Tie
a technology of tie rods and rails, applied in the field of tie rods, can solve the problems of reducing comfort, affecting the stability of the rails, and needing a lot of maintenance, so as to improve the stability of the side of the railway track, increase the effective friction of side displacement, and improve the effect of side stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will in the following be described with reference to drawings, wherein
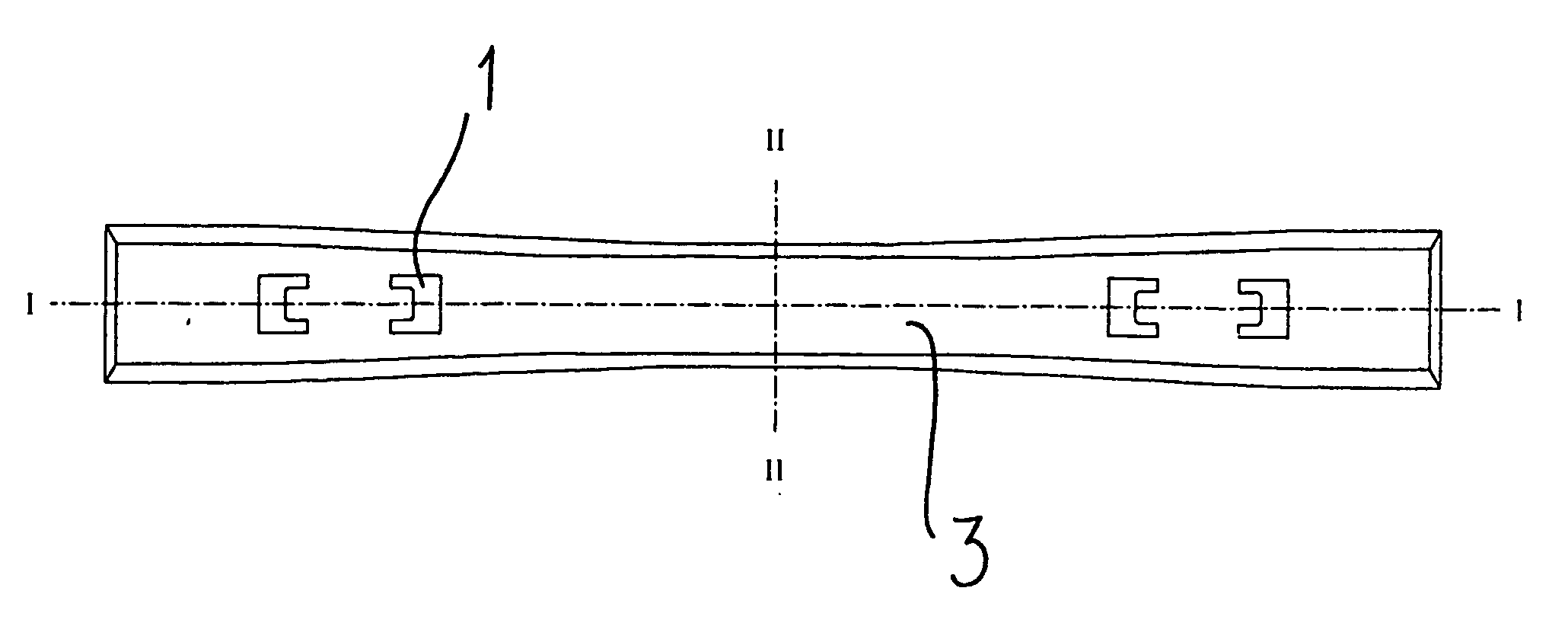
