Treatment for CD5+ B cell lymphoma
a lymphoma and cd5 technology, applied in the field of treatment of cd5 + b cell lymphoma, can solve the problems of insufficient antibody production, direct tissue infiltration of cll, and inability to produce antibodies, and achieve the effect of increasing the expression of at least one cell surface molecul
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effect of IRM1 on Costimulatory Molecule Expression by CLL Cells
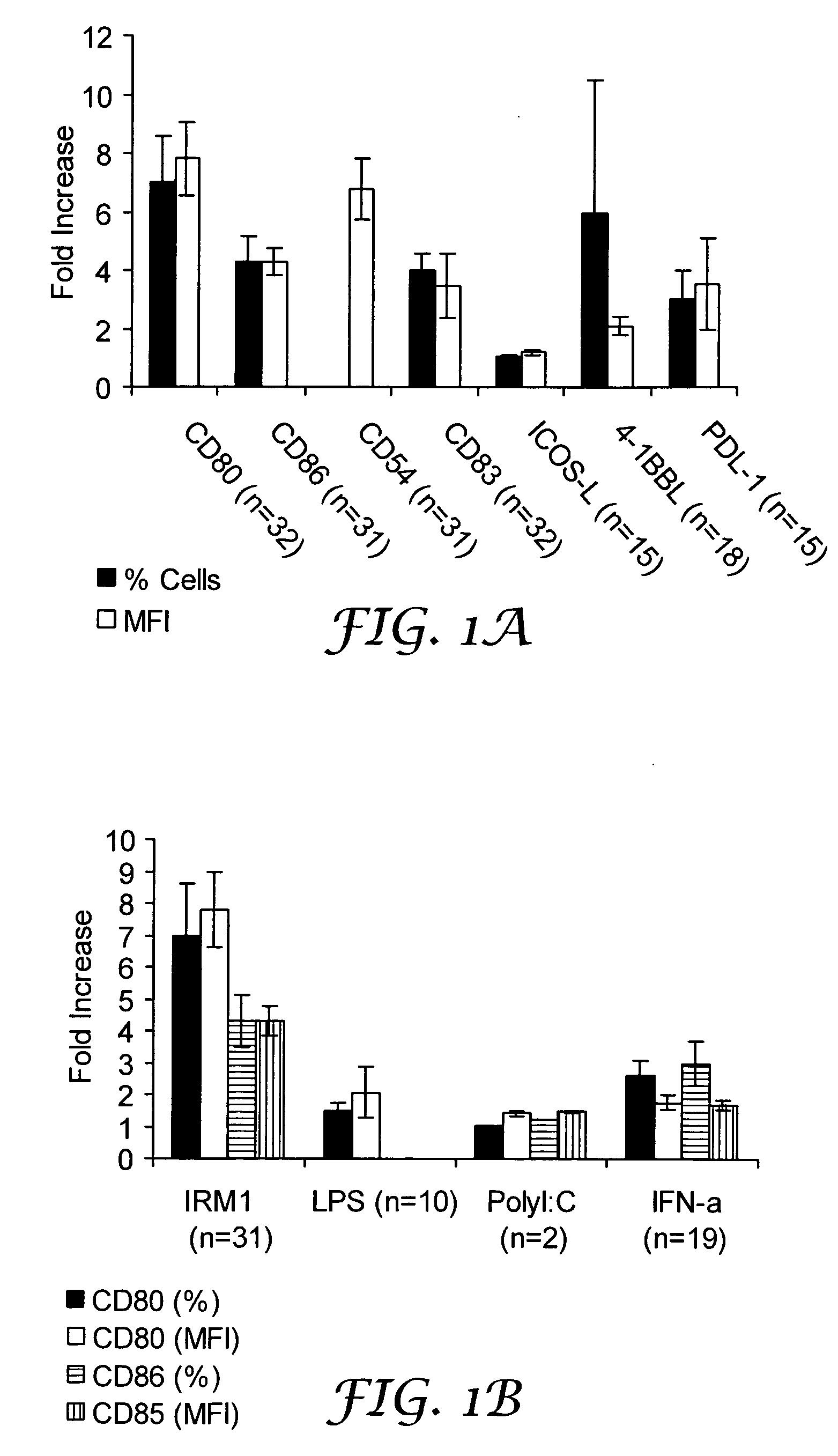
CLL cells from the indicated number of patients were cultured in IRM1 (1 μg / mL) for 3-4 days, and then assayed for expression of the costimulatory molecules indicated on the x-axis (at an intensity greater than the first decade of log fluorescence) of FIG. 1A. The percentage of cells that expressed each costimulatory molecule and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of expression were measured by flow cytometry. The “fold-increase” was then calculated from the ratio of these measurements to the percentage and MFI of control cells cultured without activating agents. The average and standard error of these relative increases in costimulatory molecule expression are shown in the FIG. 1A.
