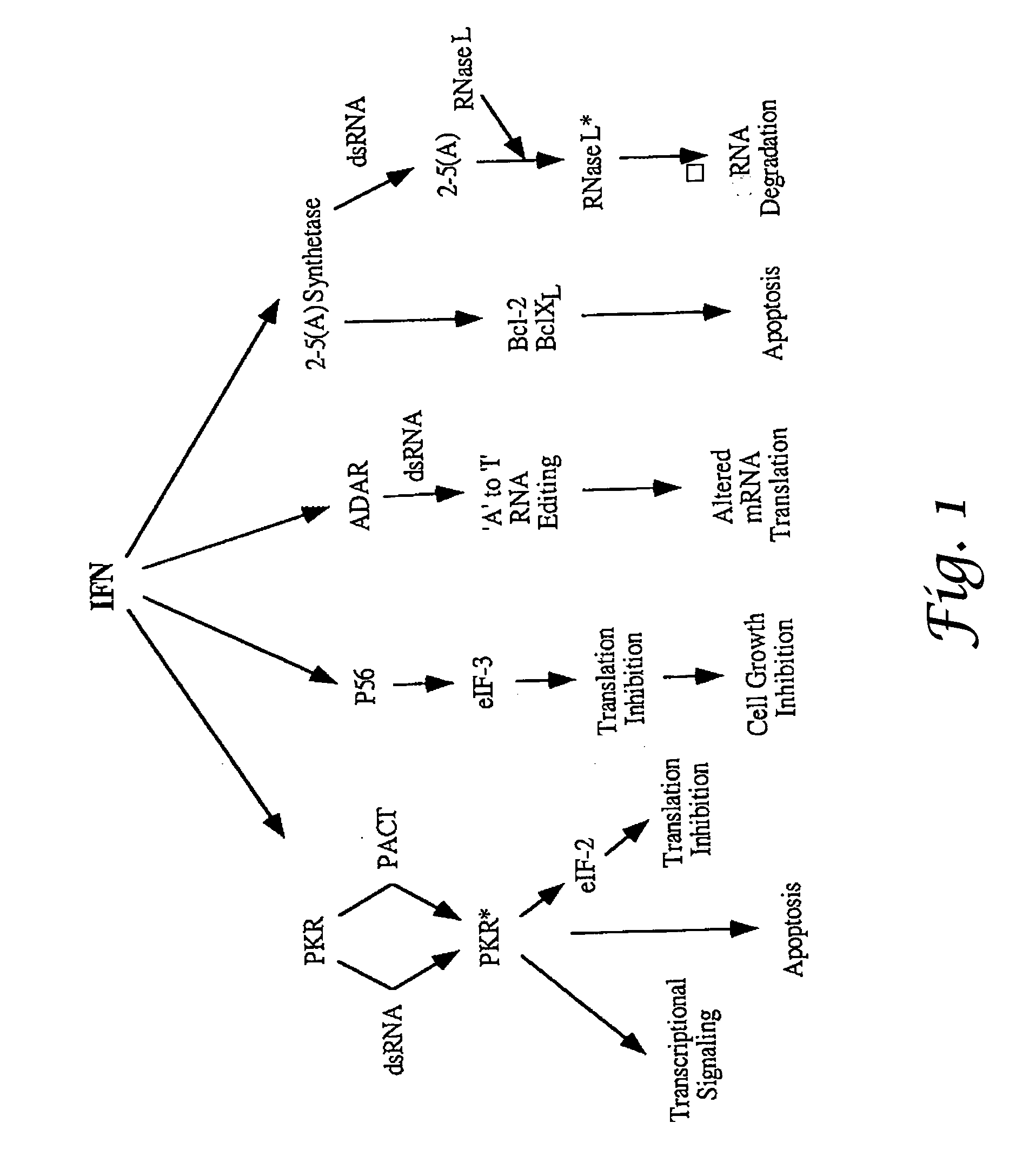
ADAR1 antiviral pathway
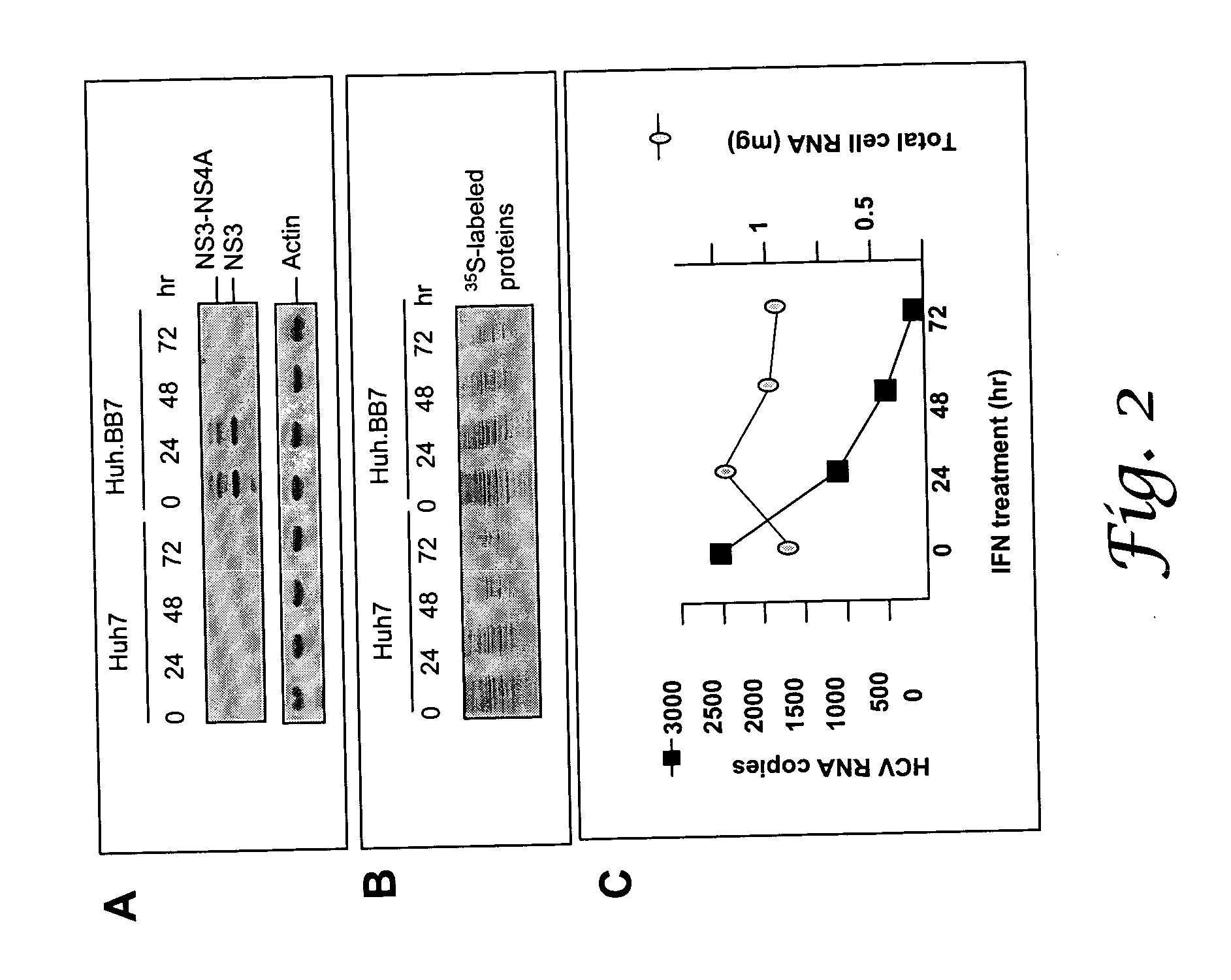
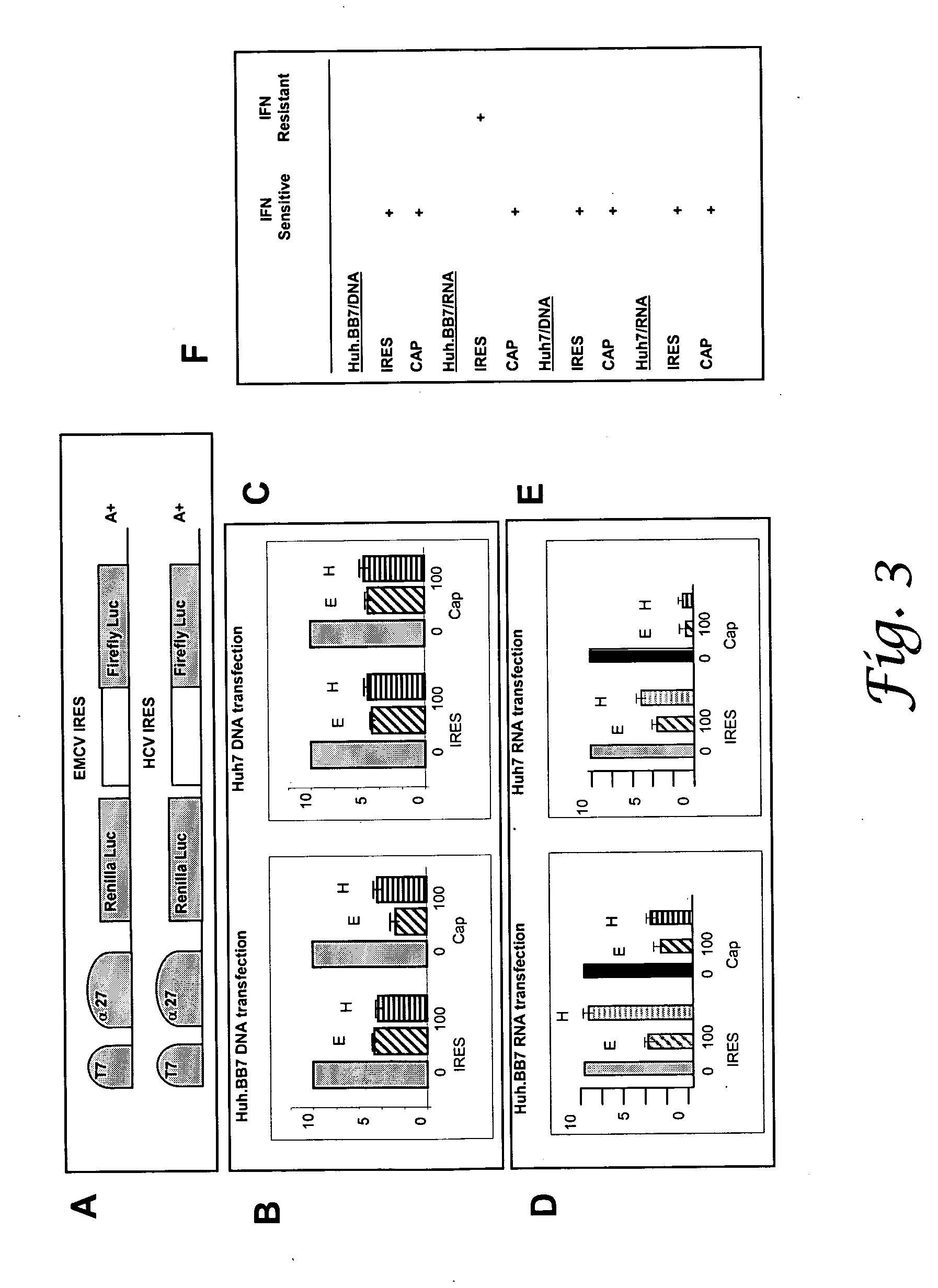
Methods for enhancing the production of viral vaccines in cell culture are described, as are the cell cultures. These methods rely on the suppression of the levels of ADAR1 in interferon-deficient cells. The methods comprise (a) infecting a cell culture with a donor virus, wherein said cell culture is an interferon-deficient cell culture that is deficient in ADAR1 activity; (b) culturing said infected cell culture under conditions sufficient to provide efficient virus growth; and (c) harvesting the virus produced.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
HLA Class II Deficient Cells, HLA Class I Deficient Cells Capable of Expressing HLA Class II Proteins, and Uses Thereof
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
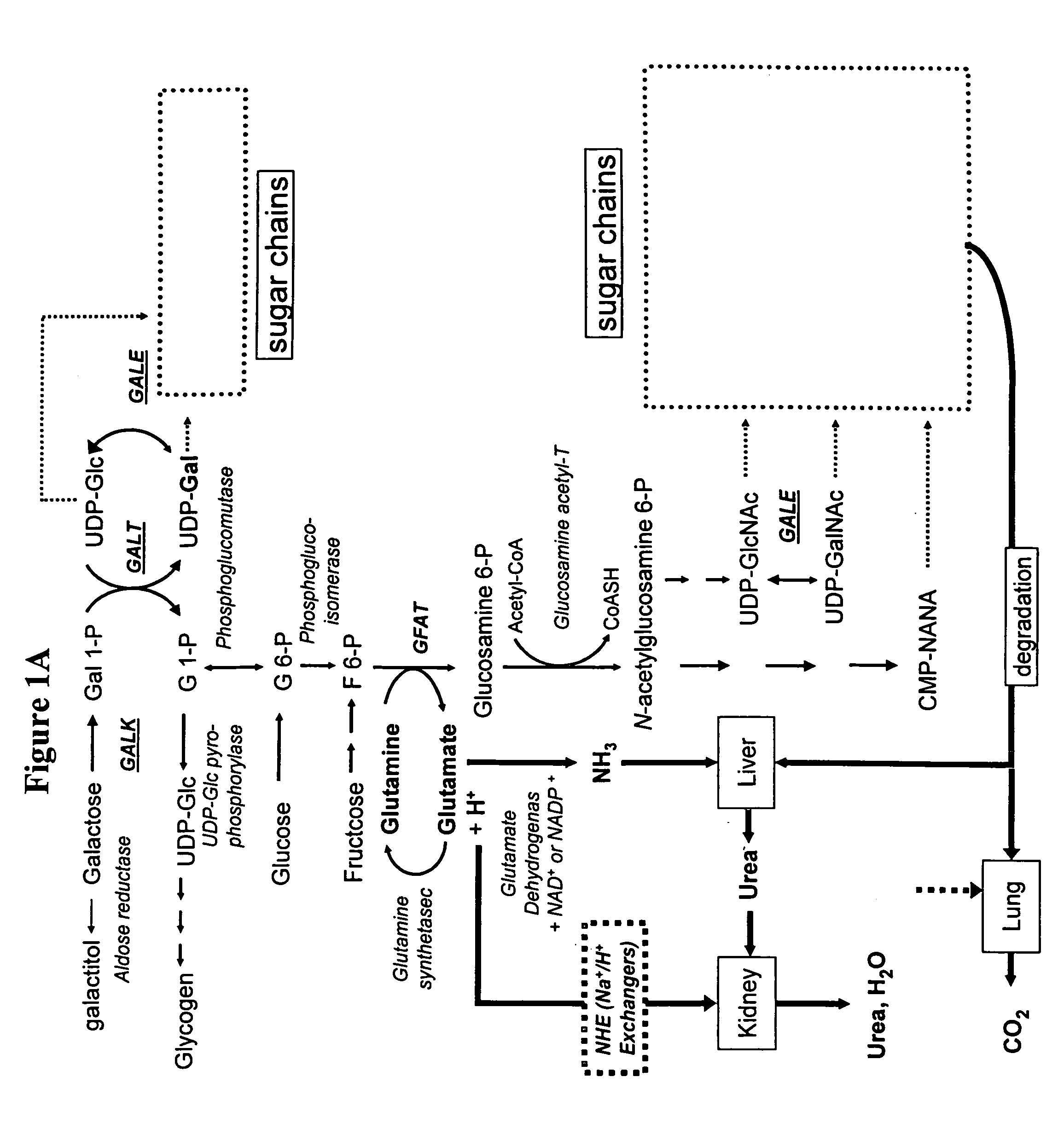
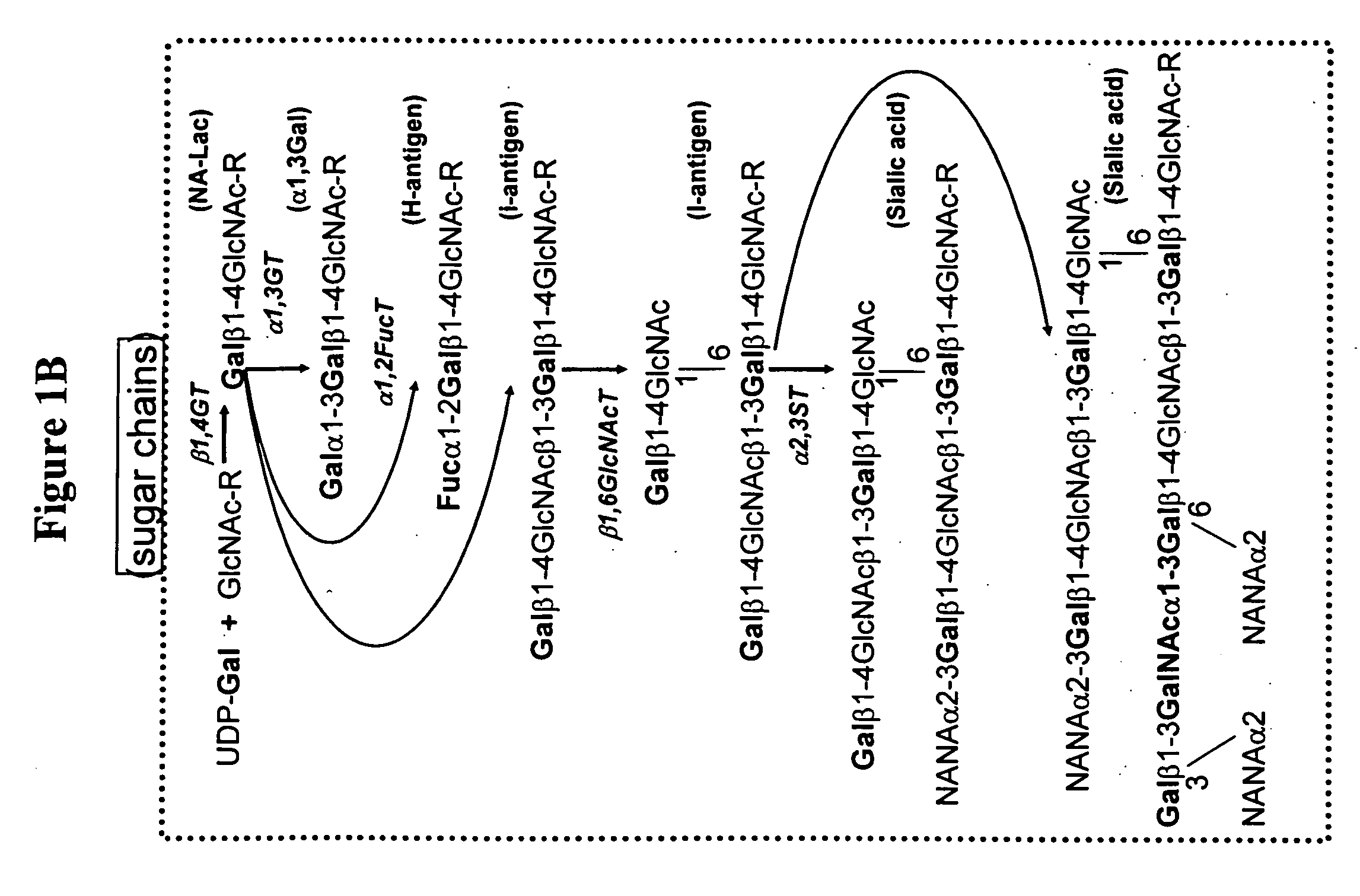
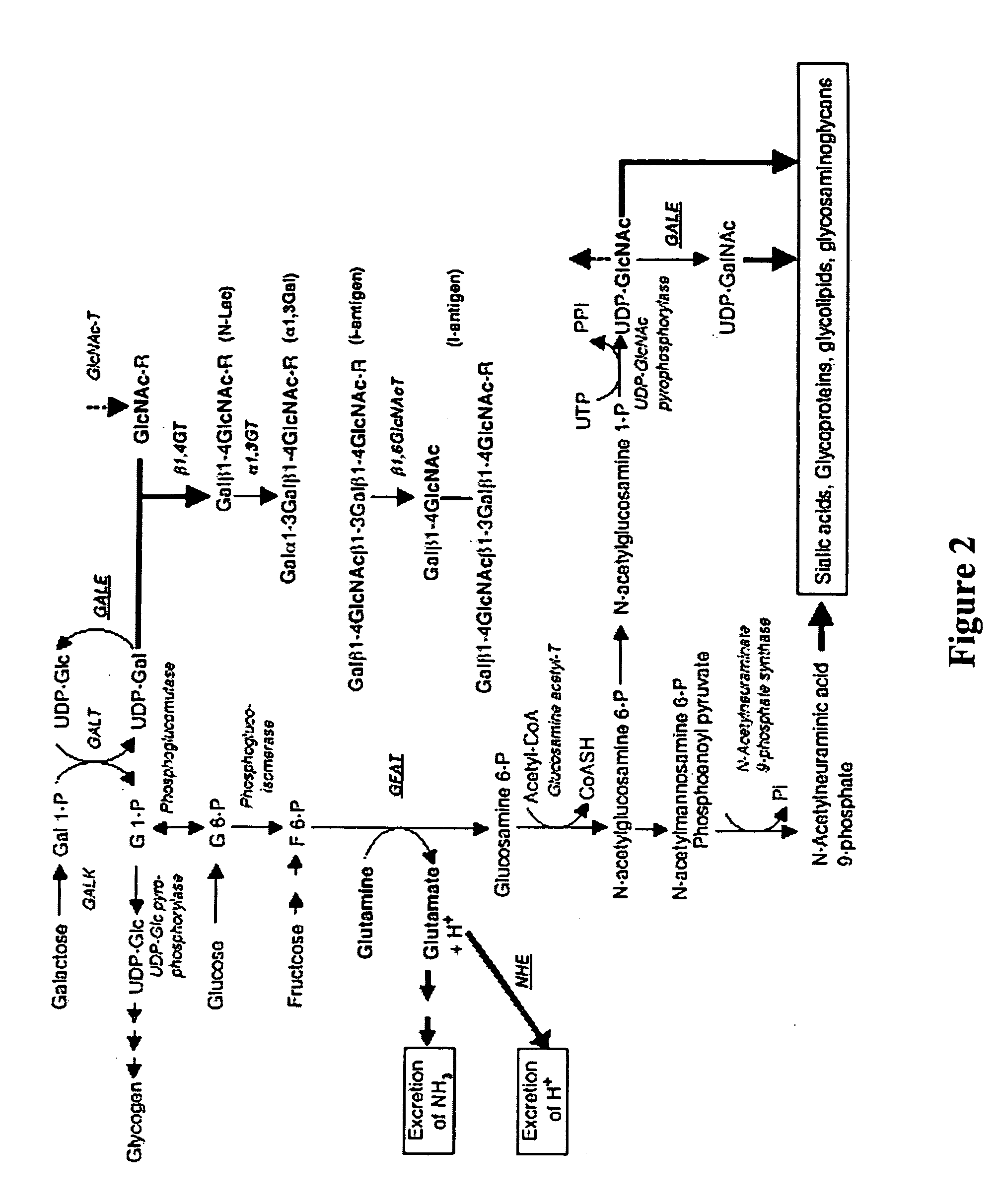
Modification of sugar metabolic processes in transgenic cells, tissues and animals
