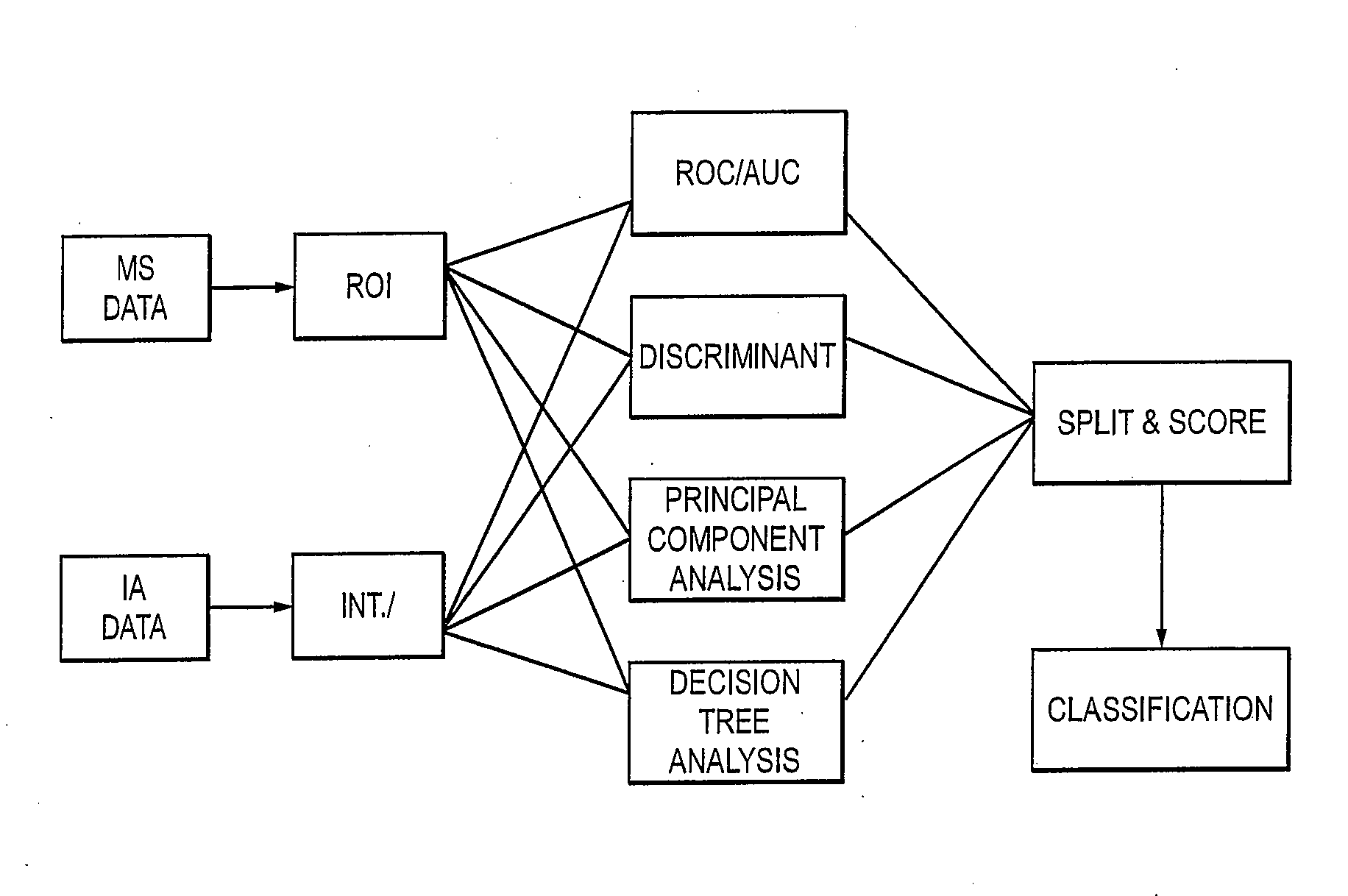
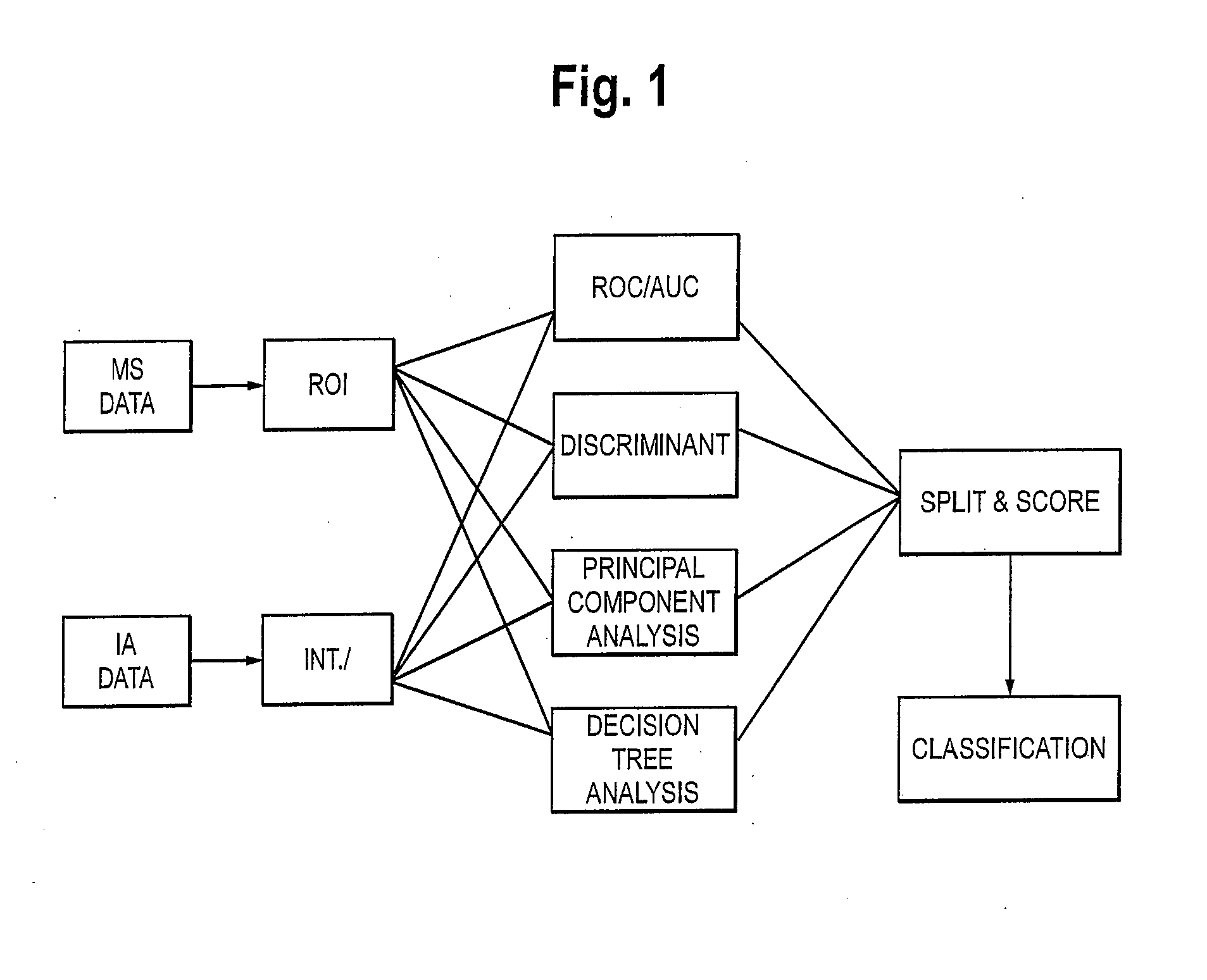
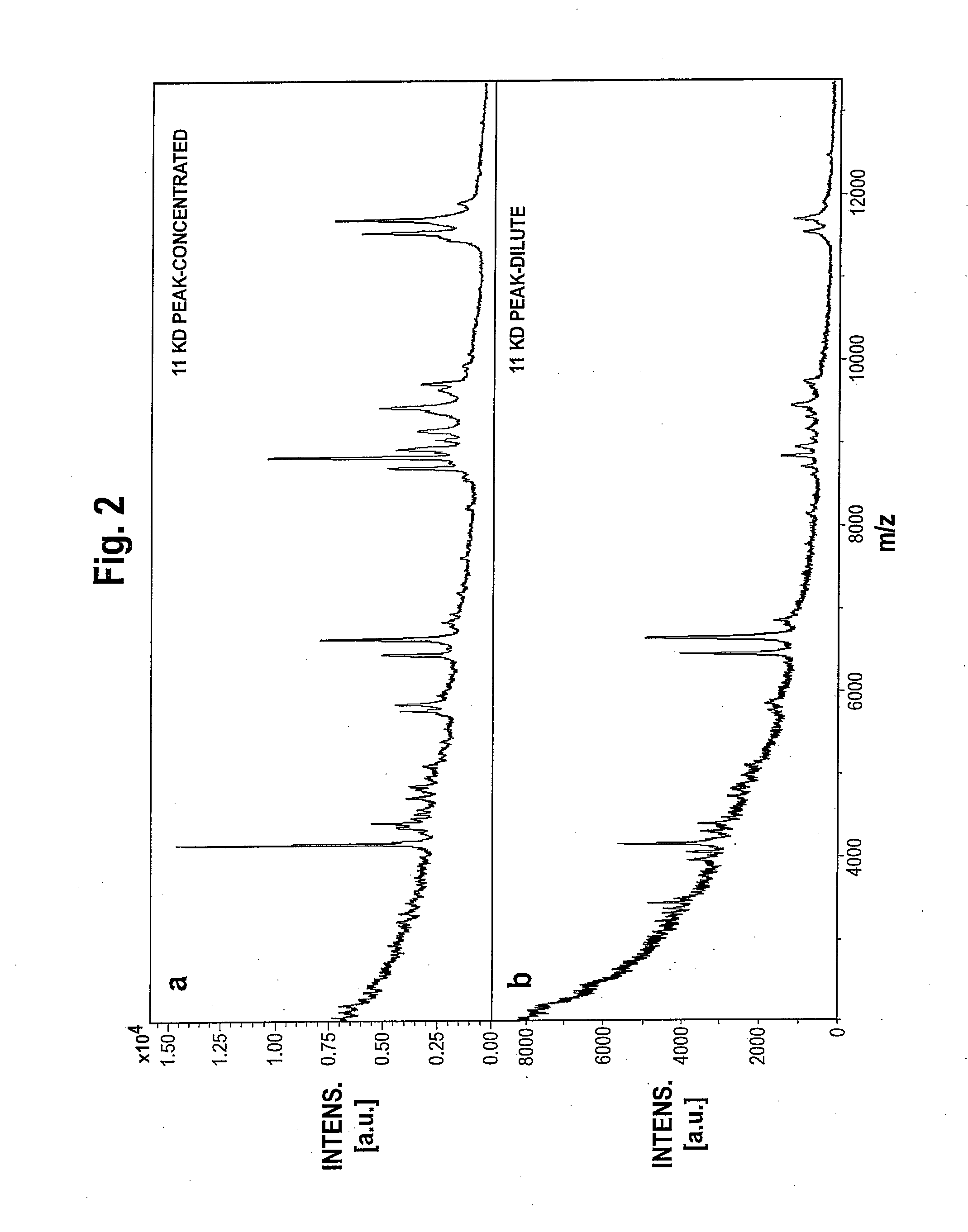
Weighted Scoring Methods and Use Thereof in Screening
a scoring method and weighted technology, applied in the field of weighted scoring methods, can solve the problems of curtailing clinical use of these statistical techniques, not widely applied in fda approved commercially available tests, and affecting the reproducibility of logistic regression models,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Clinical Specimens
[0287]Clinical samples of patient serum were collected under an Institutional Review Board approved protocol. All subjects who contributed a specimen gave informed consent for the specimen to be collected and used in this project. Serum samples were drawn into a serum separator tube and allowed to clot for 15 minutes at room temperature. The clot was spun down and the sample poured off into 2 mL aliquots. Within 24 hours the samples were frozen at −80° C. and maintained at that temperature until further processing was undertaken. Upon receipt, the samples were thawed and realiquoted into smaller volumes for convenience and refrozen. The samples were then thawed a final time immediately before analysis. Therefore, every sample in the set was frozen and thawed twice before analysis.
