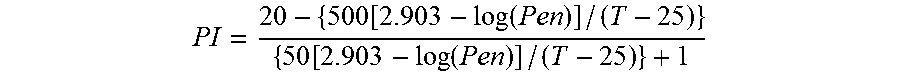Patents
Literature
33 results about "Rheometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
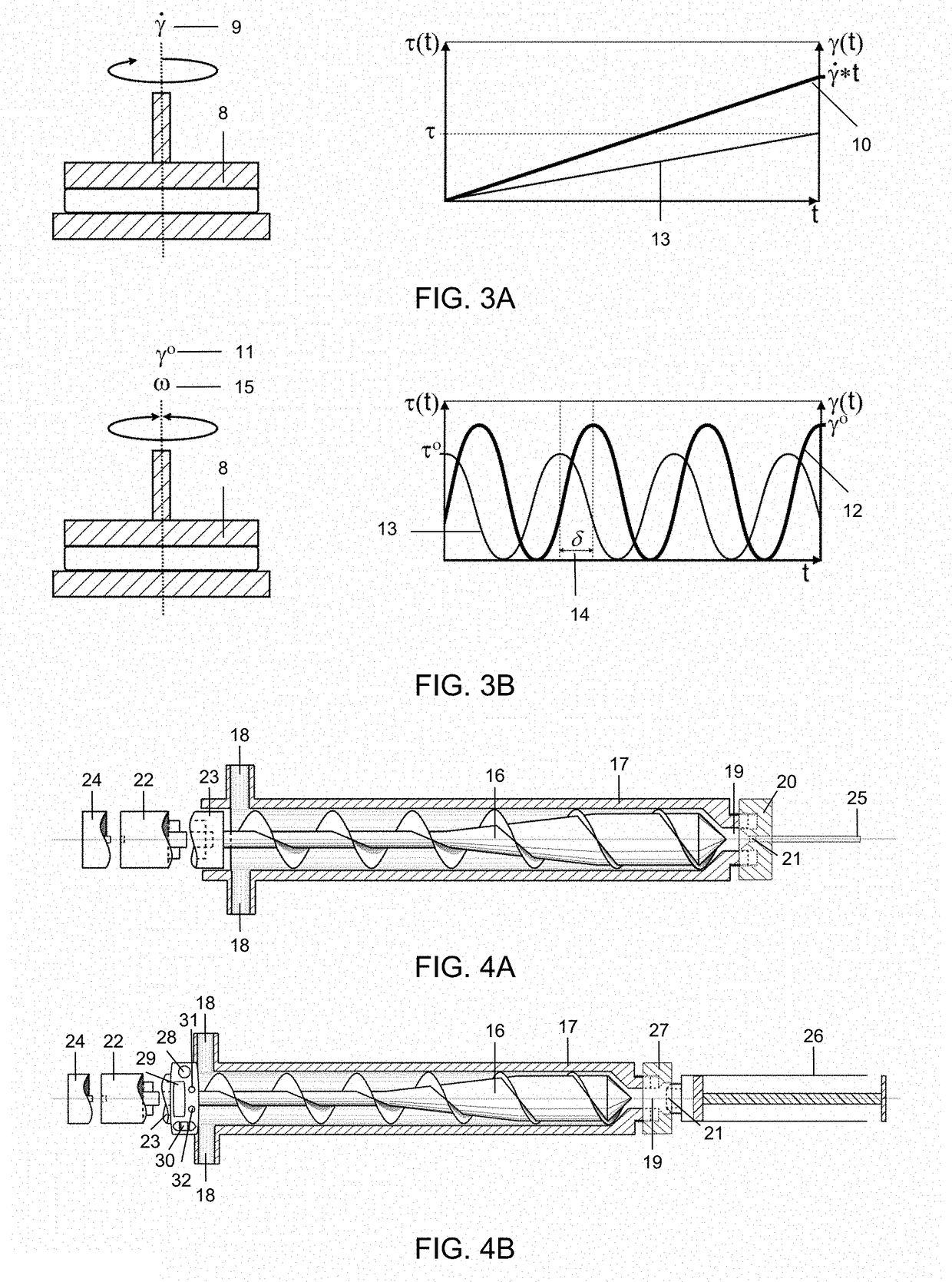
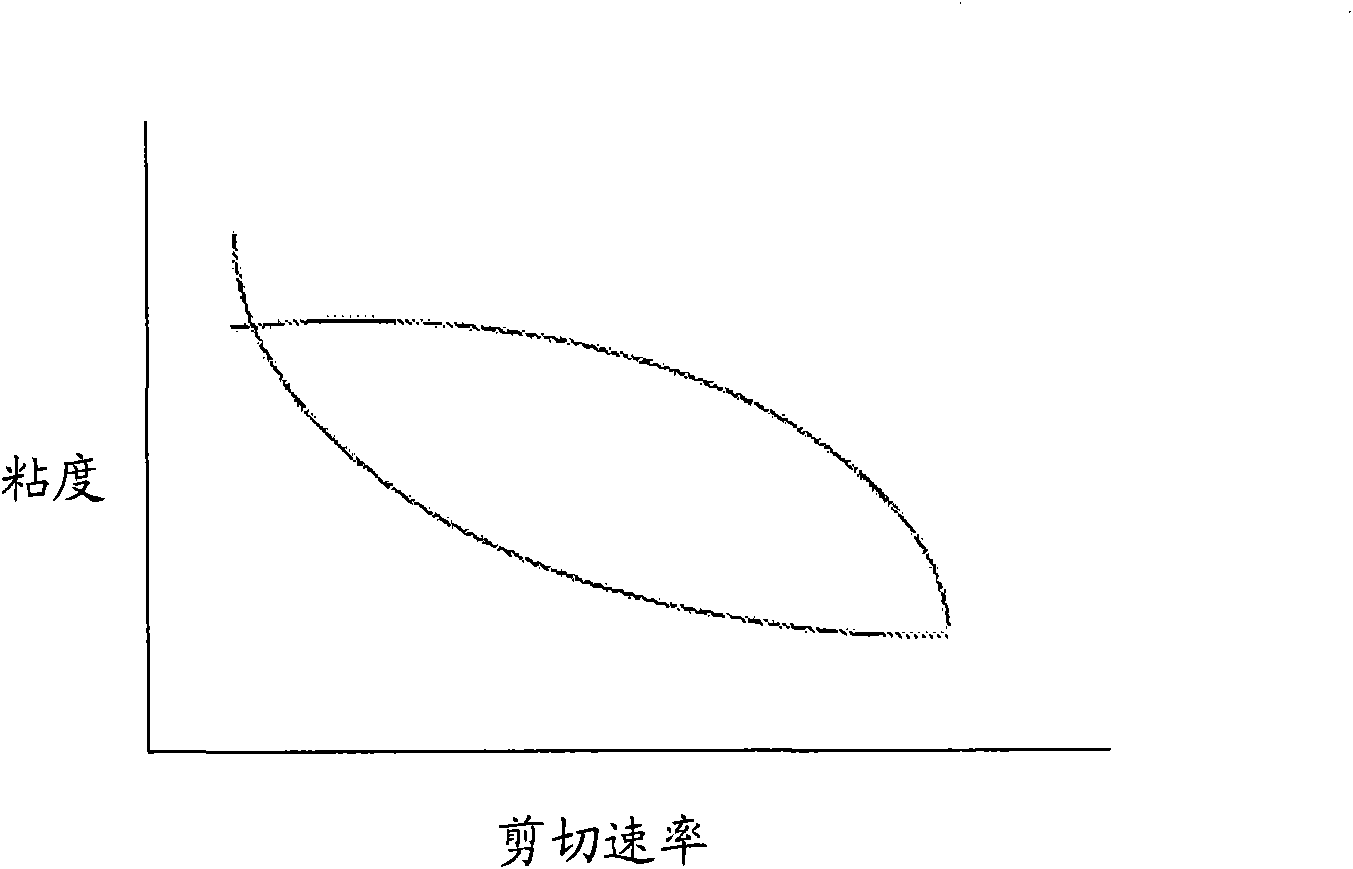
Rheometry (from the Greek ῥέος – rheos, n, meaning "stream") generically refers to the experimental techniques used to determine the rheological properties of materials, that is the qualitative and quantitative relationships between stresses and strains and their derivatives. The techniques used are experimental. Rheometry investigates materials in relatively simple flows like steady shear flow, small amplitude oscillatory shear, and extensional flow.
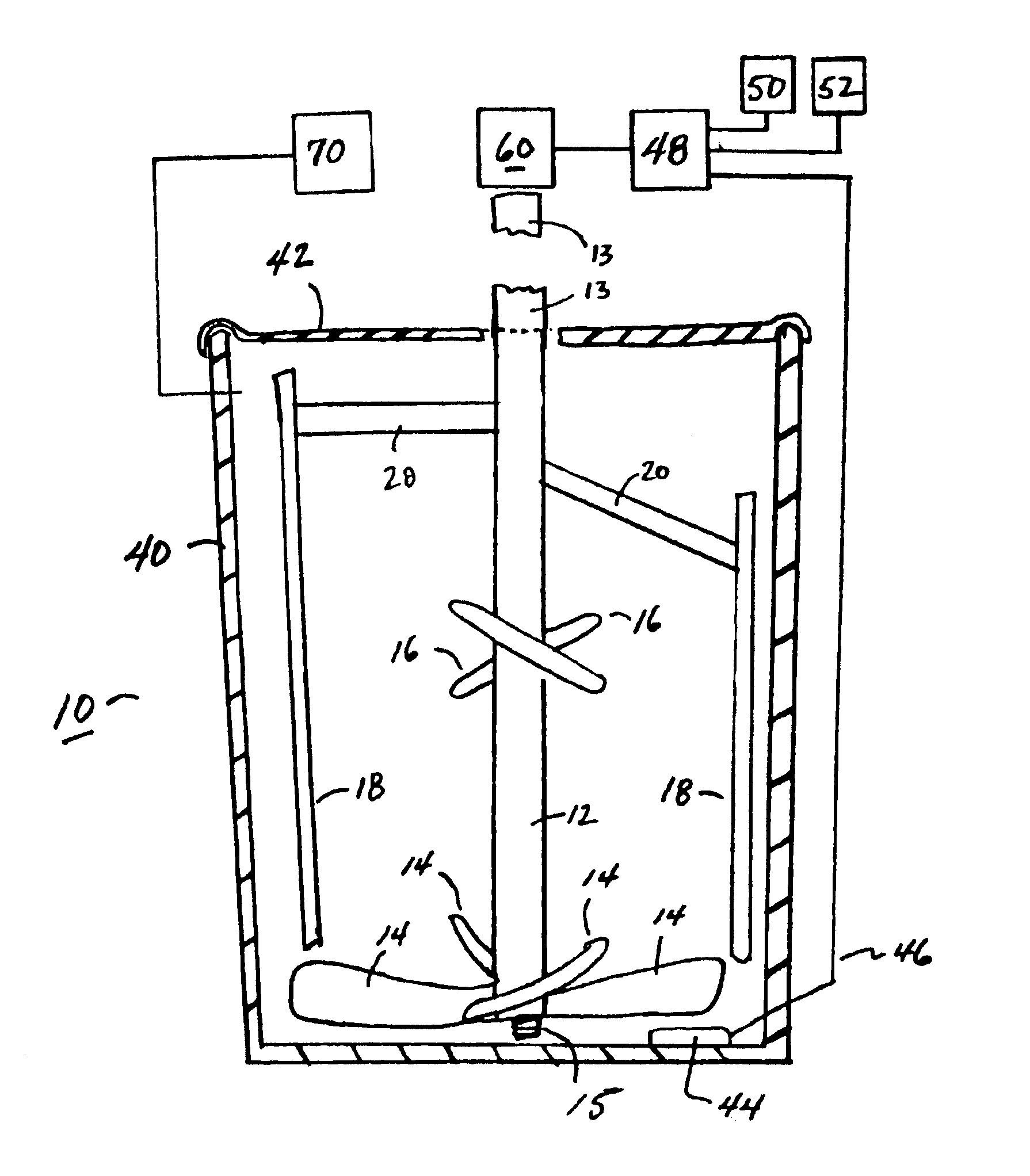
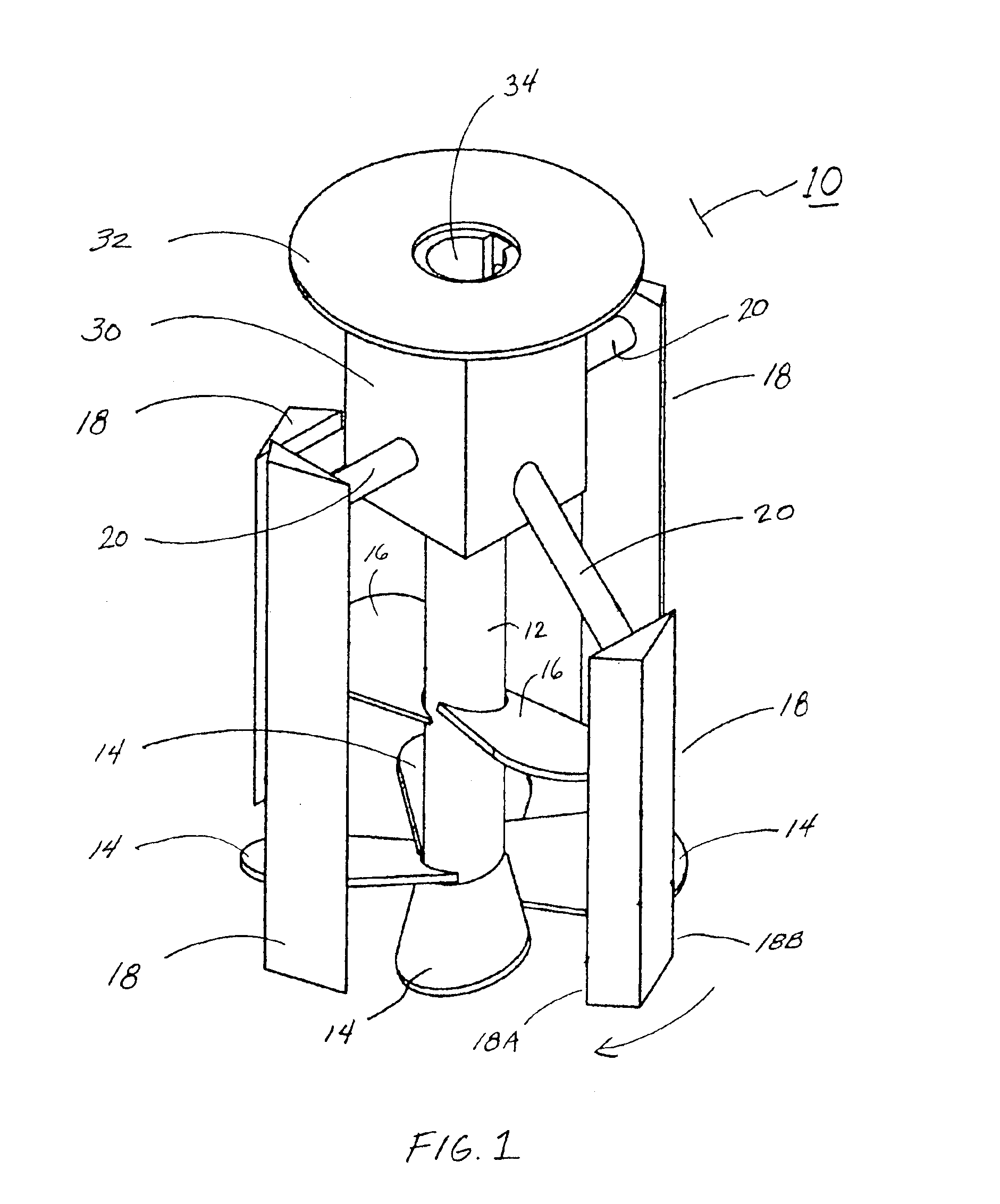
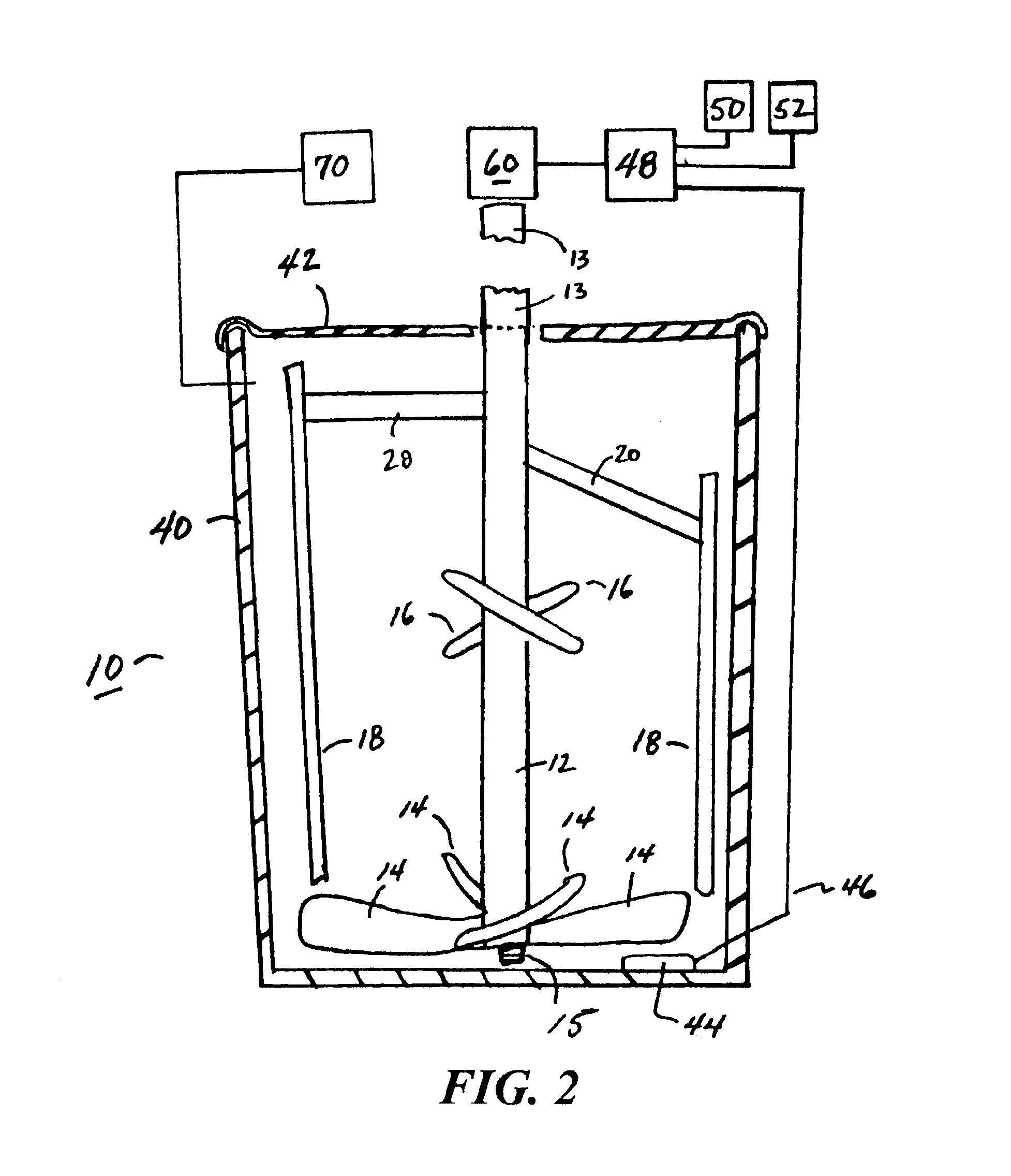
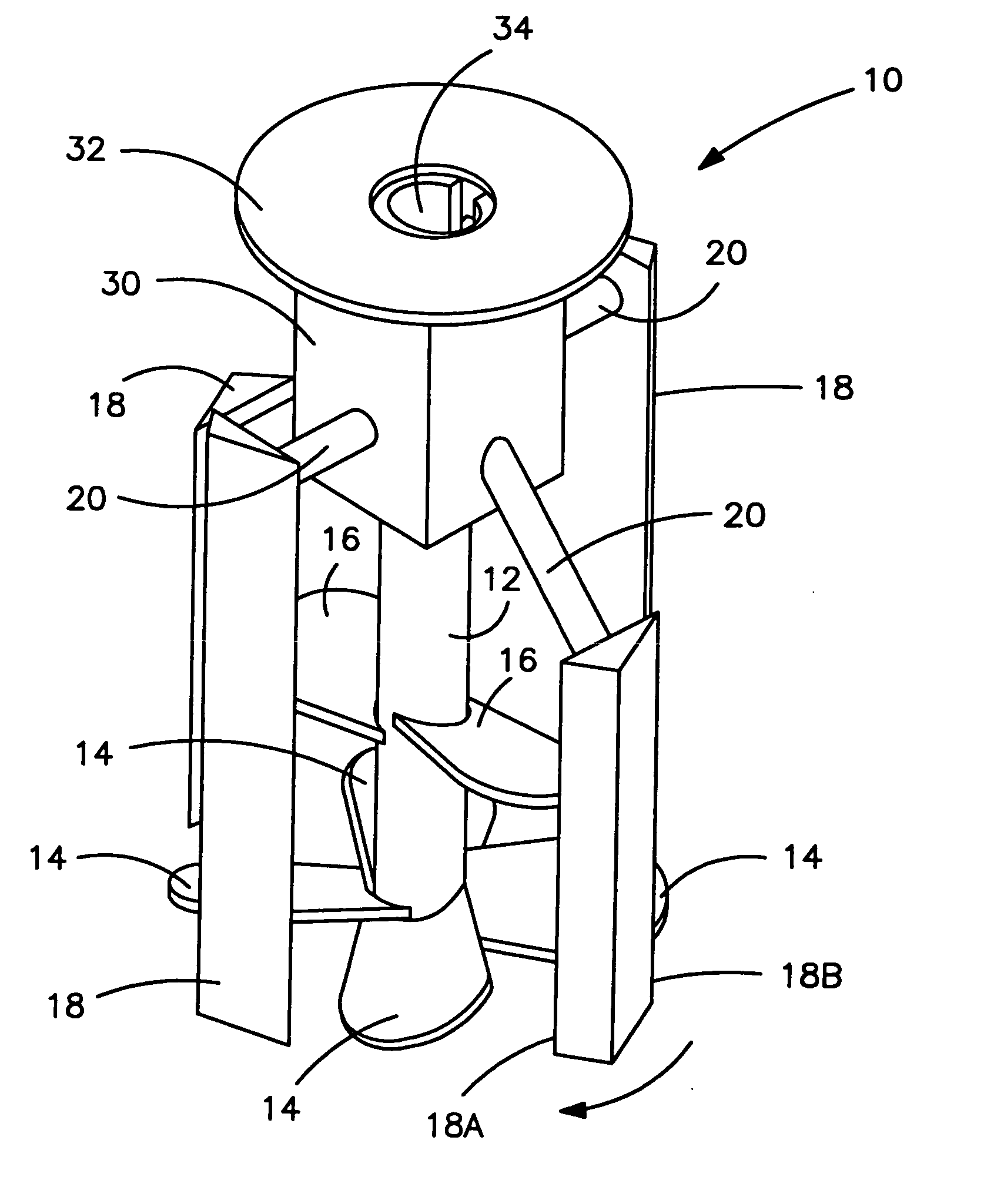
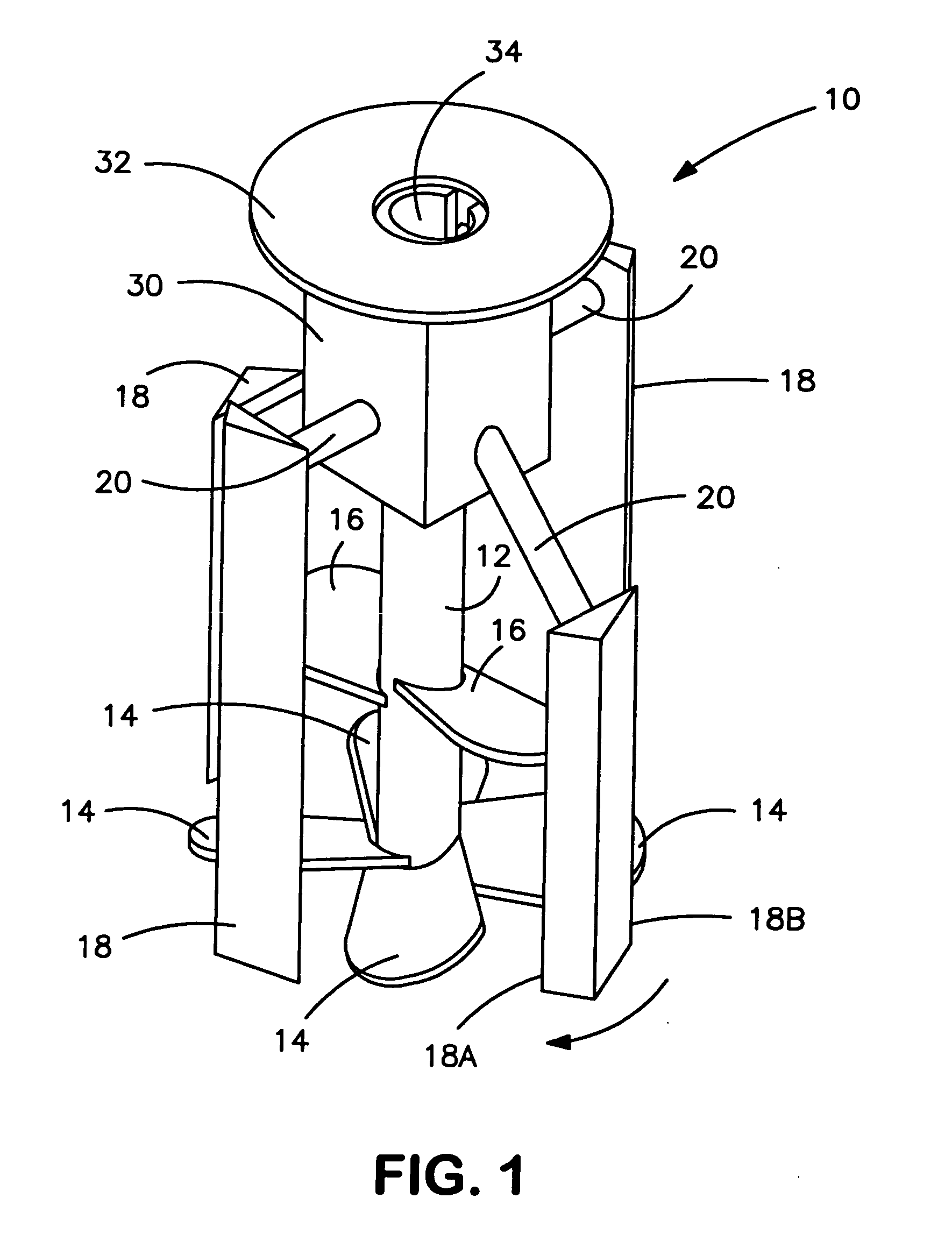
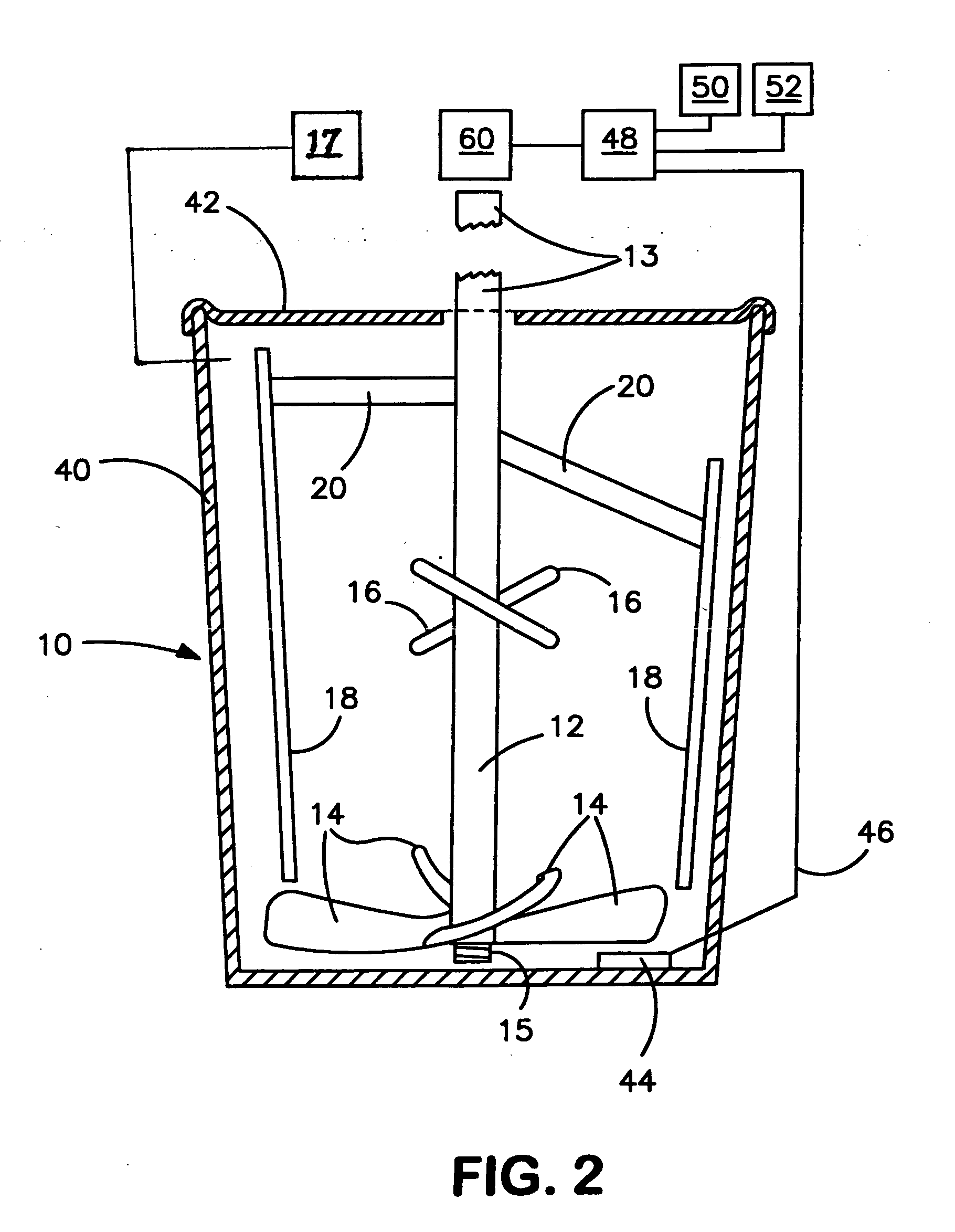
Rheomixer device
ActiveUS6997045B2Minimize inaccuracyStudy of effectFlow propertiesRotary stirring mixersRheometryEngineering
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Rheological and calorimetric testing method
InactiveUS20050138991A1Minimize inaccuracyStudy of effectTransportation and packagingFlow propertiesRheometryMaterials science
Device and methods for rotationally mixing and rheological testing of sample liquids, such as cement particle suspensions, employ mixing blades and shear-resistant members having substantially noncoincident orbital paths. Rheology is assessed by measuring the resistance of the liquid to rotation of the device. Both rheological and calorimetric testing can be performed during mixing, which ensures uniformity of rheology and hence the accuracy of results.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Polyolefin resin blends for crack-resistant pipe
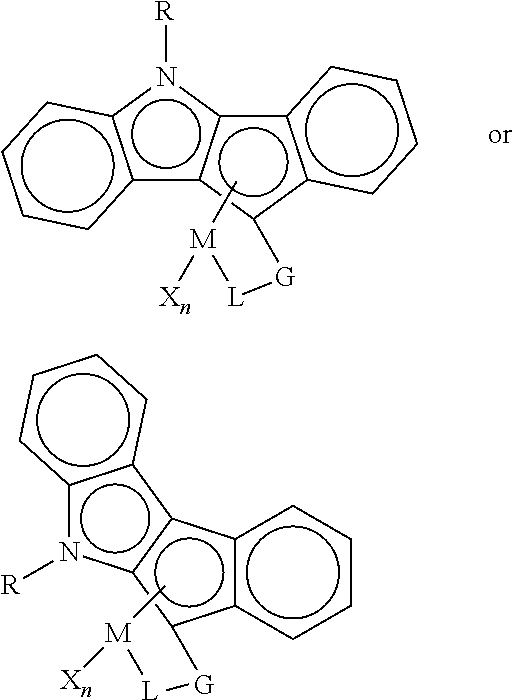
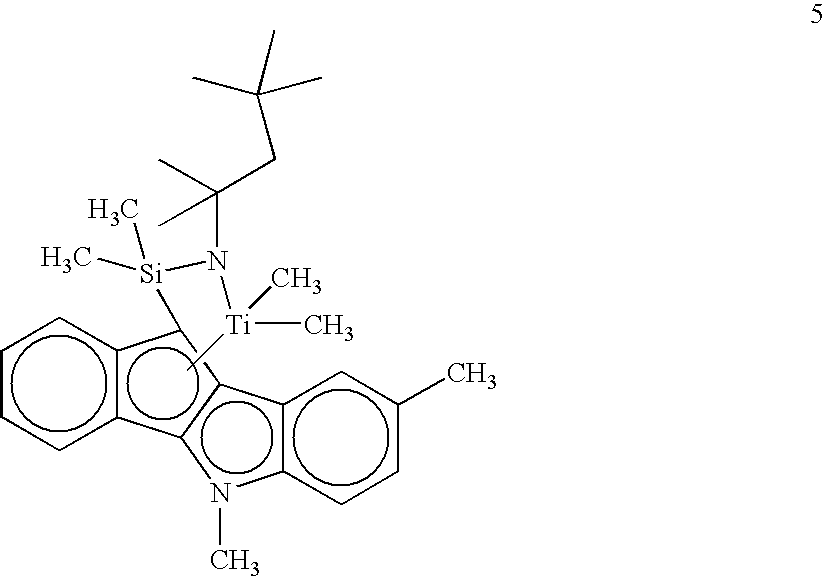
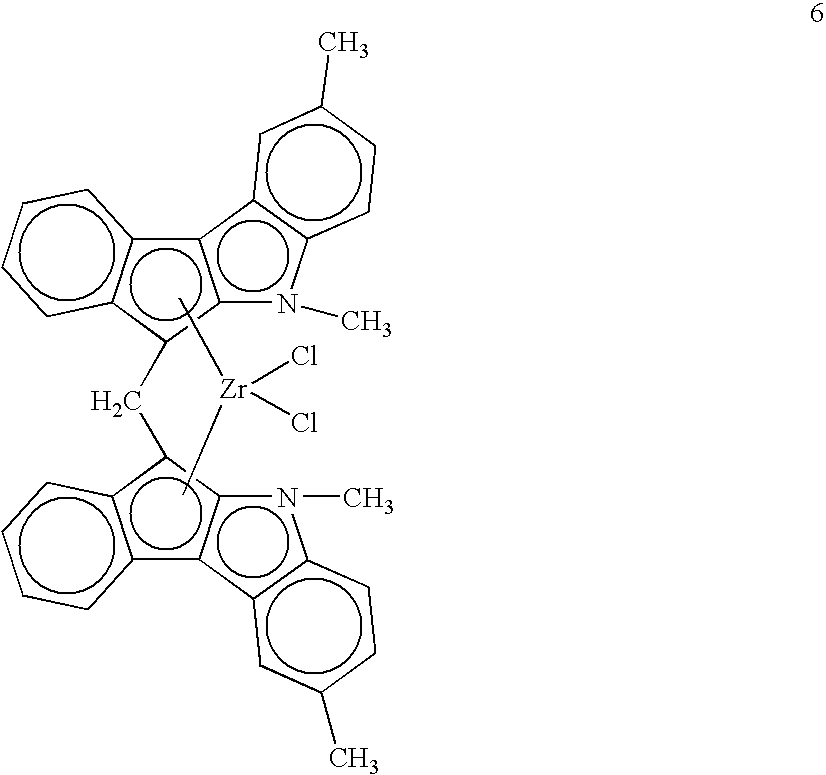
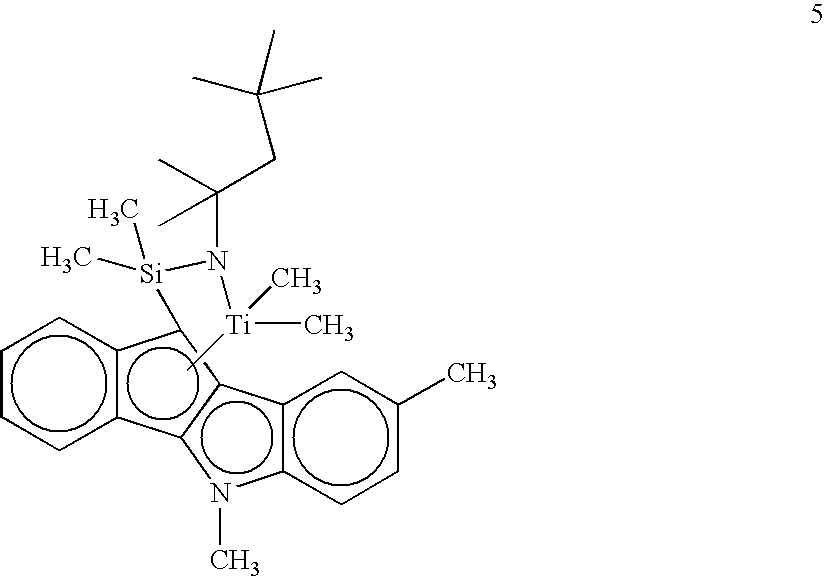
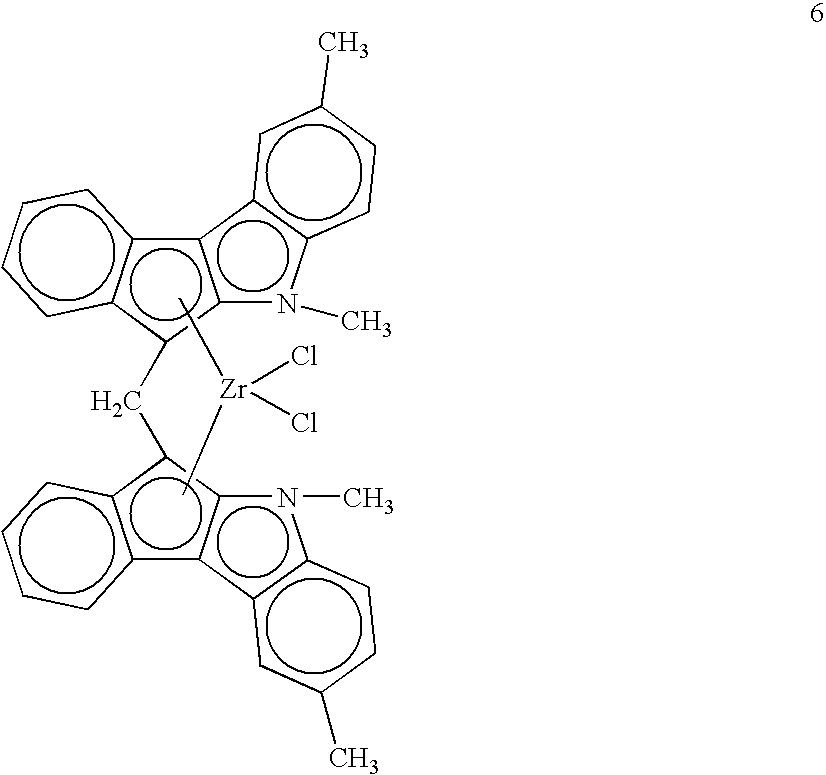
Resin blends useful for pipe and blow-molded articles are disclosed. The blends comprise a low-molecular-weight, high-density polyethylene and a high-molecular-weight, low-density ethylene copolymer. The high-molecular-weight component is made with a bridged indenoindolyl Group 4 metal complex having open architecture. Blends of the invention uniquely have high molecular weight (Mw>200,000) and low levels of long-chain branching. A quick, convenient approach for estimating levels of long-chain branching in polyethylenes from gel permeation chromatography and dynamic oscillatory rheometry (“viscosity enhancement factor”) is disclosed.