Horizontal axis wind turbine
a wind turbine and horizontal axis technology, applied in the direction of liquid fuel engines, vessel construction, marine propulsion, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in correcting the angle once set, and achieve the effect of easy change after installation and relatively easy installation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
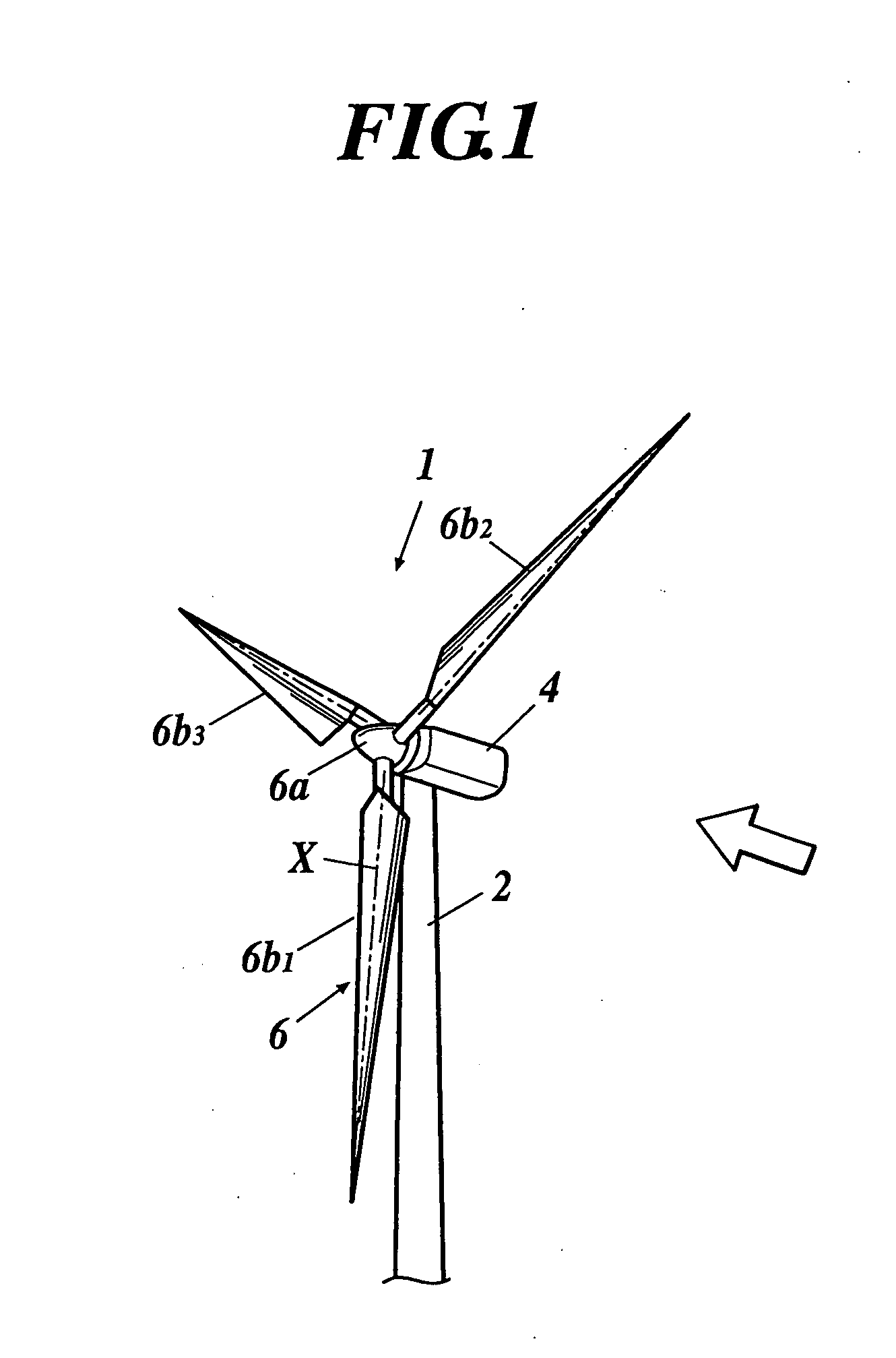
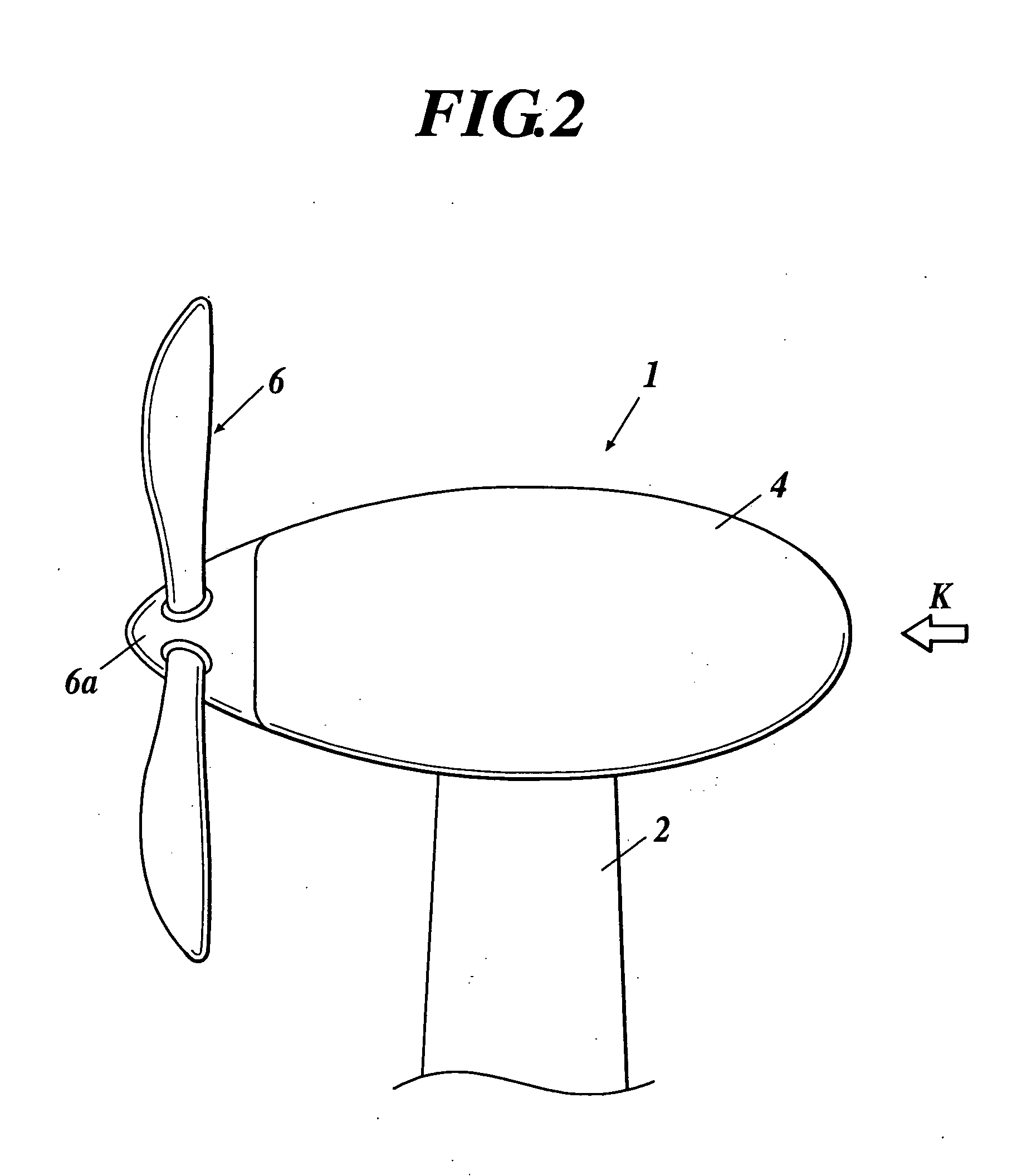
[0029] A horizontal axis wind turbine according to the invention will be explained with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2. The wind turbine will be explained by using a downwind horizontal axis wind turbine 1 as shown in FIG. 2.
[0030] Such a horizontal axis wind turbine 1 includes a tower 2 placed on the ground, an approximately cylindrical nacelle 4 directly fixed to the tower 2, a rotor shaft (not shown) rotatably supported to the nacelle 4, a hub 6a fixed to the rotor shaft, and a rotor 6 having three blades 6b1-6b3 in the embodiment, each blade attached to the hub 6a so that its pitch angle is changeable. Each of the blades 6b1-6b3 is attached to the hub 6a so as to be perpendicular to the rotor shaft.