InactiveUS20060053500A1Reduce accumulationLimited abilityTransferasesTissue cultureMetaboliteLactose
The present invention provides natural or transgenic galactose deficient cells, tissues, organs and animals that have been genetically modified to compensate for the abnormalities in galactose metabolic pathways. The present invention modifies sugar metabolic pathways to to prevent the deleterious accumulation of sugar metabolites in animals, tissues, organs, cells and cell lines that possess natural or transgenic abnormalities in the sugar metabolic pathways. Such cells, tissues, organs and animals can be used in research and medical therapy, including xenotransplantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
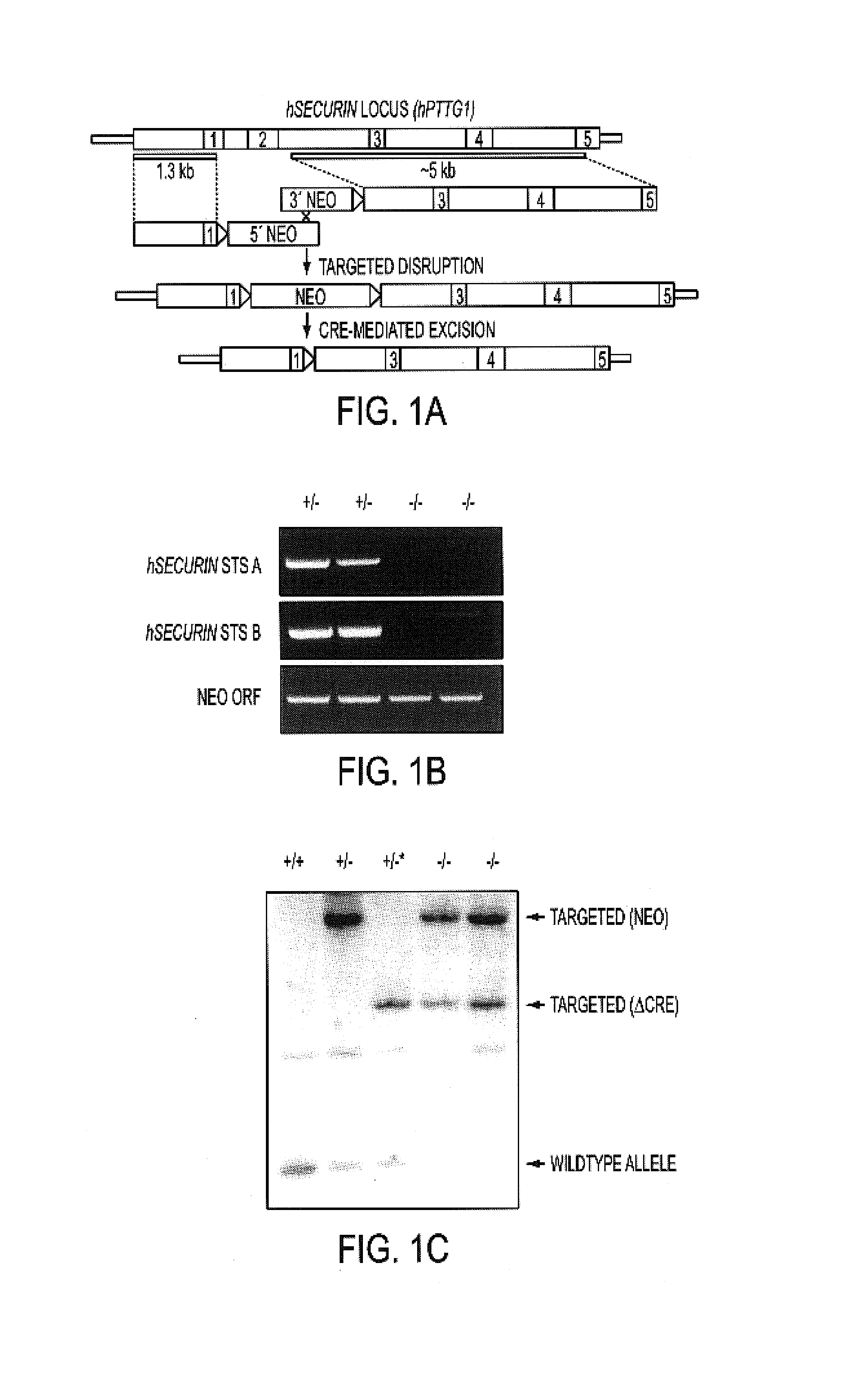
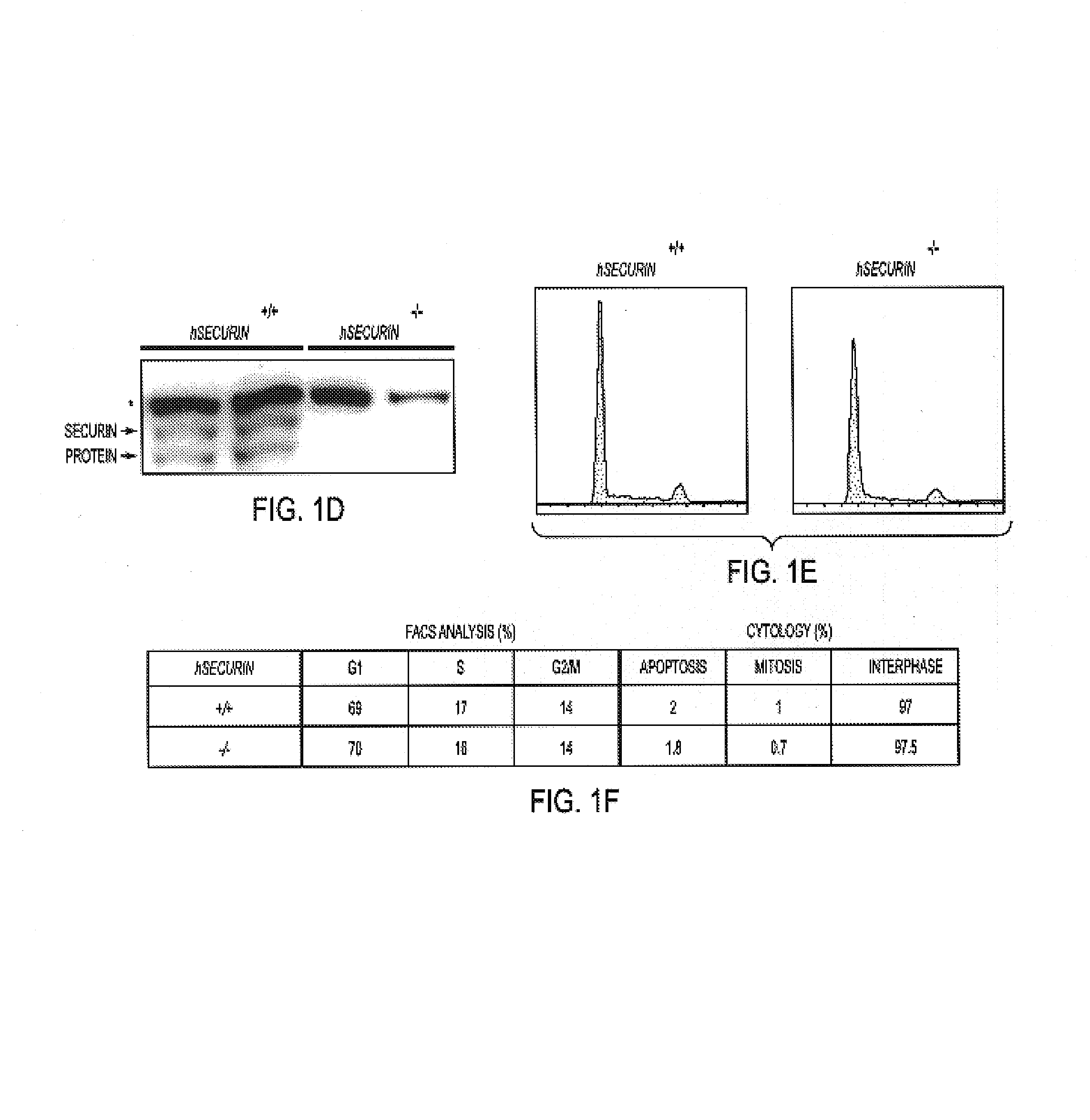
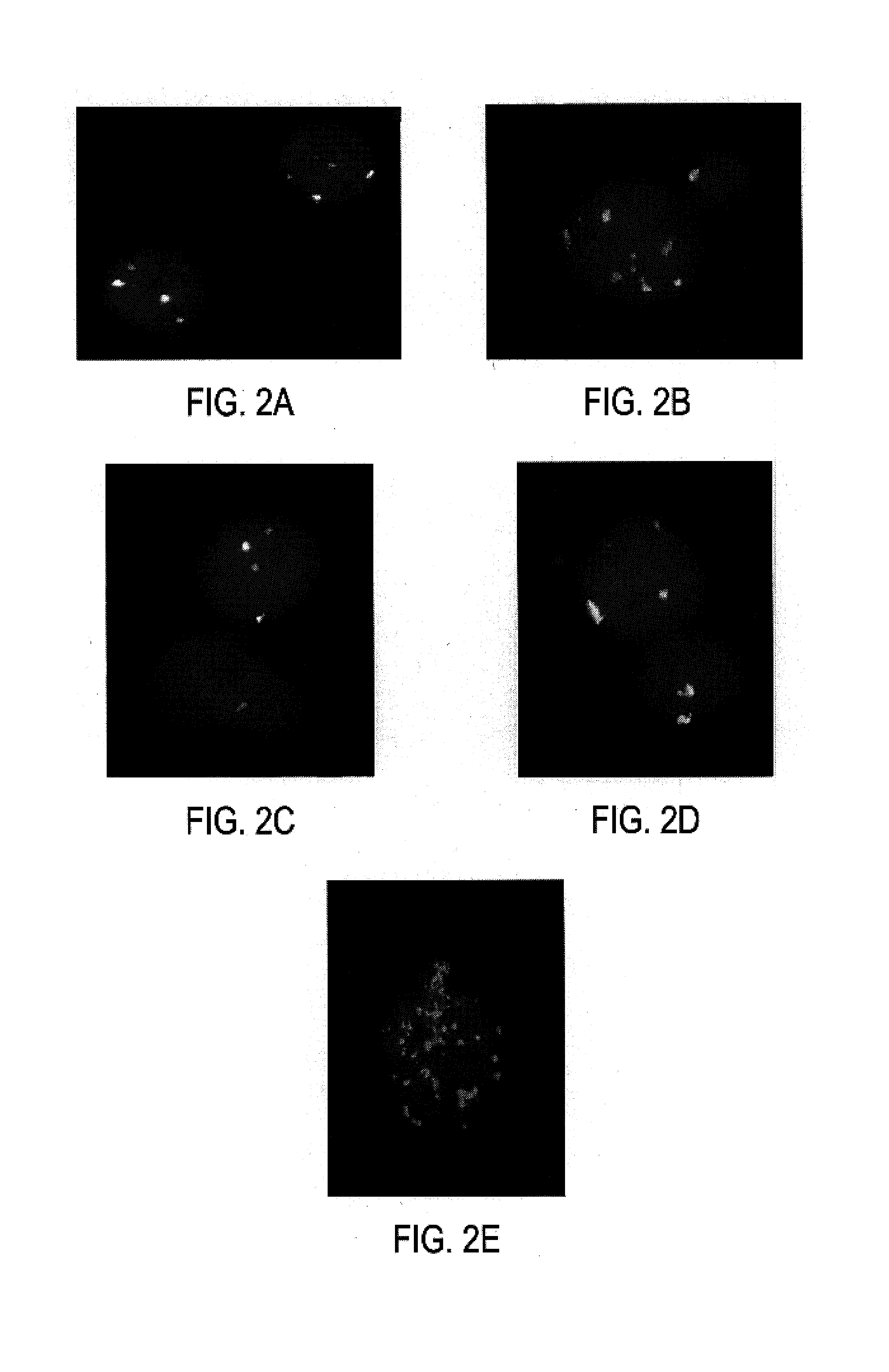
Securin is required for chromosomal stability in human cells
ActiveUS7354703B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsChemotherapeutic drugsInstability
