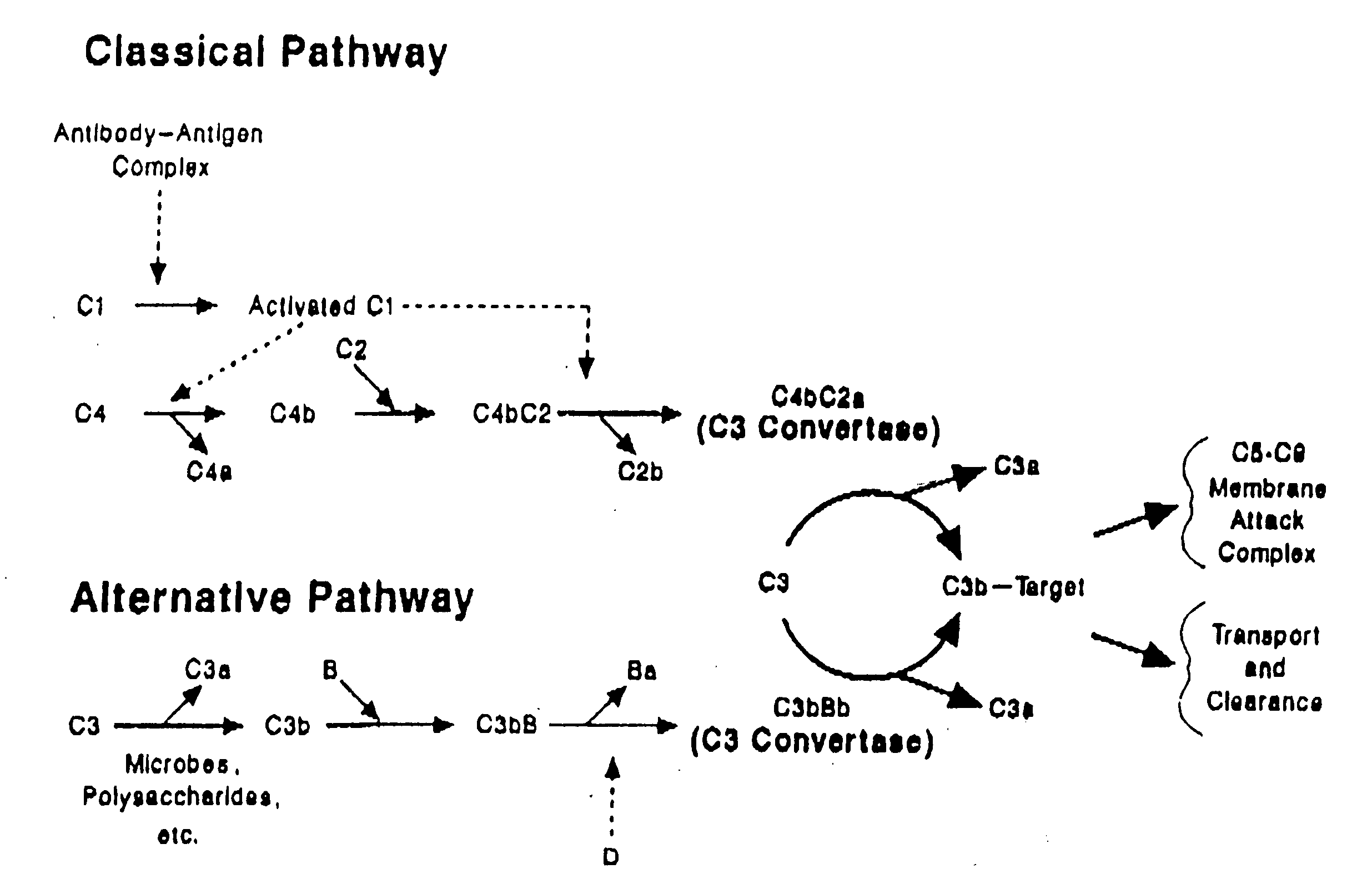
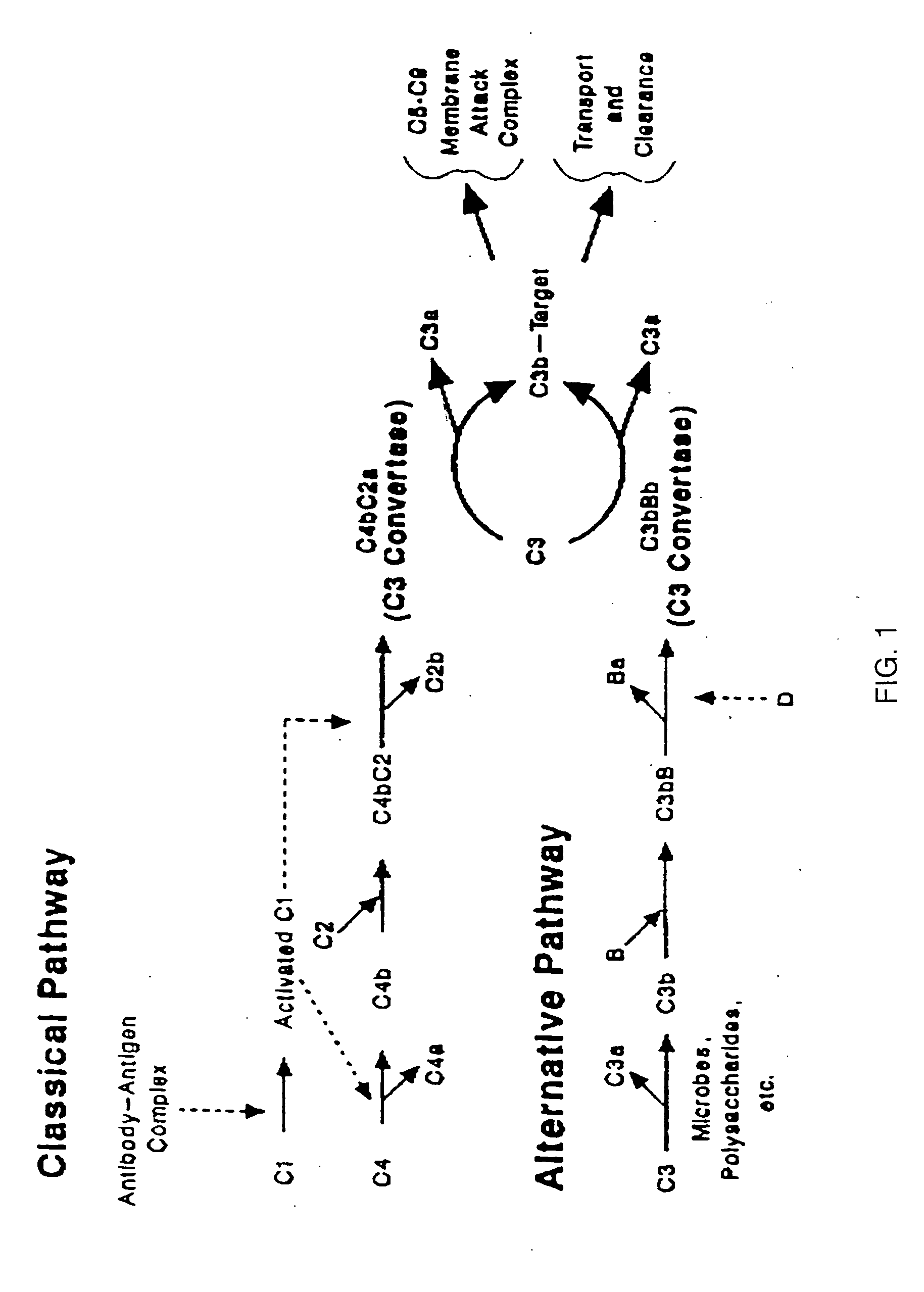
Modified truncated complement system regulators
a complement system and regulator technology, applied in the field of modified and/or shortened forms of complement system regulators, can solve the problem that the complete inhibition of the complement system on a long-term basis is not likely to be desirable in most individuals, and achieve the effect of reducing tissue damage and suppressing transplant rejection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Binding Specificity of Truncated CR1
[0108]The cDNA which encodes the first 543 amino acids of mature CR1 (SCR 1-8 and ½ of SCR-9) was transfected into COS cells to obtain a secreted protein designated CR1-4.
[0109]Two mouse monoclonal anti-CR1 antibodies were used to determine the immunoreactivity of CR1-4, and as a method to assay for this protein. Antibody E11 (Hogg, N., et al., Eur. J. Immunol. (1984) 14:236-243), and 3D9 (O'Shea, J. J., et al., J. Immunol. (1985) 134:2580-2587), recognized CR1 and bound to the recombinantly produced CR1-4.
[0110]Binding to C4b or to C3b was tested using either C4b or iC3 (C3 containing a broken thioester bond analogous in reactivity and function to C3b) bound to a Sepharose™ support as described by Dykman, T., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1983) 80:1698-1702, and Cole, J. L., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1985) 82:859-863. Binding to these solid-supported substrates was verified by testing with an ELISA for CR1.
[0111]The C4b derivatize...
