Methods and compositions for treating post-cardial infarction damage
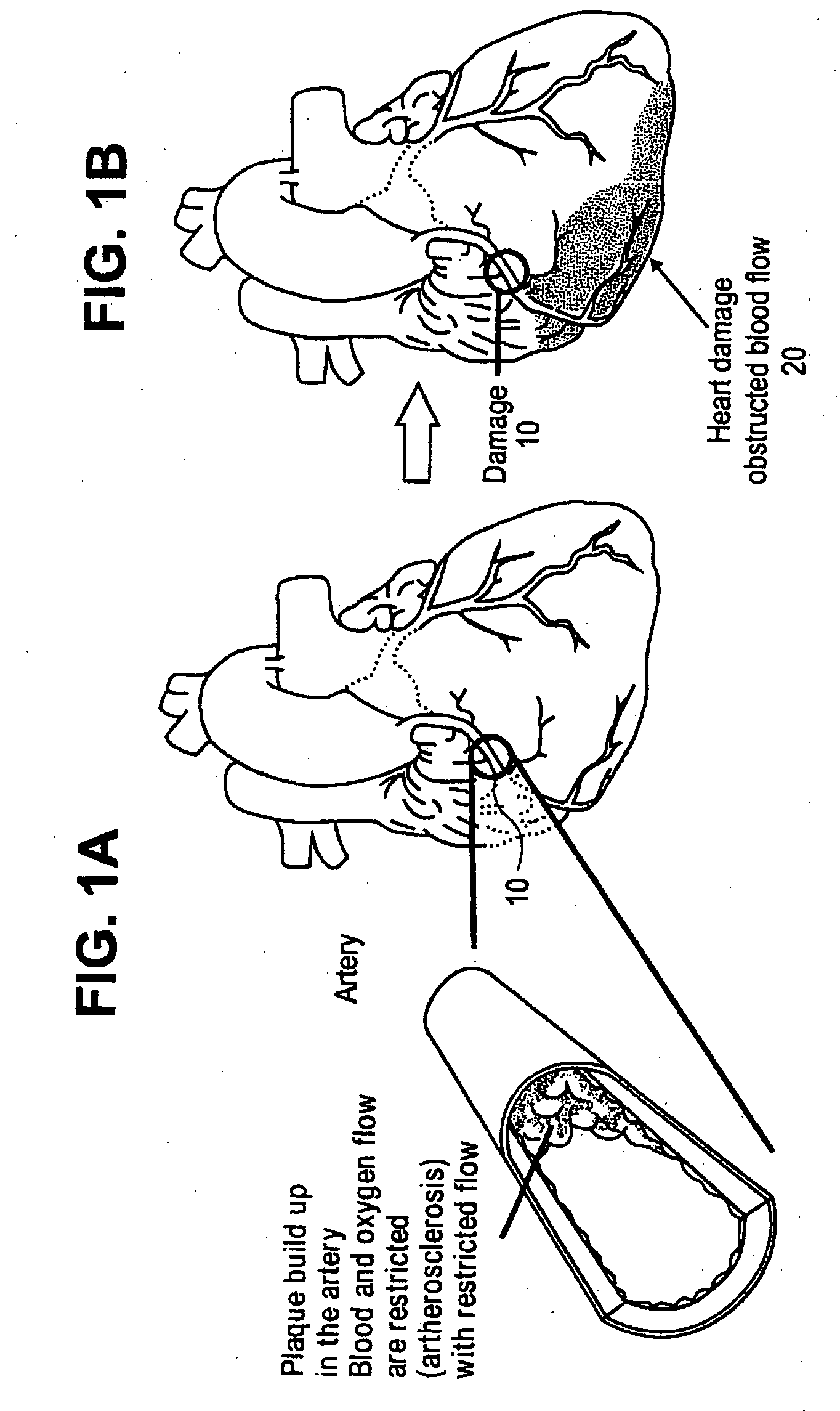
a post-infarction and composition technology, applied in the field of myocardial infarction treatments and compositions, can solve the problems of affecting blocking the flow of blood, and blood clots within the artery, so as to shorten the separation distance of the needle tips
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
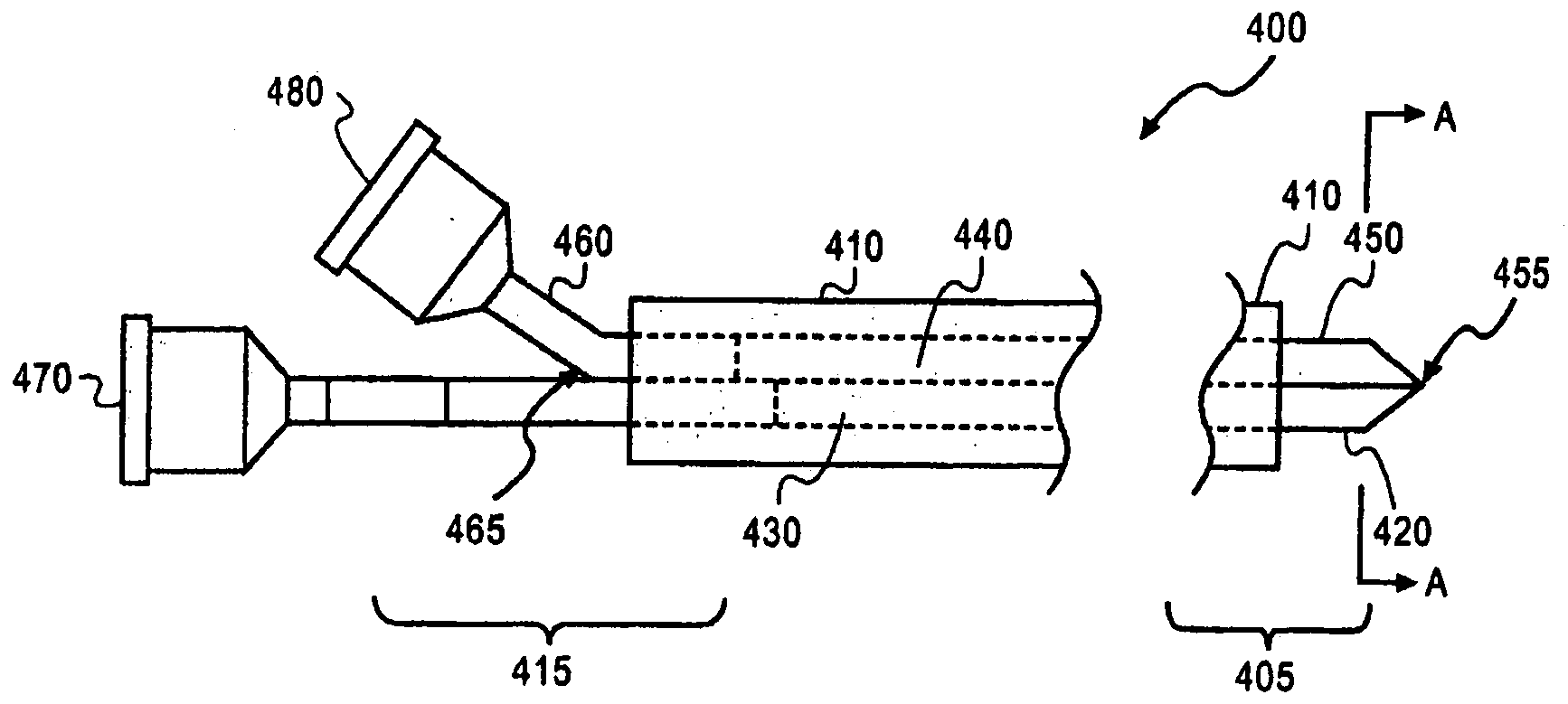
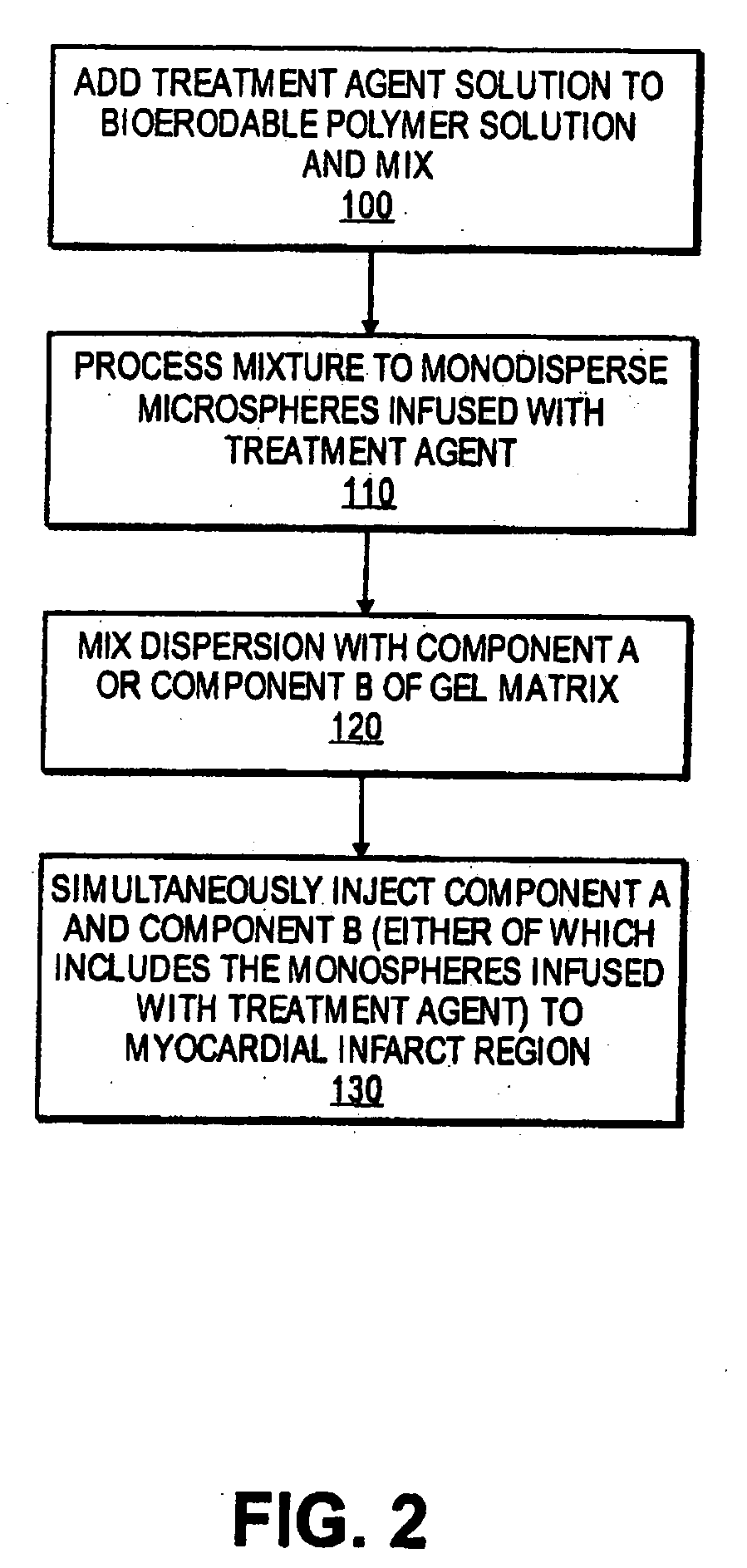
[0056]In one embodiment, collagen electrospun fibers can be processed to a range from about 200 nm and about 1300 nm. The range of electrospun fibers is approximately the range of naturally occurring type 1 and type 3 fibers which make up the heart matrix. Thus, the electrospun fibers may mimic endogenous fibers and accelerate growth of repair tissue to the infarct region, in particular, on the heart. The fibers can be dispersed throughout one component of a two-component gel. The two components can then be delivered to myocardial infarct region. The fibers can provide “docking sites” for endogenous myocardial stem cells and encourage their differentiation into cardiomyocytes. The gel can provide temporary containment of the fibers and prevent premature removal by macrophage cells.
[0057]The fibers can be fabricated such that they include an agent or no agent. Examples of agents can include a chemoattractant, such as SDF-1, or a cell survival promoting factor, such as IGF-1. In one e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com