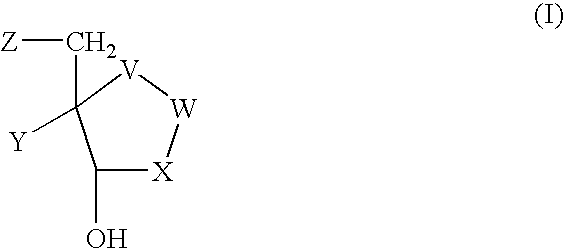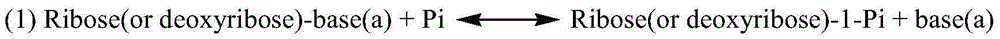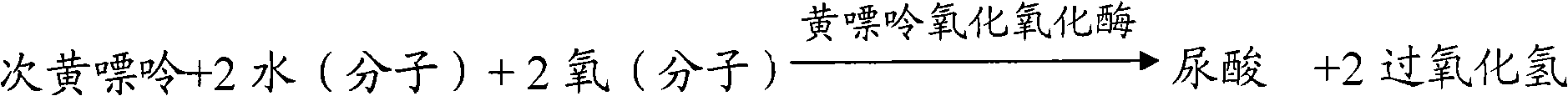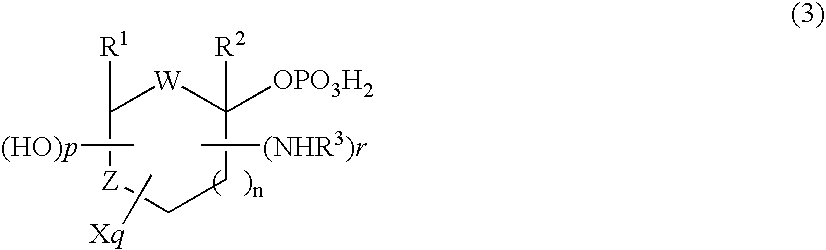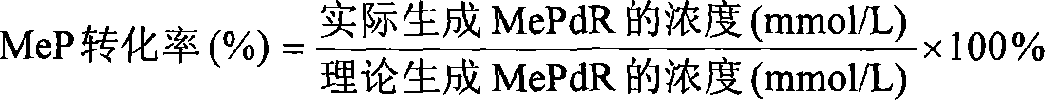Patents
Literature
66 results about "Nucleoside phosphorylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) also known as PNPase and inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene.
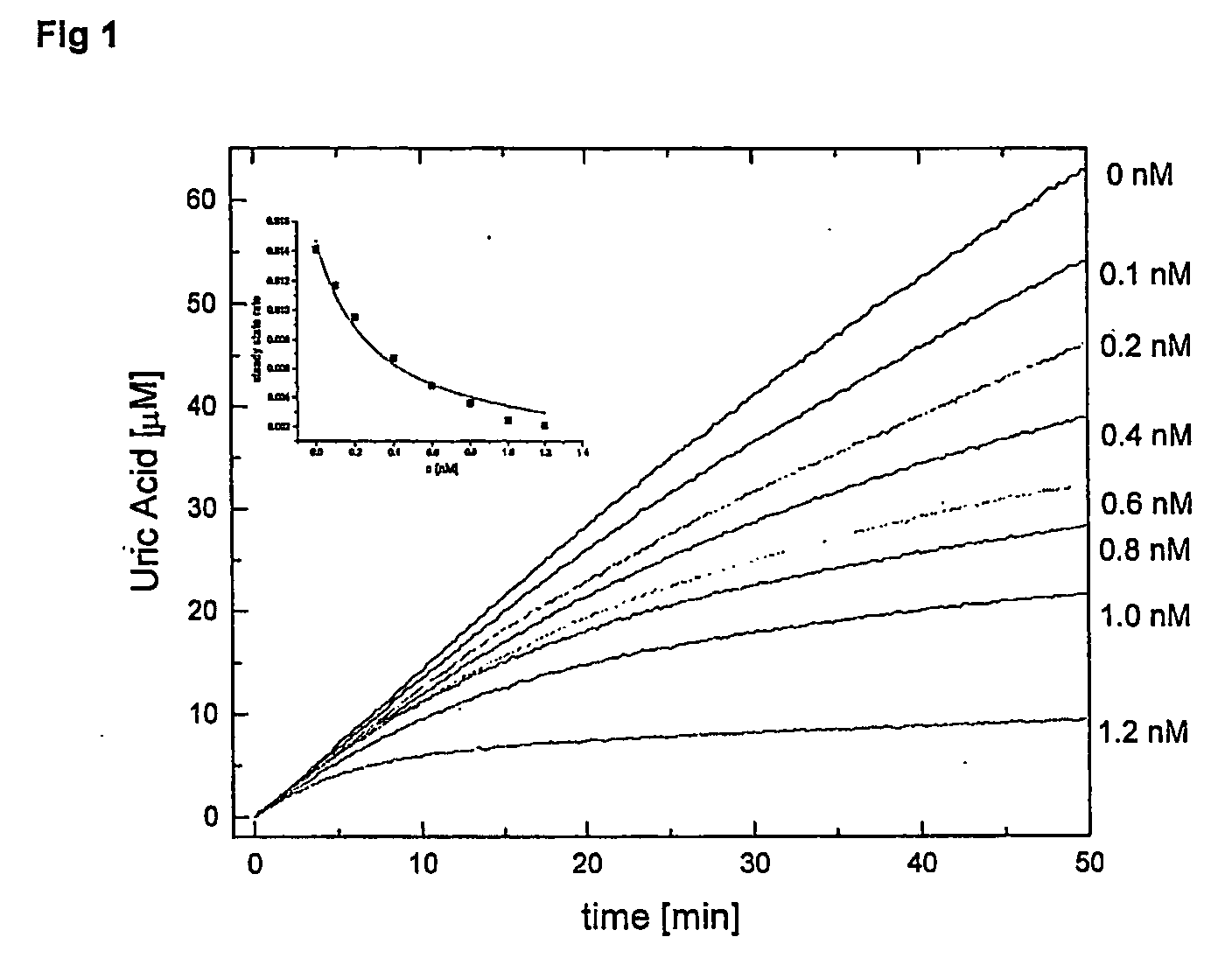
Inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
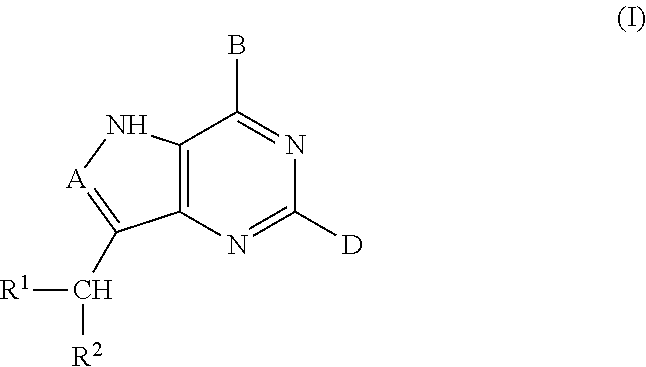
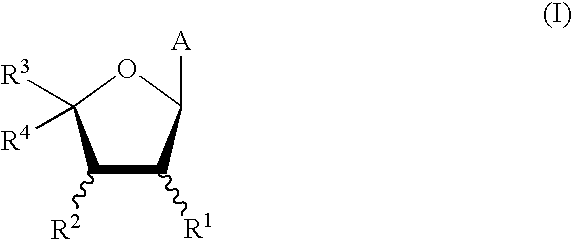
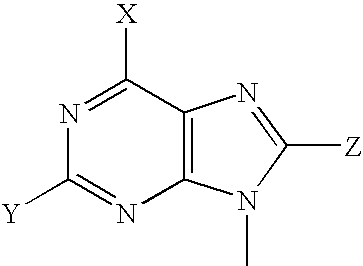
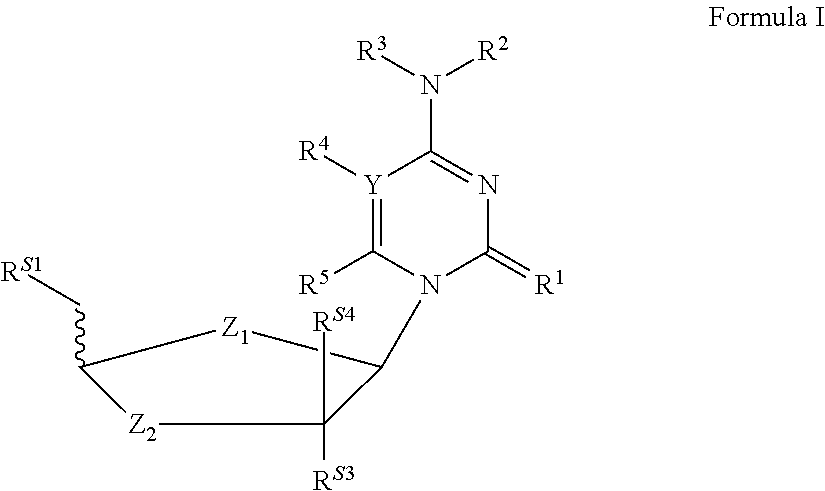
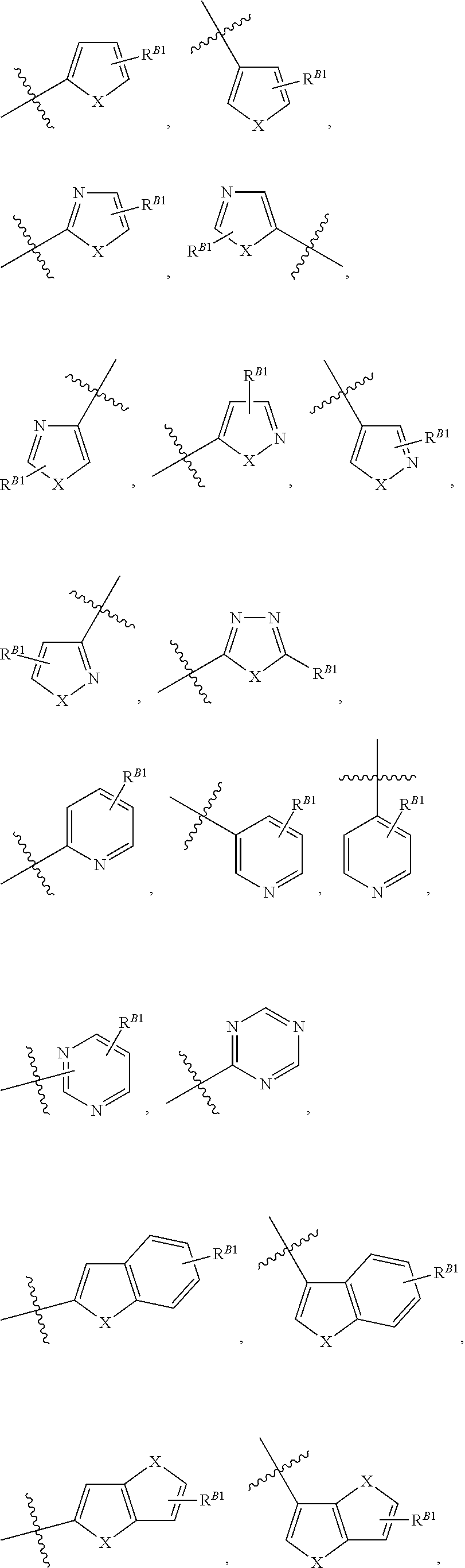
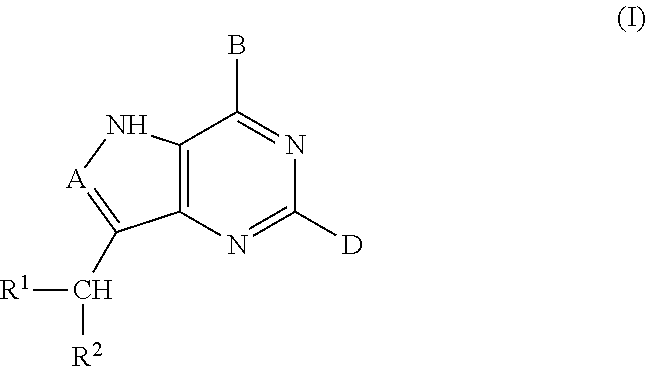
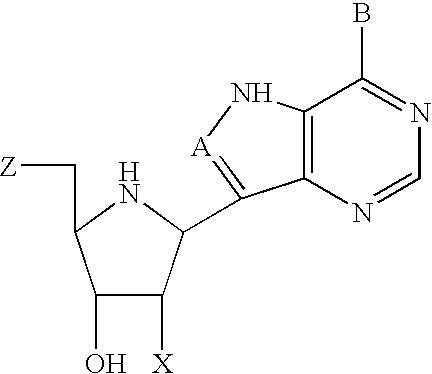
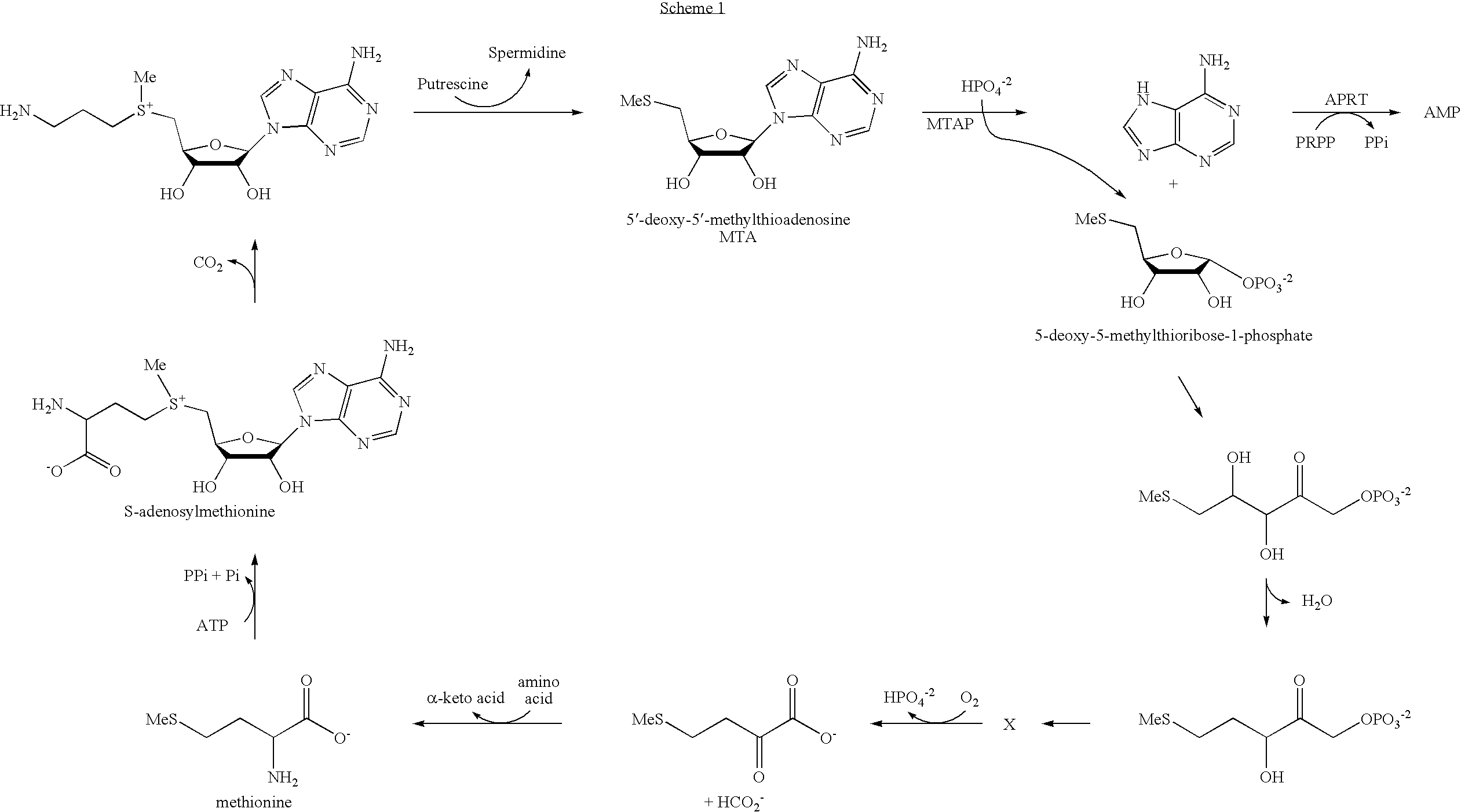
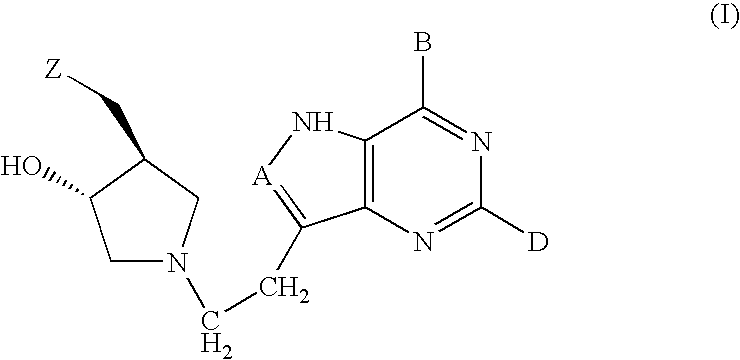
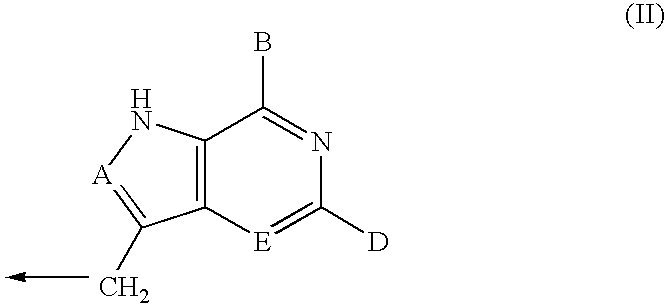
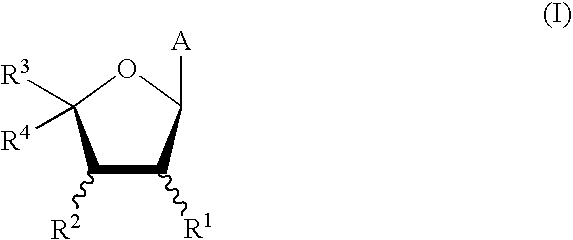
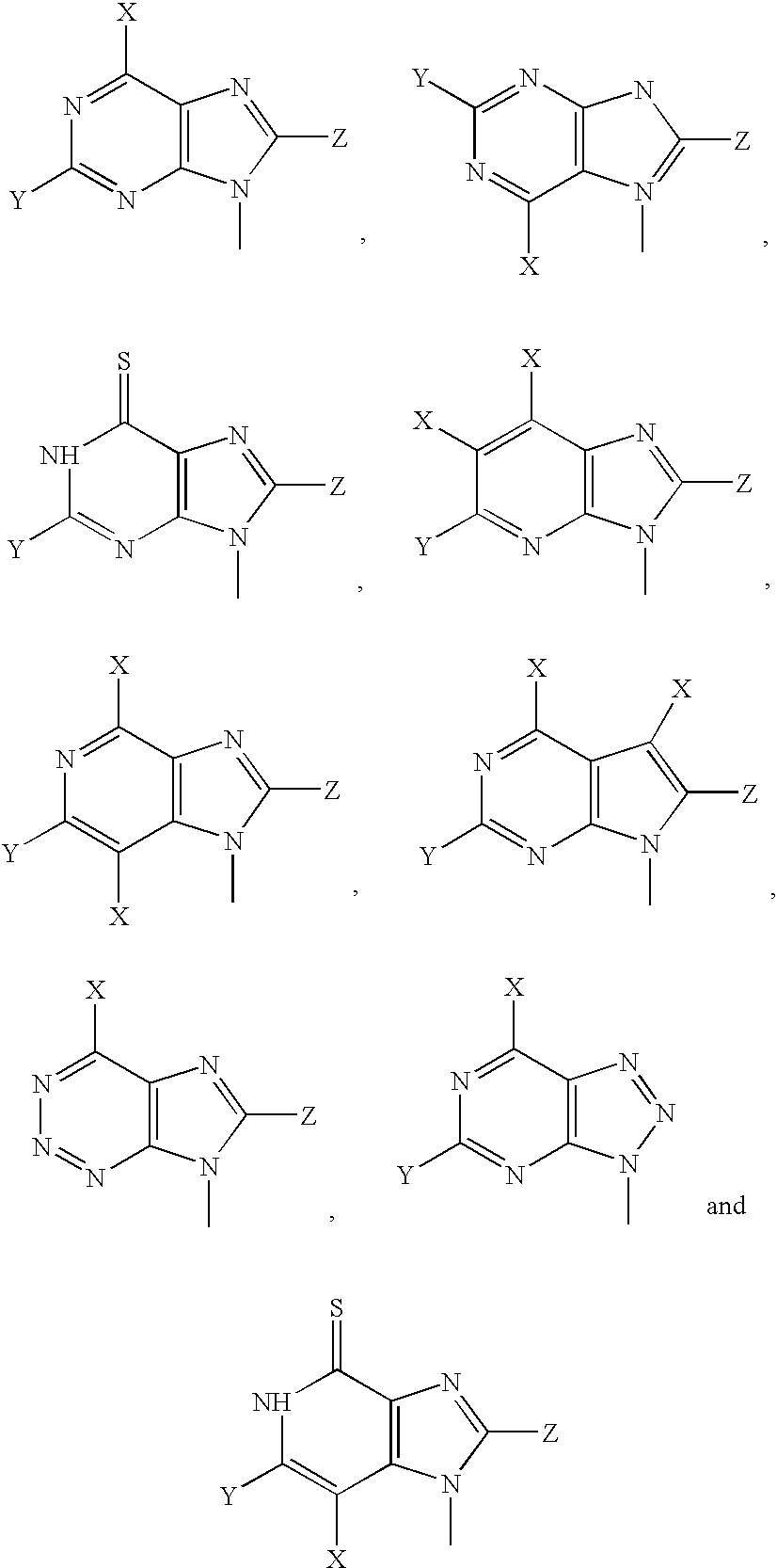
The invention provides a compound of the formula: wherein A is selected from N, CH and CR; R is selected from halogen, optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl and aryl, OH, NH2, NHR<1>, NR<1>R<2 >and SR<3>; R<1>, R<2 >and R<3 >are each optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl groups; B is selected from NH2 and NHR<4>; R<4 >is an optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group; X is selected from H, OH and halogen; Z is selected from H, Q, SQ and OQ; Q is an optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group; or a tautomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, an ester, or a prodrug thereof; with the proviso that the stereochemistry of the aza-sugar moiety is D-ribo or 2'-deoxy-D-erythro-; pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compound; and methods of treatment using said compound.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
Inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
