Method of rinsing endoscopes
a technology of endoscope and rinsing machine, which is applied in the field of rinsing endoscope, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory results in preventing the re-deposition of dirt components, the inability to guarantee the concentration of detergent in the pre-rinse vessel, and the replacement of fluid in the vessel, so as to enhance the rinsing efficiency, and effectively suppress the re-deposition of dir
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044]The endoscope rinsing method according to the present invention is described below in detail with reference to the preferred embodiments depicted in the accompanying drawings.
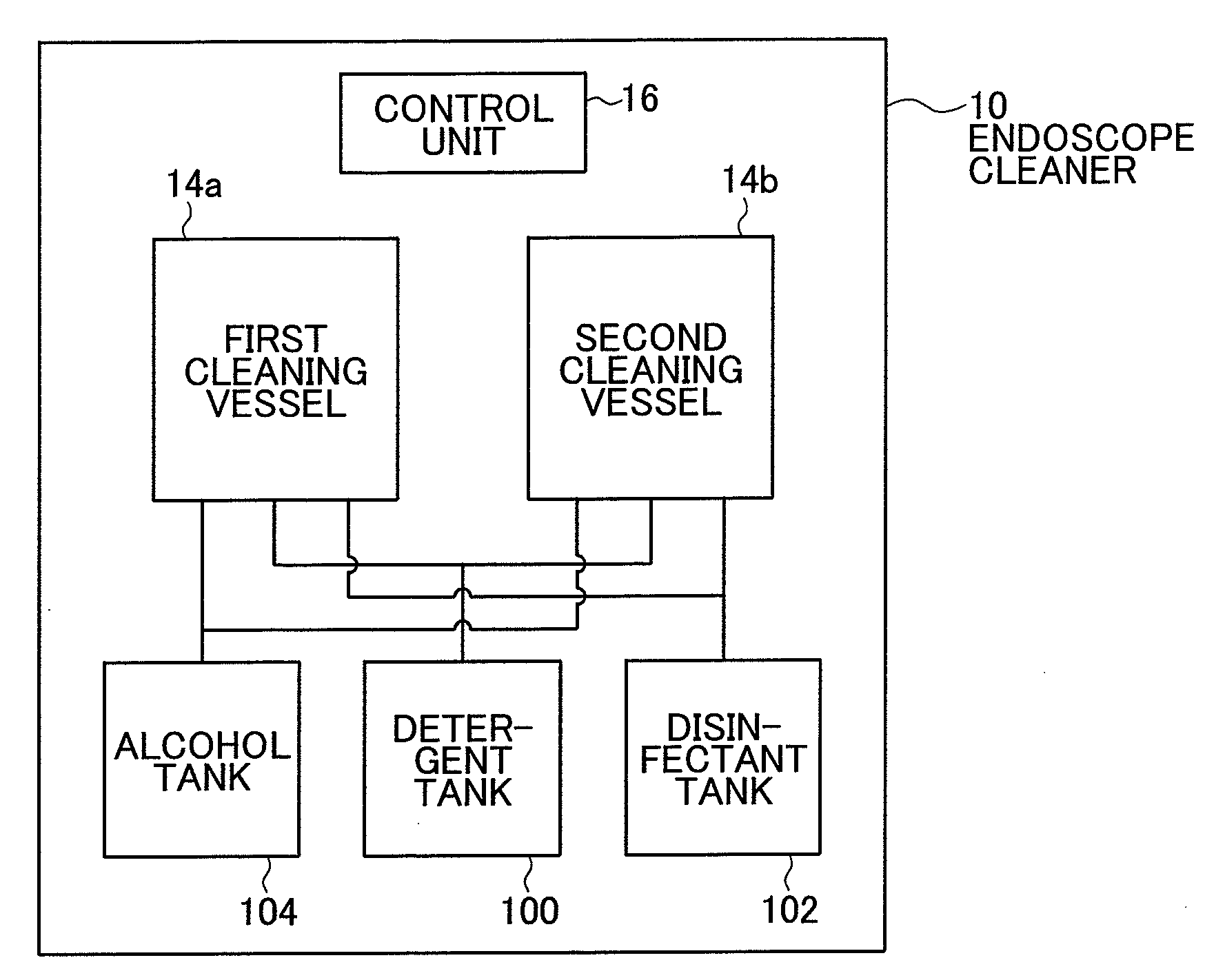
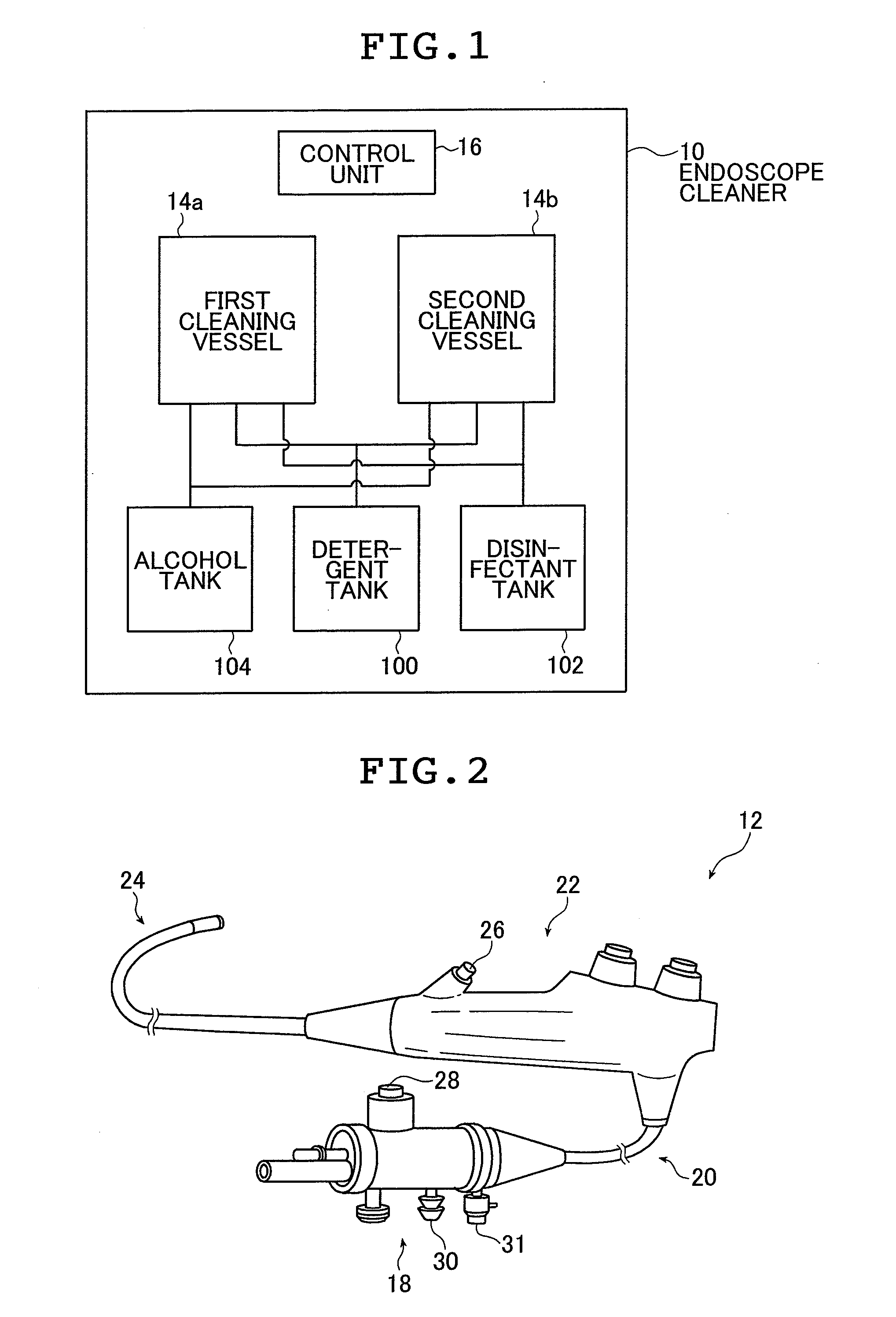
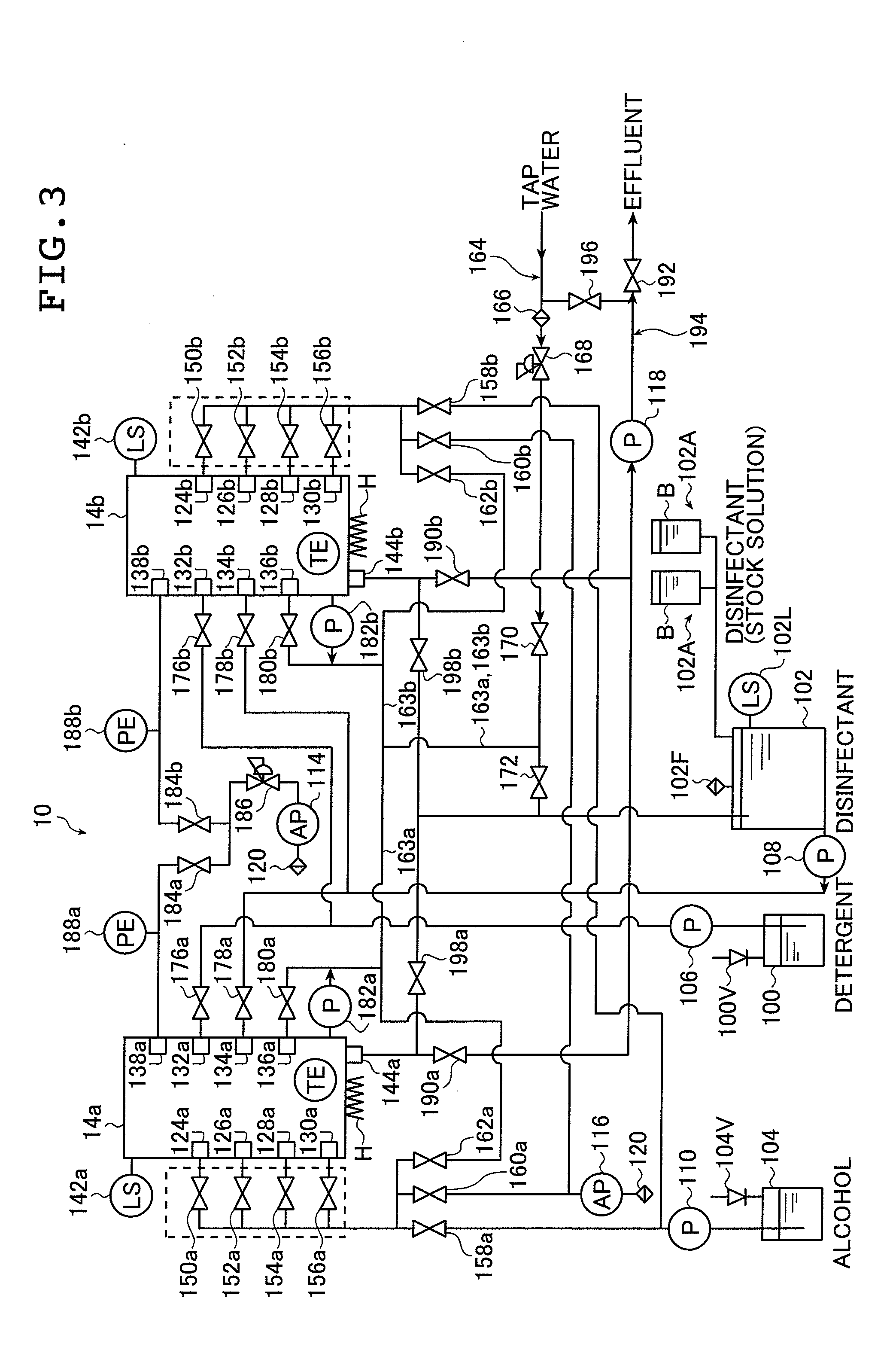
[0045]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of an exemplary endoscope cleaner for implementing the method of the present invention for rinsing endoscopes. The endoscope cleaner which is generally indicated by 10 in FIG. 1 (and which is hereinafter referred to as cleaner) is such an apparatus that two units of an endoscope which is generally indicated by 12 in FIG. 2 can be individually cleaned and disinfected. As shown, cleaner 10 comprises a first cleaning vessel 14a, a second cleaning vessel 14b, a control unit 16, a detergent tank 100, a disinfectant tank 102, and an alcohol tank 104. In the embodiment under consideration, the cleaner 10 is equipped with two cleaning vessels but it may be equipped with only one cleaning vessel or even three or more cleaning vessels.
[0046]Endoscope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com