Securin-deficient cells and their isogenic securin-proficient counterparts are useful for screening potential anti-tumor agents. Potential therapeutic agents are screened for the ability to preferentially inhibit or kill a securin-deficient cell. The association of securin deficiency and chromosomal instability leading to aneuploidy, renders securin an excellent target for chemotherapeutic drug development.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of preforming homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
InactiveUS20050210539A1Improve throughputEasy to modifyStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorHeterologousGene targeting
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertions, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene is contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells. In particular, high throughput methodology is provided for generating the modified the independent origin based cloning vectors of the present invention.
Owner:HEINTZ NATHANIEL +3
MGAT1-Deficient Cells for Production of Vaccines and Biopharmaceutical Products
InactiveUS20200231633A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusGlycan
Mannosyl (alpha-1,3)-glycoprotein beta-1,2-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase (Mgat1)-deficient cell lines and methods for use of same for producing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) envelope glycoprotein polypeptides or fragment thereof with terminal mannose-5 glycans are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hat acetylation promoters and uses of compositions thereof in promoting immunogenicity
InactiveCN101626780APromote transcriptionEnhanced surface expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMHC class ICytotoxicity
The invention provides processes and compositions for enhancing the immunogenicity of TAP-I expression-deficient cells by increasing the presentation of MHC Class I surface molecules for detection by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte cells through increased TAP-I expression, which comprises administering to the TAP-I expression-deficient cells a TAP-I expression increasing amount of a