Immediate buckling model, hysteresis model, and cloth simulation method based on the invented models, and computer-readable media storing a program which executes the invented simulation method
a simulation method and model technology, applied in the field of immediate buckling model, hysteresis model, cloth simulation method based on the invented model, and computer-readable media storing the program which executes the invented simulation method, can solve the problems of inability to react, indefinite system matrix, extreme ill-conditioned or indefinite system matrix, etc., to achieve accurate expression of the characteristics of movement and fast simulation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
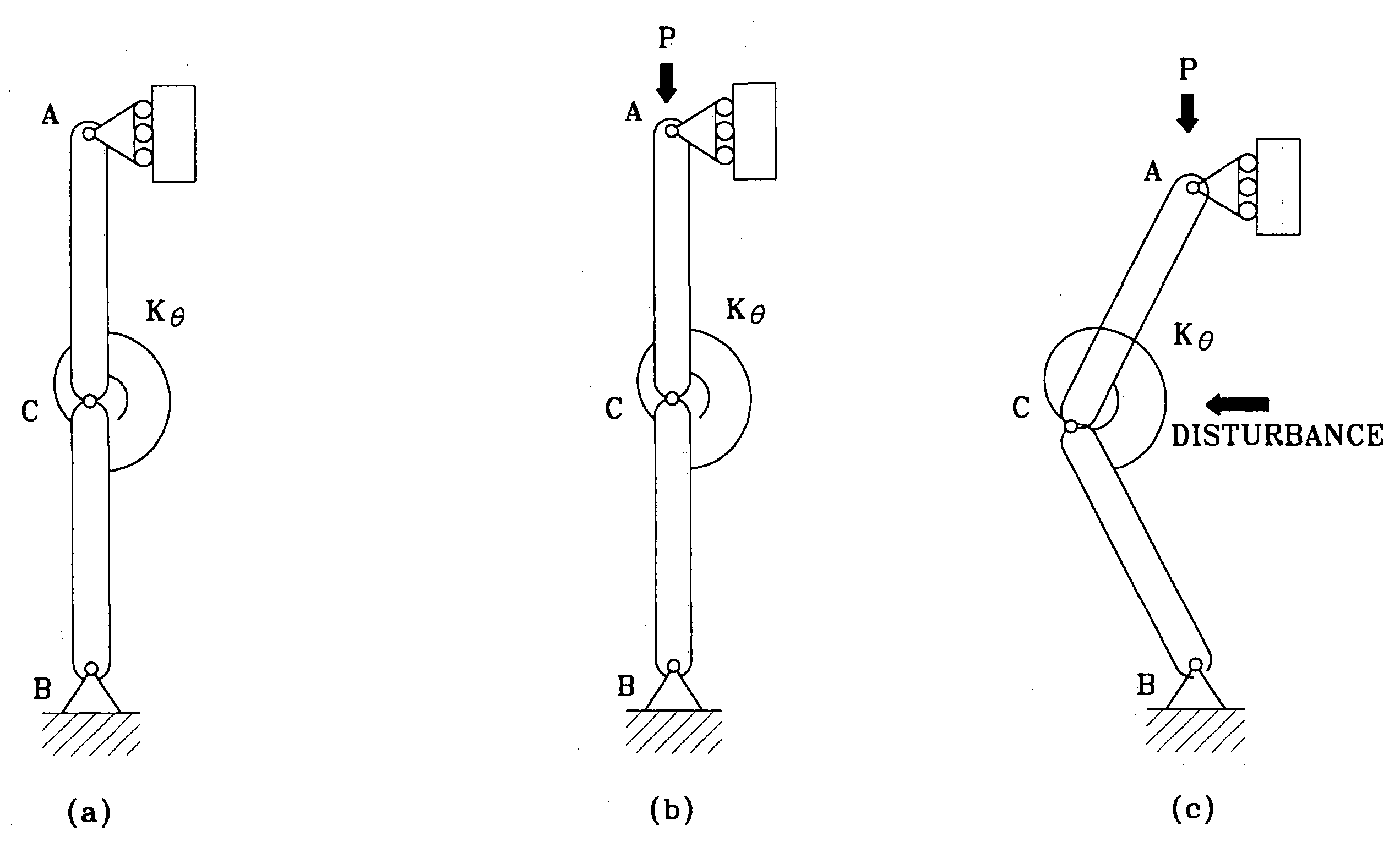
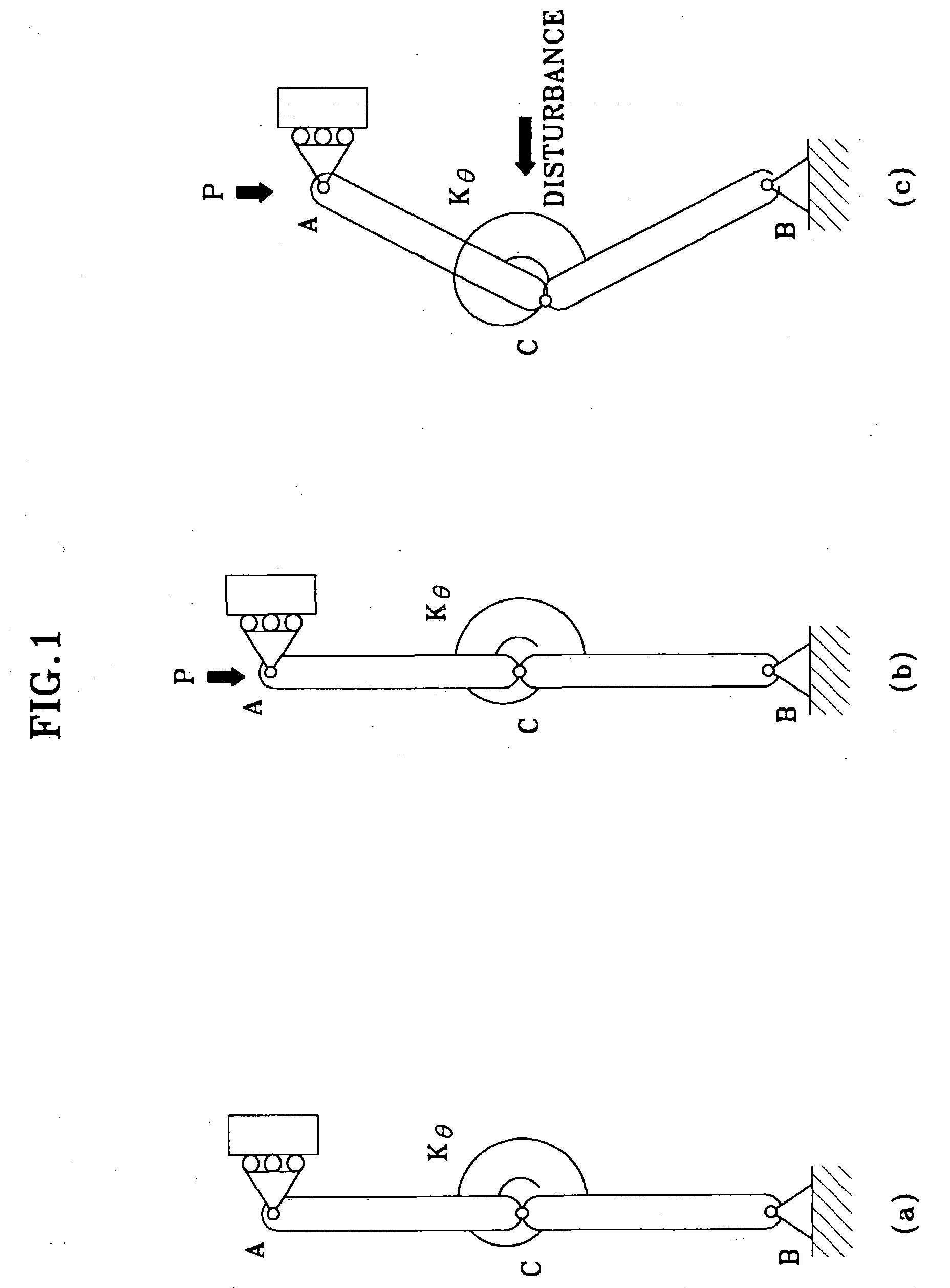
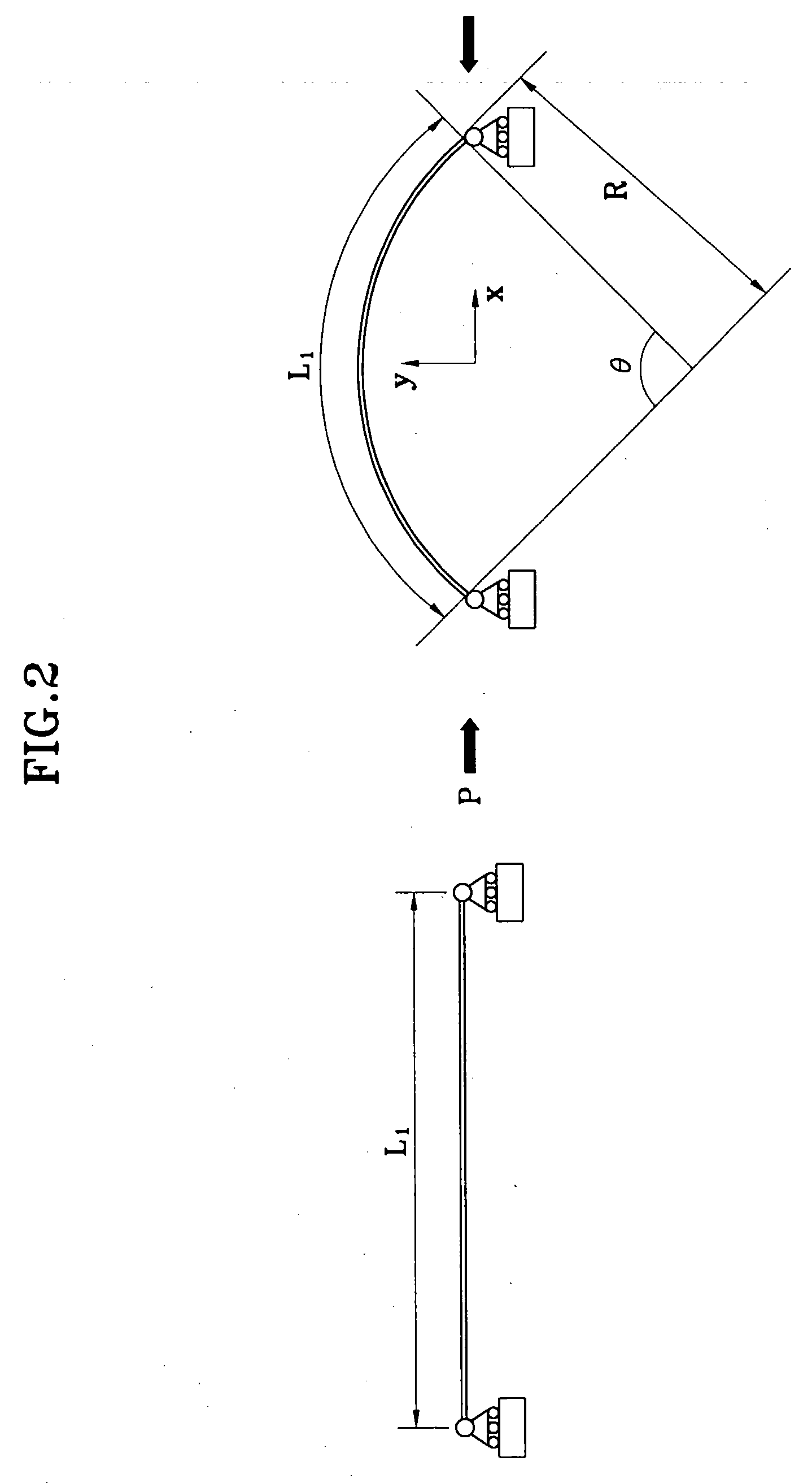
In order to accomplish the aforementioned objects, the present invention proposes to use the immediate buckling model, the “Choi-Ko Discrete Hysteresis Model” and the “Choi-Ko Continuous Hysteresis Model”. The immediate buckling model comprises deformation units which model cloth, wherein the deformation unit is bent immediately without contraction when compressive force is applied to two extremities of the deformation unit.
The hysteresis phenomenon of cloth is modeled by using finite numbers of spring-slip units in the “Choi-Ko Discrete Hysteresis Model” which is used for simulating the hysteresis characteristics between the curvature and moment. The hysteresis phenomenon of cloth is also modeled by using infinite numbers of spring-slip units in the “Choi-Ko Continuous Hysteresis Model” which is used for simulating the hysteresis phenomenon between curvature and moment more realistically.
The spring model simulates the deformation of cloth when stretching force is applied to bo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com