[0288]A total of 751 specimens were collected and analyzed. The group was composed of 250 biopsy confirmed lung cancer patients, 274 biopsy confirmed benign lung disease patients, and 227 ...
example 2
Immunoassay Detection of Biomarkers
[0289]A. Abbott Laboratories (Abbott Park, Ill., Hereinafter “Abbott”) Architect™ Assays
[0290]Architect™ kits were acquired for the following antigens: CEA, CA125, SCC, CA19-9 and CA15-3. All assays were run according to the manufacturer's instructions. The concentrations of the analytes in the samples were provided by the Architect™ instrument. These concentrations were used to generate the AUC data shown below in Table 1.
TABLE 1Large CohortSmall CohortMarker#obsAUC#obsAUCCa19-95480.5482560.559CEA5490.6882570.664Ca15-35490.6042570.569Ca1255490.6932570.665SCC5490.6152570.639
Table 1. Clinical performance (AUC) of CA125, CEA, CA15-3, CA19-9, and SCC in the small and large cohorts. The #obs refers to the total number of individuals or clinical samples in each group.
[0291]B. Roche Elecsys™ Assay
[0292]Cyfra 21-1 (Cytokeratin 19, CK-19) measurements were made on the Elecsys™ 2010 system (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufac...
example 3
[0295]A. Commercially available human proteins (See, Table 4, below) were attached to Luminex™ SeroMap™ beads (Austin, Tex.) and the individual beadsets were combined to prepare the reagent. Portions of the reagent were exposed to the human serum samples under conditions that allow any antibodies present to bind to the proteins. The unbound material was washed off and the beads were then exposed to a fluorescent conjugate of R-phycoerythrin linked to an antibody that specifically binds to human IgG. After washing, the beads were passed through a Luminex™ 100 instrument, which identified each bead according to its internal dyes, and measured the fluorescence bound to the bead, corresponding to the quantity of antibody bound to the bead. In this way, the immune responses of 772 samples (251 lung cancer, 244 normal, 277 benign) against 21 human proteins, as well as several non-human proteins for controls (bovine serum albumin (BSA) and tetanus toxin), were assess...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com