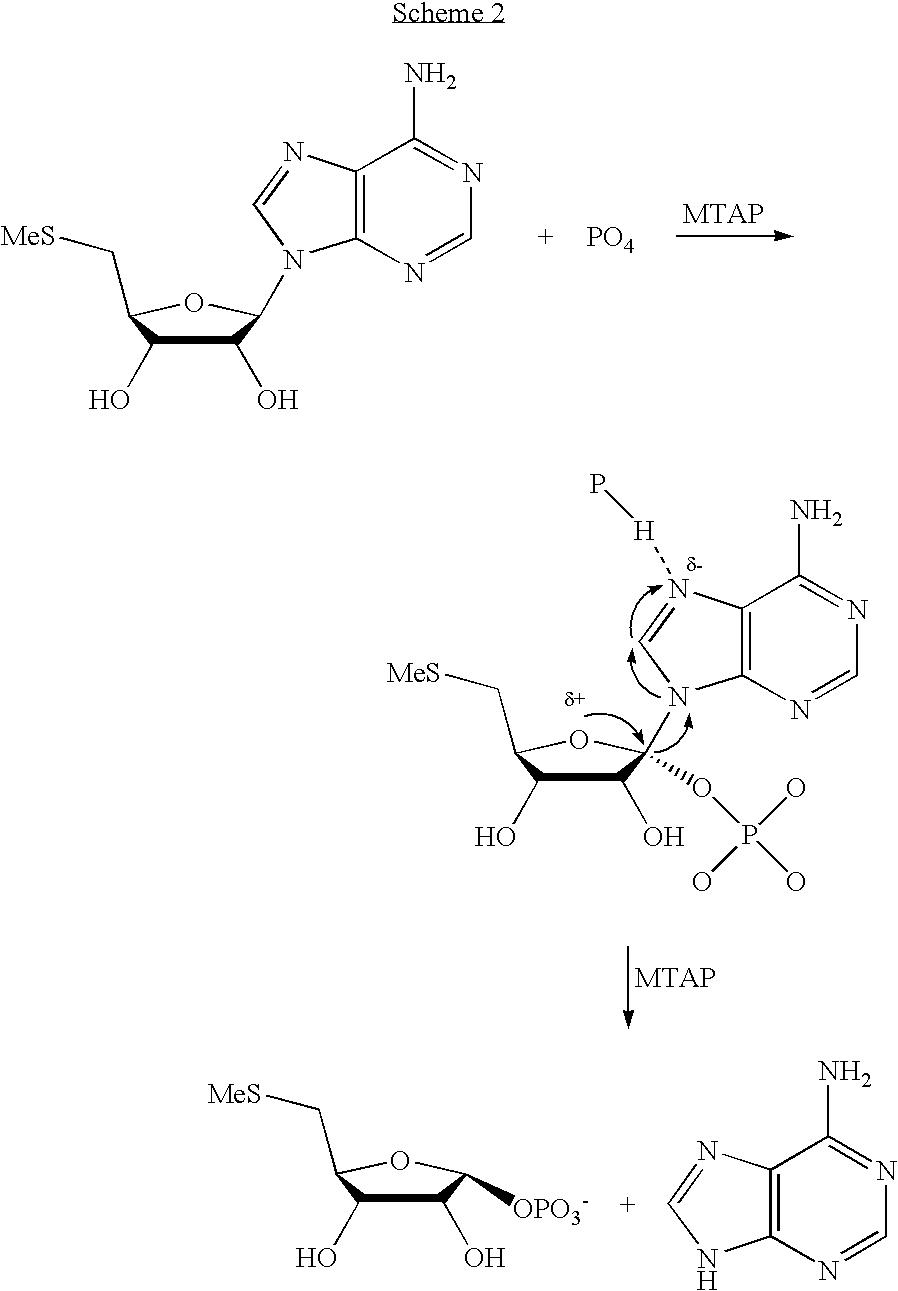
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
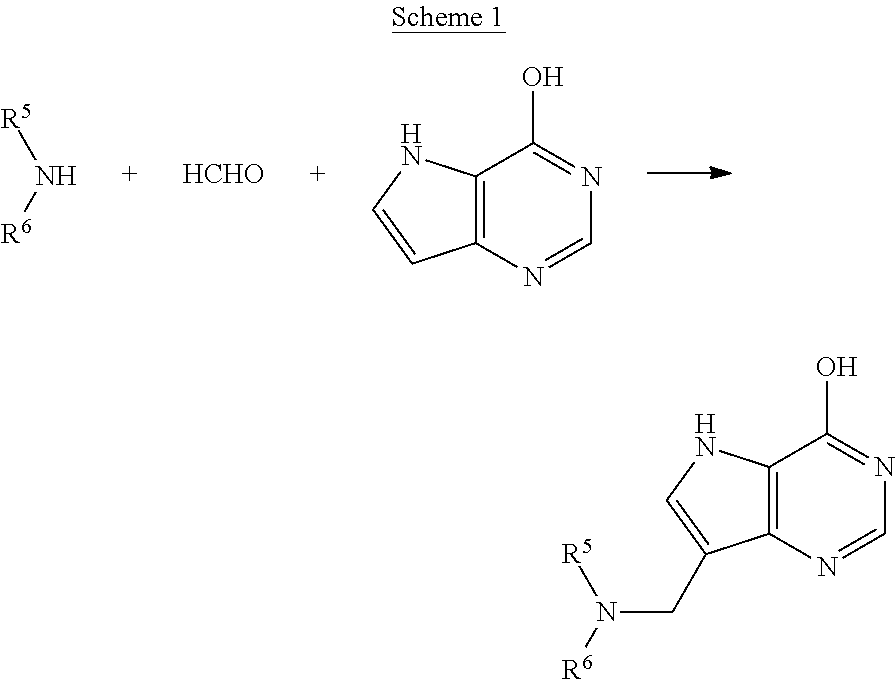
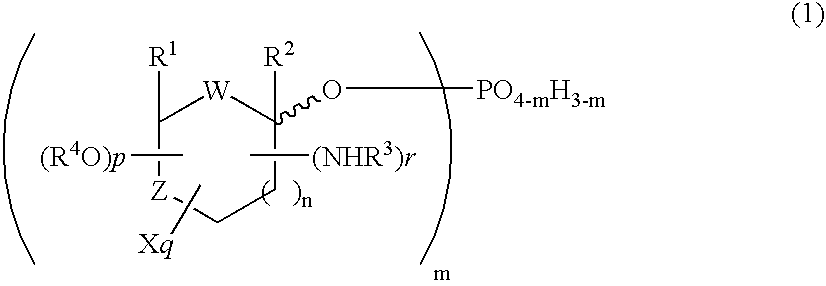
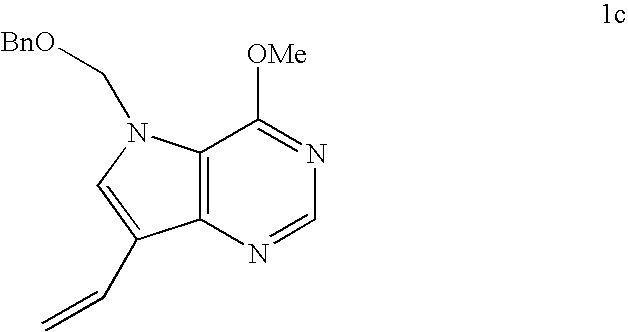
4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
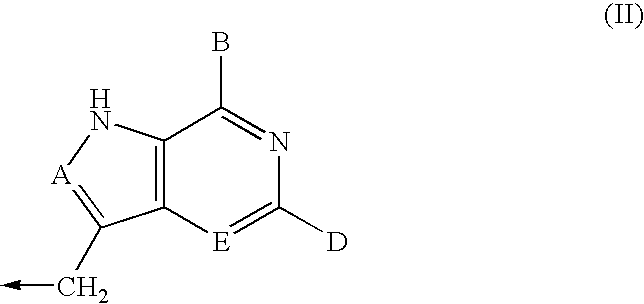
The invention provides a compound of the formula:wherein A is selected from N, CH and CR; R is selected from halogen, optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl and aryl, OH, NH2, NHR1, NR1R2 and SR3; R1, R2 and R3 are each optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl groups; B is selected from NH2 and NHR4; R4 is an optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group; X is selected from H, OH and halogen; Z is selected from H, Q, SQ and OQ; Q is an optionally substituted alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group; or a tautomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, an ester, or a prodrug thereof; with the proviso that the stereochemistry of the aza-sugar moiety is D-ribo or 2′-deoxy-D-erythro-; pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compound; and methods of treatment using said compound.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
Inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine muclioside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine mucliosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
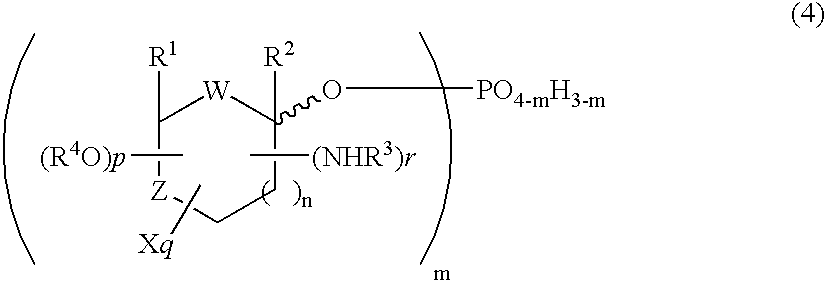
5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine muclioside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine mucliosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Process for preparing inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
InactiveUS20060217551A1Use in synthesisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound (substance)Nucleoside phosphorylase
The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH).The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH).