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Multivariate management of entrained air and rheology in cementitious mixes
ActiveUS20130145967A1Efficiently and accurately updatingHighly inventiveCement mixing apparatusControl apparatusRheometryAir entrainment
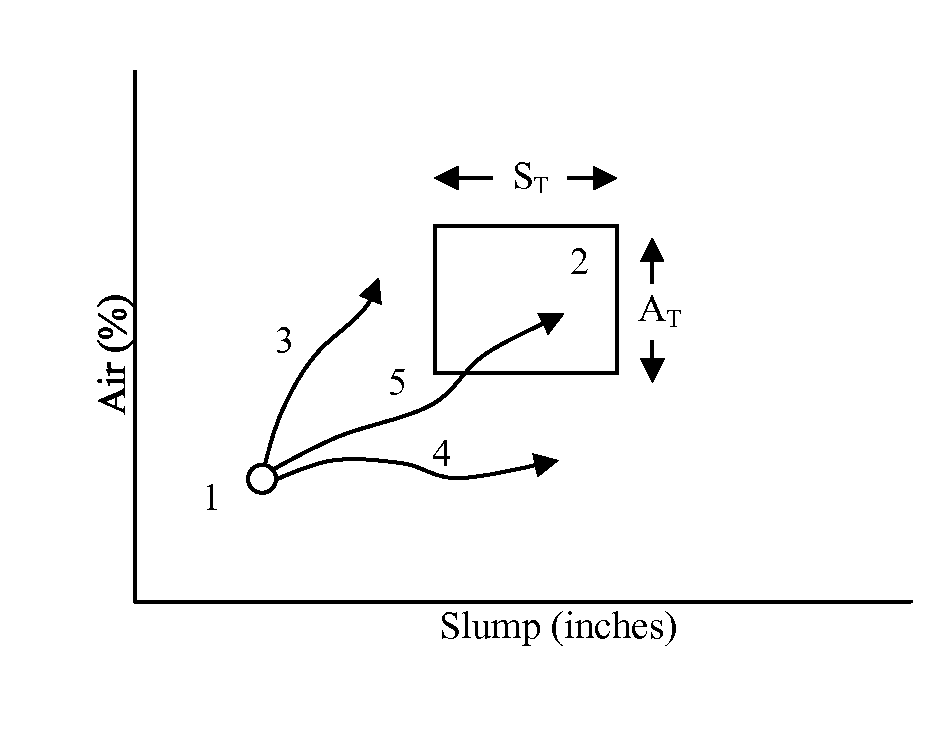
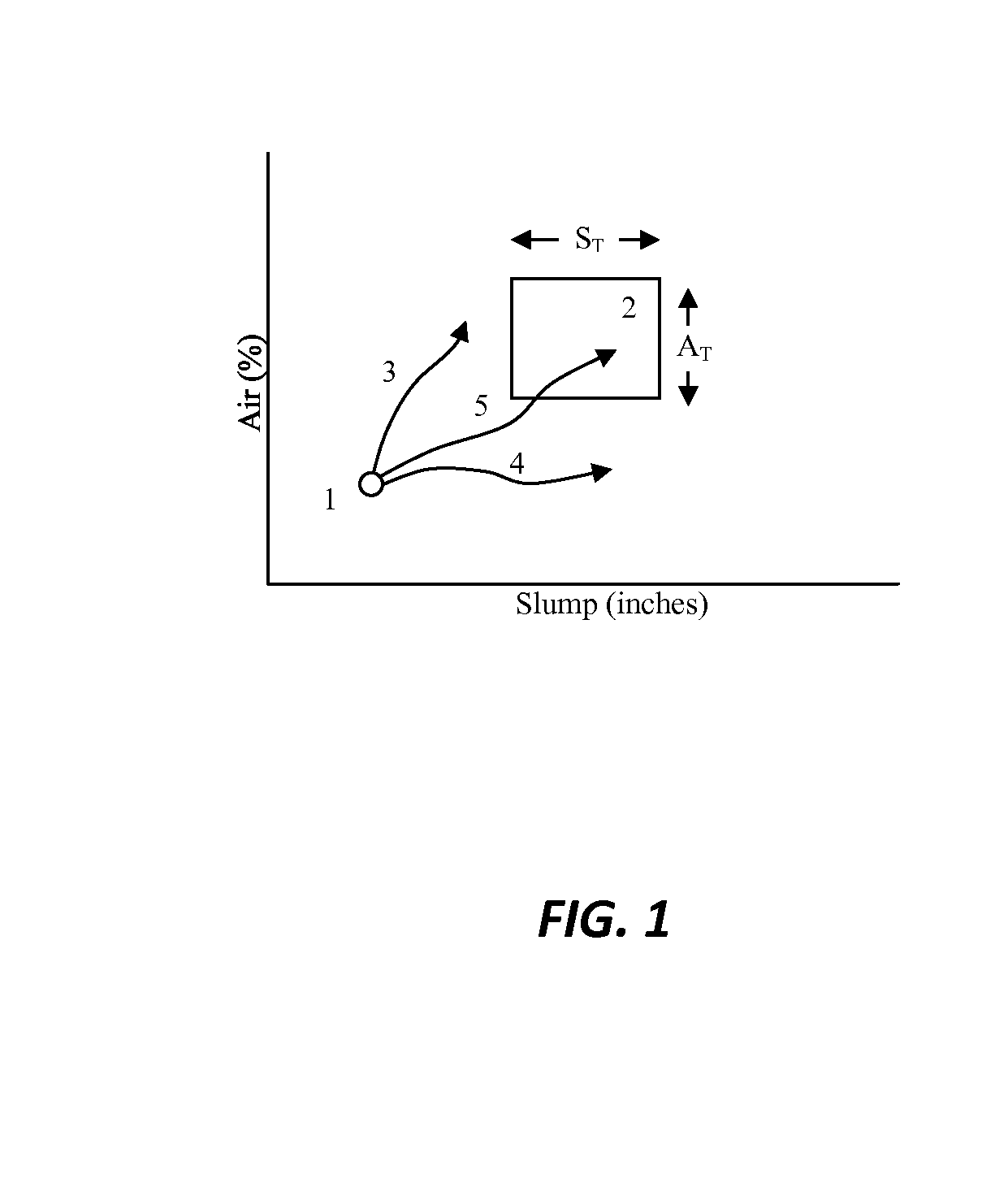
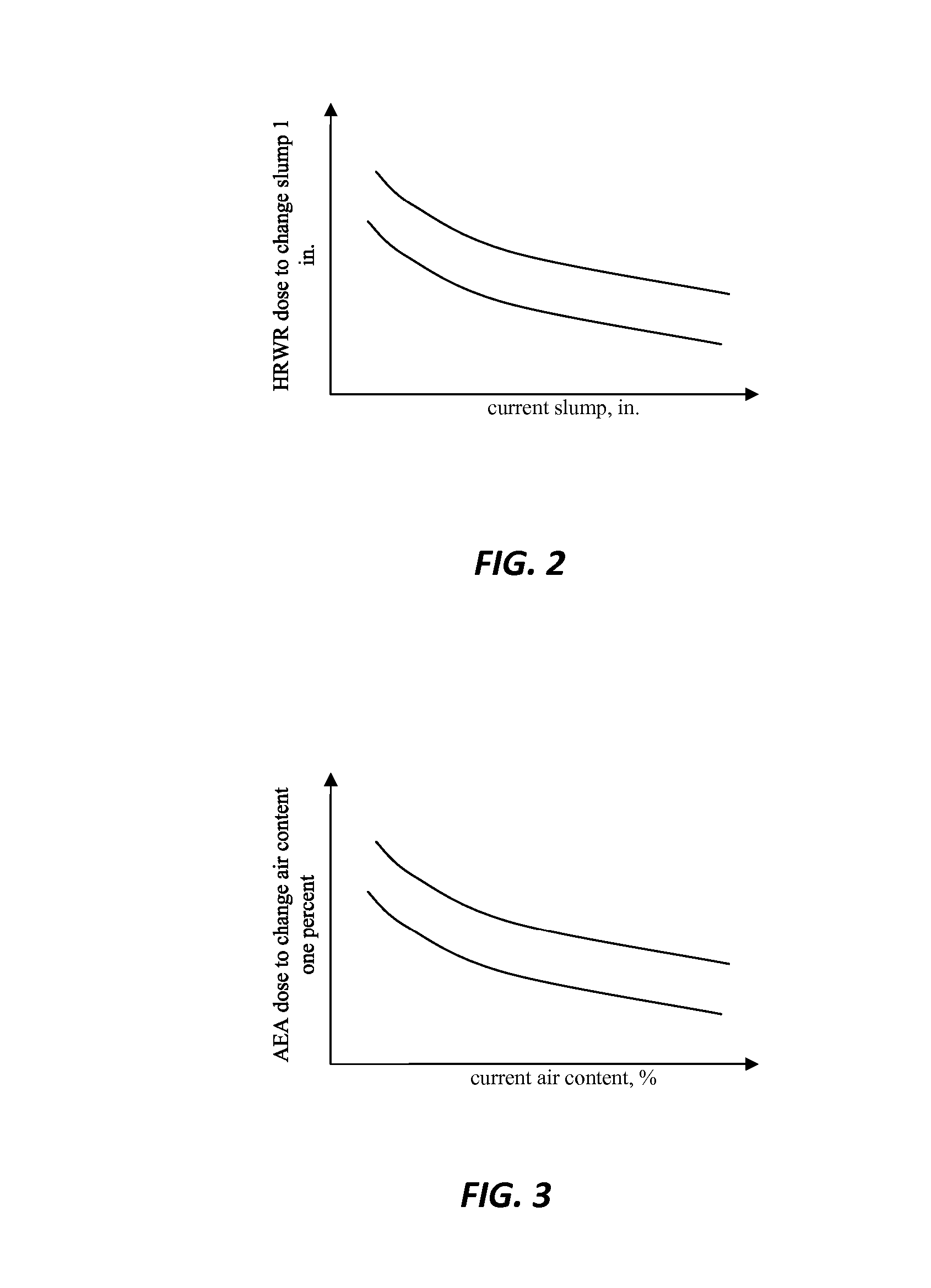
The invention relates to a method and system for monitoring and adjusting both air content and rheology (e.g., slump, slump flow) properties of a hydratable concrete mix contained within a concrete mixer. The system simultaneously tracks dosage of both rheology-modifying admixture (e.g., polycarboxylate polymer cement dispersant) and air control agent or “ACA” (e.g., air entraining agent) by reference to at least four nominal dose response (“NDR”) curves or profiles, which at least four NDR profiles are based on the respective behaviors of each of the ACA and rheology-modifying agent on air content and rheology.
Owner:VERIFI
Method for estimating proppant transport and suspendability of viscoelastic liquids
A method of determining one or more minimum rheological properties of a particle laden fluid is disclosed. The method includes determining one or more rheological properties of the fluid at a first shear rate, determining the settling velocity of the particles at the first shear rate, and obtaining a transport index for the fluid, the transport index indicating a relationship between the settling velocity and the one or more rheological properties.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Polyolefin resin blends for crack-resistant pipe
InactiveUS20090061135A1Rapidly and easily evidenceFlow propertiesLayered productsRheometryPolyolefin
Resin blends useful for pipe and blow-molded articles are disclosed. The blends comprise a low-molecular-weight, high-density polyethylene and a high-molecular-weight, low-density ethylene copolymer. The high-molecular-weight component is made with a bridged indenoindolyl Group 4 metal complex having open architecture. Blends of the invention uniquely have high molecular weight (Mw>200,000) and low levels of long-chain branching. A quick, convenient approach for estimating levels of long-chain branching in polyethylenes from gel permeation chromatography and dynamic oscillatory rheometry (“viscosity enhancement factor”) is disclosed.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
