Devices for trapping insects
a technology for insects and traps, applied in insect catchers and killers, botany apparatus and processes, animal husbandry, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective energy source, small existing traps using solar power, and ineffective catching and controlling mosquitoes. to achieve the effect of eliminating flies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
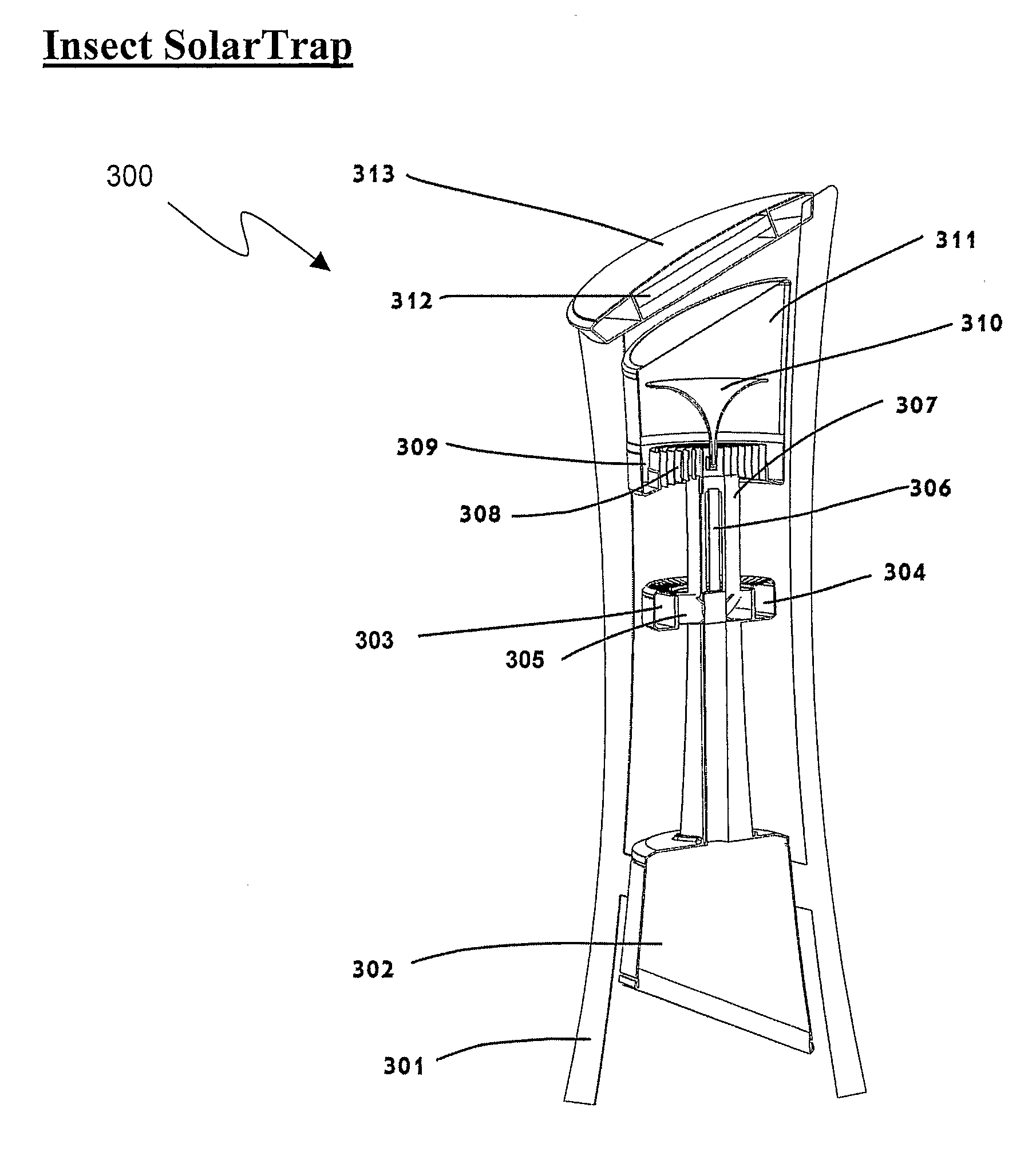
[0058]The present invention relates to insect-trapping devices utilizing: shape and color patterns as a visual target; heat, CO2, and chemical attractants to attract biting and nuisance flies toward the device; UV light to knock out the flies' orientation; and improved suction and shielded electric grids to eliminate the flies from the vicinity. The principles and operation for such insect-trapping devices, according to the present invention, may be better understood with reference to the accompanying description and the drawings.