Owner:IND RES LTD
Inhibitors of nucleoside phoshorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
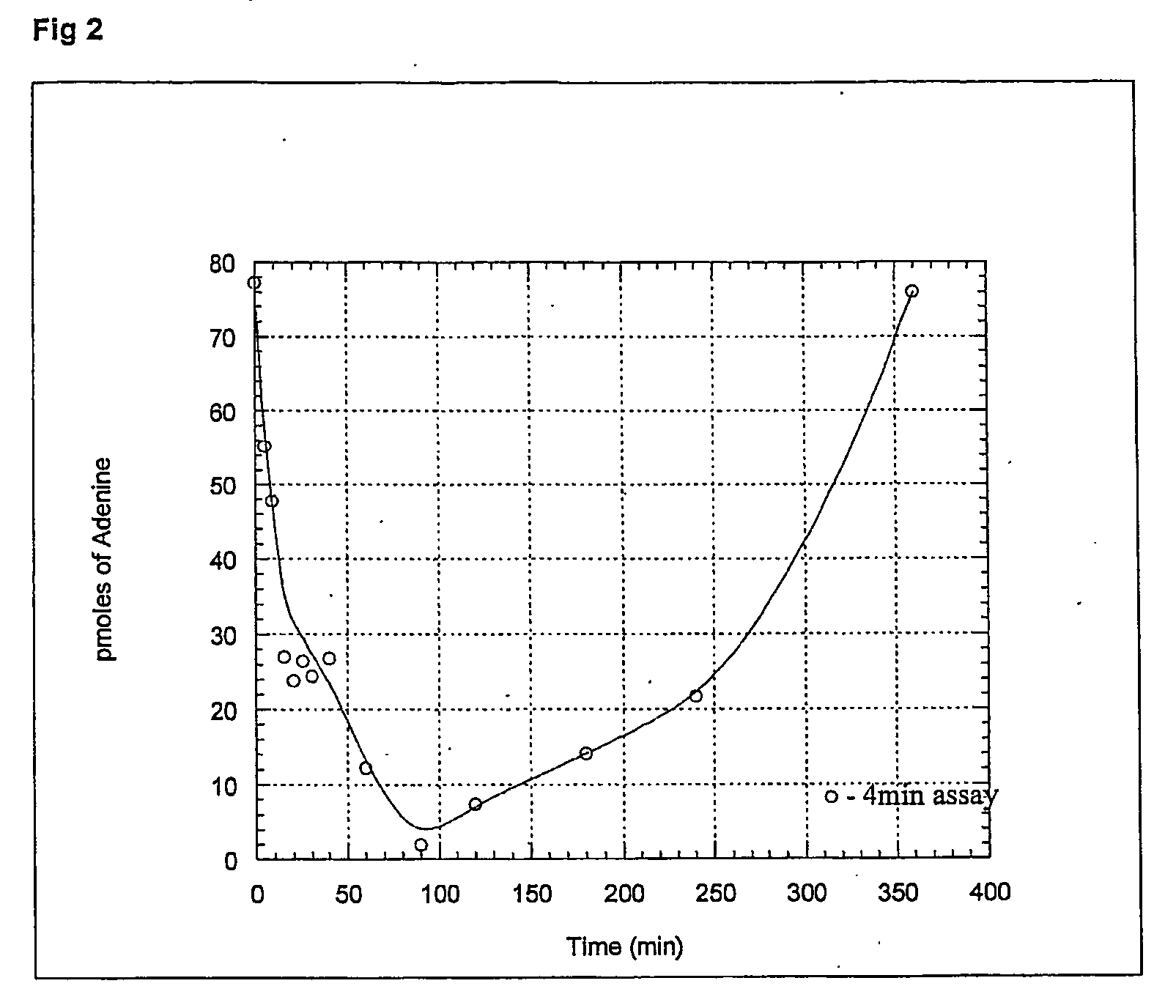
Mutant purine nucleoside phosphorylase proteins and cellular delivery thereof
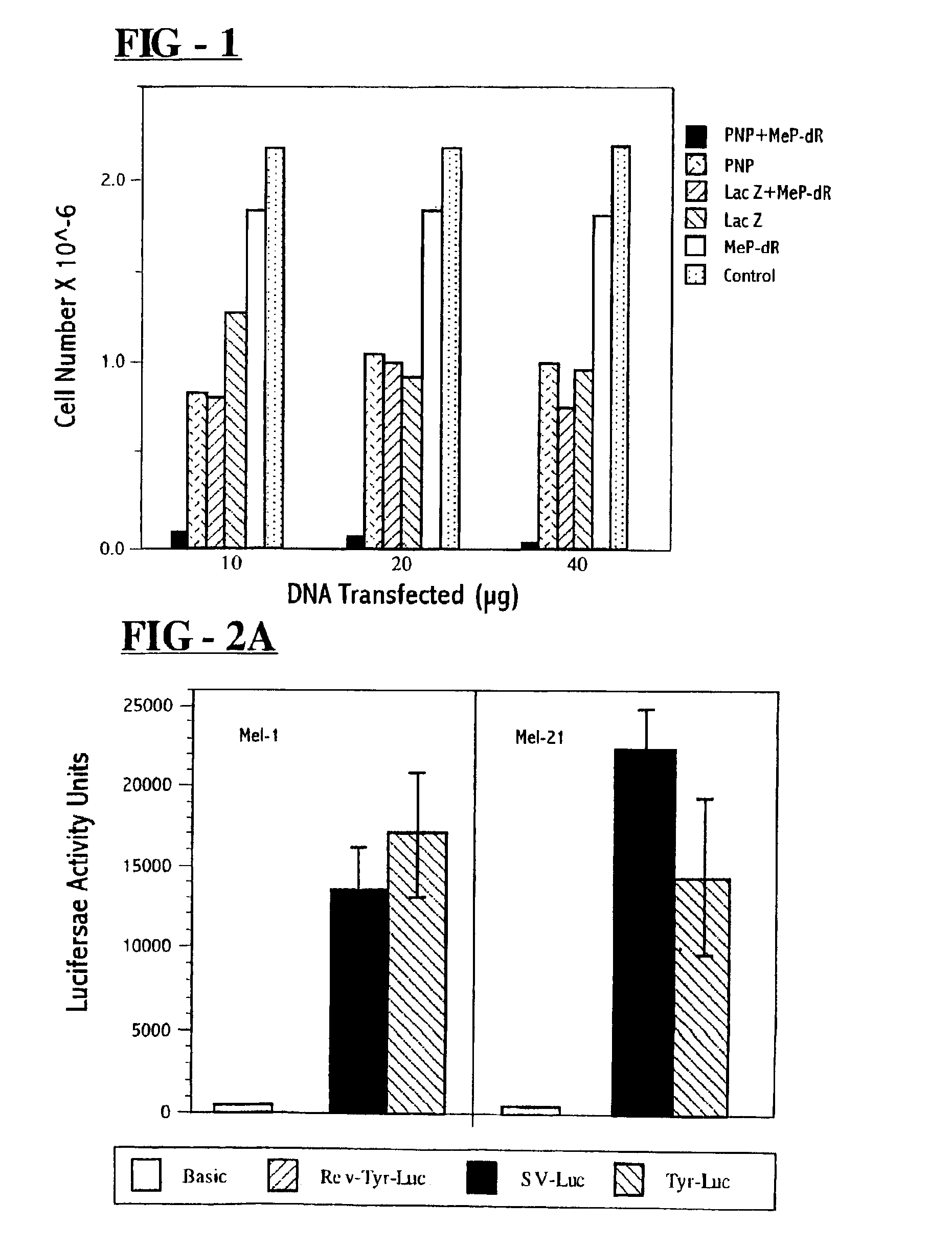
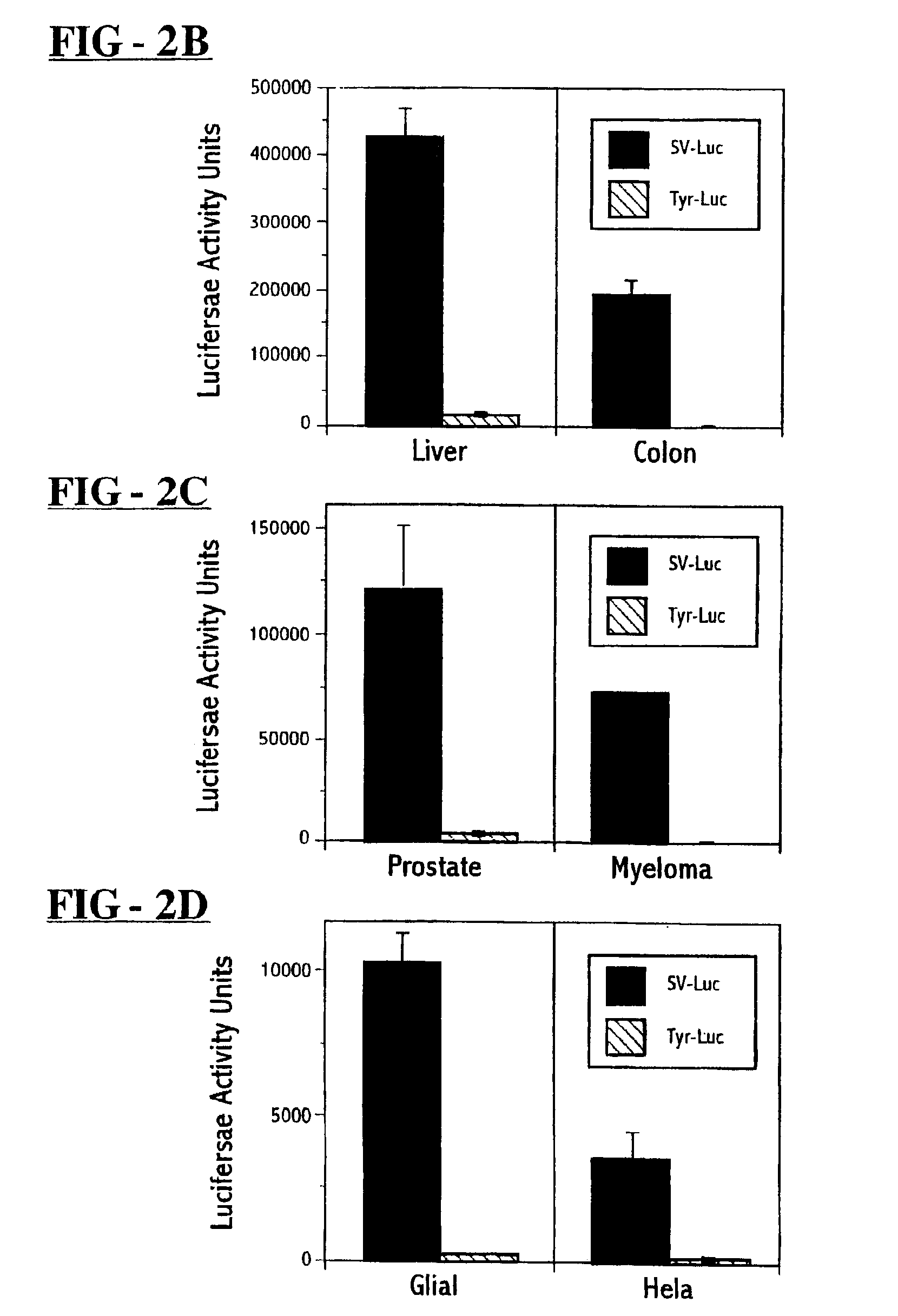
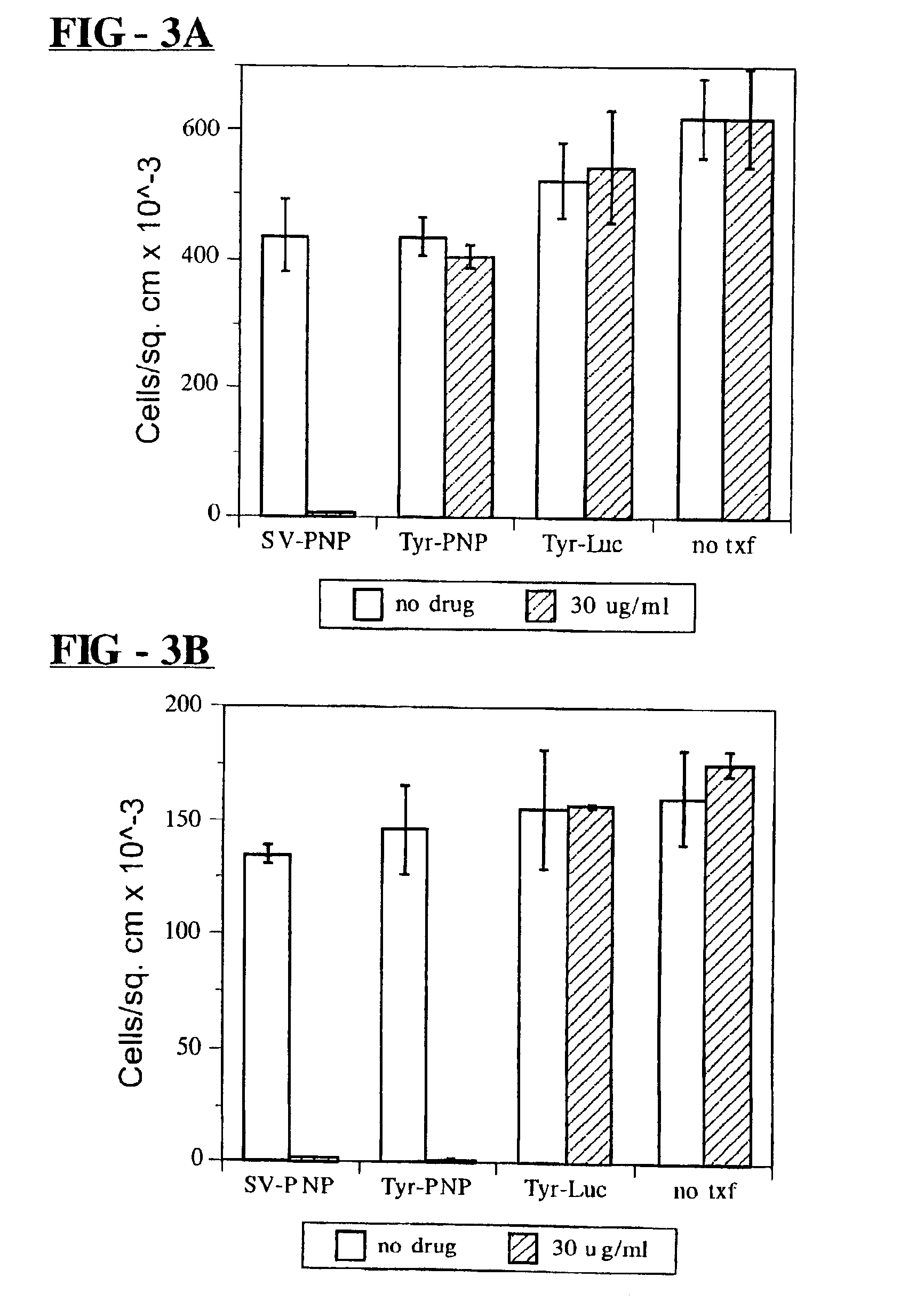
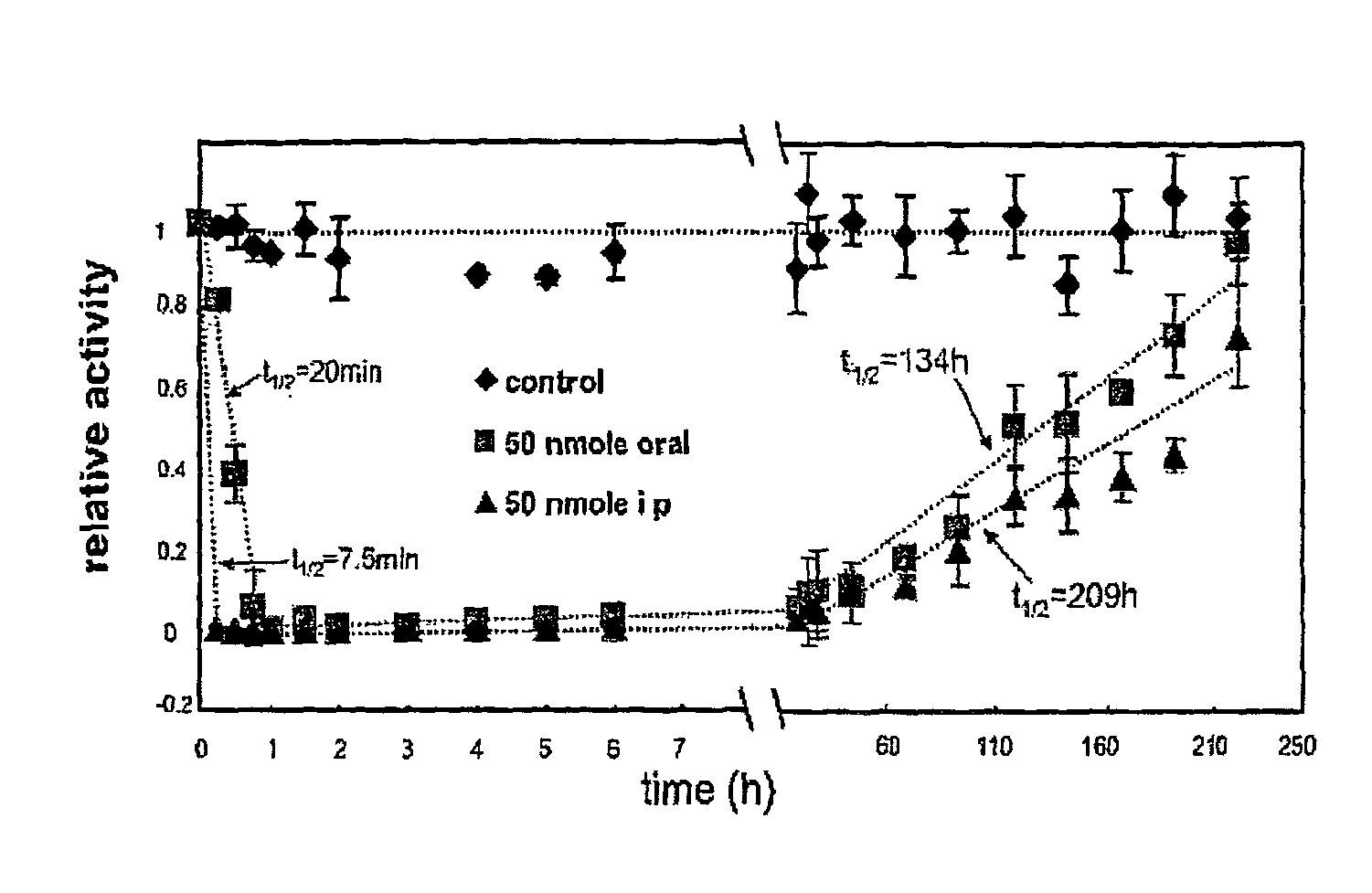
A host cell stably transformed or transfected by a vector including a DNA sequence encoding for mutant purine nucleoside cleavage enzymes is provided. The transformed or transfected host cell can be used in combination with a purine substrate to treat tumour cells and / or virally infected cells. A nucleotide sequence encoding mutant E. coli derived purine nucleoside phosphorylase proteins which can be used in conjunction with an appropriate substrate to produce toxins which impair abnormal cell growth is also provided. A method is detailed for the delivery of toxin by generation withing target cells or by administration and delivery to the cells from without. Novel purine nucleosides are detailed that yield a cytotoxic purine upn enzymatic cleavage. A synthetic process for nucleosides is also detailed.
Owner:CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COIMMERCIALIZATION +2
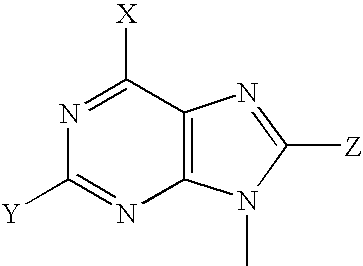
Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
Owner:IND RES LTD
Recombinant bacterial cells for delivery of PNP to tumor cells
InactiveUS6958318B2High level bystander effectLittle effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesNucleoside phosphorylase