System and method for interfacial rheometry
ActiveUS20090056423A1Impeding translational movementFacilitate communicationFlow propertiesStrength propertiesRheometryShear rate
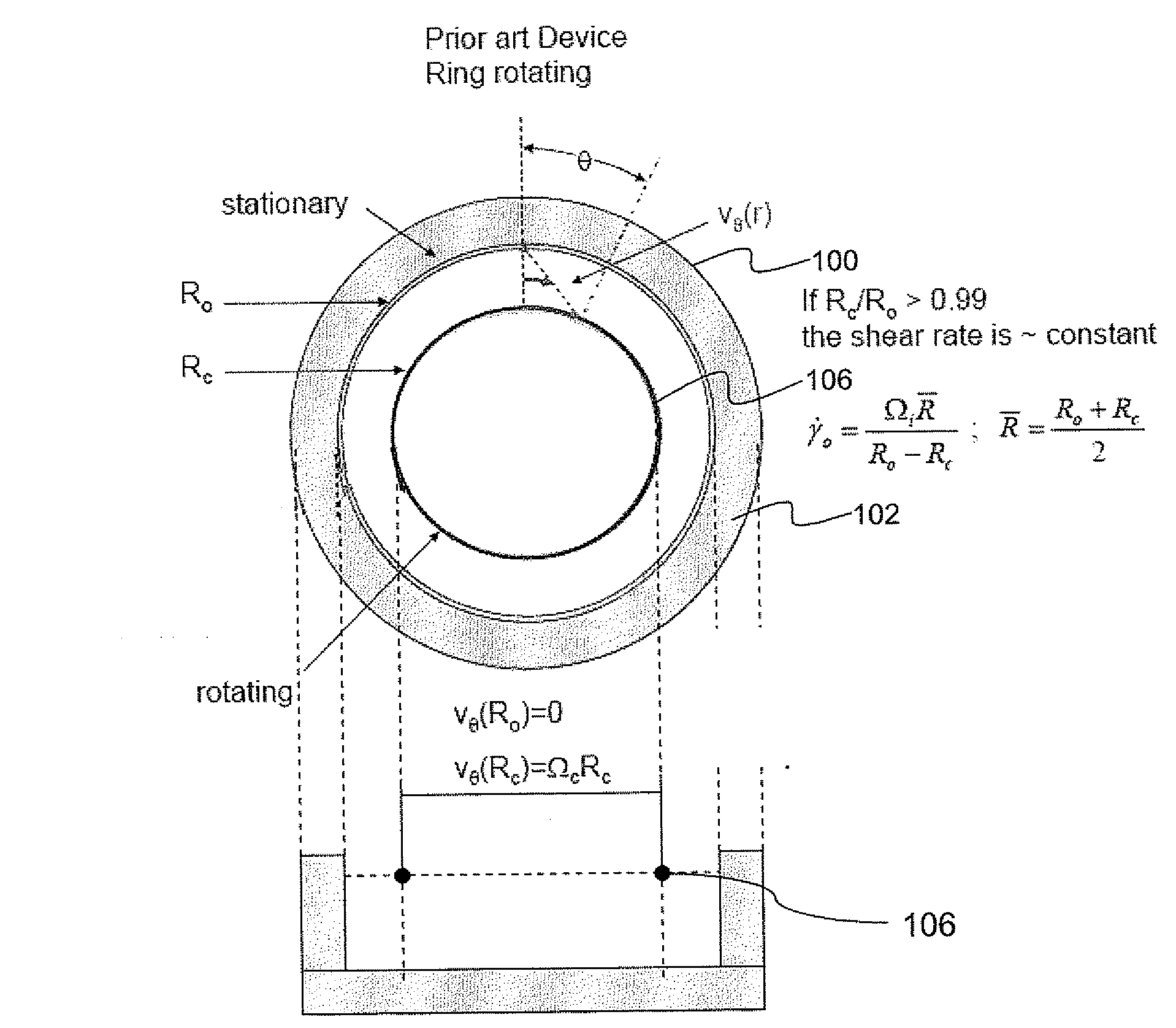
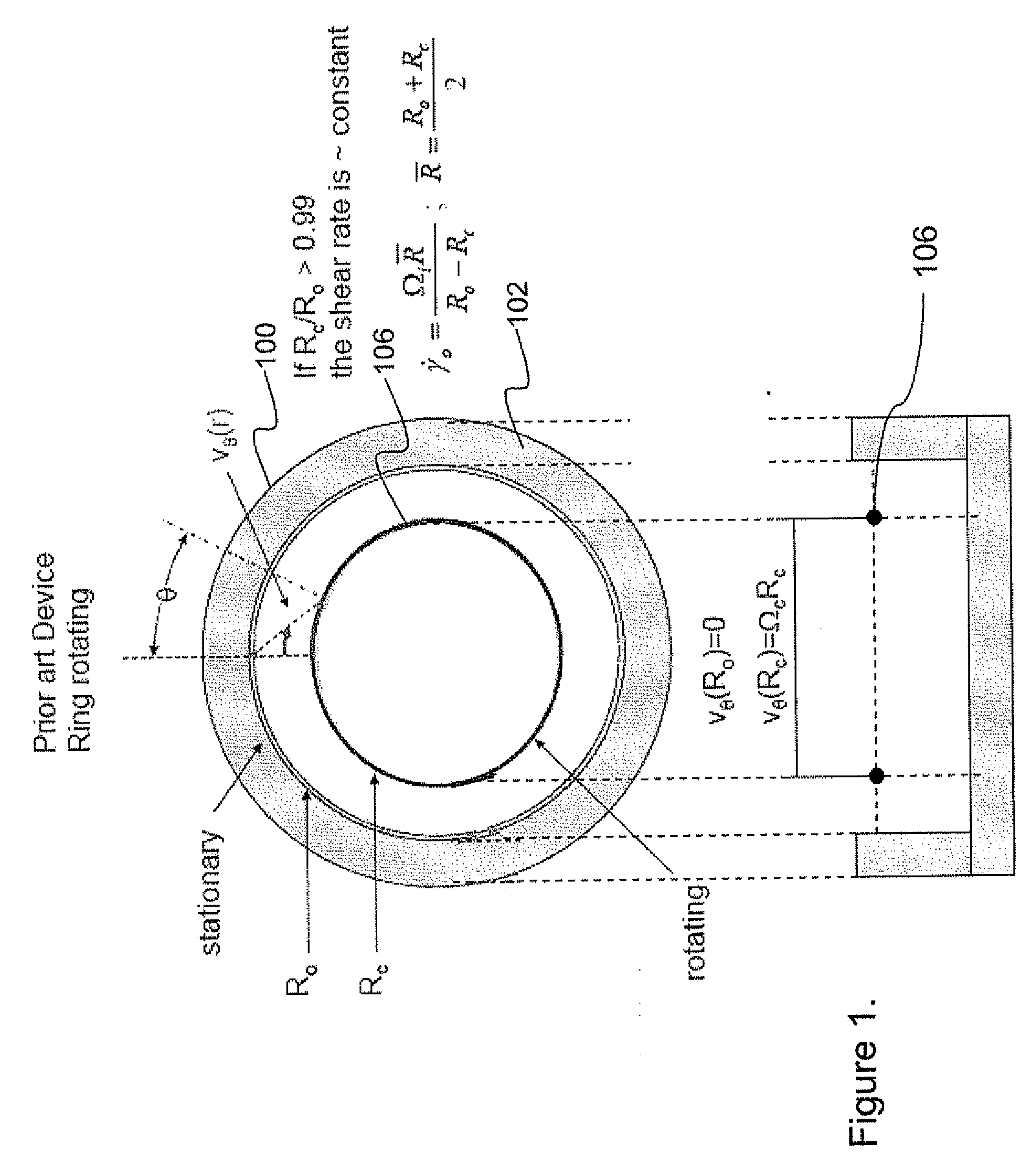
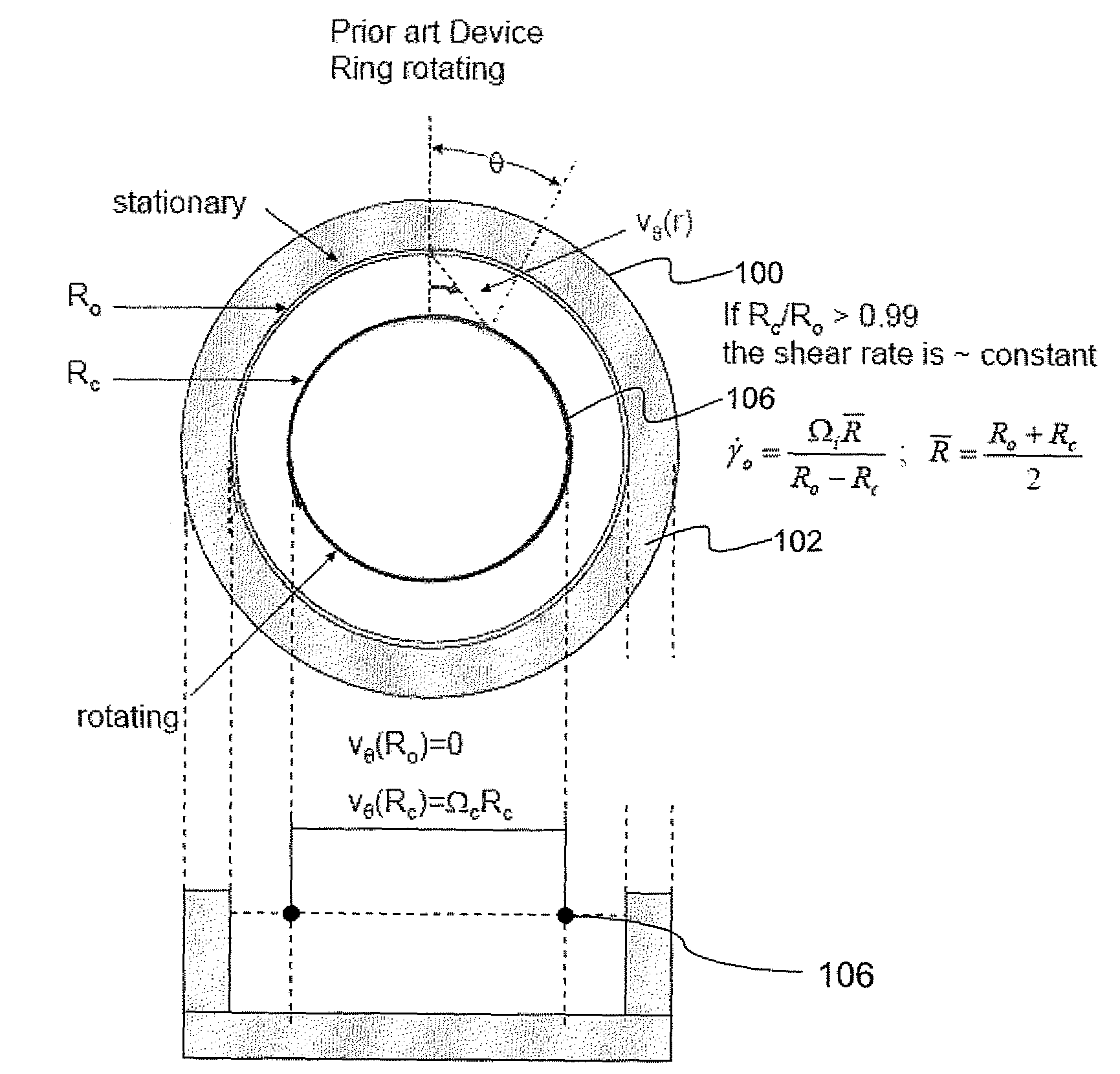
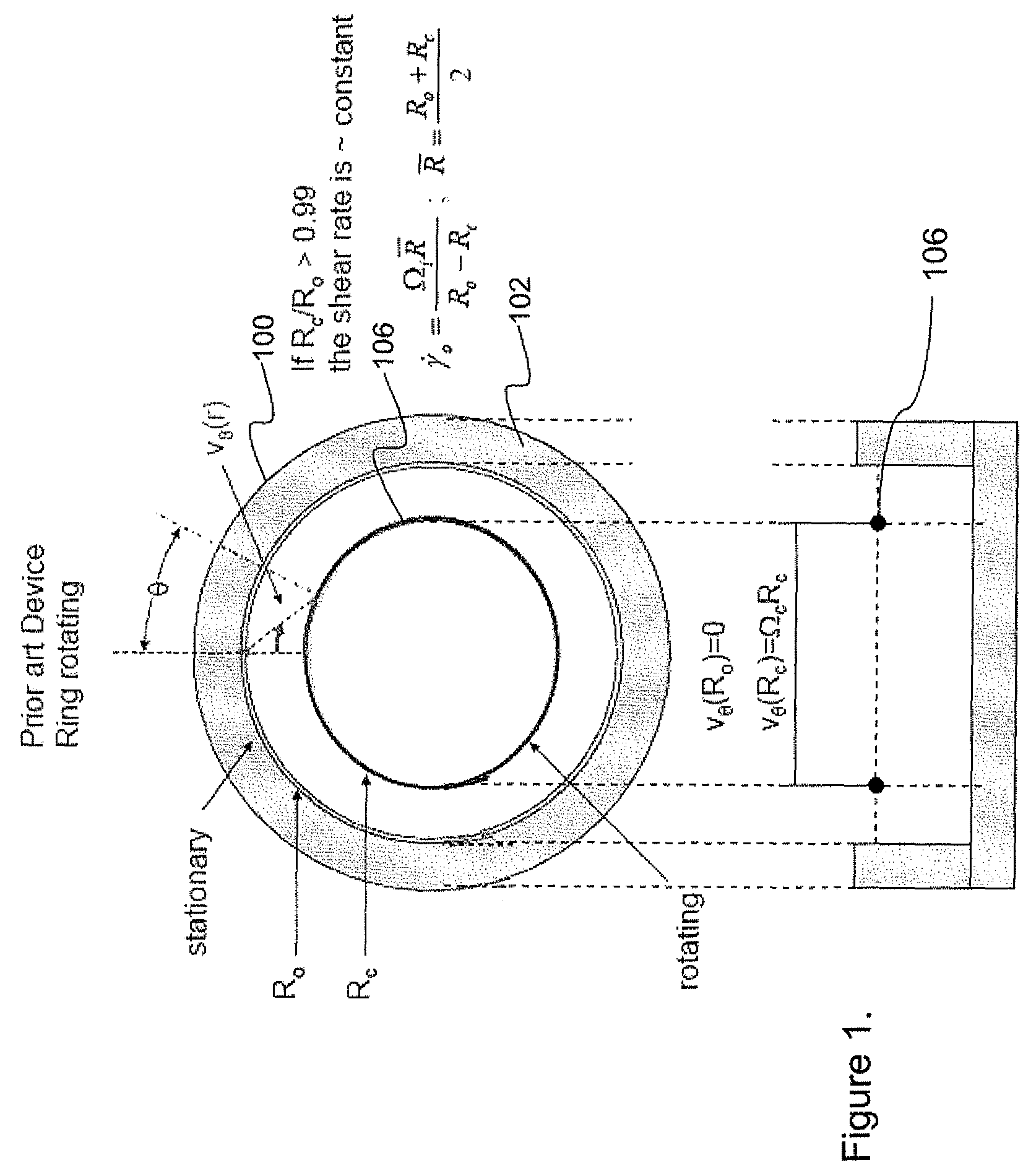
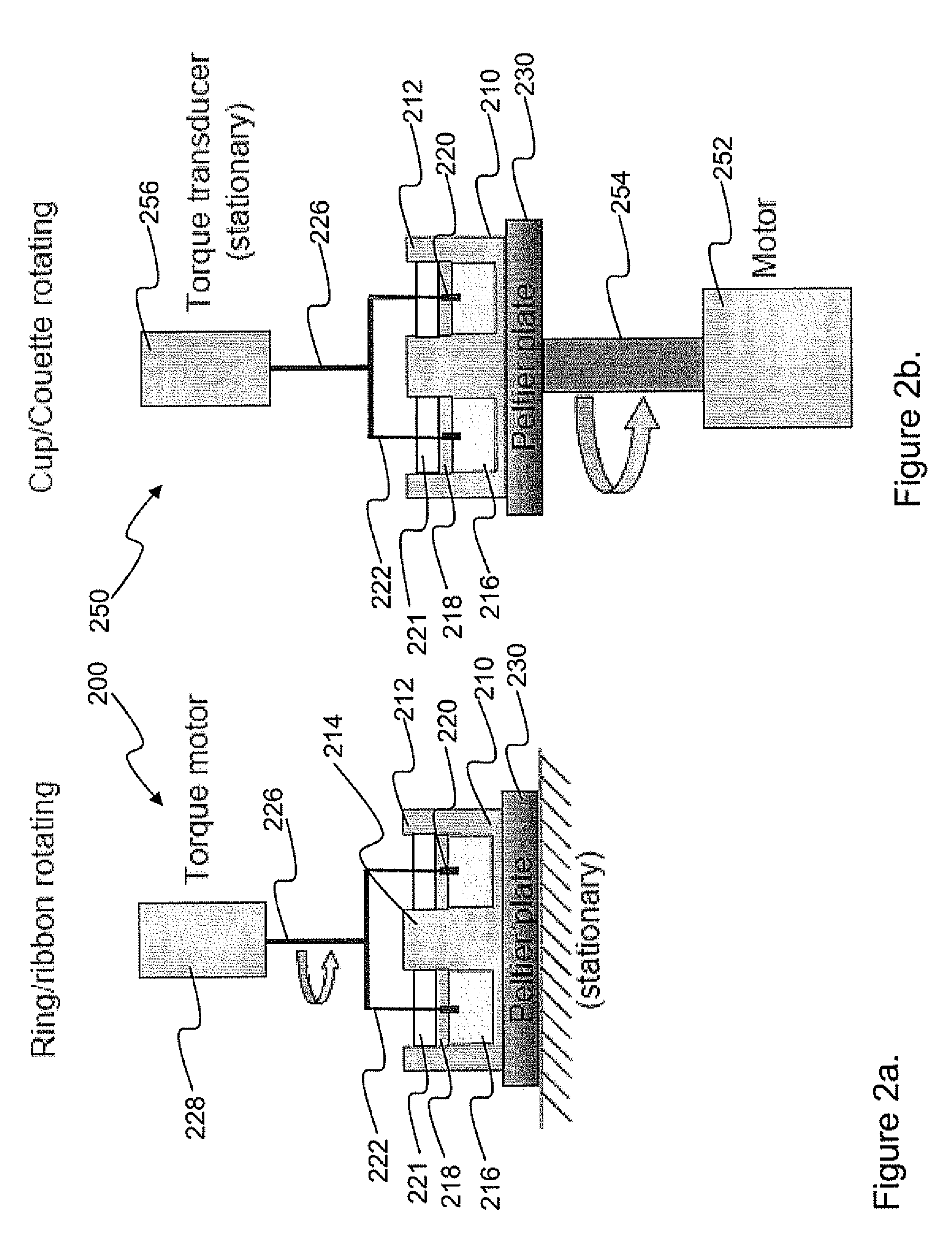
An apparatus and method for performing rheological measurements of interfaces located at the top of fluid sub-phases. In one configuration, a rotating rheometer is provided with a chamber wall whose inner surface defines an outer chamber radius and an inner cylinder disposed within the cylindrical chamber and having an inner chamber radius. The rotating rheometer is configured to hold a liquid sub-phase and interface layer that can be probed using a circular ribbon that is concentric with and suspended between the inner cylinder and chamber wall. The ratio of the ribbon radius, inner chamber radius, and outer chamber radius is designed to yield an average shear rate in the inner region that is the same as an average shear rate in the outer region. In one configuration, an interface-pinning feature is provided on at least one of the inner cylinder and the chamber wall.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
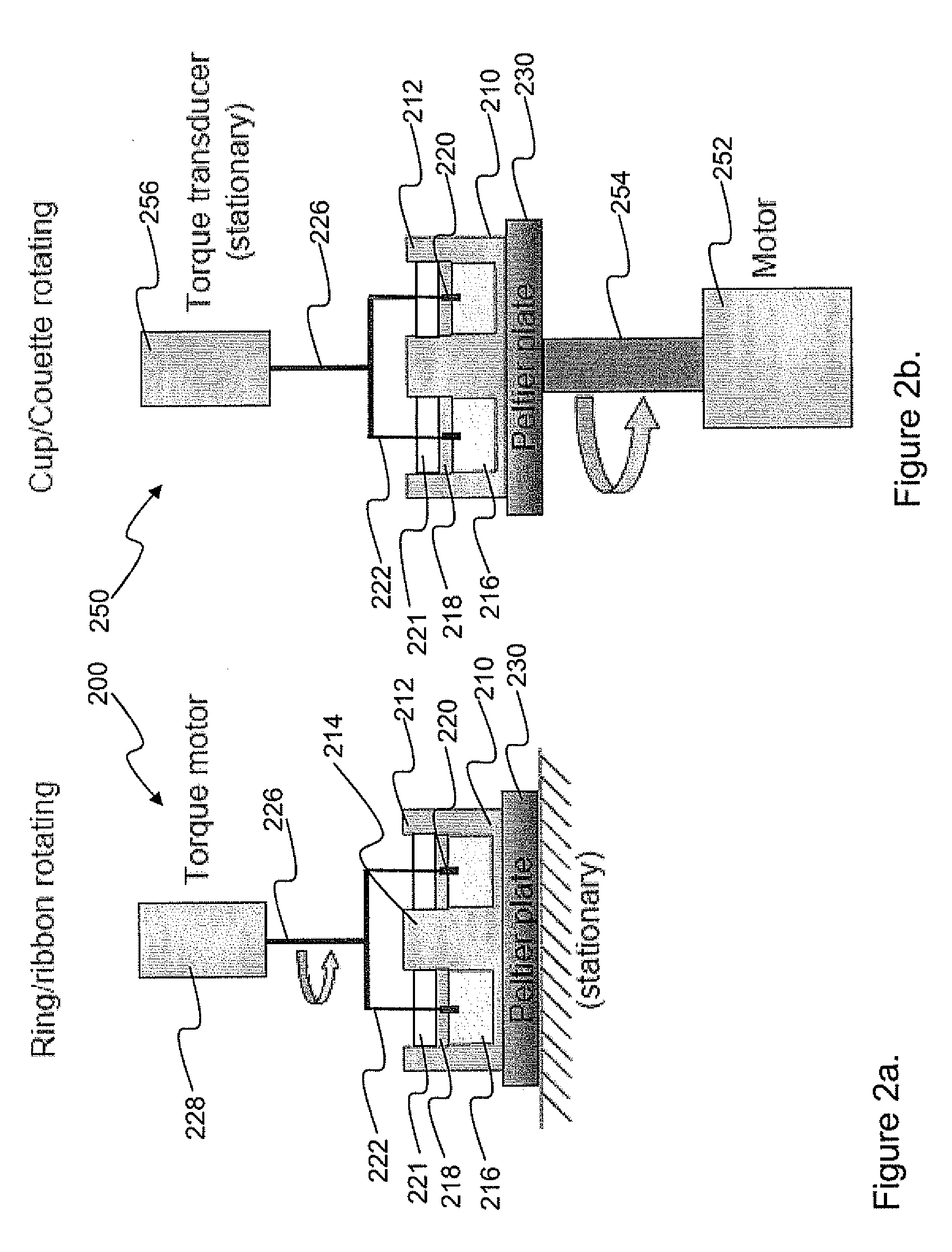
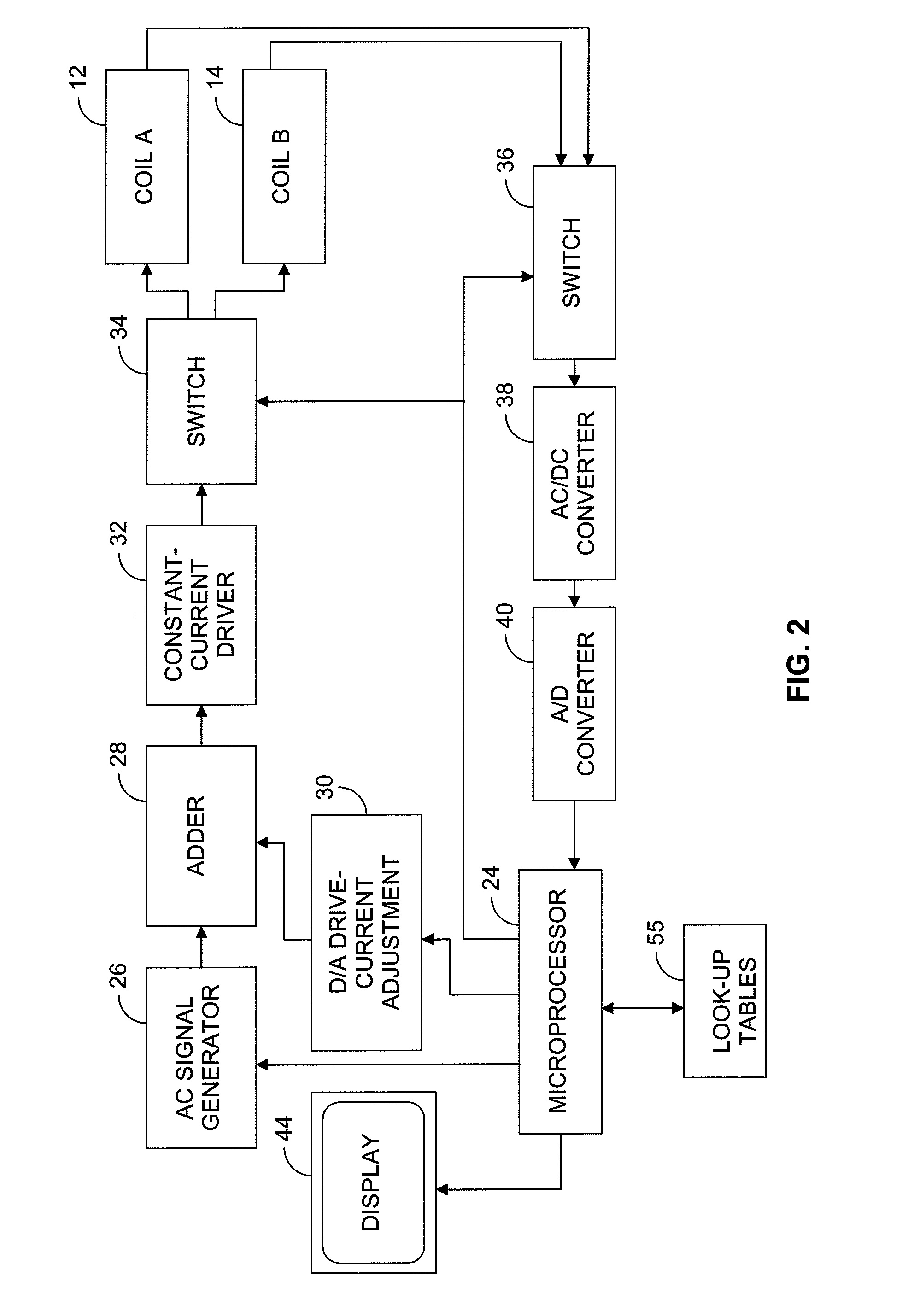
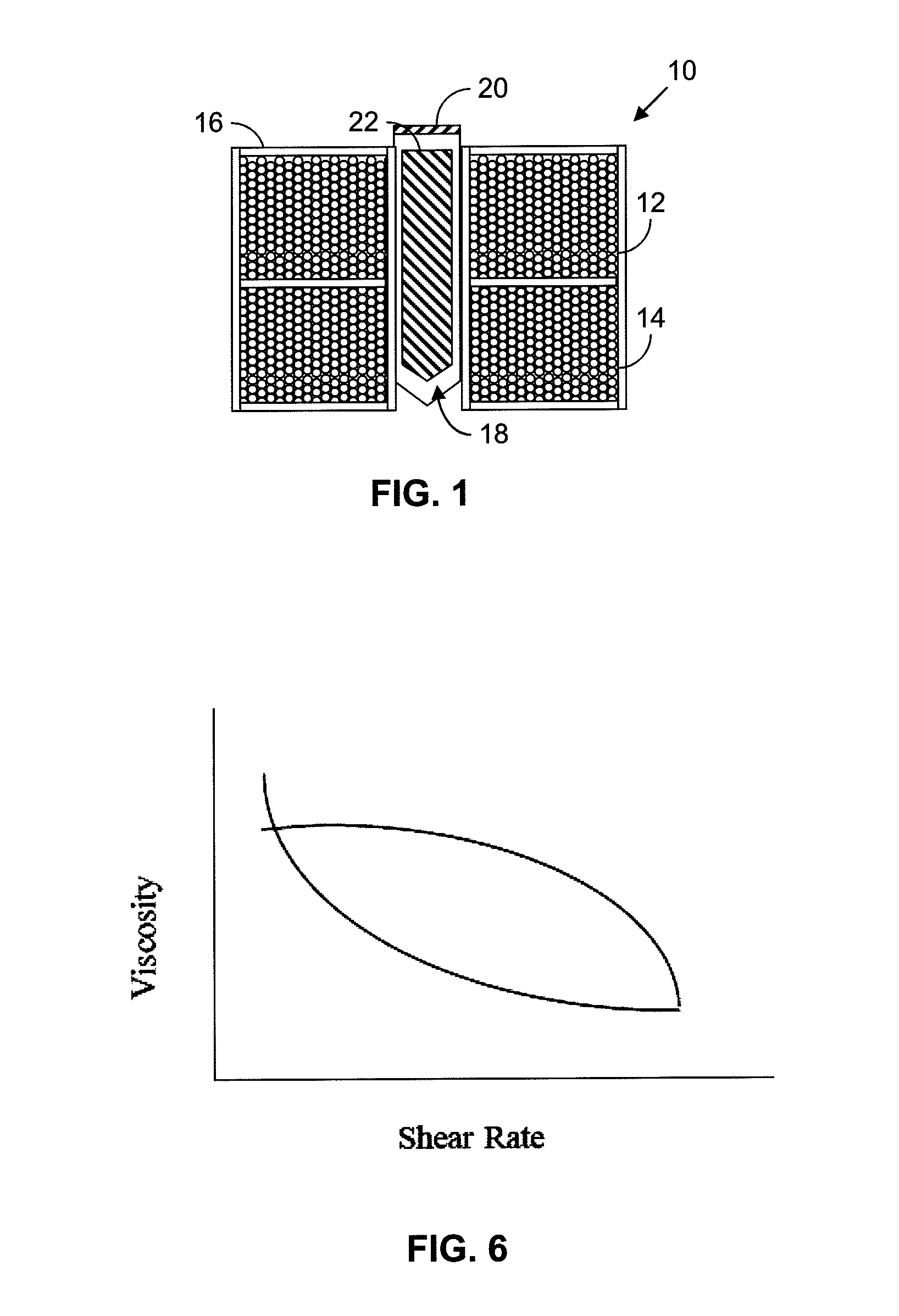
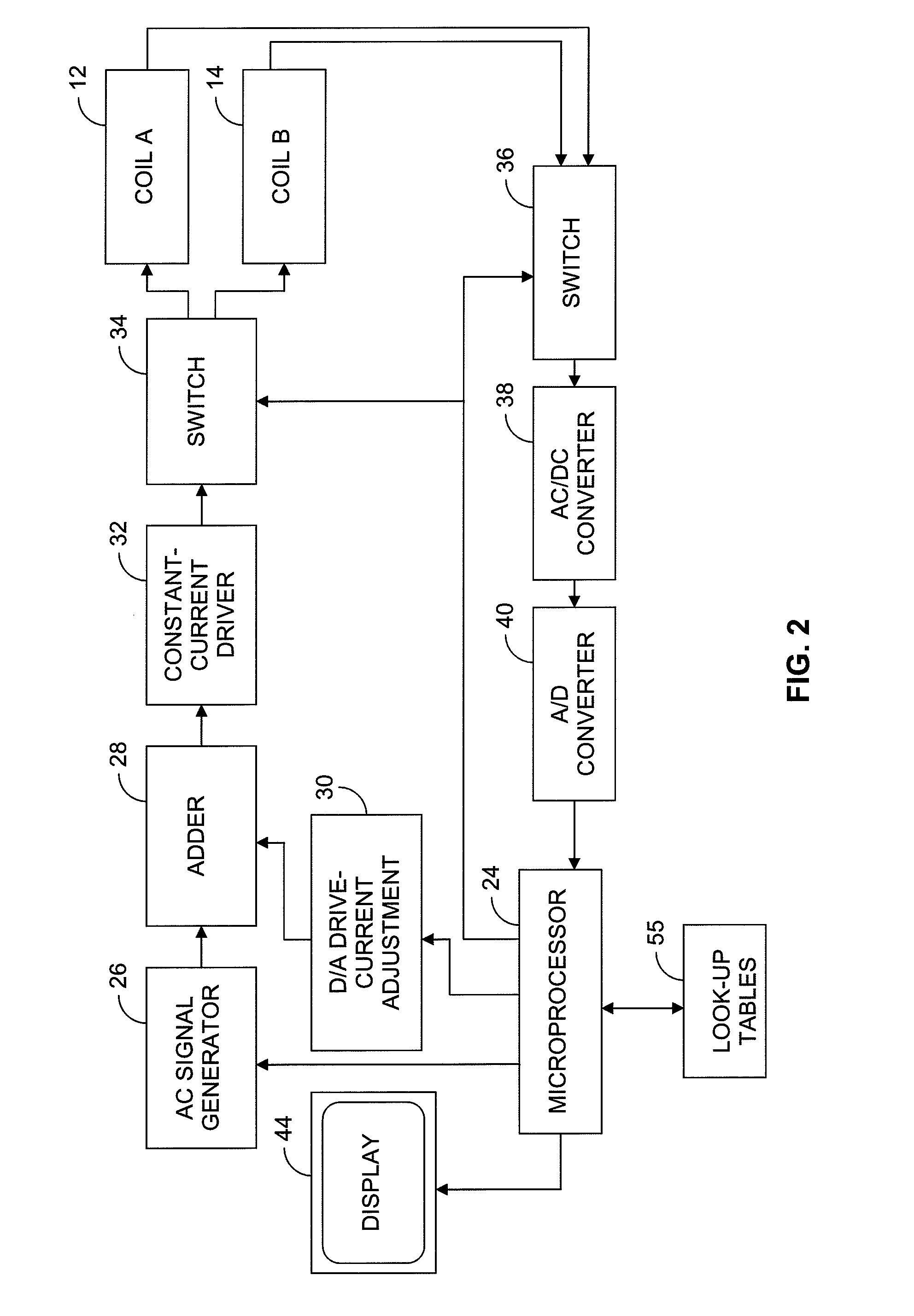
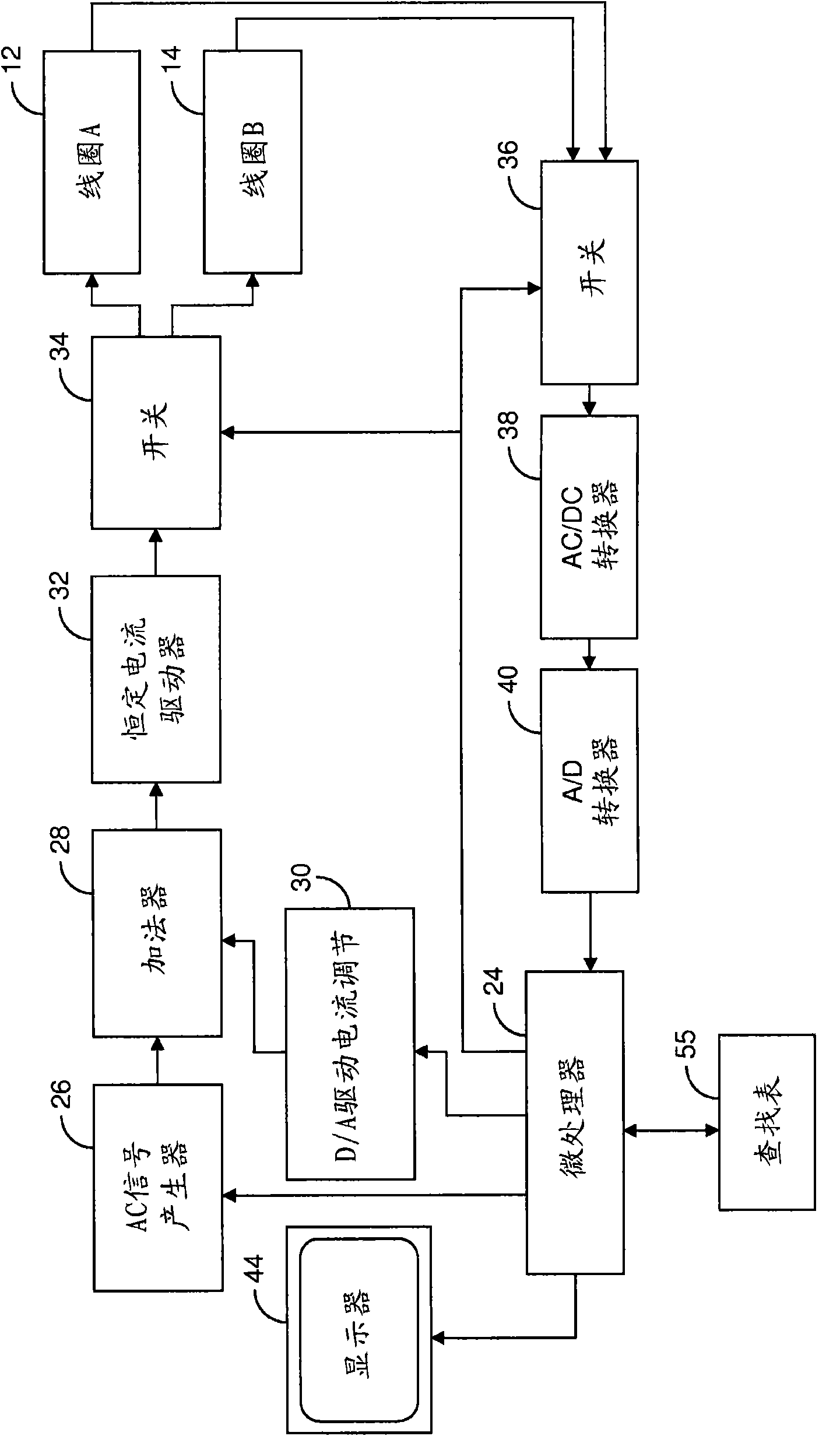
Dynamic reciprocating-bob rheometry
A sensor for making rheological measurements takes the form of a ferromagnetic bob alternately driven through a sample fluid in opposite directions by magnetic force from two alternately driven coils. The bob's position affects the mutual inductance between the coils, so it can be inferred by sensing the signal that current flowing in one coil induces in the other, and rheological properties are determined from the relationships among the bob's motion, the coil current, and the sensor geometry. Some such measurements' accuracies are enhanced by computing bob acceleration and suppressing inertial effects thereby detected.