bio-acceptable substance that promotes transcription of TAP-I gene in the cells to cause enhanced MHC Class I surface expression of the cells. The bio-acceptable substance may be a histone H3 deacetylase inhibitor such as trichostatin A, a transcriptional co-activator having intrinsic histone acetyl transferase activity or a histone acetyl transferase comprising at least one member of the CBP / p300 protein family. The process and compositions increase the immunogenicity of the target cells, e.g. tumor cells, to enhance their destruction by cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Owner:BIOMMUNE TECH
Method for generating hypermutable organisms
InactiveUS7319036B2Increase ratingsEnhanced genome wide mutation rateMutant preparationTissue cultureMammalAllele
Owner:EISAI INC
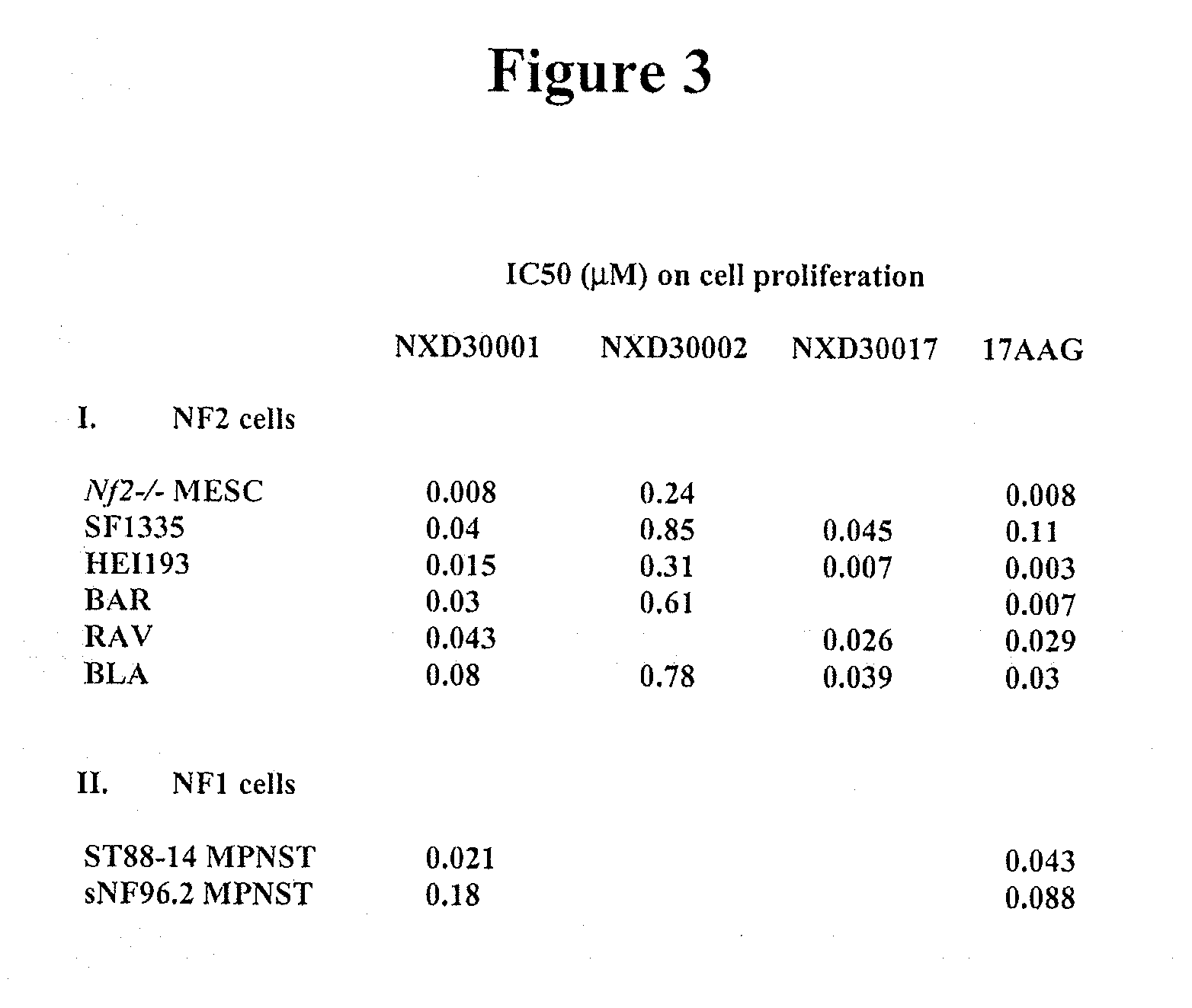
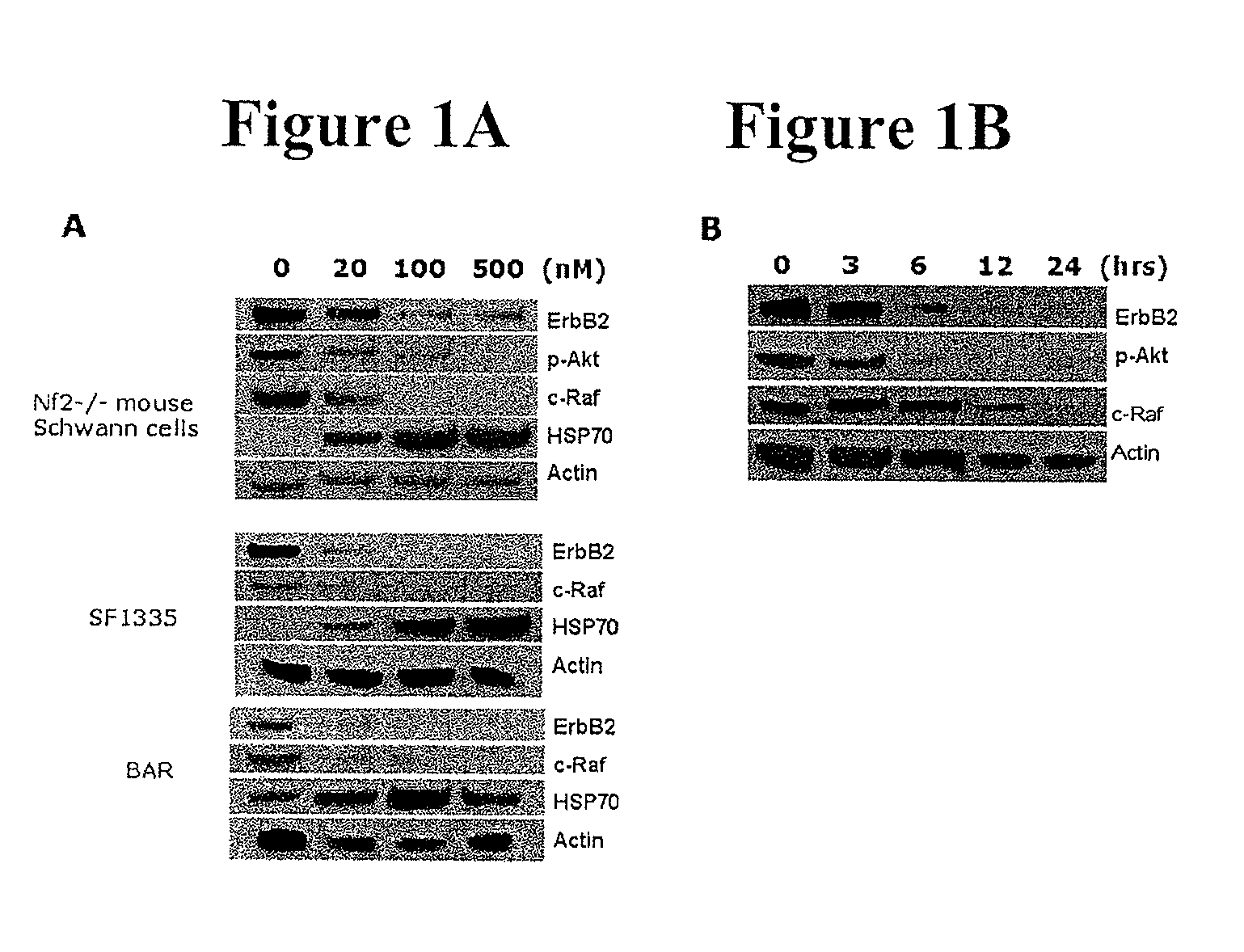
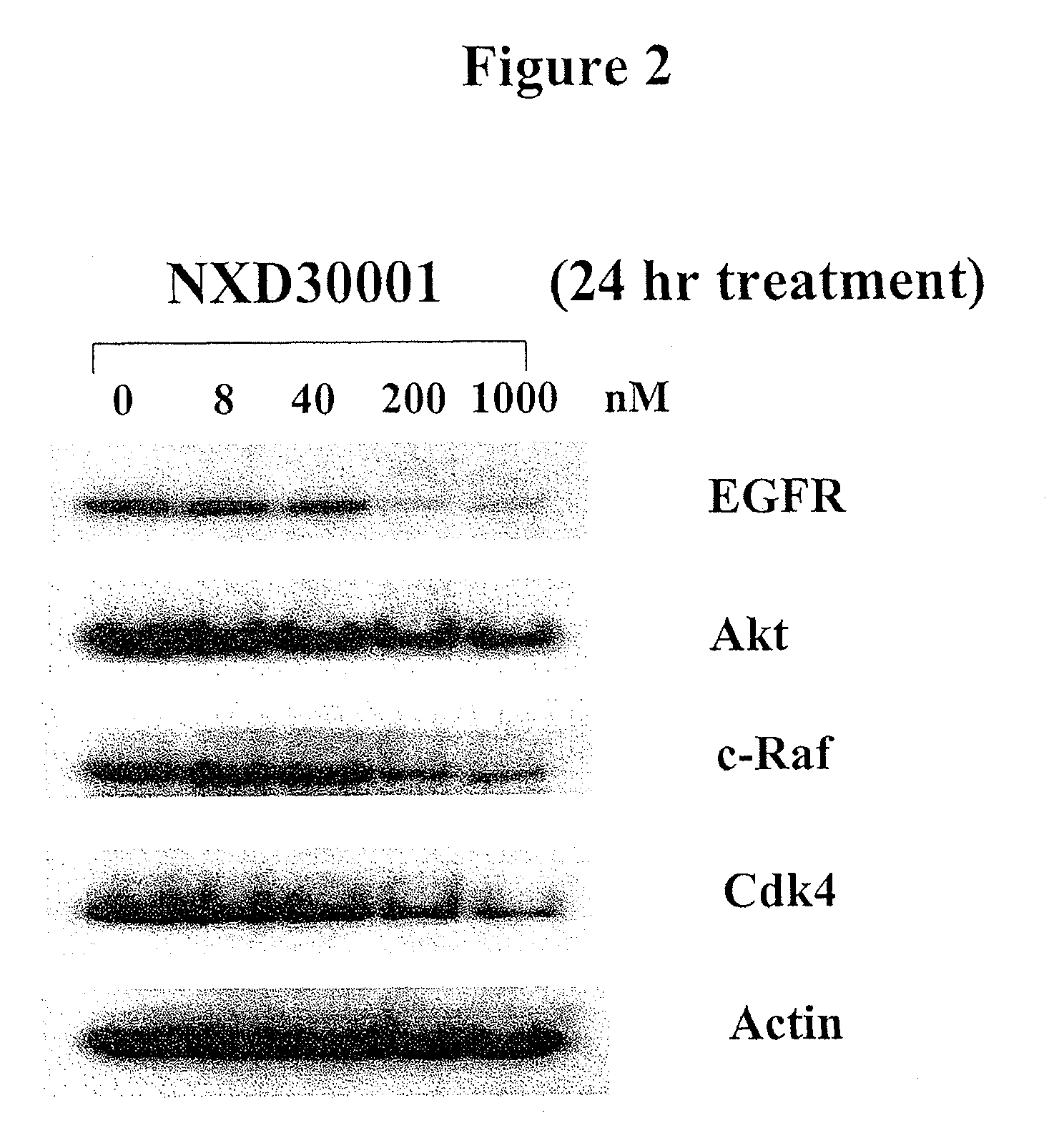
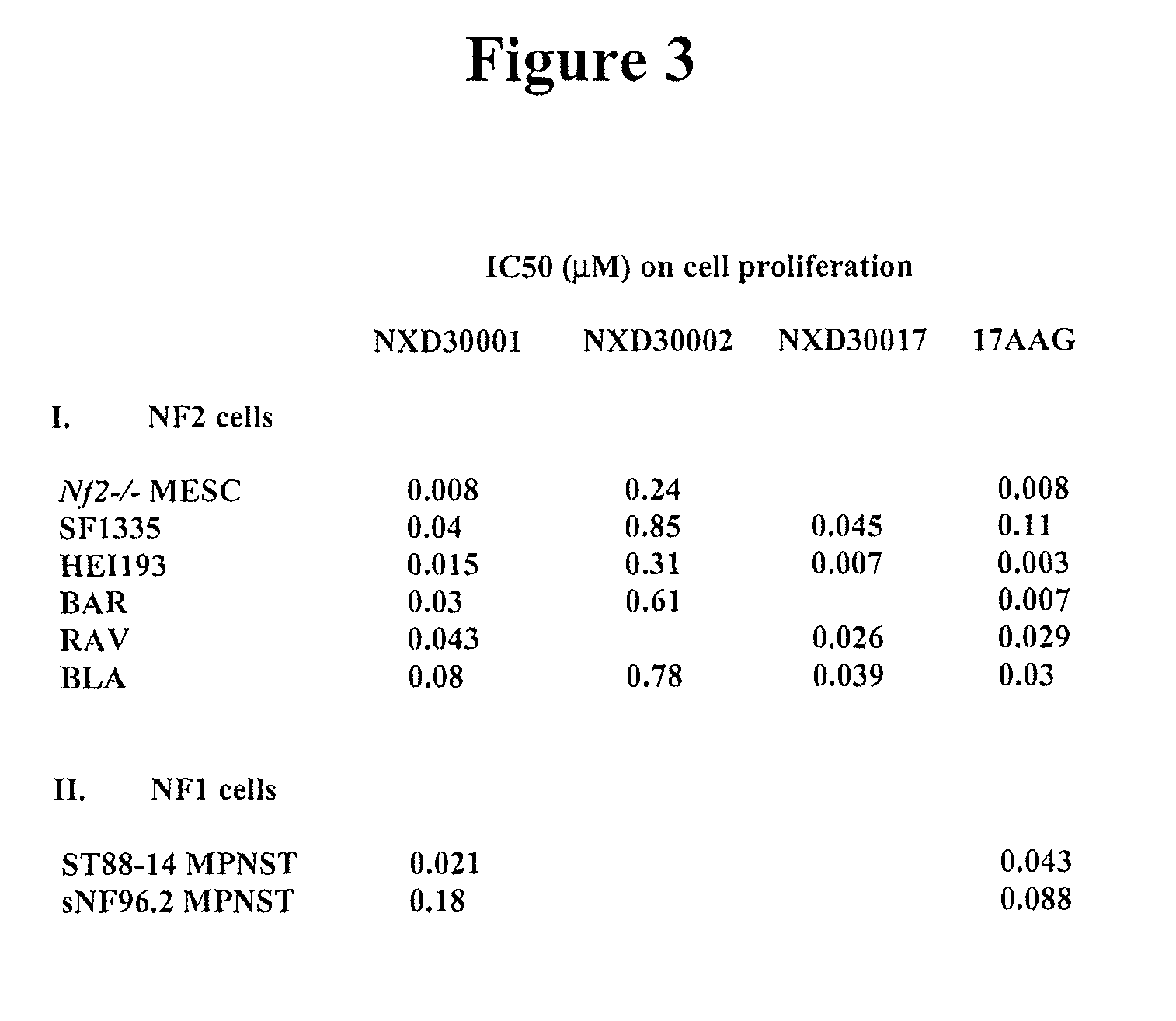
Treatment Of Neurofibromatosis With Radicicol And Its Derivatives