The present invention provides a procaryotic host cell stably transformed or transfected by a vector including a DNA sequence encoding for purine nucleoside phosphorylase or hydrolase. The transformed or transfected procaryotic host cell can be used in combination with a purine substrate to treat tumor cells and / or virally infected cells.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Process for preparing inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
InactiveUS20100094003A1Use in synthesisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphorylationMethyl palmoxirate
The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The present invention relates to a new process for the preparation of compounds of general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH).
Owner:EVANS GARY BRIAN +1
Acyclic amine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and hydrolases
The invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNPs) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NHs). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
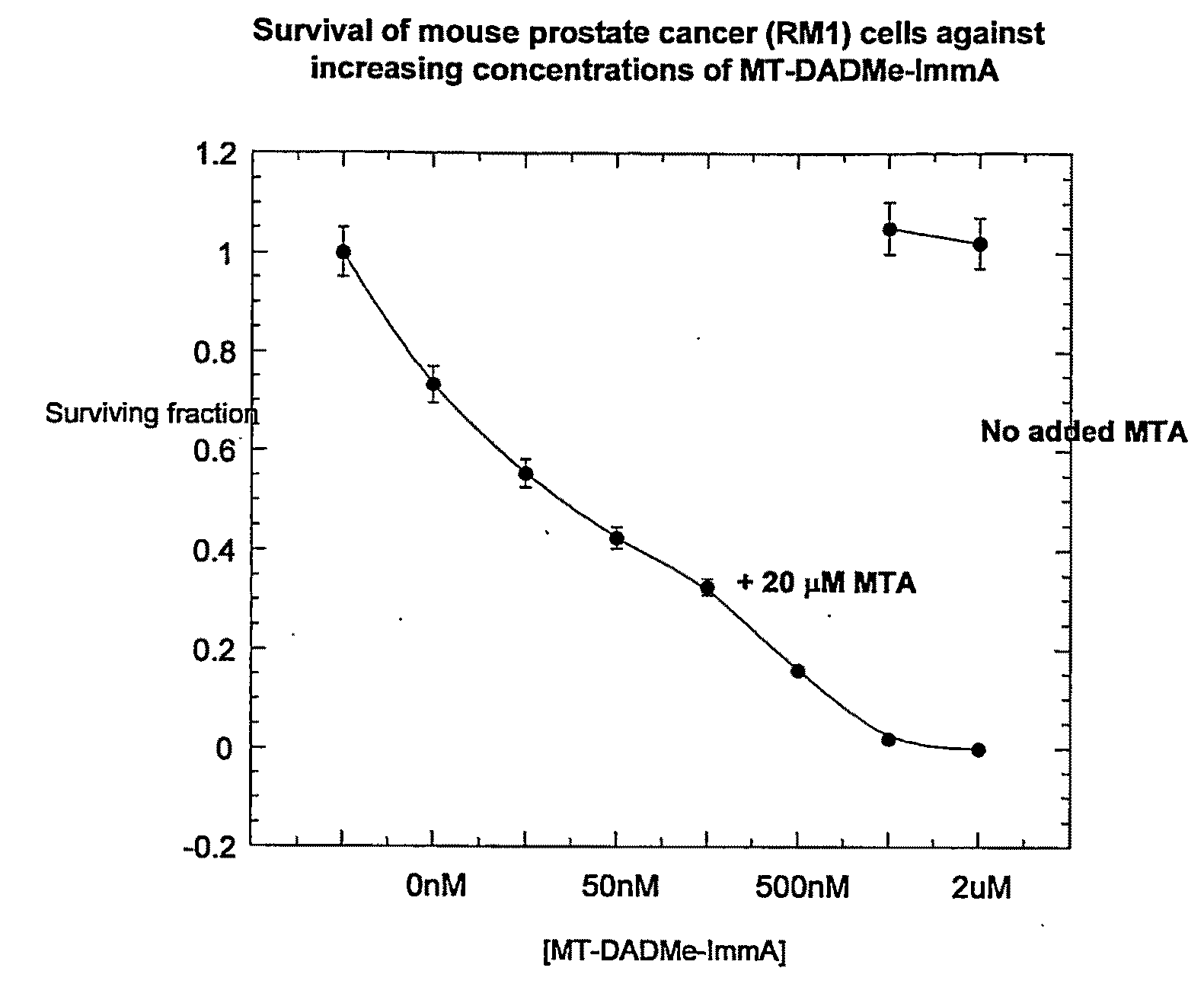
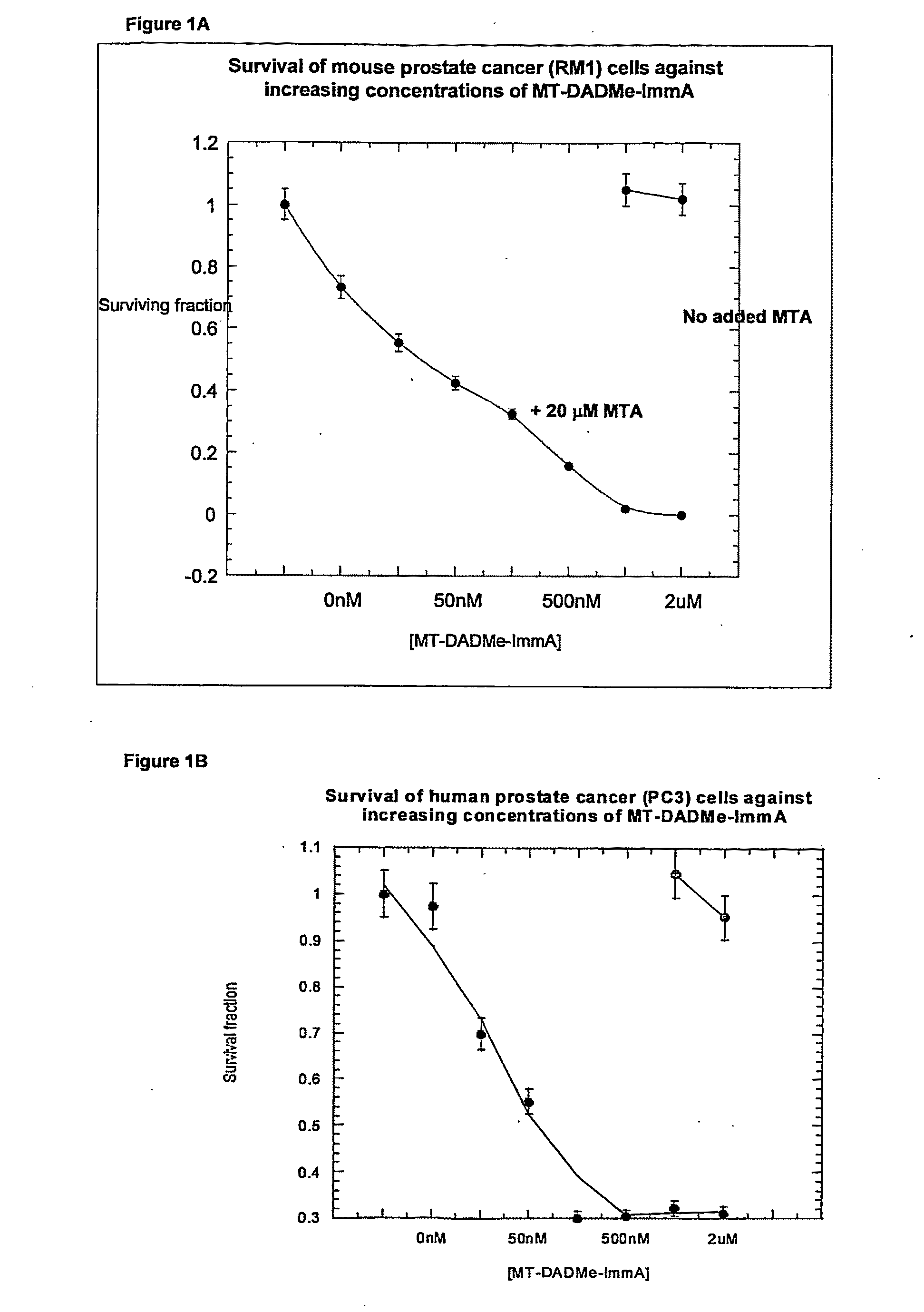
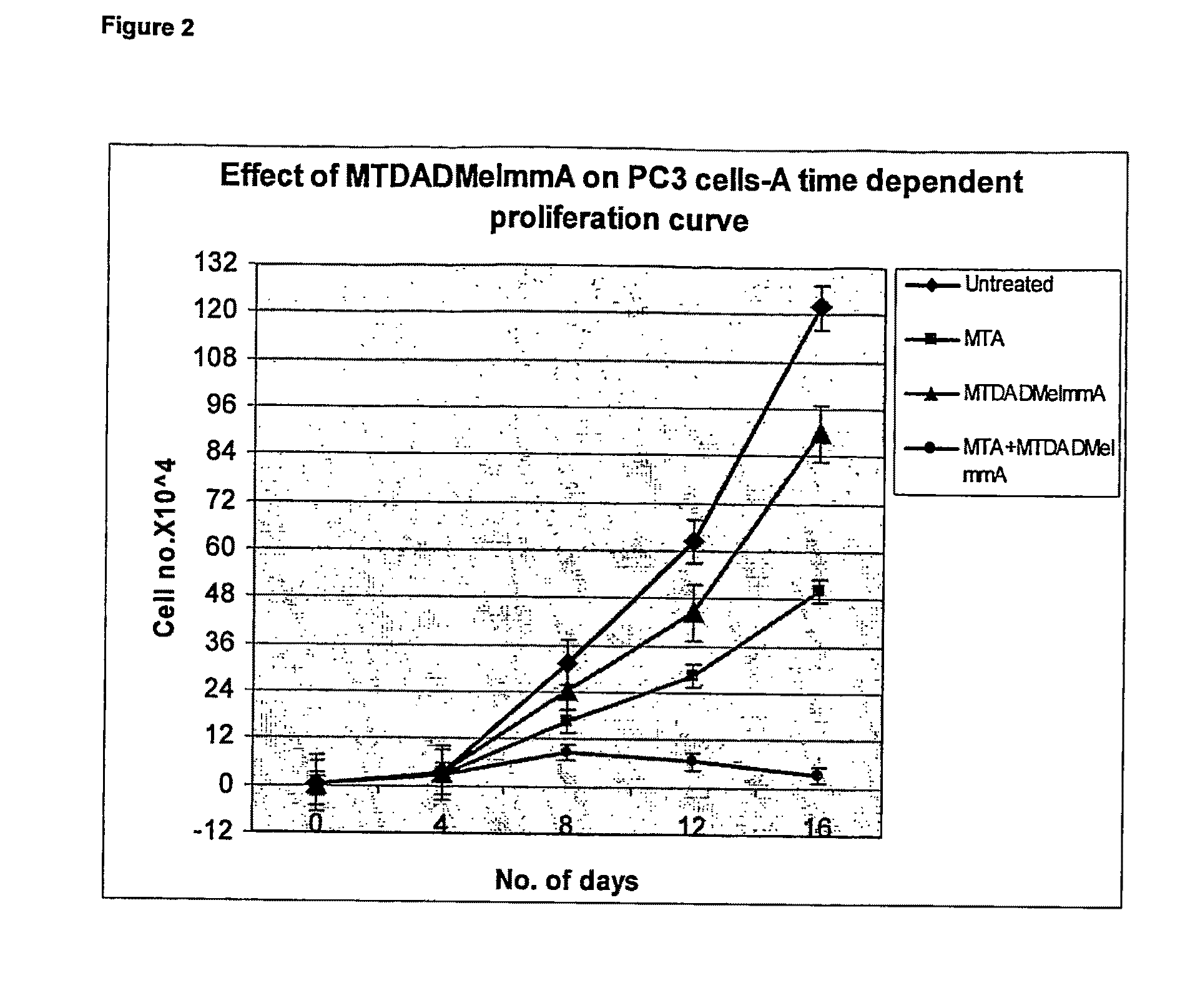
Methods of Treating Diseases Using Inhibitors of Nucleoside Phosphorylases and Nucleosidases
The invention relates to treating a disease or condition in which it is desirable to inhibit 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) and / or 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase (MTAN). The invention particularly relates to the co-administration of 5′-methylthioadenosine (MTA), or a prodrug of MTA, with one or more MTAP / MTAN inhibitors. Included among the diseases treatable are prostate cancer and head and neck cancer.
