Patents
Literature
33 results about "Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
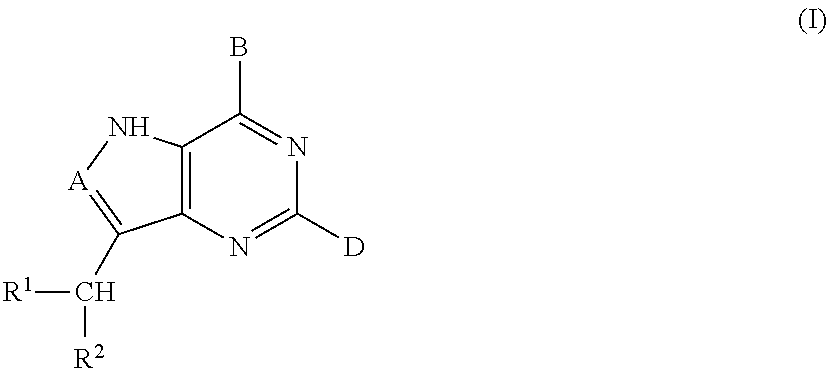
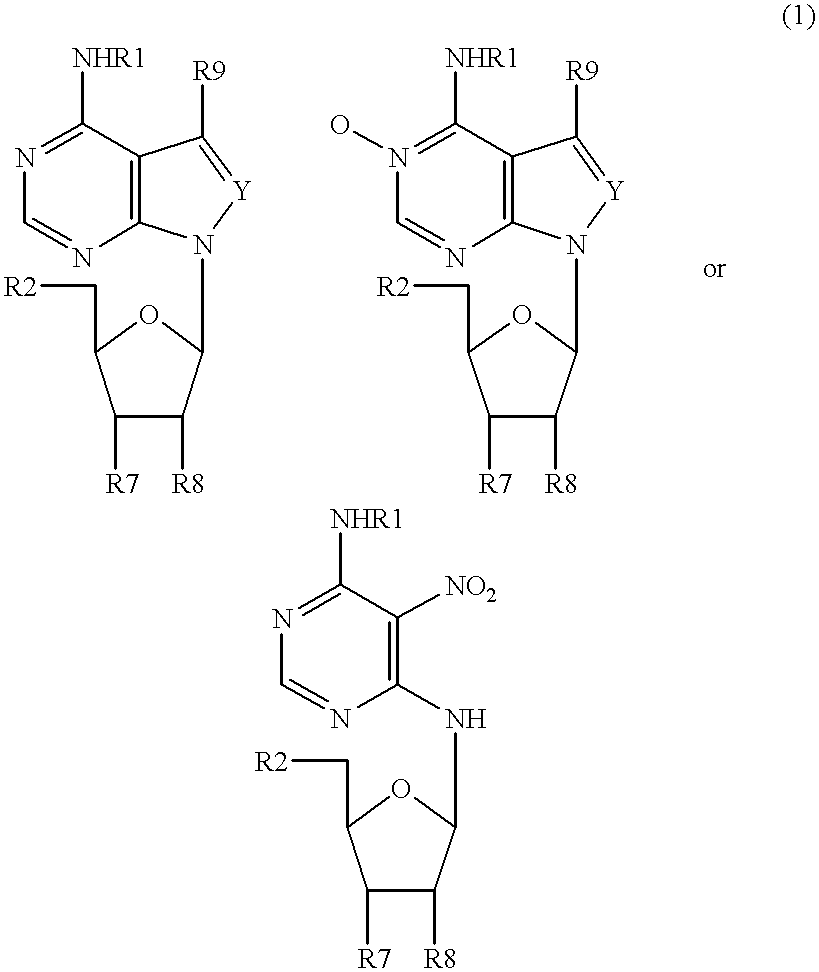
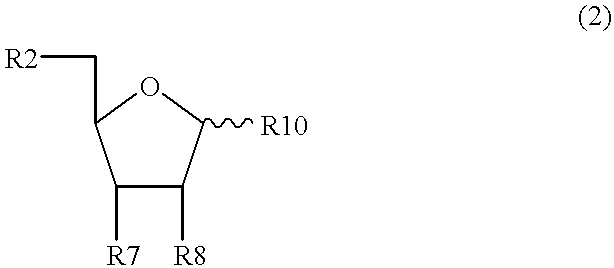
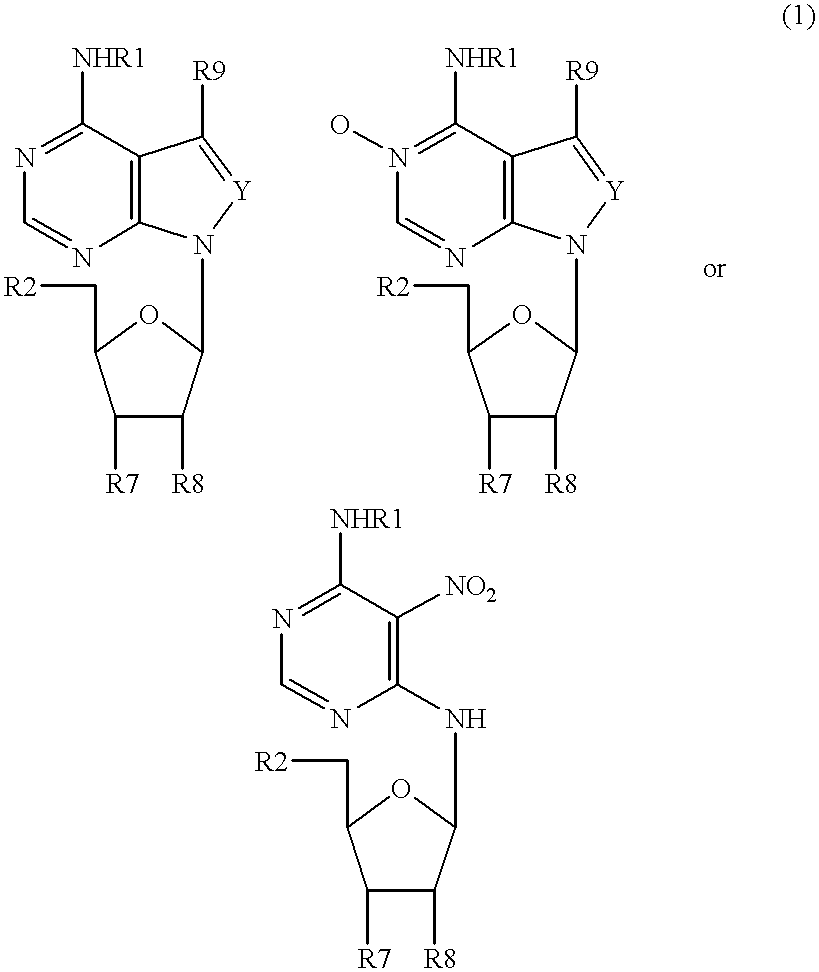
Inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
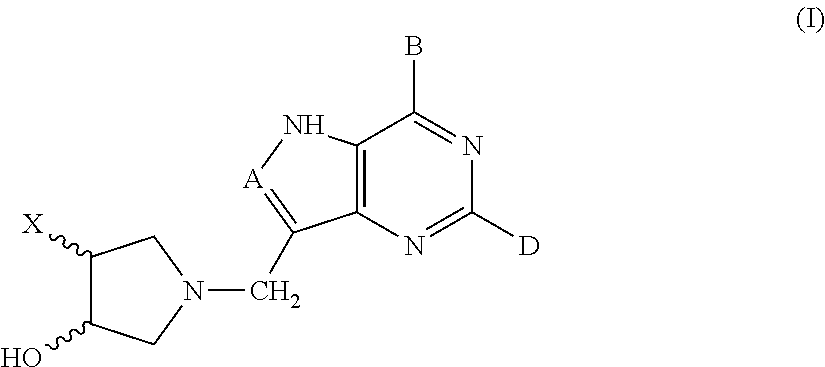
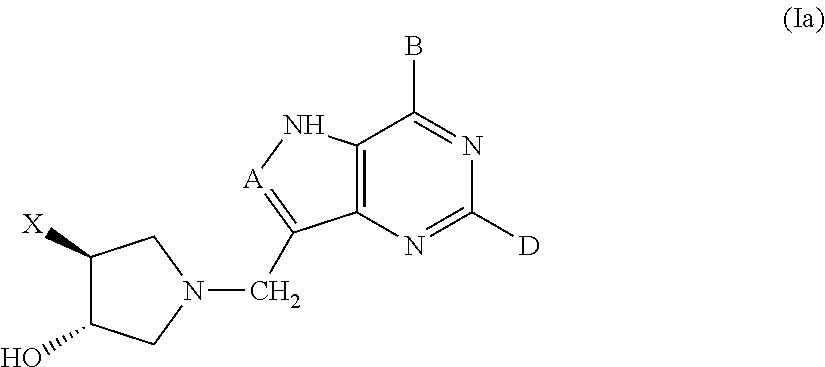
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
Inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine muclioside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine mucliosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
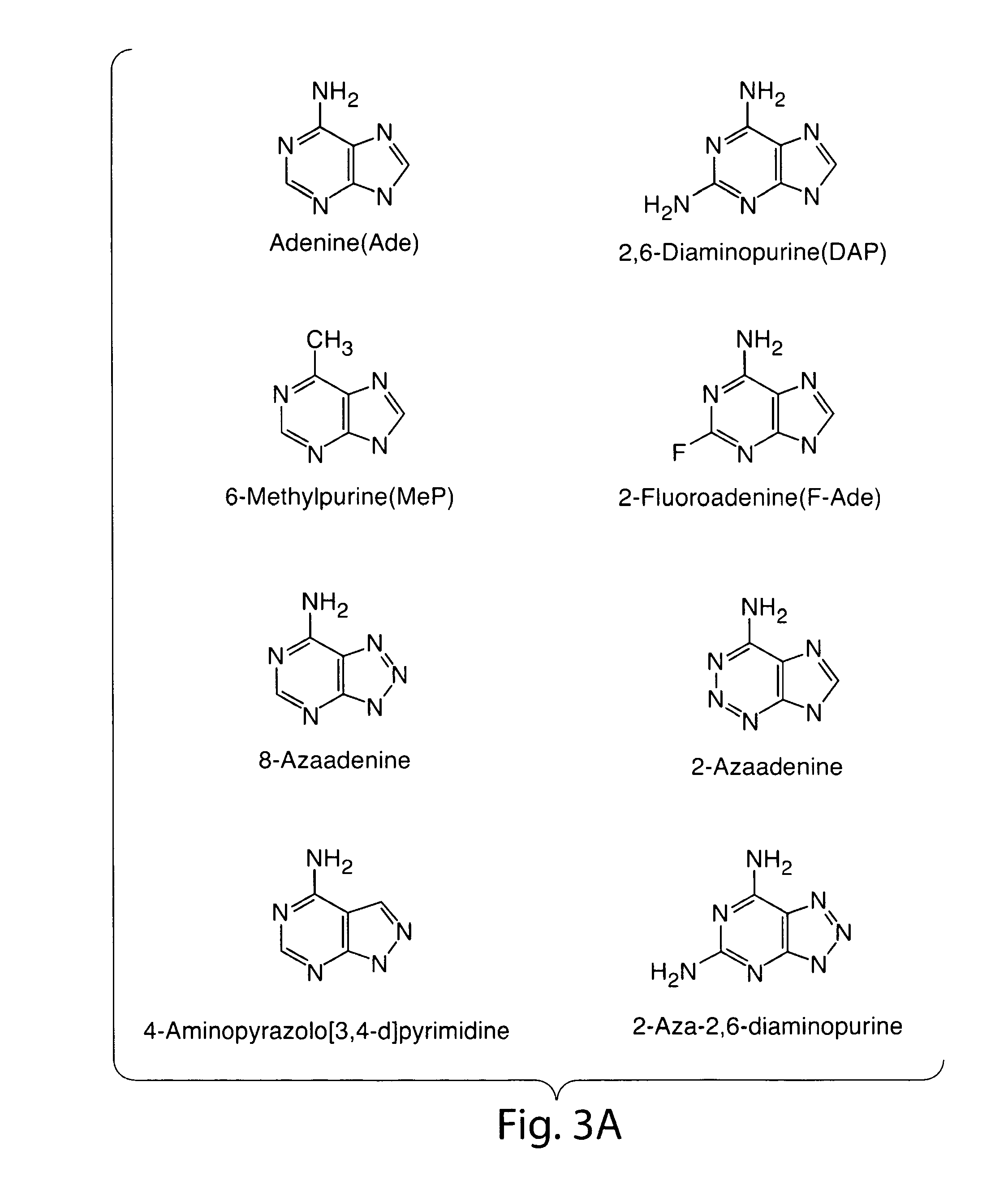
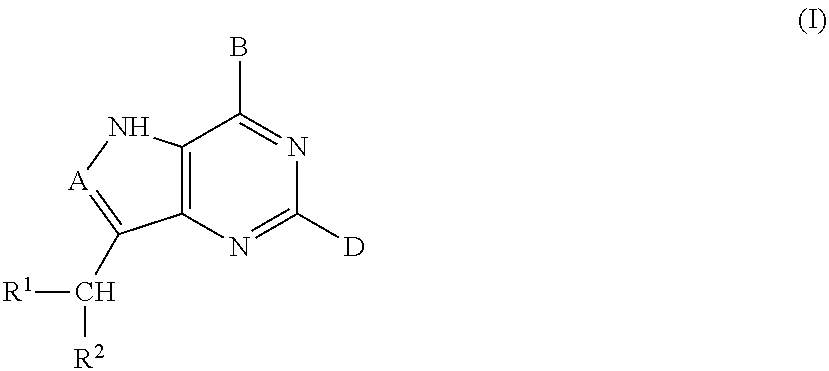
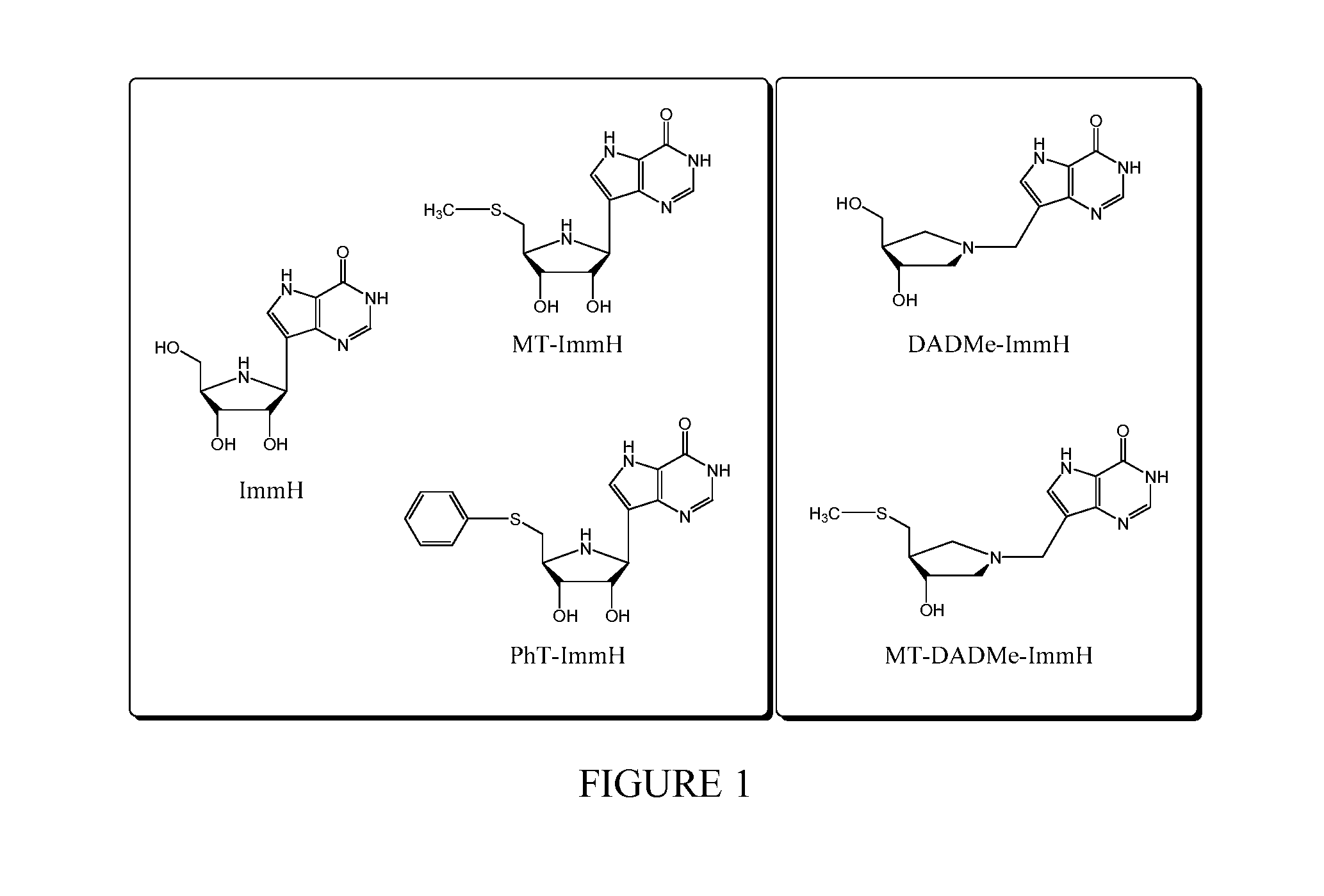
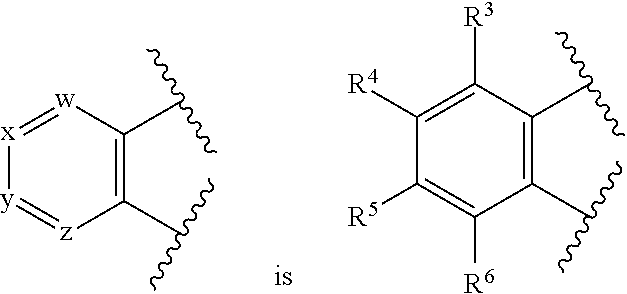
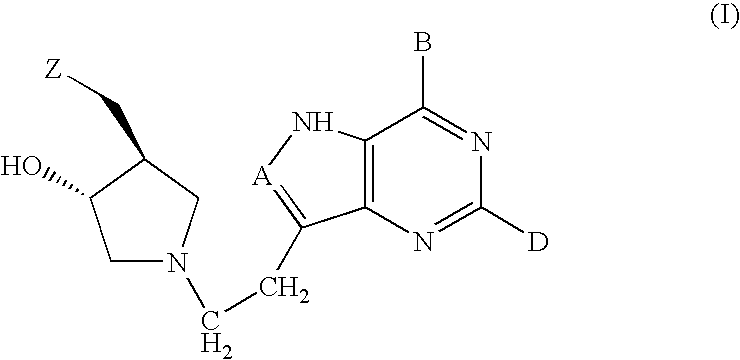
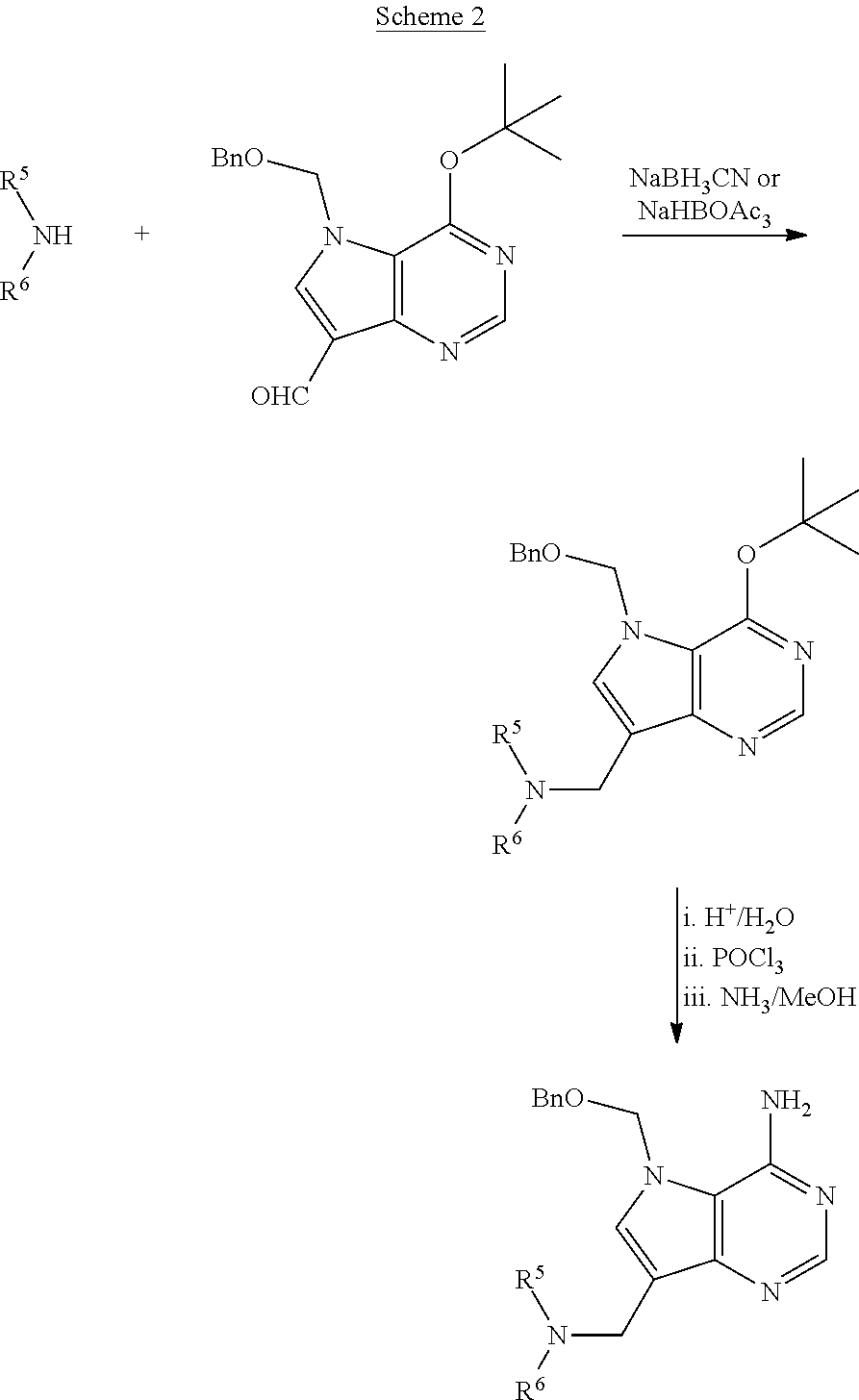
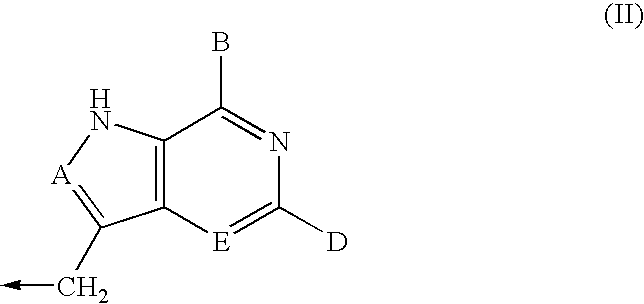
5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine muclioside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine mucliosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Compositions and methods for the detection and treatment of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase deficient cancers
