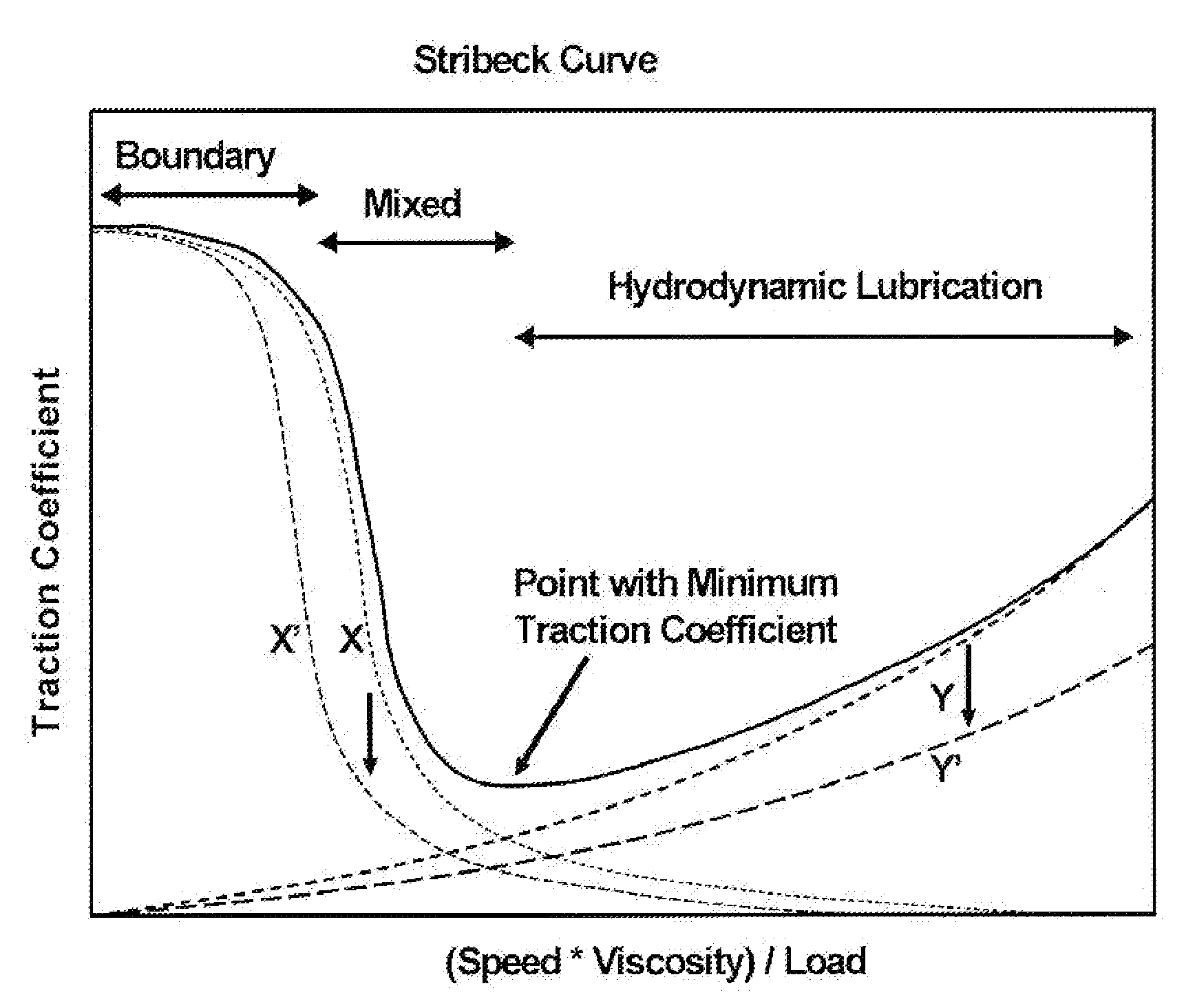
Traction coefficient reducing lubricating oil composition
a technology of lubricating oil and traction coefficient, which is applied in the direction of hydrocarbon oil treatment, lubricant composition, base materials, etc., can solve the problems of increasing wear at lower contact speeds, and achieve the effect of reducing the traction coefficient in internal combustion engines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0133]Comparative Formulations A and B and Test Formulation C were prepared as described in Table II below.