Owner:PETROLEUM ANALYZER COMPANY
Method for estimating proppant transport and suspendability of viscoelastic liquids
A method of determining one or more minimum rheological properties of a particle laden fluid is disclosed. The method includes determining one or more rheological properties of the fluid at a first shear rate, determining the settling velocity of the particles at the first shear rate, and obtaining a transport index for the fluid, the transport index indicating a relationship between the settling velocity and the one or more rheological properties.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
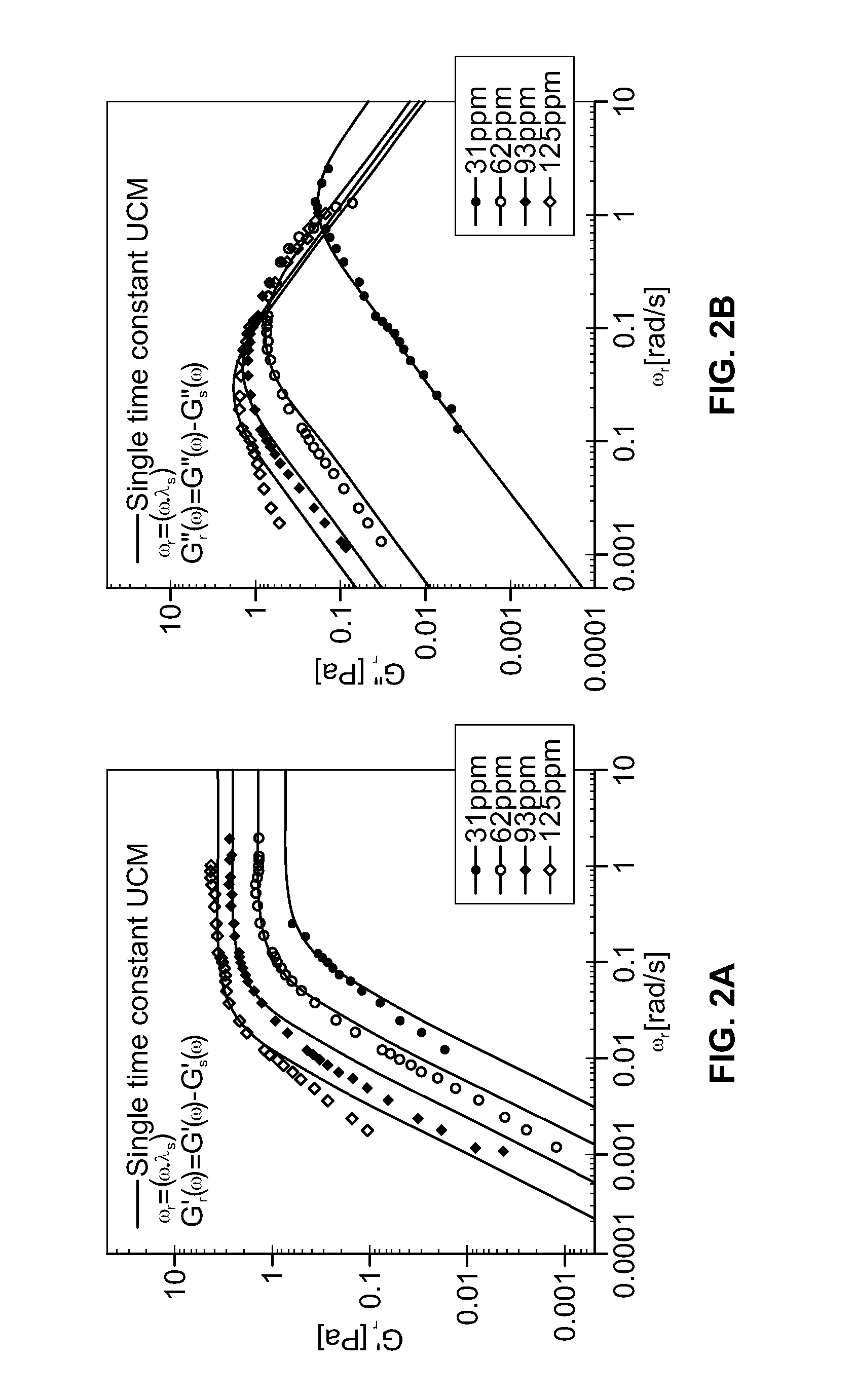
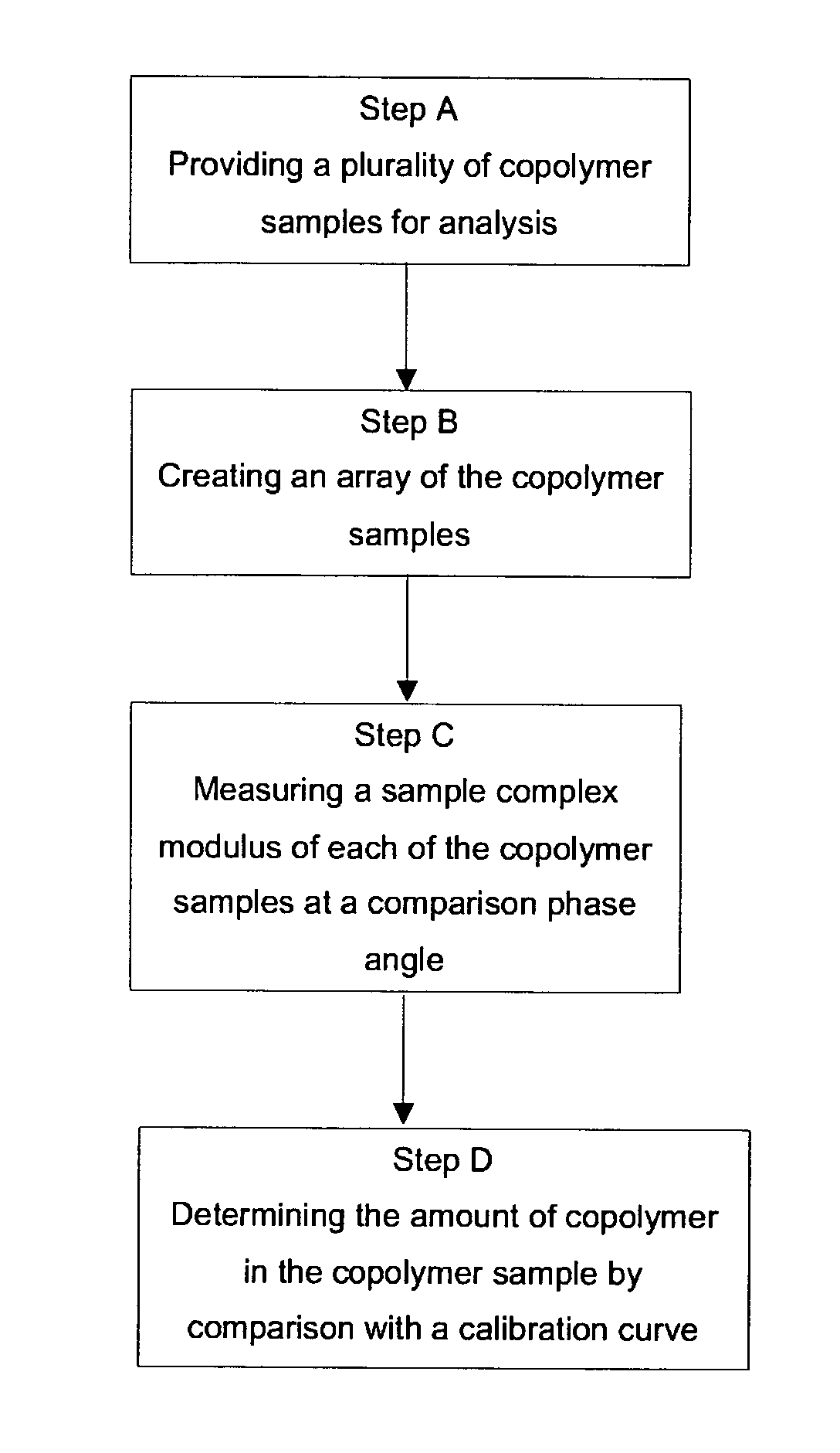
High throughput property testing of olefin copolymers using rheological determinations
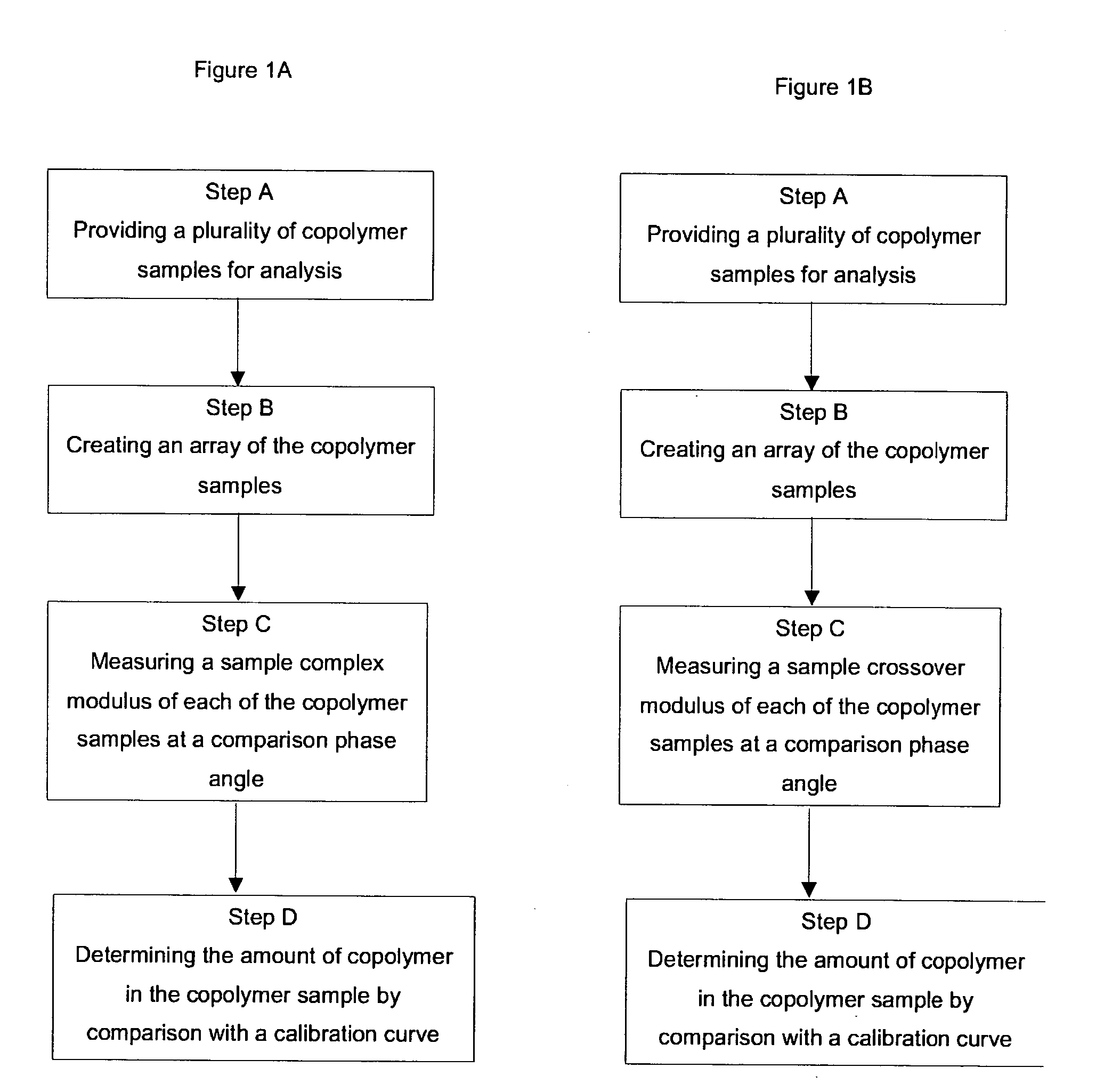
A high throughput method to determine an amount of a comonomer in a copolymer sample of a copolymer system comprises the steps of providing a plurality of copolymer samples; creating an array of the copolymer samples; measuring a sample complex modulus of each of the copolymer samples at a comparison phase angle; and determining the amount of a comonomer in the copolymer sample by comparing the sample complex modulus to a calibration curve, wherein the calibration curve relates a concentration of the comonomer in the copolymer sample to a complex moduli of the copolymer sample determined at the comparison phase angle. A method of determining the amount of a comonomer in both a single copolymer sample, and in a high throughput scheme using the crossover modulus is also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
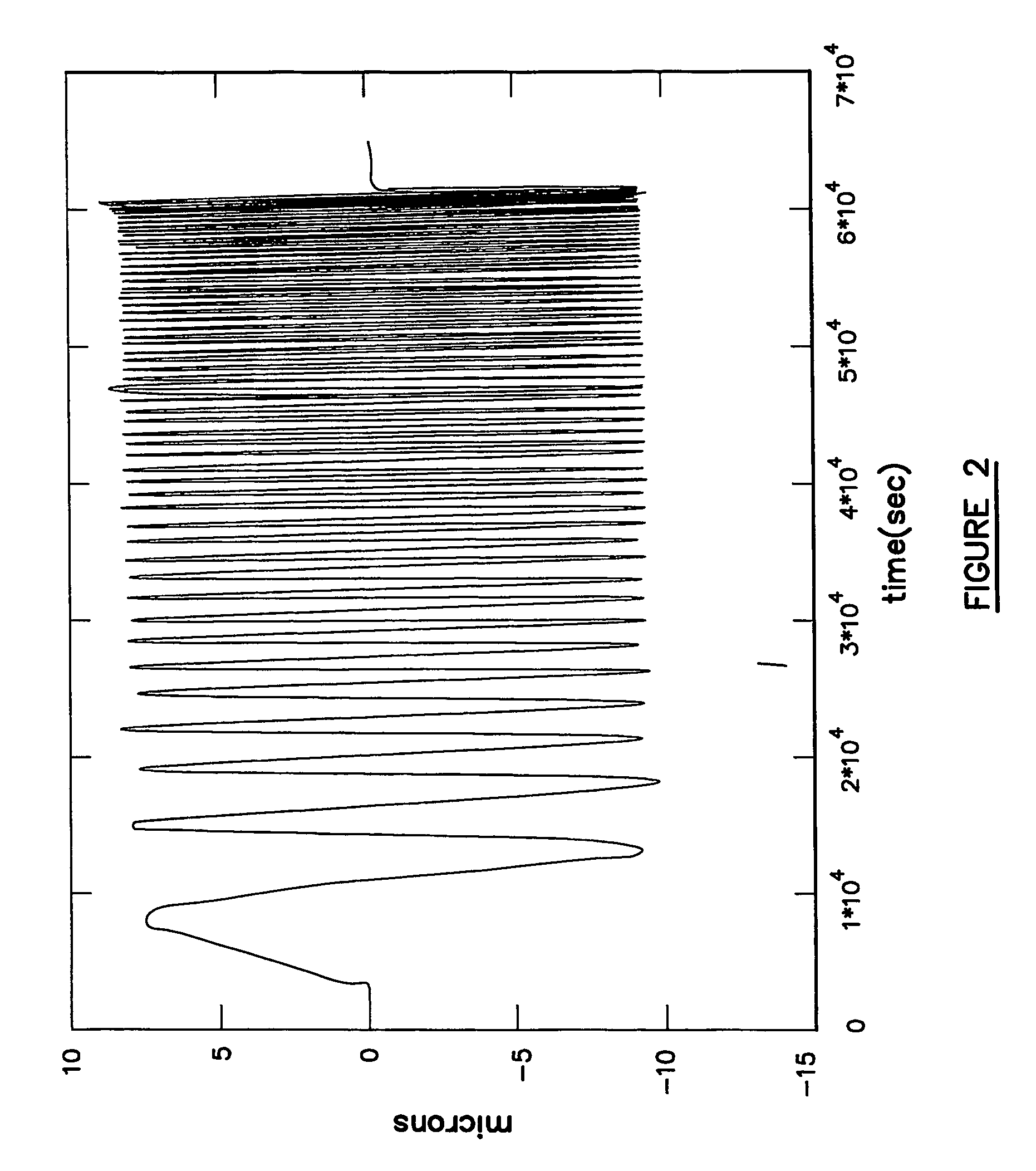
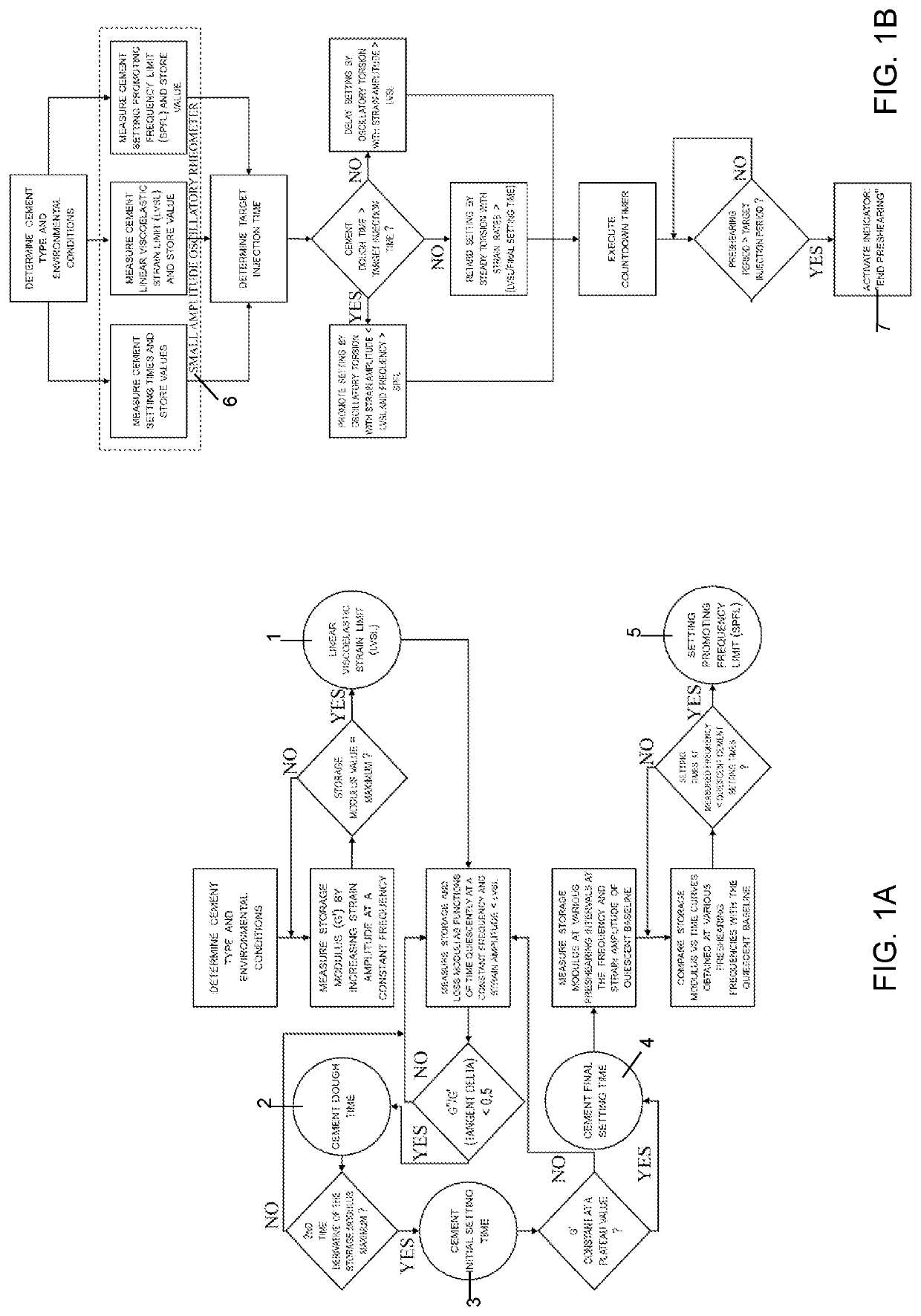
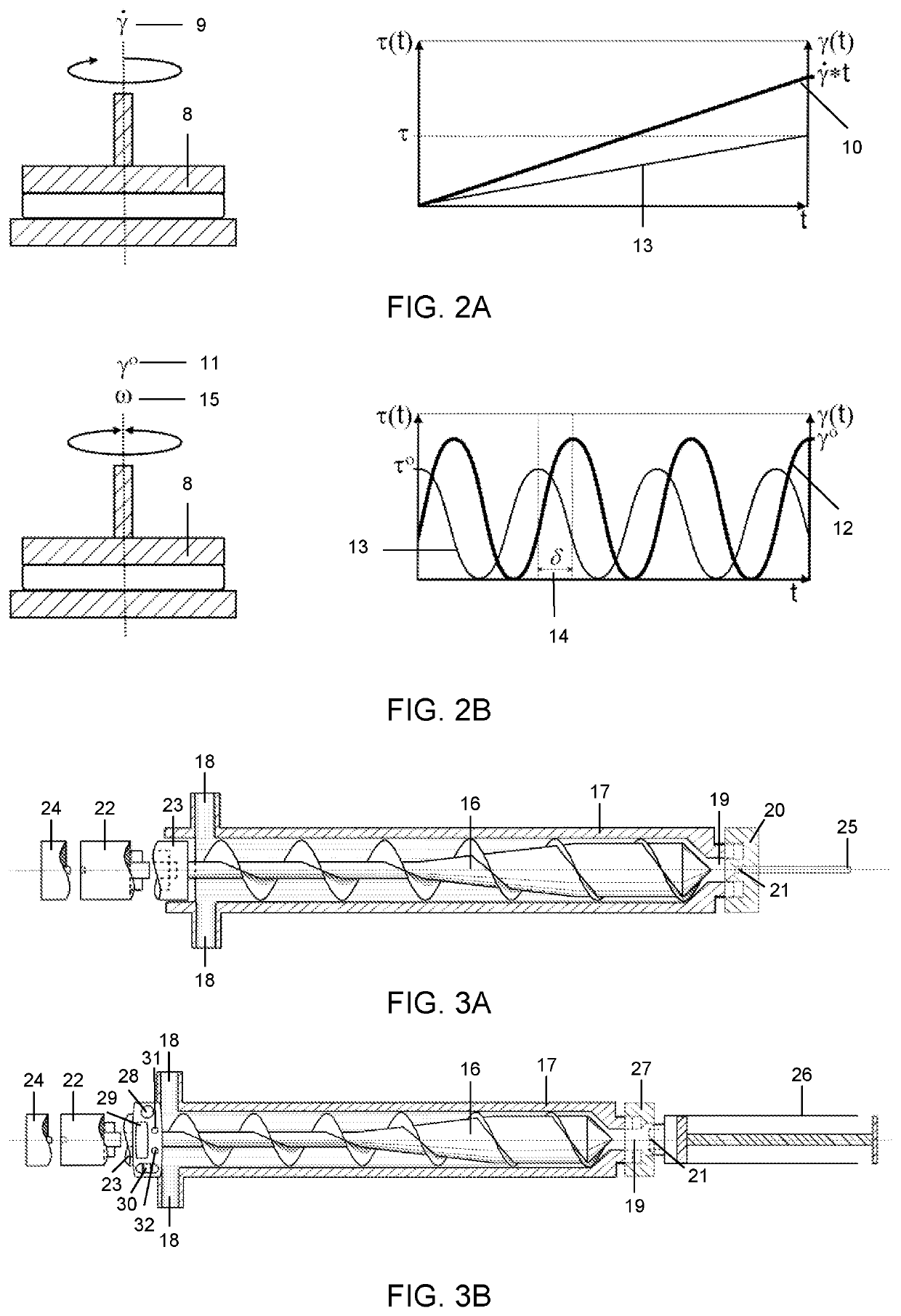
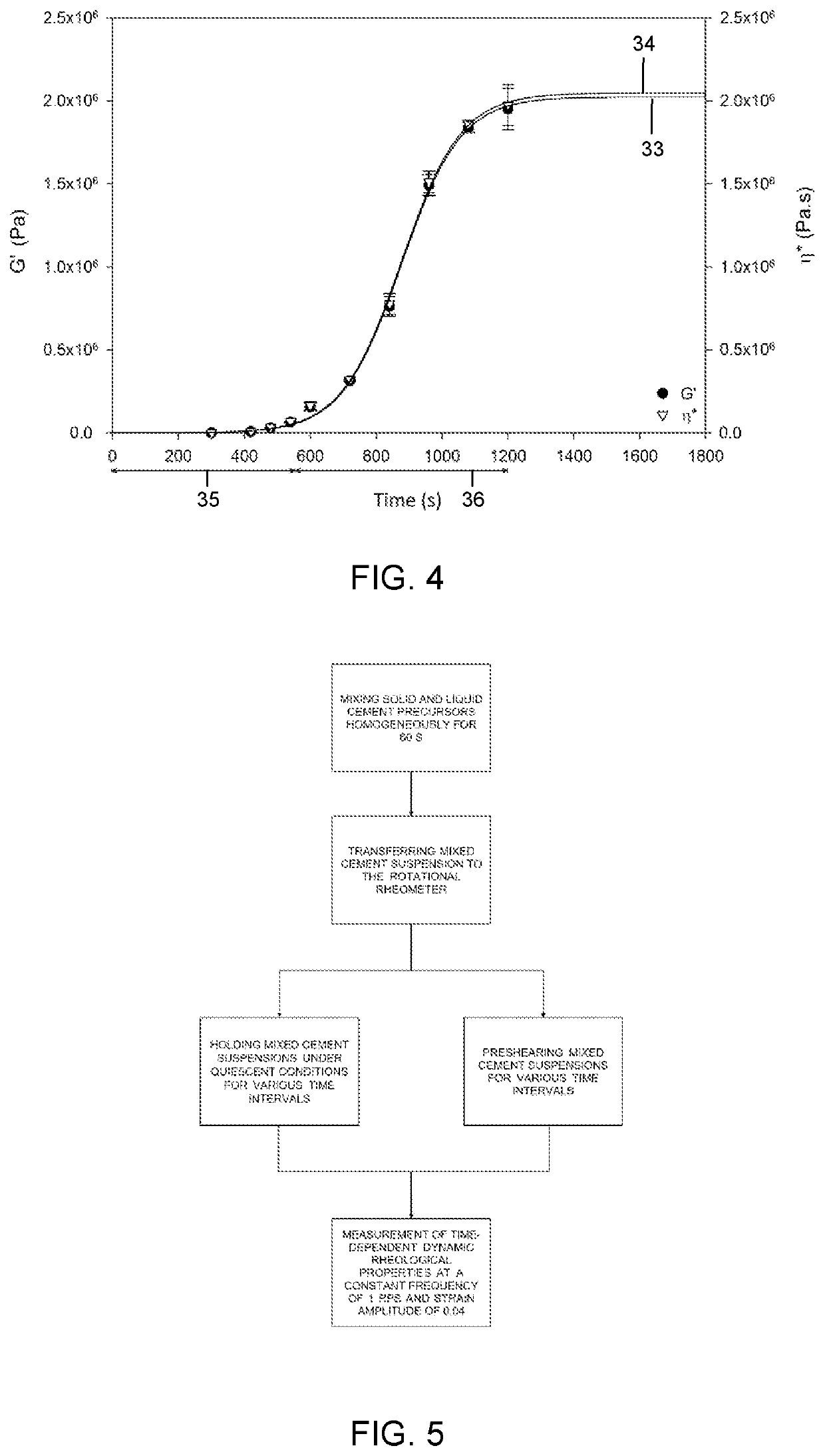
Preshearing method and apparatus for the control of the rheology and the injectability of aqueous cement suspensions for bone repair and regeneration
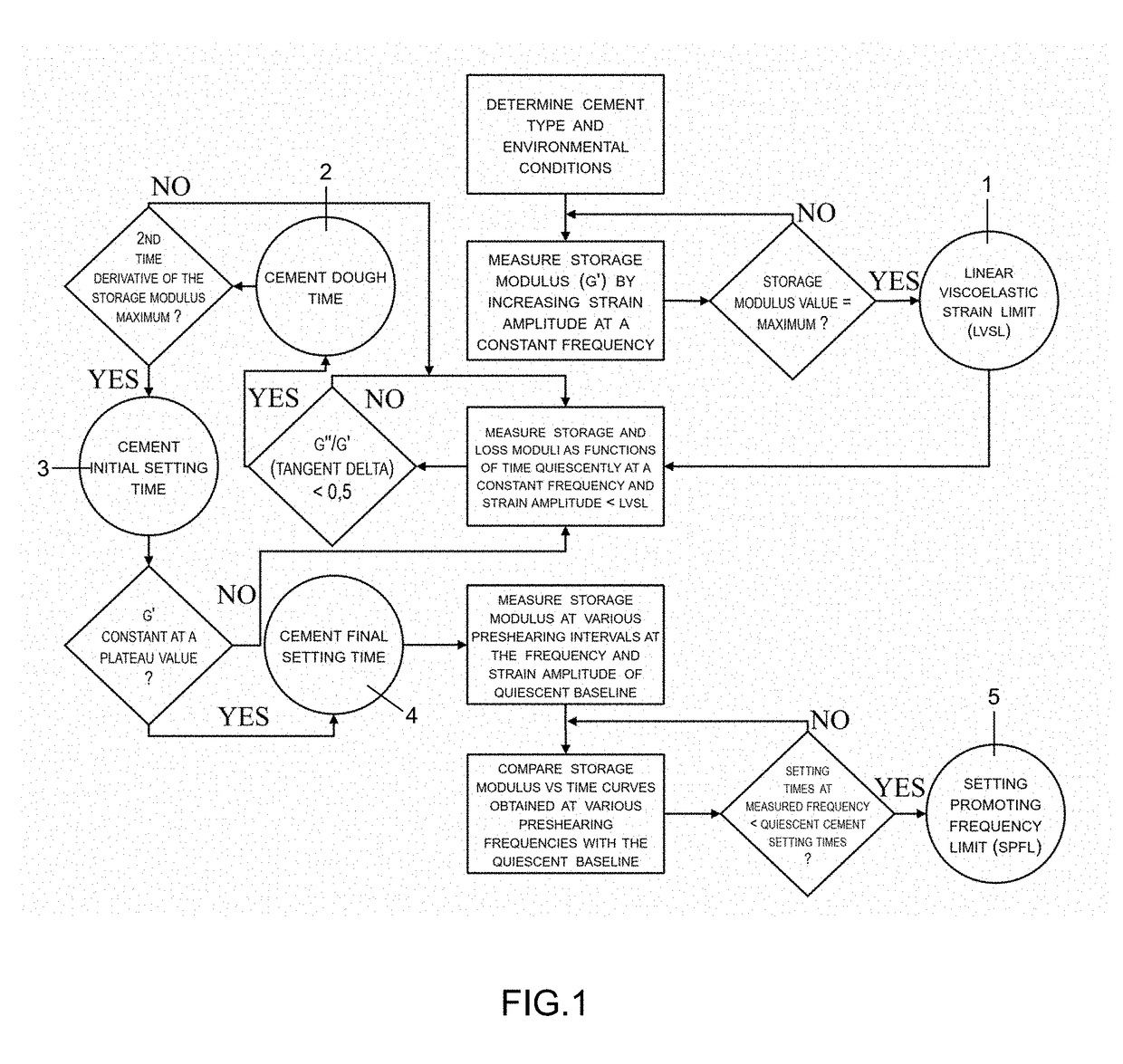
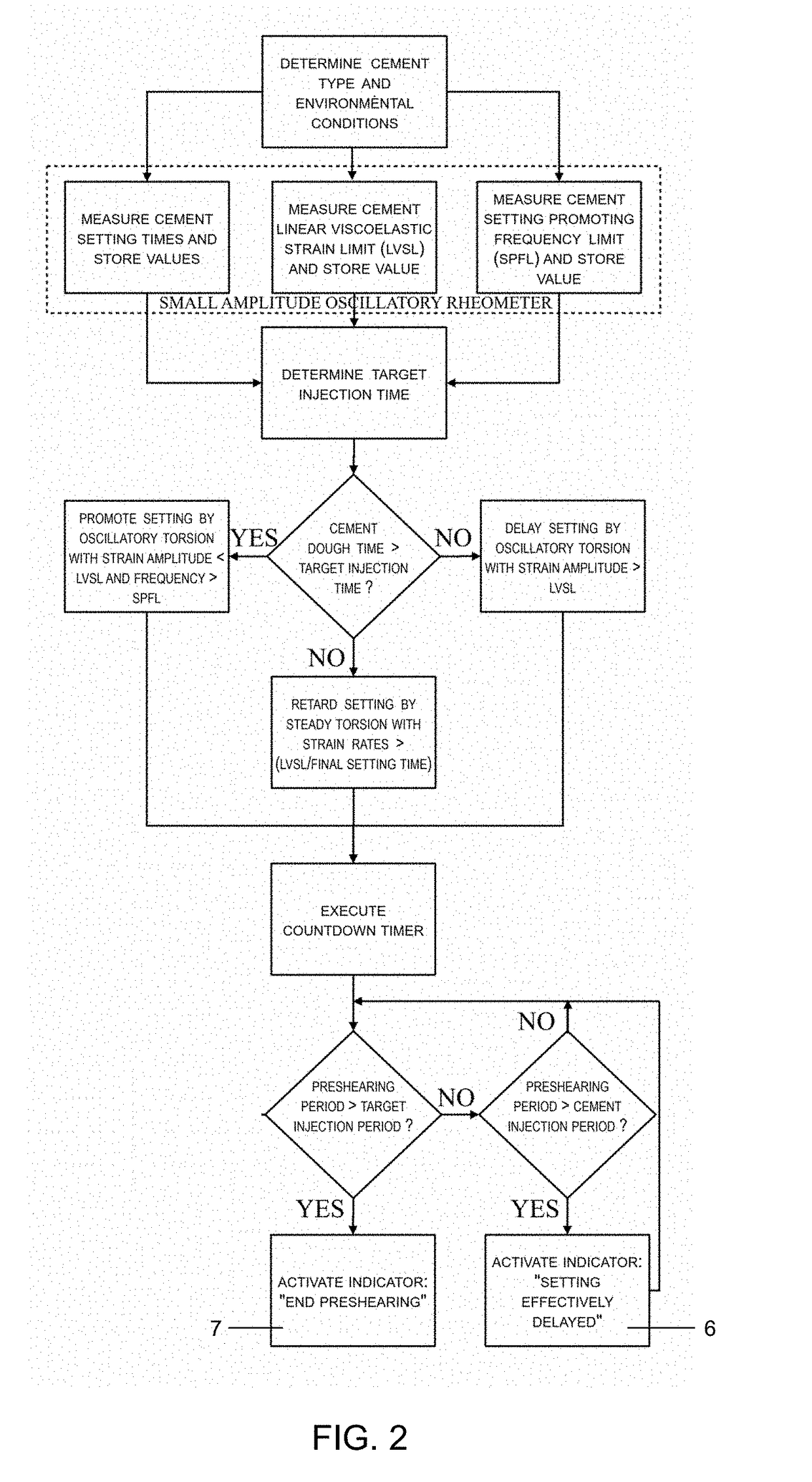
The invention provides a system for the preshearing based control of the flow and deformation behavior, i.e., the setting kinetics, and the time dependent shear viscosity, elasticity of aqueous cementitious suspensions that can be used for bone repair and regeneration. The dynamic cement microstructure is tailored to the demands of the surgical tasks (faster / slower setting) or additive manufacturing tasks (lower / higher viscosity) by application of various preshearing conditions. The relationships between the preshearing and pressurization conditions and the setting kinetics and the time dependent changes in elasticity and viscosity are complex and characterization of viscoelastic properties using advanced rheological characterization techniques including small-amplitude oscillatory and steady torsional rheometry is needed a priori to enable such tailoring. The preshearing system is intended to give control on the injectability and setting time of any calcium phosphate cement formulation to the surgeon during an orthopedic surgery where a batch of bone cement is processed. Other possible utilizations of the system include controlling the setting kinetics, shear viscosity and facilitating the resultant flow stability of cementitious ceramic suspensions processed in direct ink writing assemblies for additive manufacturing of cement constructs, in injection systems for restoration and fracking.