InactiveUS20040247600A1Easy to detectReduce chanceAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyReagent
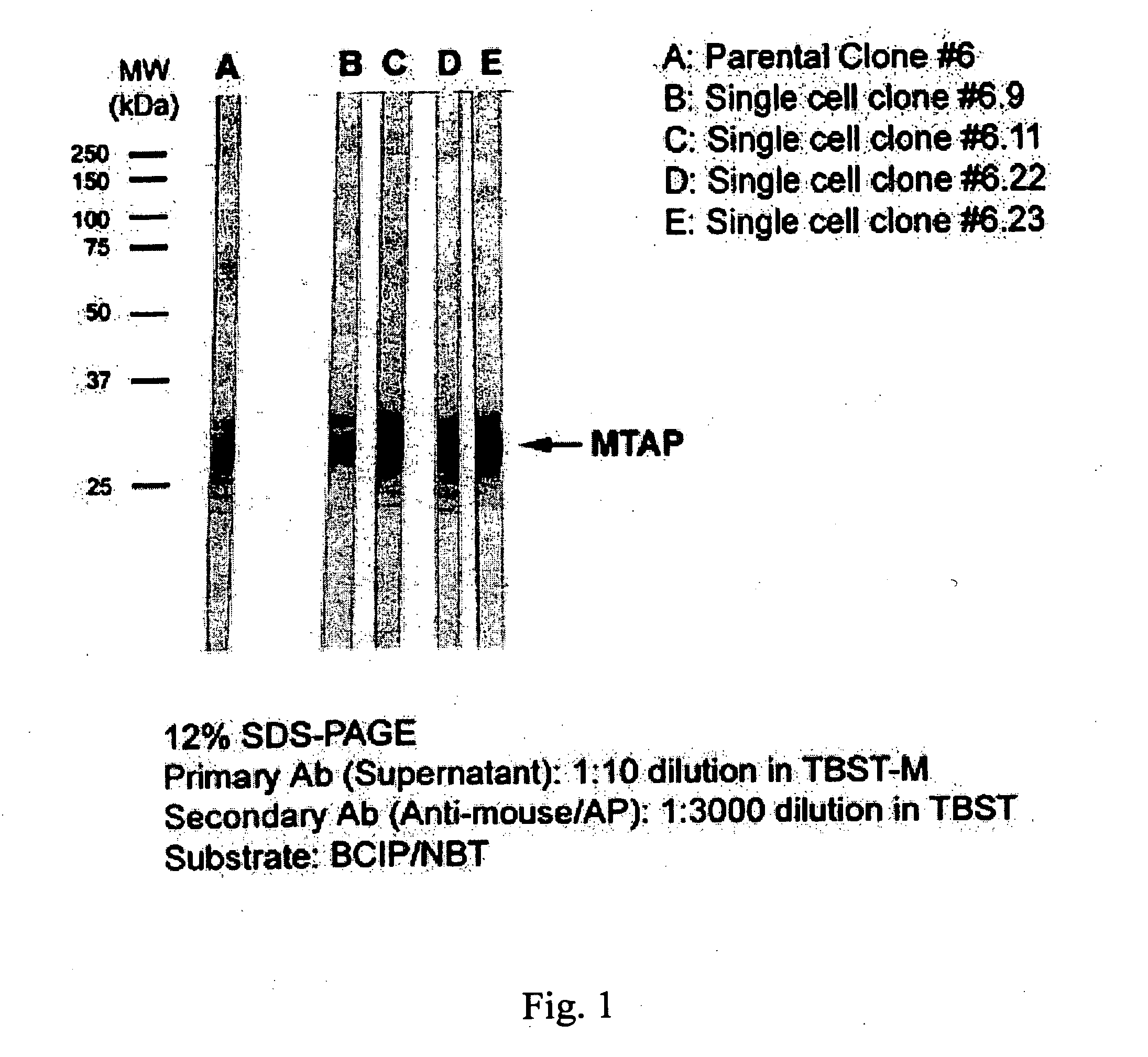
Compositions and methods involving agents that specifically bind to methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) protein are disclosed. Illustrative compositions comprise binding agents that bind to human MTAP protein in biological samples, including embedded samples. The binding agents are useful, for example, in the detection, prognosis, and / or treatment of MTAP deficient cancers. Also disclosed are kits containing the reagents necessary for the detection of human MTAP protein in an embedded sample.
Owner:CEPHALON INC
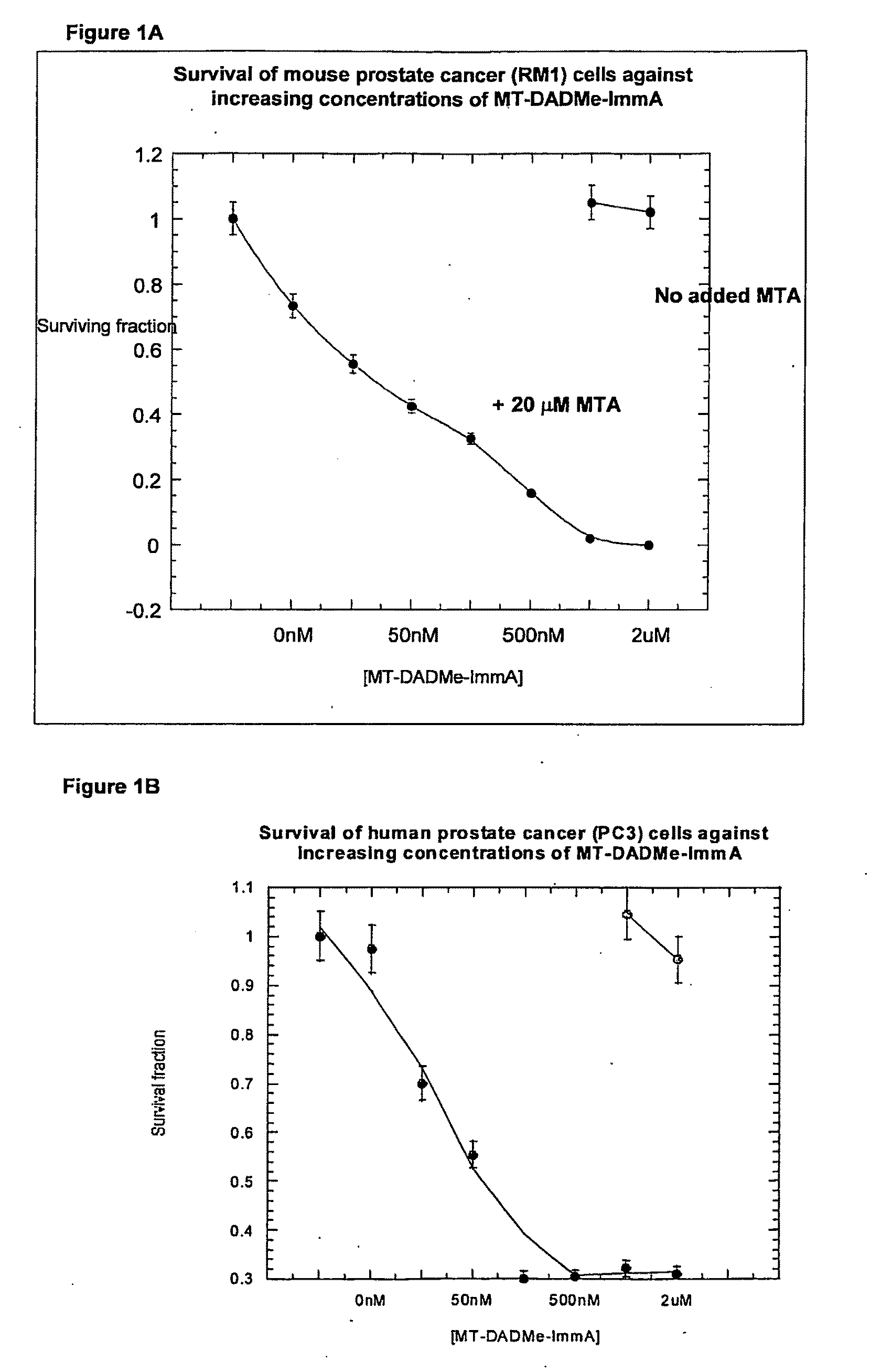
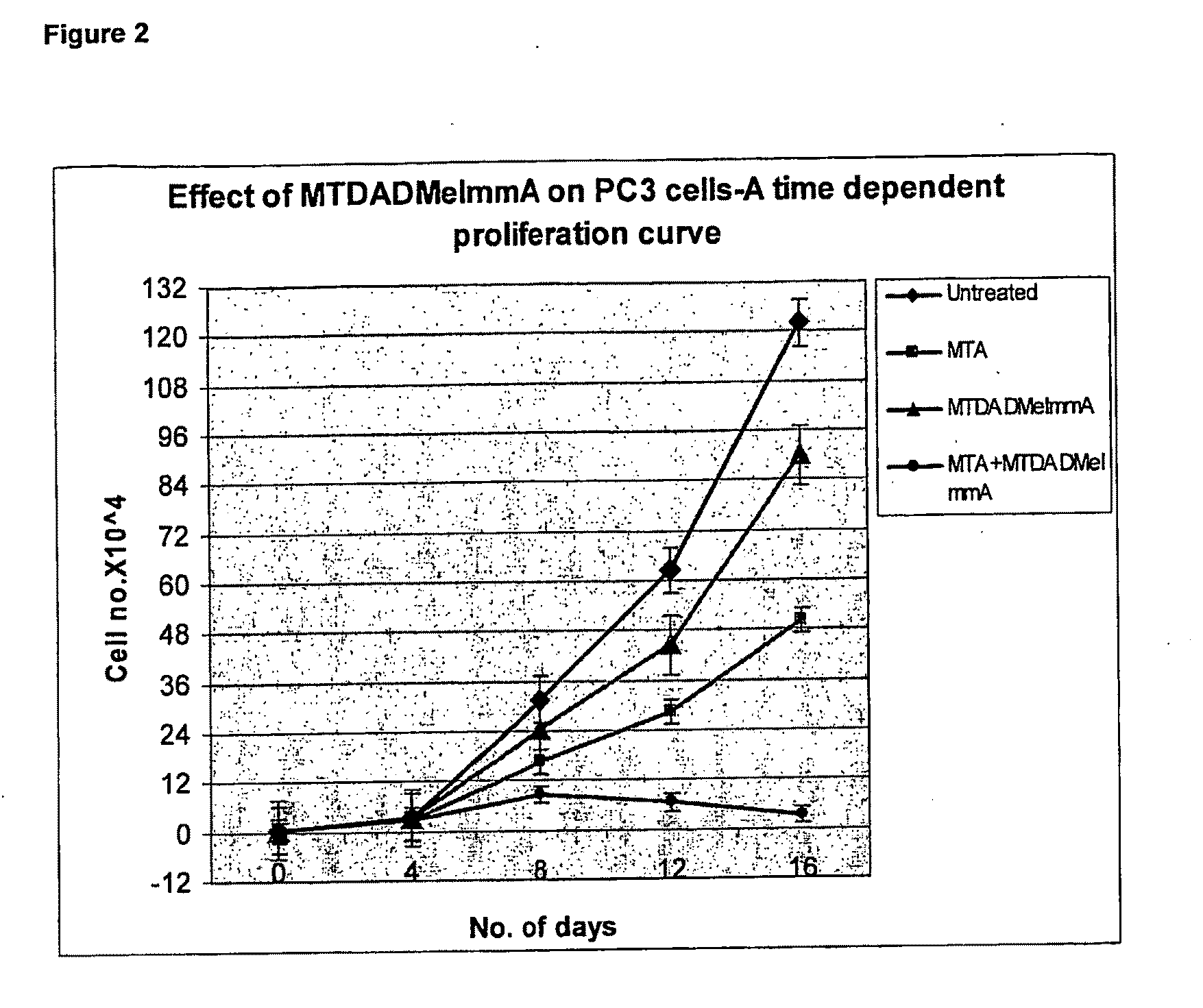
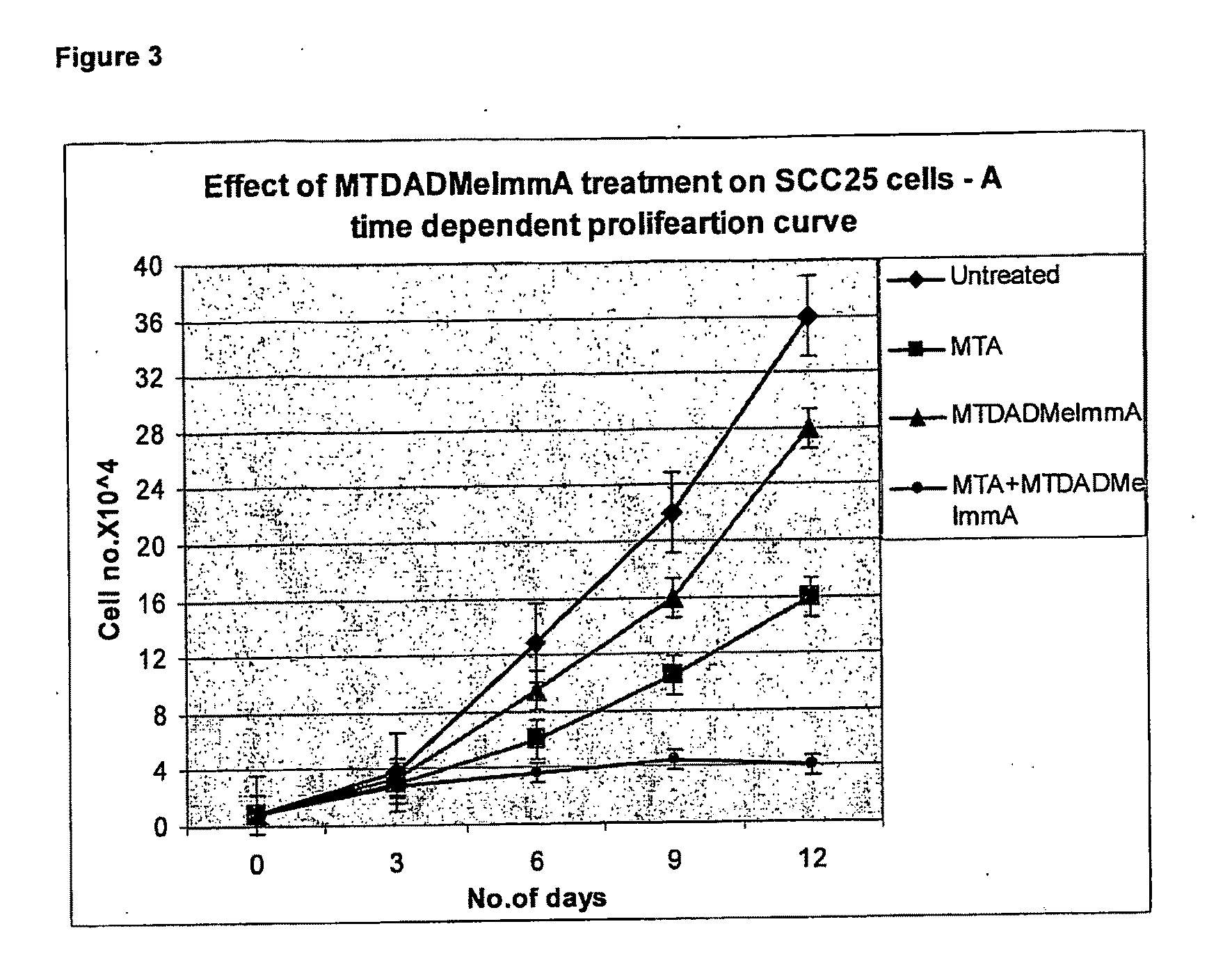
Methods of Treating Cancer
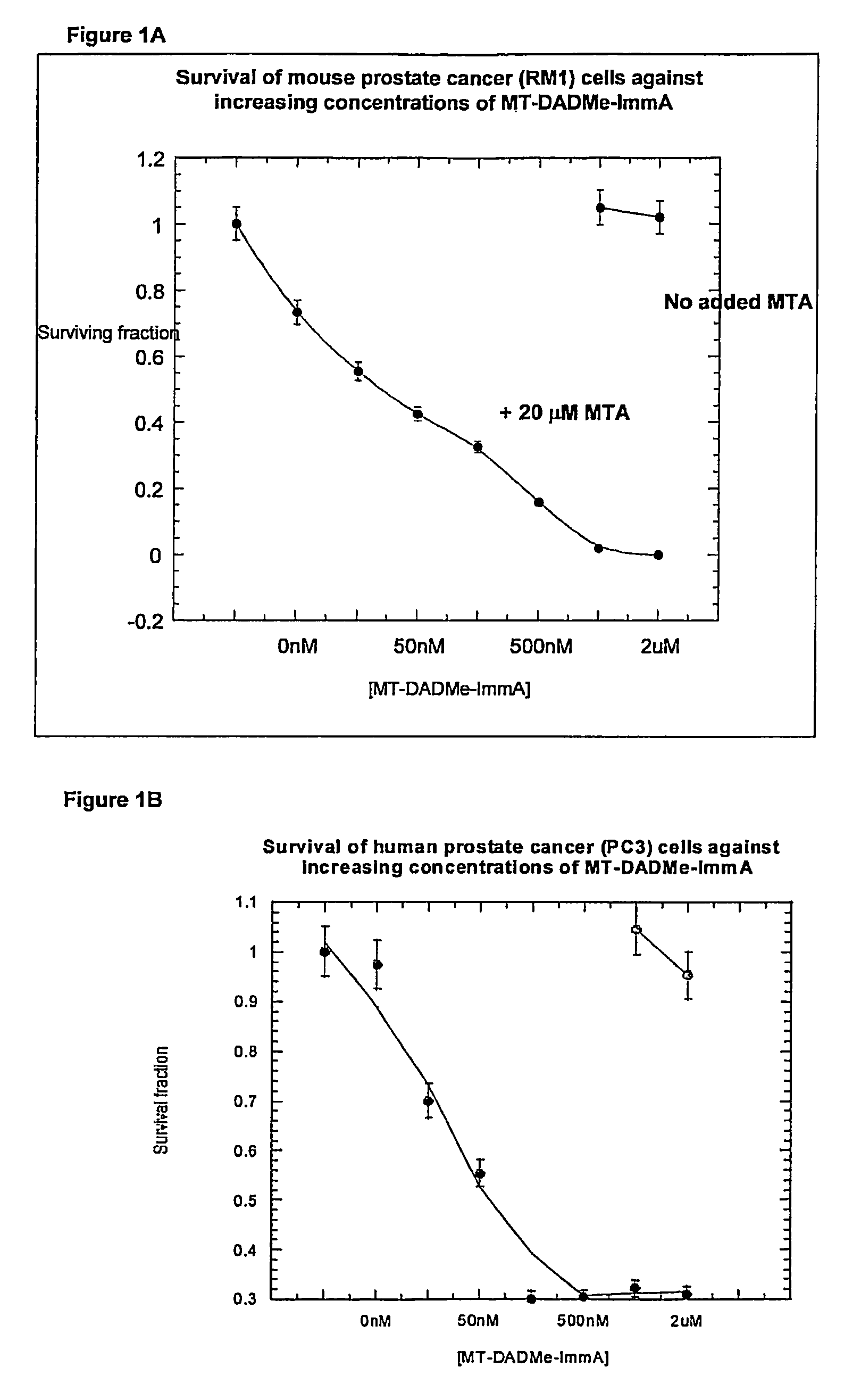
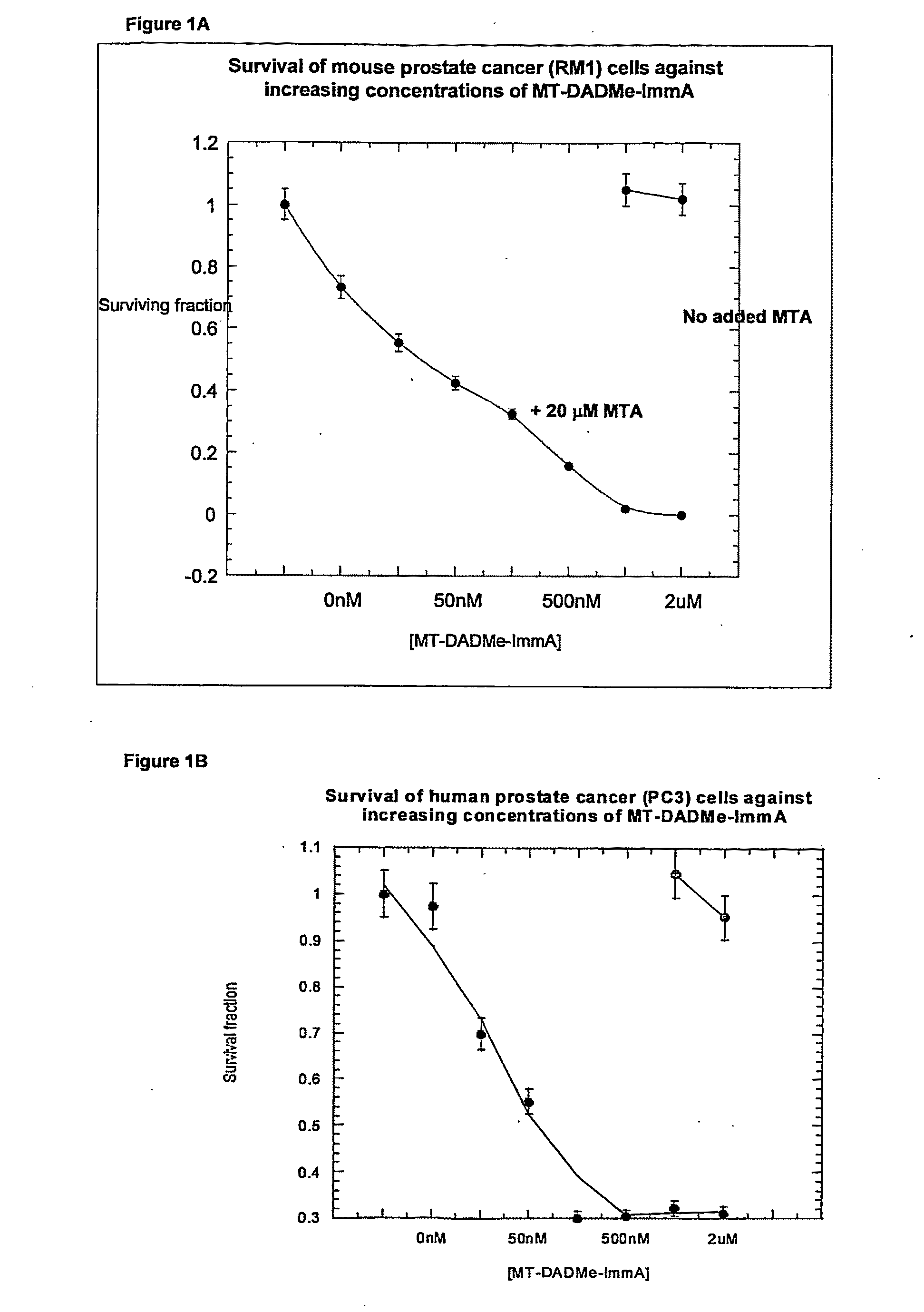
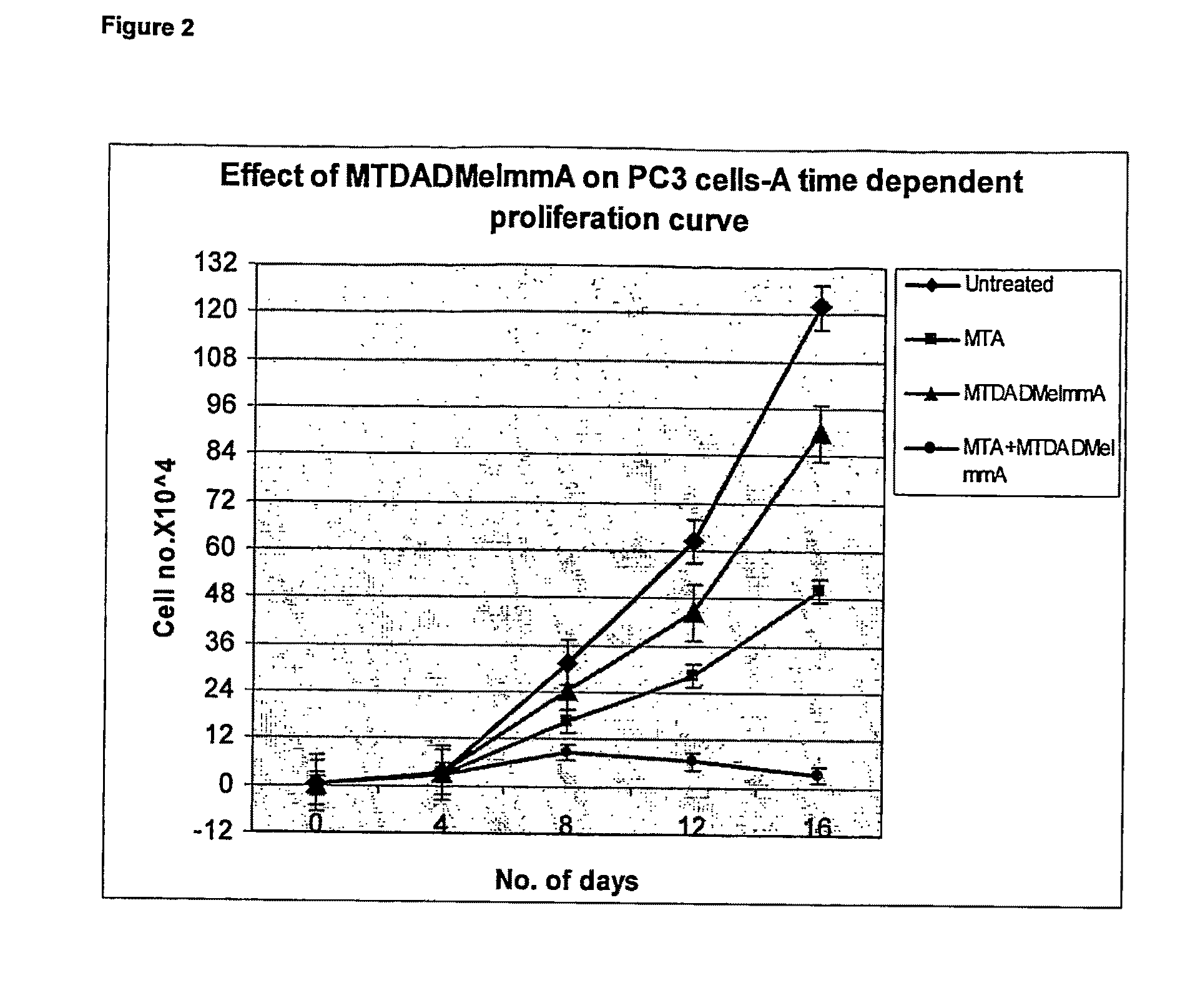
The invention relates to the treatment of cancer using an inhibitor of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP). The invention particularly relates to the treatment of prostate cancer and head and neck cancer.