Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
a technology of semiconductor devices and semiconductor chips, applied in the field of semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of difficult to adopt layout arrangements, limit the layout arrangement of wiring elements such as pads, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the size of semiconductor chips and allowing greater latitude in layout arrangements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
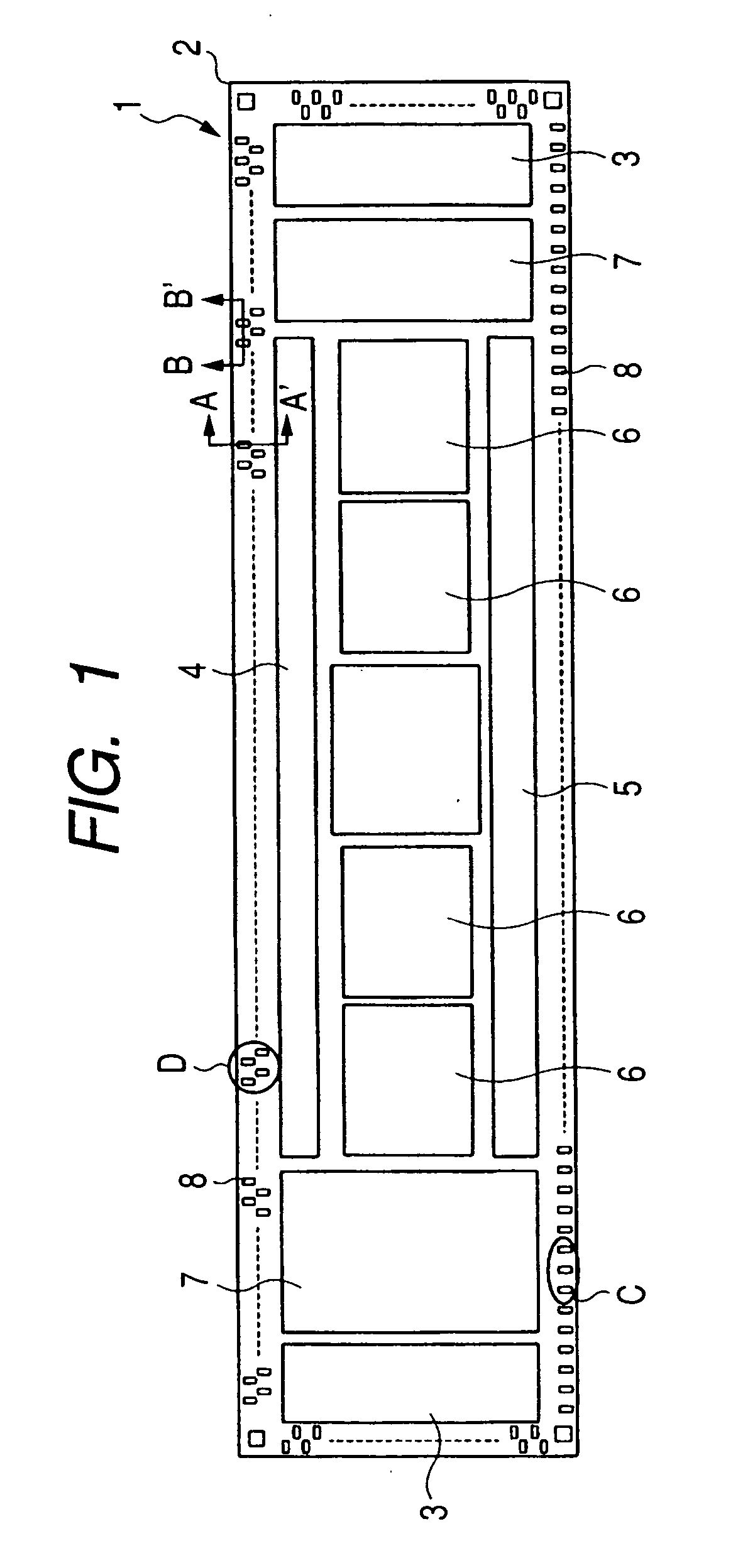
[0047]FIG. 1 is a plan view showing the structure of a semiconductor chip 1 (semiconductor device) according to the first embodiment. The semiconductor chip 1 according to the first embodiment is a driver for an LCD. Referring to FIG. 1, the semiconductor chip 1 has a semiconductor substrate 2 which takes the form of, for example, an elongated rectangle, and for example, an LCD driver which drives a liquid crystal display is formed on its main surface. This driver has the function of controlling the orientations of liquid crystal molecules by supplying voltage to each pixel in a cell array constituting the LCD and includes gate drive circuits 3, a source drive circuit 4, a liquid crystal circuit 5, graphic RAMs (Random Access Memories) 6, and peripheral circuits 7.