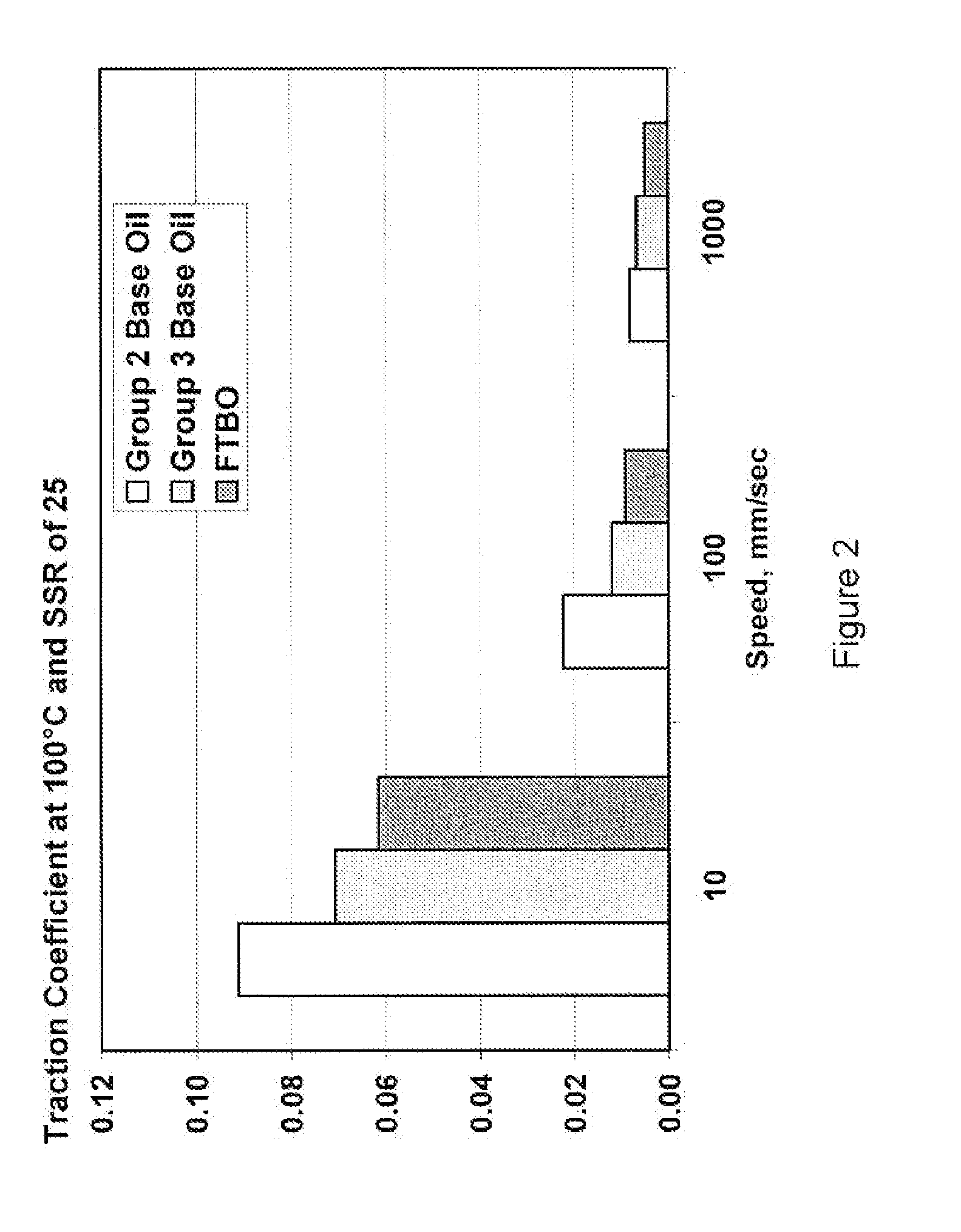
TABLE IIIComponentComparativeComparativeTest(wt %)Formulation AFormulation BFormulation CBase OilGroup IIGroup IIIFischer-TropschDerived BaseOilBorated Succinimide3.03.03.0DispersantEthylene Carbonate555Treated SuccinimideDispersantLow Overbased0.70.70.7CalciumSulfonate DetergentMedium Overbased2.42.42.4Calcium SalicylateDetergentHigh Overbased0.90.90.9Sulfurized CalciumPhenate DetergentZinc Di-thiophosphate1.61.61.6Anti-wearDi-phenylamine Anti-0.50.50.5oxidantPhenolic Anti-oxidant0.50.50.5Molybdenum0.40.40.4SuccinimideAnti-oxidantFoam Inhibitors0.160.160.16
example 2
Coefficient of Traction Measurements
[0134]The ability to reduce the coefficient of traction of Text Formulation C was compared to Comparative Formulations A and B was evaluated as described below.
[0135]Comparative Formulations A and B were compared with Test Formulation C in a series of Ball-on-Disk Rheometer experiments. As noted in Table II above, the three Formulations differ only in the selection of the base oils used to make the formulations. The rheometry experiments were designed to measure the traction coefficient under a variety of different conditions. The main variables were:[0136]1. Slide to Roll Ratio (SRR)—which varied from 25 to 50, and to 75.[0137]2. Temperature—all measurements were conducted at a temperature of 100° C. and repeated at a temperature of 120° C.
[0138]3. Pressure—was measured in a configuration with a 19.05 mm diameter steel ball on a flat steel disk, both made of AISI-SAE 52100 steel with Young's Modulus of 207 GPa and Poisson Ratio 0.293, at an appli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com