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Inhibitors of nucleoside phoshorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Acyclic amine inhibitors of 5-methytioadenosine phosphorylase and nucleosidase
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase. The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases or conditions in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase including cancer, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
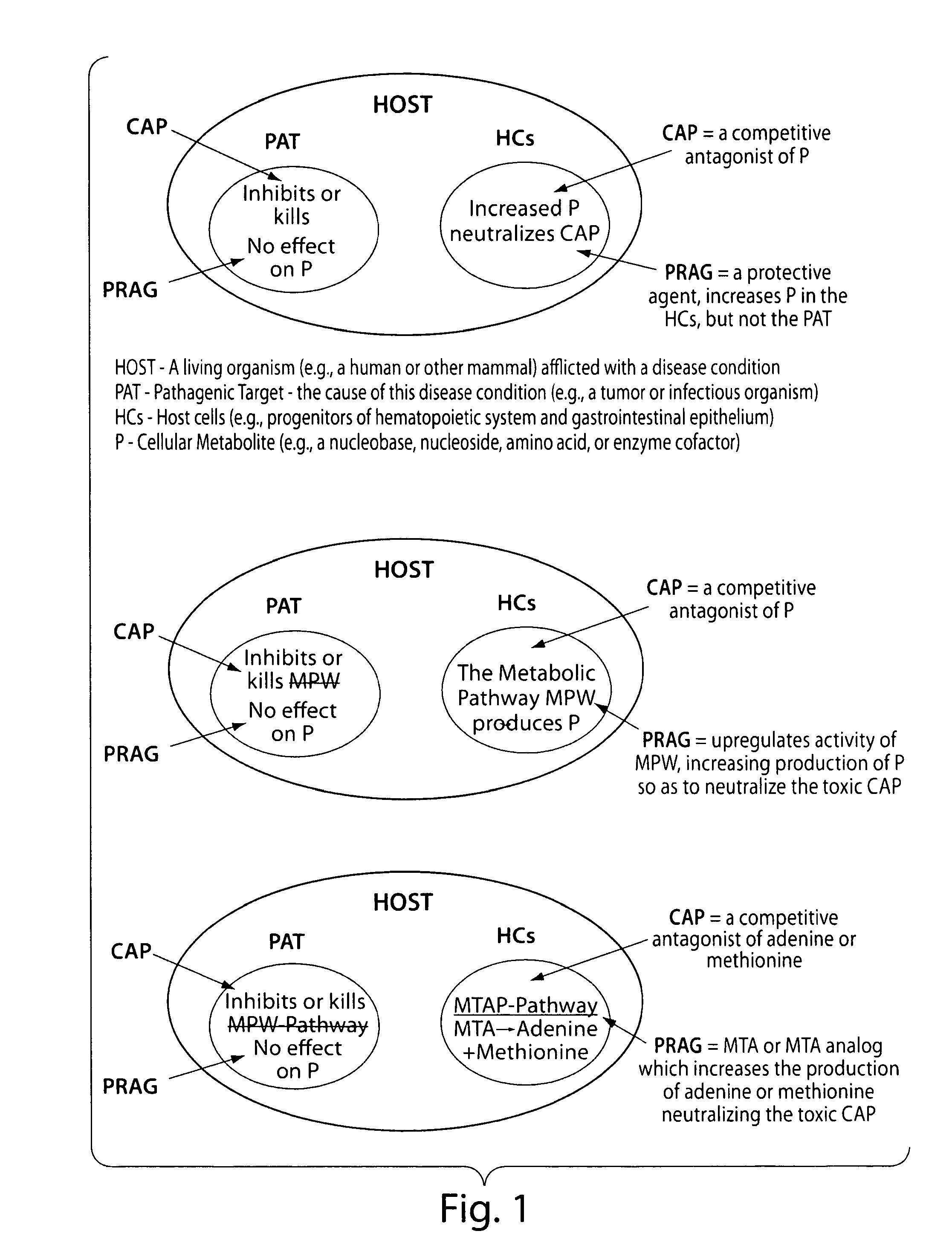
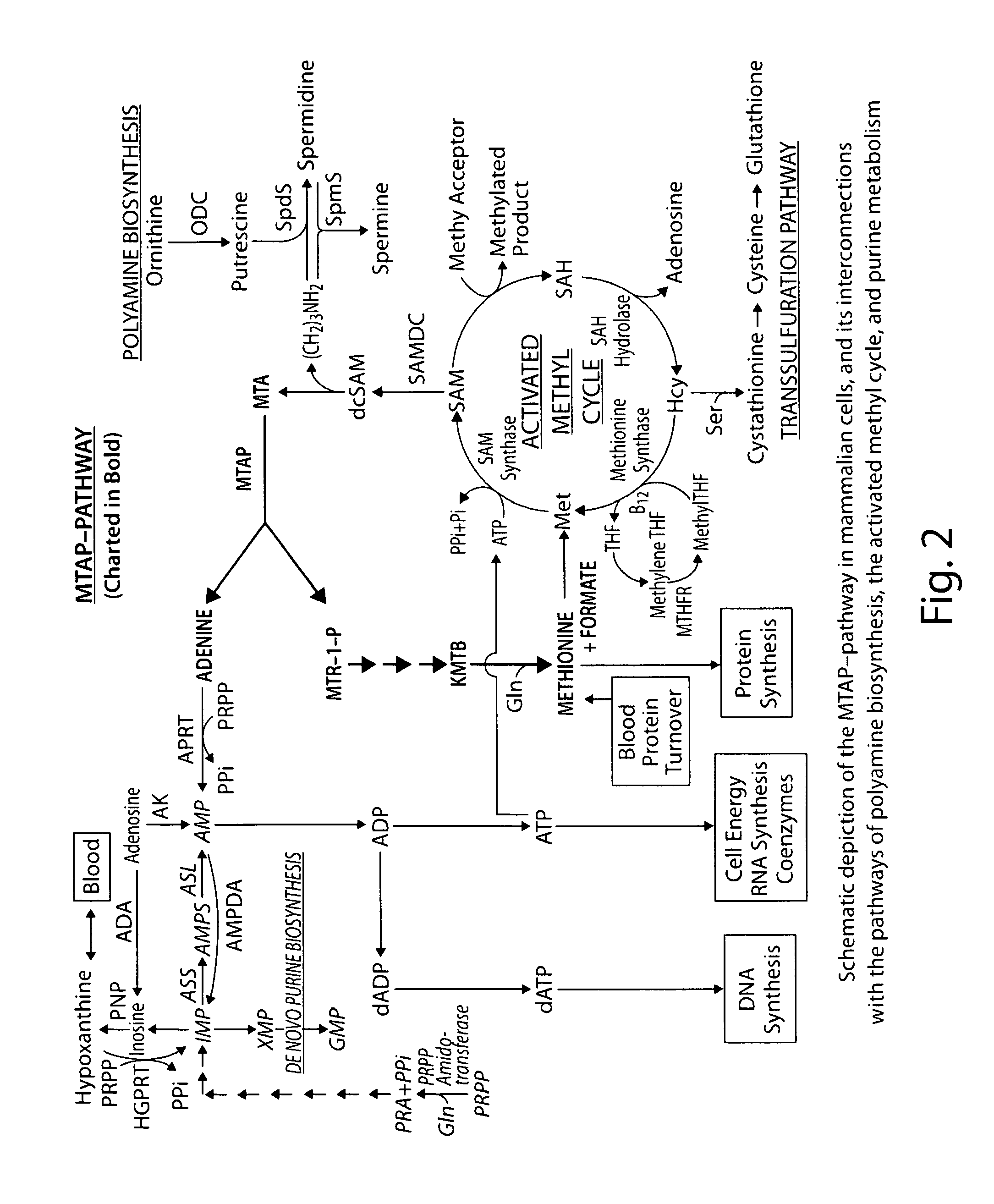
Method for suppressing multiple drug resistance in cancer cells
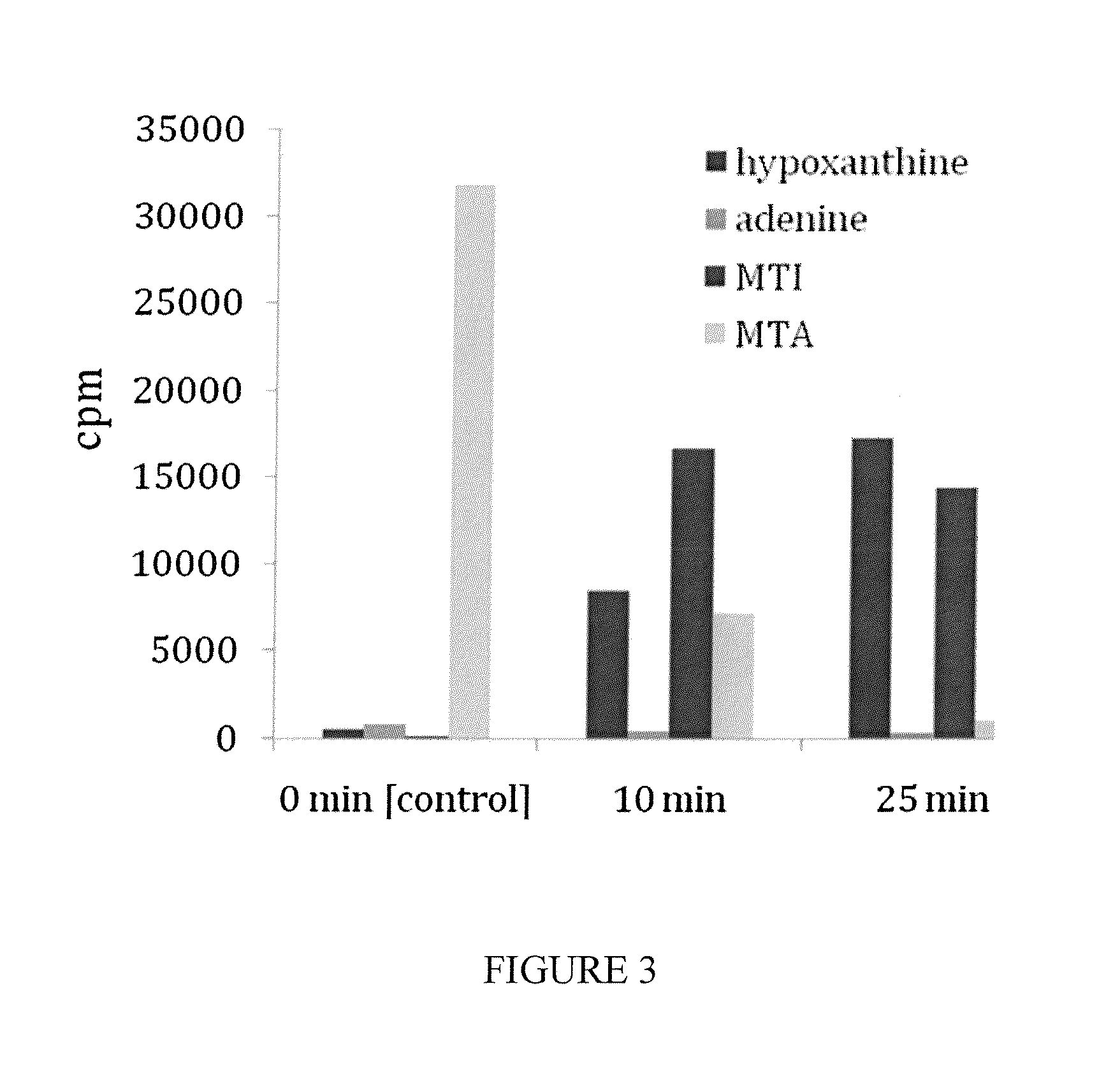
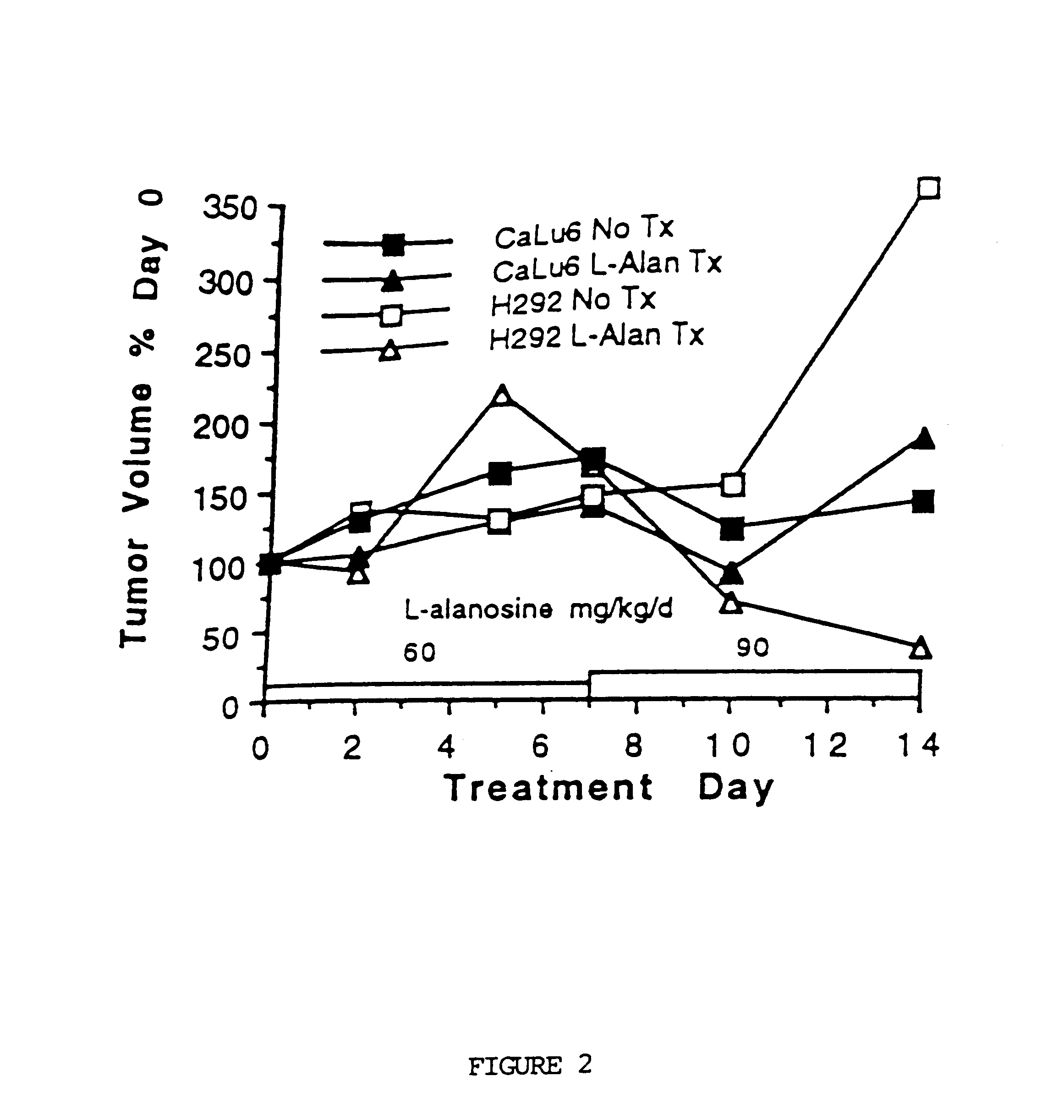
Methods for treating and preventing the onset and maintainance of multiple drug resistance (MDR) in animals undergoing chemotherapy for cancer are provided. According to the methods, target cells are depleted of adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) such that the cells are unable to support P-glycoprotein activity. According to one method, a population of target cells is obtained from a host and assayed for loss of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAse) activity. MTAse catabolizes