Electromagnetic pump driving method
a technology of electromagnetic pump and electromagnetic field, which is applied in the direction of pump control, motor parameter, dynamo-electric machines, etc., can solve the problems of water hammer also producing vibration and noise, the timing of the valve closing from an opened state is slightly delayed, and the plunger movement speed is eased, and the cylinder side walls are sped up. , the effect of reducing the vibration of the cylinder side walls
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
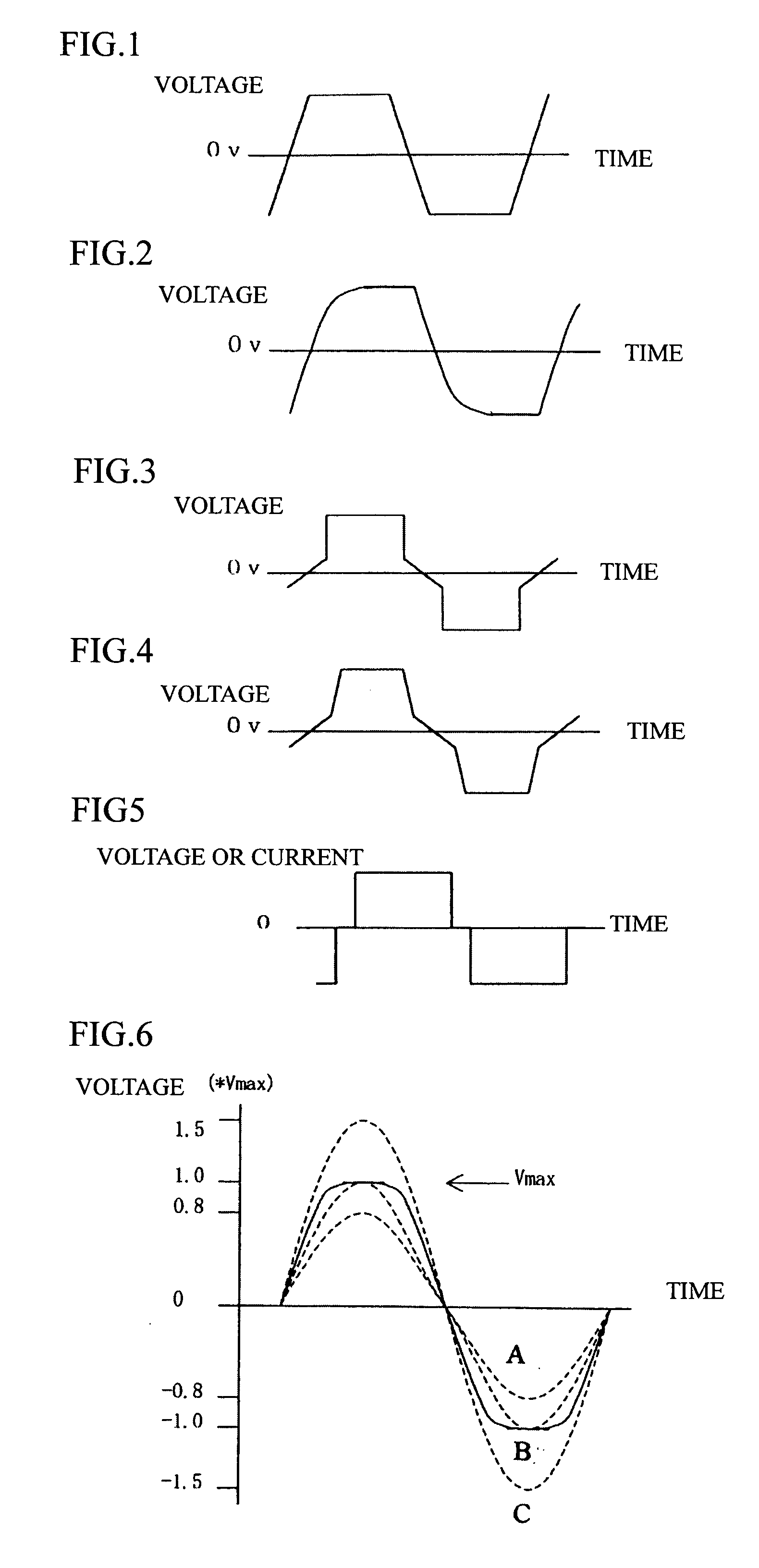
[0046] Next, to overcome the problems that accompany the opening and closing of the valves described above, preferred embodiments of a method of driving an electromagnetic pump will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 4. FIGS. 1 to 4 show voltage waveforms applied to both ends of the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b. It should be noted that the driving voltage (pulse voltage) supplied to the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b is generated by a driving control circuit, not shown, and as examples, a DC pulse voltage may be generated from a DC power supply voltage or a DC pulse voltage may be generated by rectifying an AC power supply voltage.
