Methods for the treatment of breast cancer
a breast cancer and treatment method technology, applied in the field of breast cancer treatment methods, can solve the problems of neoplastic disease states, serious and often life-threatening conditions, and limited benefit of additional conventional treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1a
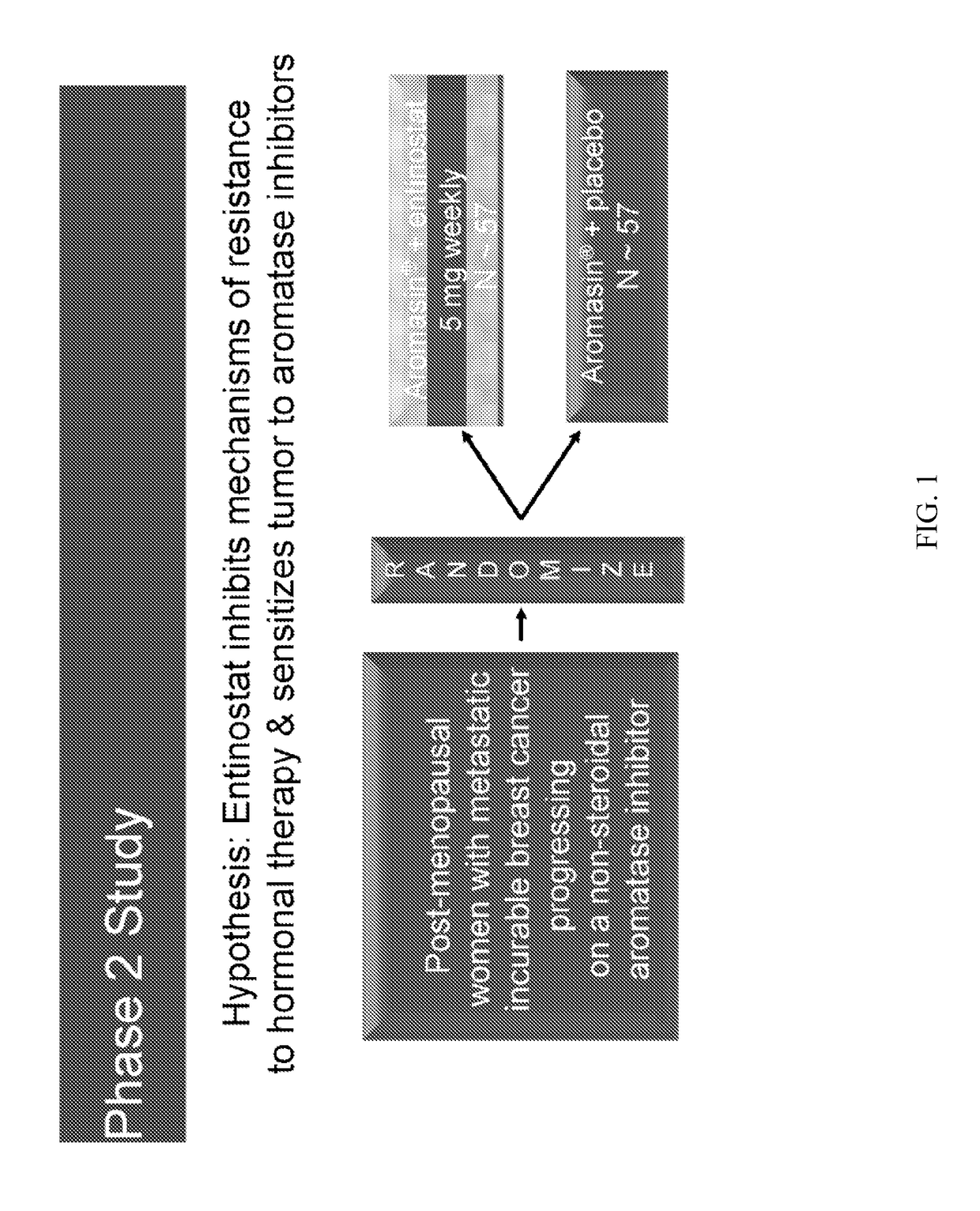
[0155]A Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Study of Exemestane With and Without Entinostat in Postmenopausal Women With Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer, Progressing on Treatment With a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor
[0156]The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of entinostat in combination with exemestane in the treatment of advanced breast cancer.
[0157]Primary Outcome Measures are to compare the efficacy of exemestane alone with exemestane plus entinostat, as determined by the duration of progression free survival (PFS) measured from the date of randomization.
[0158]Secondary Outcome Measures are to compare objective response rate (ORR) and clinical benefit rate (CBR), and to evaluate the safety and tolerability of entinostat in combination with exemestane as measured by adverse events and laboratory safety parameters.
[0159]Study Design
[0160]
ArmAssigned Interventions1: ExperimentalDrug: entinostatexemestane (Aromasi...
example 1b
[0197]In a 23-month patient follow up of the study described above in Example 1a, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of exemestane with and without entinostat in 130 patients with locally recurrent or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, the median overall survival of exemestane plus entinostat patients reached 26.9 months versus 19.8 months for exemestane plus placebo. This represents a 42% reduction (p=0.04) in the risk of dying for these patients. Earlier data from this study demonstrated a near doubling in the progression-free survival (PFS) (4.3 vs. 2.3 months) with exemestane plus entinostat and the identification of a subset of these patients whose median PFS reached 8.5 months.
