Valve timing control apparatus and internal combustion engine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
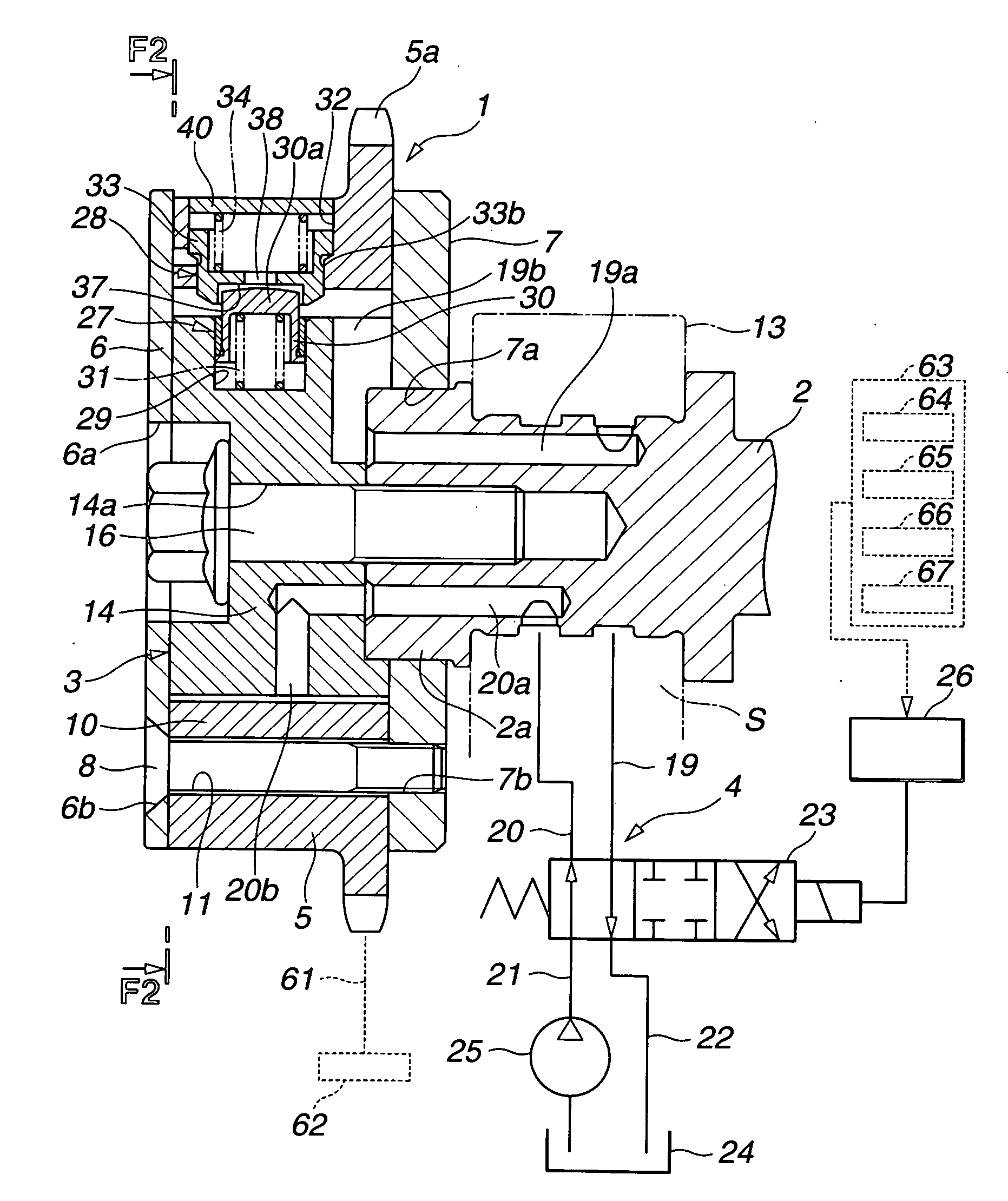
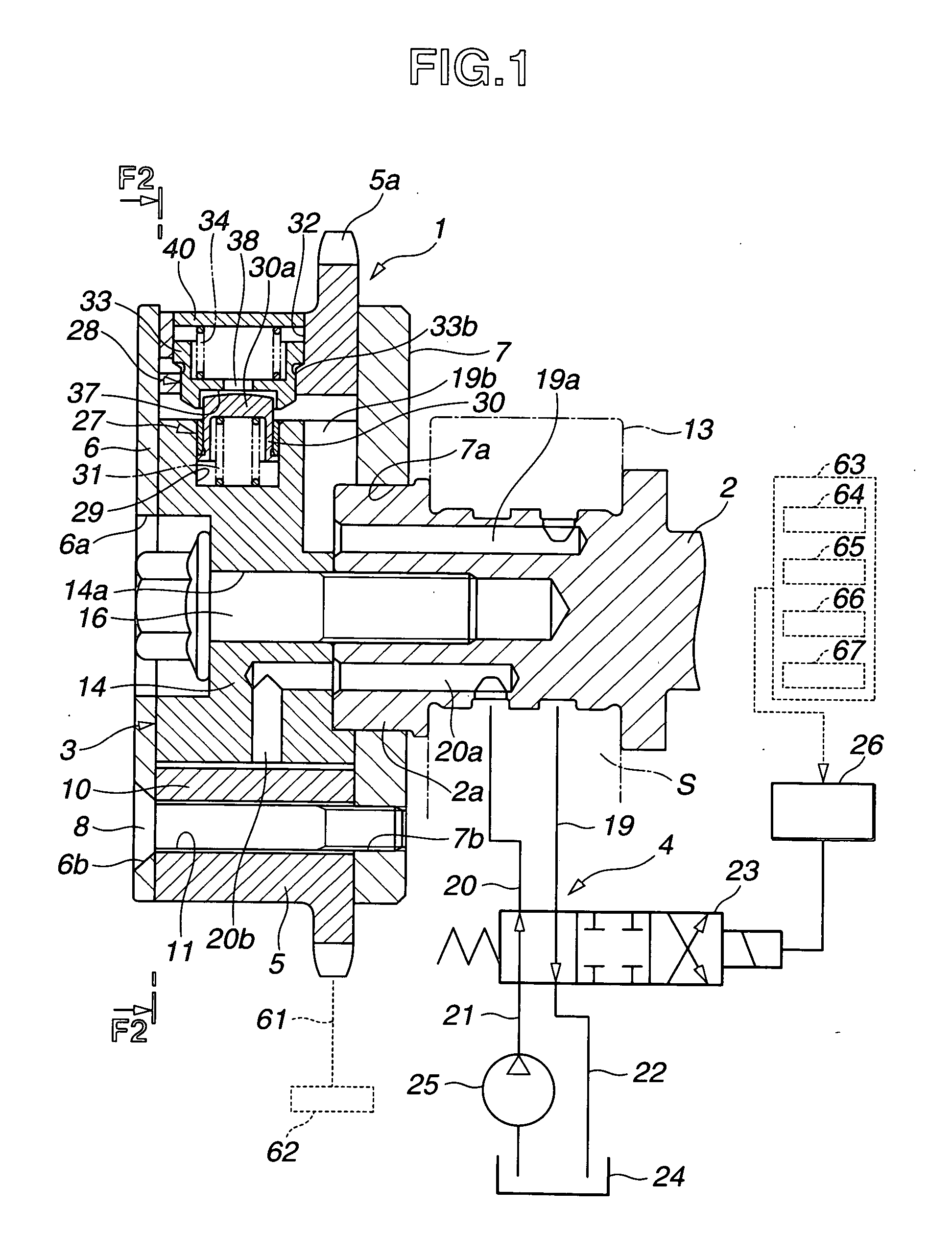
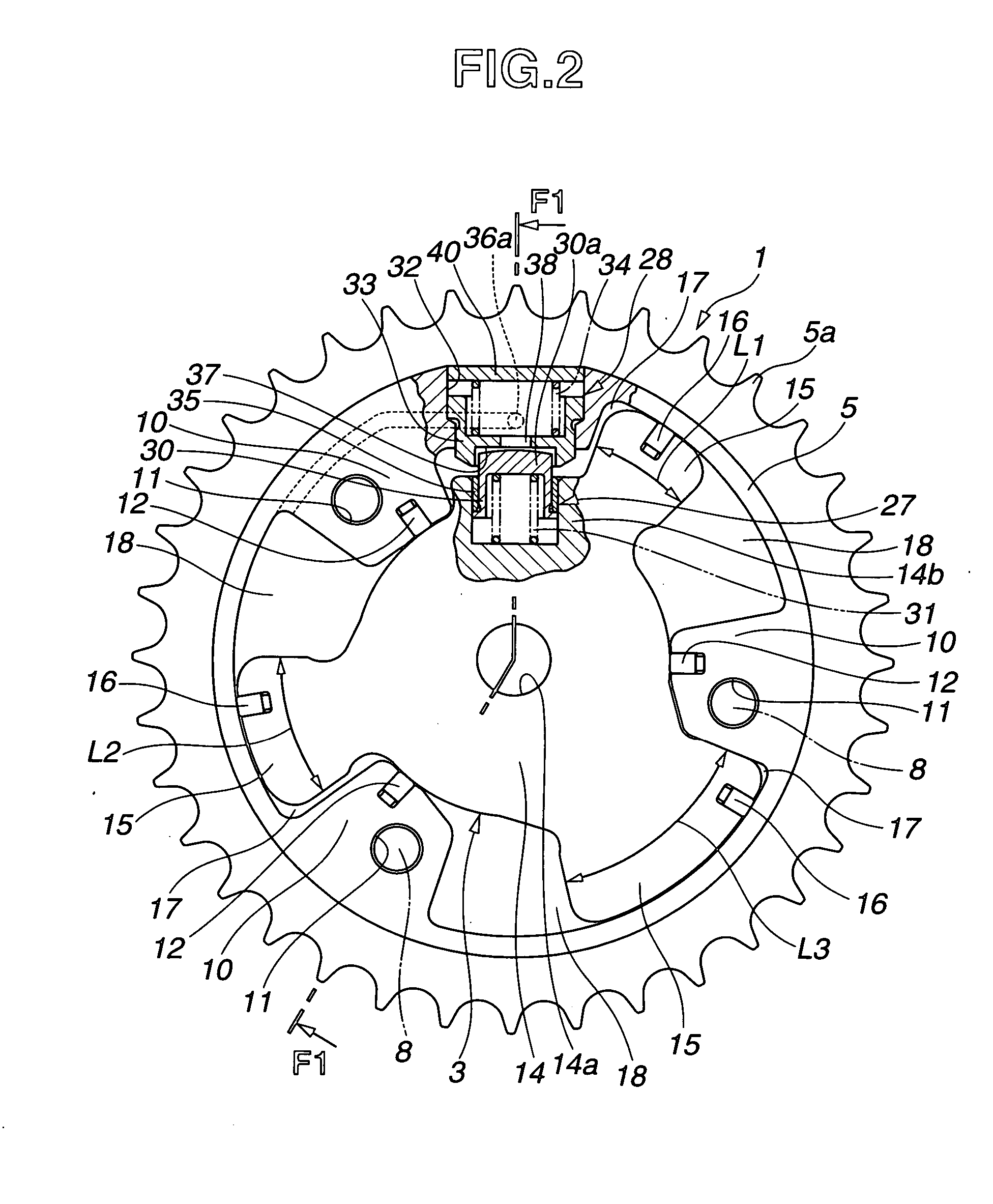
[0023]FIG. 1 shows an internal combustion engine equipped with a valve timing control apparatus or system according to the present invention. FIG. 2 shows the valve timing control apparatus in section taken across a line F2-F2 in FIG. 1 whereas FIG. 1 is a sectional view taken across a line F1-F1 shown in FIG. 2. In this embodiment, the present invention is applied to an intake valve's side. However, it is possible to apply the invention to an exhaust valve's side.
[0024] A timing sprocket member 1 is a driving rotary member driven through a timing chain 61 by a crankshaft 62 of the internal combustion engine. A camshaft 2 is rotatable relative to sprocket member 1. A vane member 3 is a driven rotary member which is fixed at an end of camshaft 2 so that they rotate as a unit, and which is encased rotatably in sprocket member 1. A hydraulic circuit 4 is a component of a control section to rotate vane member 3 in a forward rotational direction and a reverse rotational direction in spro...