methylthioadenosine to adenine for endogenous salvage incorporation into the intracellular AMP pool. MTAse deficient cells are treated with a purine synthesis inhibitor, such as L-alanosine, which starves the cells of adenine and suppresses P-glycoprotein activity. MTAse competent cells are also treated for MDR with purine synthesis inhibitors. In conjunction with treatment according to the invention, MTAse competent and deficient cells are also treated for malignancy with other anti-cancer drugs. A method for protecting non-malignant cells from adenine starvation during treatment of malignant cells according to the invention is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
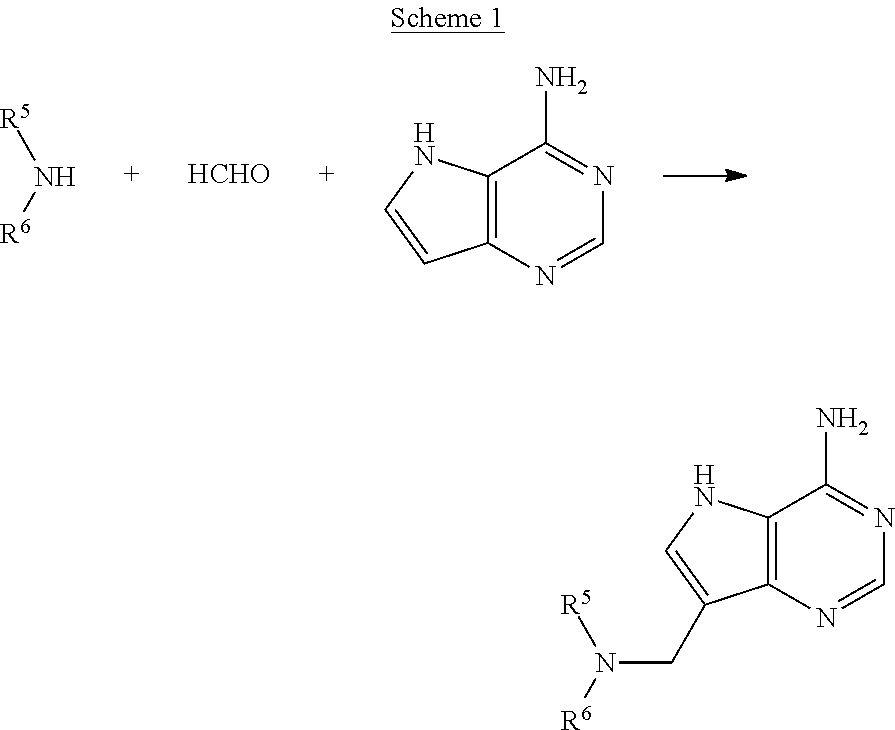
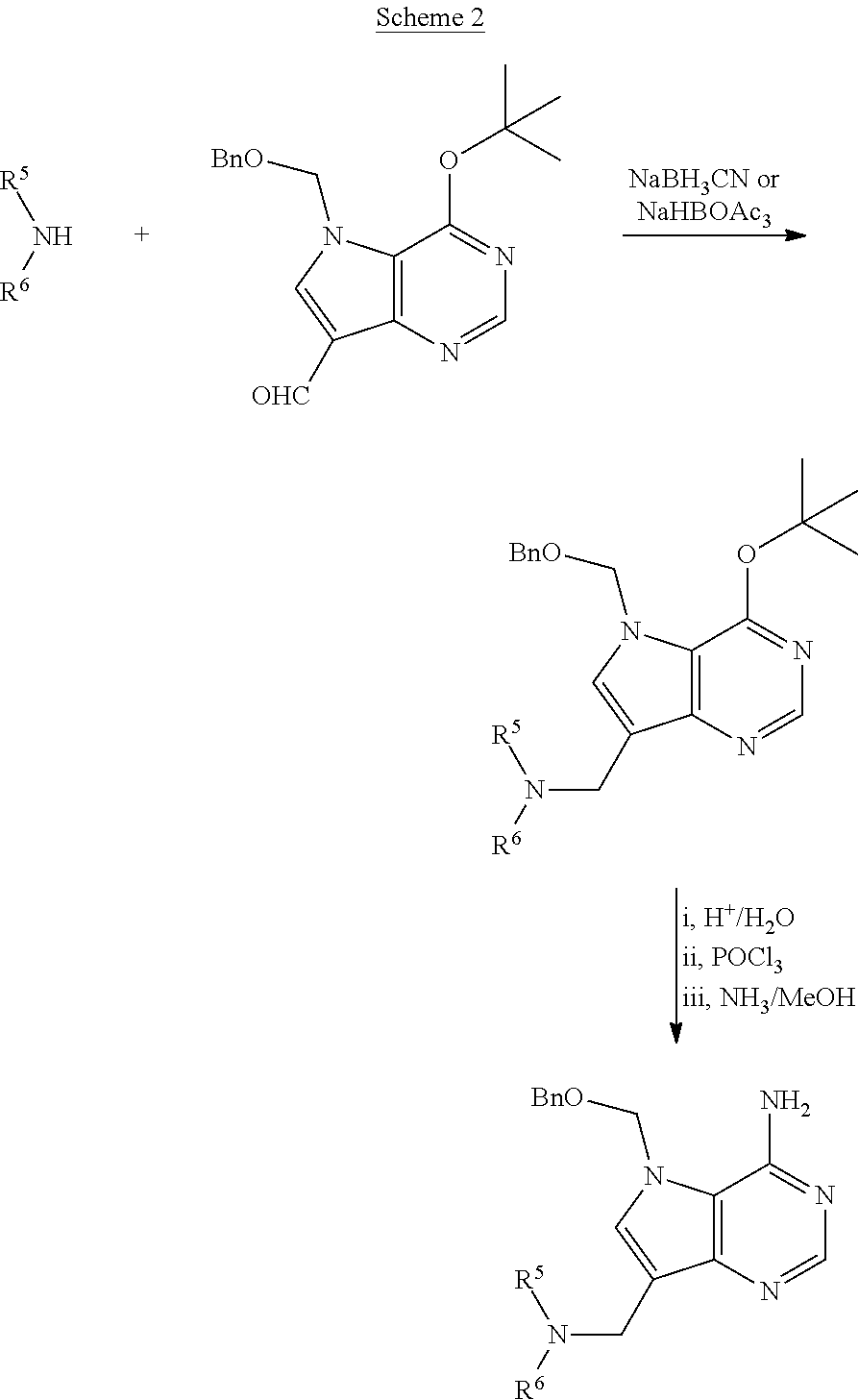
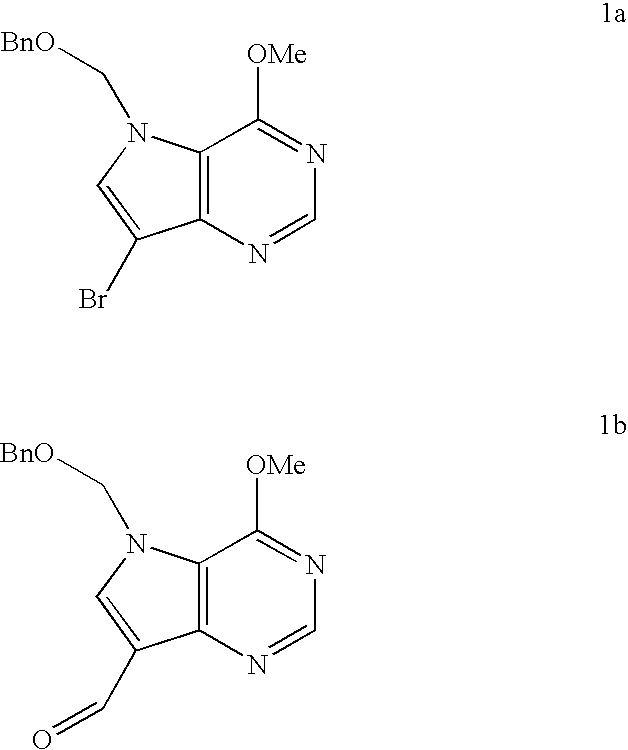
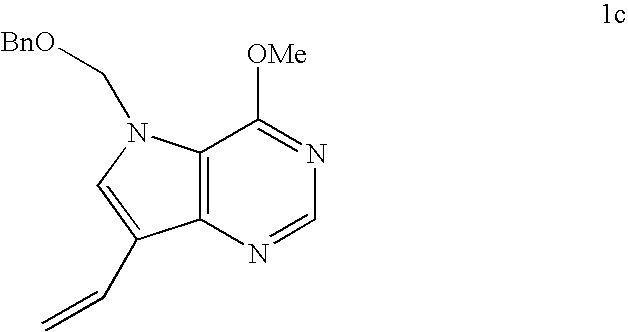
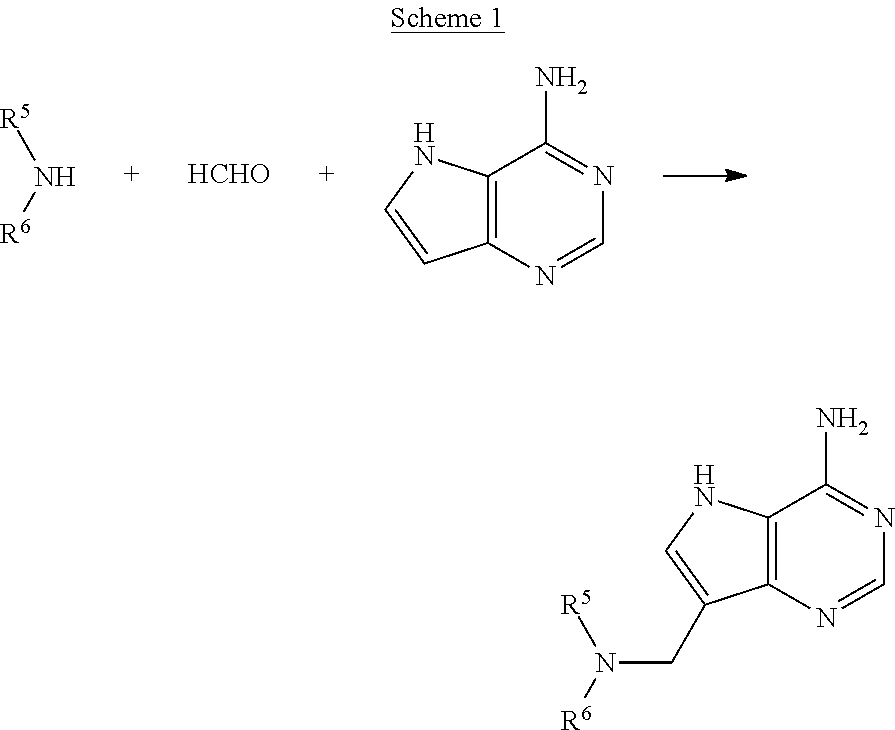
Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
Owner:IND RES LTD
Process for preparing inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
InactiveUS20100094003A1Use in synthesisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphorylationMethyl palmoxirate
The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH).
