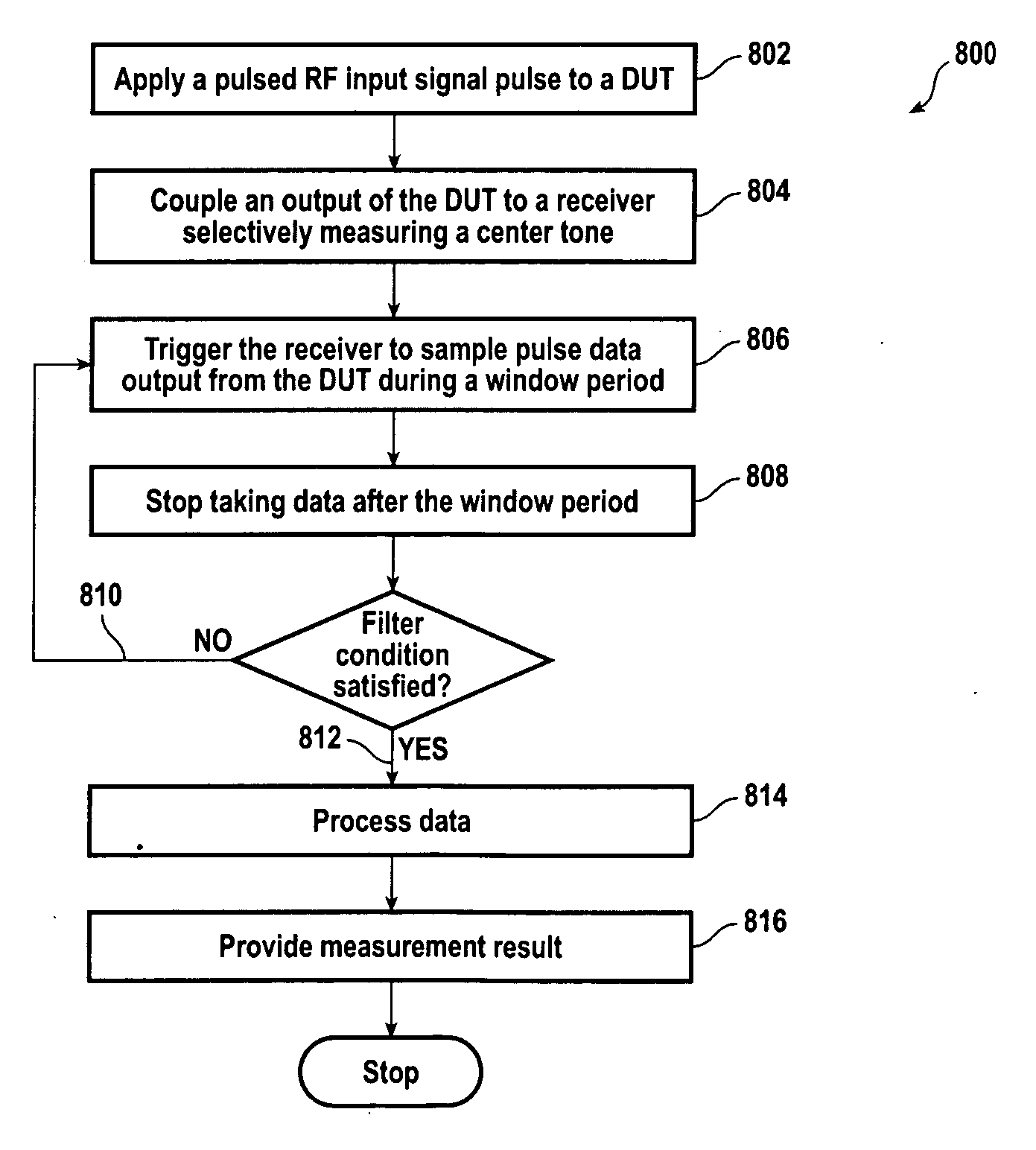
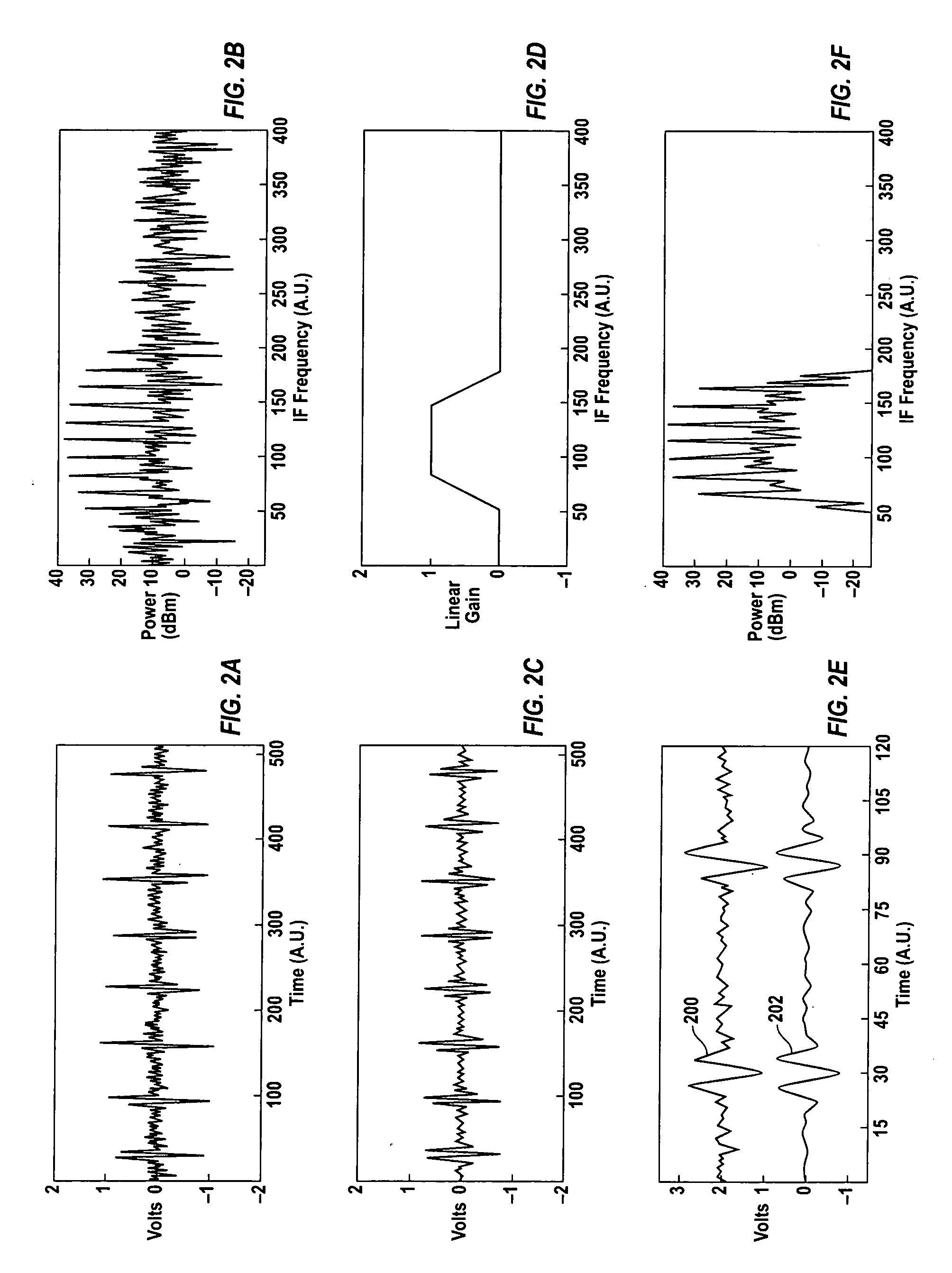
Triggered narrow-band method for making pulsed-rf networking measurements
a technology of pulsed rf and triggered narrowband, which is applied in the direction of resistance/reactance/impedence, instruments, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of destroying a dut that is not adequately heat sunk, other duts that are not designed to operate in cw mode, and cw signal might destroy the du
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
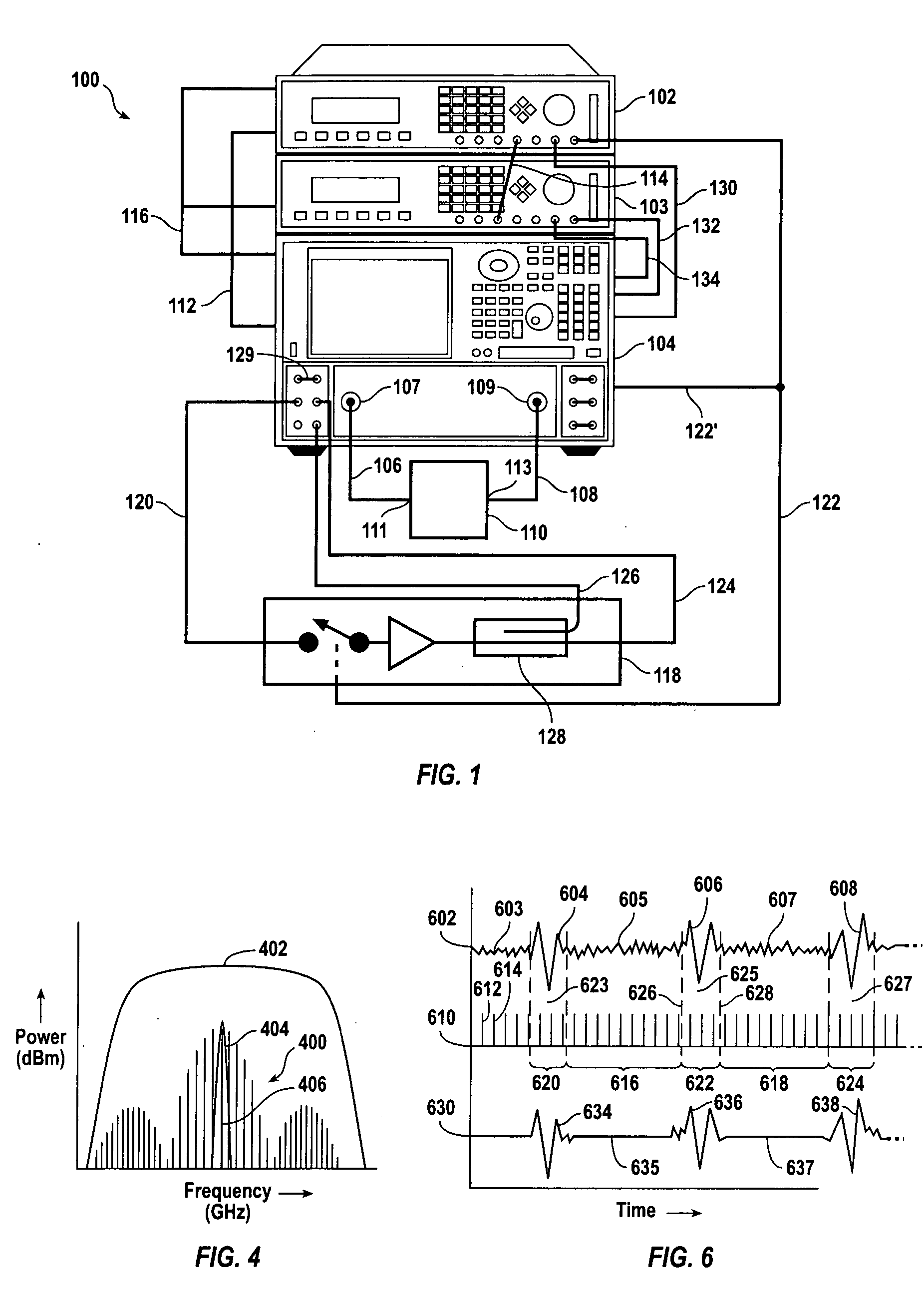
[0025]FIG. 1 shows an exemplary test set 100 for measuring electronic devices according to embodiments of the invention. The test set 100 includes a first pulse generator 102, a second pulse generator 103, and a receiver 104, such as a spectrum analyzer, a network analyzer, or a specialized receiver. In a particular embodiment, the receiver is a MODEL E8362B™ network analyzer, available from AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES, INC., of Palo Alto, Calif., and the pulse generator is a MODEL 81110A™, also available from AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES, INC. A spectrum analyzer is useful as a receiver when amplitude versus frequency measurements are desired. A network analyzer is useful as a receiver when amplitude versus frequency and / or phase versus frequency measurements are desired. A spectrum analyzer can measure signals generated by a DUT, or signals provided to a DUT from a signal source, such as a sweeper or synthesizer, and output from the DUT to the receiver. A network analyzer makes stimulus-response...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com