Owner:IND RES LTD +1
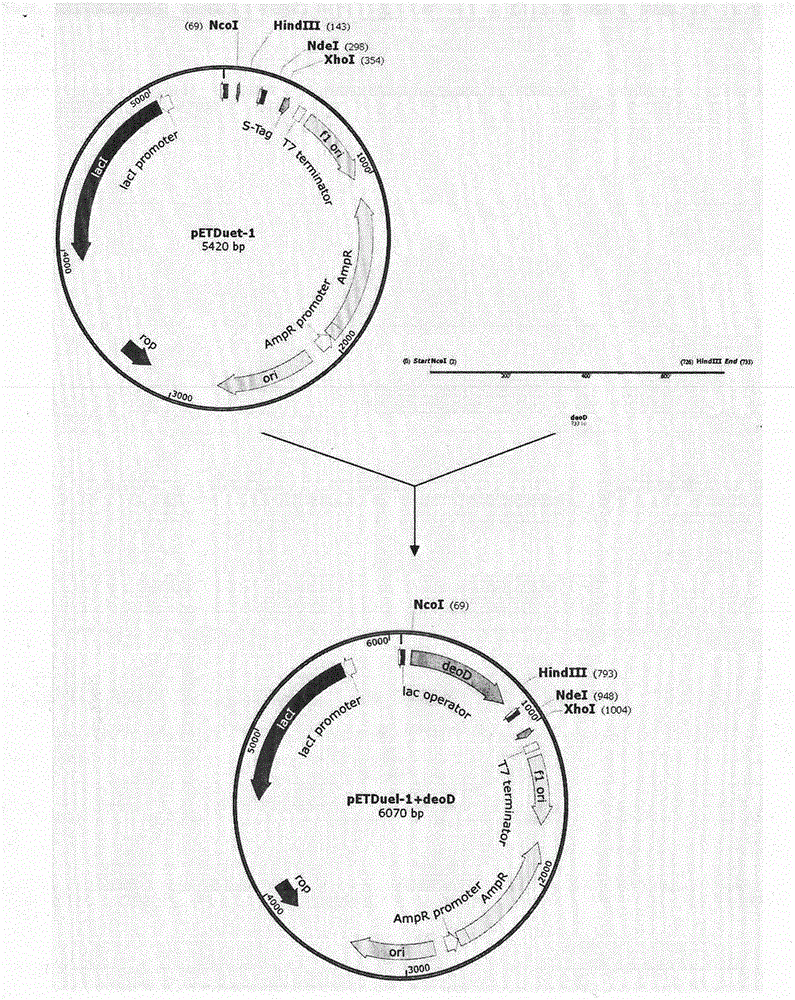
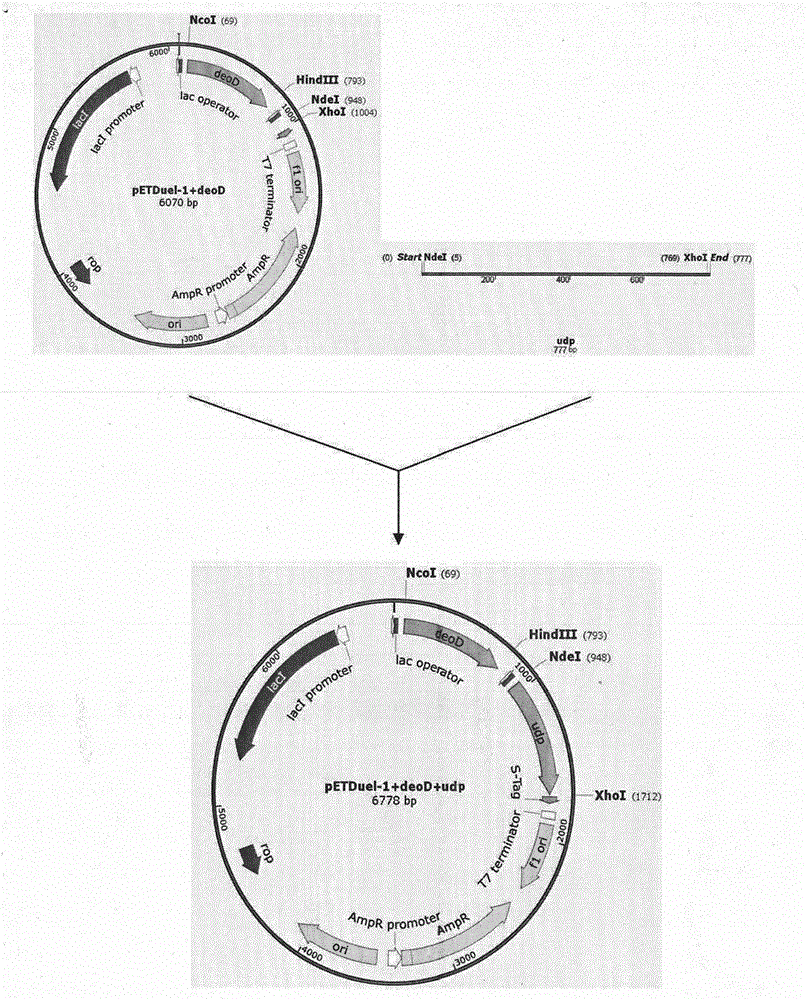
Pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase gene and application thereof
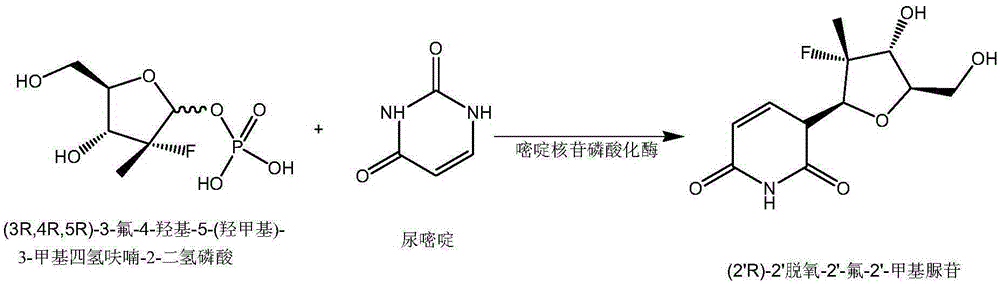
The invention relates to the fields of biotechnology and biological medicine, in particular to a pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase gene and the application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase coded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. A genetically engineered bacterium containing the gene is obtained by transferring the gene into escherichia coli. By culturing the genetically engineered bacterium and optimizing the fermentation technology, large-scale production of recombined pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase is achieved, and the recombined pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase can be used for catalyzed synthesis of Sofosbuvir midbody (2'R)-2'-deoxygenation-2'-fluorine-2'-methyl uridine and production of other nucleoside bulk pharmaceutical chemicals and medical intermediates.
Owner:JIANGSU ALPHA PHARM CO LTD
Mutant purine nucleoside phosphorylase proteins and cellular delivery thereof
A host cell stably transformed or transfected by a vector including a DNA sequence encoding for mutant purine nucleoside cleavage enzymes is provided. The transformed or transfected host cell can be used in combination with a purine substrate to treat tumor cells and / or virally infected cells. A nucleotide sequence encoding mutant E. coli derived purine nucleoside phosphorylase proteins which can be used in conjunction with an appropriate substrate to produce toxins which impair abnormal cell growth is also provided. A method is detailed for the delivery of toxin by generation within target cells or by administration and delivery to the cells from without. Novel purine nucleosides are detailed that yield a cytotoxic purine upon enzymatic cleavage. A synthetic process for nucleosides is also detailed.
Owner:CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COIMMERCIALIZATION +2
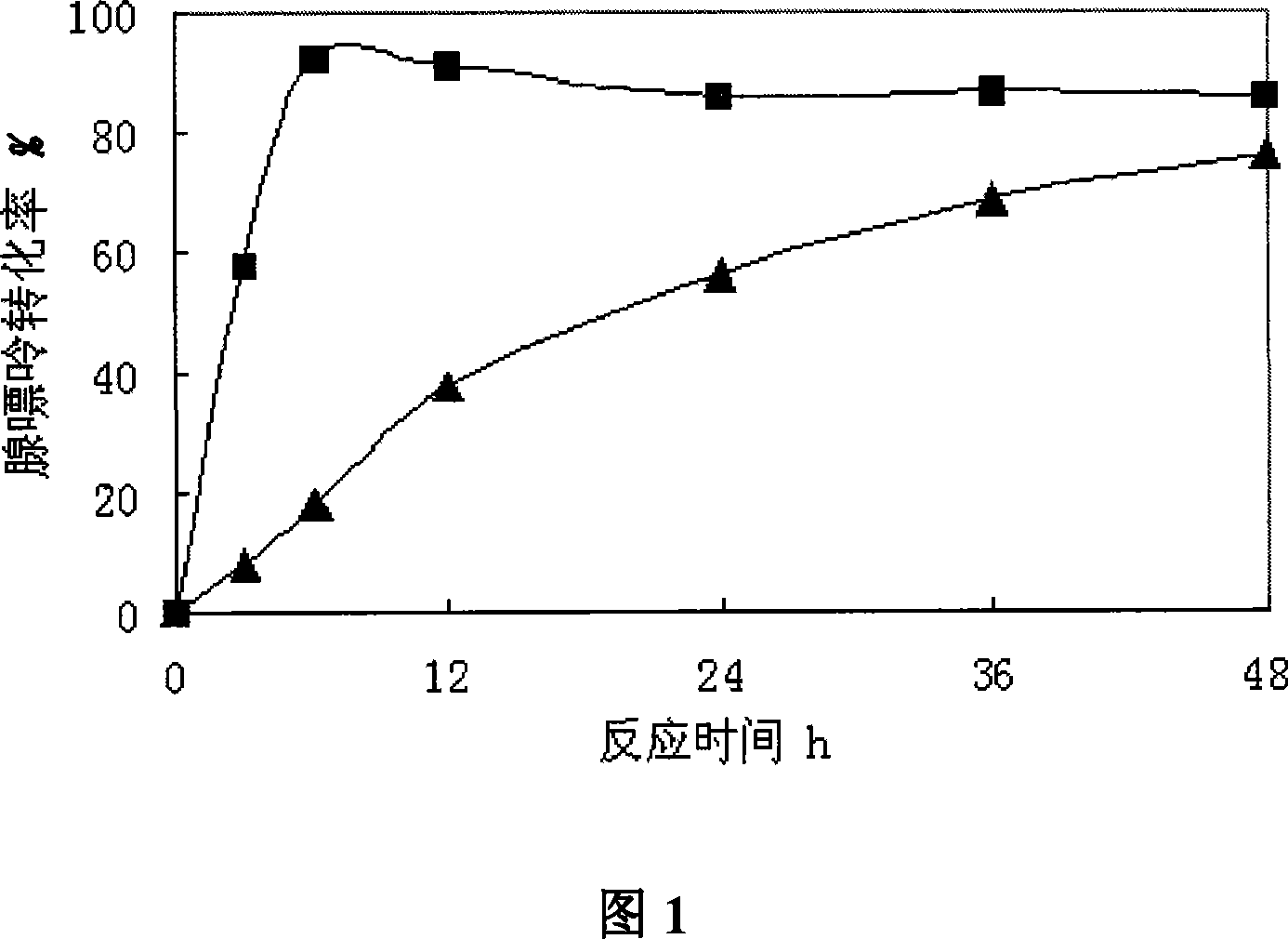
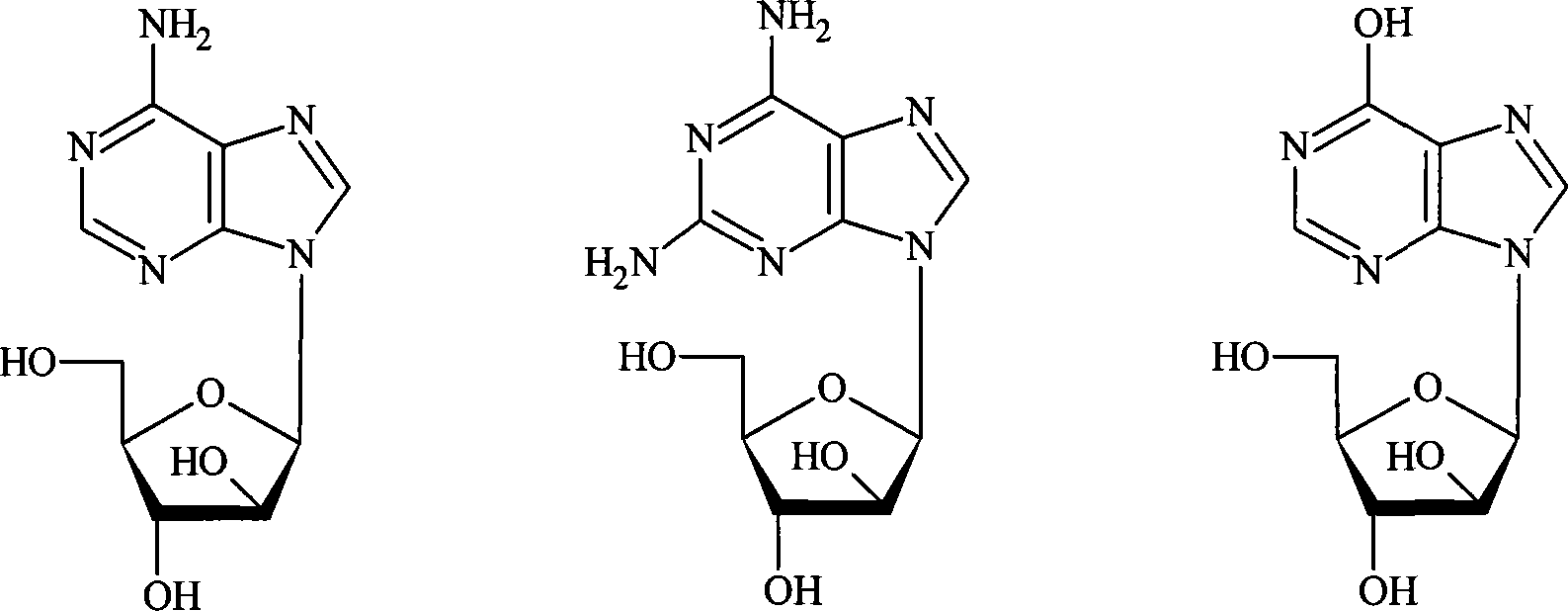
Method for converting escherichia coli to produce 2'-deoxyadenosine
ActiveCN104178541AEasy to separate and purifyImprove conversion rateSugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses a method for converting escherichia coli to produce 2'-deoxyadenosine. Escherichia coli thallus with high nucleoside phosphorylase activity is directly adopted as an enzyme source to mix with deoxythymidine which is taken as a conversion reaction substrate as well as adenine to carry out conversion reaction to synthesize 2'-deoxyadenosine. The method has the advantages of simple process, high conversion ratio, low production cost and gentle reaction conditions; moreover, the by-products are fewer, green and pollution-free, and the products are easy to separate and purify. A conversion ratio of adenine is over 72.5%. Besides, the 2'-deoxyadenosine is separated and purified by adopting a method of crystallization and recrystallization, so that the purity of the 2'-deoxyadenosine is over 99%.