Owner:EVANS GARY BRIAN +1
Methods of Treating Diseases Using Inhibitors of Nucleoside Phosphorylases and Nucleosidases
The invention relates to treating a disease or condition in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) and / or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase (MTAN). The invention particularly relates to the co-administration of 5′-methylthioadenosine (MTA), or a prodrug of MTA, with one or more MTAP / MTAN inhibitors. Included among the diseases treatable are prostate cancer and head and neck cancer.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
Method for inhibiting adenylosuccinate synthetase activity in malignant methylthioadenosine phosphorylase deficient cells
InactiveUS6214571B1High activityMinimize ToxicityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalPhosphoric acid
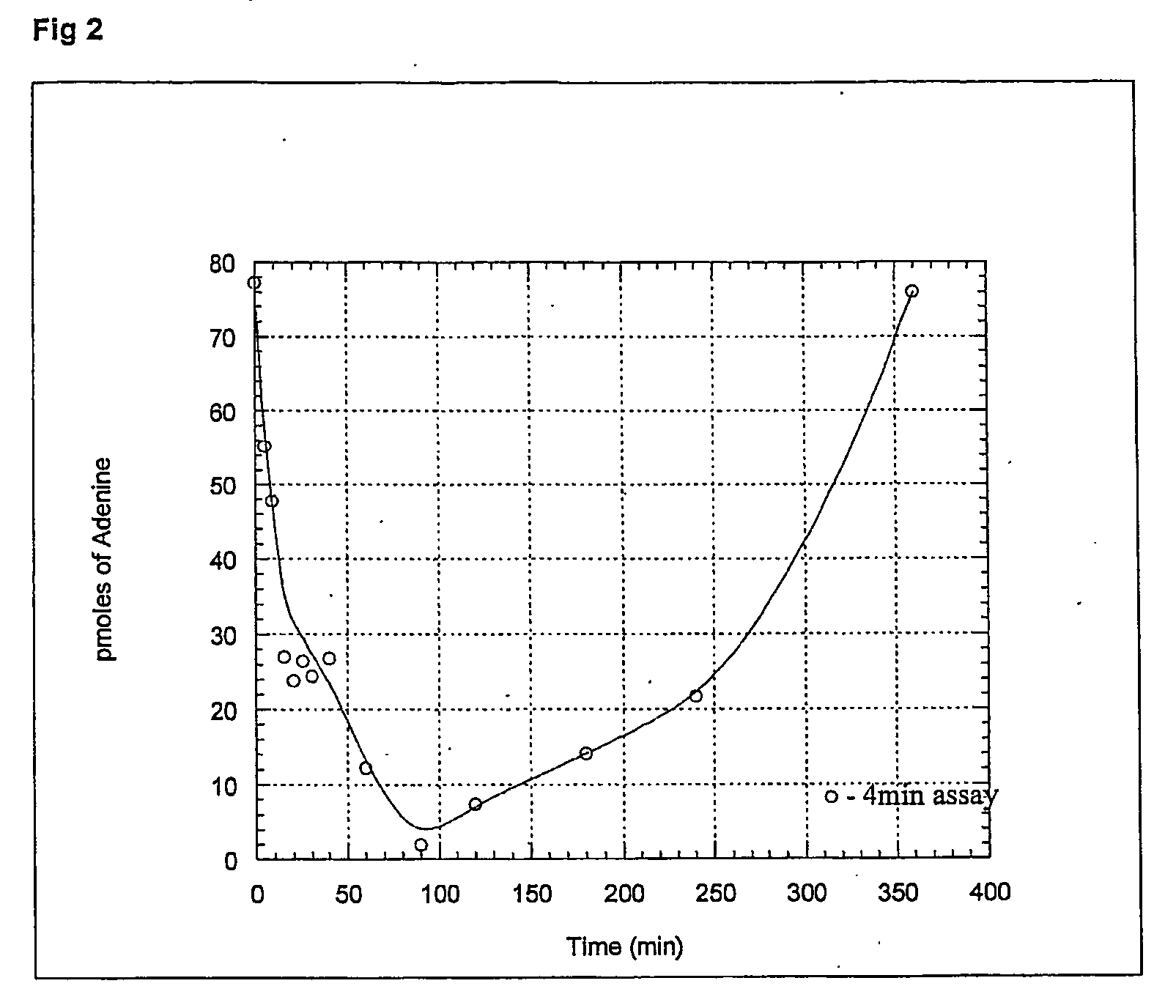
An in vivo method for depleting mammalian cells of adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) useful in the treatment of certain cancers is provided. According to the method, a population of cells is obtained from a host and assayed for loss of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAse) activity. MTAse catabolizes methylthioadenosine to adenine for endogenous salvage incorporation into the intracellular AMP pool. The preferred method for assaying loss of MTAse activity is a hybridization technique for detection of a homozygous loss of the gene which encodes MTAse. Hosts having MTAse deficient tumors are treated with a therapeutically effective amount of an agent which inhibits the activity of adenylsuccinate synthetase, which converts inosine 5-monophosphate to AMP, thus depleting the tumor cells of substrates for de novo AMP production. L-alanosine is the preferred ASS inhibitory agent for use in the method of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
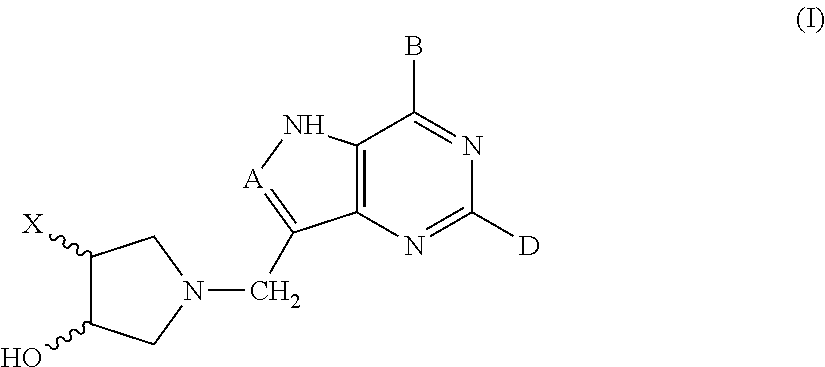