ActiveUS20100292218A1Inhibiting and reducing growthInhibiting and reducing and numberBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseActive agent
The present invention provides compounds of formulae Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va and the therapeutic use thereof. The present invention also includes methods of treating NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient cells or neurodegenerative diseases with radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va. Furthermore, the present invention is directed to methods of inhibiting the growth of NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient tumors. The methods comprise contacting NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient tumor cells with radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va. The present invention is also directed to the combinational use of radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va with at least one additional active agent, such as one or more HSP90 inhibitors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG +1
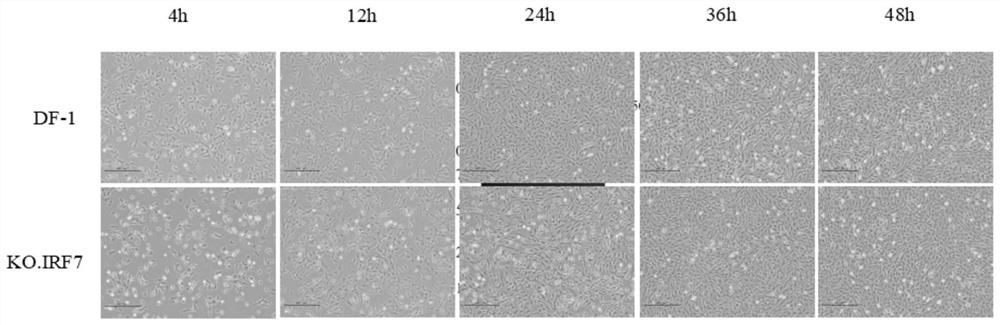