Owner:西藏天虹科技股份有限责任公司
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103468656AImprove thermal stabilityLong storage timeBacteriaTransferasesPurine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitorNucleotide
The invention relates to purine nucleoside phosphorylase and a preparation method of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase, in particular to a mutational pseudoalteromonas-genus purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Compared with a wild-type amino acid sequence, the amino acid sequence of the mutational purine nucleoside phosphorylase is characterized in that Asp at the 98th bit is mutated into Tyr. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase. The purine nucleoside phosphorylase and the preparation method of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase have the advantages of being high in yield and good in heat stability. The invention further discloses polynucleotide for encoding the amino acid sequence of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase, a carrier containing the polynucleotide and a host cell containing the polynucleotide.
Owner:AILEX TECH GRP CO LTD +1
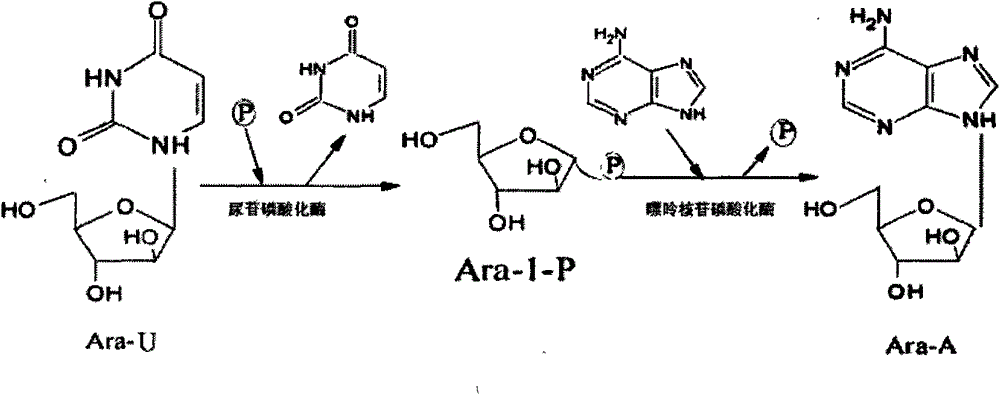
Bacterial with high-yield of nucleoside phosphorylase and method for synthesizing arabinose nucleoside
InactiveCN101113420AIncrease vitalityImprove conversion rateBacteriaFermentationFlucytosineNucleoside phosphorylase
A compound method of high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase strains and arabinose nucleoside pertains to biochemical engineering field, in particular to the high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase strains and a method for compounding arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains by an enzyme method. The invention aims at solving a technical problem for providing the strains of the high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase and strains of uridine phosphorylase and the method for producing the arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains. The invention discloses enterobacter aerogenes with a preservation number of CGMCC No.2035 and the method for producing the arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains, and the invention comprises steps that (1) the enterobacter aerogenes DWOQ-58 of the invention is cultured and collected, and (2) the enterobacter aerogenes DWOQ-58 is contacted with arabinose donor and receptors of purine base. The strains of the invention are rich in vigor and resists 5-flucytosine with an average conversion rate of more than 80 percent in general and the reaction time of the invention is shortened to less than 12 hours.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEIPING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation method of vidarabine monophosphate
InactiveCN104372050ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleoside phosphorylaseGenetically engineered
The invention discloses a preparation method of vidarabine monophosphate. The method first prepares genetically engineered bacterium with co-expression of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase, and then uses the genetically engineered bacterium to prepare vidarabine monophosphate. The method is characterized in that coexpression of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase is realized in genetically engineered bacterium by using a molecular cloning method, so as to obtain vidarabine biotransformation bacteria with high enzyme specific activity; the thalli obtained by the invention is used to produce vidarabine; and the reaction substrate concentration can be increased to more than 100 mM, the reaction conversion rate is more than 90%, the dosage of reaction thalli is less than 0.3% (thalli wet weight / reaction volume ml), and reaction time is shortened to 6 h.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIANQIANG PHARMA
Method for preparing purine nucleoside phosphorylase by solid state fermentation
ActiveCN101638641ADense growthHigh activityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesNucleoside phosphorylaseHigh activity
The invention provides a method for preparing purine nucleoside phosphorylase by solid state fermentation of bacillus subtilis, wherein, the mould-free corn cobs after sterilization with the particlediameter of 20-40 meshes and the water content of 30% are adopted as the solid matrix of the solid state fermentation culture medium. The inventor of the invention overcomes the prejudice that 'purinenucleoside phosphorylase products are more easily separated from liquid state fermentation of bacillus subtilis, compared with solid state fermentation of bacillus subtilis' which is held by the prior art; by utilizing the solid state fermentation method of the invention, efficient separation of purine nucleoside phosphorylase products from bacillus subtilis can be realized. The method of the invention has the advantages of less energy consumption, less time consumption and higher activity of the obtained purine nucleoside phosphorylase products.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
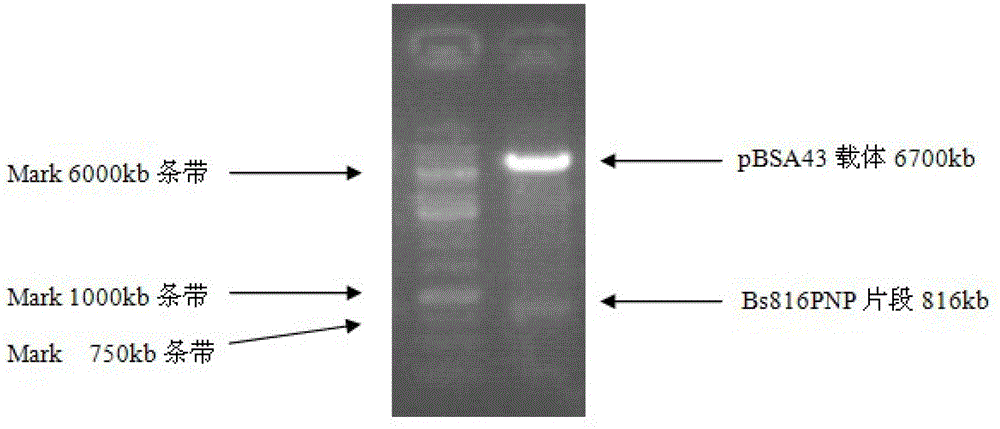
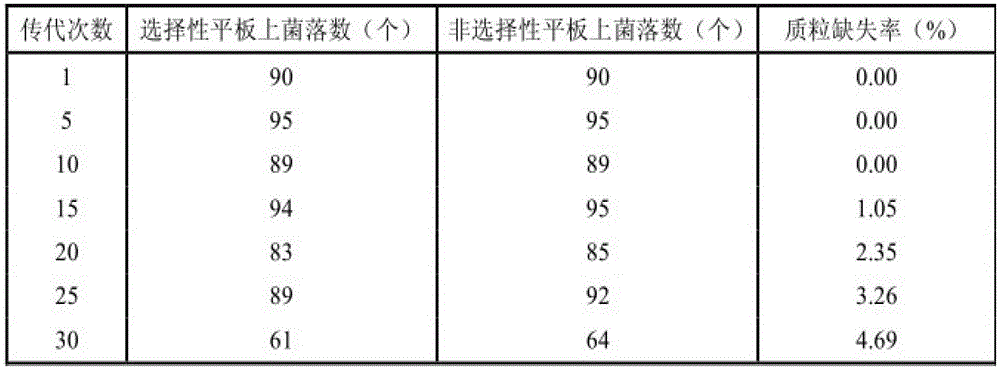
Production process for producing antiviral medicament ribavirin through bacillus amyloliquefaciens precursor addition fermentation method
InactiveCN103146785AIncrease vitalityPromote secretionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationBiotechnology
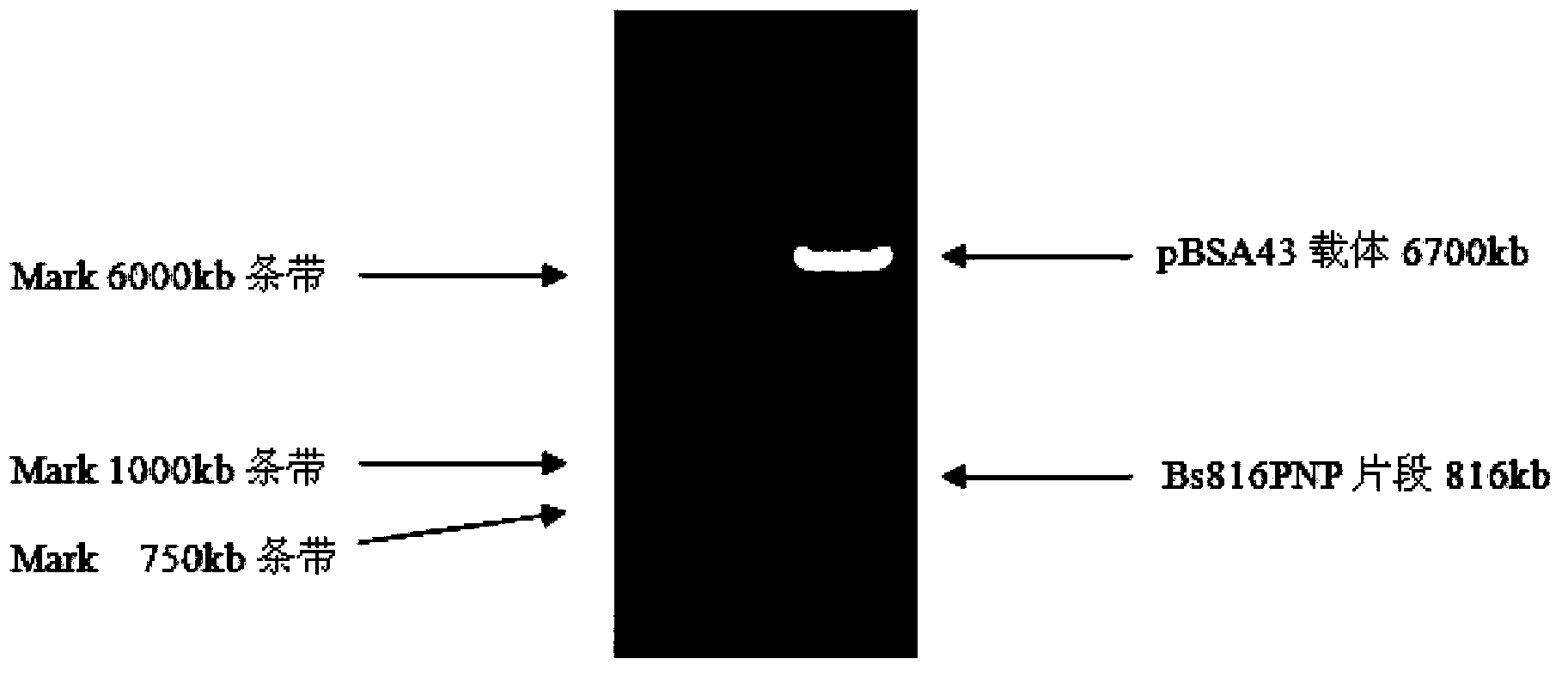
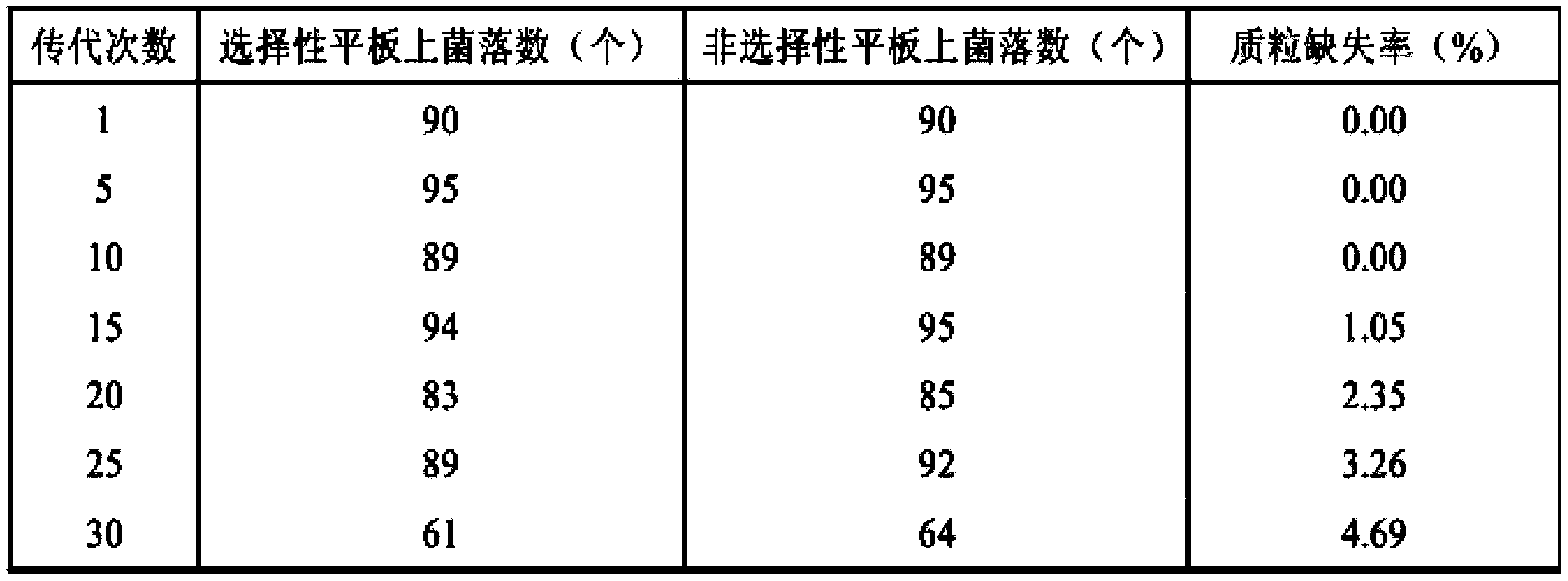
The invention discloses a production process for producing antiviral medicament ribavirin through a bacillus amyloliquefaciens precursor TCA addition (1, 2, 4-triazole-3-carboxyformamide) fermentation method. The process comprises the following steps: establishing recombinant plasmid pBSA43-Bs816PNP which can be stably replicated in bacillus amyloliquefaciens cells and efficiently secretes and expresses purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase); converting the plasmid into vernine for producing the bacillus amyloliquefaciens TA208, thereby obtaining a genetically engineered bacterium RBVM (pBSA43-Bs816PNP) with the two characteristics of high-efficiency production and high-efficiency expression of PNPase. By adoption of the genetically engineered bacterium, by taking glucose, yeast extract, bean concentrate, corn steep liquor, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate and running water as raw materials, the precursor TCA is added for fermenting, and high-concentration ribavirin can be detected in the culture medium after the precursor is added within several hours. The process has the advantages of short fermentation period, high yield, high glucoside conversion rate, easy and convenient process, low cost, low energy consumption, slight pollution and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Exiguobacterium sp. MY02 strain pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase gene and its preparation method
InactiveCN1800409AHigh transferase activitySugar derivativesFermentationEscherichia coliPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a structure gene of pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase which is characterized in that its coder is Exiguobacterium sp.MY02. When preparing for the gene, it first uses PCR method to sieve the gene group DNA base of the Exiguobacterium sp.MY02 strain and measures the sequence to ascertain the gene sequence of the pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase; it recombines the gene, purifies the recombining enzyme and measuring the activity in bacillus coli so that the result expresses that the pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase can coding generate recombining pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase with phosphorylation activity and higher transfer enzyme activity.