Insect ComboTrap
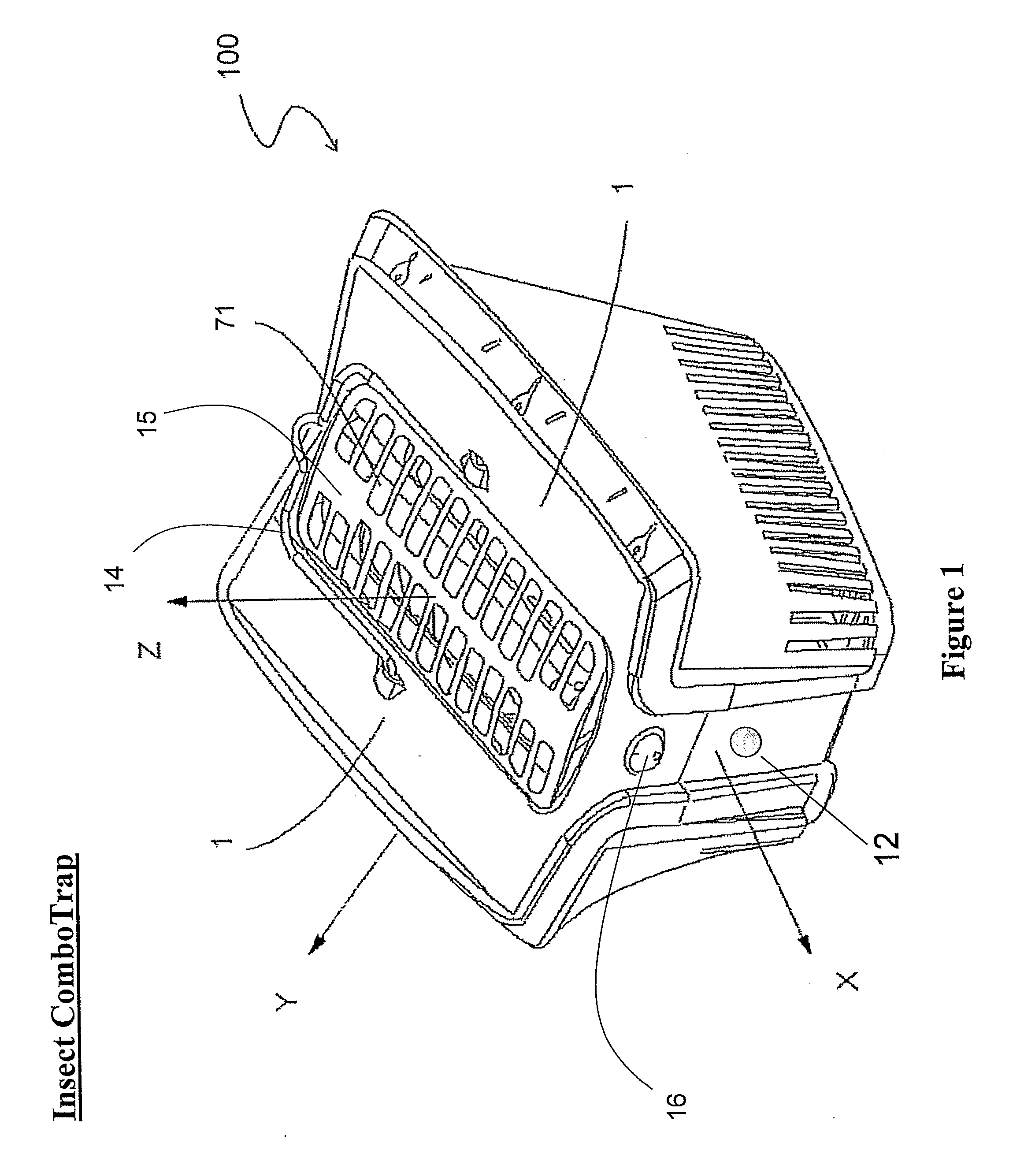
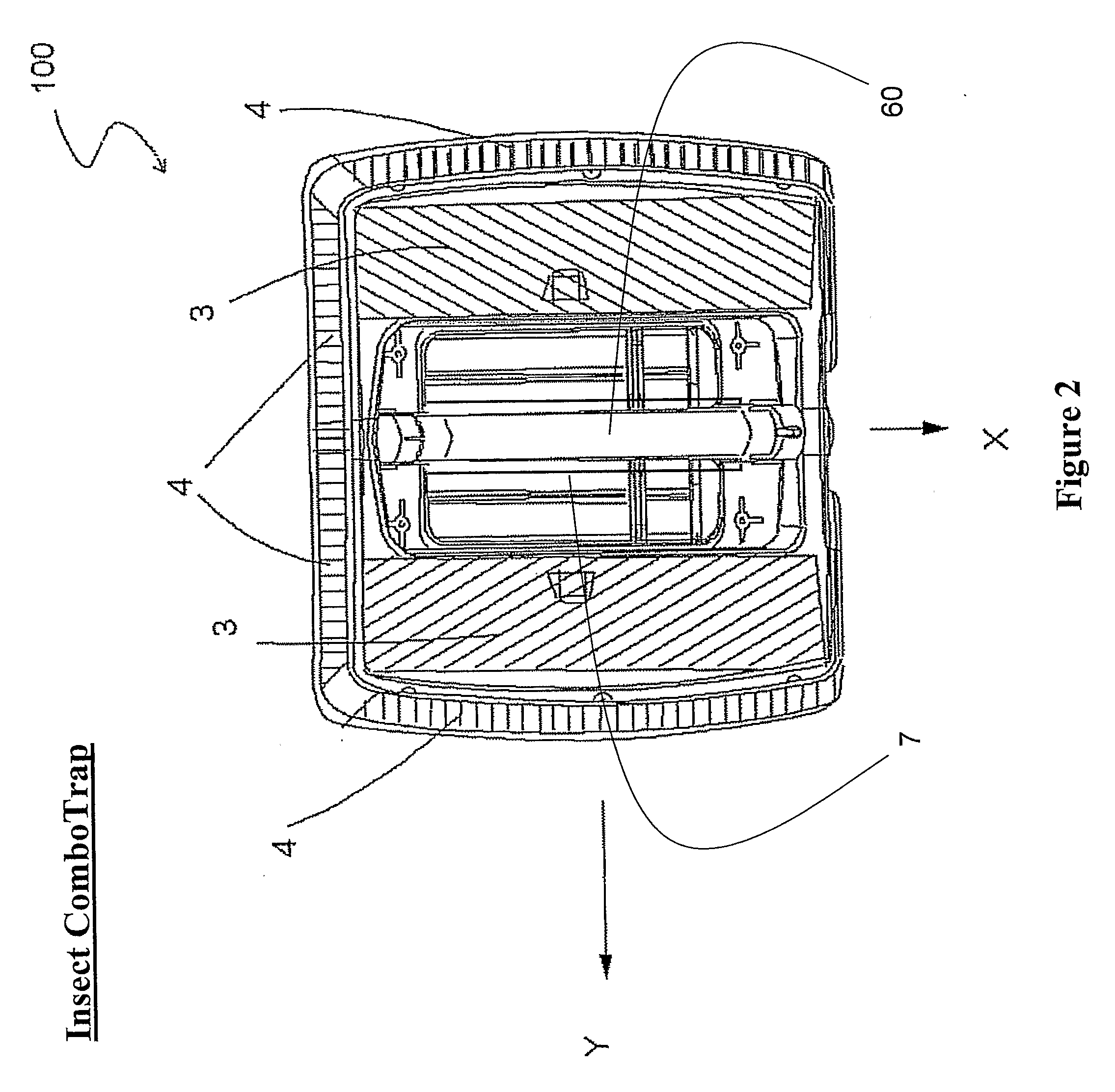
[0059]Referring now to the drawings, FIG. 1 shows an isometric view of an insect trap for catching insects, in particular mosquitoes and houseflies, according to preferred embodiments of the present invention. An insect ComboTrap 100 having a heated surface 1 (preferably a concave dark-colored heated surface) is shown. Heated surface 1 may have various shapes (e.g. elliptical or square). Heated surface 1 is heated by a heating film (or wire)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com