Well Treating Agents of Metallic Spheres and Methods of Using the Same
a technology of metallic spheres and treatment agents, which is applied in the direction of sealing/packing, borehole/well accessories, separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient interstitial space, tight holding, and difficult transportation of proppants, and achieve the effect of reducing or substantially preventing the passage of formation particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0055]The following examples will illustrate the practice of the present invention in preferred embodiments. Other embodiments within the scope of the claims herein will be apparent to one skilled in the art from consideration of the specification and practice of the invention as disclosed herein. It is intended that the specification, together with the example, be considered exemplary only, with the scope and spirit of the invention being indicated by the claims which follow.
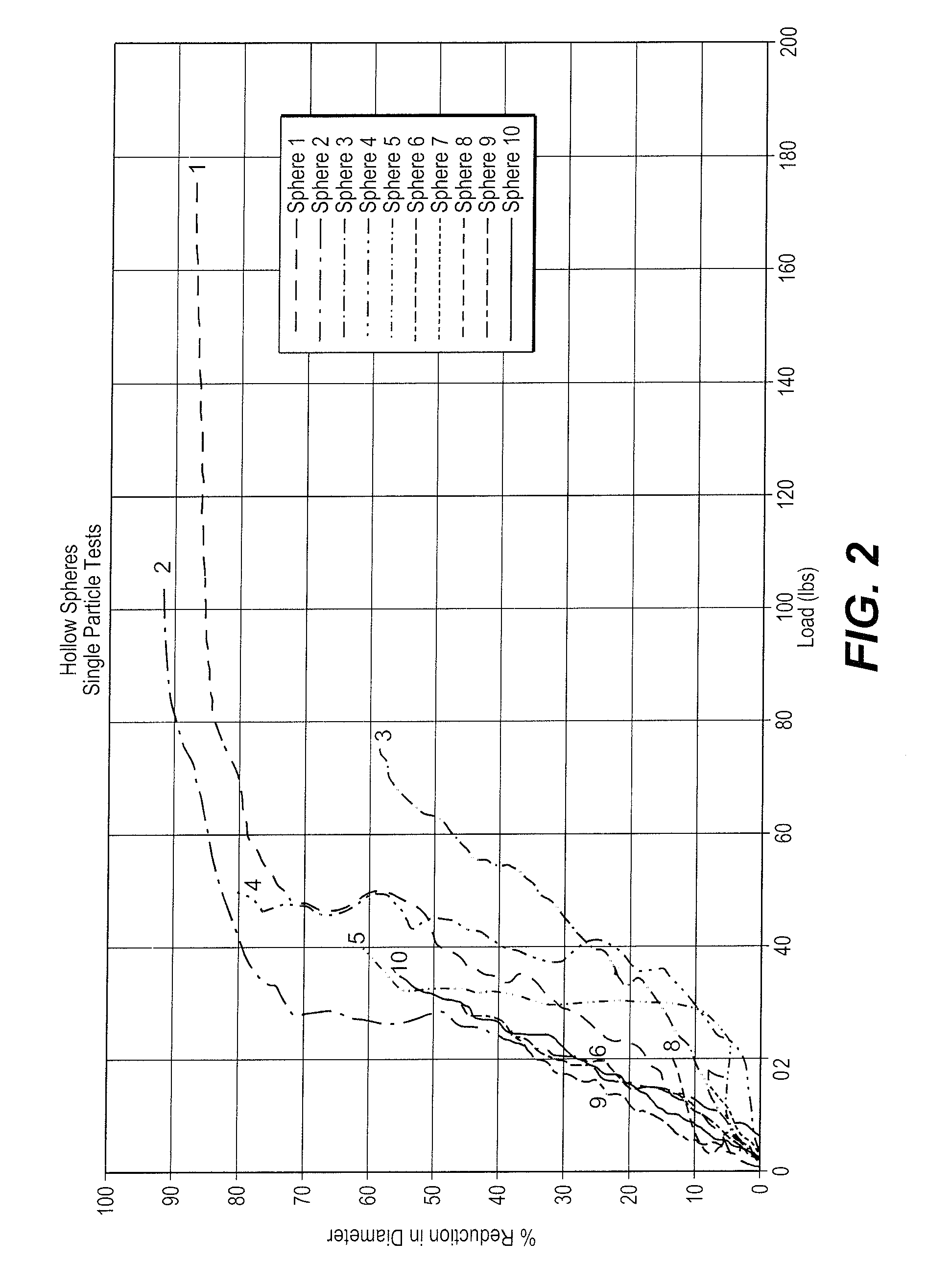
[0056]Strength and stiffness are the basic physical properties that are measured to evaluate the effectiveness and deformation characteristics of hollow non-porous metallic spheres. The following test procedures were used to measure the deformation versus applied load for single metallic spheres. All the tests were conducted at 22° C.
