Manufacture of FRP composites
a technology of reinforced plastics and composites, which is applied in the field of manufacturing of frp composites, can solve the problems of performance gap, difficult impregnation, and conventionally lacking mechanical properties of thermoset resins of thermoplastic resins, and achieves the effect of low cost and good performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
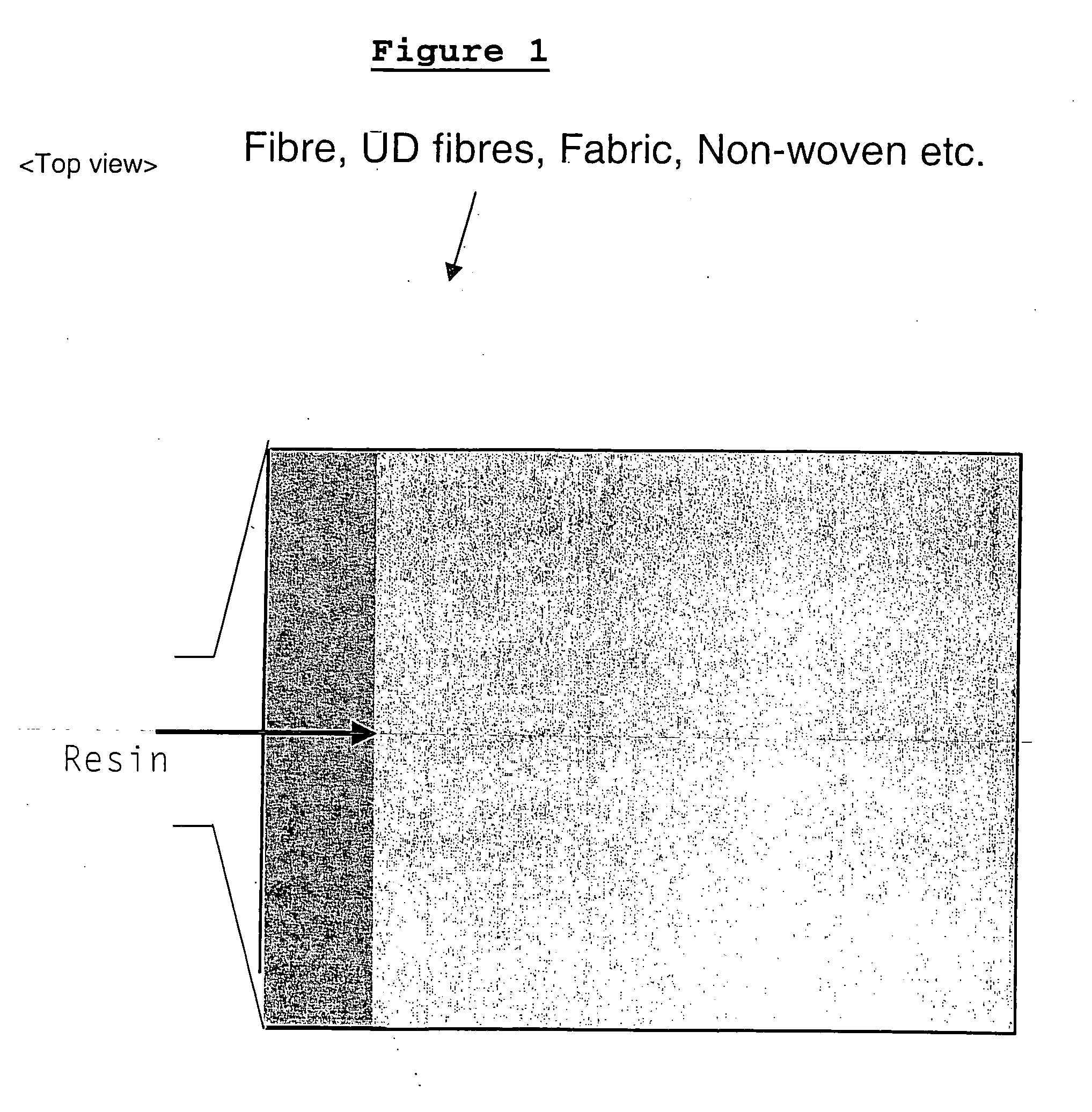
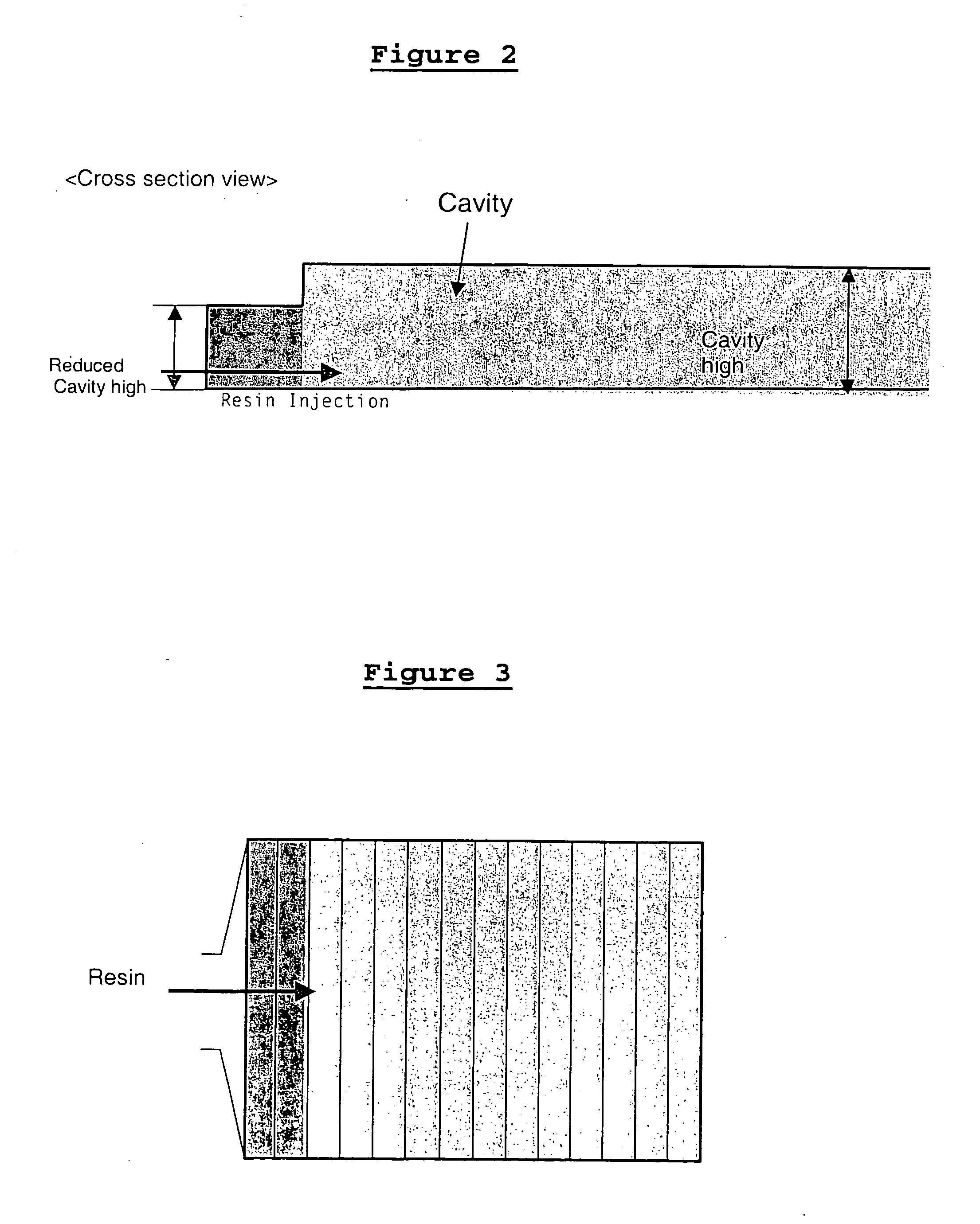
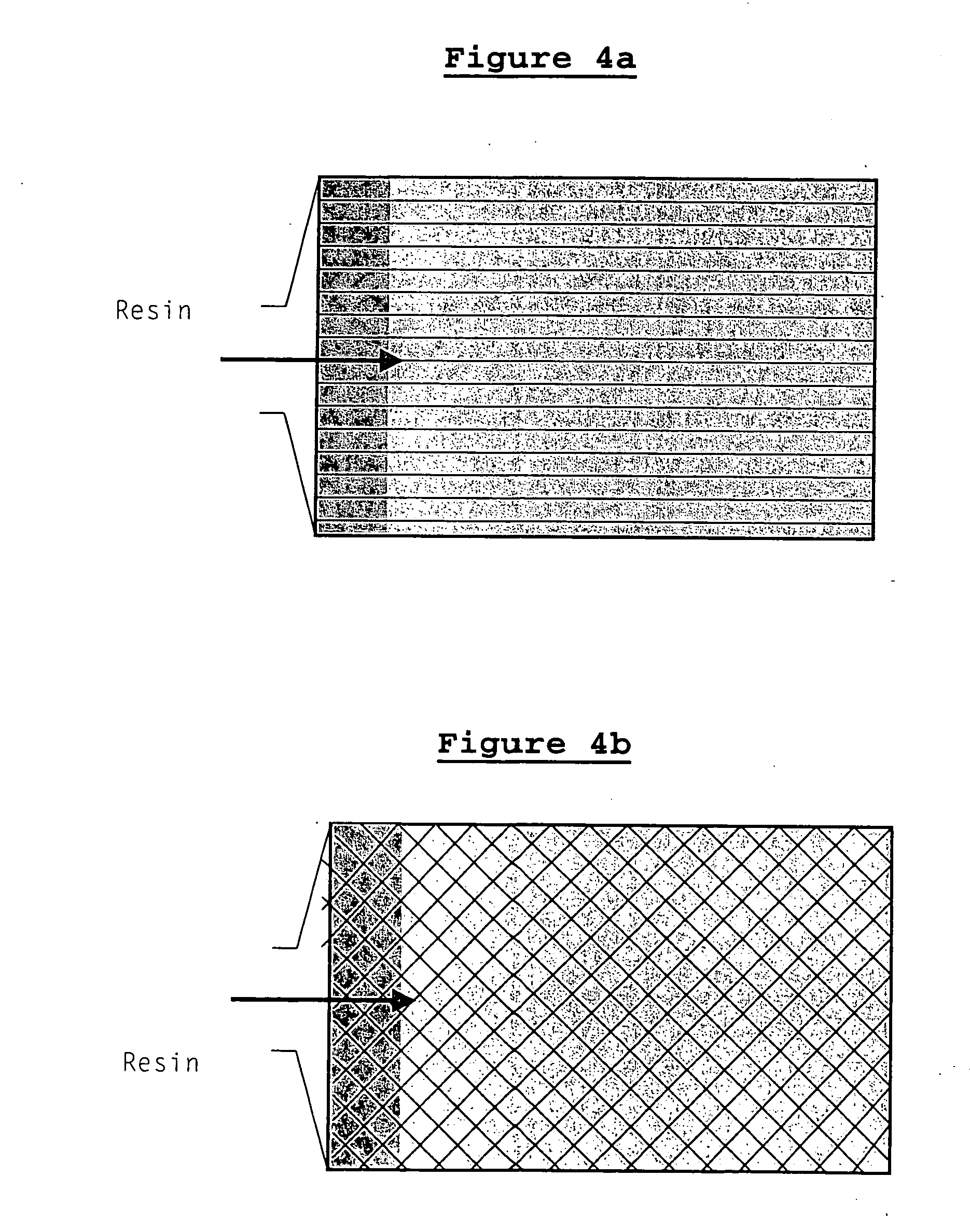
[0039] One embodiment of the present invention provides a process for the manufacture of fibre reinforced plastics (FRP) composites, comprising impregnation of fibres with resin.
[0040] One embodiment of the present invention is described herein with reference to carbon fibre reinforced plastics (CFRP). However, one skilled in the art will recognize that that embodiments of the invention may also be used for the manufacture of other fibre reinforced plastics such as glass fibre reinforced plastics (GFRP).
[0041] Carbon fibres, also referred to as graphite fibres, can be industrially produced from polyacrylonitrile fibre or pitch. According to one embodiment of the present invention, oxidation of these starting materials followed by carbonizing / graphitizing stages yield carbon fibre filaments which can then be grouped to form tows.
[0042] One embodiment of the present invention uses heavy tow fibres or fibre tows comprising at least 24000 filaments.
[0043] Fibres can be assembled in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com