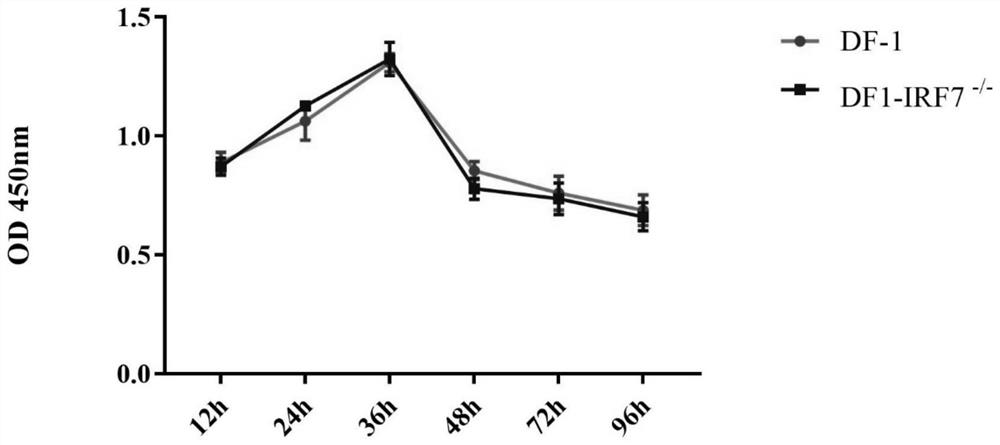
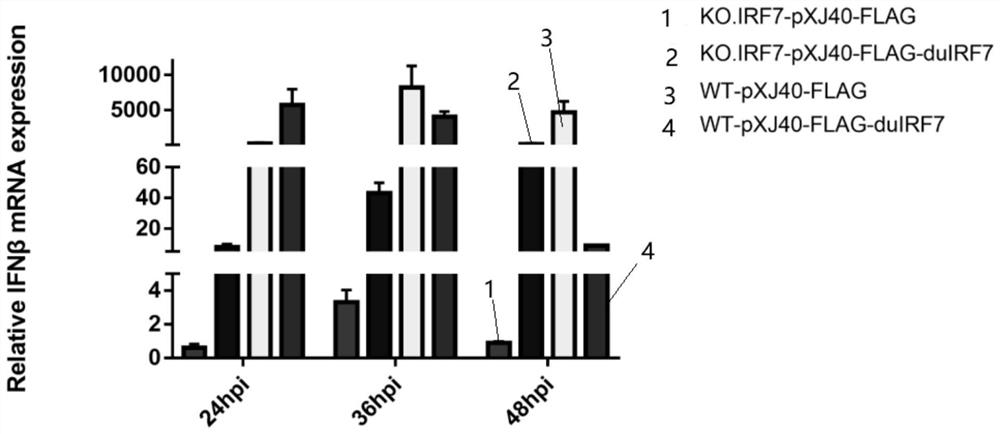
Cell line with sgRNA, plasmid and IRF7 function deficiency as well as construction method and application of cell line
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides sgRNA for specifically targeting an IRF7 gene, and the sequence of the sgRNA is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. The sgRNA primer and a proper carrier structure can form a plasmid, and the plasmid is used for knocking out a corresponding gene to realize deletion of an IRF7 function. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a plasmid, an IRF7 function-deficient cell line, and a construction method and application of the IRF7 function-deficient cell line. The cell line disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the IFN-beta mRNA level, the IRF1 mRNA level, the VIPERIN mRNA level and the CMPK 2 mRNA level can be remarkably inhibited. Compared with the mode that CN201910352557.4 only inhibits the expression level of interferon beta, inhibition in other aspects is more remarkable.
