Method and program for scenario provision in a simulation system
a simulation system and scenario technology, applied in the field of simulation systems for weapons training, can solve the problems of difficult and costly training under various real-life situations, inconvenient use of training ammunition, and injuring officers or citizens, so as to improve decision-making skills, encourage teamwork, and reinforce the use of appropriate tactics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
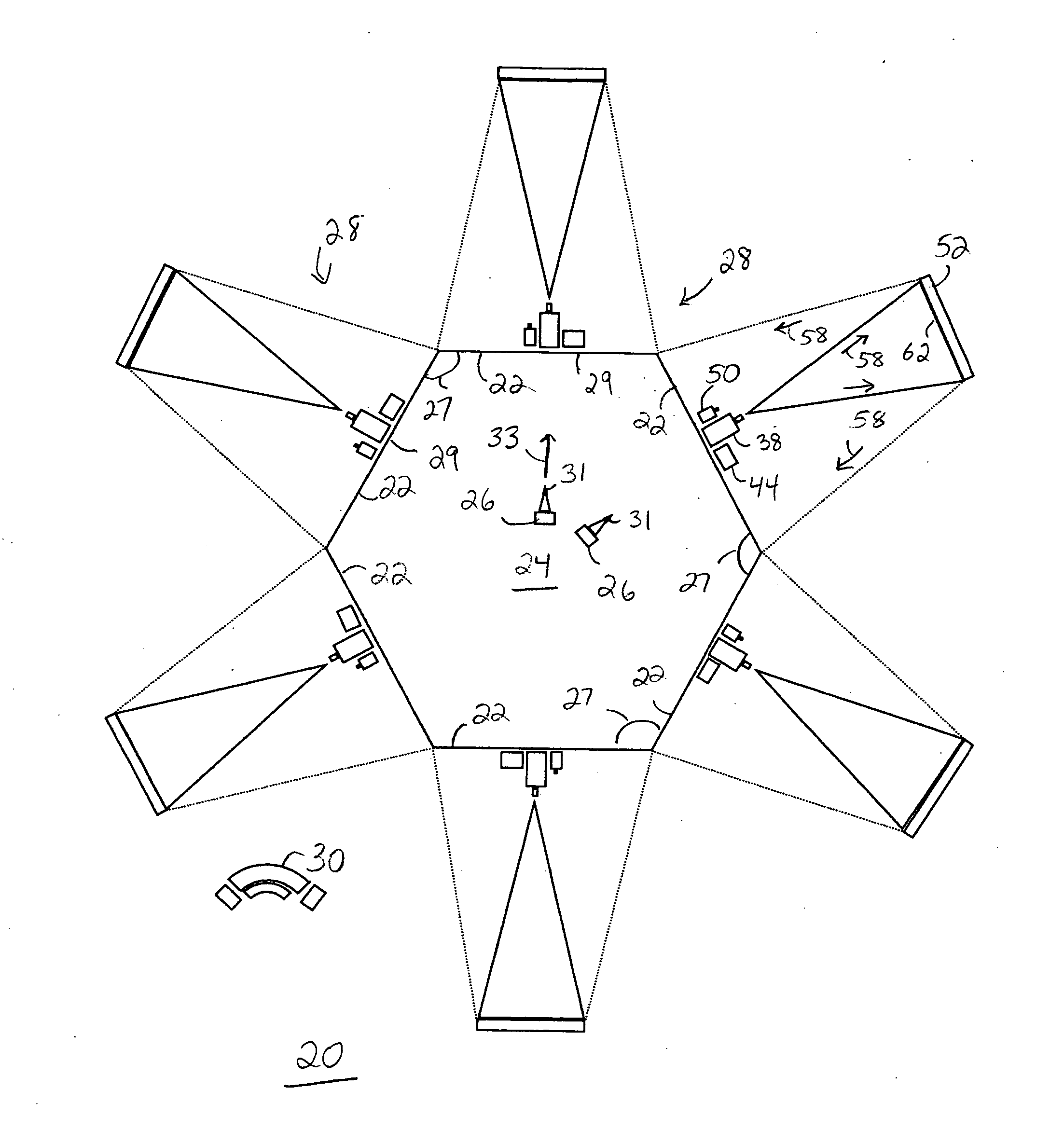
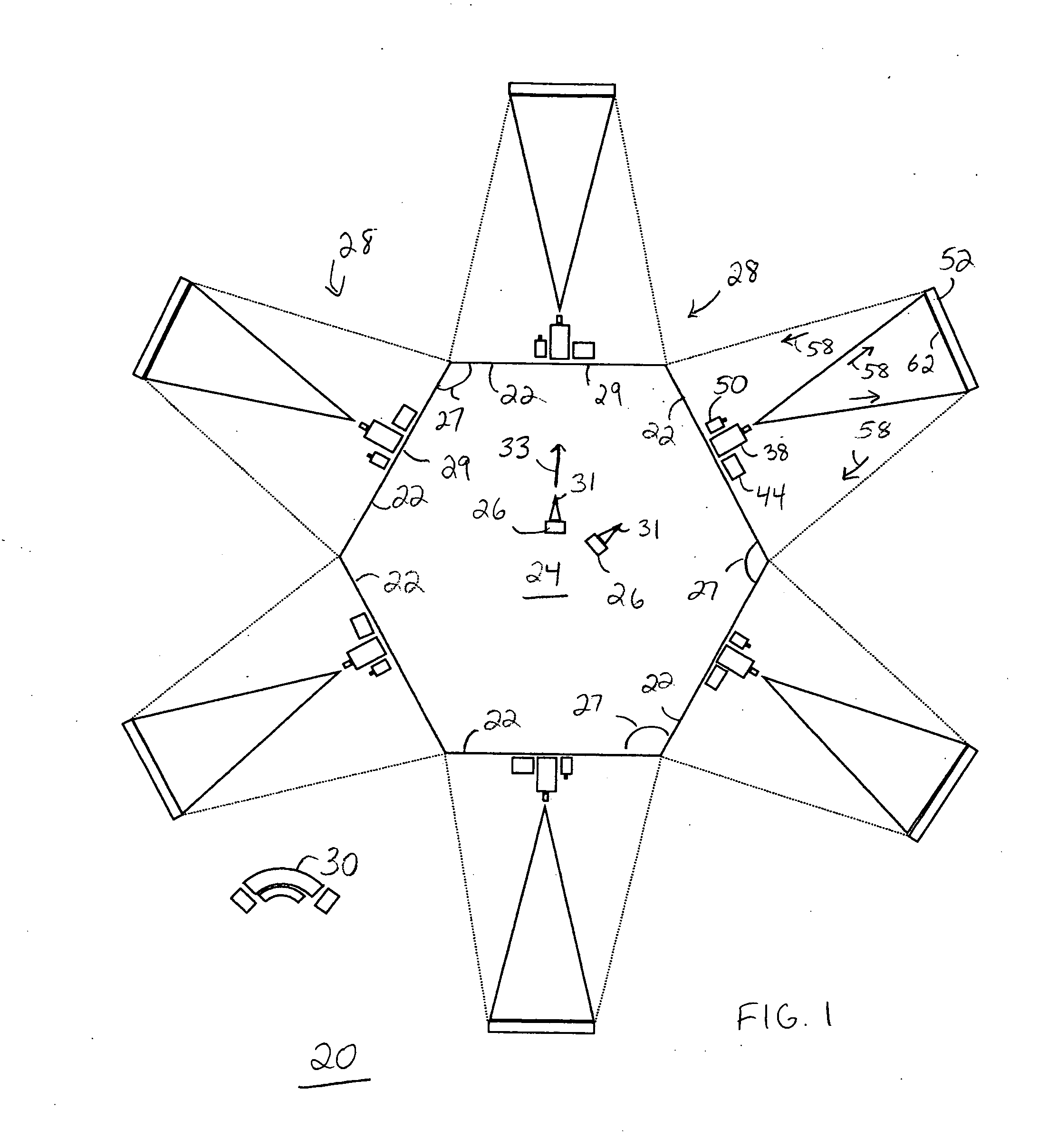
[0054]FIG. 1 shows a diagram of a full surround simulation system 20 in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. Full surround simulation system 20 includes multiple screens 22 that fully surround a participation location 24 in which one or more participants, i.e., trainees 26, may be positioned. Since multiple screens 22 fully surround participation location 24, at least one of screens 22 is configured to swing open to enable ingress and egress. For example, screens 22 may be hingedly coupled to one another, and one of screens 22 may be mounted on casters that enables it to roll outwardly enough to allow passage of trainees 26 and / or trainers (not shown).