3-hydroxypyrrolidine inhibitors of 5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase and nucleosidase
The present invention relates to 3-hydroxypyrrolidine compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase. The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases or conditions in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase including cancer, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
Heterobicyclic inhibitors of mat2a and methods of use for treating cancer
The present disclosure provides for compounds according to Formula I or Formula II and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, stereoisomers, and / or tautomers thereof. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and the compounds of formulae I and II for use in methods of treating cancers via inhibition of MAT2B, including some cancers in which the gene encoding methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) is deleted.
Owner:LES LAB SERVIER
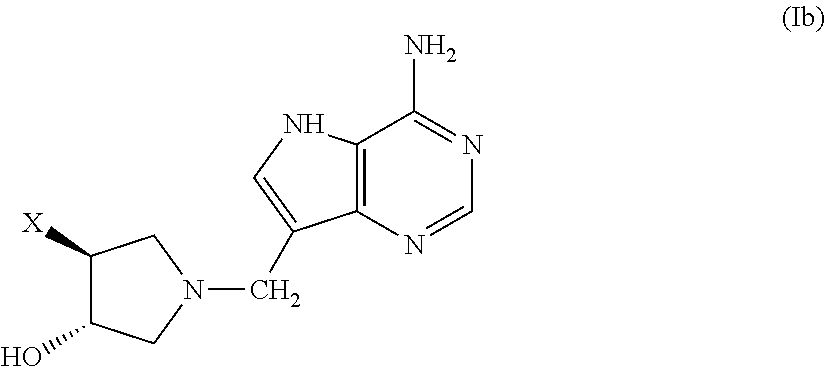
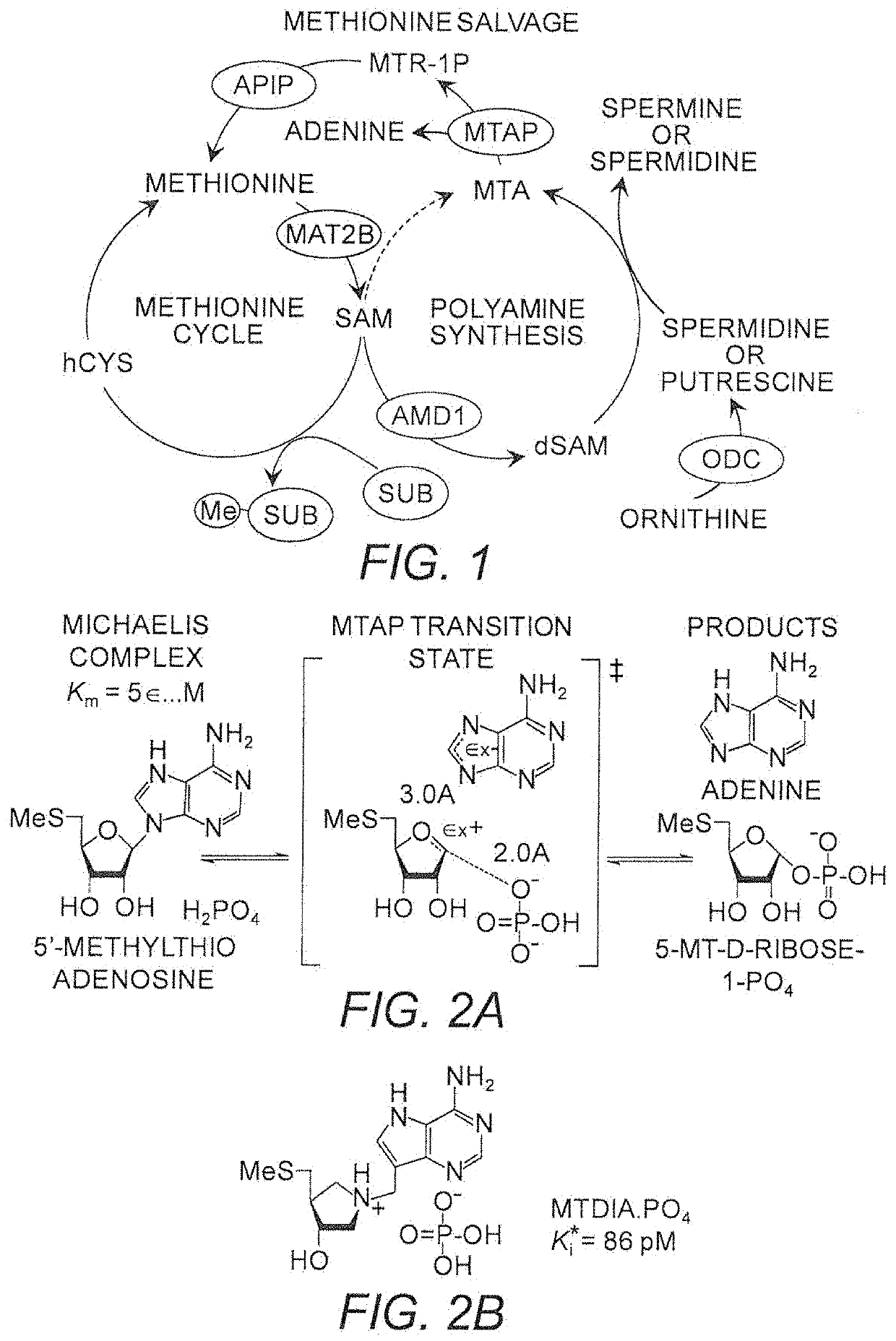
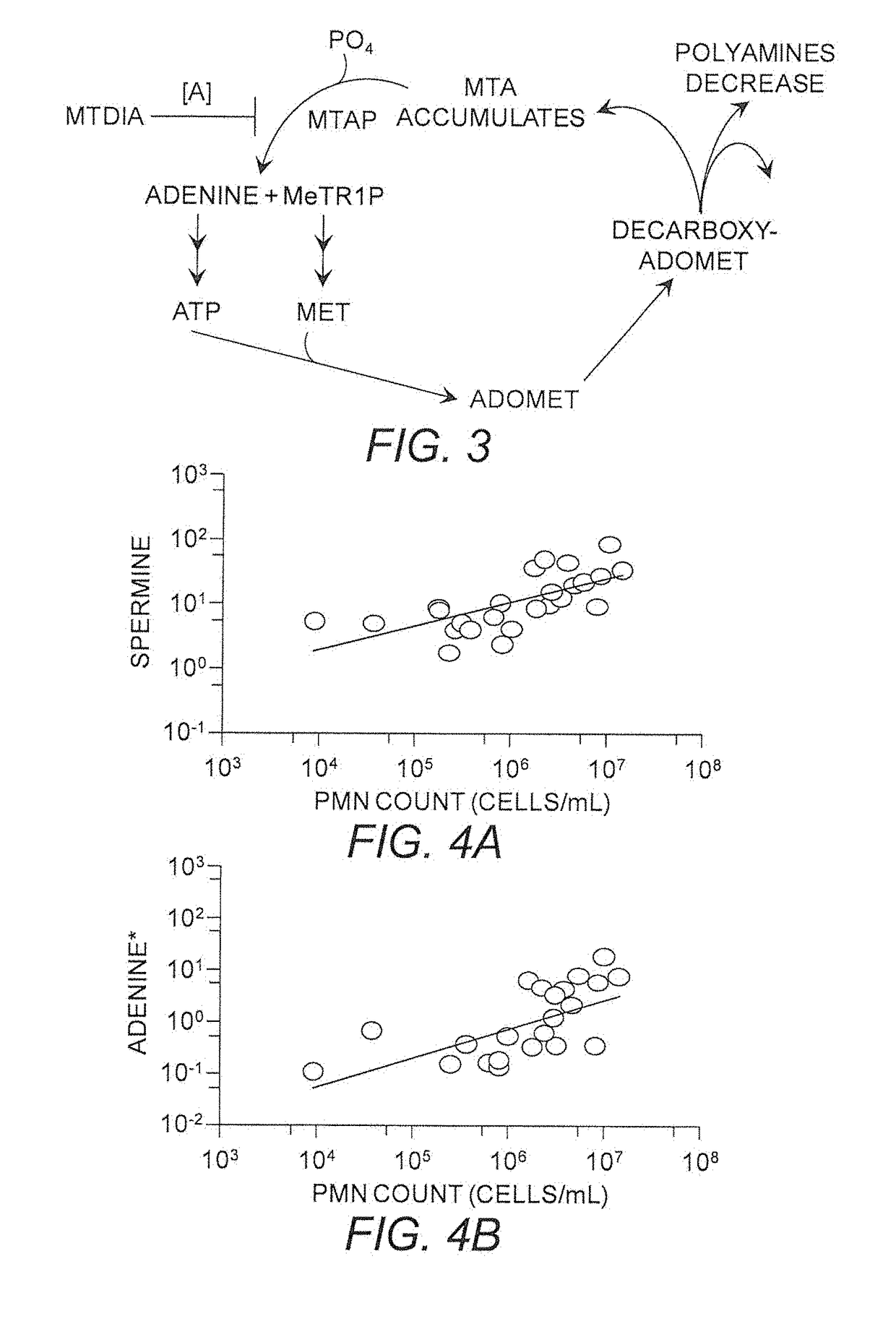
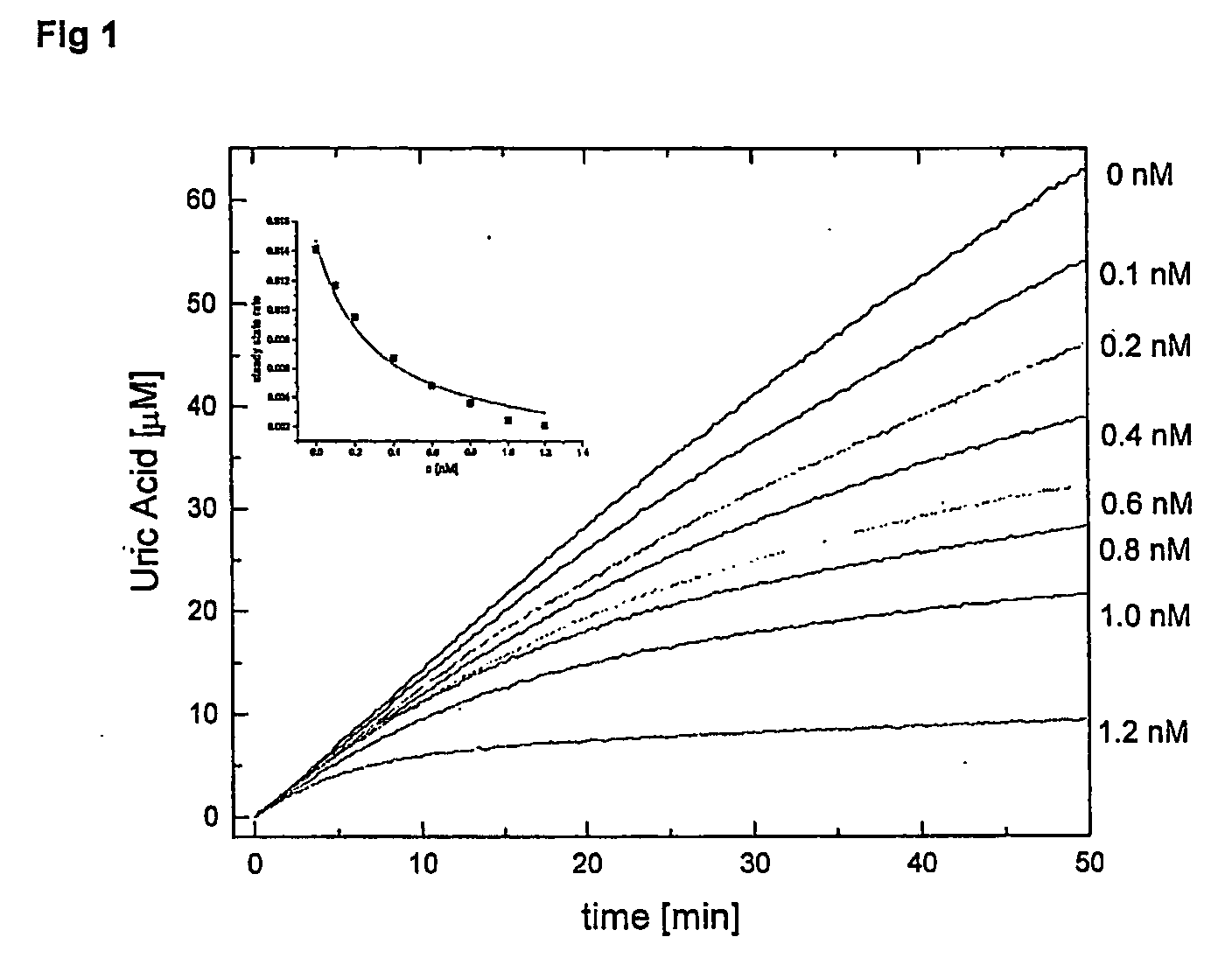
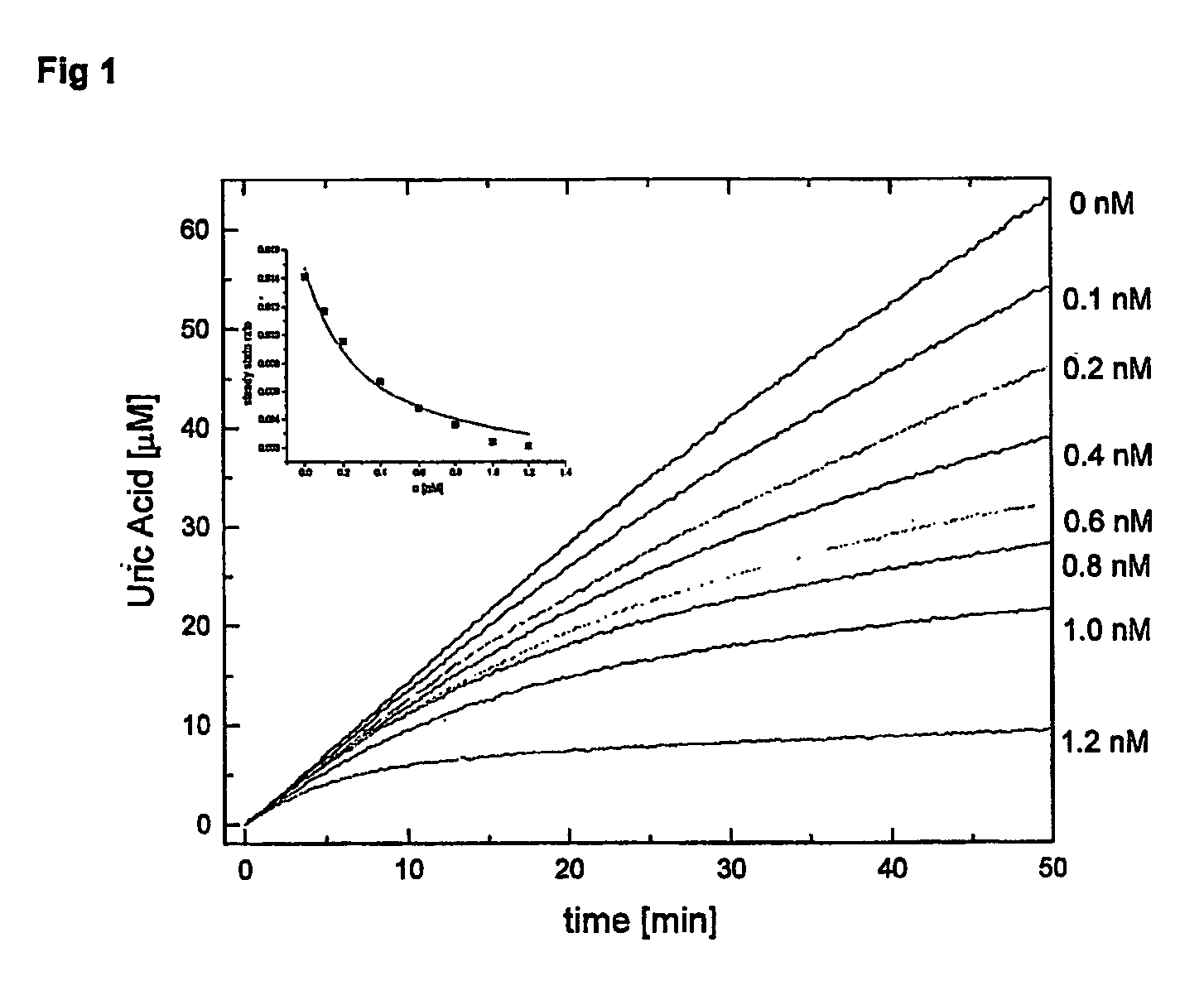
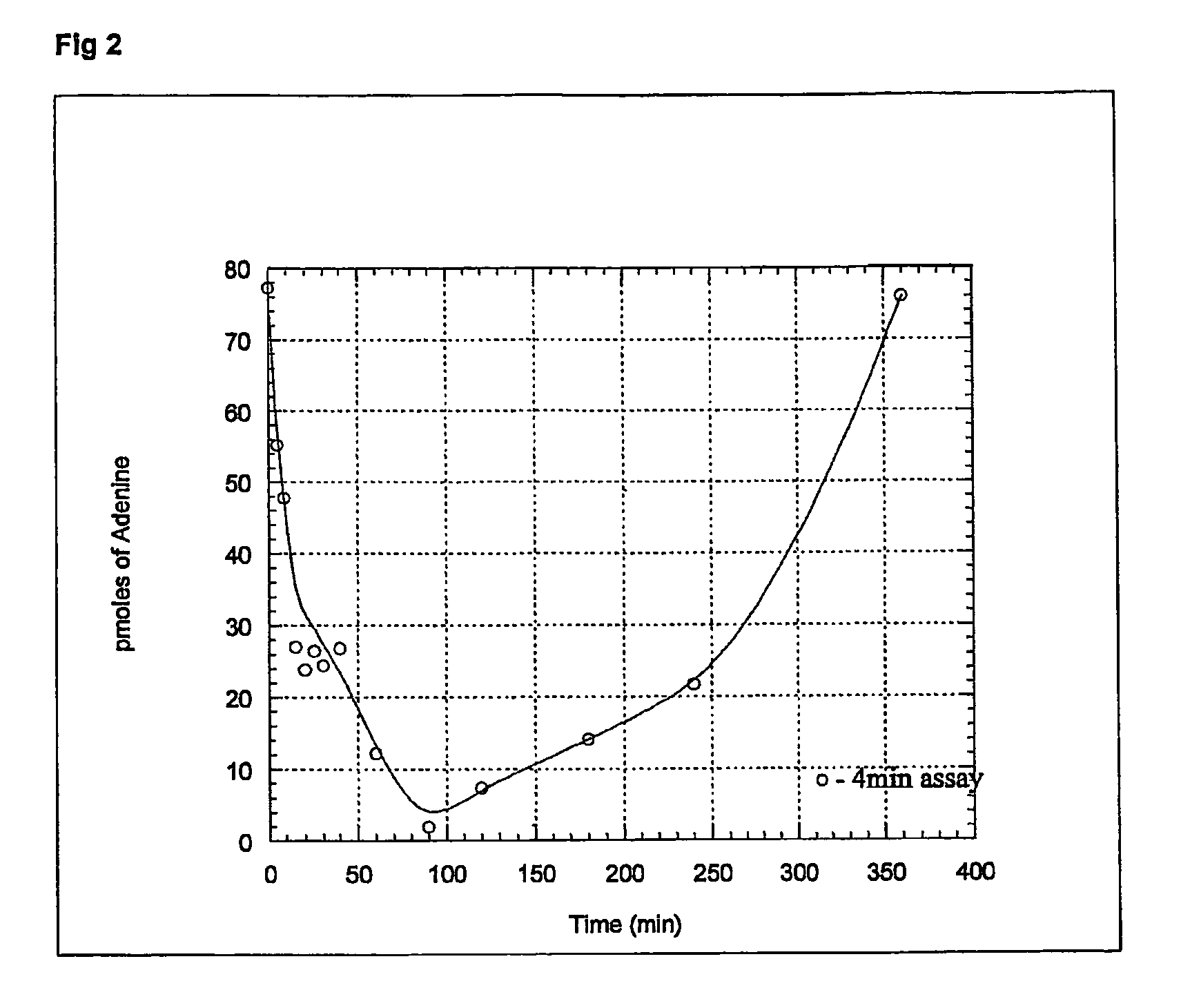
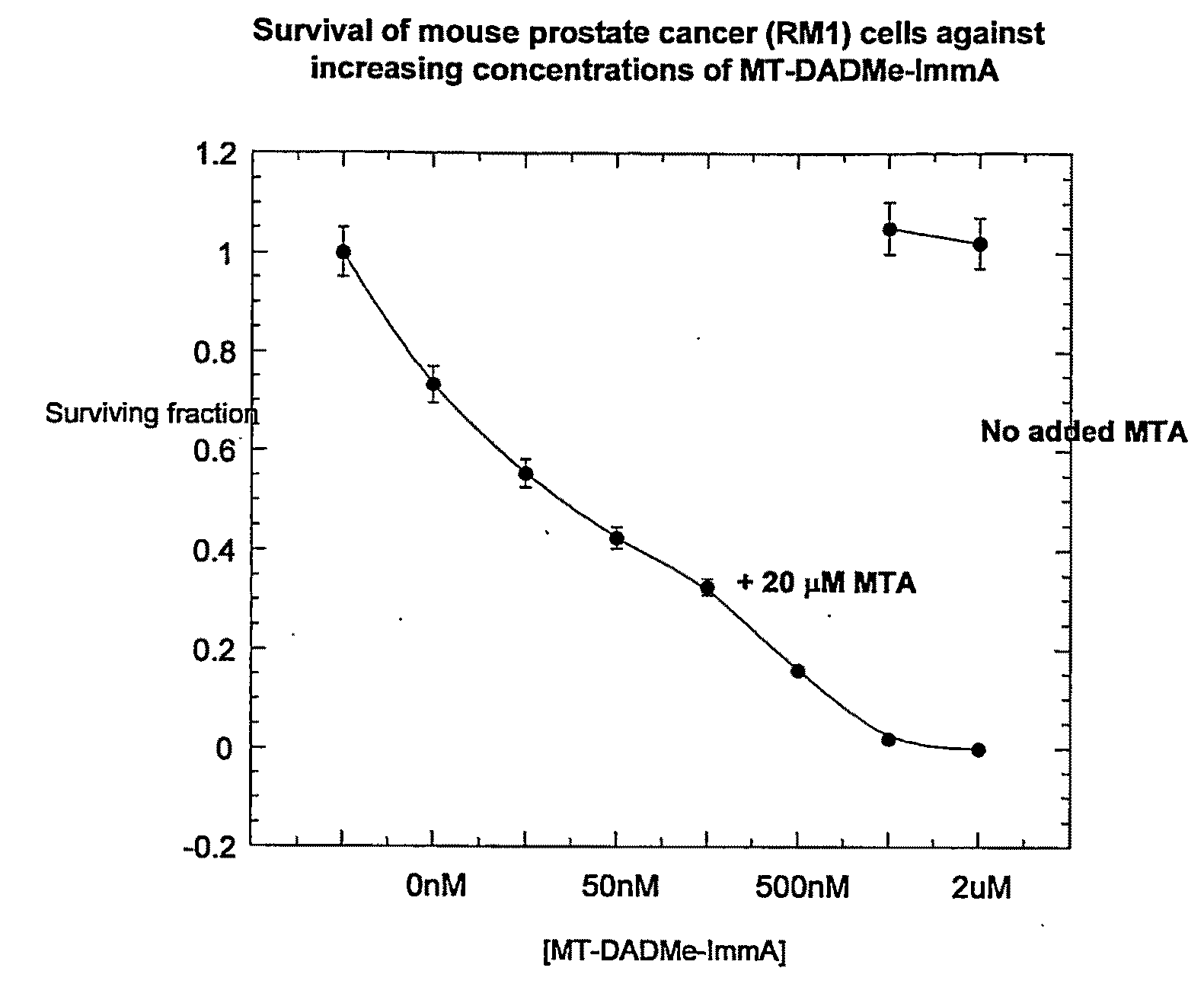
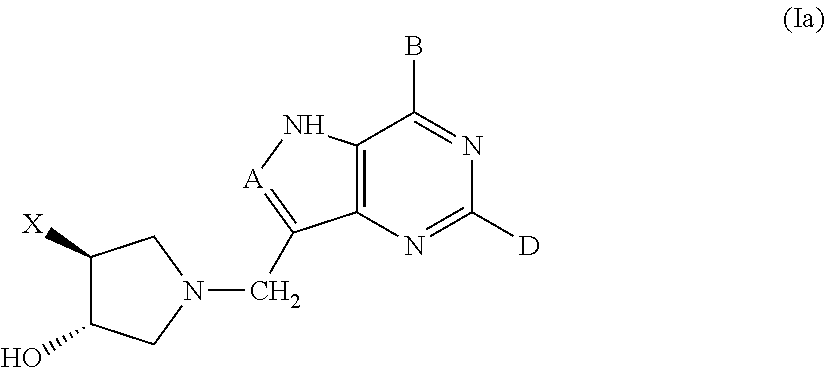
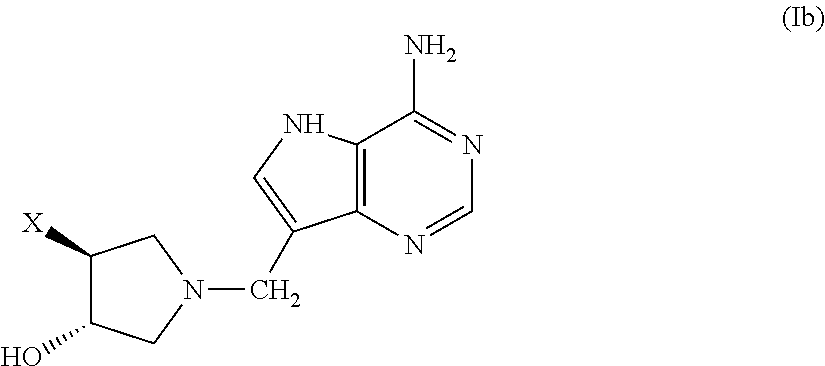
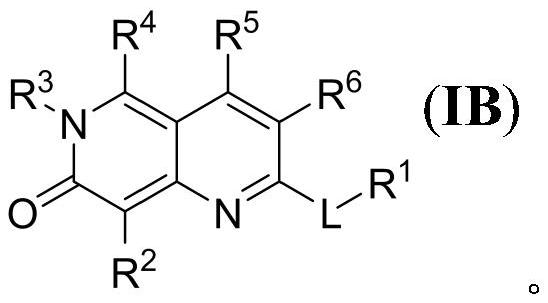
Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA)
ActiveUS20150274741A1Minimizing useMinimize degradationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicinal chemistry
The invention relates to salt forms of (3R,4S)-1-((4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4-(methyl-thiomethyl)pyrrolidin-3-ol, as well as polymorphic forms of the salts. The invention further relates to processes for preparing the salt forms and to the use of the salt forms in the treatment of diseases and disorders where it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP).
