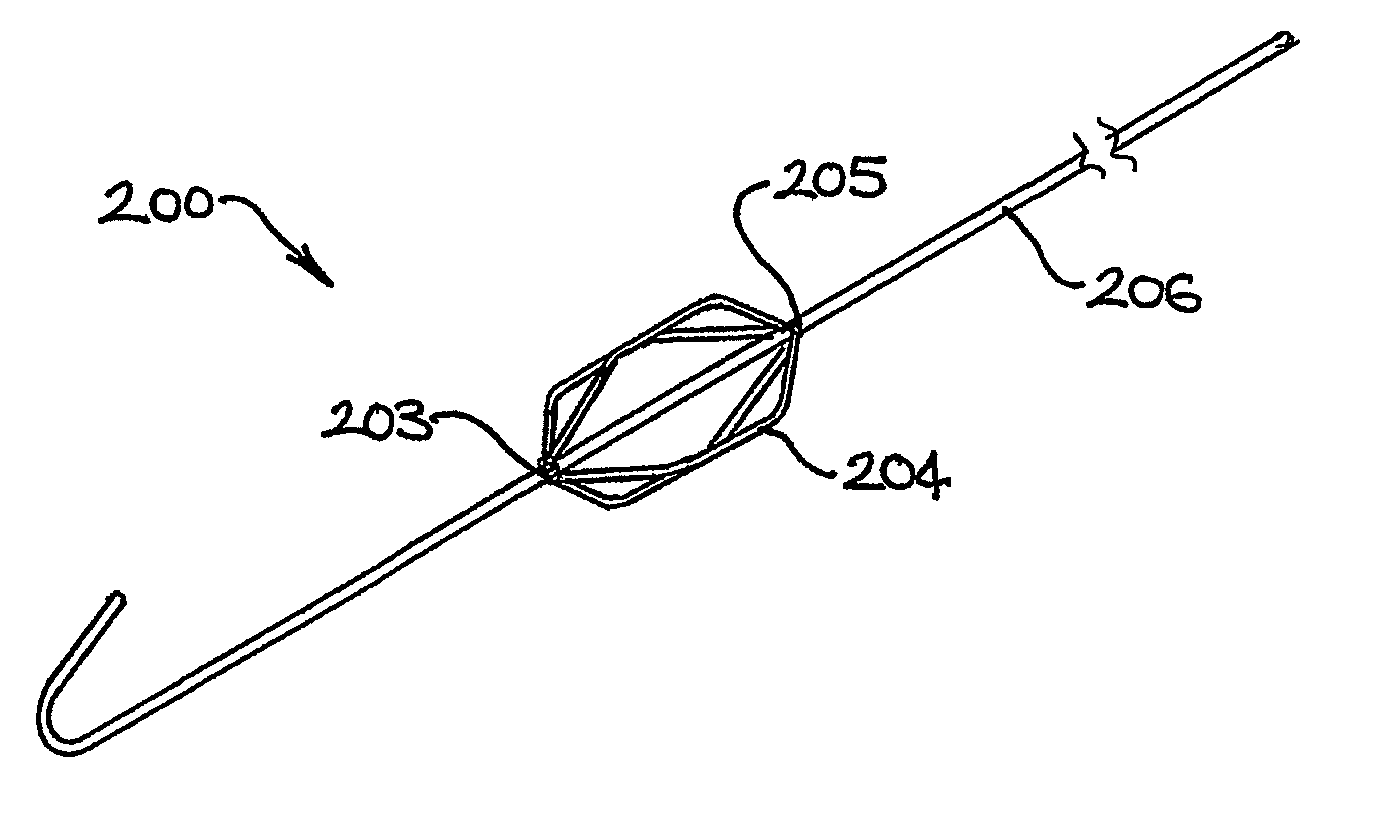
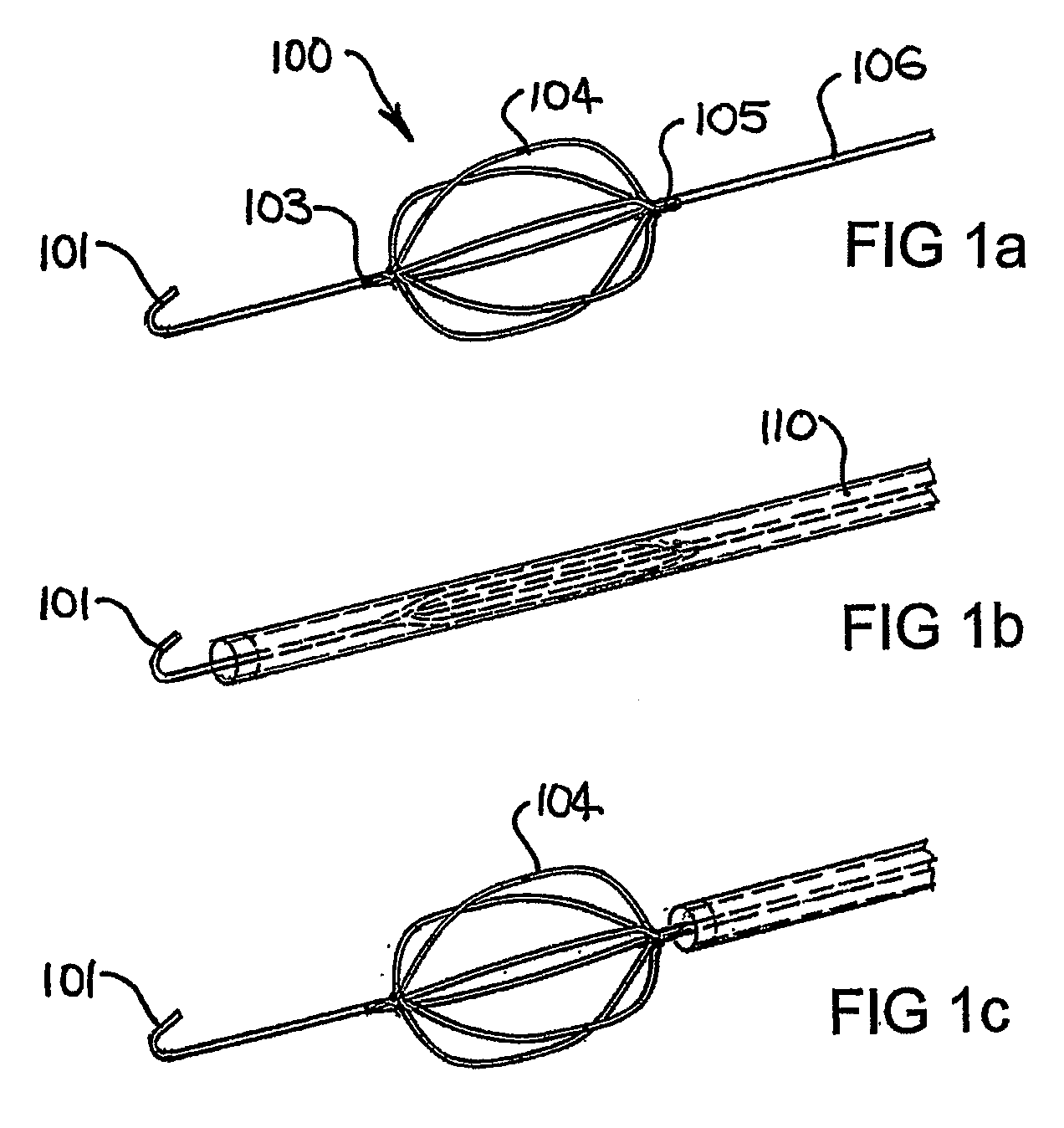
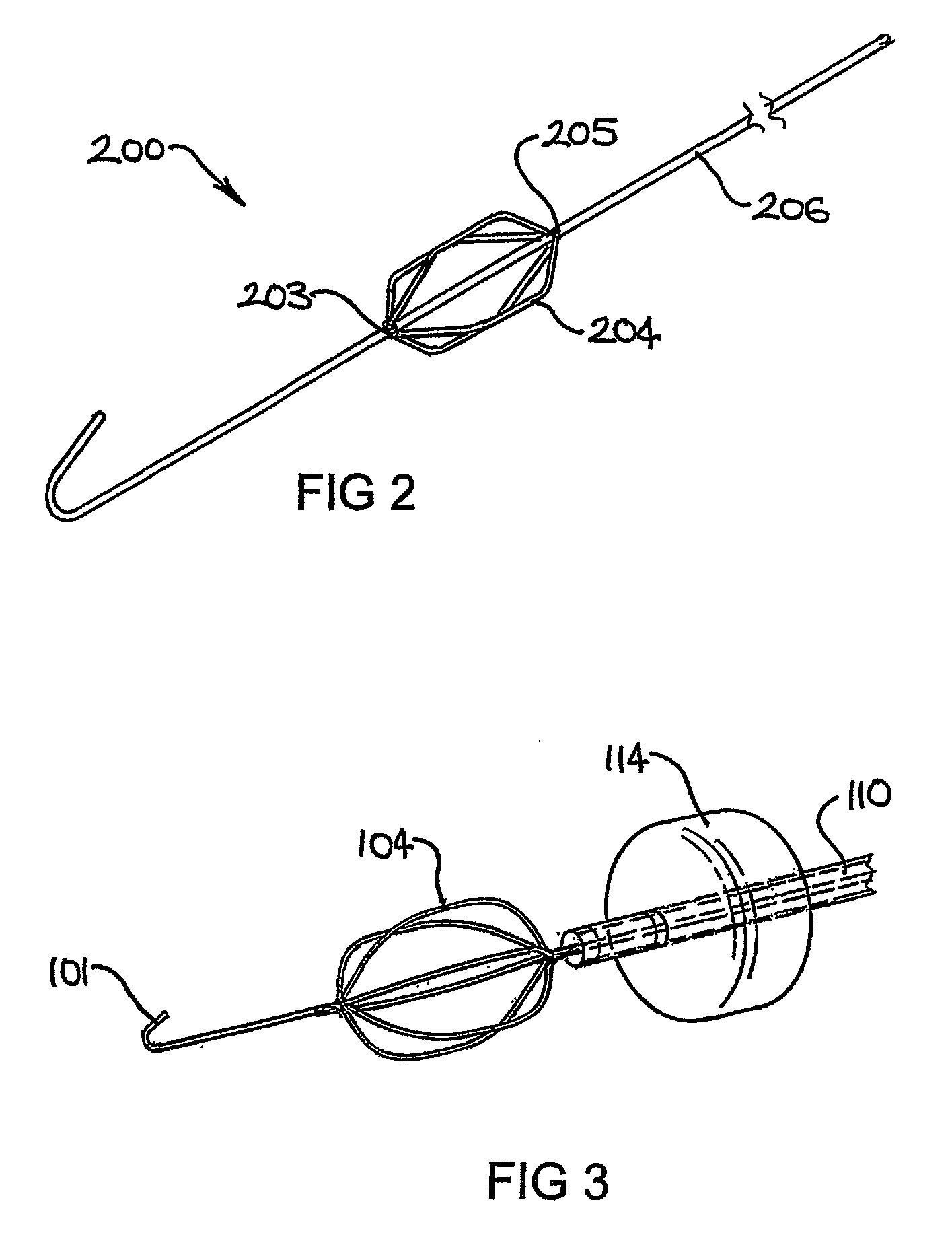
Devices and Methods for Perfusing an Organ
a technology for supporting devices and organs, applied in the field of supporting devices, can solve the problems of reduced pressure in the vessel, deformation of the vessel wall, and complete obstruction of the vessel, and achieve the effects of preventing collision of collection catheters, reducing flow rates, and maintaining patency of the vessel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effect of Support Device on Flow Rates and Pressures Achievable During Recirculation in Sheep Right Hepatic Vein, Cephalic Vein, Coronary Sinus and Renal Vein During Recirculation
[0105]A 0.014″ diameter superelastic nitinol wire stem of 1.35 m length was used, coupled to an expandable member having 6 pre-shaped elliptical loop portions welded to the stem. A 0.024″ OD atraumatic tip of 2 cm length attached to the distal end of the expandable member was used to position the device in the blood vessel. A balloon occlusion catheter was positioned in the vessel and the expandable member deployed at the tip of the catheter. The balloon was inflated to isolate and capture flows in the vessel and the catheter was connected to a standard extracorporeal circuit for blood circulation.
TABLE 1Perfusion of the right hepatic and cephalic veins.pressure (mmHg)Flowright hepatic veincephalic vein(mL / min)deviceno devicedeviceno device20−20040−10−13−11↓60−20−19−18no flow80−30−23achievable100−30−47−3212...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com