Stabilizing motion in a radar detection system using ultrasonic radar range information
a radar detection and ultrasonic technology, applied in the field of microwave radar systems, can solve the problems that the homoodyne radar cannot effectively determine if the detected movement is detected, and the need for a solution in the industry has not yet been addressed, and achieve the effect of suppressing motion artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
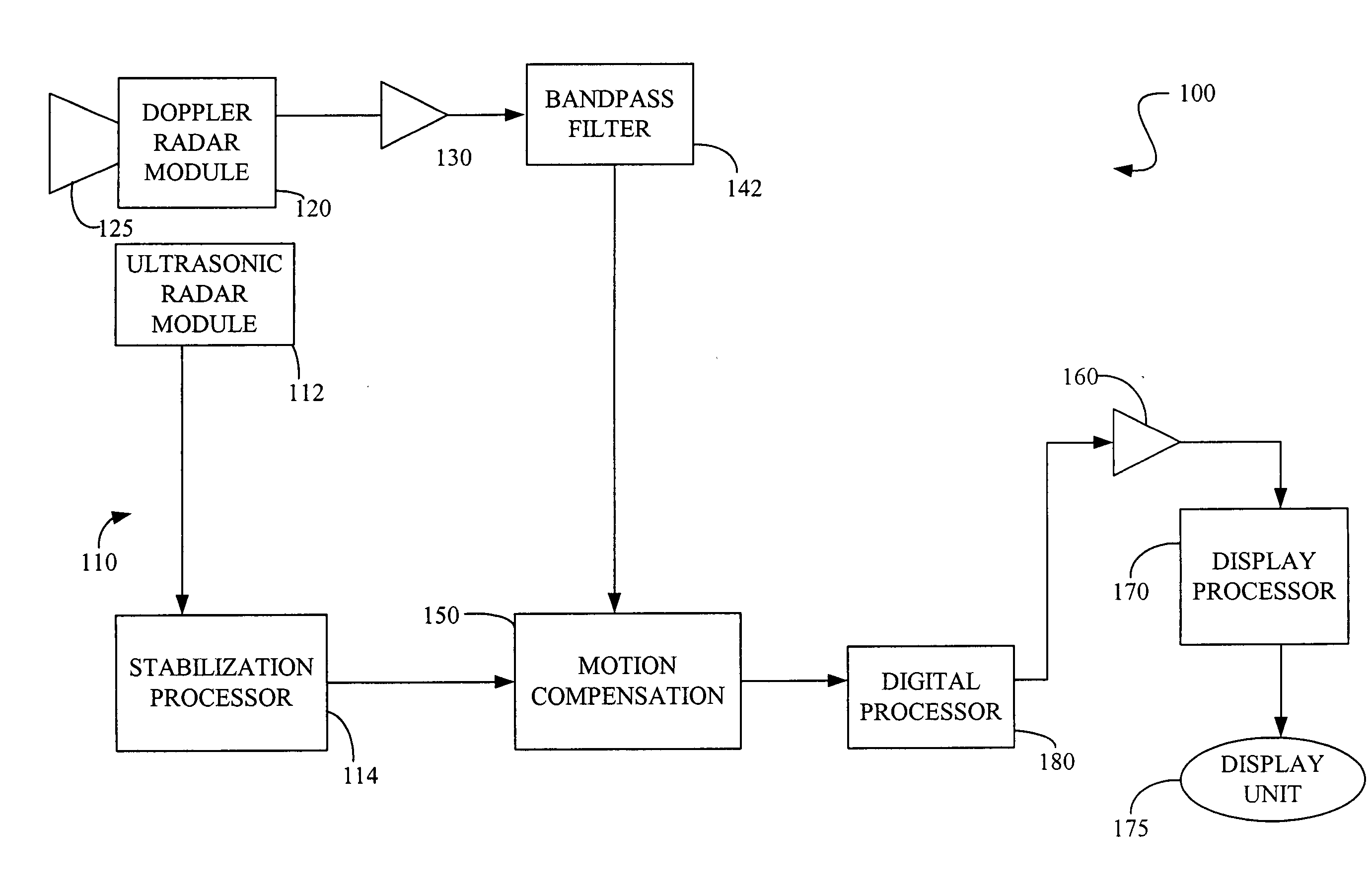
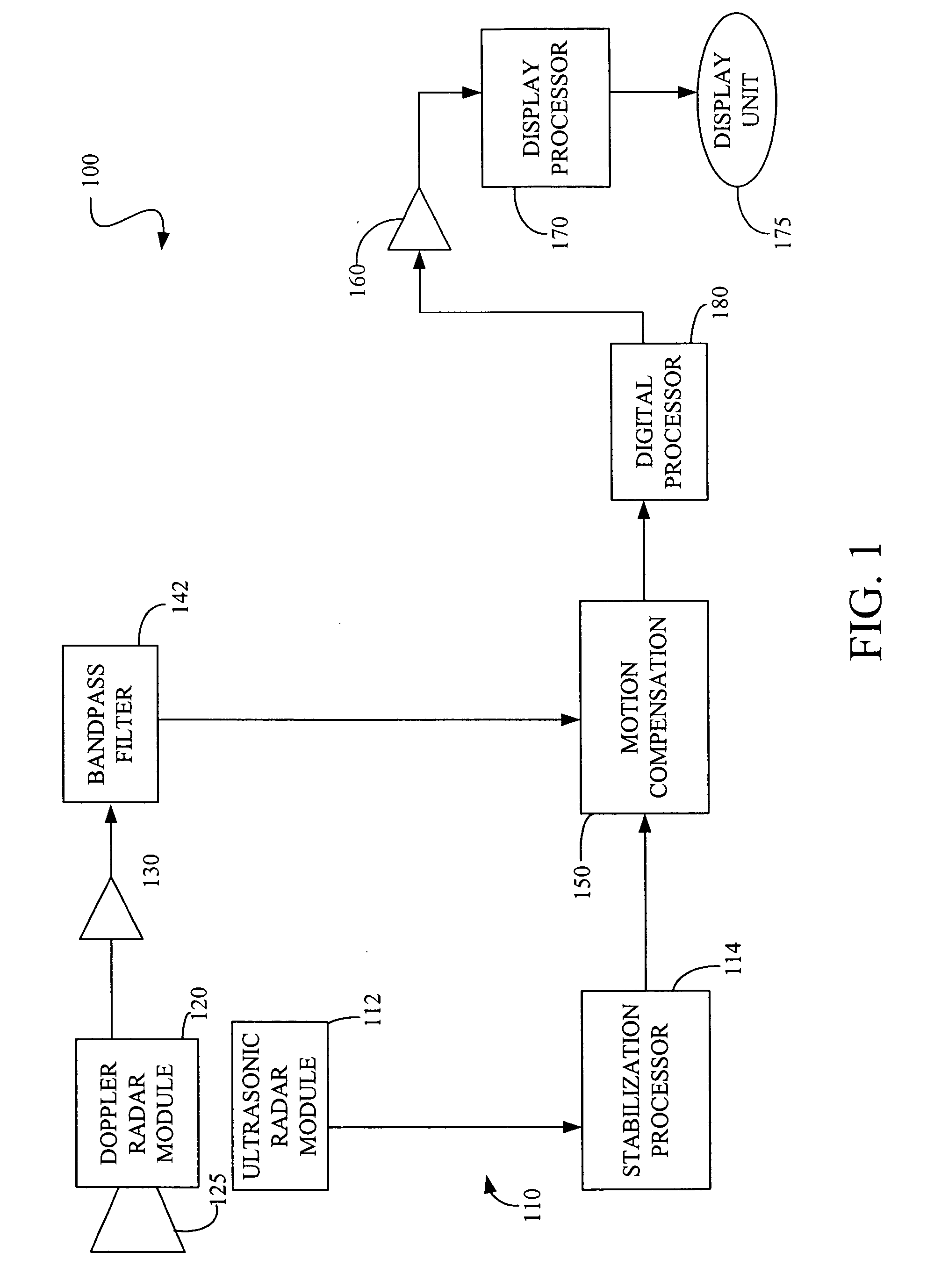
[0017]FIG. 1 shows a diagram of one embodiment of a radar detection device (100) employing one embodiment of the stabilization system (110) of the present invention. In this example, the radar detection device (100) comprises a Doppler radar module (120) that generates a microwave continuous wave (CW) signal at 10.525 GHz. However, other microwave frequencies may also be used.
[0018] The CW signal is generated using a solid state Gunn device transmitter (not shown). The resulting CW signal is transmitted through an antenna (125). When a person, for example, is located in front of the antenna (125), the transmitted signal is reflected off the body of the target individual. Thus, any motion of the person's body causes a phase shift in the reflected signal proportional to the amount of motion in the radial direction to the Doppler radar module (120). At a frequency of 10.525 GHz, for example, the typical phase shift is 360 degrees for every 1.75 centimeters of radial motion toward or w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com