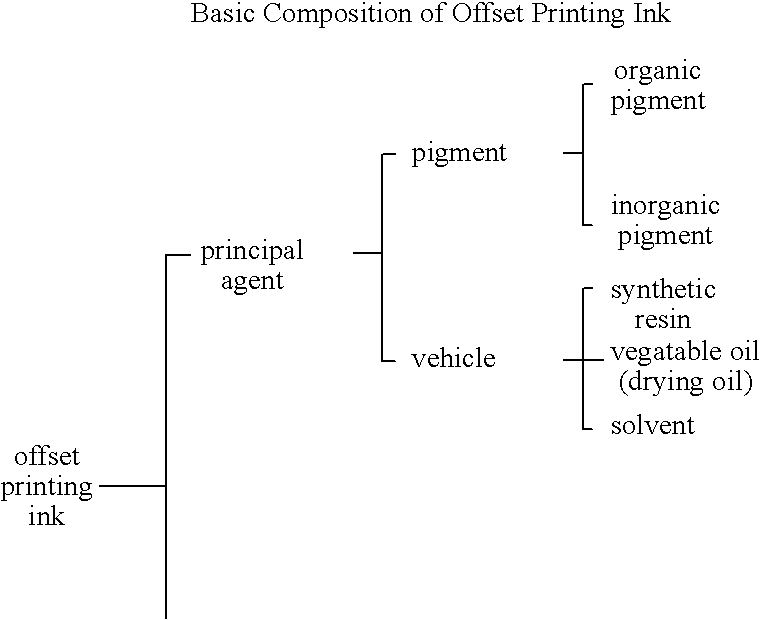
Stretched resin film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0229] The amorphous resin, the polyolefinic resin and the inorganic fine powder, that are indicated in Table 3, were admixed in amounts shown in Table 3 to prepare composition (A). Composition (A) was melted and kneaded in an extruder set to 270° C., extruded through a die to obtain a sheet, and cooled by a cooling device to obtain an unstretched sheet. This sheet was heated to 155° C. and longitudinally stretched five-fold by exploiting the difference in peripheral speed of a group of rolls. The five-fold stretched sheet was then heated to 155° C., transversely stretched 7.5-fold with a tenter, and annealed at 163° C., yielding a single-layer film. The surface of the single-layer film was treated by corona discharge, yielding a stretched film of single-layer structure consisting solely of layer (A) (having a film thickness of 150 micrometers).
example 2
[0230] The amorphous resin, the polyolefinic resin and the inorganic fine powder, that are indicated in Table 3, were admixed in amounts shown in Table 3 to prepare composition (A). Separately, 40 wt % of heavy calcium carbonate (E) was added to a mixture containing 50 wt % of propylene homopolymer (1) and 10 wt % of high-density polyethylene (γ) to obtain composition (B). Heavy calcium carbonate (E), propylene homopolymer (β 1) and high-density polyethylene (γ) are indicated in Table 2.
[0231] Compositions (A) and (B) were melted and kneaded in separate extruders set to 270° C., laminated in a die to achieve the configuration (B) / (A) / (B), coextruded through a single die, and cooled by a cooling device to obtain an unstretched sheet. This sheet was heated to 155° C. and longitudinally stretched five-fold by exploiting the difference in peripheral speed of a group of rolls. The three-layer laminate was heated to 155° C., transversely stretched 7.5-fold with a tenter, and annealed at ...
example 3
[0232] The amorphous resin, the polyolefinic resin and the inorganic fine powder, that are indicated in Table 3, were admixed in amounts shown in Table 3 to prepare composition (A). Composition (A) was melted and kneaded in an extruder set to 270° C., extruded through a die to obtain a sheet, and cooled by a cooling device to obtain an unstretched sheet. This sheet was heated to 150° C., longitudinally stretched five-fold by exploiting the difference in peripheral speed of a group of rolls, and annealed at 155° C. to obtain a single-layer film. The surface of the single-layer film was treated by corona discharge, yielding a stretched resin film of single-layer structure consisting solely of layer (A) (having a film thickness of 150 micrometers).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com