Owner:MIANYANG TEACHERS COLLEGE
Selective process for producing an anomer of a 1-phosphorylated saccharide derivative and process for producing a nucleoside
InactiveUS20060094869A1Improve conversion rateLow costEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesIsomerizationPhosphorylation
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
CO2 content determination method and CO2 diagnosis kit
InactiveCN1763221AFree from pollutionThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseCO2 content
The present invention relates to one CO2 (bicarbonate) content determining method and CO2 (bicarbonate) diagnosis kit, and belongs to the field of medical detection technology. The kit includes buffering solution, phosphoenolpyruvic acid, inosine, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, nucleoside phosphorylase, xanthine oxidase, peroxidase, urease and stabilizer. Through mixing the sample and reagent in certain volume ratio to generate enzyme coupling reaction, detecting the main wavelength absorbance variation of the reaction product under biochemical analyzer and calculation, CO2 (bicarbonate) content is obtained. The present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, high precision and no contamination of inner and outer matters.
Owner:王尔中
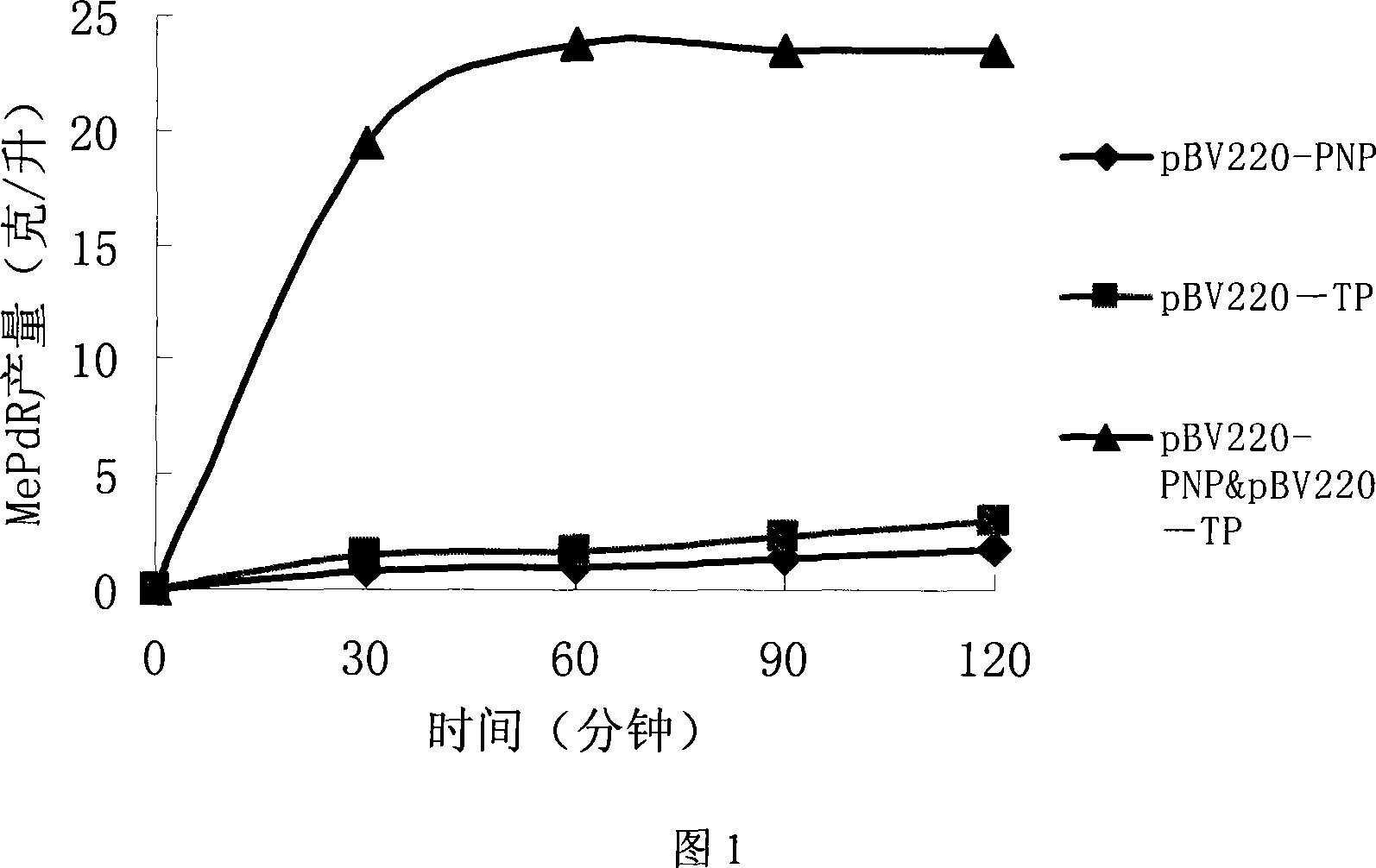
Process of synthesizing 6-methylpurine-2'-deoxyncleoside with gene engineering bacterium
InactiveCN101067145AShort cycleLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase
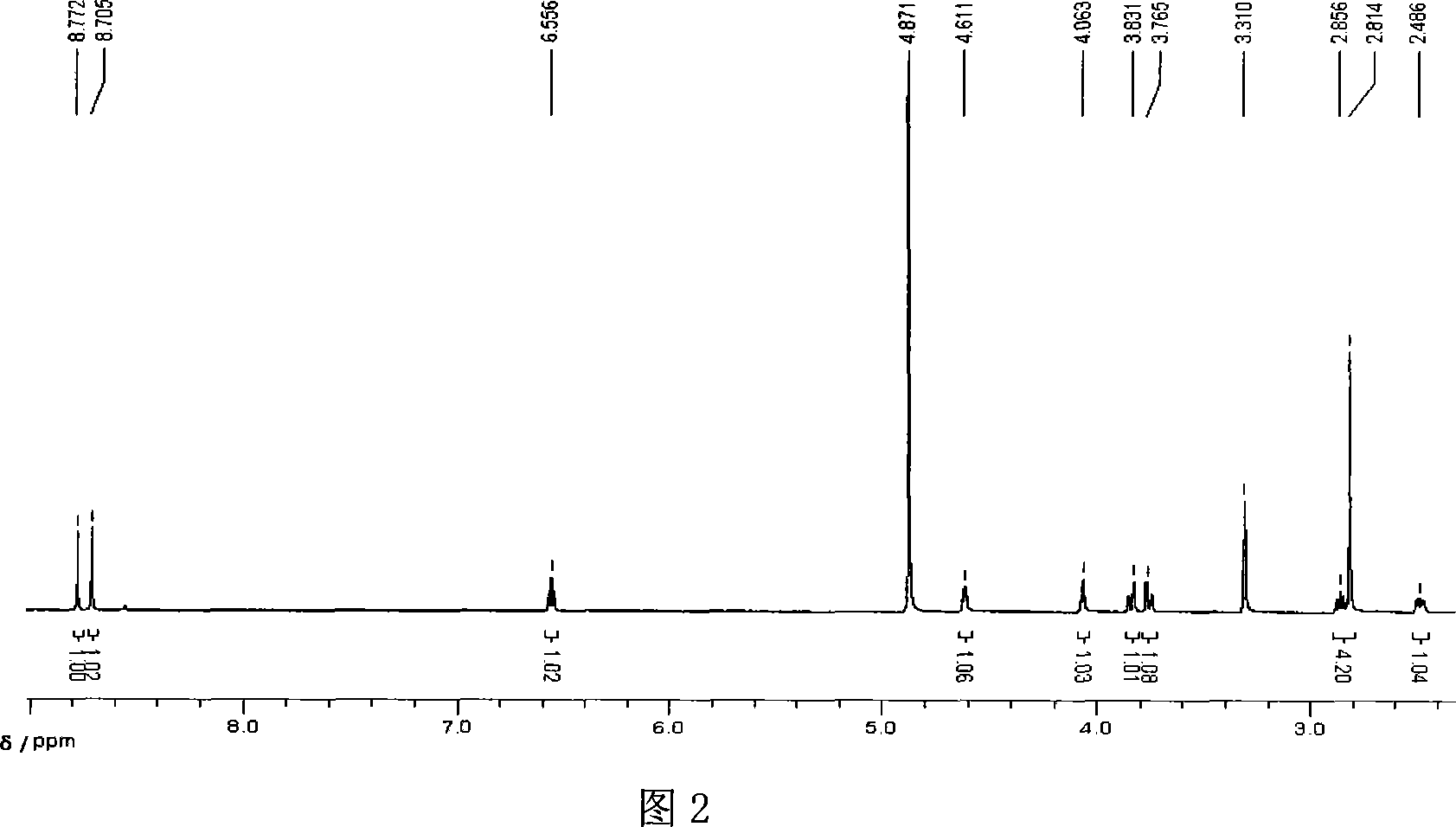
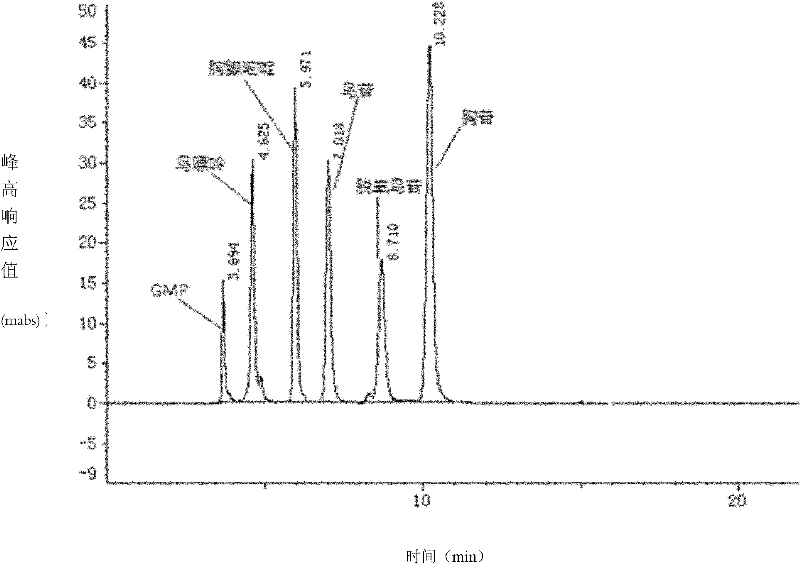
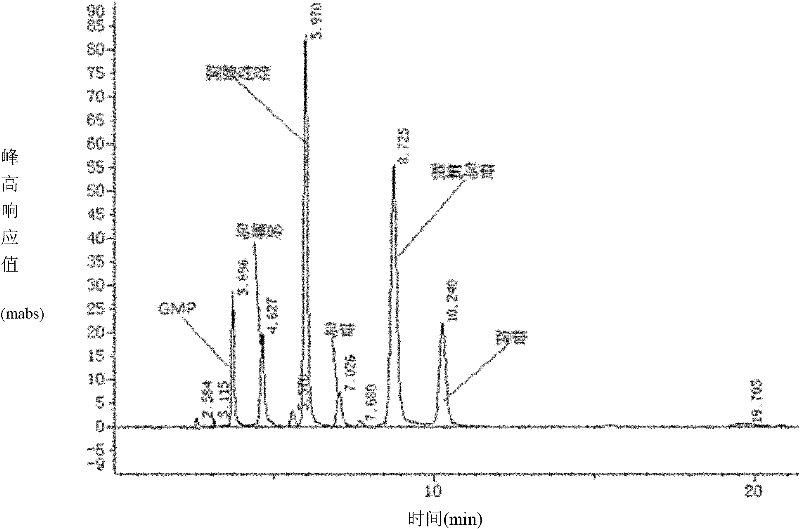
The present invention belongs to the field of biomedicine preparing technology, and is especially the process of constructing gene engineering bacterium by means of DNA recombining technology and synthesizing 6-methylpurine-2'-deoxyriboside (MePdR) with the gene engineering bacterium. The process includes the following steps: 1. constructing purine nucleoside phosphorylase and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase expressing vector, and transforming to colibacillus to obtain gene engineering bacterium with high efficiency expression of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase; 2. catalyzing the reaction between pyrimidine deoxyriboside and 6-methylpurine with the purine nucleoside phosphorylase and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase to synthesize MePdR; and 3. separating and purifying MePdR. The catalytic synthesis process of MePdR has the features of simplicity, high efficiency, ets, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Synthesis method of 2'-deoxyguanosine by adopting nucleoside phosphorylase of brevibacterium acetylium
InactiveCN102174618AHigh yieldLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentation3-deoxyribosePhosphate
The invention provides a synthesis method of 2'-deoxyguanosine by adopting nucleoside phosphorylase of brevibacterium acetylium, which comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing the brevibacterium acetylium QD96-CGMCCNo.0472; and (2) adding thalli obtained in the step (1) into a substrate solution or reaction, wherein deoxyribose receptors, deoxyribose donors and phosphate buffer solution are contained in the substrate solution, and collecting the 2'-deoxyguanosine from the reaction product. When the enzymes of the brevibacterium acetylium QD96 are used for synthesizing the 2'-deoxyguanosine, the cost can be reduced, and the 2'-deoxyguanosine can be effectively obtained; moreover, the conversion rate can reach more than 60%.