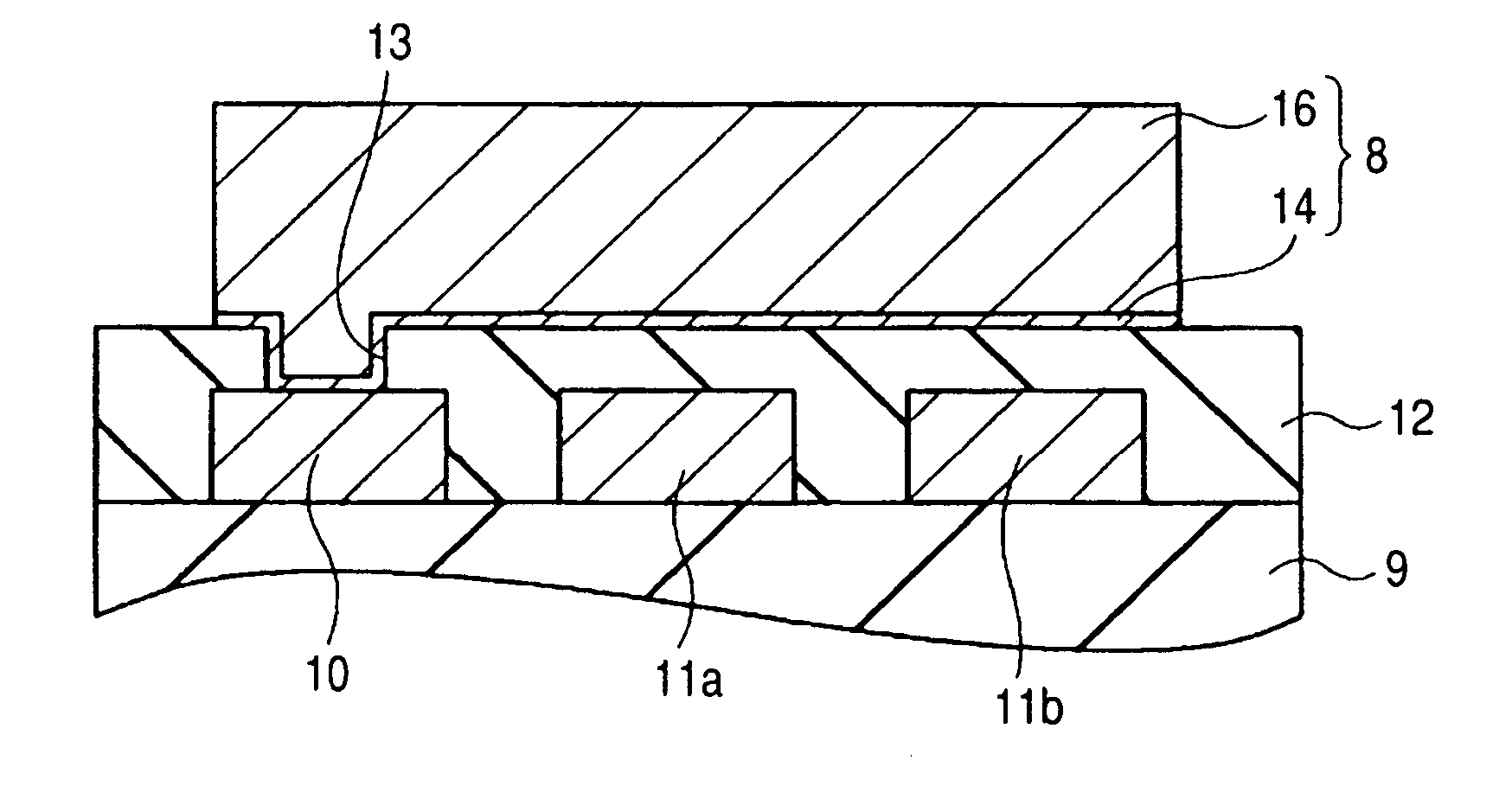
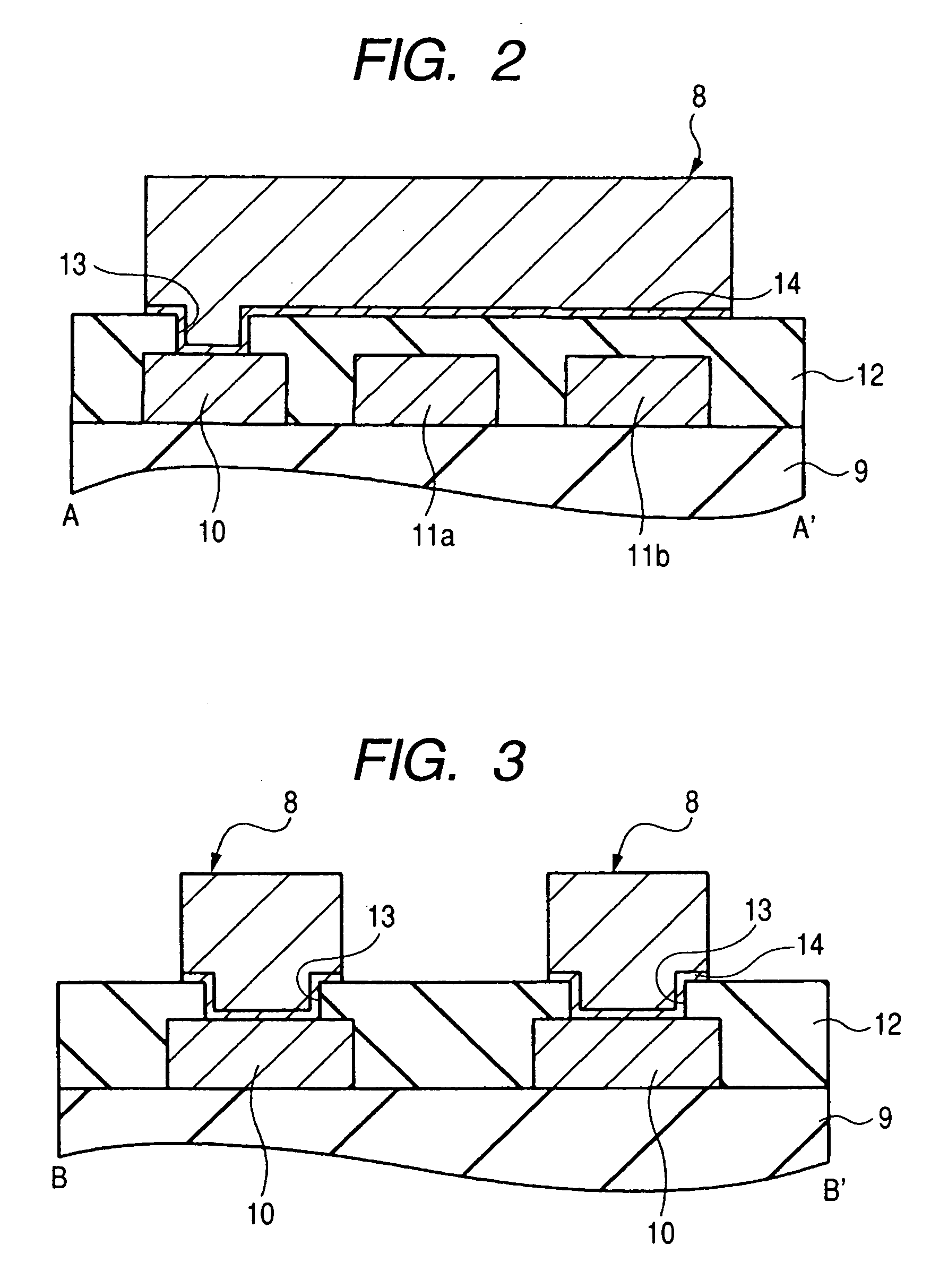
[0048] In the vicinity of the periphery of the semiconductor chip 1, a plurality of bump electrodes 8 are arranged at regular intervals along the periphery of the semiconductor chip 1. These bump electrodes 8 lie over act...
second embodiment
[0076] The second embodiment concerns a semiconductor device with wide layout latitude which optimizes pad positions regardless of bump electrode positions.
[0077]FIG. 20 is a fragmentary plan view of a semiconductor chip according to the second embodiment. Referring to FIG. 20, a pad 10 is connected with a pad connection portion 8a as a part of a bump electrode 8 through an opening 13 made in a surface protective film 12. The bump electrode 8 consists of: a pad connection portion 8a to be connected with the pad 10; a terminal connection portion 8c to be connected with a terminal of a packaging substrate; and a wiring portion 8b which connects the pad connection portion 8a and the terminal connection portion 8c. A conventional bump electrode consists of only a terminal connection portion which is connected with a pad. In other words, in a conventional bump electrode, the terminal connection portion also functions as a pad connection portion, which means that the pad connection porti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com