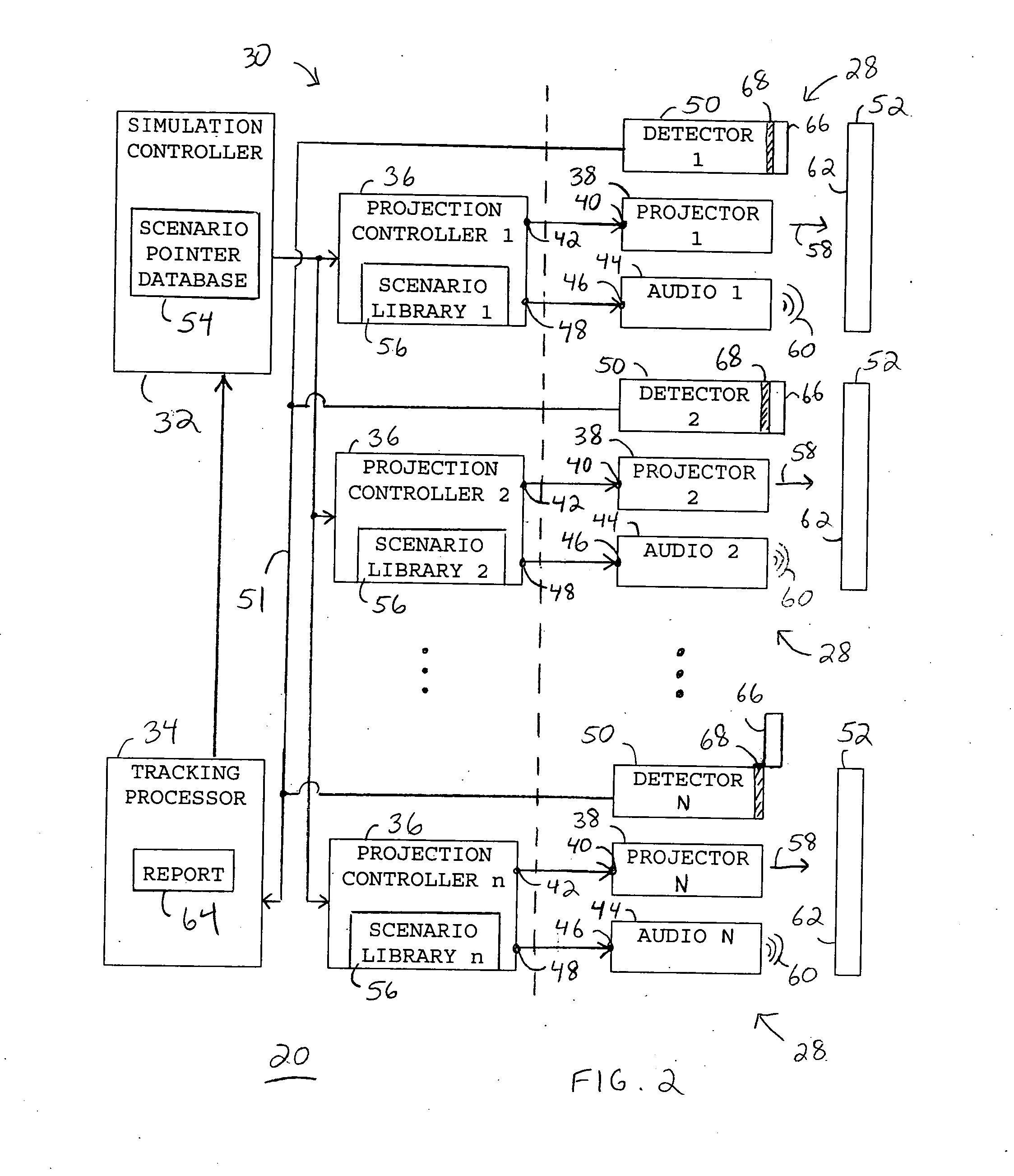
[0055] Each of multiple screens 22 has a rear projection system 28 associated therewith. Rear projection system 28 is operable, and trainees 26 actions may be monitored from, a workstation 30 located remote from participation location 24. Workstation 30 is illustrated as being positioned proximate screens 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com