FCC-CFE CAT FINE EXTRACTION: METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EXTRACTING CATALYST FINES FROM SLURRY OIL CAT FINE BOTTOMS (SOCFBs) INTO AN AQUEOUS LAYER
a technology of cat fines and cat bottoms, which is applied in the field of fcccfe cat fine extraction : method and system for extracting catalyst fines from slurry oil cat fine bottoms, which can solve the problems of fccu catalyst deterioration, ash content, and fccu attrition,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]While the invention is susceptible of embodiment in many different forms, there is described in detail preferred embodiments of the invention. It is to be understood that the present disclosure is to be considered only as an example of the principles of the invention. This disclosure is not intended to limit the broad aspect of the invention to the illustrated embodiments. The scope of protection should only be limited by the claims.
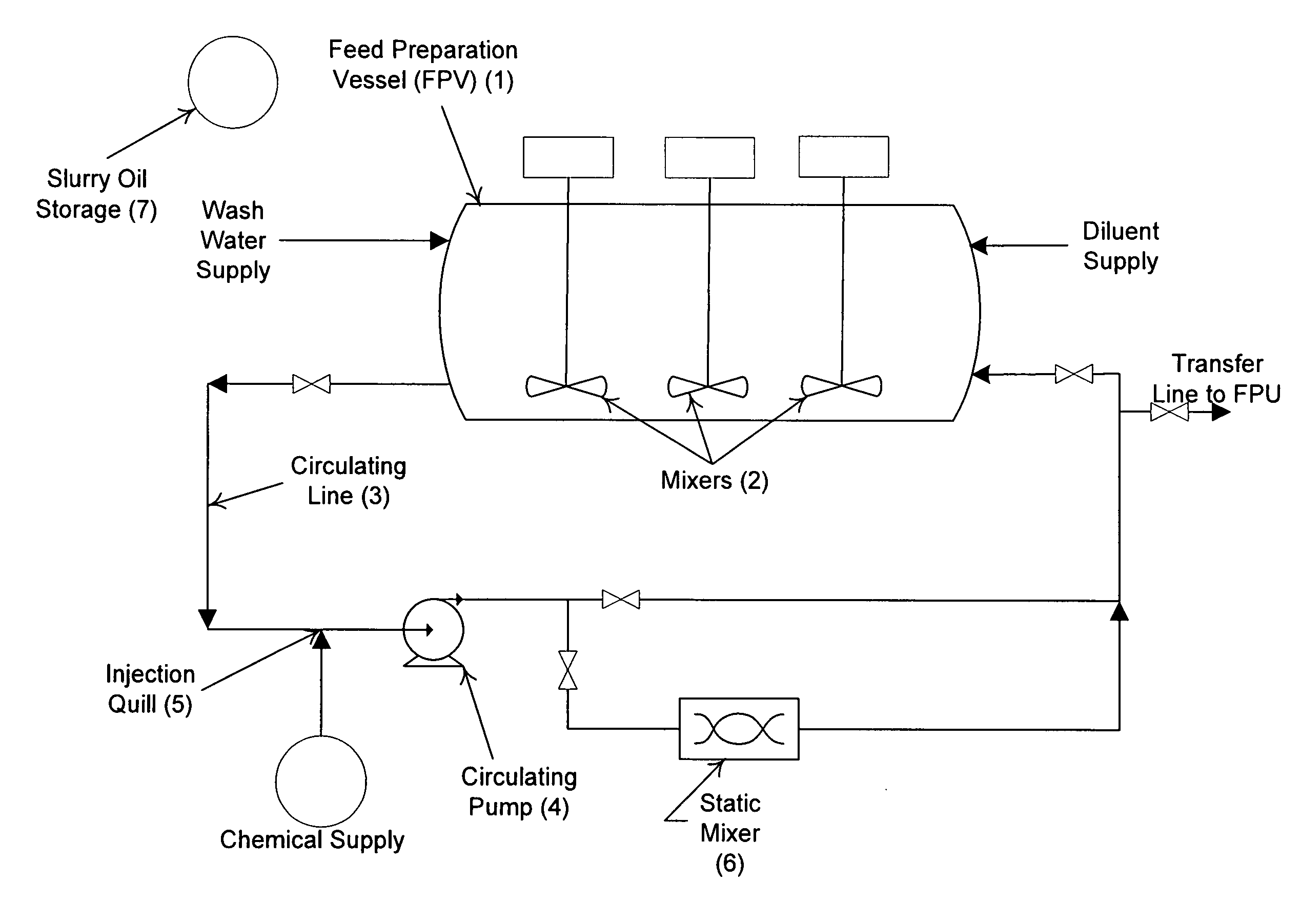
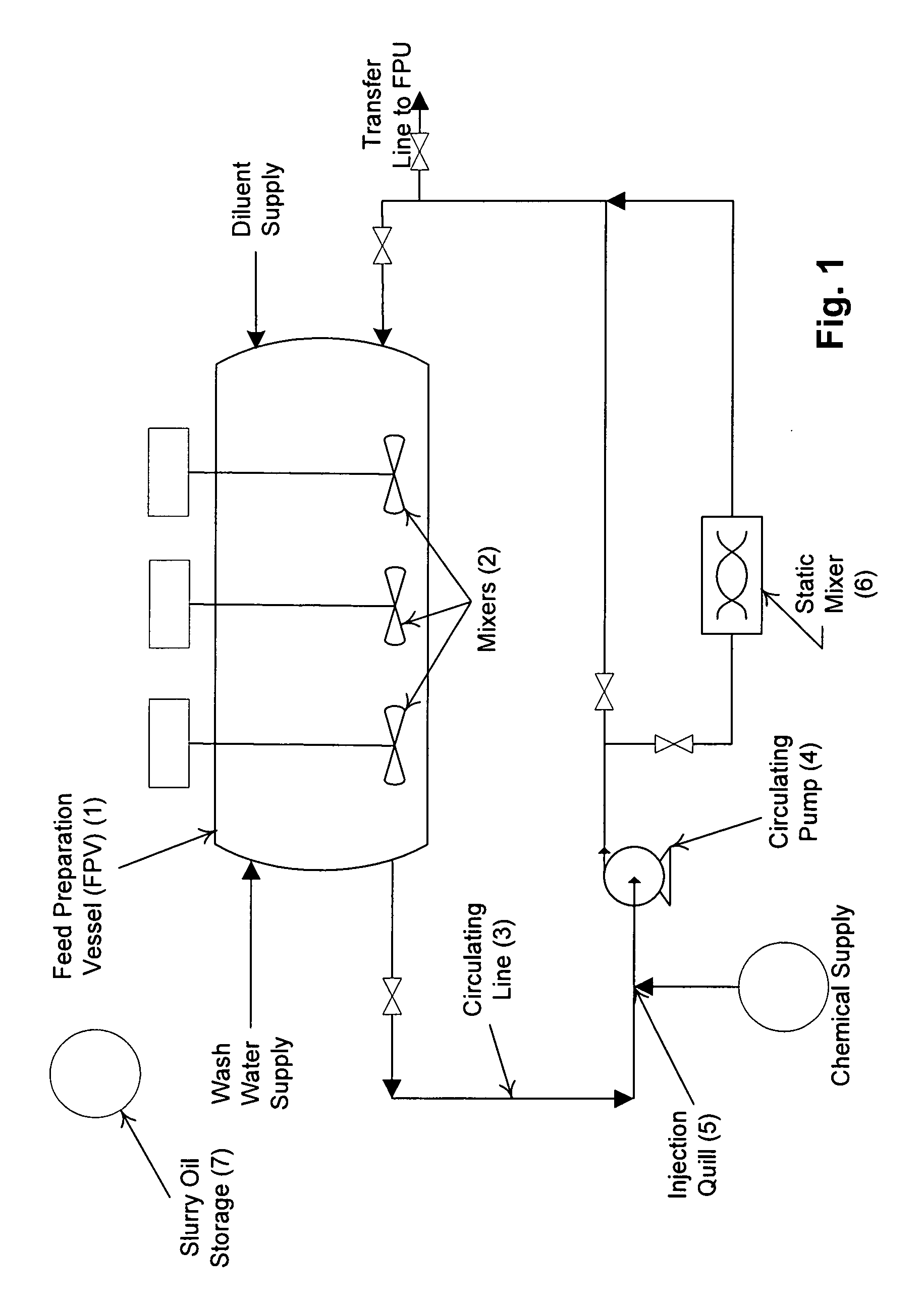
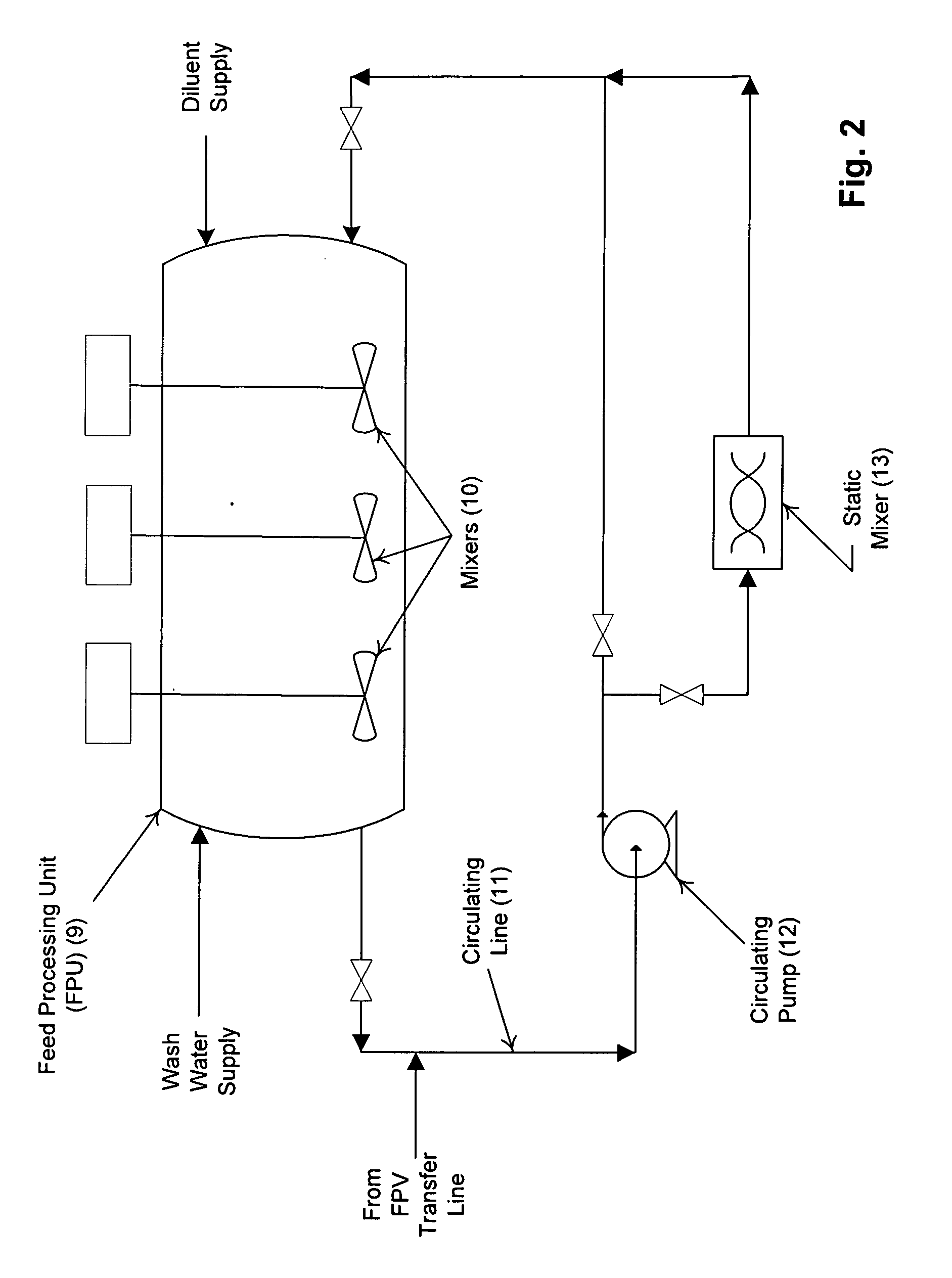
[0019]The present invention comprises a method for separating catalyst particles from Slurry Oil Cat' Fine Bottoms comprising the steps of preparing a heated and treated Slurry Oil Cat' Fines Diluent Mixture (SCDM) in a specialized processing vessel referred to as a Feed Preparation Vessel (FPV) and transferring the prepared feed to a Feed Processing Unit (FPU). A SCDM is prepared in the FPV. Water is added to the SCDM and mixed in a manner predetermined by bench modeling the specific SCDM / water solution to ascertain a treatment formulation, a trea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com