second embodiment
[0079] FIGS. 7˜10 show a valve timing control apparatus according to the present invention. In the second embodiment, second lock member 33 is arranged to move backwards against the spring force of second spring 34 by the effect of a centrifugal force, instead of the hydraulic pressure in retard chambers 18. The spring force of second spring 34 is set smaller than a centrifugal force of a predetermined magnitude produced in housing 5 during rotation. In this example, second spring 34 is so set that second spring 34 starts compression by the centrifugal force of housing 5 when the engine rotational speed becomes equal to or higher than an idle speed of about 900 rpm.
[0080] An air release passage 41 is formed in the circumferential wall of housing 5 of sprocket member 1. Air release passage 41 connects the annular pressure chamber 33b with the outside, and thereby opens the inside of the annular pressure chamber 33a to the atmosphere to allow free movement of second lock member 33 in ...
third embodiment
[0088] With the circuit section including second control valve 43 for controlling the fluid pressure in the pressure chamber 33b independently from the fluid pressures in the advance and retard chambers 17 and 18, the valve timing control system can move the second lock member 33 forwards and backwards quickly by supplying and draining the hydraulic pressure directly to and from the pressure chamber 33b. Thus, the locking and unlocking operations of first and second lock members 30 and 33 are quick, and the response in the valve timing control is improved.
[0089] FIGS. 12˜15 show a valve timing control apparatus or system according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention. In the fourth embodiment, the first and second lock members 30 and 33 are in the form of a pin. In this embodiment, the first and second lock members or lock pins 30 and 33 are identical in size and shape. Each of first and second lock pins 30 and 33 includes a flange or slide portion 30c or 33c formed inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com