[0031] Regarding the change of the pitch angle in the horizontal axis wind turbine 1, each pitch angle of the blades 6b1-6b3 is independently changeable, though not shown particularly. For the blade 6b1, for example, the base end thereof is attached to a ring gear which is rotatably supp...
second embodiment
[0034] Next, a horizontal axis wind turbine according to the invention will be explained with reference to FIGS. 3A, 3B and 4. Here, the elements in FIGS. 3A, 3B and 4 which are substantially the same as corresponding elements in FIGS. 1 and 2 are designated by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
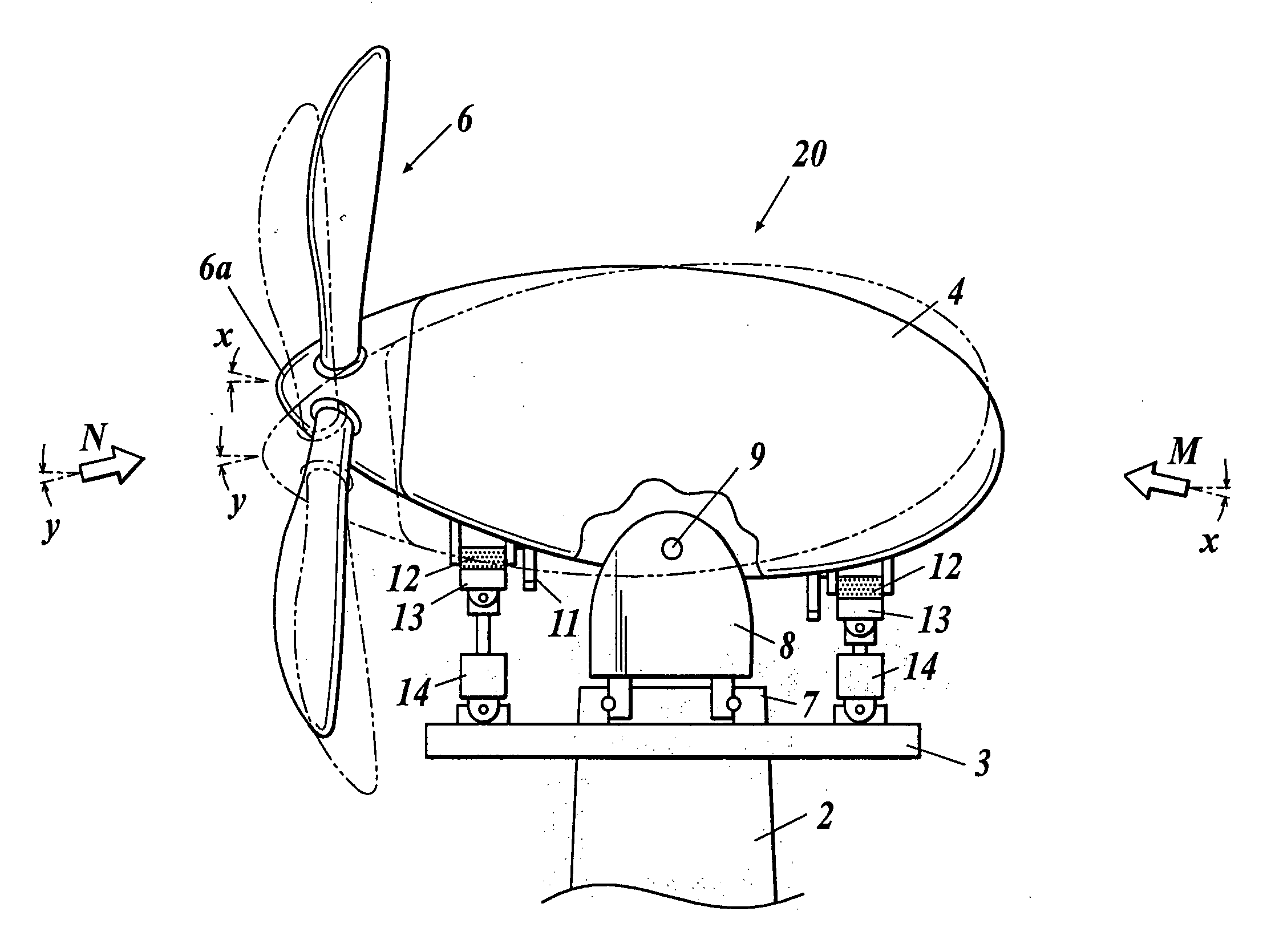
[0035] A horizontal axis wind turbine 20 is a downwind horizontal axis wind turbine similar to the above-described wind turbine 1. However, the wind turbine 20 can control azimuth angles and tilt angles according to the change of wind direction which is indicated by an arrow in FIG. 3A.
[0036] The horizontal axis wind turbine 20 includes, as shown in FIG. 3A, a tower head pedestal 3 arranged on the above-described tower 2 which is placed on the ground, and a nacelle support member 8 on which the nacelle 4 is disposed to be rotatable about a vertical axis above the pedestal 3 through a bearing 7. The support member 8 supports the nacelle 4 by a pin 9 disposed a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com