Owner:SAHIN ERDEM +1
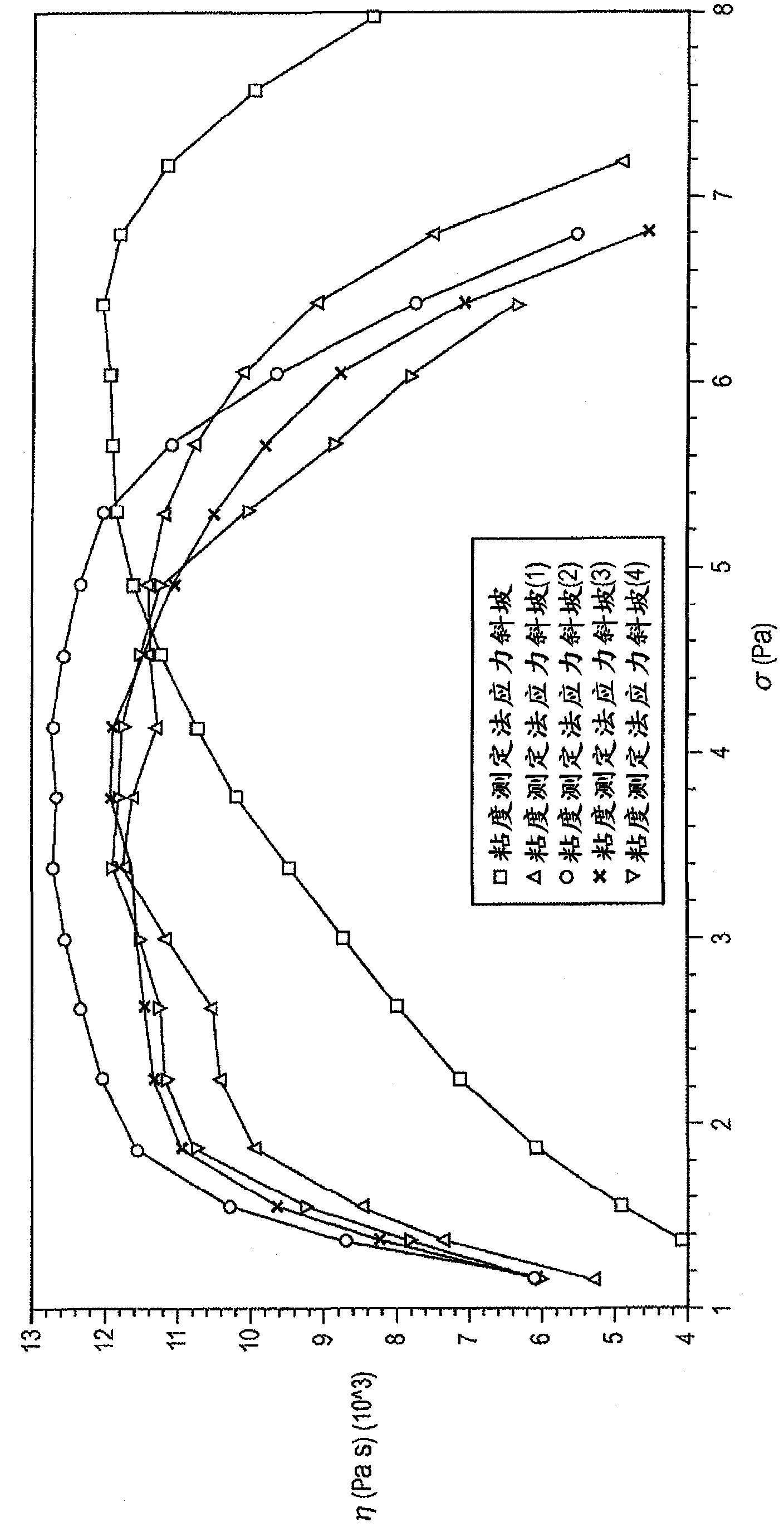
Rotational rheometer capable of testing normal stress
InactiveCN106872311AFlow propertiesFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesRheometrySmall amplitude
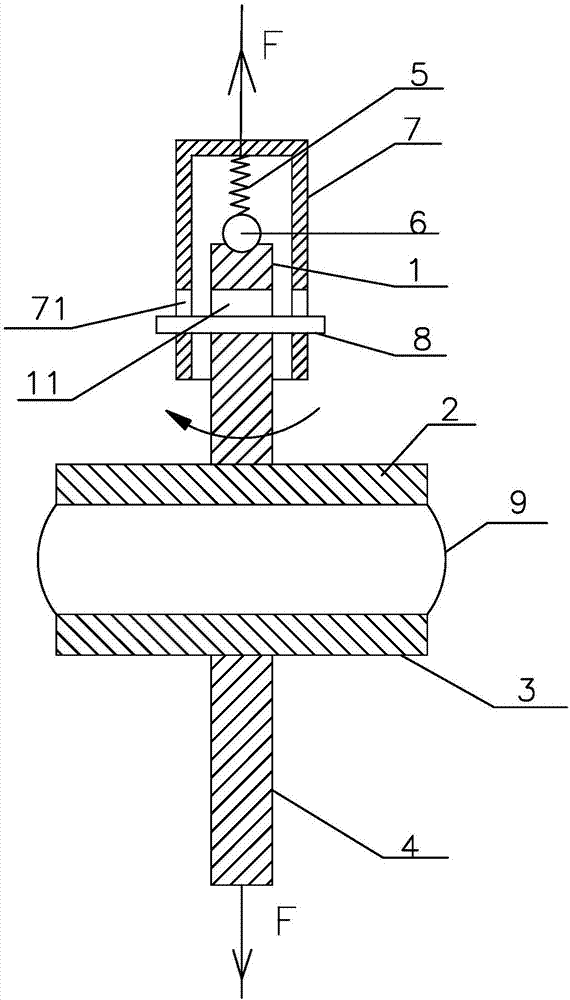
The invention relates to the technical field of rheological measurement and particularly relates to a rotational rheometer capable of testing normal stress. The rotational rheometer disclosed by the invention is improved on the basis of a traditional rotational rheometer, and a spring is increased, so that an upper plate can make a small-amplitude axial movement during test, the axial displacement is tested, the normal force is calculated, and a testing principle of the traditional rotational rheology parameters is still applicable to the rotational rheometer disclosed by the invention. A torque sensor is arranged on a rotating shaft of the rheometer. The rheometer is controlled by software, and experimental data and curves can be recorded and processed by computer software.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Rejuvenation of reclaimed asphalt
ActiveUS20150240081A1Low cloud and pour pointImprove thermal stabilityIn situ pavingsSolid waste managementRheometryVitrification
Asphalt compositions comprising reclaimed asphalt and an ester-functional rejuvenating agent derived from tall oil are disclosed. Rejuvenated binder compositions are also included. The rejuvenating agents restore to reclaimed asphalt desirable properties of virgin asphalt. Reduced glass-transition onset temperatures and improved creep stiffness in the rejuvenated binders translate to improved low-temperature cracking resistance in the asphalt. The rejuvenating agents impart desirable softening at low dosage while also maintaining acceptable penetration values. Dynamic shear rheometry results demonstrate that criteria for asphalt compositions under low, intermediate, and high temperature conditions can be achieved, and the asphalt will have good fatigue cracking resistance and rutting avoidance. The rejuvenating agents reduce the temperature needed to compact or mix asphalt compositions, which conserves energy and reduces cost. The rejuvenated asphalt and binder compositions enable greater use of reclaimed asphalt, especially RAP, and help the road construction industry reduce its reliance on virgin, non-renewable materials.
Owner:ARIZONA CHEM CO
System and method for interfacial rheometry
ActiveUS7926326B2Facilitate communicationPrevent movementFlow propertiesStrength propertiesRheometryInterface layer
An apparatus and method for performing rheological measurements of interfaces located at the top of fluid sub-phases. In one configuration, a rotating rheometer is provided with a chamber wall whose inner surface defines an outer chamber radius and an inner cylinder disposed within the cylindrical chamber and having an inner chamber radius. The rotating rheometer is configured to hold a liquid sub-phase and interface layer that can be probed using a circular ribbon that is concentric with and suspended between the inner cylinder and chamber wall. The ratio of the ribbon radius, inner chamber radius, and outer chamber radius is designed to yield an average shear rate in the inner region that is the same as an average shear rate in the outer region. In one configuration, an interface-pinning feature is provided on at least one of the inner cylinder and the chamber wall.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Dynamic reciprocating-bob rheometry
A sensor for making rheological measurements takes the form of a ferromagnetic bob alternately driven through a sample fluid in opposite directions by magnetic force from two alternately driven coils. The bob's position affects the mutual inductance between the coils, so it can be inferred by sensing the signal that current flowing in one coil induces in the other, and rheological properties are determined from the relationships among the bob's motion, the coil current, and the sensor geometry. Some such measurements' accuracies are enhanced by computing bob acceleration and suppressing inertial effects thereby detected.
Owner:PETROLEUM ANALYZER COMPANY
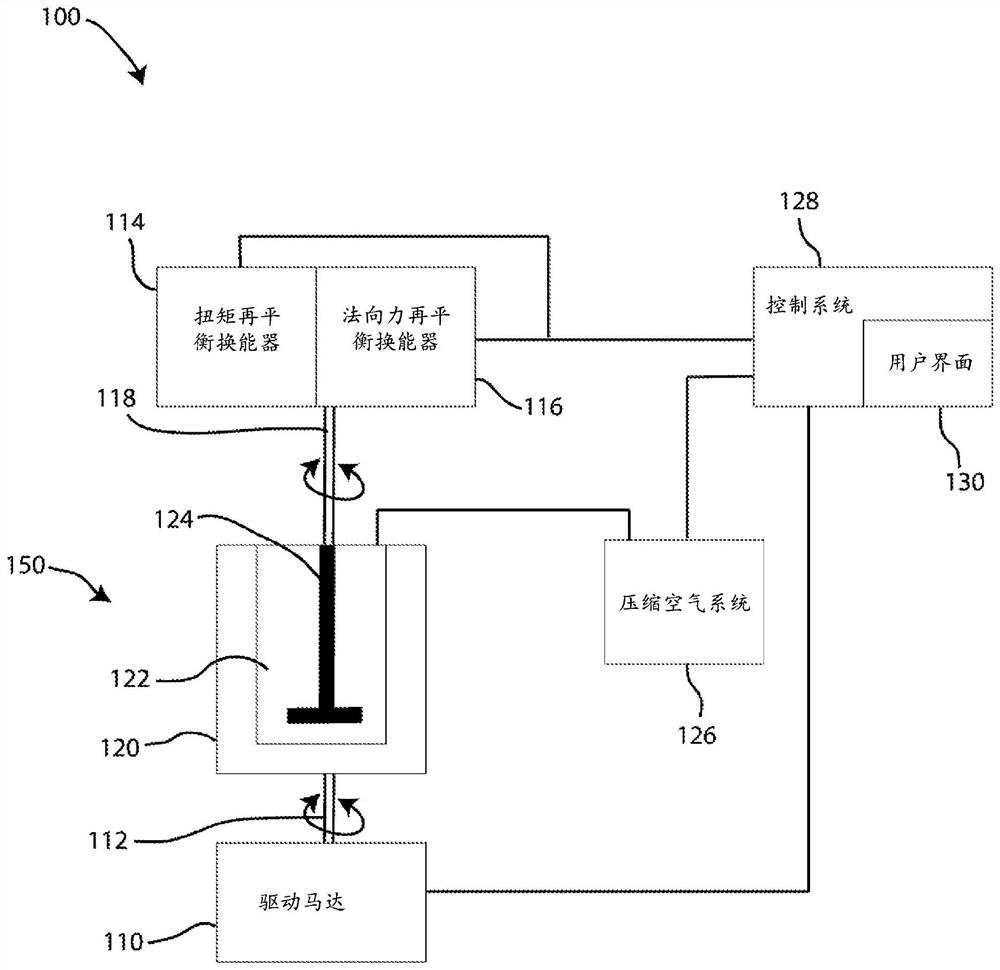
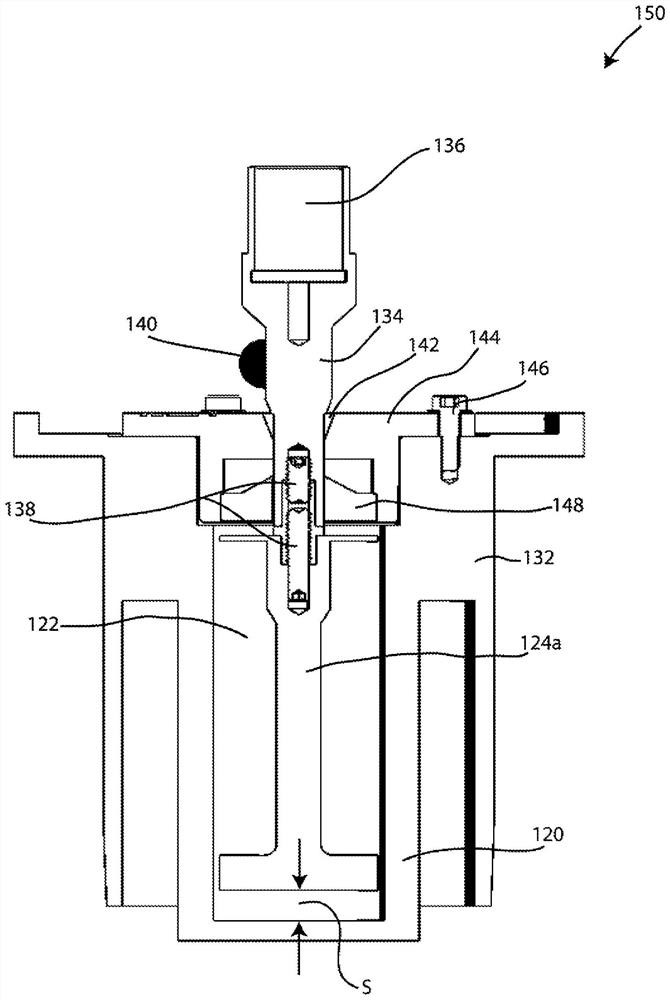
Rotor for rheometry of material with variable volume
The invention provides a rheological system. The rheological system comprises a sample chamber; a compressed air system configured to provide compressed air to pressurize the sample chamber; and a rotor configured for rheological measurement of a material having a variable volume, the rotor including an elongate shaft extending to a measurement portion, the measurement portion having a widened geometry relative to the elongate shaft. The rotor is dimensioned such that a compression ratio of at least 5: 1, defined by a ratio of a decompressed volume of the sample when the sample chamber is not pressurized to a compressed volume of the sample when the sample chamber is pressurized, is achieved while maintaining a material coverage of the sample over the entire measurement portion of the rotor. Methods of employing rheological measurements using such rotors are also disclosed.
Owner:TA仪器 沃特世有限责任公司
Expert-system-based rheology
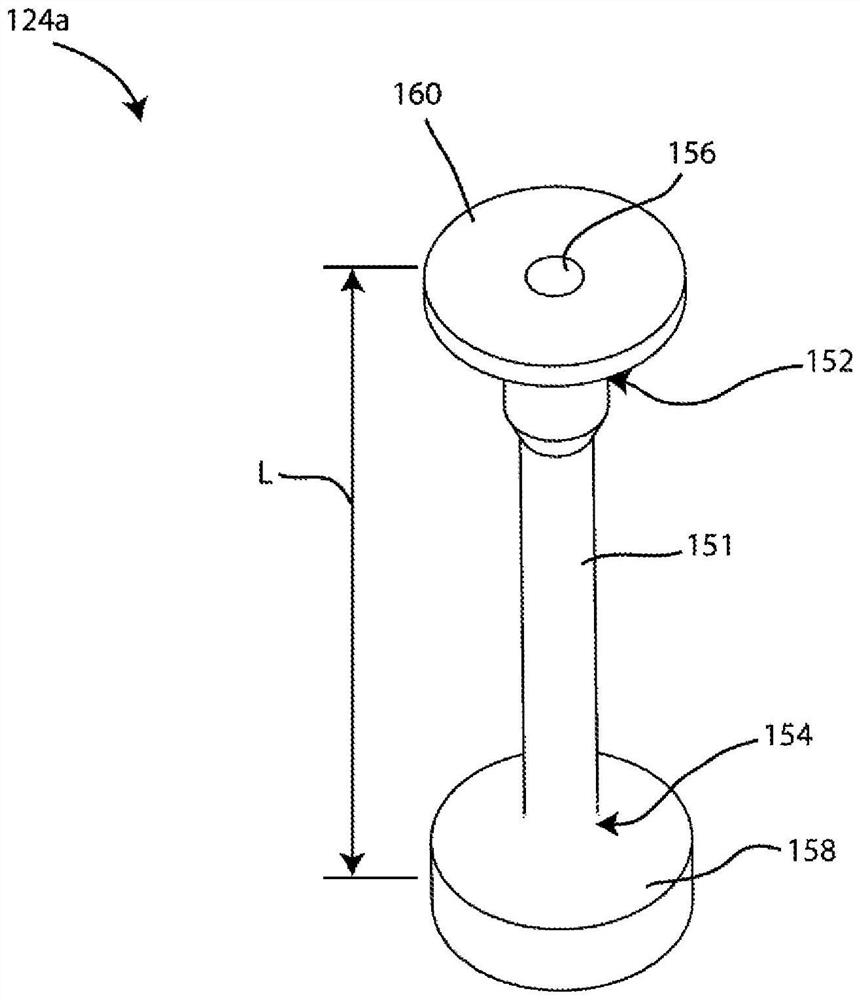
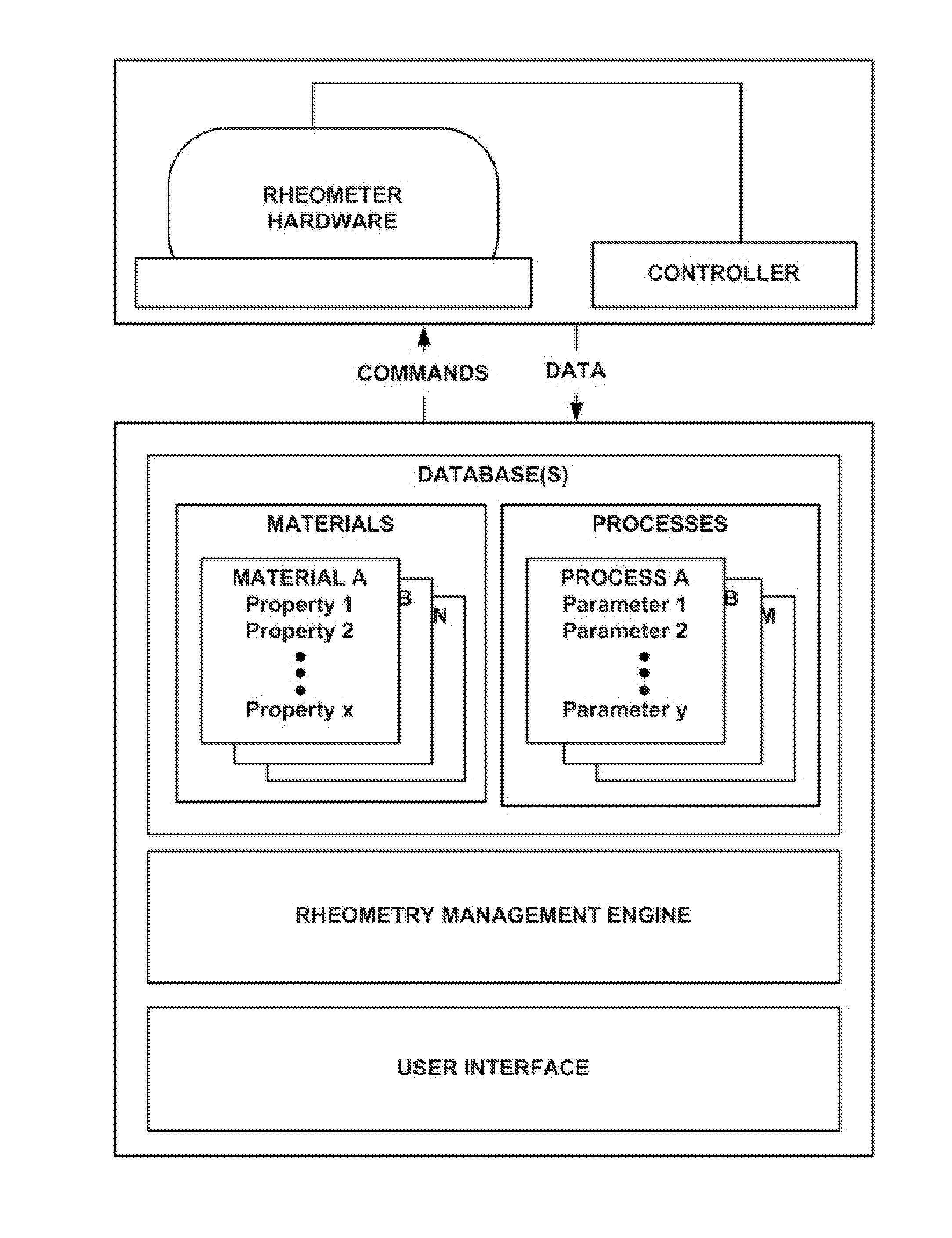
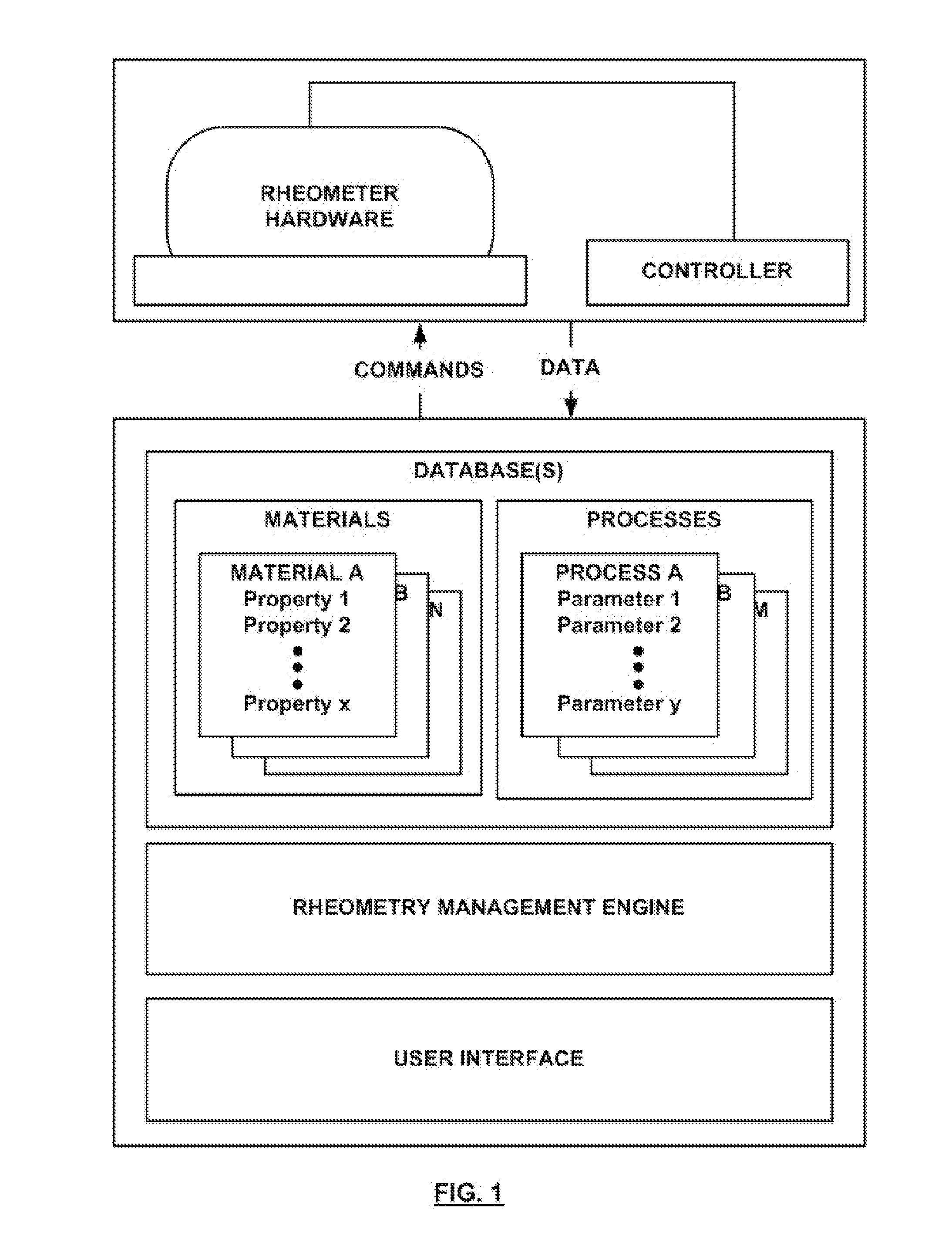
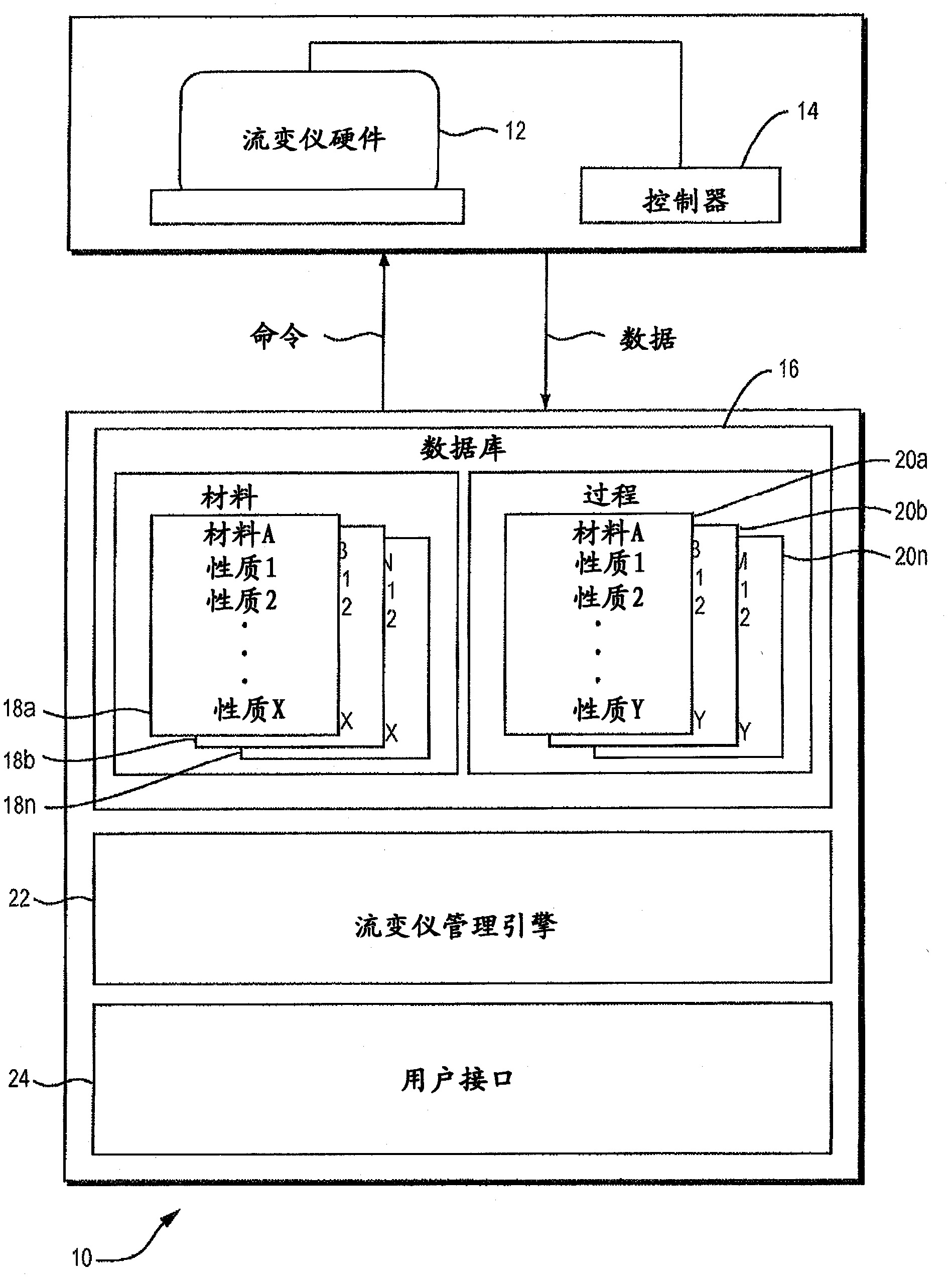
A rheometer is disclosed that includes rheometry logic that is responsive to a material selection control, to an objective selection control, to material property storage, and to process parameter storage, and is operative to assist the user with a measurement using the rheometer. In another general aspect, a rheometer includes sample history storage operative to store a history that spans a plurality of different operations performed by the rheometer on a same sample.