Owner:岭南现代农业科学与技术广东省实验室肇庆分中心 +1
Recovery serum and application thereof
InactiveCN108403450AMaintain normal functionNot easy to breedCosmetic preparationsHeavy metal active ingredientsSkin sensitizationOral ulcers
The invention provides a recovery serum and application thereof. Each liter of the recovery serum comprises, by mg, at least a solute component listed in the description. The recovery serum can act aseffective ingredient for skin metabolism and recovery, can kill bacteria grown on the skin surface, can activate activity of water-deficient cells, and deeply moisturize the bottom of the skin, and quickly supplement tissue liquid and electrolyte lost due to damage; therefore, the recovery serum can provide relief and even healing for skin beauty and whitening, skin allergy, skin inflammation, oral ulcers, skin burns and scalds, dry eyes, eye fatigue and the like; the recovery serum has good effect and has a healing period of 12-15 days after being sprayed to the skin scald wounds.
Owner:深圳市盛凯元科技有限公司
Treatment of neurofibromatosis with radicicol and its derivatives
ActiveUS8329683B2Inhibiting and reducing growthInhibiting and reducing and numberBiocideAnimal repellantsActive agentHsp Inhibitor
The present invention provides compounds of formulae Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va and the therapeutic use thereof. The present invention also includes methods of treating NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient cells or neurodegenerative diseases with radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va. Furthermore, the present invention is directed to methods of inhibiting the growth of NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient tumors. The methods comprise contacting NF2-deficient or NF1-deficient tumor cells with radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va. The present invention is also directed to the combinational use of radicicol or its derivatives, such as one or more compounds of formula I, II, III, IV, V, Ia, Ia′, IIa, IIa′, IIIa, IIIa′, IVa, or Va with at least one additional active agent, such as one or more HSP90 inhibitors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG +1
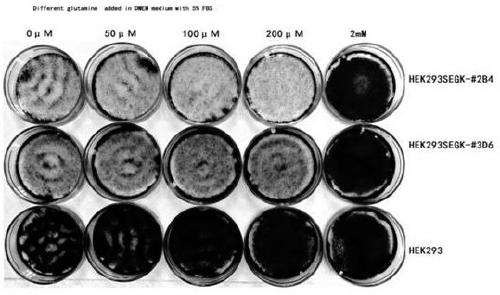
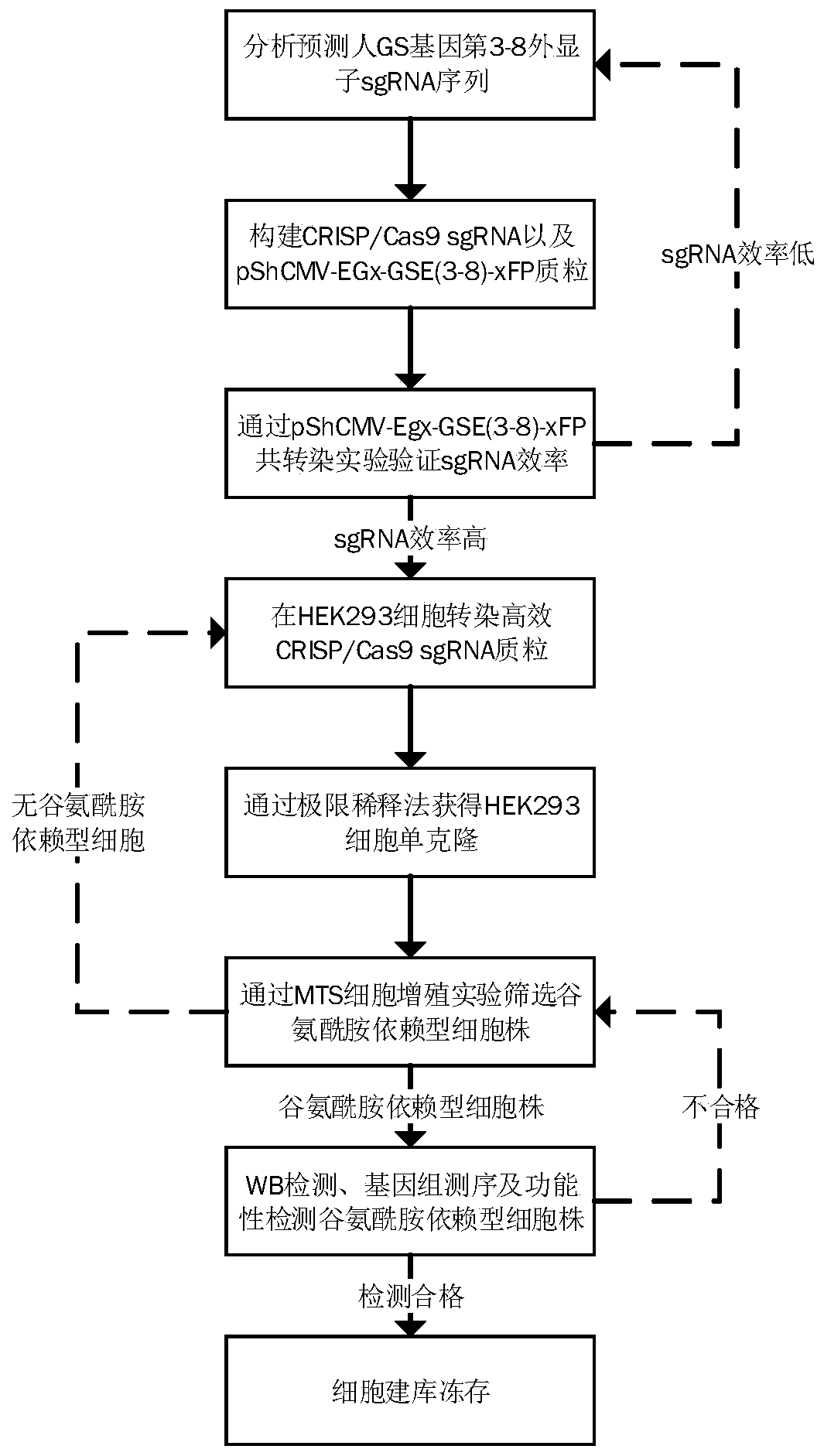
A method for screening glutamine synthetase-deficient hek293 cell line
ActiveCN107893073BHigh expressionSimplify the upstream cultivation processHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetGlutamine synthase
Provided is an HEK293 cell-based glutamine synthetase-deficient cell line HEK293-GS- / - that can be stably passaged, adapted to a suspension culture, and is applicable to recombinant protein expression constructed using a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The cell line can express various recombinant proteins through screening using a GS / MSX screening system, can stably express a target protein after multiple passages, and can adapt to most commercial serum-free media.
Owner:EUREKA BIOTECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com