Gas filling system
a filling system and gas technology, applied in the direction of fluid pressure control, container discharging methods, packaged goods types, etc., can solve the problems of system lack of desired reliability, gas in the receiving tank does create an overheating concern, and none of the systems have recognized the benefit of controlling or the desire to control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
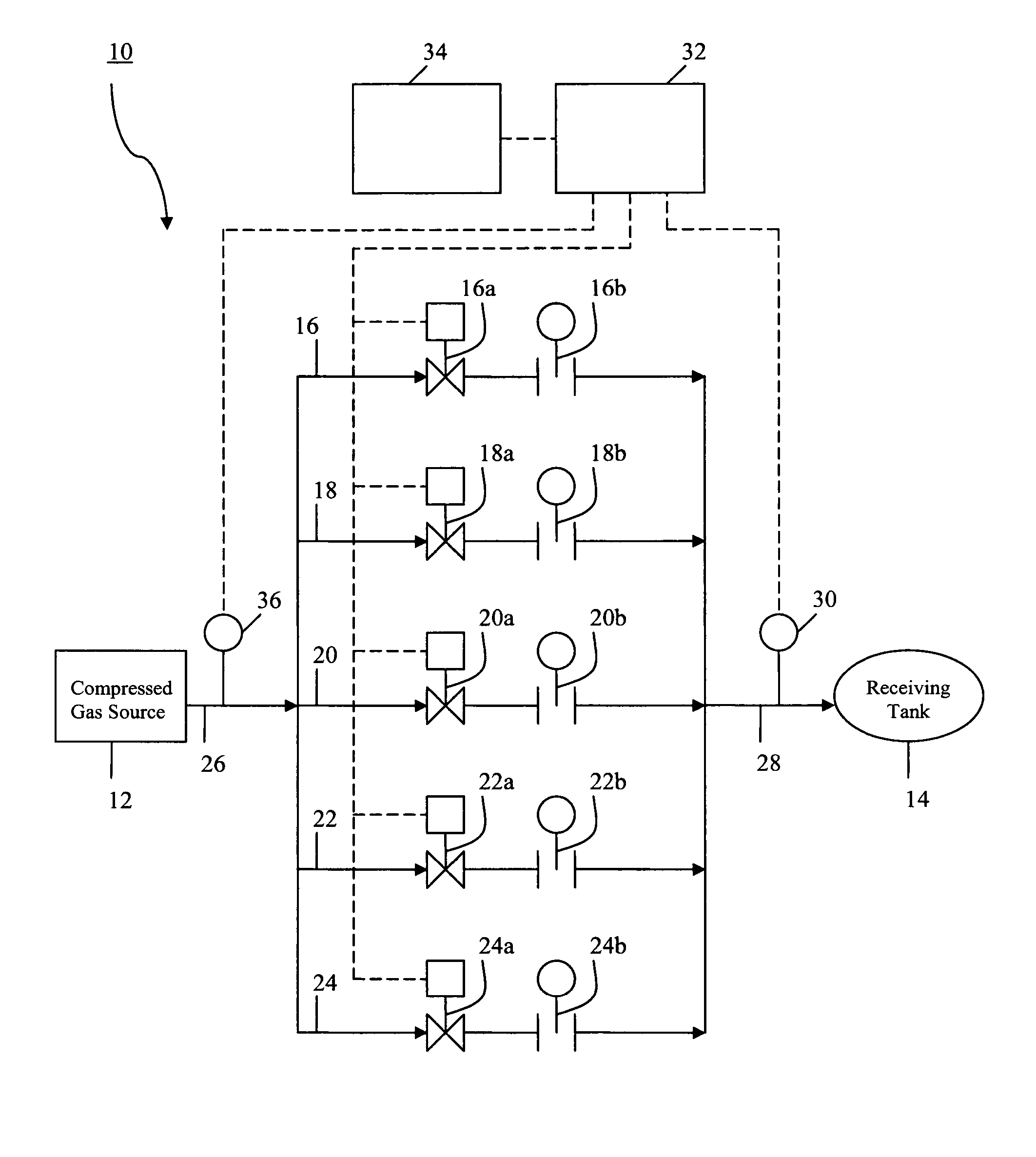
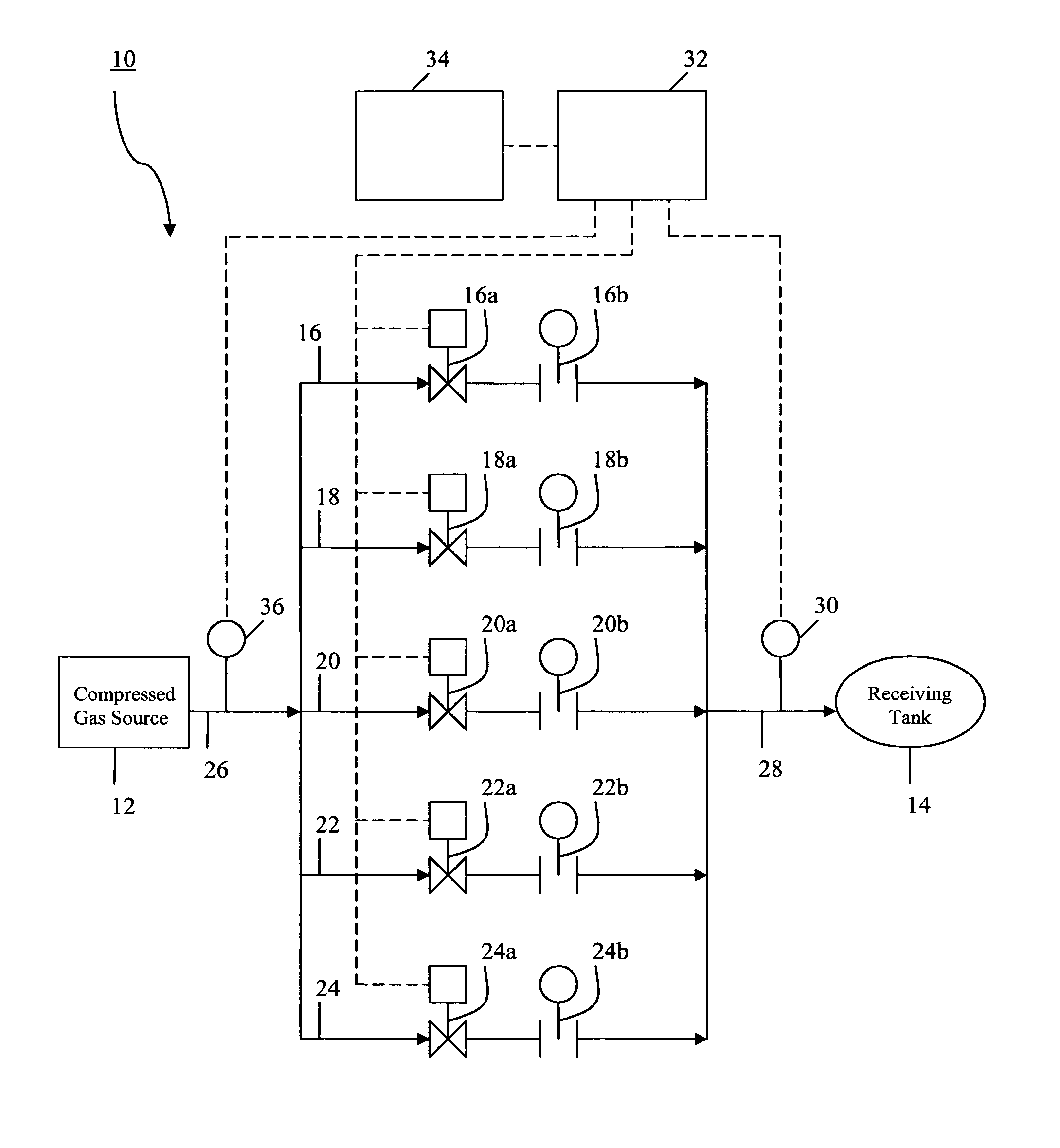
[0026] Referring to the FIGURE, a gas filling system for supplying a gas from a supply of compressed gas 12 to a receiving tank or vessel 14 is schematically illustrated at 10. The gas filling system 10 can be employed to fill a receiving vessel or tank 14 with a variety of different gases, e.g., hydrogen, helium, or natural gas. A particularly desirable use of the filling system 10 is for filling a receiving tank or vessel 14 with hydrogen, and in particular, to a system for filling a receiving tank or vessel of a vehicle with hydrogen.
[0027] Still referring to the FIGURE, the gas filling system 10 includes a supply of gas, e.g., hydrogen, from a pressurized source 12. A variety of pressurized sources can be employed, such as a single storage tank, a number of storage tanks, a pipe line supply, or a supply from a compressor. The gas is directed from the pressurized source 12 to a receiving tank 14 through a plurality of gas transmission lines in parallel with each other. In the il...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com