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
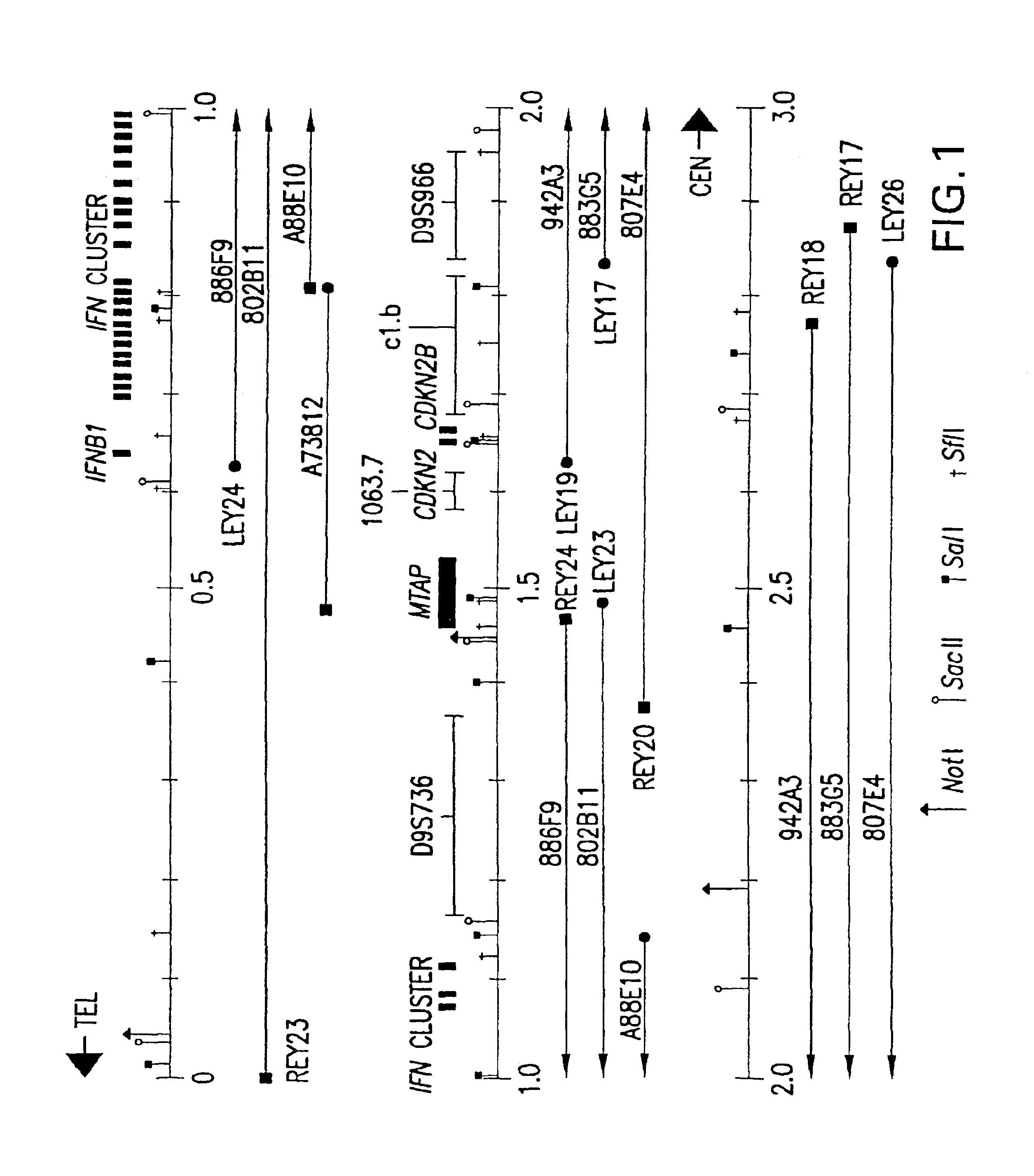
Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase compositions and methods of use in the diagnosis and treatment of proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6870037B1Overcomes drawbackIncrease ratingsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome regionsWilms' tumor
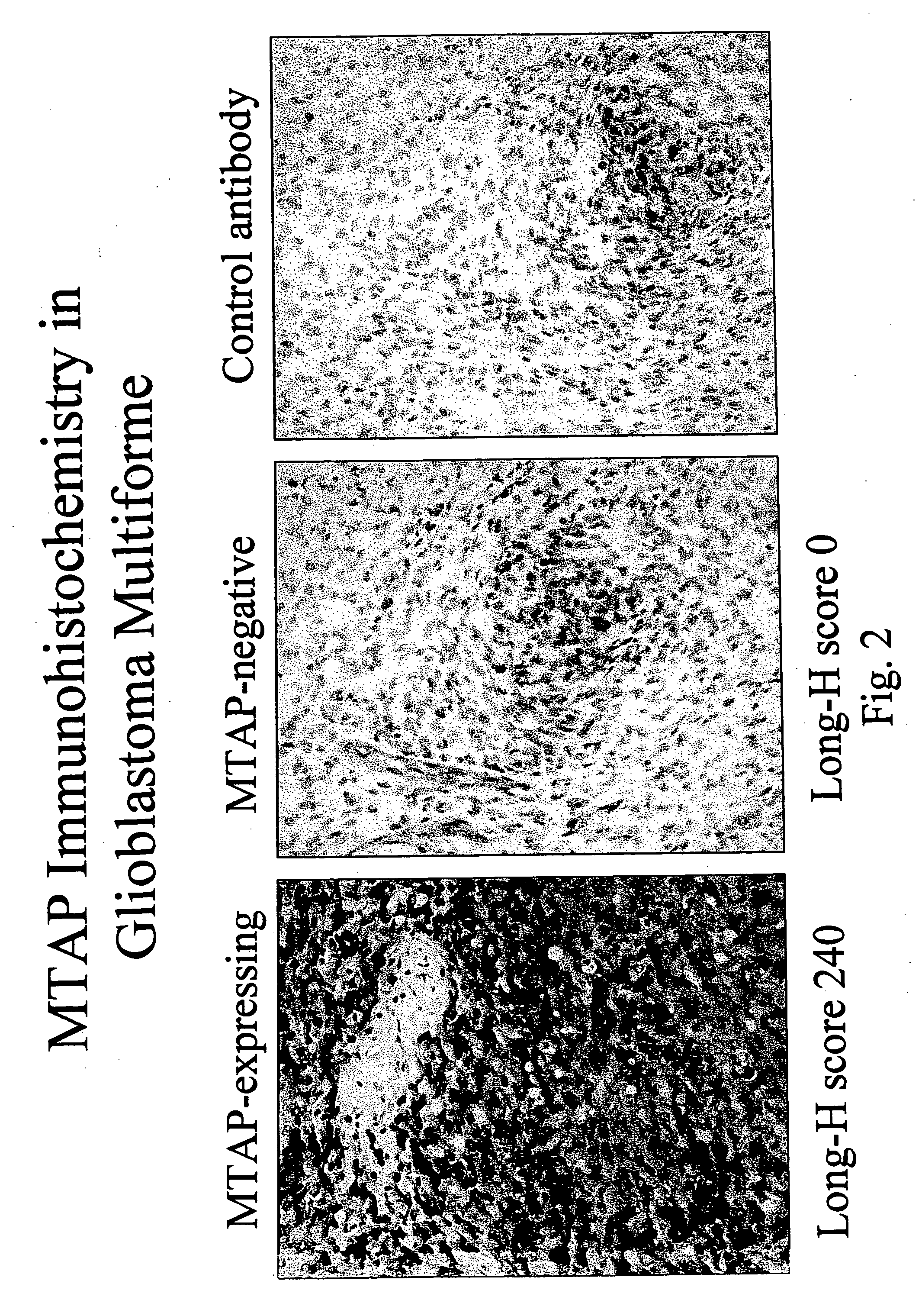
Disclosed are novel nucleic acid and peptide compositions comprising methythioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) and methods of use for MTAP amino acid sequences and DNA segments comprising MTAP in the diagnosis of human cancers and development of MTAP-specific antibodies. Also disclosed are methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors and other proliferative cell disorders, and idenification tumor suppressor genes and gene products from the human 9p21-p22 chromosome region. Such methods are useful in the diagnosis of multiple tumor types such as bladder cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, brain tumors, lymphomas, gliomas, melanomas, and leukemias.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
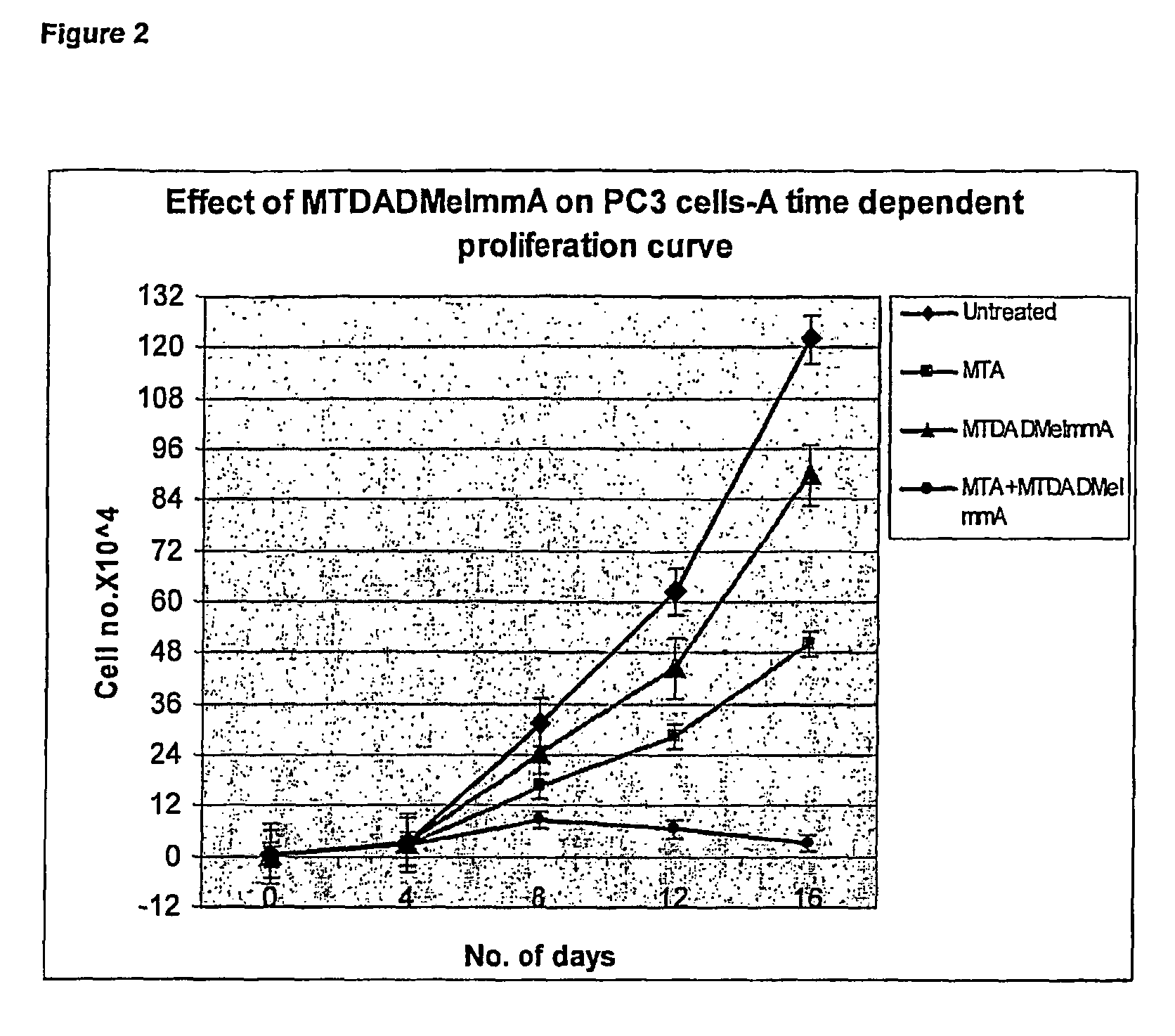
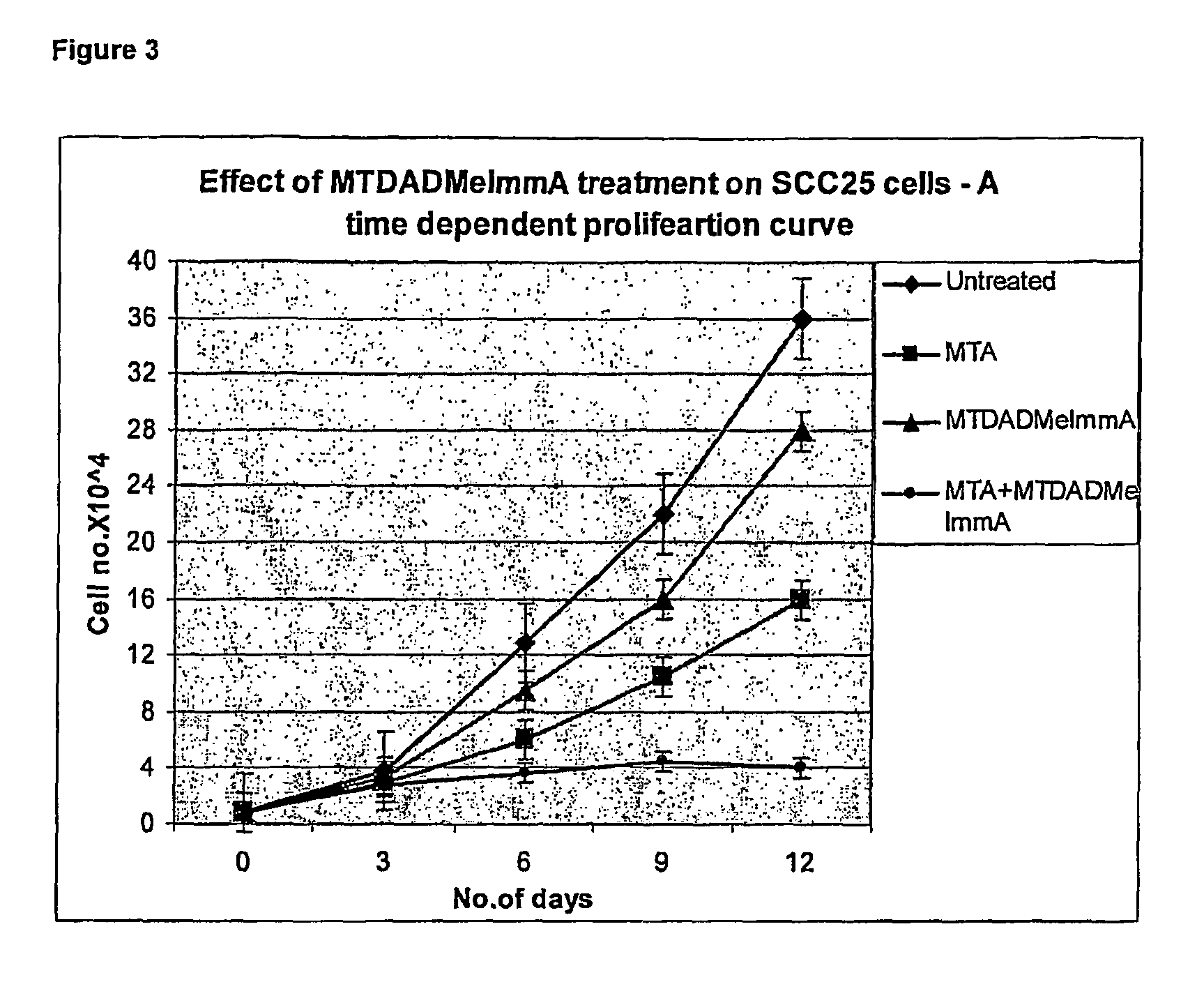
Therapy of tumors and infectious agents deficient in methylthioadenosine phosphorylase
ActiveUS8796241B2Low toxicityImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideAdenosineCompetitive antagonist
Owner:LUBIN ADAM +1
Acyclic amine inhibitors of 5-methytioadenosine phosphorylase and nucleosidase
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase. The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases or conditions in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase including cancer, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Methods, assays and compounds for treating bacterial infections by inhibiting methylthioinosine phosphorylase
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
3-hydroxypyrrolidine inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase and nucleosidase
The present invention relates to 3-hydroxypyrrolidine compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase. The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases or conditions in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase including cancer, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
Methods of treating cancer
InactiveUS20190365710A1Prevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein-arginine methyltransferasePolynucleotide
This invention relates to methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof, e.g., in a human in need thereof, comprising determining the level of 5-Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) polynucleotide or polypeptide or the presence or absence of a mutation in MTAP in a sample from the human, and administering to the human an effective amount of a Type I protein arginine methyltransferase (Type I PRMT) inhibitor if the level of the MTAP polynucleotide or polypeptide is decreased relative to a reference or if a mutation in MTAP polynucleotide or polypeptide is present, thereby treating the cancer in the human.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Methods of treating cancer using inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
In-vivo energy depleting strategies for killing drug-resistant cancer cells
This invention also provides a method for treating a cancer subject comprising administering to the subject a combination of ATP-depleting agents at concentrations which deplete the ATP level to, or close to, at least 15% of normal in cancer cells wherein at least one of the ATP-depleting agents is a mitochondrial ATP-inhibitor, a methylthioadenosine phosphorylase inhibitor or an inhibitor of De Novo purine synthesis other than 6-Methylmercaptopurine riboside, wherein said composition produces a substantially better effect than a composition without at least one of the ATP-depleting agents: a mitochondrial ATP-inhibitor, a glycolytic inhibitor, a methylthioadenosine phosphorylase inhibitor and an inhibitor of De Novo purine synthesis other than 6-Methylmercaptopurine riboside.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
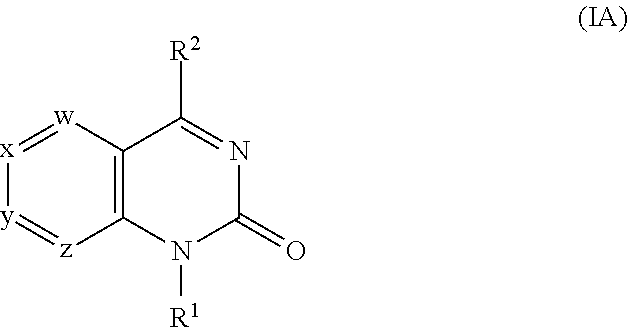
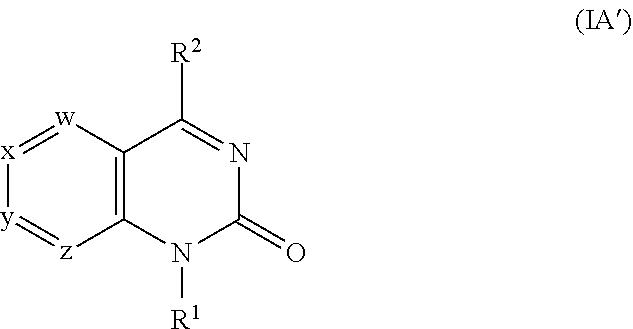
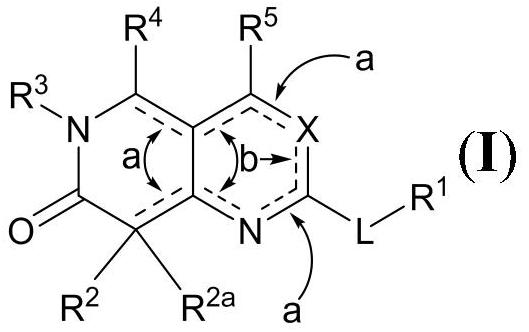
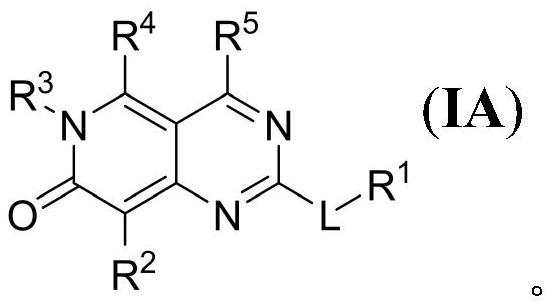
2-oxoquinazoline derivatives as methionine adenosyltransferase 2A inhibitors
Disclosed herein are certain 2-oxoquinazoline derivatives of Formula (IA):that are methionine adenosyltransferase 2A (MAT2A) inhibitors. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of treating diseases treatable by inhibition of MAT2A such as cancer, including cancers characterized by reduced or absence of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) activity.
