Split Core Hockey Stick Blade
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
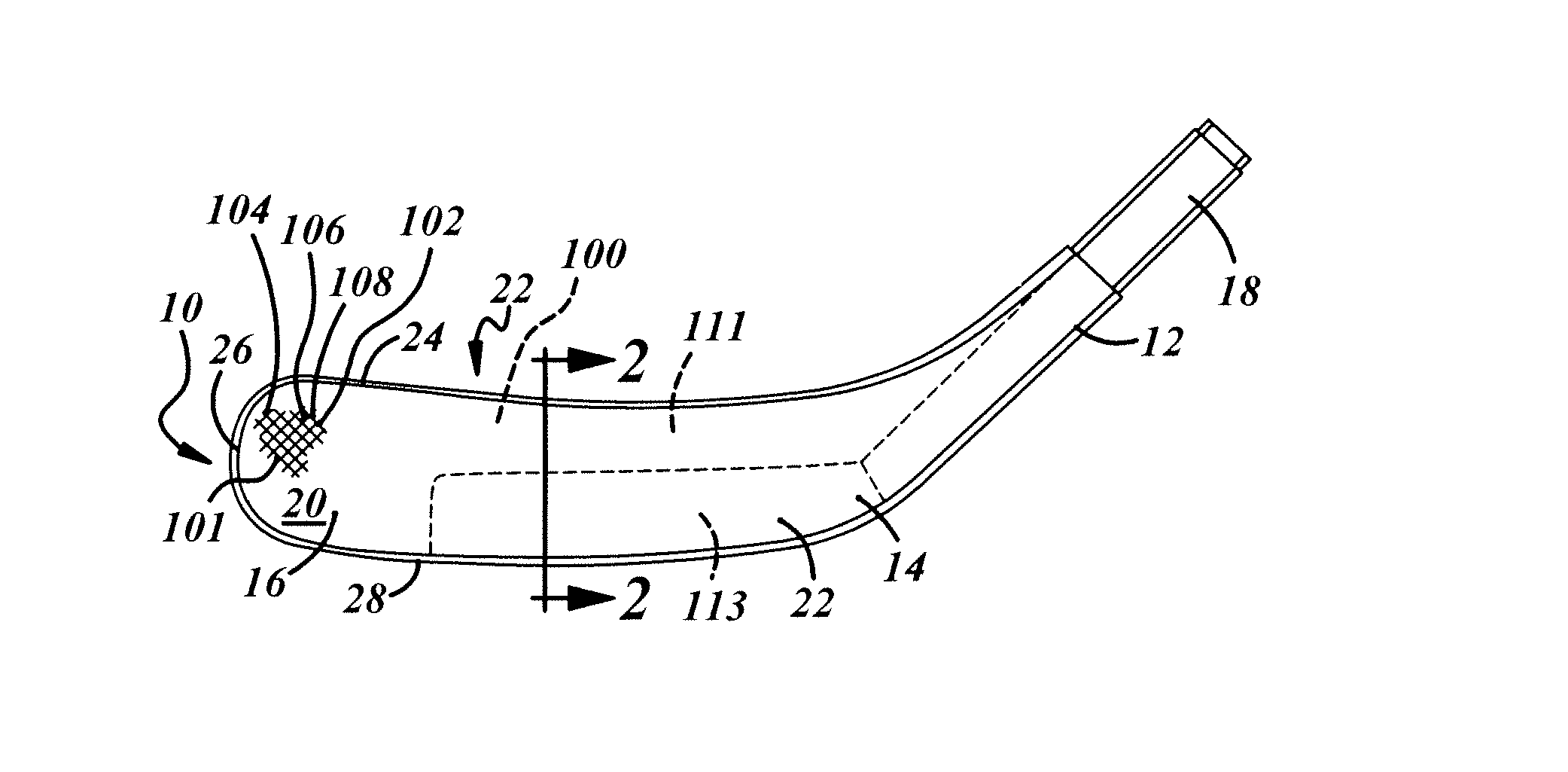
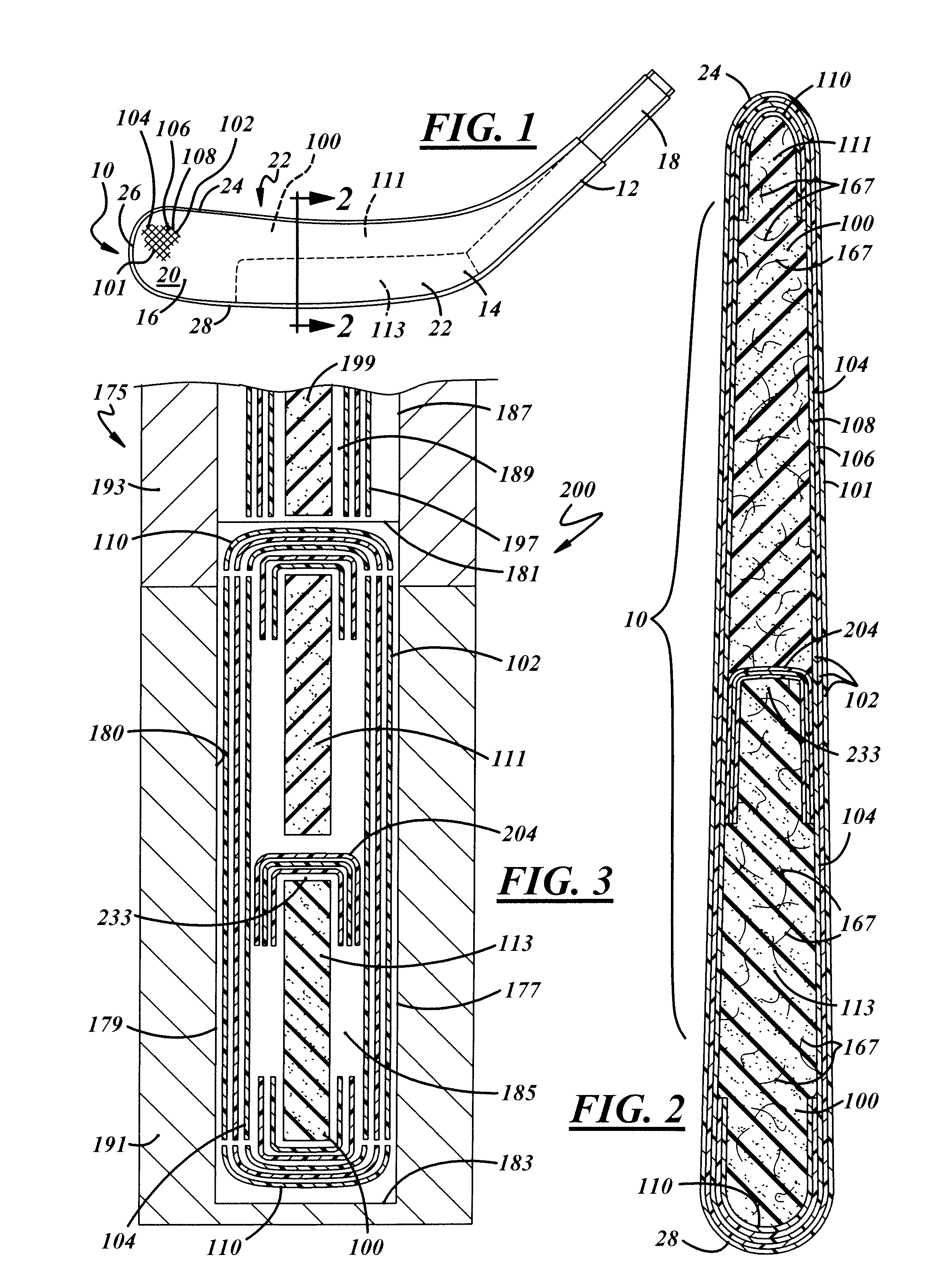
[0017]Referring now to the FIG. 1, a hockey blade 10 is depicted in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. It should be understood that while the preferred blade is intended for use in the sport of ice hockey, it can also be utilized in other sports, including roller hockey and field hockey. In general, the blade 10 comprises a hosel 12, a heel section 14, and a paddle (blade portion) 16. The heel section 14 is generally located at the junction of the hosel 12 and the paddle 16. The hosel 12 includes a tenon 18, or insert, adapted to be inserted into a hollow hockey stick shaft (not shown) made of aluminum, composite or graphite. Alternatively, the hockey stick shaft can be constructed of wood or a wood laminate. It will also be understood that the hockey stick shaft can be constructed of a variety of other materials. The paddle 16 includes a front face 20 and a rear face 22 and further comprises a top edge 24, a tip region 26 and a bottom edge 28.
[0018]As ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com