example 2
Construction of CR1-4 Analogs
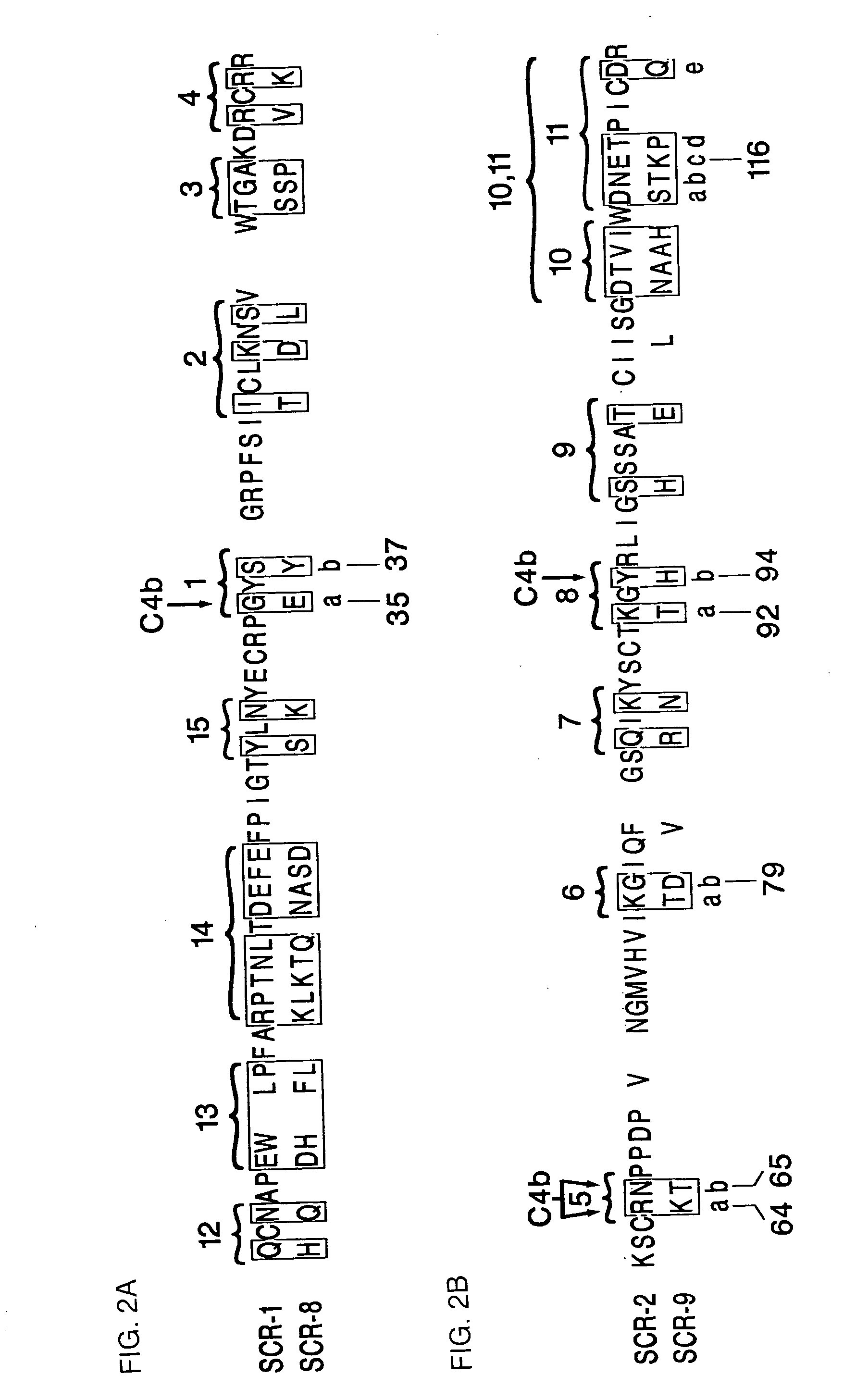
[0113]Various mutated forms of CR1-4 were constructed and tested for binding activity to C4b and iC3 as described above in Example 1. Table 2 shows the analogs constructed and the binding and cofactor activities of the analogs. In Table 2, the modifications are shown by the number of the amino acid and the conversion effected. The numbers correspond to those set forth in FIGS. 2A and 2B and FIGS. 3A and 3B which set forth the amino sequences of SCR-1 (SEQ ID NO: 1), SCR-2, (SEQ ID NO: 3) SCR-8 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and SCR-9 (SEQ ID NO: 4) in CR1.
[0114]The combined changes shown in truncated forms should be predictive of the activity of a modified full length protein. There is strong evidence available that establishes three primary binding and cofactor sites in the major polymorphic form (30 SCRs) of CR1. One site interacts almost exclusively with C4b (SCRs 1-4) while the other two sites, nearly identical in amino acid sequence, interact with both C4b and C3b ...
example 5
DAF Analogs
[0133]The membrane-bound complement regulator DAF facilitates the dissociation of C3b and C4b-containing convertases but does not bind C3b or C4b, nor does it serve as cofactor for factor I-mediated proteolytic inactivation of C3b or C4b. It would be desirable, under certain situations, to increase the complement regulatory activity of DAF or of truncated, recombined or hybrid forms of DAF.
[0134]Based on amino sequence homology, DAF SCRs 2-3 corresponds to the CR1 active regions. Homology between DAF SCRs 2-3 and CR1 SCRs 1-2 is 40% while homology between DAF SCRs 2-3 and CR1 SCRs 8-9 is 39%. Since there are several unmatched amino acids in these alignments, the position numbers of DAF do not precisely match those of CR1.
[0135]One or more substitutions are introduced into the DAF SCRs 2-3. Specific substitutions designed to confer C3b and C4b cofactor activity and binding activity are selected from the following:
[0136]DAF position(s) enumerated as in Lublin and Atkinson, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| internal diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com