Owner:NETZSCH GERATEBAU GMBH
Tensile shear rheometer and method for testing rheological properties of alloy solid-liquid two-phase region by using tensile shear rheometer
InactiveCN106596334ASimple, convenient and accurateSimple, convenient and accurate expressionIndirect flow property measurementRheometryFiber
The invention discloses a tensile shear rheometer and a method for testing rheological properties of an alloy solid-liquid two-phase region by using the tensile shear rheometer, and relates to the tensile shear rheometer and the method for testing the rheological properties of the alloy solid-liquid two-phase region by using the tensile shear rheometer. The invention aims at improving the accuracy and efficiency of a conventional method for testing rheological properties of an alloy solid-liquid two-phase region. The tensile shear rheometer is composed of a pull bar, a positioning pin, an upper end cover, a crucible, a high-aluminum fiber, and a lower end cover. Then, a molten metal liquid flows into the rheometer and is cooled to prepare a rheological test specimen; finally, creep properties of the alloy melt are tested on a high-temperature creepmeter, and the rheological properties of the alloy in the solid-liquid two-phase region are obtained. The method can more accurately measure the rheological properties of the alloy in the solid-liquid two-phase region, the specimen only needs to be prepared in the method, and a used loading device and heating device are both realized in the high-temperature creepmeter; the method is simple and easy to control, and easy to popularize.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
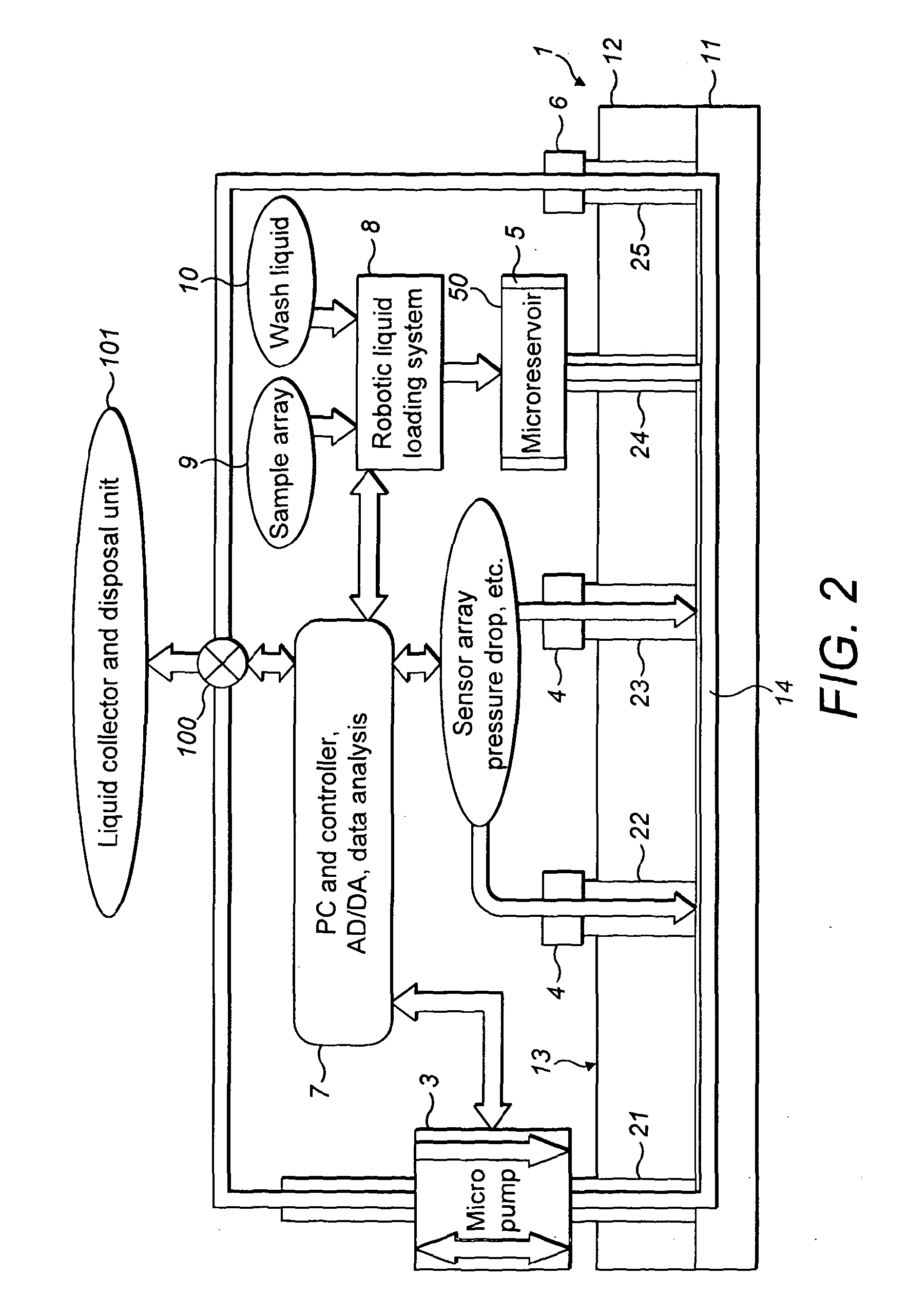
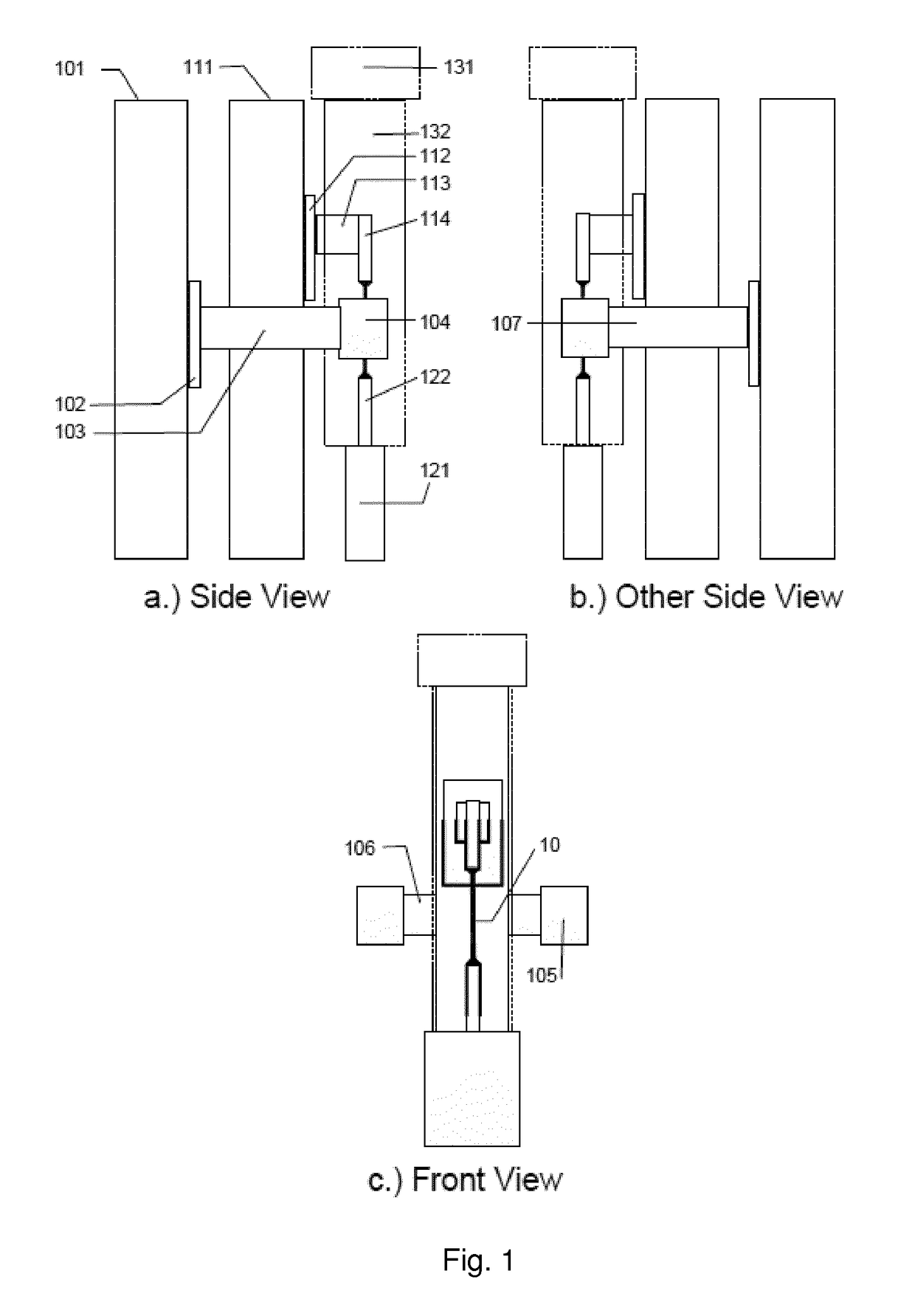
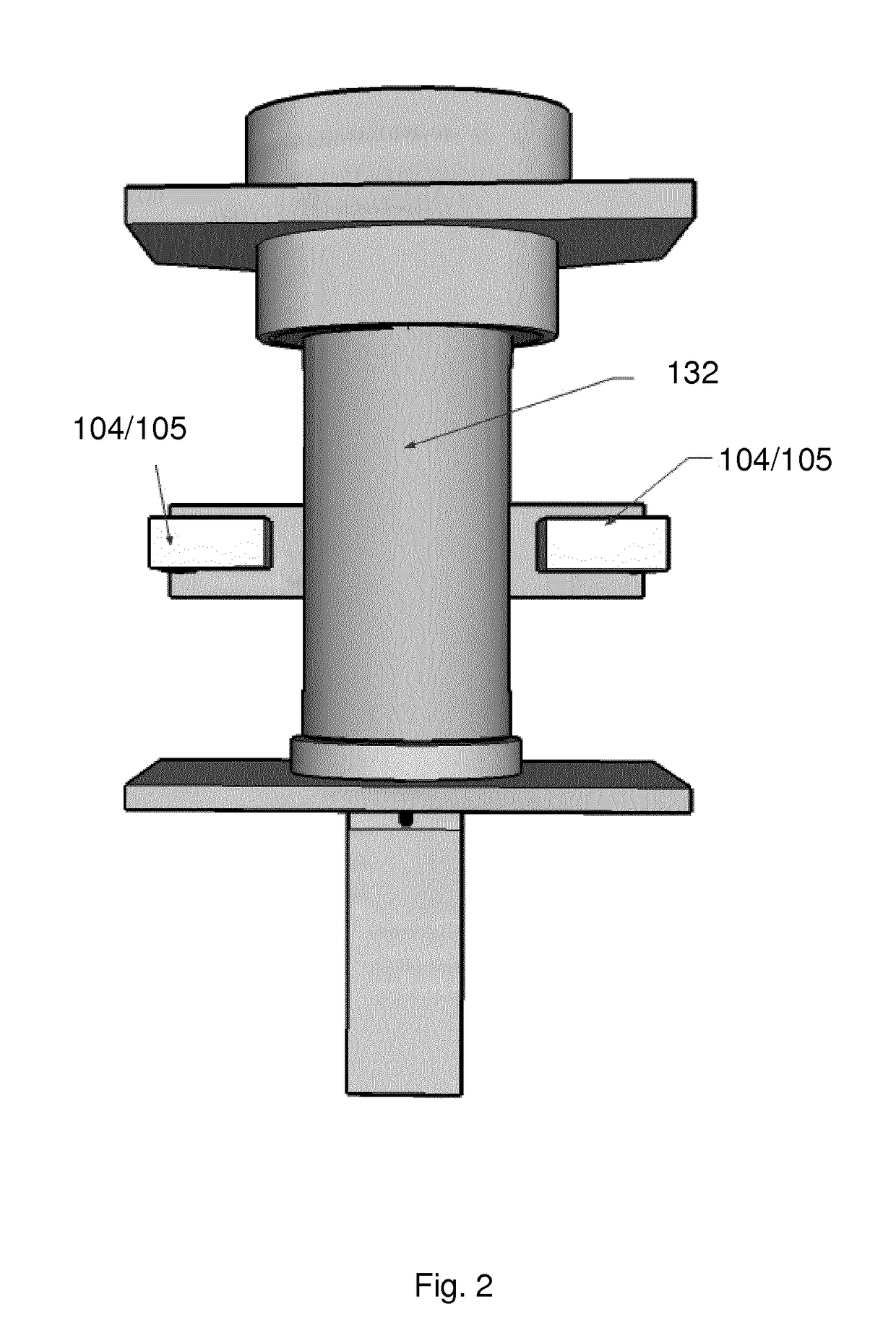
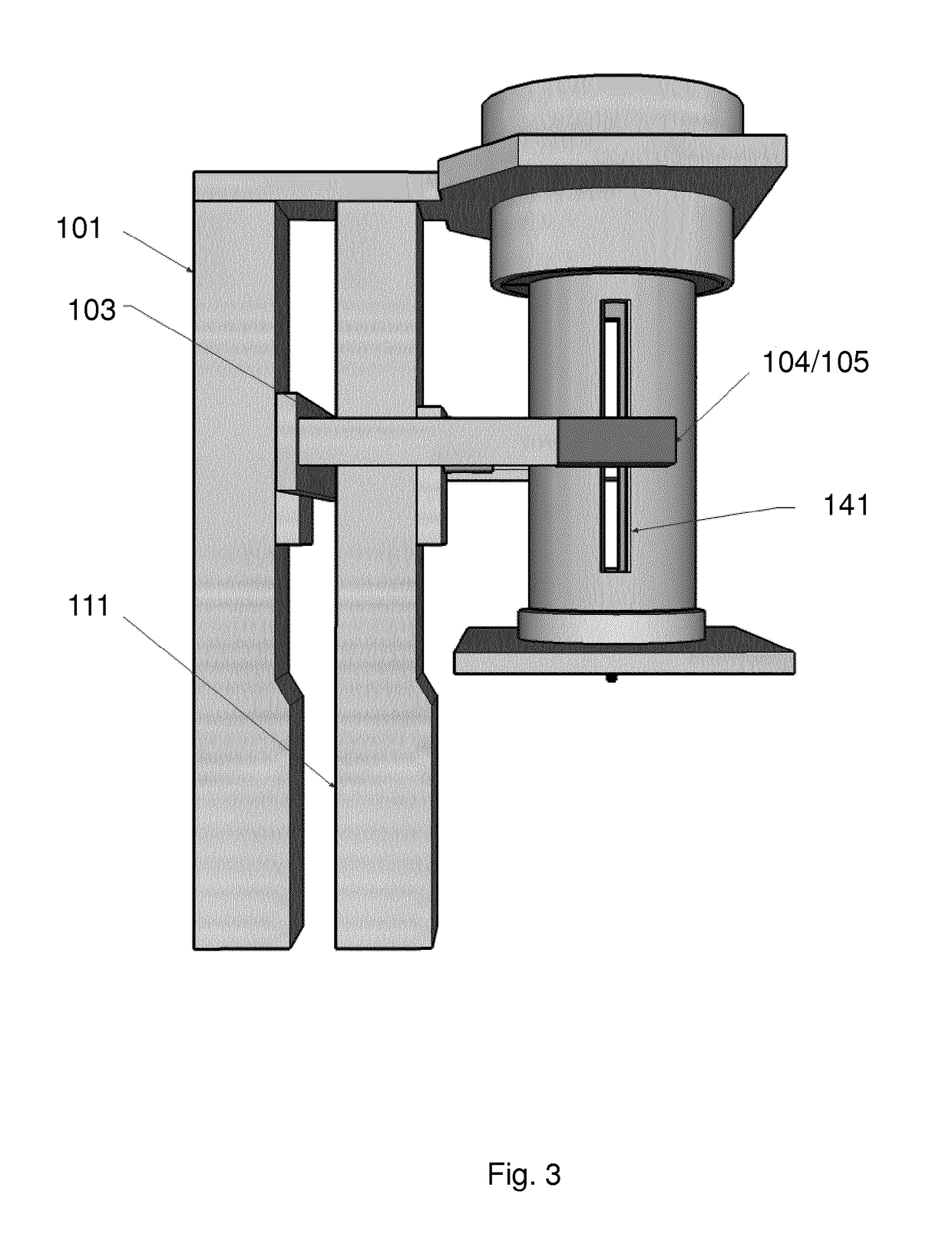
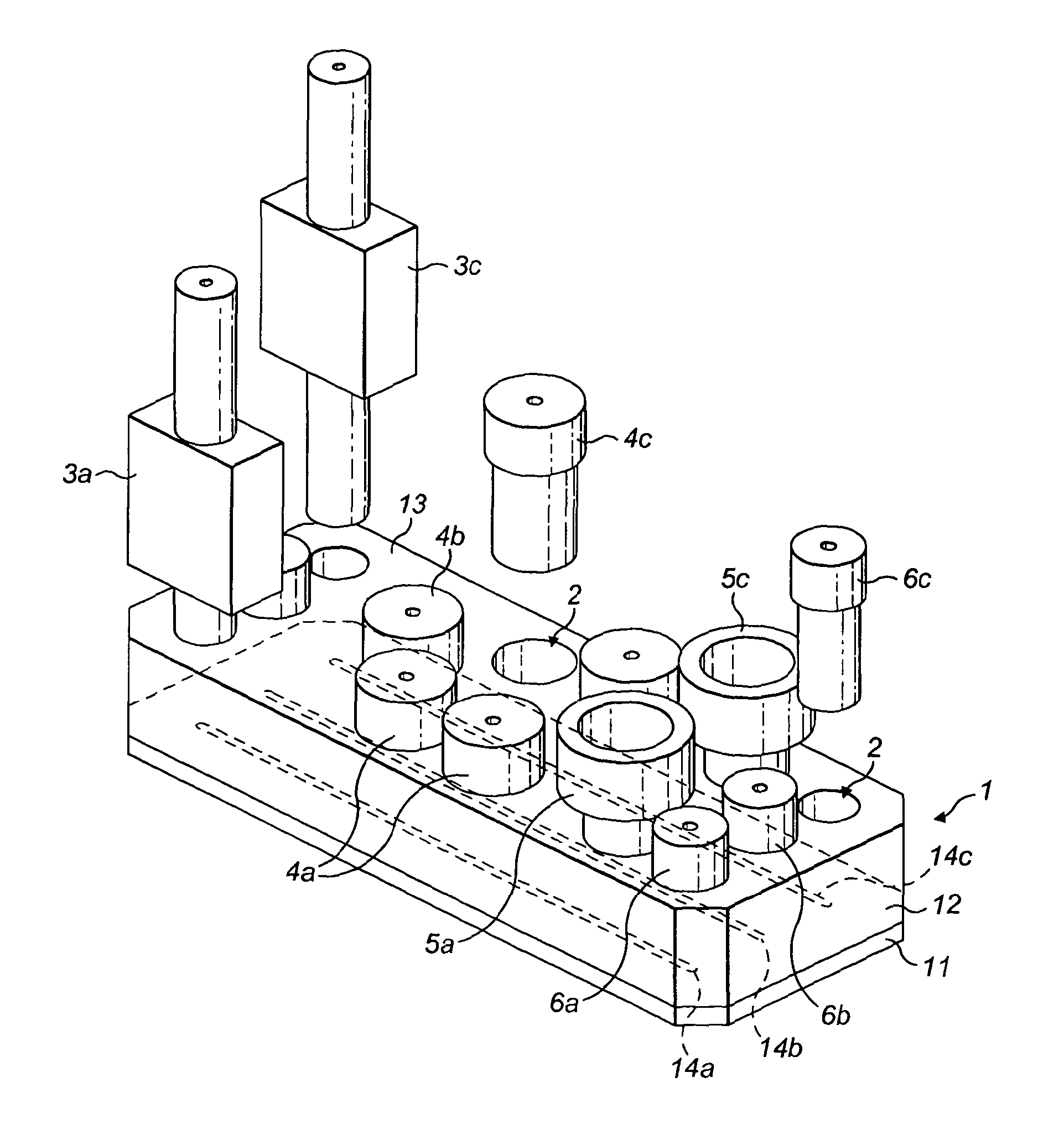
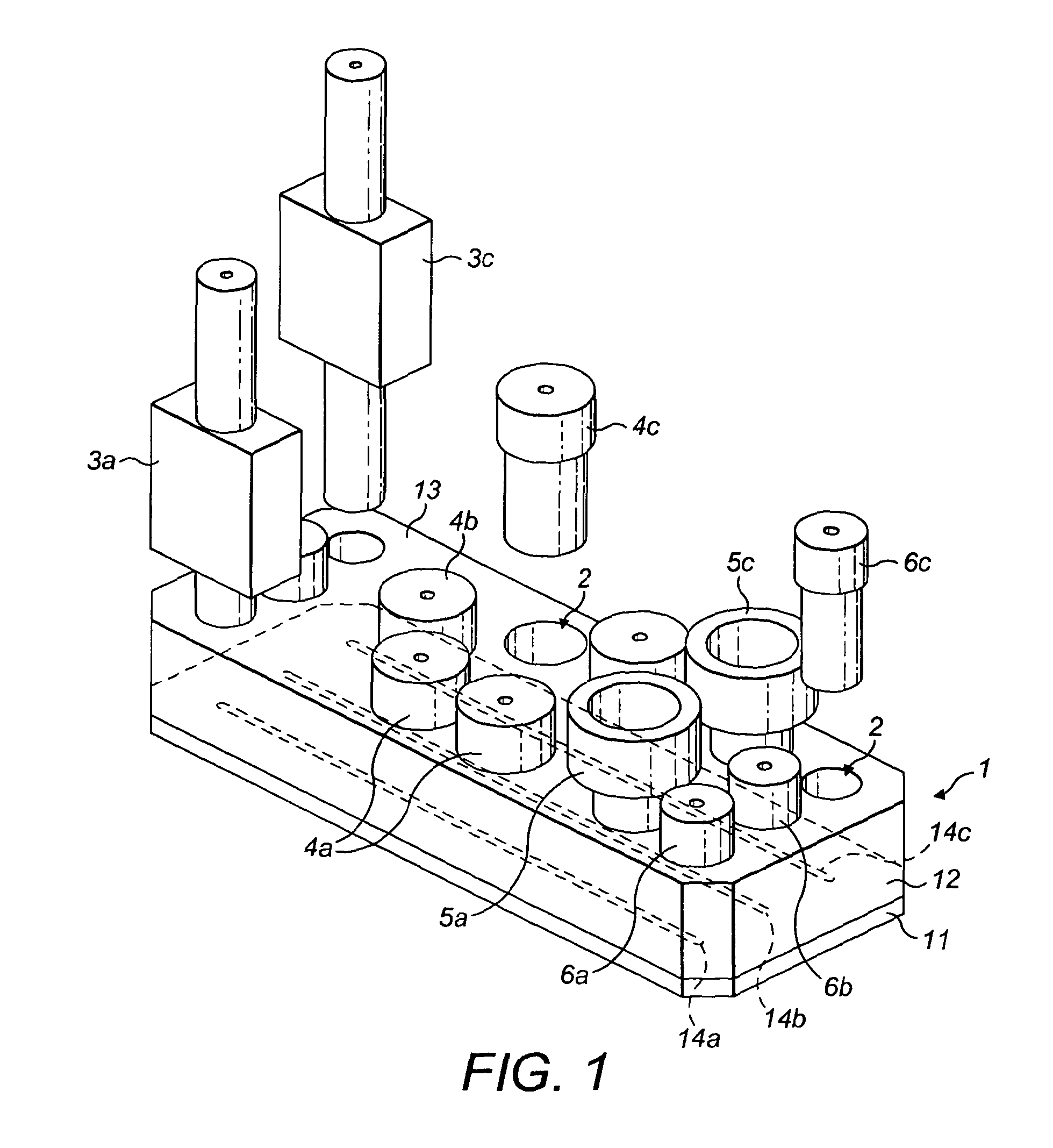
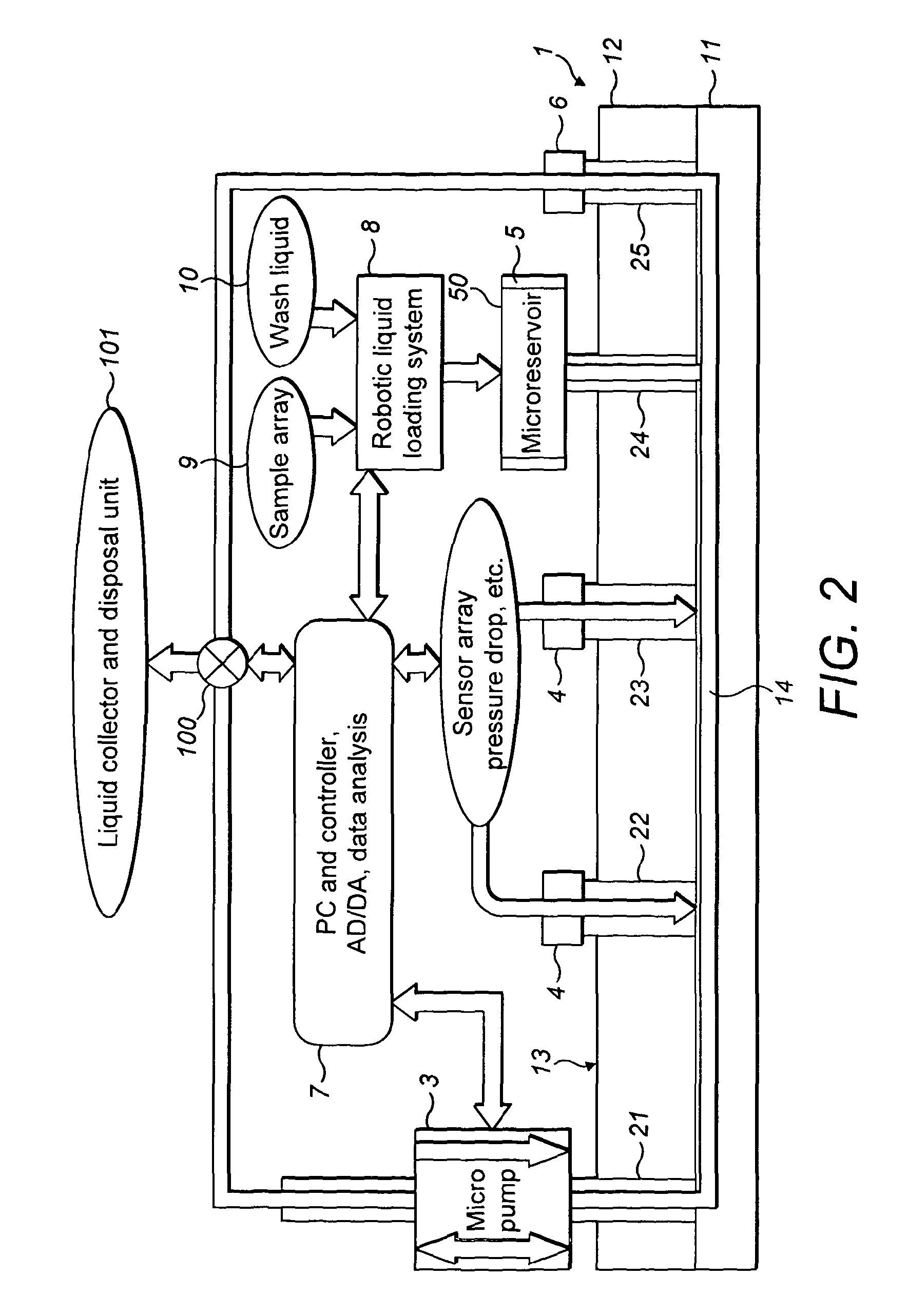
Rheometry apparatus
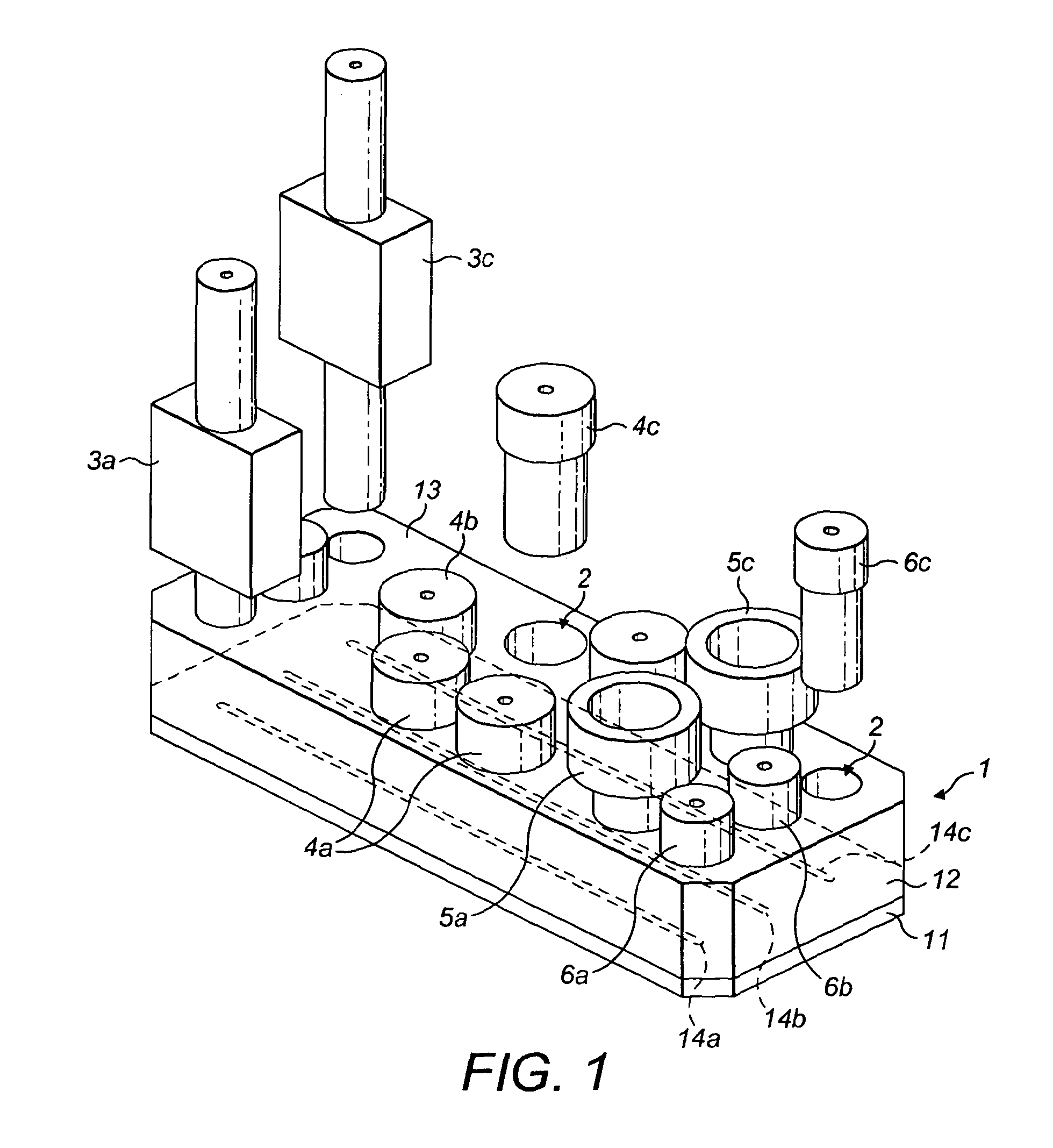
InactiveUS20130125627A1Convenient ArrangementSimpler and cheap to produceMetal working apparatusDirect flow property measurementRheometryEngineering
Rheometry apparatus comprises a block of substantially rigid material having an external surface and at least a first internal flow channel, the first internal flow channel being arranged inside the block and substantially in a plane and the block further comprising a plurality of holes, each hole communicating with the first internal flow channel at a respective position along the first internal flow channel and extending from the respective position to said external surface so as to provide access to the first internal flow channel from the external surface, the plurality of holes comprising a first hole communicating with a first said position, for connection to pumping means to drive fluid flow along said first internal flow channel, a second hole communicating with a second position and in which a sensor may be located to measure a property of fluid at the second position, and a third hole communicating with a third position and in which a sensor may be located to measure a property of fluid at the third position.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
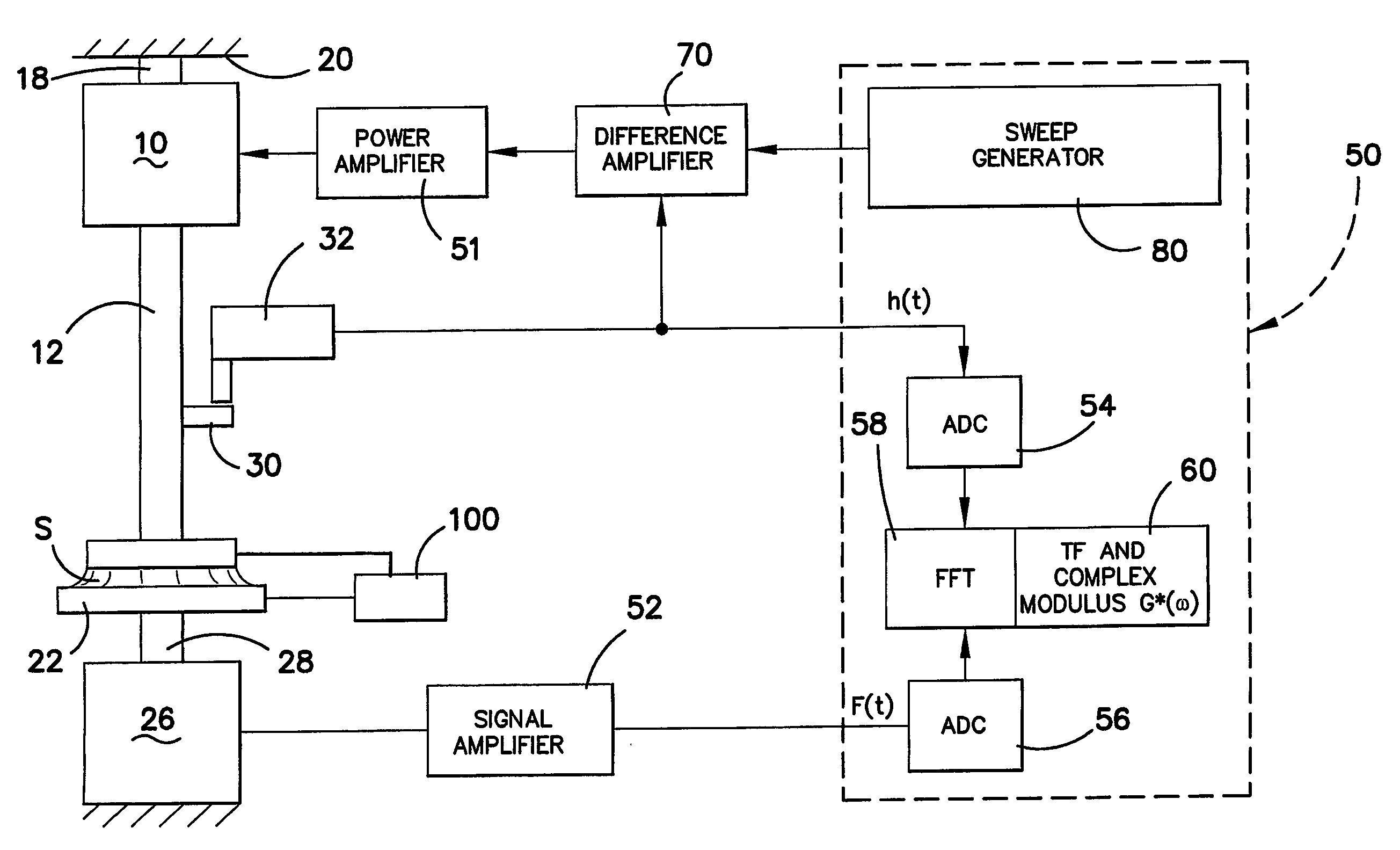