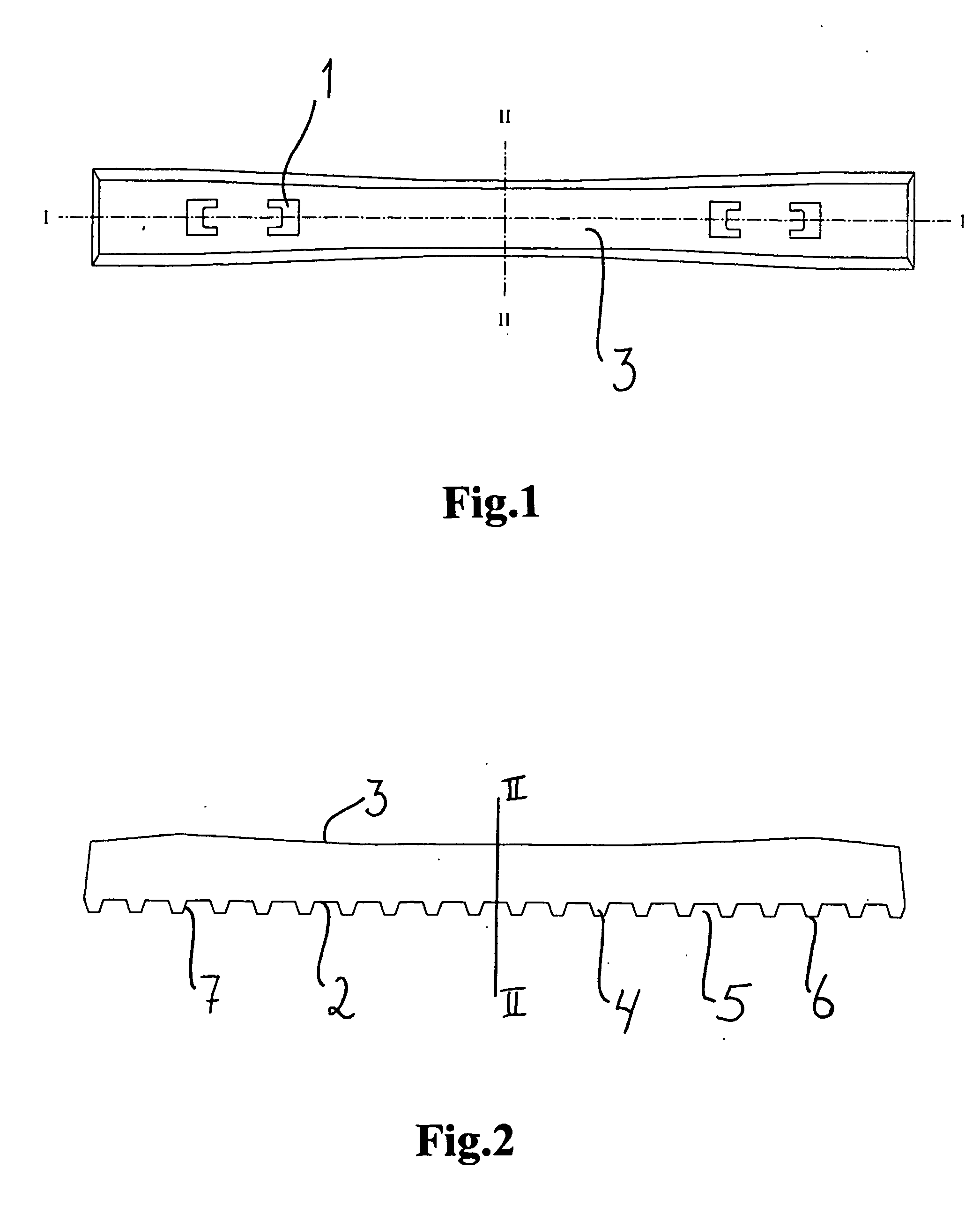
[0028] FIG. 1 is a view from above of a tie according to the present invention,
[0029] FIG. 2 is a longitudinal section of a tie, along line I-I in FIG. 1,
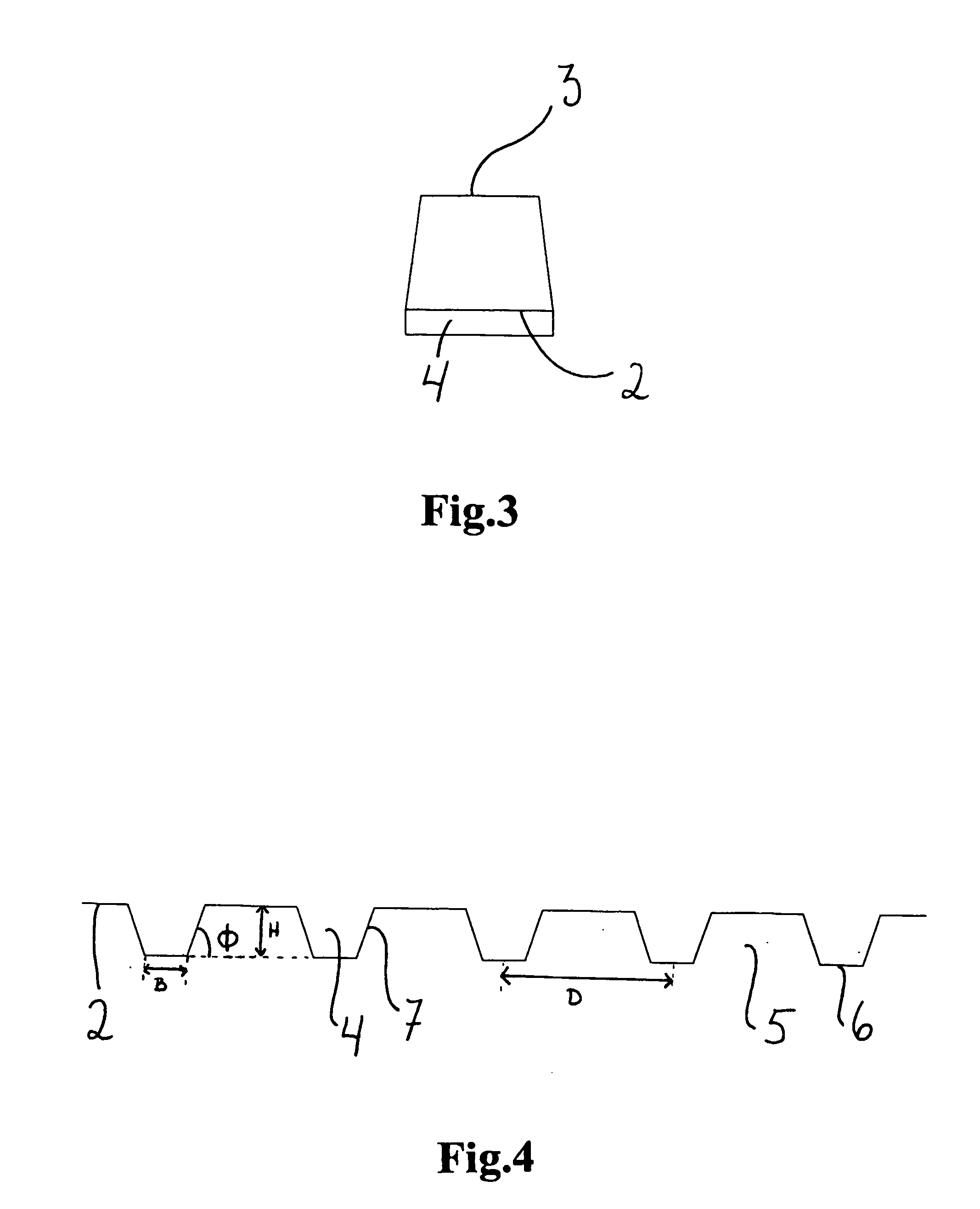
[0030] FIG. 3 is a cross section of a tie, along line II-II in FIG. 1 and 2, and
[0031] FIG. 4 is an enlarged section of the underside of a tie according to the present invention.
[0032] As shown in FIG. 1, a tie according to the present invention is mainly embodied as a traditional pot sleeper tie, with the exception of the underside. The upper side is provided with means 1 for fastening rails to the tie. The central part of the tie is a bit narrower than the end parts. The cross section of the tie (FIG. 3) has the form of a trapeze, wherein the face 2 turning down towards the foundation, is larger than the face 3 turning up towards the rails. With the exception of the underside, the tie may have any shape, as this is not part of the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com