IRM1 has especially strong effects on CD80, CD86, and CD54 expression, with IRM1 increasing the expression of CD54, CD80, and CD86 on CLL cells from all patients studied (n=31). The effect on CD80 was greater than on CD86 (compare FIGS...
example 2
Effects of IL-2 and IRM1 on Costimulatory Molecule Expression by CLL Cells
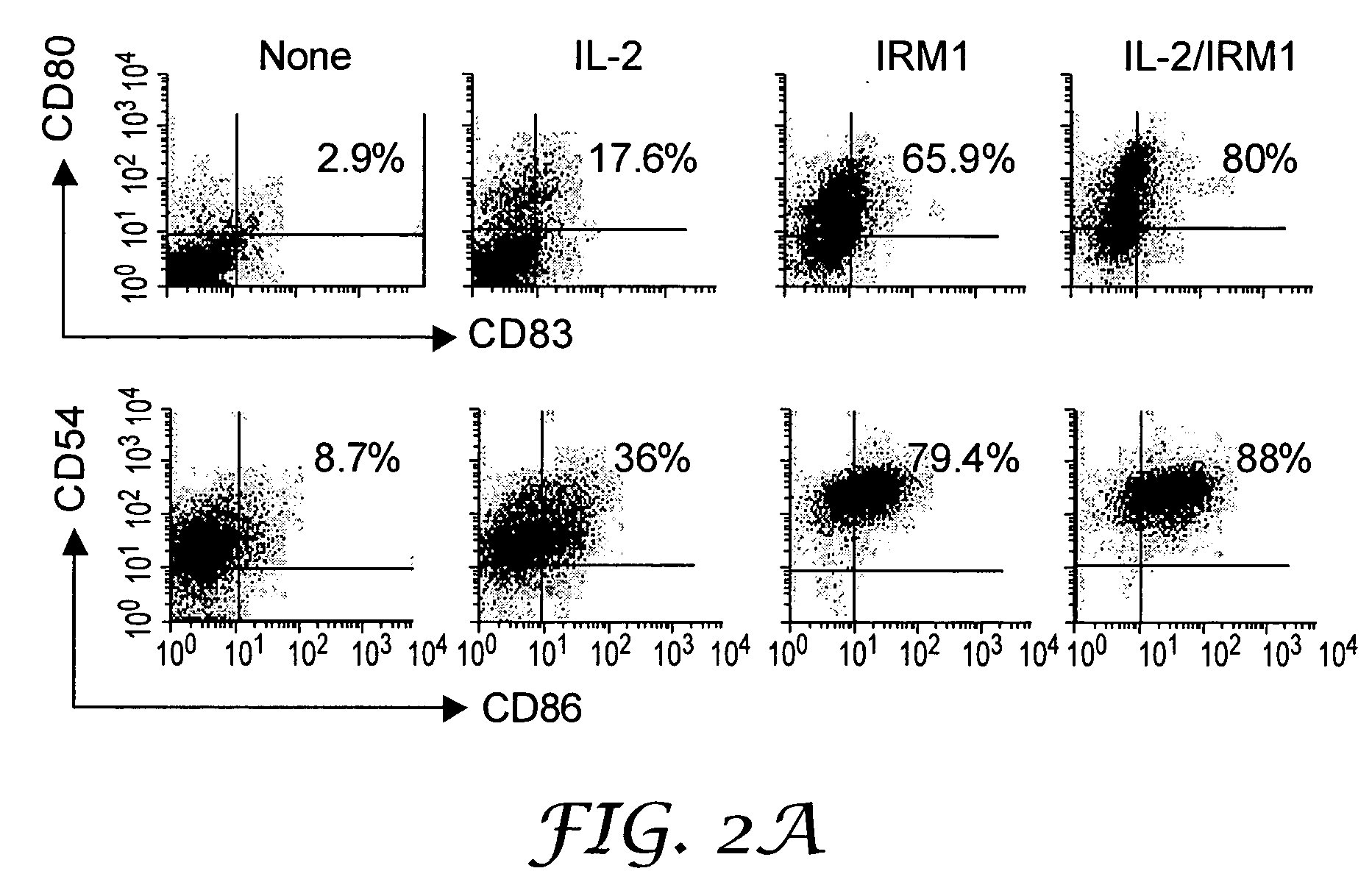
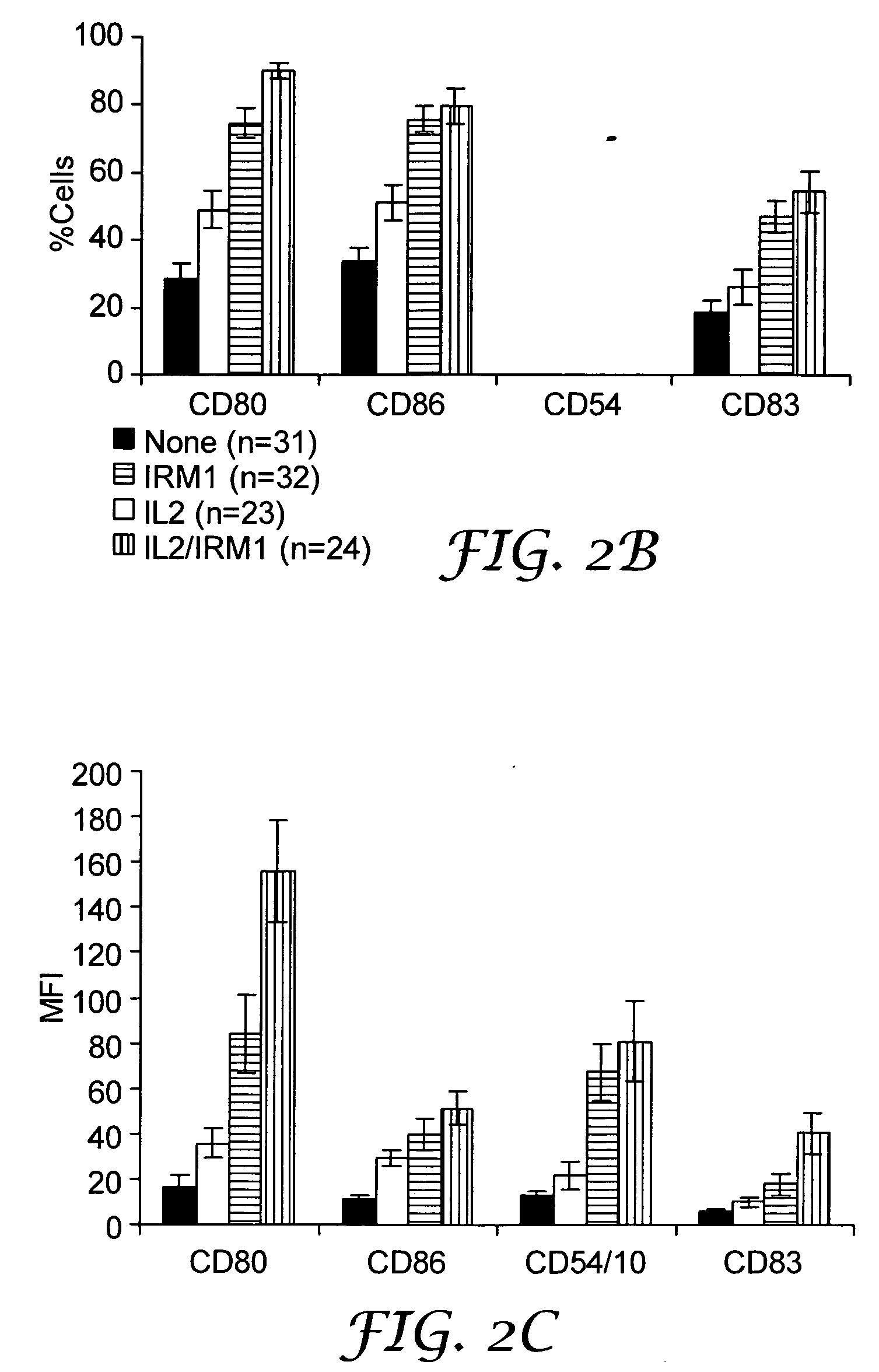
CLL cells were isolated and cultured alone or with IL-2 (5000 U / mL), IRM1 (1 μg / mL), or both IL-2 and IRM1 for 3-4 days. The expression of CD80, CD86, CD54, and CD83 was then determined by flow cytometry. FIG. 2A shows a characteristic example. The numbers in the dot plots in the upper and lower rows are the percentages of CD80+ and CD86+ CLL cells, respectively. FIG. 2B is a graphical representation of the percentage of CLL cells expressing the different costimulatory molecules (determined by the percentage of cells with staining intensity above the first decade of log fluorescence) from the number of patients indicated in the graph legend. The average and standard error for each of these measurements are shown in the graphs. The numbers over the double-headed arrows represent the p-values for the differences between sample means. FIG. 2C is a graphical representation of the mean fluorescence index (MFI) of...
example 3
Effect of PKC Activation on Costimulatory Phenotype and T Cell Stimulatory Ability of IL-2- and IRM1-Activated CLL Cells
CLL cells were purified from individual patients and cultured alone or with IL-2, IRM1, IL-2 and IRM1, PDB, PDB and IL-2, PDB and IRM1, or PDB, IL-2, and IRM1. After 3-4 days, these cells were harvested, washed extensively, irradiated (2500 cGy) and used to stimulate allogenic or autologous T cells from CLL patients (obtained at the same time as the CLL cells and rested in culture until added to the Mixed Lymphocytic Response (MLR) assay) after 5-6 days of culture, alamar blue was added and proliferation was measured in an optical density colorimetric microplate reader at wavelengths of 540 (reduced state) and 595 (oxidized state). The difference between these readings was used as a measure of the number of viable cells in the culture. Results are shown in FIG. 3A. The results from the T cell source that exhibited the greatest stimulation (after subtraction of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cell surface | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com