[0198]The conclusion is that after two years of follow up the patients treated with entinostat and exemestane benefited from an additional seven months of overall survival. This study illustrates not only a progression-free survival advantage (4.3...
example 1c
Confirmatory Phase 2 Study
[0204]The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected in a subset of patients pre- and post-dose in cycle 1 for evaluation of protein lysine acetylation as a biomarker of entinostat activity (FIG. 11).
Patients and Methods
[0205]Study Design:
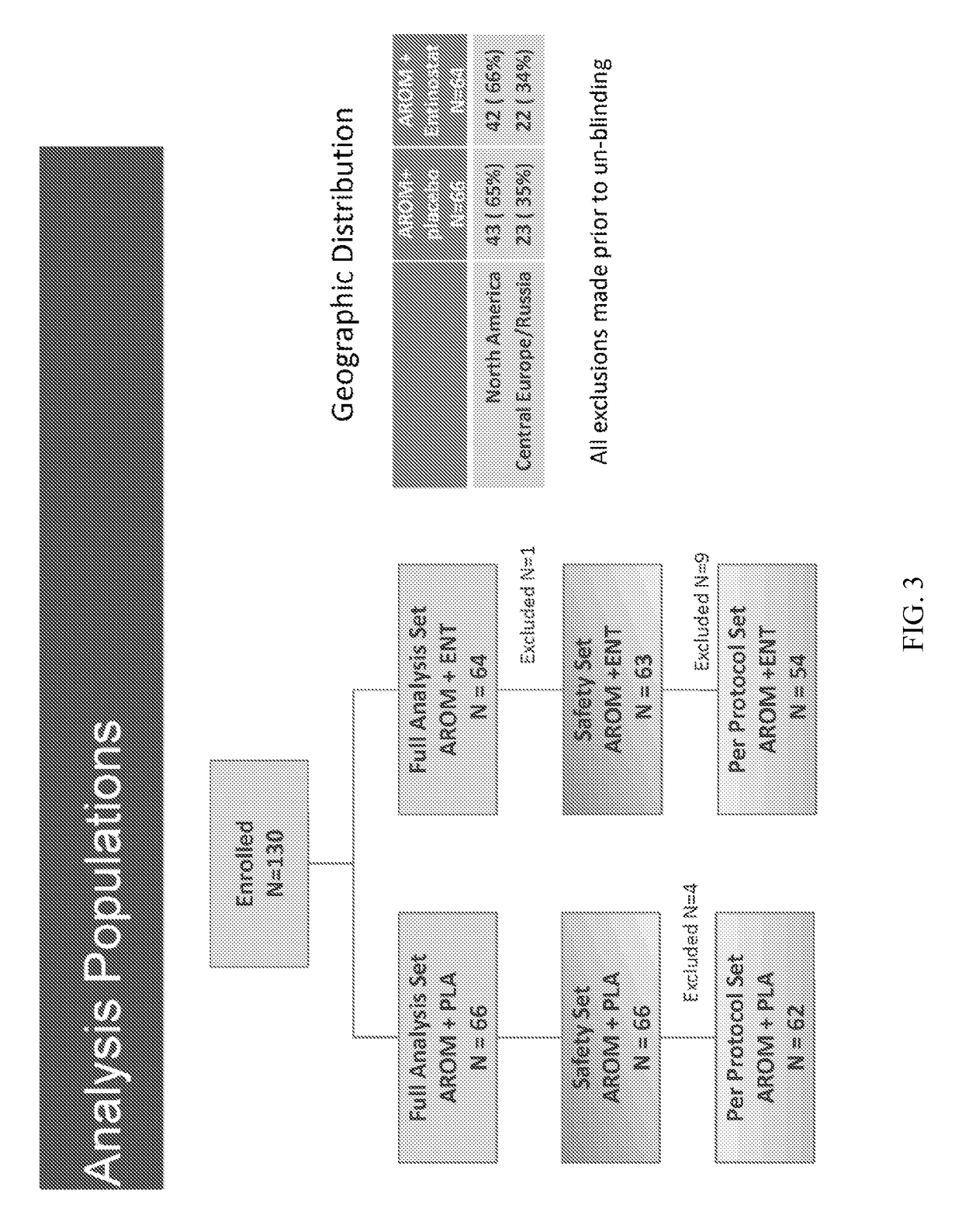
[0206]This was a Phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of exemestane±entinostat in patients with locally advanced or metastatic BC that had progressed on a NSAI (FIG. 12). One hundred thirty (130) patients were enrolled between June 2008 and July 2010 at 38 sites in North America, Central Europe, and Russia. All patients provided written informed consent. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio using a blocked randomization scheme to exemestane plus entinostat (EE; n=64) or exemestane plus placebo (EP; n=66). Randomization was stratified by 1) prior NSAI treatment setting (adjuvant / metastatic); 2) metastases in bone only (yes / no); and 3) geo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com