Trimming of local oscillation in an integrated circuit radio
a technology of integrated circuit radio and local oscillation, which is applied in the direction of dc level restoring means or bias distortion correction, digital transmission, baseband system details, etc., can solve the problem that the frequency of the receiver local oscillation will most likely not exactly match the known frequency, and achieve the effect of reducing the dc offset and the adverse effects caused by this
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
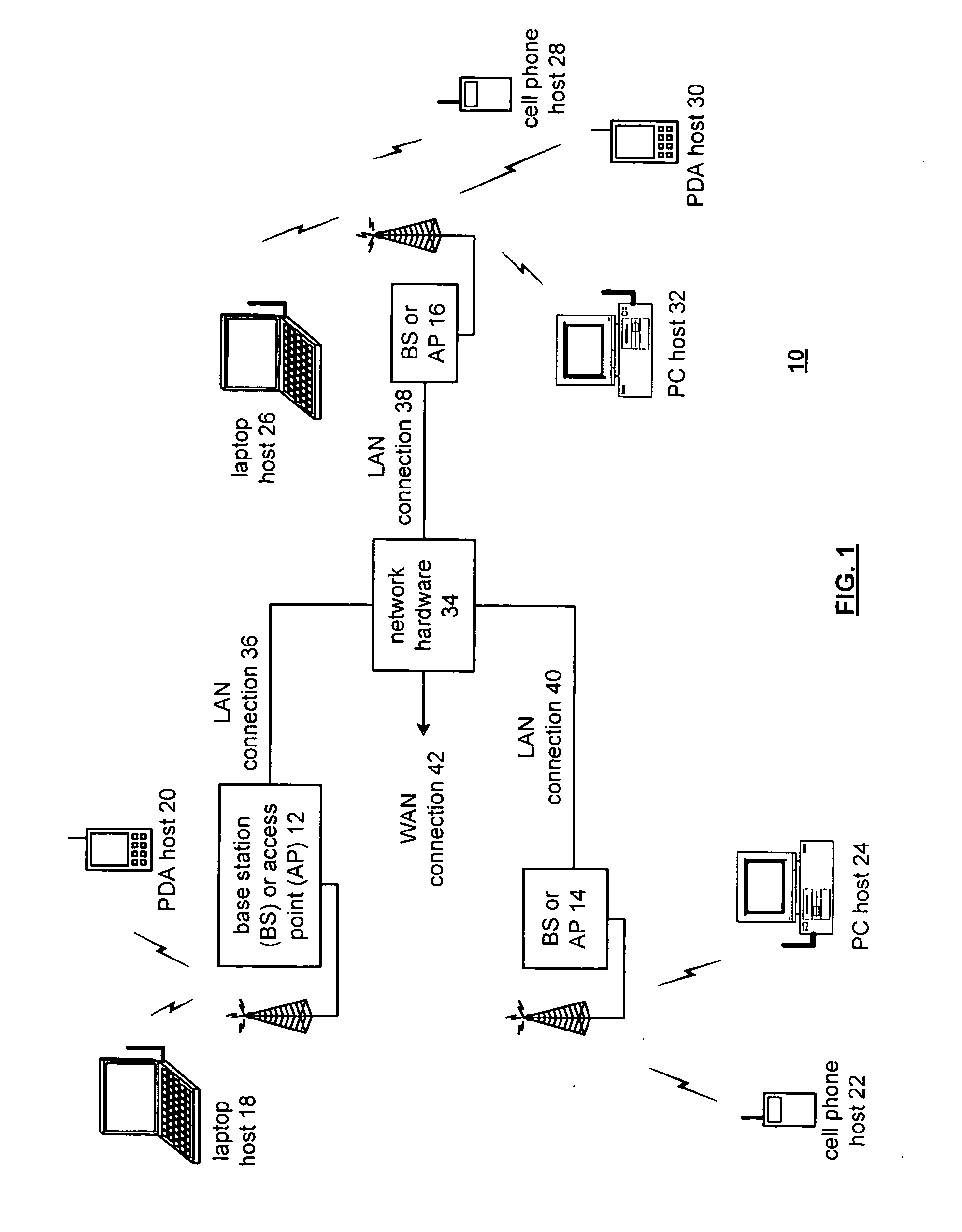
[0021]FIG. 1 illustrates a schematic block diagram of a communication system 10 that includes a plurality of base stations and / or access points 12-16, a plurality of wireless communication devices 18-32 and a network hardware component 34. The wireless communication devices 18-32 may be laptop host computers 18 and 26, personal digital assistant hosts 20 and 30, personal computer hosts 24 and 32 and / or cellular telephone hosts 22 and 28. The details of the wireless communication devices will be described in greater detail with reference to FIG. 2.
[0022] The base stations or access points 12 are operably coupled to the network hardware 34 via local area network connections 36, 38 and 40. The network hardware 34, which may be a router, switch, bridge, modem, system controller, et cetera provides a wide area network connection 42 for the communication system 10. Each of the base stations or access points 12-16 has an associated antenna or antenna array to communicate with the wireless...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com