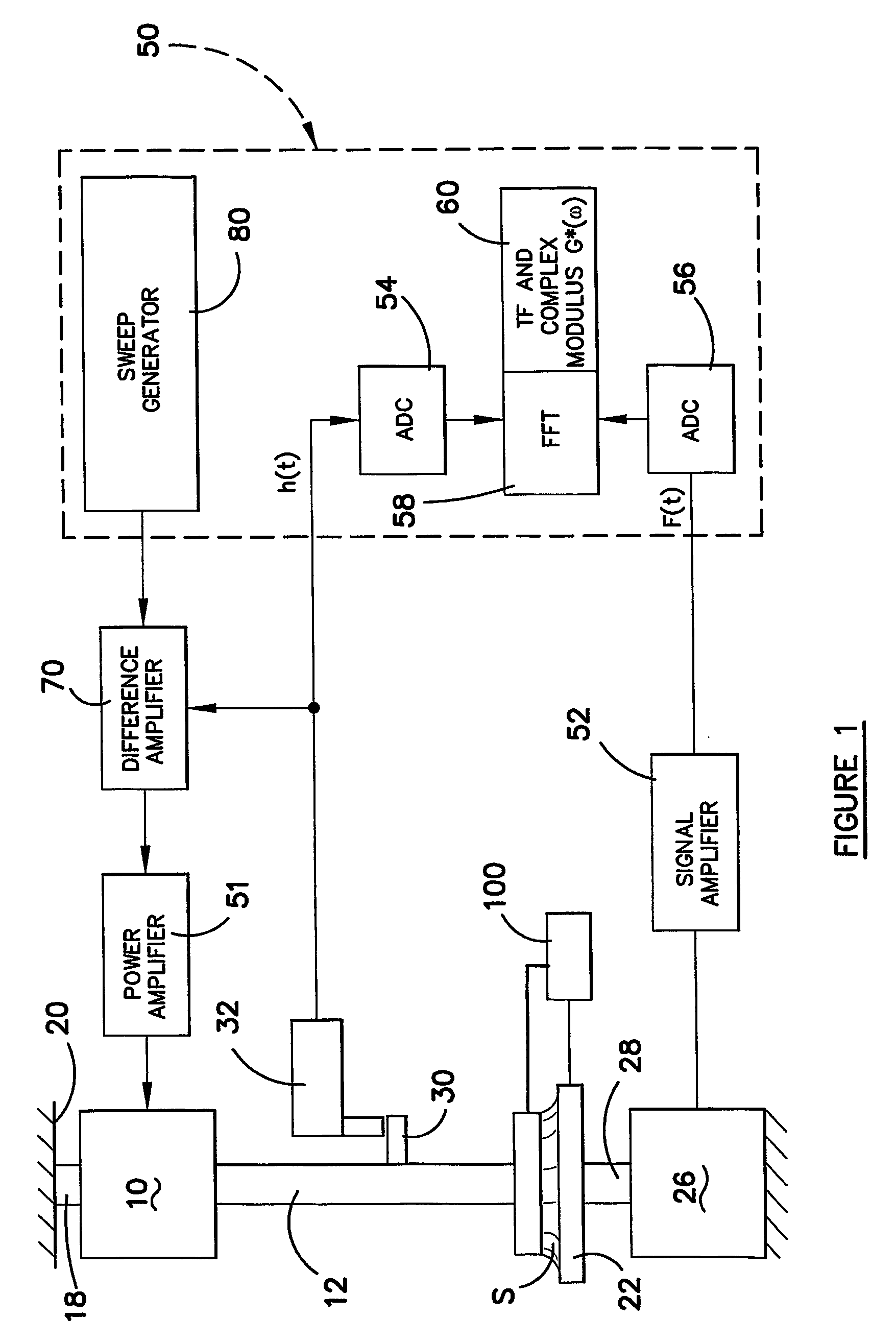
Rheometer
InactiveUS7194895B2Accurate measurementFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsMachines/enginesRheometryThermal expansion
A rheometer and method of making rheological measurements is disclosed, in which a sample is supported between plates and an alternating movement is applied by a driver, support rod and plate. Force and displacement measurements are taken and the property determined from those measurements. The vibrating signal which is applied is in the form of a frequency sweep signal having a monotonic group delay function. The top plate is provided with a surface which causes a meniscus to form up a side edge of the plate to reduce the spring nature of the sample when the movement is supplied to the sample, and a supporting rod which supports the top plate is preferably formed from a material having a low coefficient of thermal expansion so that the gap between the plates is maintained substantially constant if the sample is heated to take measurements at different temperatures.
Owner:GBC SCI EQUIP
Preshearing method for the control of the rheology and the injectability of aqueous inorganic cements
The invention provides a system for the preshearing based control of the flow and deformation behavior, i.e., the setting kinetics, and the time dependent shear viscosity, elasticity of aqueous cementitious suspensions that can be used for bone repair and regeneration. The dynamic cement microstructure is tailored to the demands of the surgical tasks (faster / slower setting) or additive manufacturing tasks (lower / higher viscosity) by application of various preshearing conditions. Since the relationships between the preshearing and pressurization conditions and the setting kinetics and the time dependent changes in elasticity and viscosity are complex, a priori characterization of viscoelastic properties using the advanced rheological characterization technique of small-amplitude oscillatory rheometry is needed to enable such tailoring. The preshearing system is intended to give control on the injectability and setting time of any calcium phosphate cement formulation to the surgeon during an orthopedic surgery where a batch of bone cement is processed. Other possible utilizations of the system include controlling the setting kinetics, shear viscosity and facilitating the resultant flow stability of cementitious ceramic suspensions processed in direct ink writing assemblies for additive manufacturing of cement constructs, in injection systems for oil wells, restoration and fracking.
Owner:SAHIN ERDEM
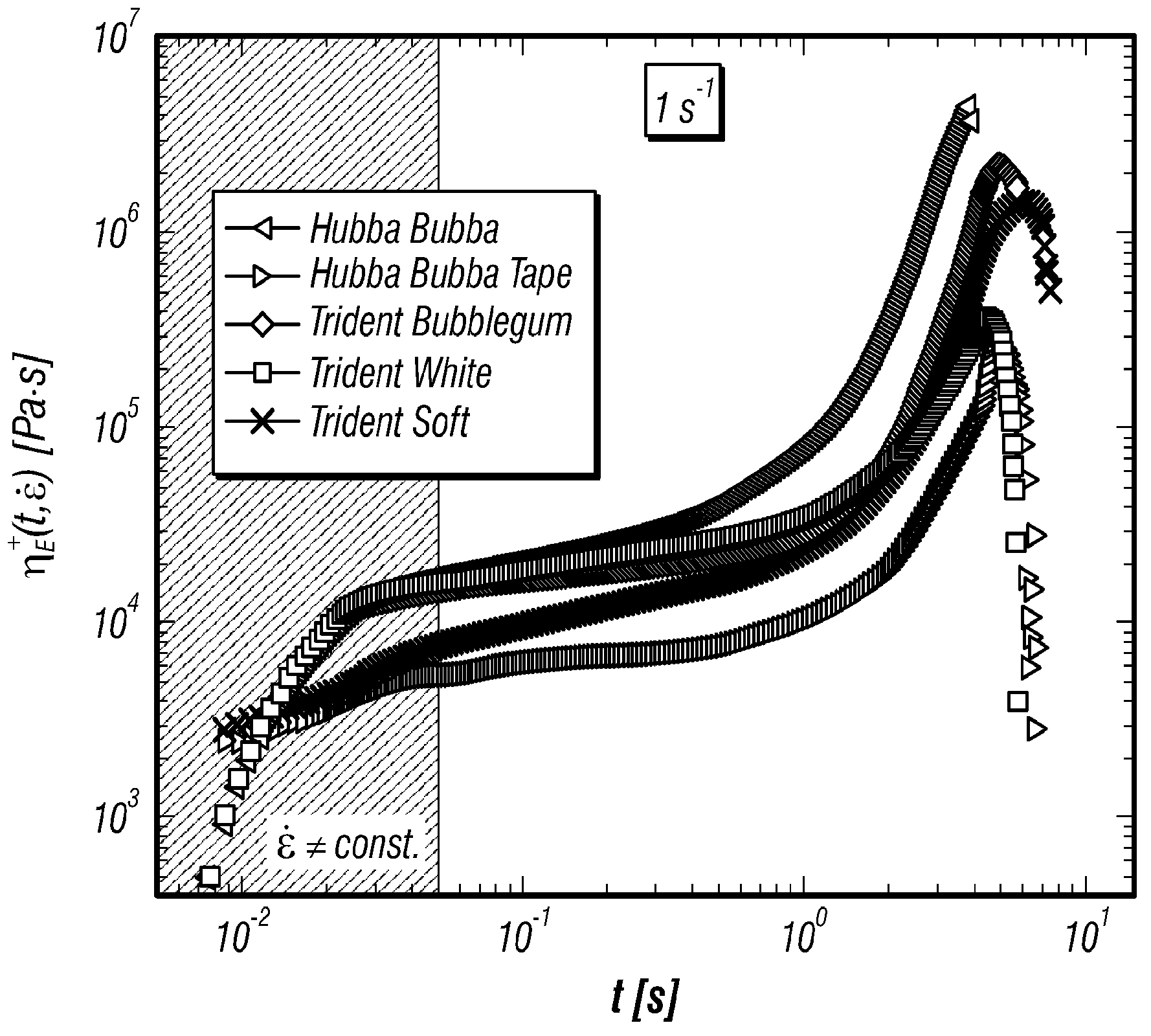
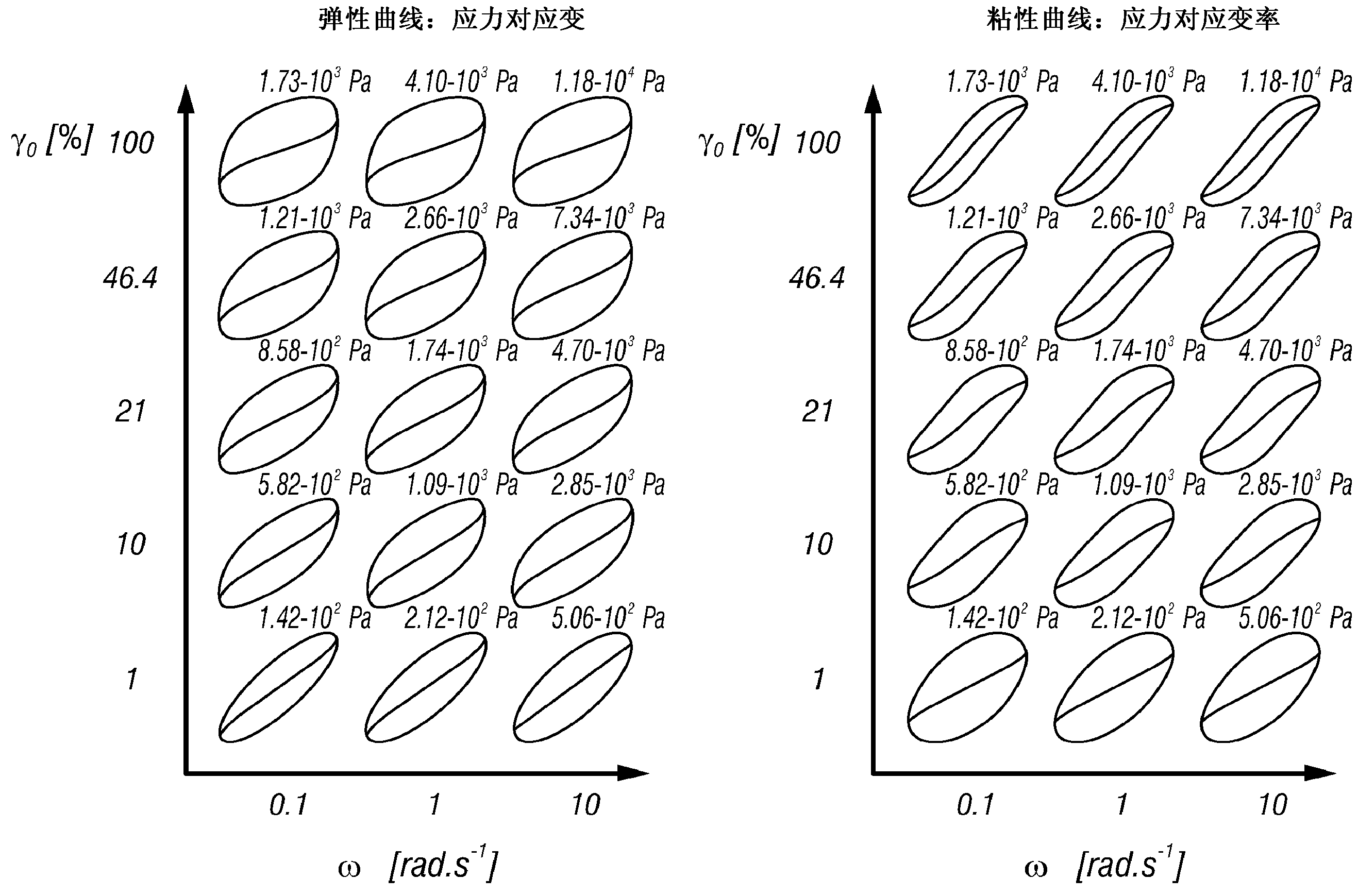
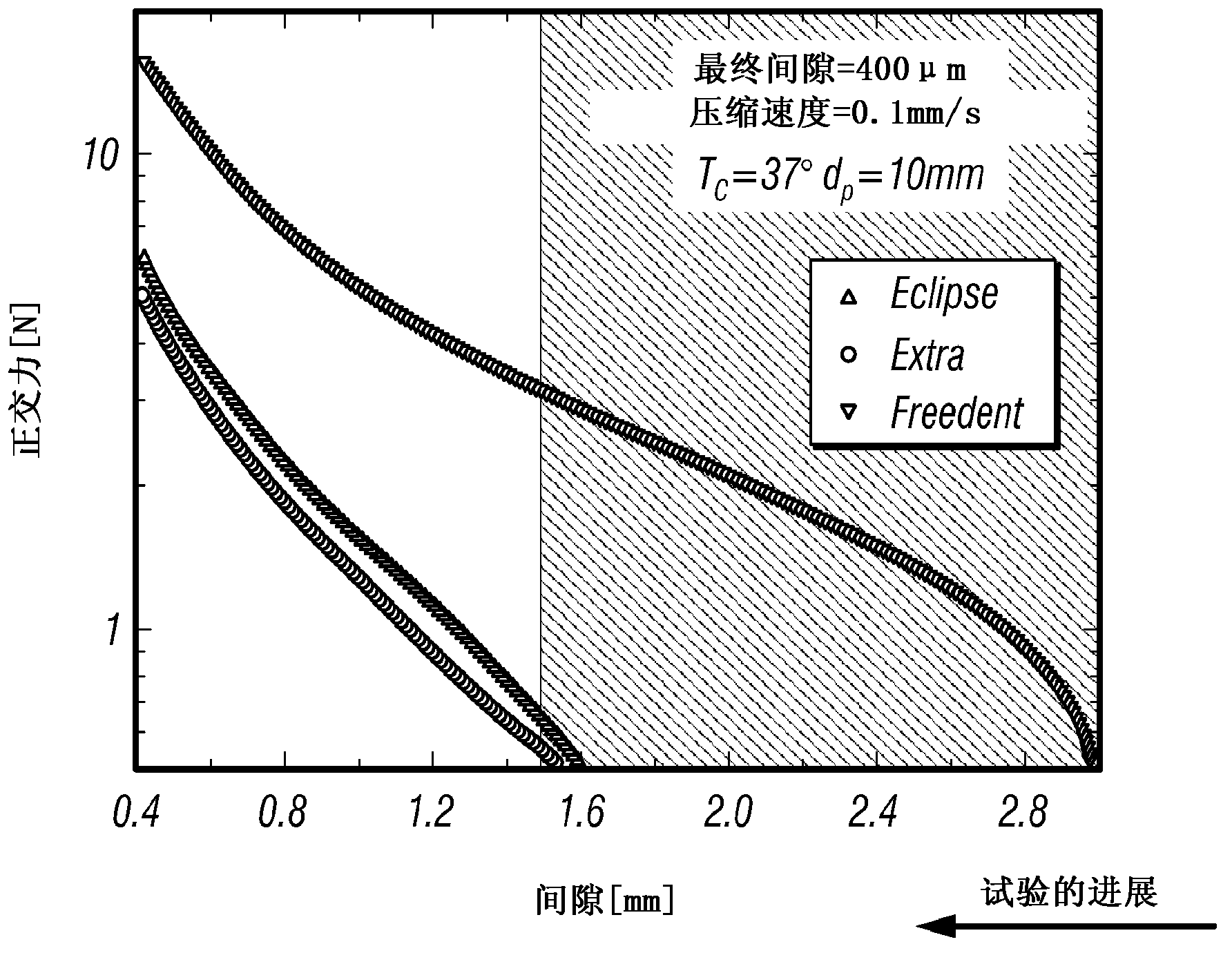
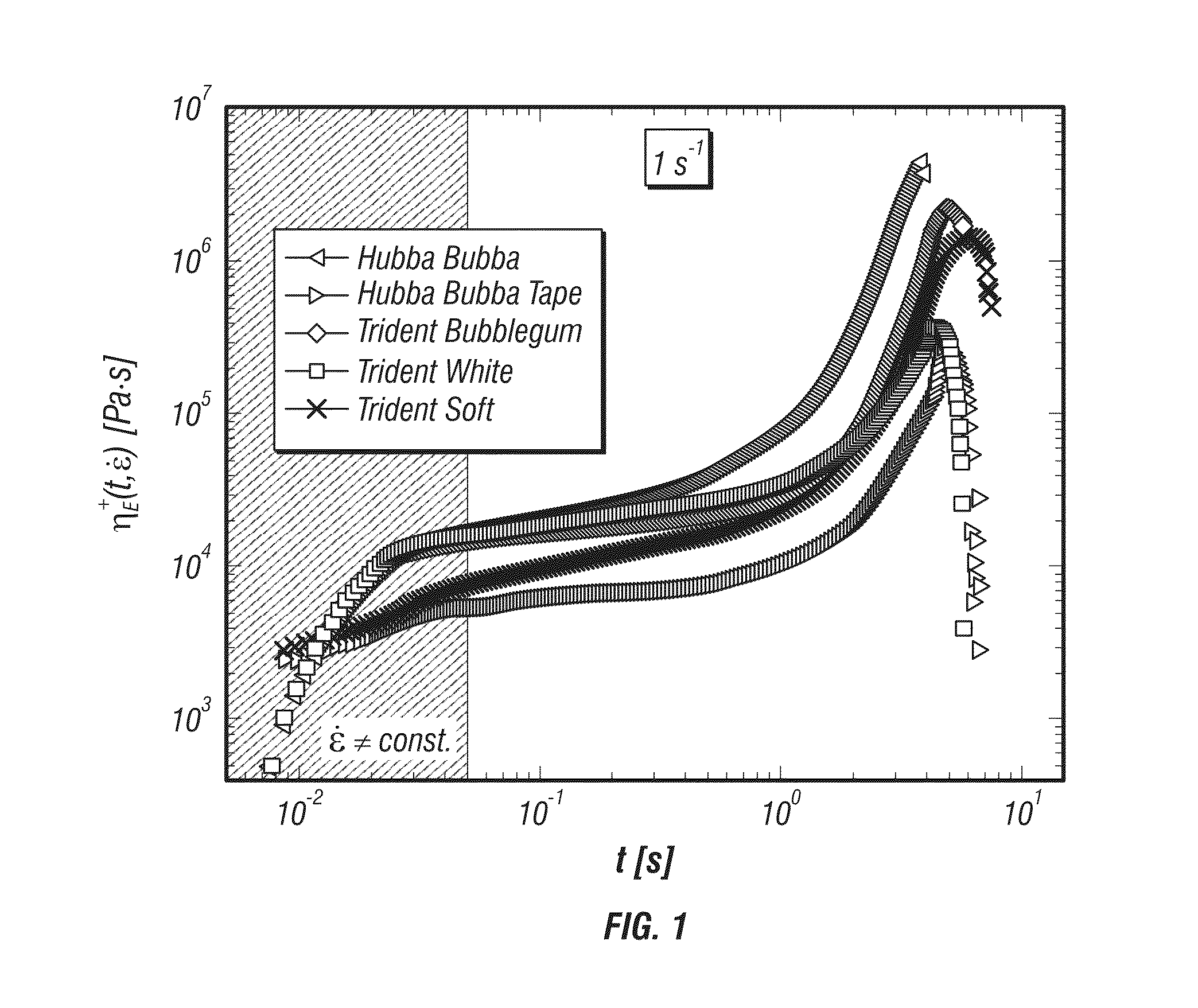
Nonlinear rheology of chewing gum and gum base
A method of selecting a commercially viable chewing gum including testing a chewing gum using nonlinear rheology, compiling rheological data from the nonlinear rheology, and then comparing the rheological data obtained to rheological data ranges of commercially acceptable chewing gum. The nonlinear rheology can include large amplitude oscillatory shear test, start-up of steady uniaxial extension test, and uniaxial compression test (lubricated or unlubricated) and relaxation.