Owner:NANTONG QIUZHIYOU BIOSCI & BIOTECH +1
Production process for producing antiviral medicament ribavirin through bacillus amyloliquefaciens precursor addition fermentation method
InactiveCN103146785BIncrease vitalityPromote secretionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention discloses a production process for producing antiviral medicament ribavirin through a bacillus amyloliquefaciens precursor TCA addition (1, 2, 4-triazole-3-carboxyformamide) fermentation method. The process comprises the following steps: establishing recombinant plasmid pBSA43-Bs816PNP which can be stably replicated in bacillus amyloliquefaciens cells and efficiently secretes and expresses purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase); converting the plasmid into vernine for producing the bacillus amyloliquefaciens TA208, thereby obtaining a genetically engineered bacterium RBVM (pBSA43-Bs816PNP) with the two characteristics of high-efficiency production and high-efficiency expression of PNPase. By adoption of the genetically engineered bacterium, by taking glucose, yeast extract, bean concentrate, corn steep liquor, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate and running water as raw materials, the precursor TCA is added for fermenting, and high-concentration ribavirin can be detected in the culture medium after the precursor is added within several hours. The process has the advantages of short fermentation period, high yield, high glucoside conversion rate, easy and convenient process, low cost, low energy consumption, slight pollution and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enzymatic production of cytosinic nucleoside analogues
InactiveUS20160312261A1Sugar derivativesFermentationPyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylaseCytosine nucleoside
The invention relates to the enzymatic production of cytosinic nucleoside analogues. In particular it relates to a new synthesis process of cytosine nucleoside analogues by using nucleoside phosphorylase enzymes, particularly Pyrimidin Nucleoside Phosphorylases (PyNPs) or mixtures of Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylases (PNPs) and PyNPs.
Owner:PLASMIA BIOTECH
Acyclic amine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and hydrolases
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase as enzymatic activator of nucleoside prodrugs
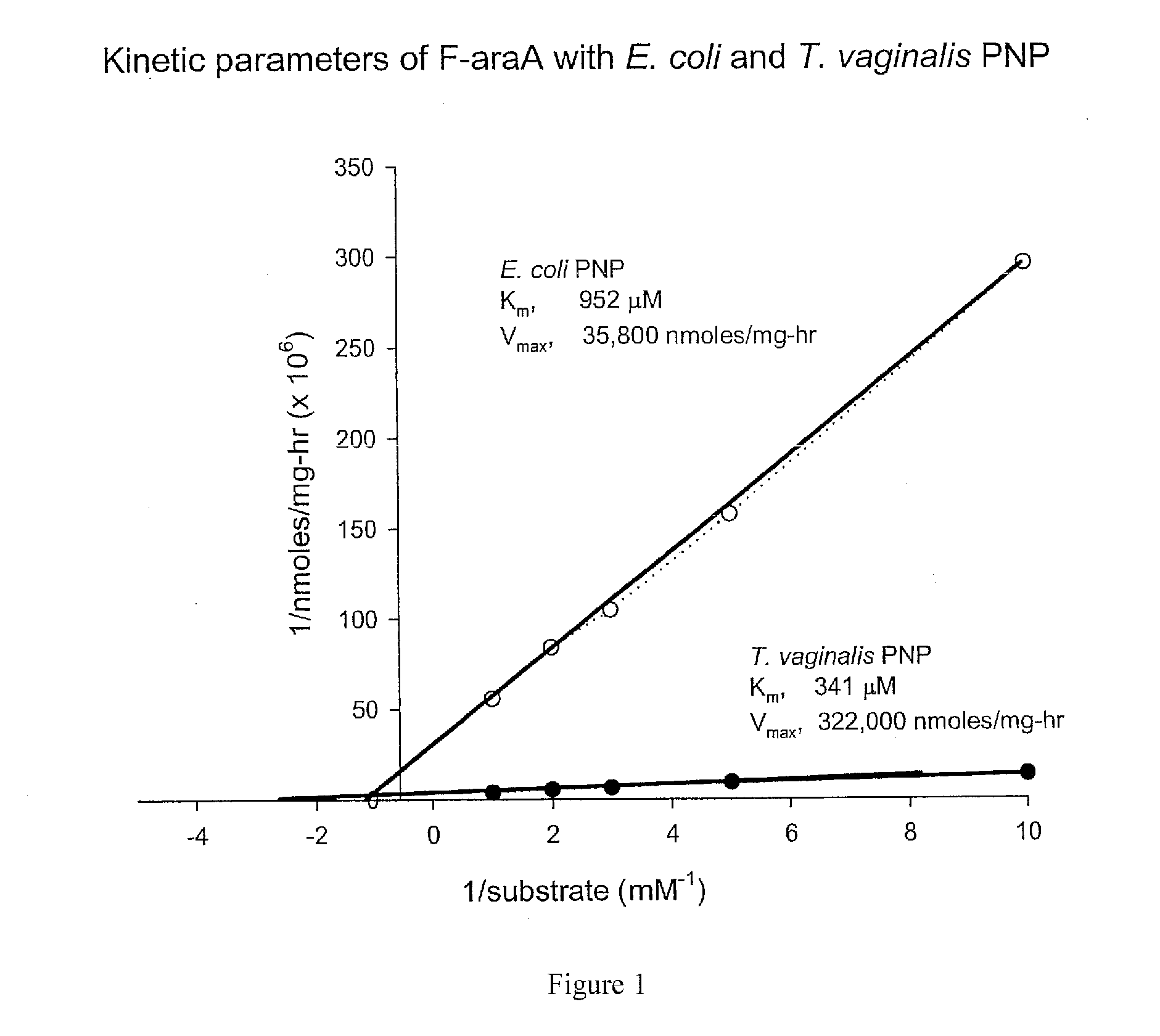
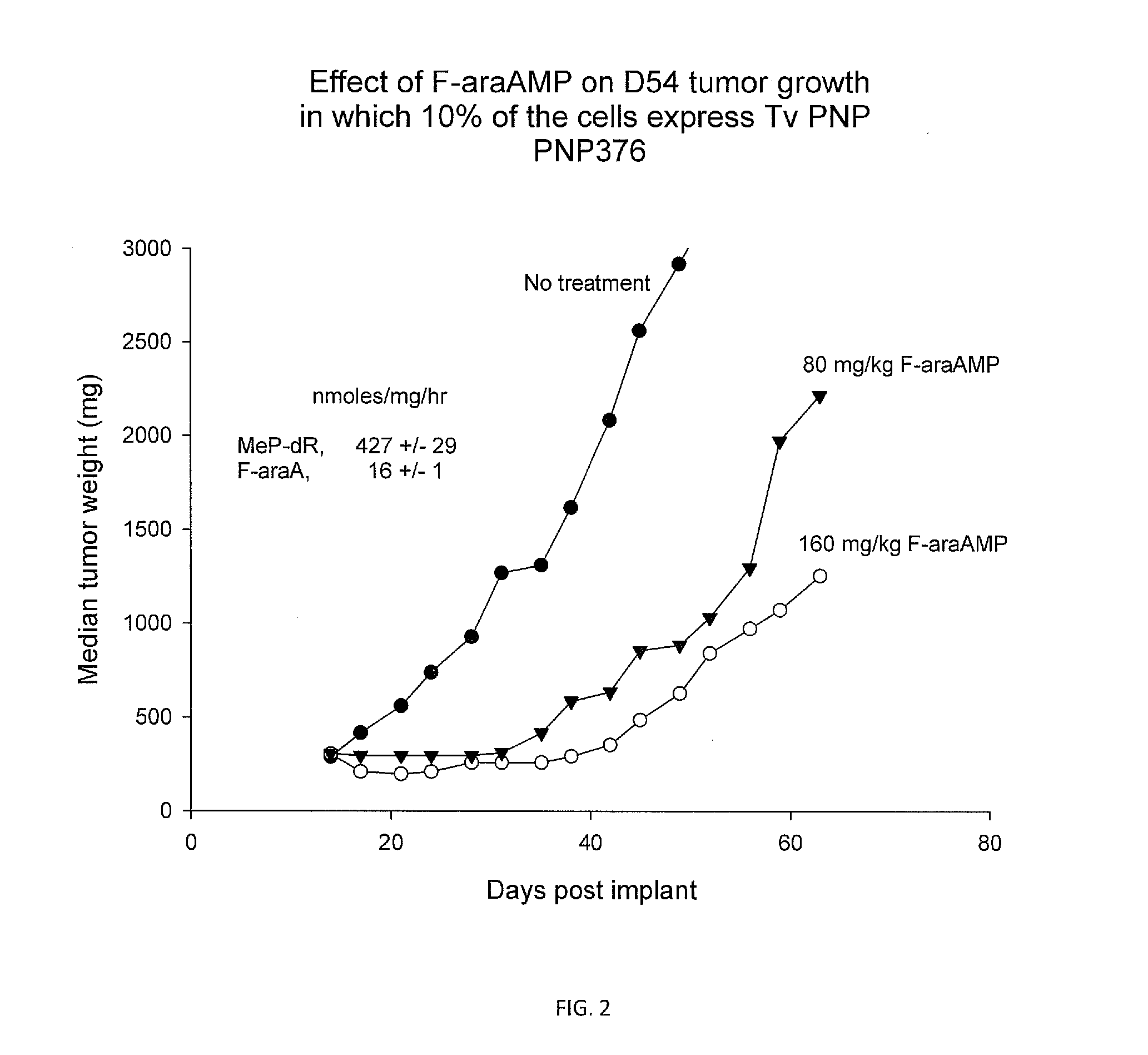
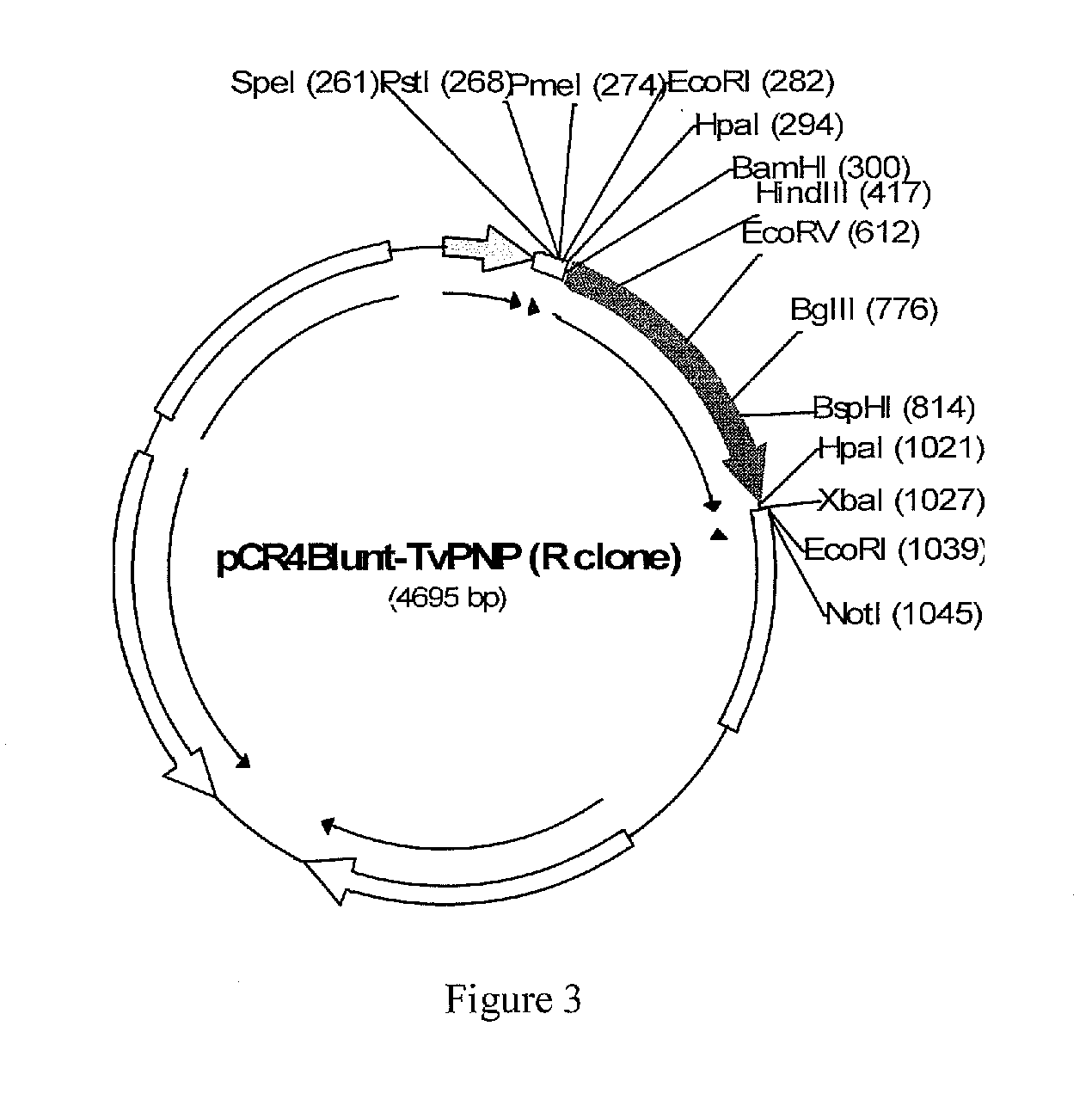
A process for inhibiting a mammalian cancerous cell or virally infected cell includes providing a Trichomonas vaginalis purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme or a tail mutant purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme in proximity to the mammalian cancerous cell or the virally infected cell and exposing the enzyme to a purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme cleavable substrate to yield a cytotoxic purine analog. The process includes introducing to the cell a vector containing the phosphorylase enzyme, or a DNA sequence coding for the same and delivering to the cell an effective amount of the substrate such as 9-(β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-2-fluoroadenine (F-araA).
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/da2db1d4-0a4a-4bcd-a68e-7ffb84ea6111/US07098334-20060829-D00001.png)
![4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/da2db1d4-0a4a-4bcd-a68e-7ffb84ea6111/US07098334-20060829-D00002.png)
![4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 4-amino-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/da2db1d4-0a4a-4bcd-a68e-7ffb84ea6111/US07098334-20060829-D00003.png)
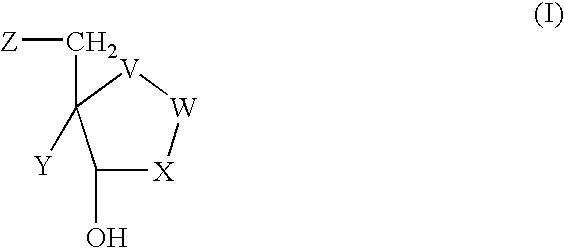
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00001.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00002.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-C00001.png)
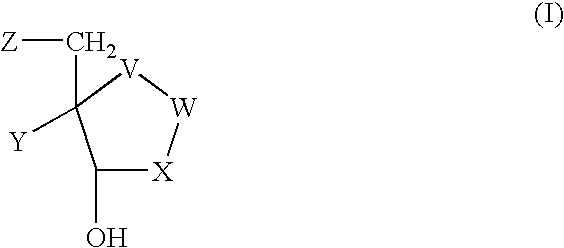
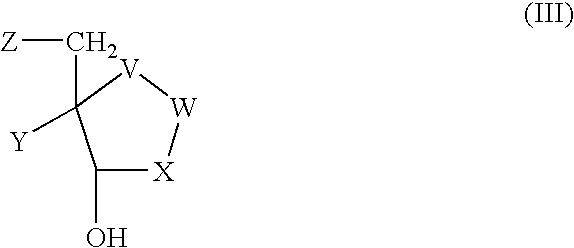
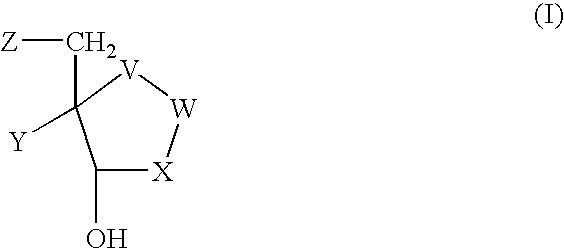
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases Process for preparing pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fe32c66b-1725-4a1f-89c2-4927e09490a3/US07655795-20100202-C00003.png)