Owner:IDEAYA BIOSCI INC
Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase compositions and methods of use in the diagnosis and treatment of proliferative disorders
InactiveUS20050272069A1Increase ratingsSmall sizeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
Disclosed are novel nucleic acid and peptide compositions comprising methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) and methods of use for MTAP amino acid sequences and DNA segments comprising MTAP in the diagnosis of human cancers and development of MTAP-specific antibodies. Also disclosed are methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors and other proliferative cell disorders, and identification of tumor suppressor genes and gene products from the human 9p21-p22 chromosome region. Such methods are useful in the diagnosis of multiple tumor types such as bladder cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, brain tumors, lymphomas, gliomas, melanomas, and leukemias.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Method of detecting 5'-methioadenosine phosphorylase defect type mammarian cell
A method for the detecting whether methyladenosine phosphatase (MTAse) is present in a cell sample in either a catalytically active or catalytically inactive form. In one respect, the method comprises adding oligonucleotide probes to the sample, which probes are capable of specifically hybridizing to any MTAse encoding nucleic acid in the sample under conditions favoring that hybridization. Absence of MTAse in a sample is considered to be indicative of malignancy. Polynucleotides encoding MTAse, MTAse peptides and antibodies to MTAse, as well as kits for performing the methods of the invention, are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
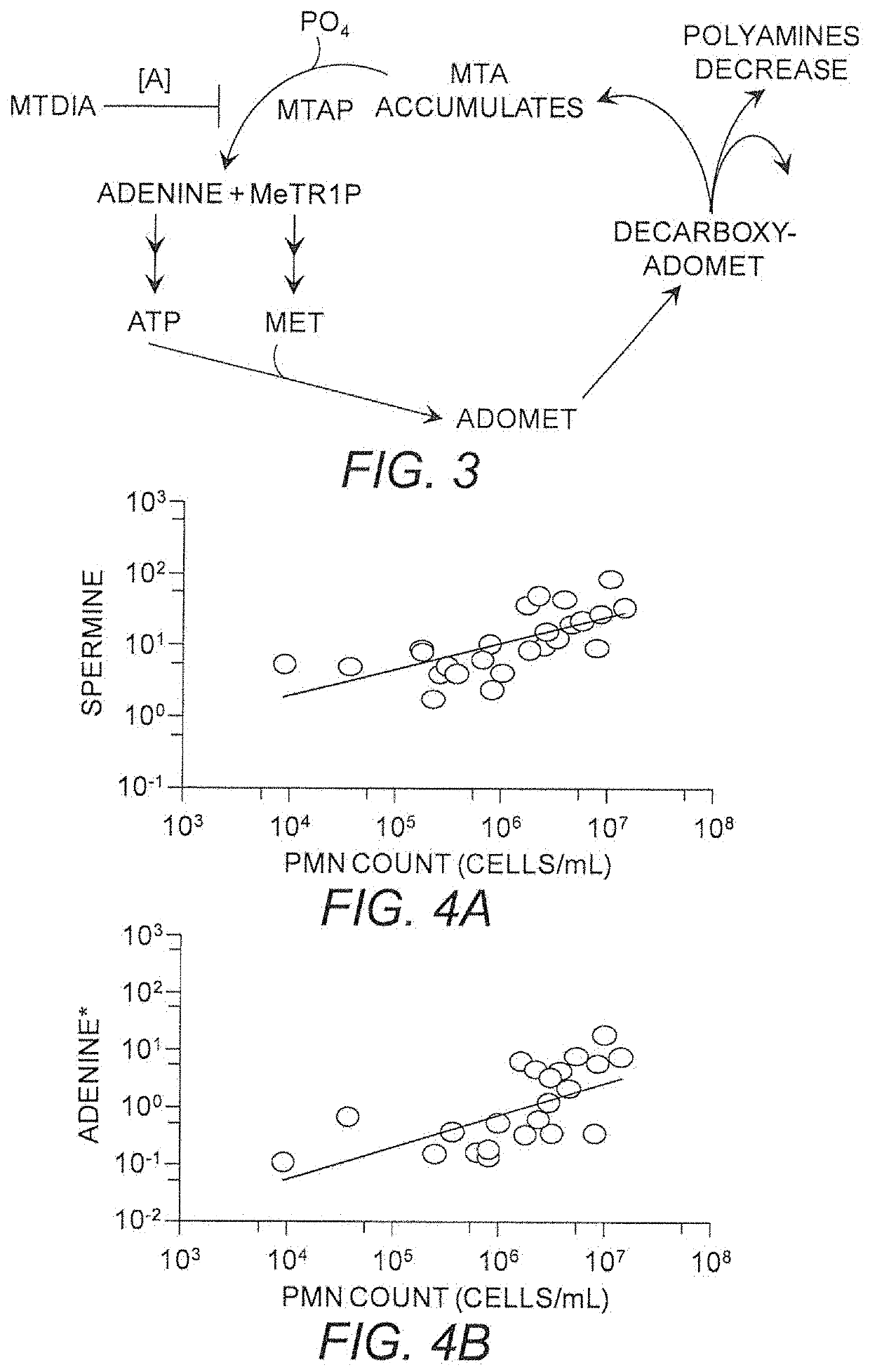
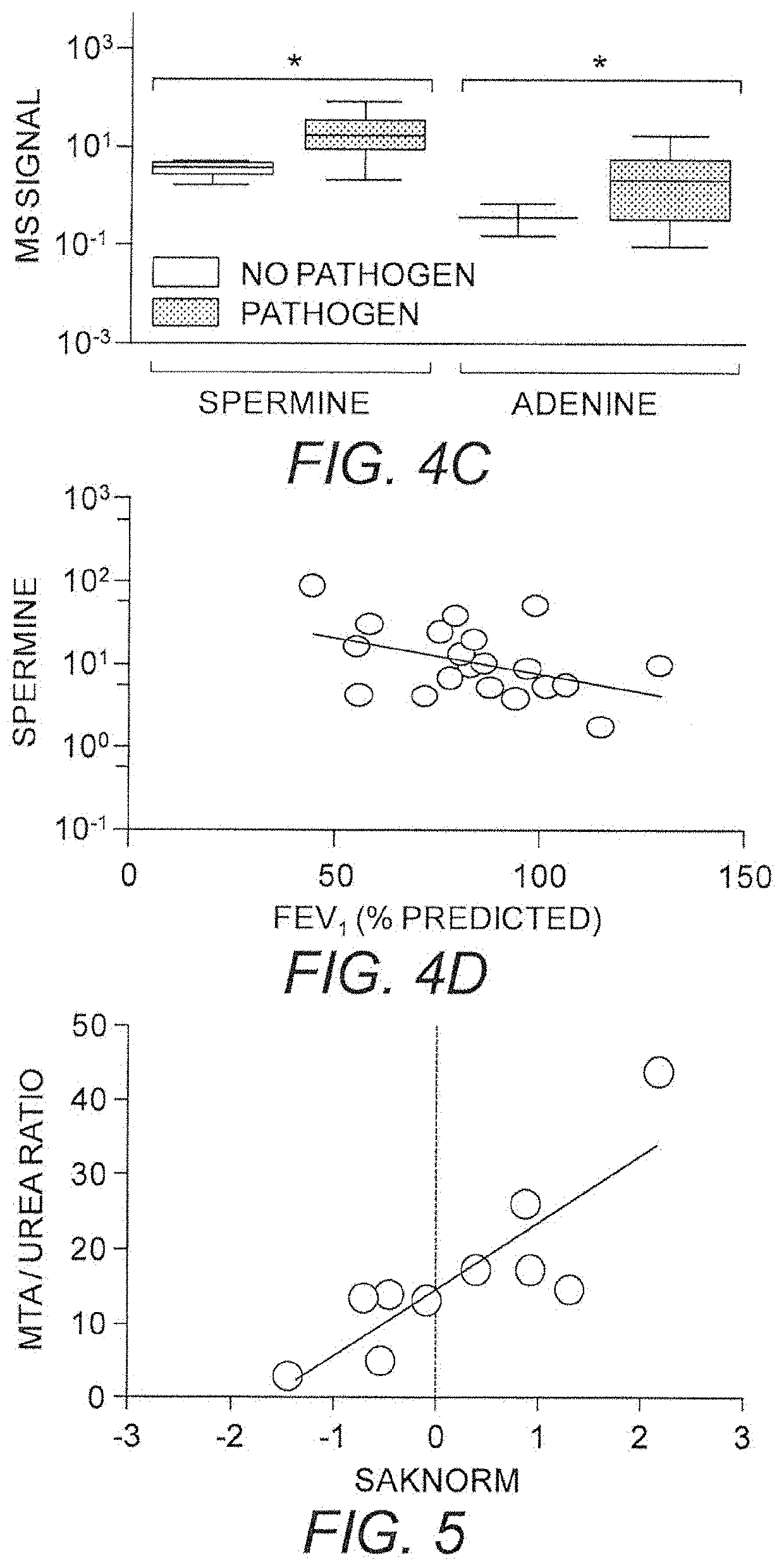
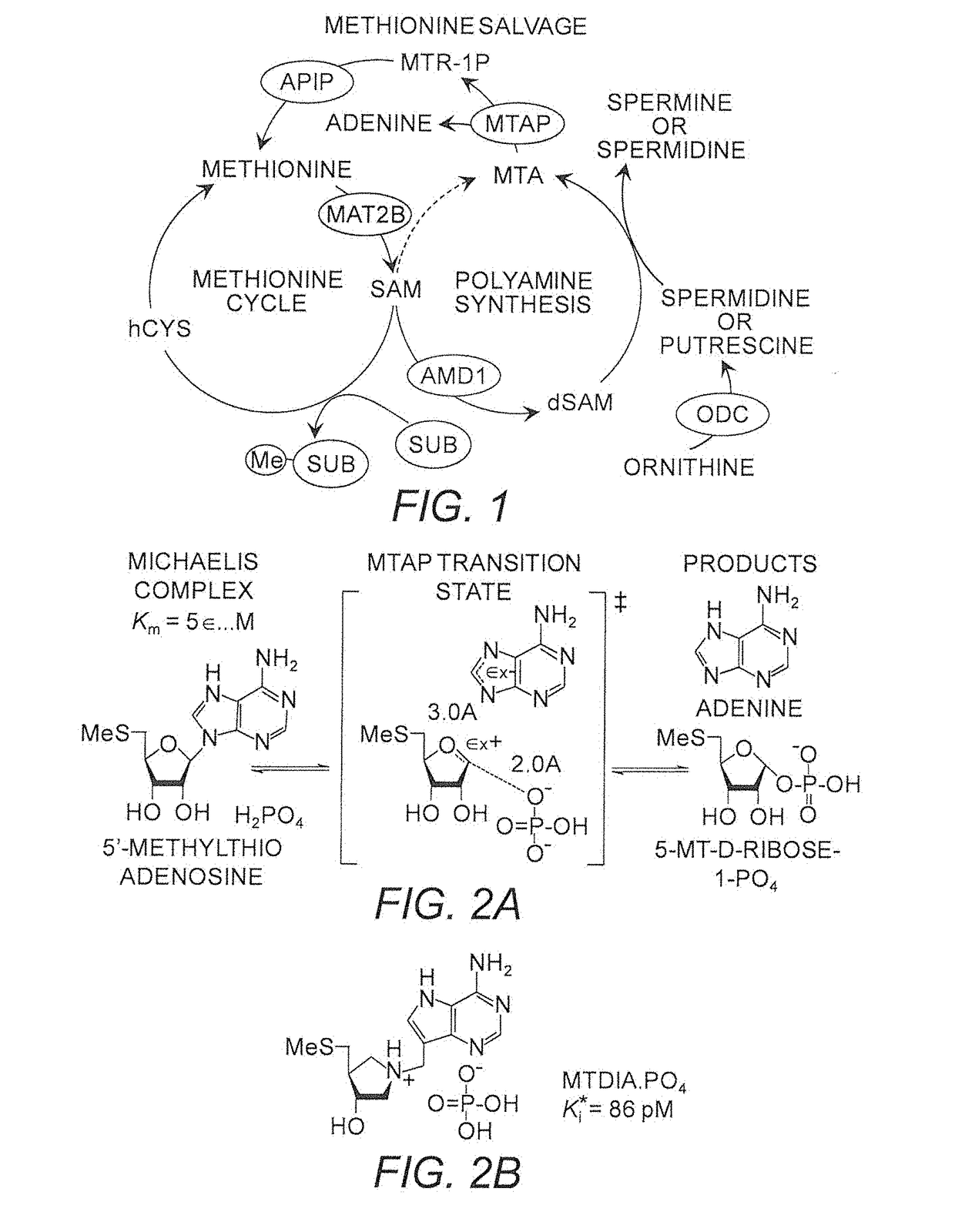
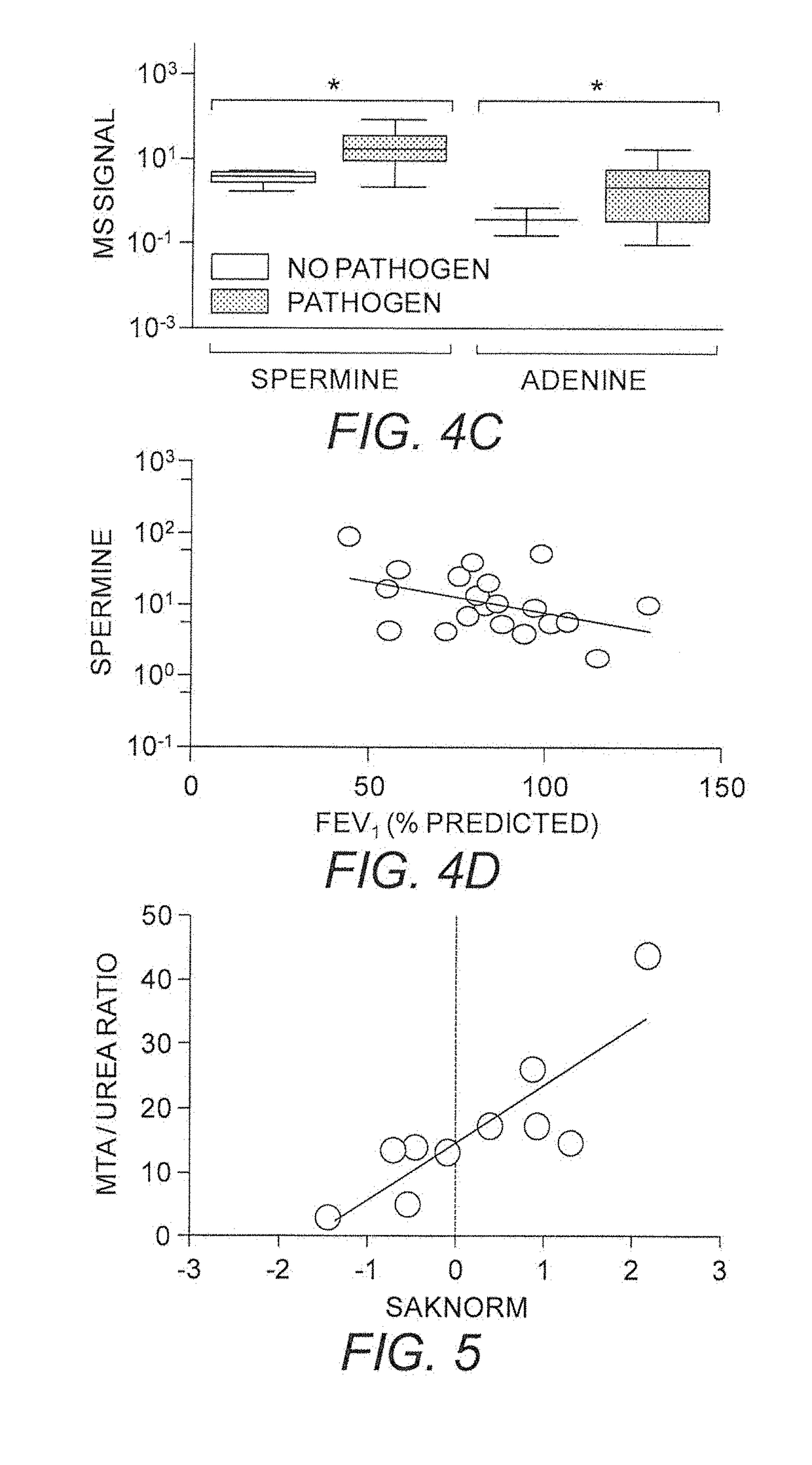
Use of MTAP inhibitors for the treatment of lung disease
This invention relates generally to the use of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) inhibitors for the treatment of lung diseases associated with inflammation, such as cystic fibrosis (CF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Small molecule inhibitors of MTAP can sustain accumulation of endogenous MTA to therapeutically beneficial levels resulting in decreased inflammation in CF and COPD.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +2
In-vivo energy depleting strategies for killing drug-resistant cancer cells
This invention also provides a method for treating a cancer subject comprising administering to the subject a combination of ATP-depleting agents at concentrations which deplete the ATP level to, or close to, at least 15% of normal in cancer cells wherein at least one of the ATP-depleting agents is a mitochondrial ATP-inhibitor, a methylthioadenosine phosphorylase inhibitor or an inhibitor of De Novo purine synthesis other than 6-Methylmercaptopurine riboside, wherein said composition produces a substantially better effect than a composition without at least one of the ATP-depleting agents: a mitochondrial ATP-inhibitor, a glycolytic inhibitor, a methylthioadenosine phosphorylase inhibitor and an inhibitor of De Novo purine synthesis other than 6-Methylmercaptopurine riboside.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Use of MTAP Inhibitors for the Treatment of Lung Disease
ActiveUS20180353511A1Inhibit metabolismImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
This invention relates generally to the use of 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) inhibitors for the treatment of lung diseases associated with inflammation, such as cystic fibrosis (CF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Small molecule inhibitors of MTAP can sustain accumulation of endogenous MTA to therapeutically beneficial levels resulting in decreased inflammation in CF and COPD.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +2
Methods of treating cancer
PendingCN110225983AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideProtein-arginine methyltransferase
The invention relates to methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof, e.g., in a human in need thereof, comprising determining determining the level of 5- Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase(MTAP) polynucleotide or polypeptide or the presence or absence of a mutation in MTAP in a sample from the human, and administering to the human an effective amount of a Type I protein arginine methyltransferase (Type I PRMT) inhibitor if the level of the MTAP polynucleotide or polypeptide is decreased relative to a reference or if a mutation in MTAP polynucleotide or polypeptide is present, thereby treating the cancer in the human.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
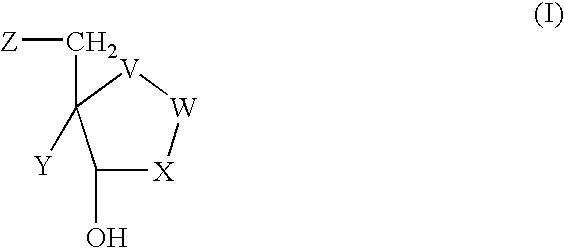
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00001.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00002.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-C00001.png)
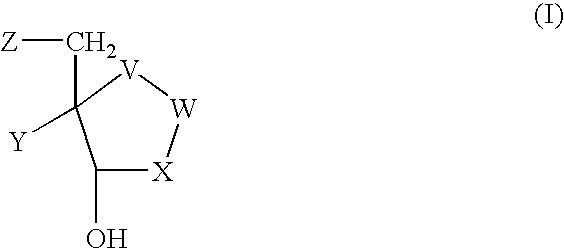
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00003.png)
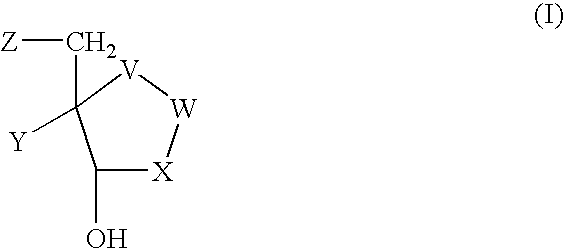
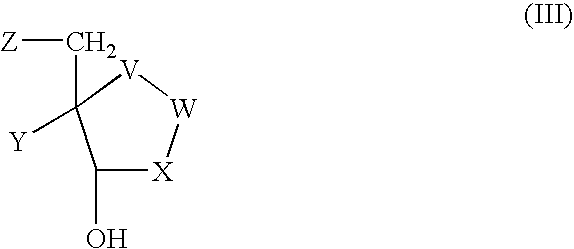


![Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA) Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA)](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d522eebf-412f-4a80-894d-3686f3b13ba7/US20150274741A1-20151001-D00001.PNG)
![Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA) Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA)](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d522eebf-412f-4a80-894d-3686f3b13ba7/US20150274741A1-20151001-D00002.PNG)
![Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA) Salt and polymorphic forms of (3r,4s)-l-((4-amino-5h-pyrrolo[3,2,-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)methyl)-4(methylthiomethyl)pyrodin-3-ol(MTDIA)](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d522eebf-412f-4a80-894d-3686f3b13ba7/US20150274741A1-20151001-D00003.PNG)