Coating compositions having improved performance
a coating composition and performance technology, applied in the field of coating compositions with improved performance, can solve problems such as adverse or toxic side effects for patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0109]While substrate-binding peptides can be identified using any one of several methods known to those skilled in the art, Illustrated in this example are various methods for utilizing phage display technology to produce a substrate-binding peptide having binding specificity for substrate, such substrate-binding peptide useful as a component in producing a compound according to the present invention.
Phage Screening and Selections.
[0110]Phage display technology is well-known in the art, and can be used to identify additional peptides for use as binding domains in the compositions according to the present invention. In general, using phage display, a library of diverse peptides can be presented to a target substrate, and peptides that specifically bind to the substrate can be selected for use as binding domains. Multiple serial rounds of selection, called “panning,” may be used. As is known in the art, any one of a variety of libraries and panning methods can be employed to identify...
example 2
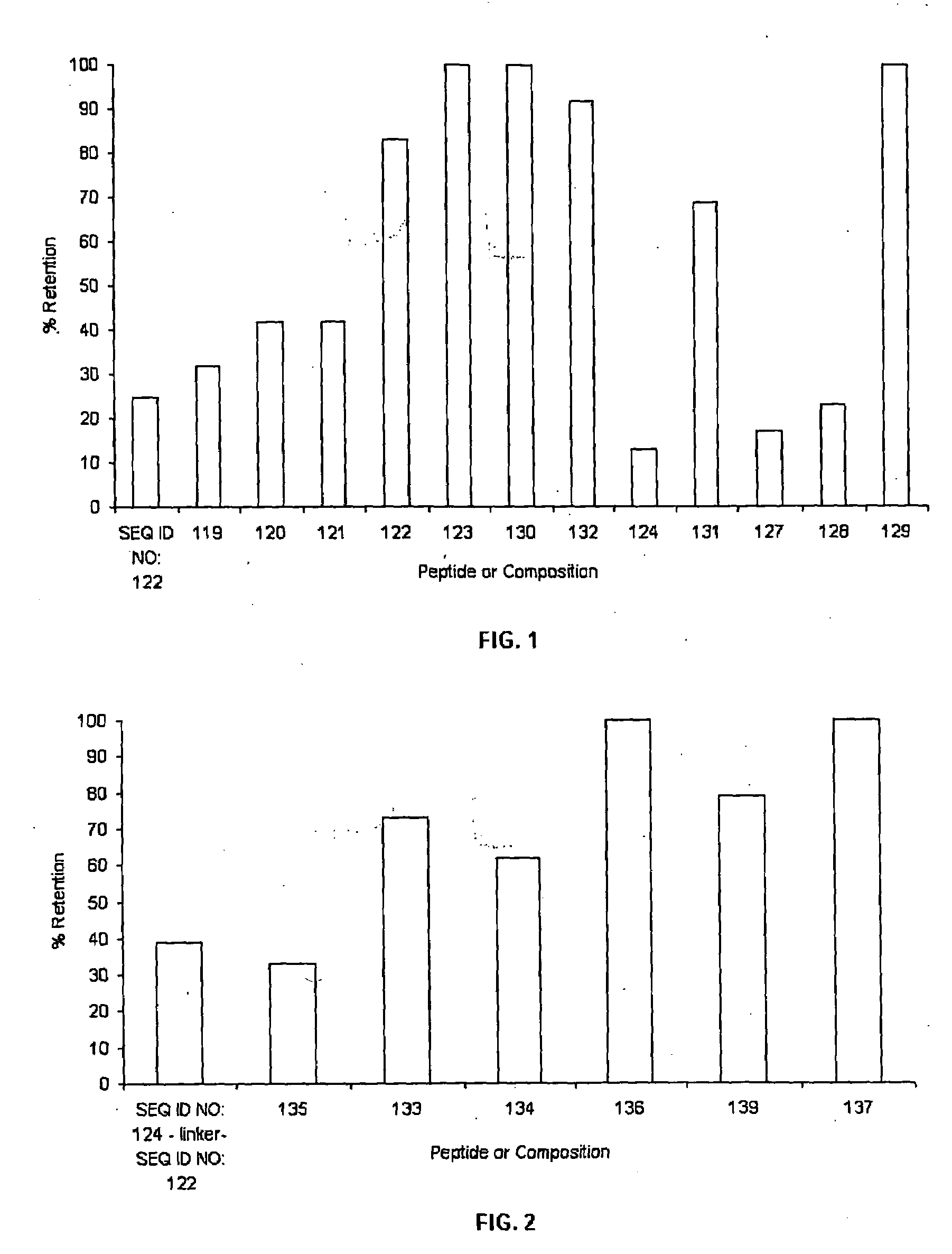
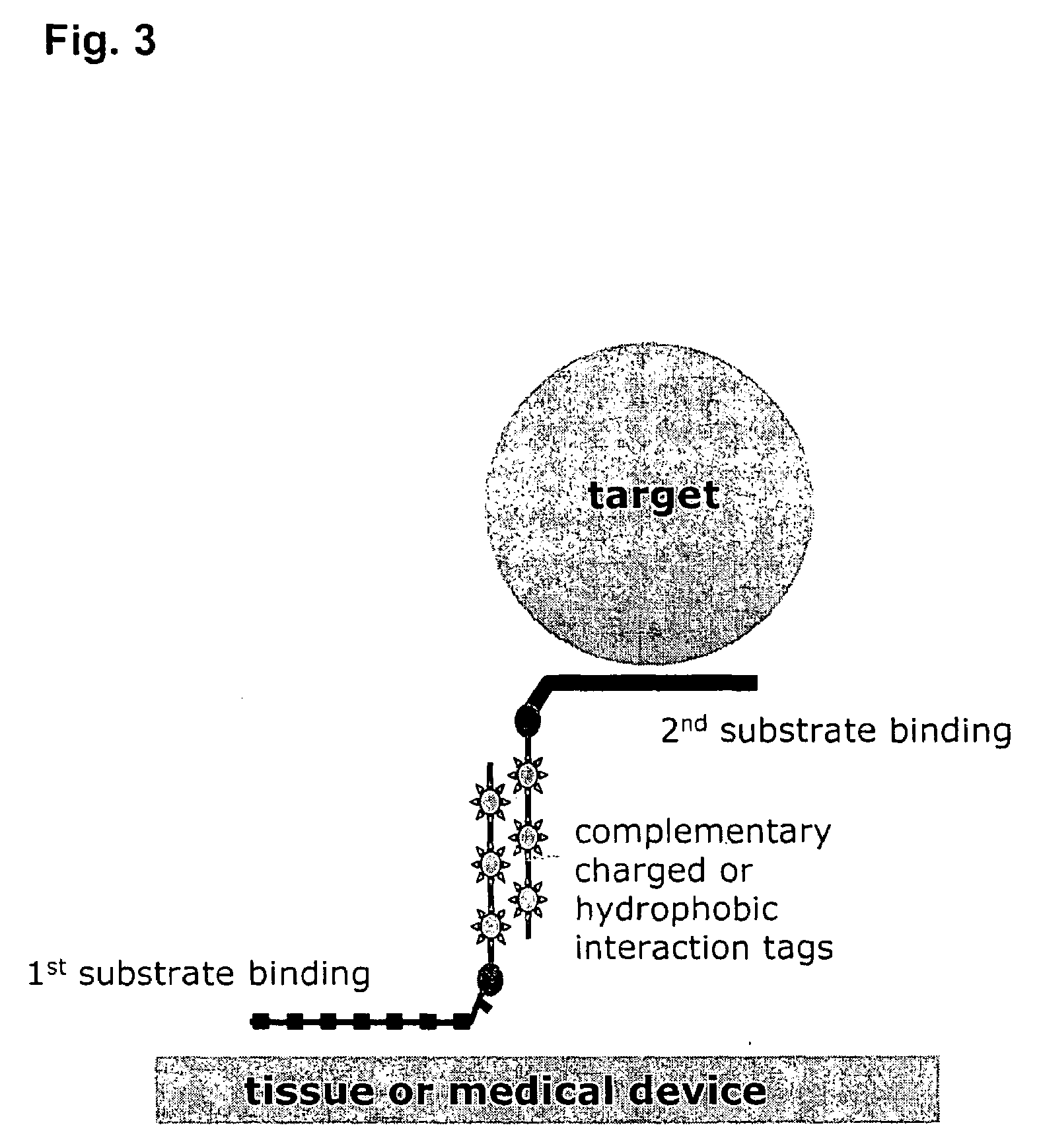
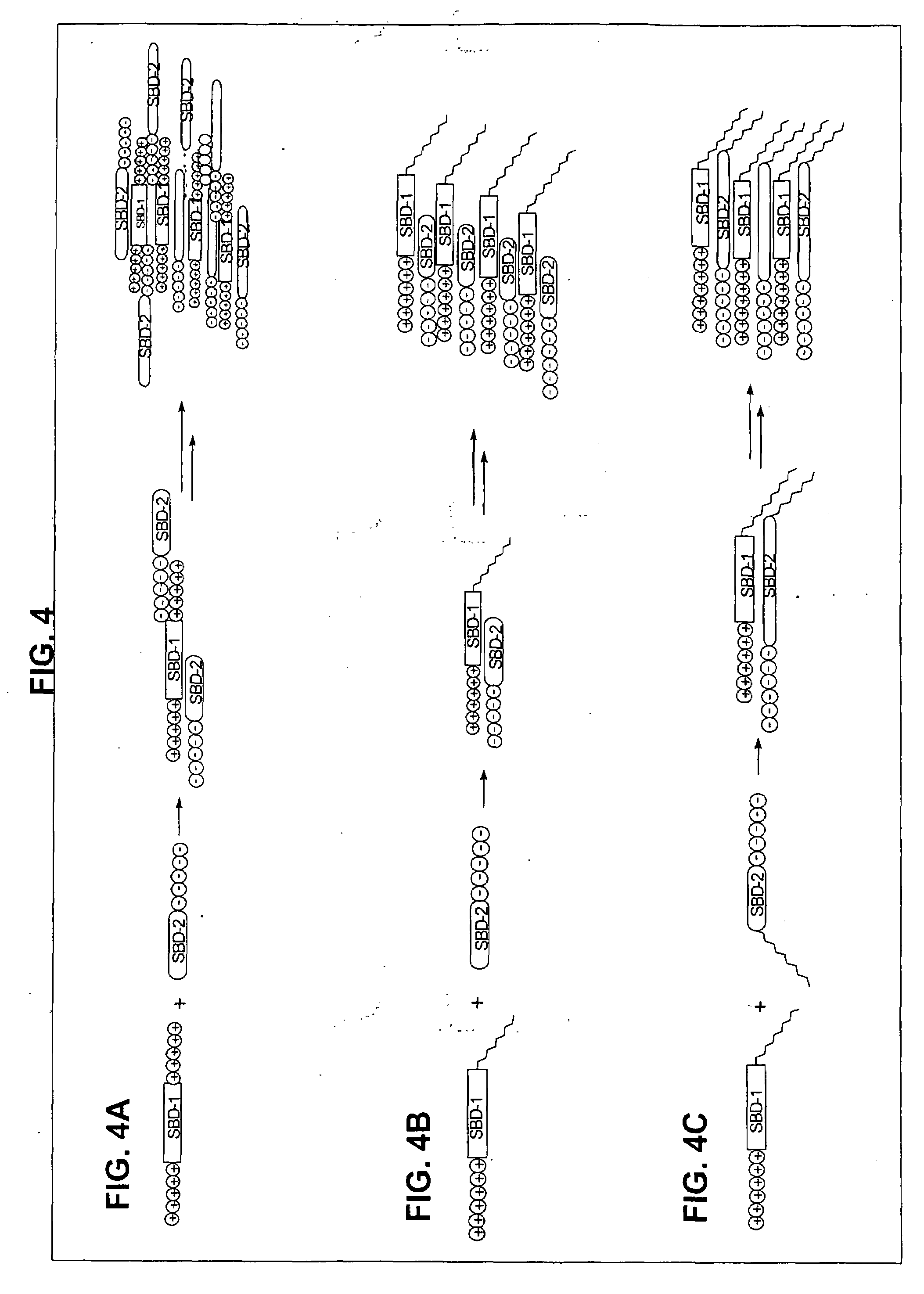
[0112]As summarized previously herein, the compound useful in making a composition of the invention is comprised of fatty acid covalently coupled to substrate-binding peptide. The composition may comprise substrate-binding peptide of a single type (e.g., “type” defined by the substrate for which the substrate-binding peptide has binding specificity), or may comprise more than one type of substrate-binding peptide. Further, as illustrated and described in more detail in Examples 4 & 5 herein, the peptide component of the compound may comprise a peptide comprised of a single binding specificity (see, e.g., Example 4); or may comprise two or more binding domains, with each binding domain comprised of a substrate-binding peptide, and with the two or more binding domains covalently coupled (directly or via a linker) (see, e.g., Example 5).
[0113]In one example, the substrate, for which a substrate comprising a material comprising a surface of a device, and more preferably a medical device...
example 3
[0121]Substrate-binding peptides, which bind to a biological substrate, can be used to produce a compound according to the invention. Thus, a fatty acid may be covalently coupled to a substrate-binding peptide having binding specificity for a biological substrate, whether it is a substrate-binding peptide by itself, or forms part of a biofunctional composition comprised of two or more substrate-binding peptides, wherein two or more substrate-binding peptides are covalently coupled together to form the biofunctional composition. For example, the biological substrate may comprise a biological molecule. In an illustrative example, wherein the biological molecule is a protein, and may further comprise a growth factor, disclosed is a substrate-binding peptide having binding specificity for BMP. For example, disclosed in commonly owned U.S. patent application US 20060051396 are families of peptides having binding specificity for BMP; one example being a peptide comprising the consensus am...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com