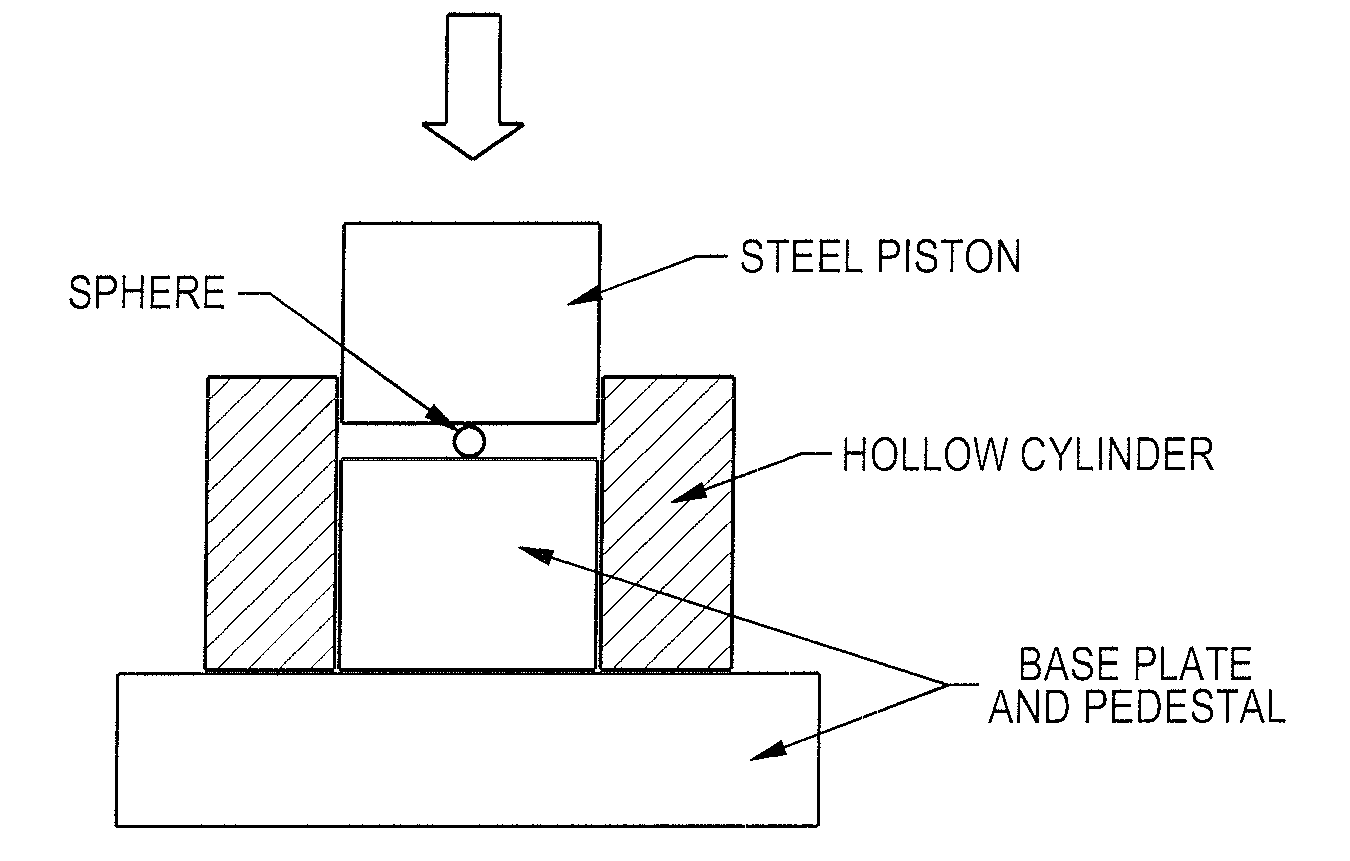
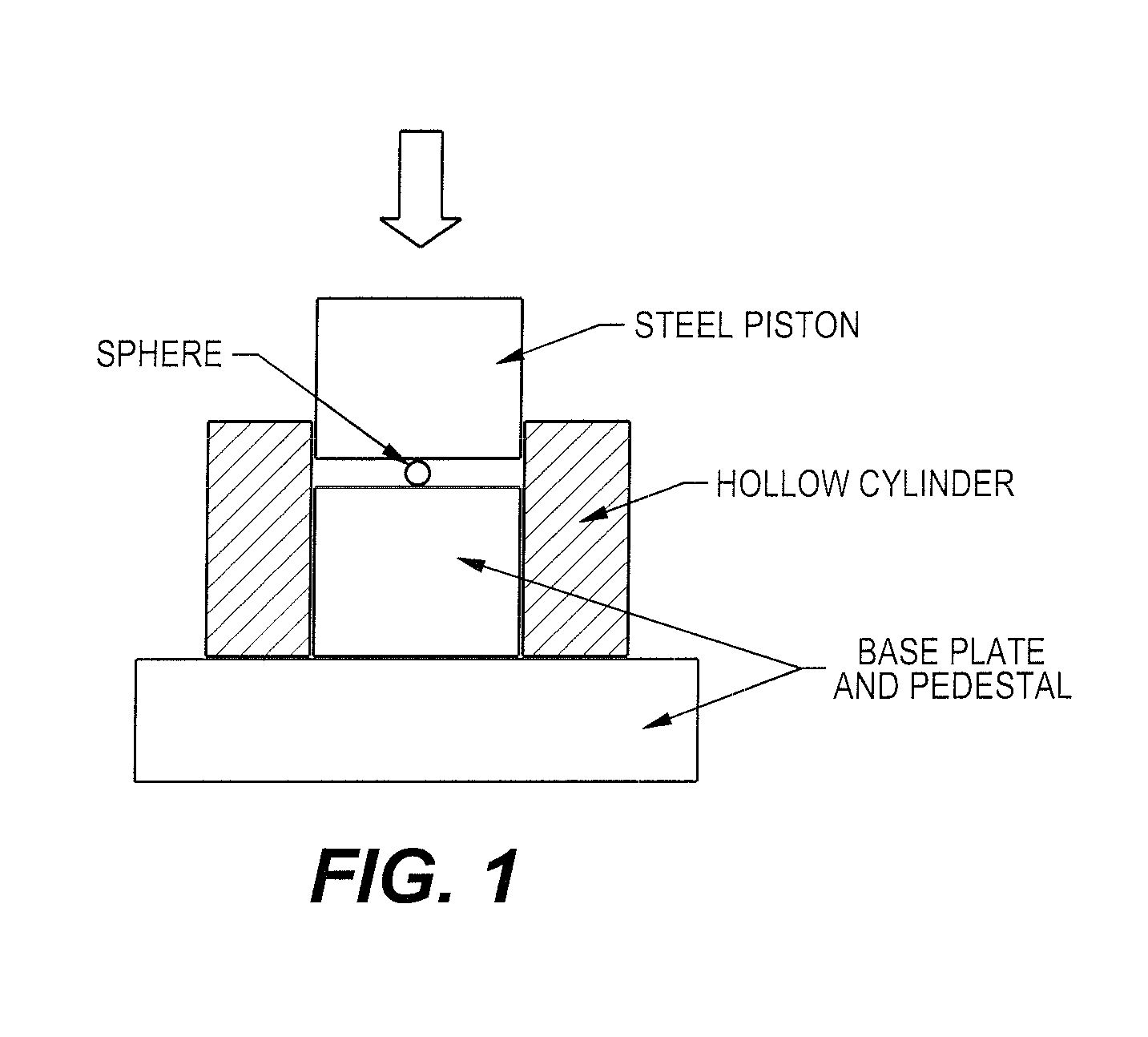
[0057]The test cell, as shown in FIG. 1, consisted of a cylindrical stainless steel base-pedestal and a movable steel piston. A single particulate of a hollow non-porous metallic s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific gravity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific gravity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific gravity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com