Owner:WM WRIGLEY JR CO +1
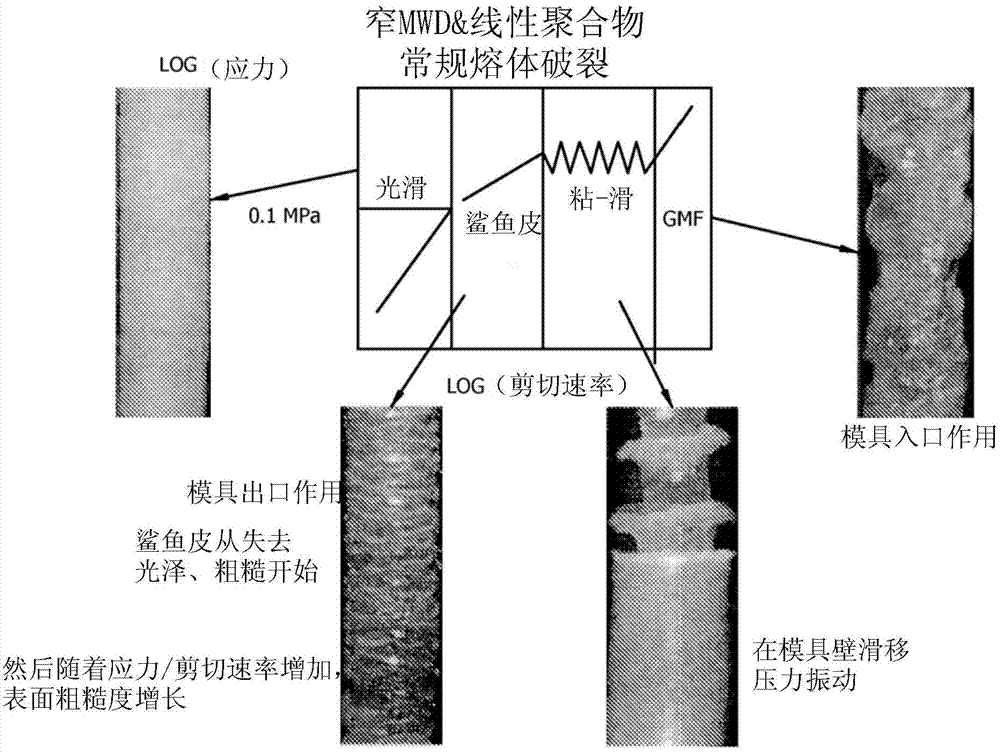
Controlling melt fracture in bimodal resin pipe
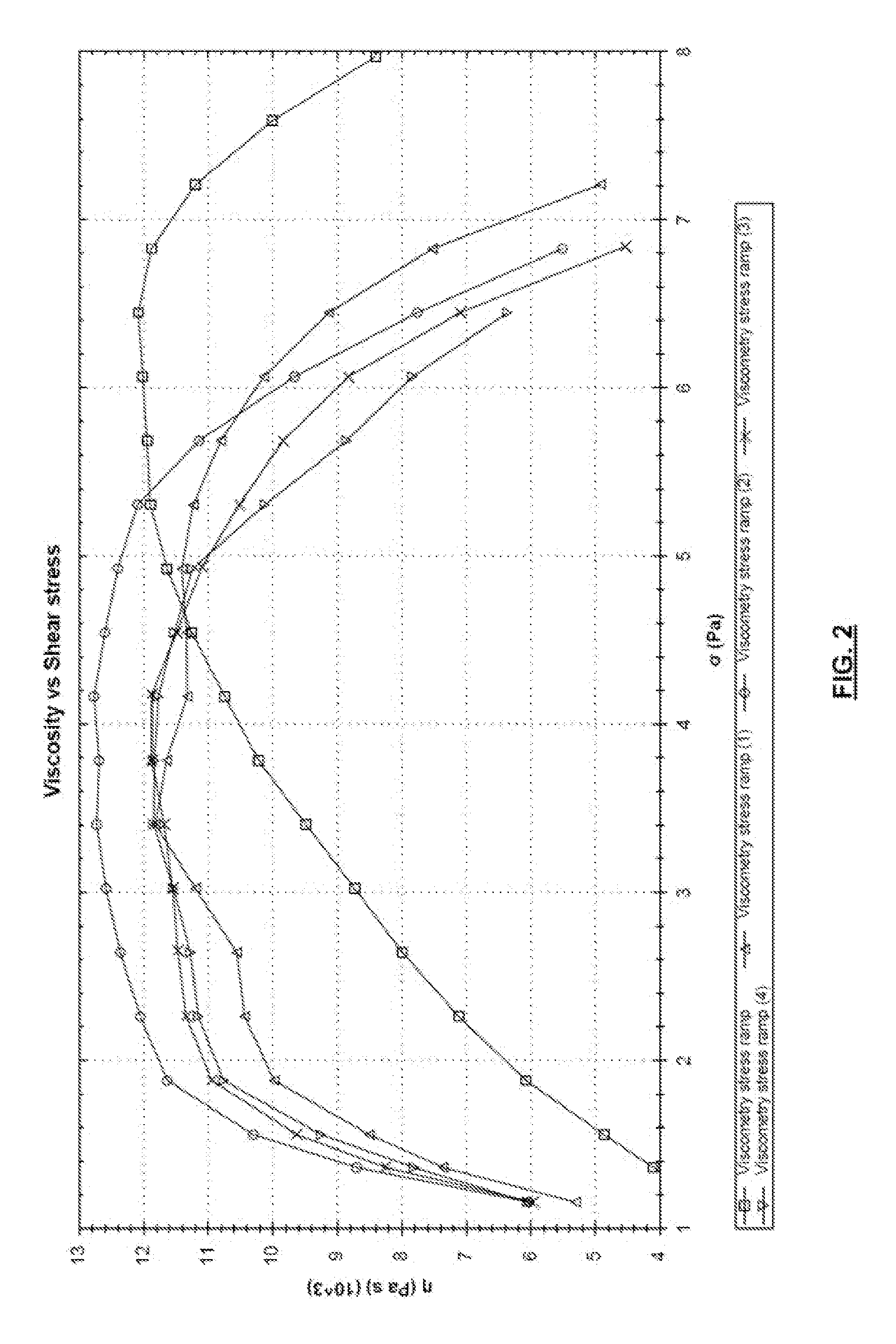
InactiveCN104508453AMolecular entity identificationMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesRheometryShear stress
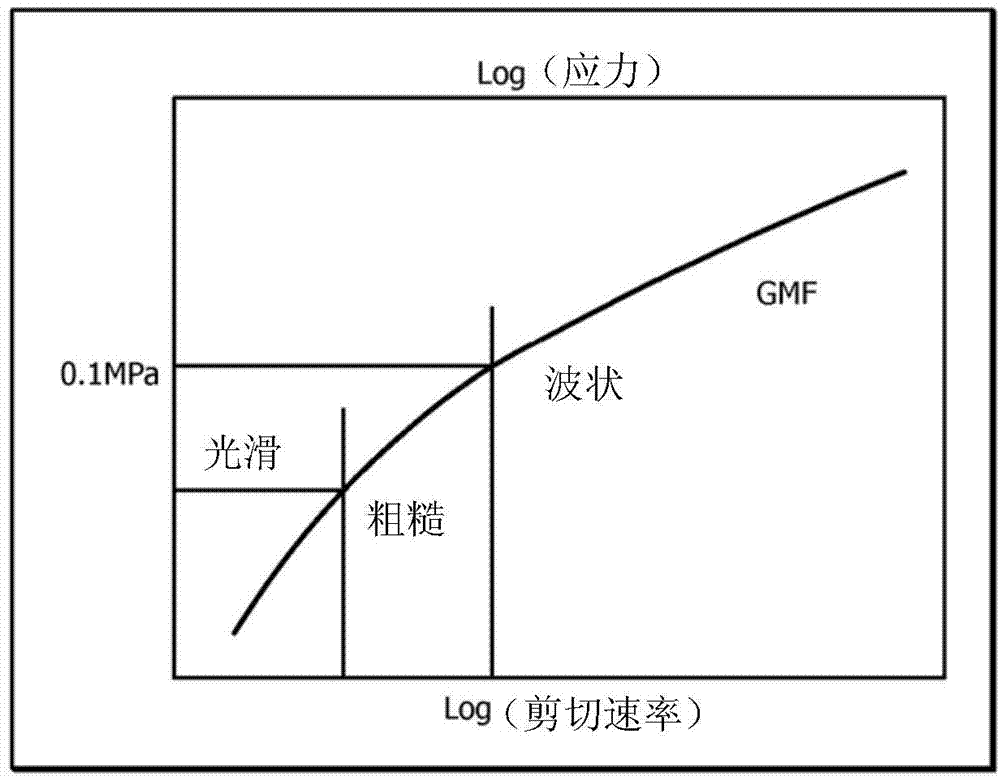
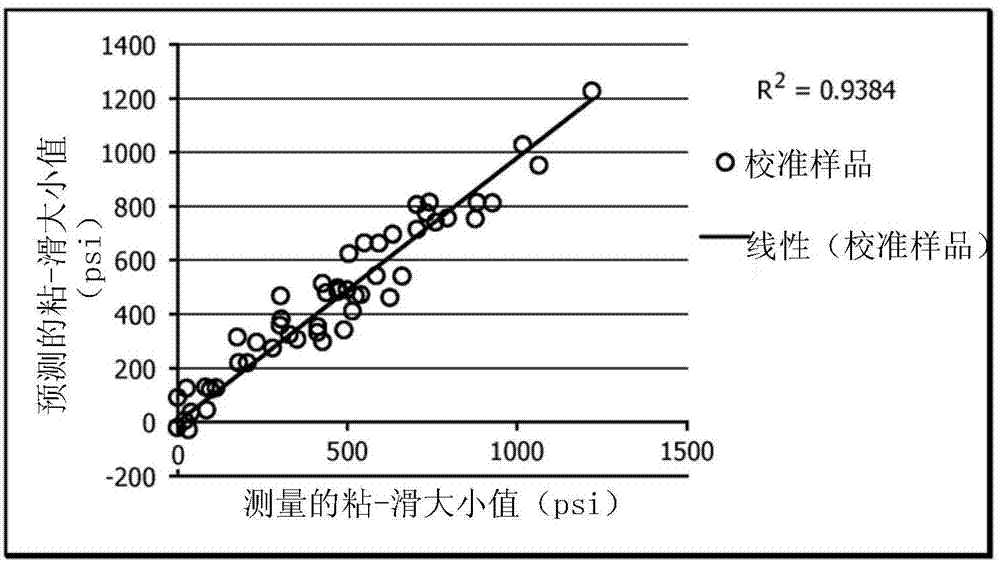
A system for improving processing of polyethylene resins, comprising a processor; a memory; an output device; and an analysis component stored in the memory, that when executed on the processor, configures the processor to receive a shear stress as a function of shear rate for a plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples, wherein the determination of the shear stress as a function of the shear rate comprises using capillary rheometry; determine values for a magnitude of slip-stick, a stress for smooth to matte transition, and a shear rate for smooth to matte transition for each of the plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples based on the shear stress and the shear rate measured from capillary rheometry; identify individual multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene resins from the plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples having a reduced tendency to melt fracture characterized by a magnitude of slip-stick greater than about 300 psi, a stress for smooth to matte transition greater than about 90 kPa, and a shear rate for smooth to matte transition greater than about 10 s-1; and output an identification of the individual multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene resins to the output device.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Dynamic reciprocating-bob rheometry
A sensor for making rheological measurements takes the form of a ferromagnetic bob alternately driven through a sample fluid in opposite directions by magnetic force from two alternately driven coils. The bob's position affects the mutual inductance between the coils, so it can be inferred by sensing the signal that current flowing in one coil induces in the other, and rheological properties are determined from the relationships among the bob's motion, the coil current, and the sensor geometry. Some such measurements' accuracies are enhanced by computing bob acceleration and suppressing iner-tial effects thereby detected.
Owner:PETROLEUM ANALYZERS LLC
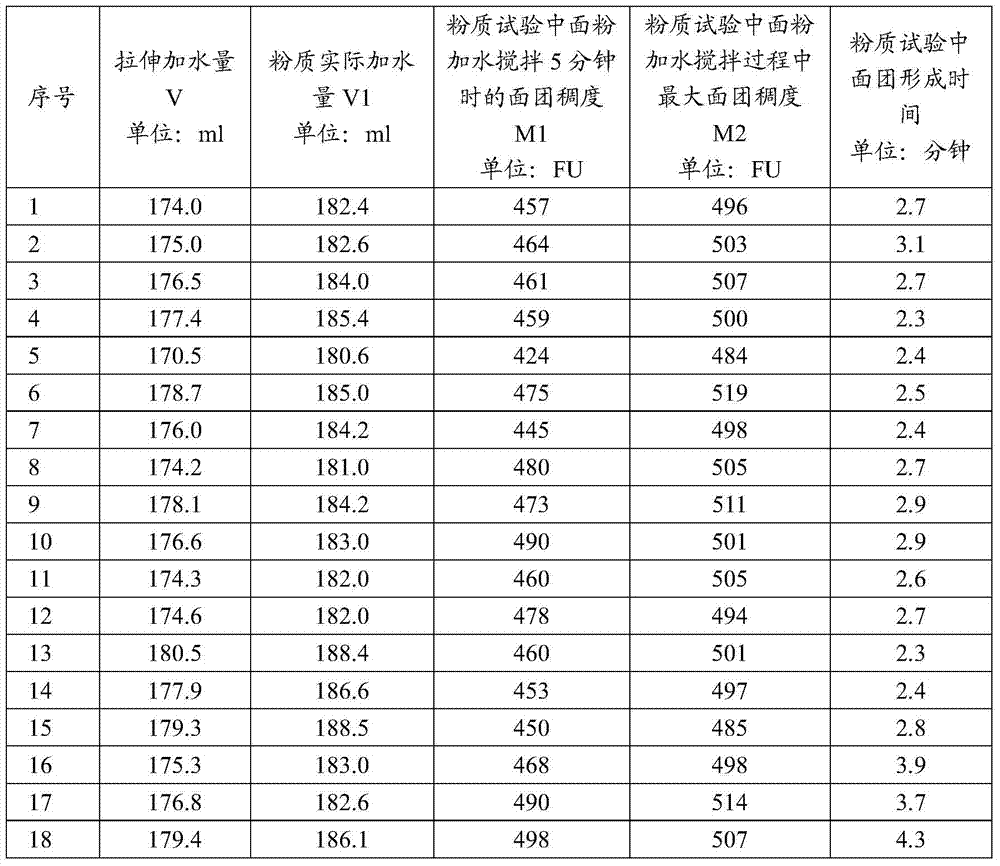
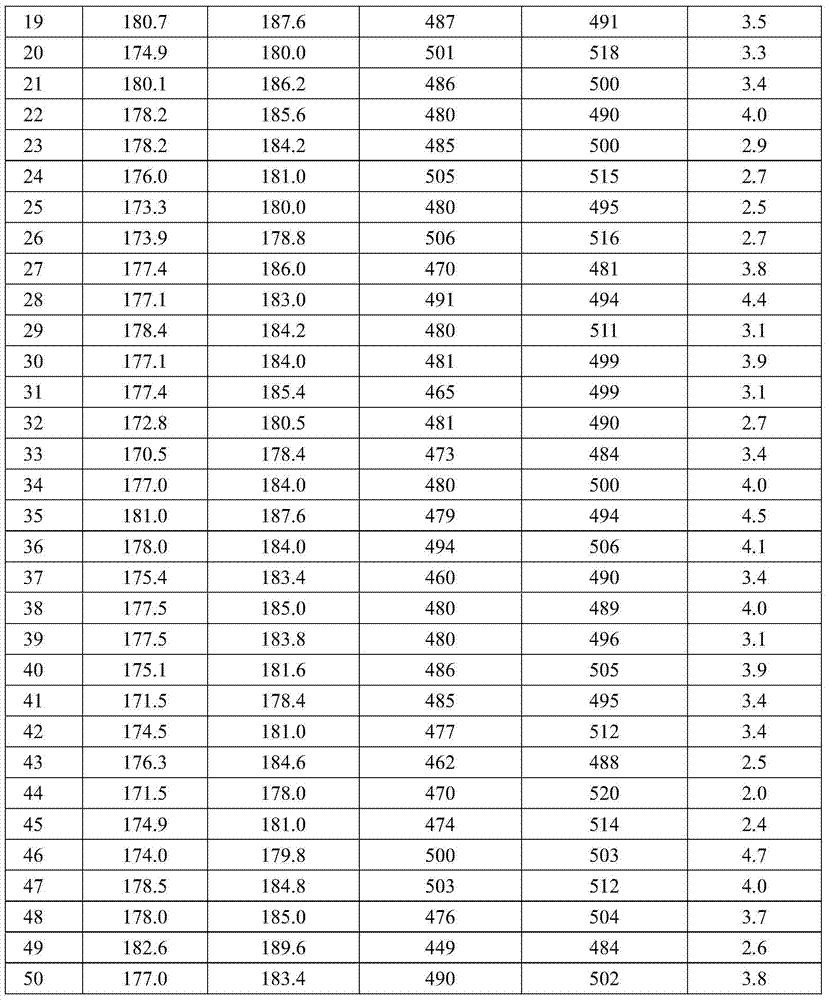
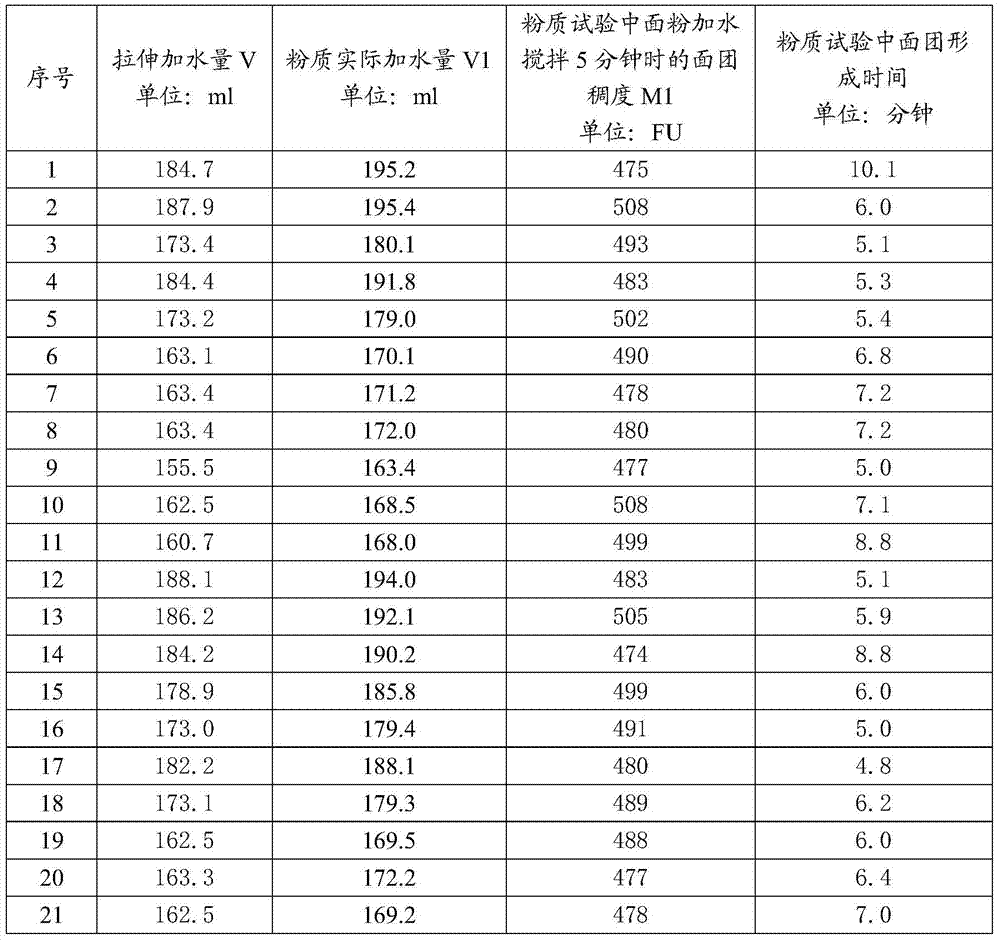
A method for controlling the amount of stretching water added in the determination of dough rheological properties
ActiveCN105067409BImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRheometryTensile testing
The invention relates to a method for controlling the amount of stretching and adding water in the determination of the rheological properties of dough, in particular to a method for controlling the amount of water added to stretch when measuring the rheological properties of dough made of wheat flour by using the extensometer method. In order to improve the accuracy of the test results and test efficiency, the method takes the amount of water added in the dough tensile test as the objective function, and according to the formation time of the dough in the flour quality test, the actual amount of water added to the flour quality and the flour quality stirring The consistency in the process (consistency and maximum consistency when the powder is stirred for 5 minutes) linearly fits the amount of water added to the dough tensile test. After applying this method, the control of the amount of water added to the tensile test will be quantified, which can be used by the application personnel to have precise control A standard method for adding water to improve the accuracy and test efficiency of dough rheological properties testing.
Owner:山东省粮油检测中心
Scanning rheometer
ActiveUS10161842B2Few constraintsFlexible FSRFlow propertiesUsing optical meansRheometryAxial displacement
Owner:RHEO FILAMENT APS
Nonlinear rheology of chewing gum and gum base
A method of selecting a commercially viable chewing gum including testing a chewing gum using nonlinear rheology, compiling rheological data from the nonlinear rheology, and then comparing the rheological data obtained to rheological data ranges of commercially acceptable chewing gum. The nonlinear rheology can include large amplitude oscillatory shear test, start-up of steady uniaxial extension test, and uniaxial compression test (lubricated or unlubricated) and relaxation.
Owner:WM WRIGLEY JR CO
Highly viscous, largely amorphous polyolefin
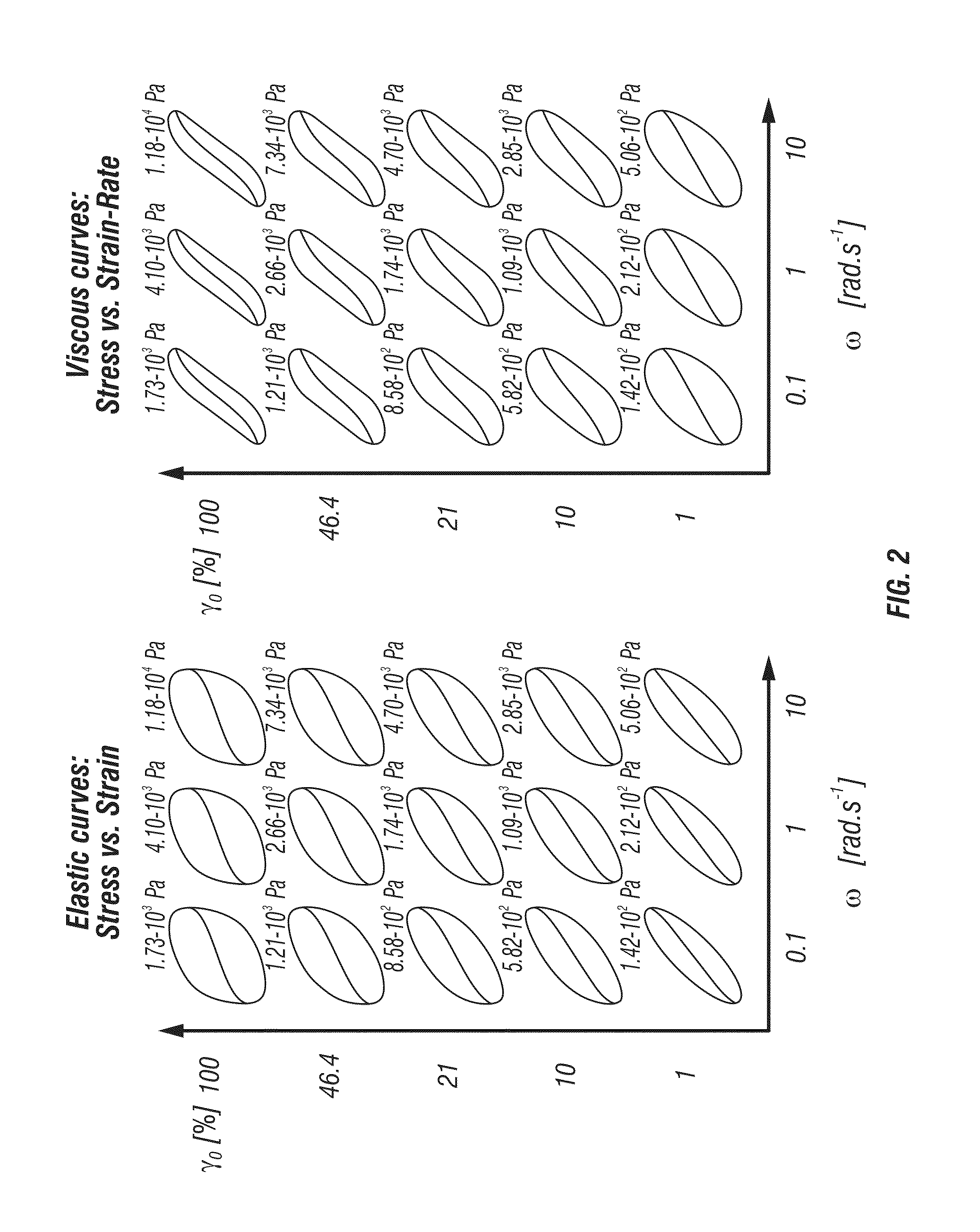
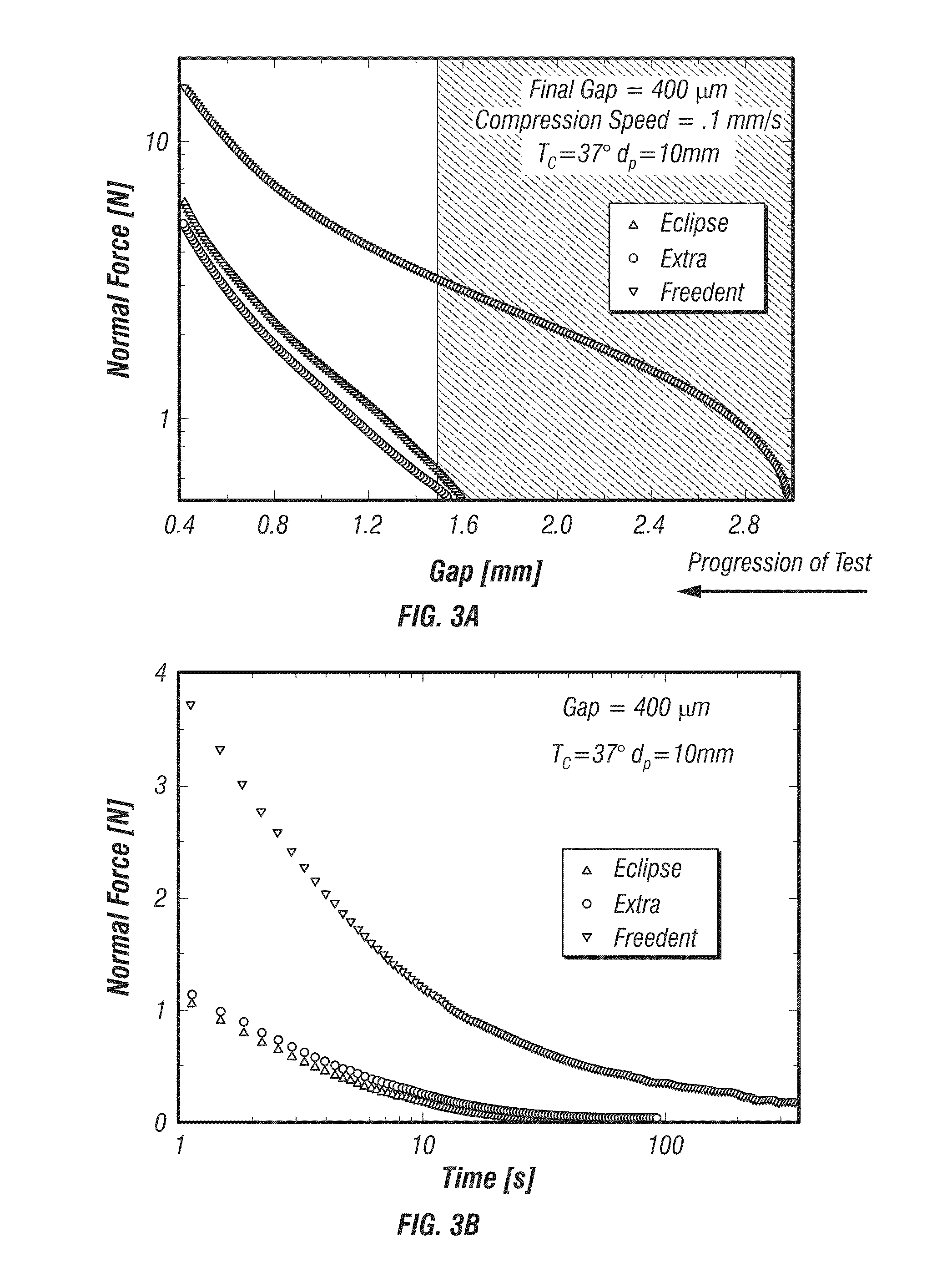
The invention relates to a polyolefin containing the following monomer units: a) a maximum of 25 wt. % of units derived from ethene, b) a maximum of 75 wt. % of units derived from propene, and c) between 5 and 100 wt. % of units derived from an a-olefin containing between 4 and 20 C atoms. The inventive polyolefin has the following parameters: d) a weight-average molecular weight of between 70,000 and 10,000,000 g / mol, e) a polydispersity of between 4 and 60, f) a melting viscosity, measured by oscillation rheometry with a shearing speed of 1 Hz at 190 DEG C, of between 100,000 and 100,000,000 mPa s, g) a needle penetration of between 3 and 70 0.1 mm, h) a melting enthalpy of between 2 and 100 J / g, i) a glass transition temperature Tg of between -15 DEG C and -80 DEG C, and j) an end of the crystalline part melting range at between 85 and 175 DEG C. The inventive polyolefin is compatible both with ethylene polymers and propylene polymers, and is suitable for using in films, sealing strips, and moulded parts.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Rheometry apparatus
InactiveUS9354152B2Simpler and cheap to produceAccurate measurementMetal working apparatusDirect flow property measurementRheometryEngineering
Rheometry apparatus comprises a block of substantially rigid material having an external surface and at least a first internal flow channel, the first internal flow channel being arranged inside the block and substantially in a plane and the block further comprising a plurality of holes, each hole communicating with the first internal flow channel at a respective position along the first internal flow channel and extending from the respective position to said external surface so as to provide access to the first internal flow channel from the external surface, the plurality of holes comprising a first hole communicating with a first said position, for connection to pumping means to drive fluid flow along said first internal flow channel, a second hole communicating with a second position and in which a sensor may be located to measure a property of fluid at the second position, and a third hole communicating with a third position and in which a sensor may be located to measure a property of fluid at the third position.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
Expert-system-based rheology
ActiveCN102112860AAccurate measurementSelection of Accelerated ExperimentsFlow propertiesRheometryEngineering
A rheometer is disclosed that includes rheometry logic that is responsive to a material selection control, to an objective selection control, to material property storage, and to process parameter storage, and is operative to assist the user with a measurement using the rheometer. In another general aspect, a rheometer includes sample history storage operative to store a history that spans a plurality of different operations performed by the rheometer on a same sample.
Owner:NETZSCH GERATEBAU GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com