[0047]FIG. 1 shows the case where a pulse voltage is applied alternately on a positive side and a negative side to drive the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b such that a change in voltage that occurs when the polarity of the pulse voltage is inverted has a continuous linear slope at least between the positive side and the negative side. FIG. 2 show...
second embodiment
[0049] Next, another example of a method of driving an electromagnetic pump will be described with reference to FIGS. 5 and 6. FIGS. 5 and 6 show_voltage waveforms applied to both ends of the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b or current waveforms that flow in the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b. FIG. 5 shows the case where a sinewave-shaped pulse voltage is applied to drive the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b. By applying the sinewave-shaped pulse voltage, the change in voltage is made more gentle when the polarity is inversed, so that the speed of movement of the plunger 10 is eased and abrupt fluctuations in the pressure inside the pump chambers 30a, 30b can be reduced. By doing so, vibration of the cylinder wall surfaces due to abrupt changes in the forces that act on the inner surfaces of the pump chambers can be reduced, and vibration of the stator due to the abrupt fluctuations in the electromagnetic force that acts on the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b of the stator can be reduced...
third embodiment
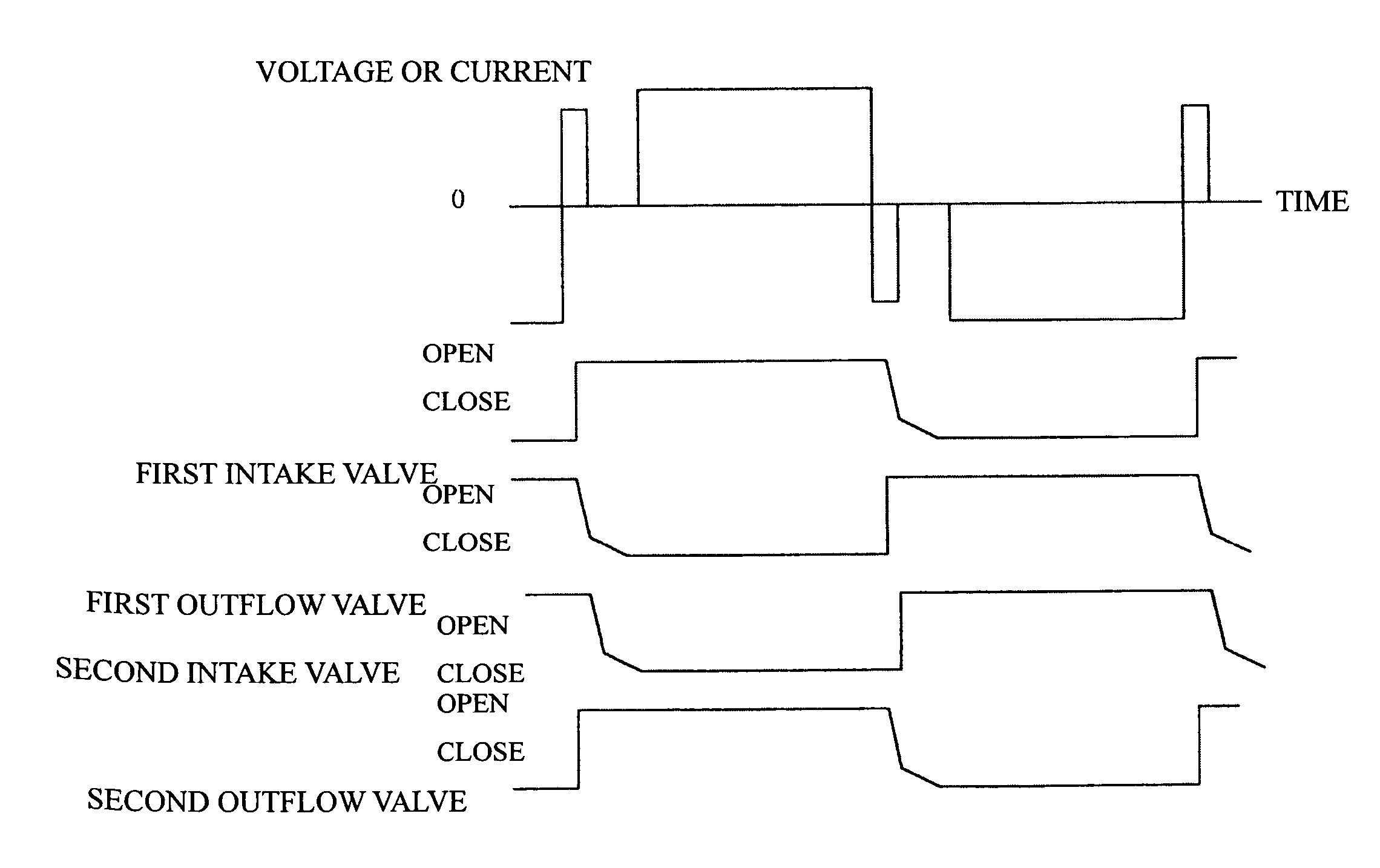
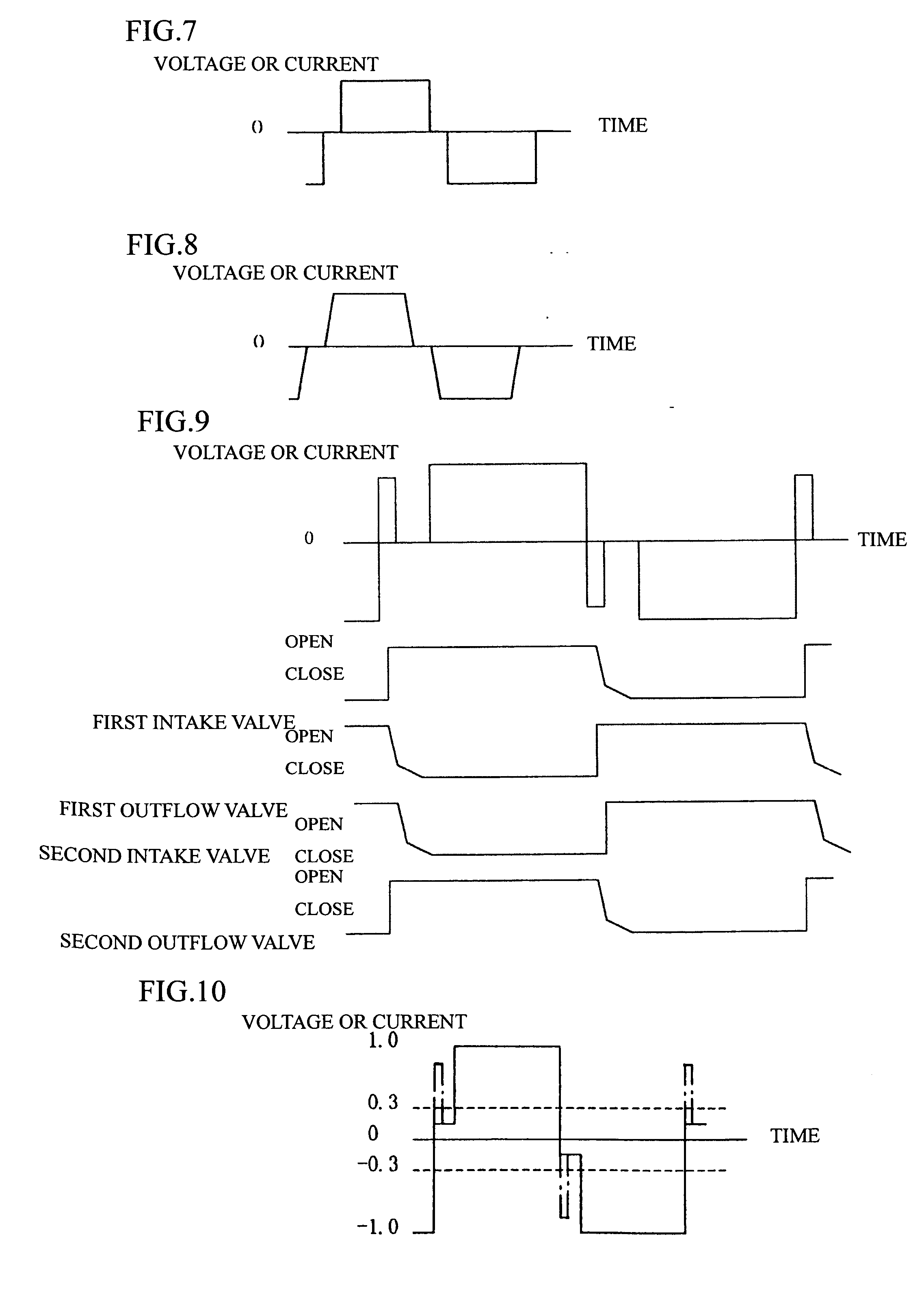
[0055] Next, another example of a method of driving an electromagnetic pump will be described with reference to FIGS. 7 to 9. FIGS. 7 to 9 show_voltage waveforms applied to both ends of the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b or current waveforms that flow in the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b.
[0056]FIGS. 7 and 8 show the case where a pulse voltage is applied or a pulse current flows so that there is a period where the voltage or current value is zero when the polarity of the driving voltage or the supplied current of the electromagnetic coils 50a, 50b is inverted. FIG. 8 shows the case where current or voltage changes with a linear slope before and after the zero voltage or zero current. By doing so, it is possible to reduce the speed of the valves opening and closing, to reduce the reverse flow, and to ease the water hammer phenomenon, and thereby to reduce the production noise and vibration. As one example, the noise level is 23 dB when the method of driving shown in FIG. 7 is used, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com